A New Misfit Function for Multimode Dispersion Curve Inversion of Rayleigh Waves
-
摘要: 反演瑞雷波频散曲线能有效地获取横波速度和地层厚度,传统的多模式瑞雷波频散曲线反演需要正确的模式判别.然而,当地层中含有低速软弱夹层或高速硬夹层等复杂结构时,瑞雷波可能会出现"模式接吻"和"模式跳跃"等现象,这些现象极易造成模式误判,进而导致错误的反演结果;同时,传统的频散曲线反演方法需要进行求根运算,进而导致现有的瑞雷波非线性反演速度慢,运算时间长.鉴于此,对传统的Haskell-Thomson频散曲线正演模拟算法进行了改进,提出了一种新颖有效的目标函数.该目标函数直接利用实测频散曲线与迭代更新模型频散函数表面形状进行最佳拟合,无需将多模式频散数据归于特定的模式,可有效避免多模式瑞雷波频散曲线反演模式误识别;同时,该目标函数不需要求根运算,进而大大加快了非线性反演速度.基于粒子群优化算法,利用实际工作中经常遇到的3种典型理论地质模型和某一高速公路路基实测资料进行了理论模型试算和实例分析,检验了本文提出的瑞雷波多模式频散曲线反演新方法的有效性和实用性.Abstract: Inversion of the Rayleigh wave dispersion curve can effectively obtain the shear wave velocity and stratum thickness. And the classical inversion of multimode Rayleigh wave dispersion curve requires correct mode identification. However, there may be "mode-kissing" and "mode-jumping" phenomena in the Rayleigh waves when the stratum contains complex structures such as low-velocity soft intercalations or high-speed stiff sandwich layers. These phenomena can easily lead to mode misidentification, and lead to wrong inversion results. At the same time, the classical dispersion curve inversion method needs to seek the roots, which leads to that the nonlinear inversion of Rayleigh wave is slow and the computation time is long. In view of these, the classical Haskell-Thomson dispersion curve forward modeling algorithm is improved, and a novel and effective misfit function is proposed. The misfit function is directly used to fit the dispersion function surface shape of the iterative updating model by using the measured dispersion curve. It is not necessary to assign the multimode dispersion data to a specific mode, which can effectively avoid the mode misidentification in the inversion of multimode Rayleigh wave dispersion curve. And the misfit function does not require the seeking root operation, thus greatly accelerating the nonlinear inversion speed. In this paper, based on the particle swarm optimization algorithm, three theoretical geological models and a certain roadbed test data often encountered in practical work are used to calculate the theoretical model and analyze the example. And the validity and practicability of the new method of Rayleigh wave multimode dispersion curve inversion are verified.
-
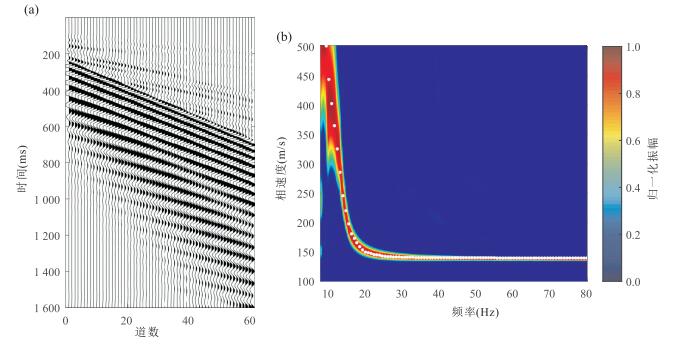
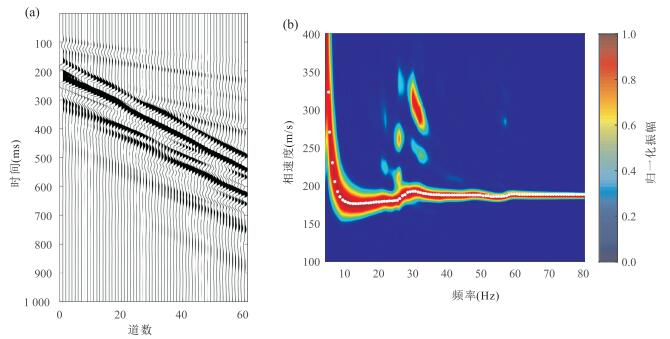
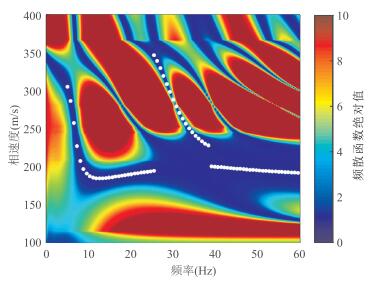
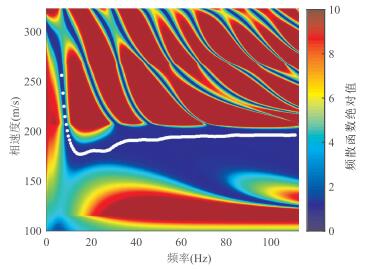
图 2 基于模型B模拟的理论瑞雷波地震记录及其高分辨率频散能量谱
a.60道高精度理论瑞雷波地震记录;b.由图 2a提取的高分辨率频散能量谱.图中白色实点为根据频散能量极大值提取的瑞雷波频散曲线,该频散数据将作为实测频散曲线进行反演
Fig. 2. The theoretical Rayleigh wave seismic record and the high-resolution dispersion energy spectra based on model B
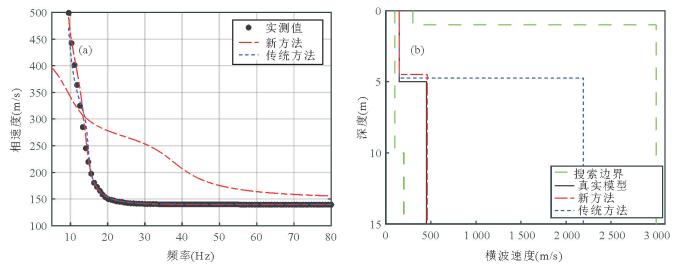
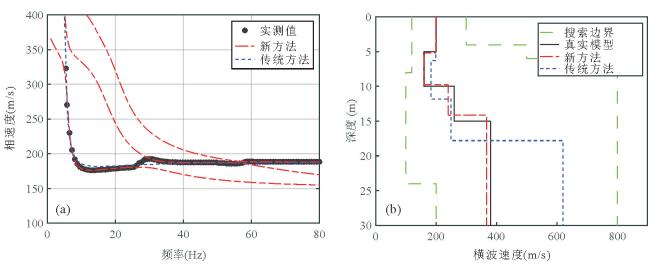
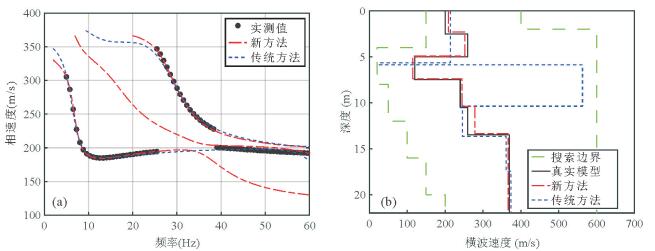
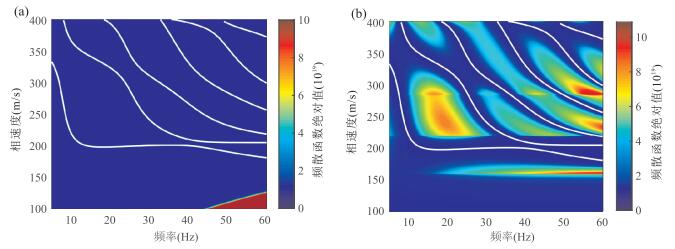
图 3 传统方法与新方法反演模型正演模拟的频散曲线与实测频散曲线的对比(a)和传统方法与新方法反演模型剖面与模型B的对比(b)
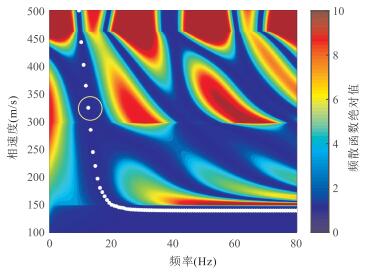
图a中:黑色实点为从图 2b中提取的瑞雷波频散曲线;蓝色虚线为利用传统方法反演模型正演模拟的基阶波频散曲线;红色虚点线为利用新方法反演模型正演模拟的多模式频散曲线,该多模式频散曲线在13 Hz处相速度几乎一样,此现象称为“模式接吻”现象.图b中:绿色虚线表示粒子群优化算法反演时模型参数搜索范围;黑色实线表示真实模型B;蓝色虚线表示传统方法反演获得的横波速度剖面;红色虚点线表示新方法反演获得的模型剖面
Fig. 3. Comparison of the dispersion curves inverted by classical method and new method and the measured dispersion curve (a), and comparison of the S-wave velocity profiles inverted by classical method and new method and the profile of model B (b)
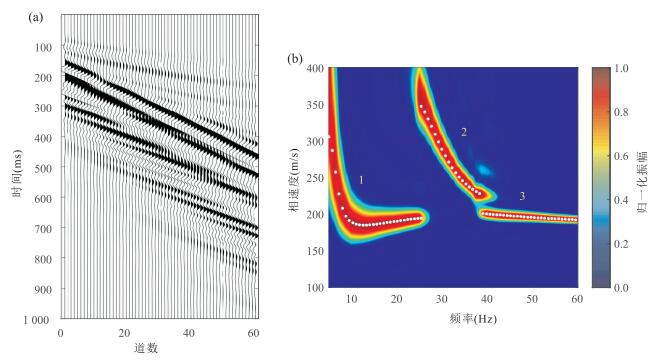
图 6 基于模型C模拟的理论瑞雷波地震记录及其高分辨率频散能量谱
a.60道高精度理论瑞雷波地震记录;b.由图 6a提取的高分辨率频散能量谱.图中白色实点为根据频散能量极大值提取的瑞雷波频散曲线, 该频散数据将作为实测频散曲线进行反演
Fig. 6. The theoretical Rayleigh wave seismic record and the high-resolution dispersion energy spectra based on the model C
图 7 传统方法与新方法反演模型正演模拟的频散曲线与实测频散曲线的对比(a)和传统方法与新方法反演模型剖面与模型C的对比(b)
图a中:黑色实点为从图 6b中提取的瑞雷波频散曲线;蓝色虚线为利用传统方法反演模型正演模拟的基阶波频散曲线;红色虚点线为利用新方法反演模型正演模拟的多模式频散曲线.图b中:绿色虚线表示粒子群优化算法反演时模型参数搜索范围;黑色实线表示真实模型C;蓝色虚线表示传统方法反演得到的模型剖面;红色虚点线表示新方法反演获得的模型剖面
Fig. 7. Comparison of the dispersion curves inverted by classical method and new method and the measured dispersion curve (a) and comparison of the S-wave velocity profiles inverted by classical method and new method and the profile of model C (b)
图 9 基于模型D模拟的理论瑞雷波地震记录及其高分辨率频散能量谱
a.60道高精度理论瑞雷波地震记录;b.由图 9a提取的高分辨率频散能量谱.图中白色实点为根据频散能量极大值提取的瑞雷波频散曲线,该频散数据将作为实测频散曲线进行反演
Fig. 9. The theoretical Rayleigh wave seismic record and the high-resolution dispersion energy spectra based on the Model D
图 10 传统方法与新方法反演模型正演模拟的频散曲线与实测频散曲线的对比(a)和传统方法与新方法反演模型剖面与模型D的对比(b)
图a中:黑色实点为从图 9b中提取的瑞雷波频散曲线;蓝色虚线为利用传统方法反演模型正演模拟的多模式瑞雷波频散曲线;红色虚点线为利用新方法反演模型正演模拟的多模式频散曲线.图b中:绿色虚线表示粒子群优化算法反演时模型参数搜索范围;黑色实线表示真实模型D;蓝色虚线表示传统方法反演得到的模型剖面;红色虚点线表示新方法反演获得的模型剖面
Fig. 10. Comparison of the dispersion curves inverted by classical method and new method and the measured dispersion curve (a), and comparison of the S-wave velocity profiles inverted by classical method and new method and the profile of model D (b)
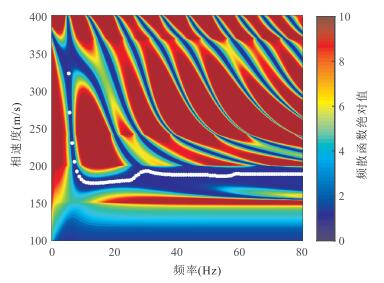
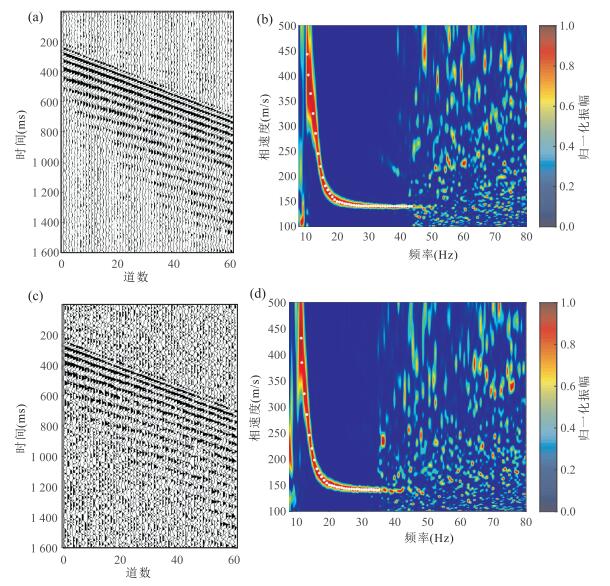
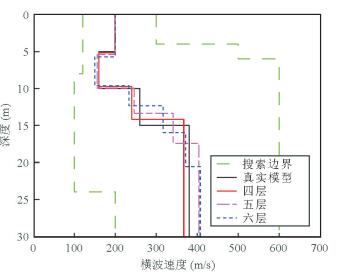
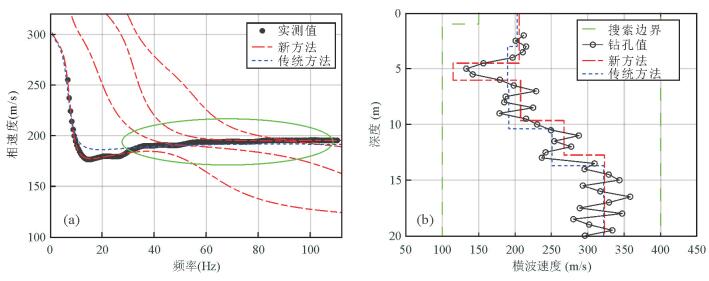
图 15 某高速公路路基瑞雷波勘探实例
a.野外实测的24道瑞雷波地震记录;b.由图 15a中的多道瑞雷波炮集地震记录提取的f-k域频散能量谱.图中白色实线为提取的f-k域实测瑞雷波频散曲线
Fig. 15. Exploration case of Rayleigh wave of a highway roadbed
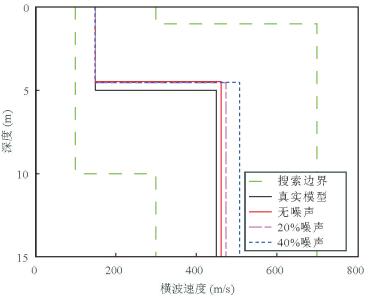
图 16 传统方法与新方法反演模型正演模拟的频散曲线与实测频散曲线的对比(a)和传统方法与新方法反演的横波速度剖面与钻孔资料的对比(b)
图a中:黑色实点为从图 15中提取得到的实测频散数据变换到f-v域的频散曲线; 红色虚点线为利用新方法反演模型正演模拟获得的多模式频散曲线;蓝色虚线表示利用传统方法反演模型正演模拟获得的基阶波频散曲线.图b中:绿色虚线为粒子群优化算法反演时模型参数搜索范围;带有圆圈的实线表示钻孔资料剖面;红色虚点线表示新方法反演的横波速度剖面;蓝色虚线表示传统方法反演得到的横波速度剖面
Fig. 16. Comparison of the dispersion curves inverted by classical method and new method and the measured dispersion curve (a), and comparison of the S-wave velocity profiles inverted by classical method and new method and the borehole data (b)
表 1 模型A:三层含低速软弱夹层地质模型参数
Table 1. Model A: a three-layer model with a soft layer trapped between two stiff layers
层序号 VS(m/s) VP(m/s) ρ(g/cm3) h(m) 1 220 437 1.8 6 2 160 285 2.0 3 均匀半空间 400 794 2.1 表 2 模型B:两层速度递增型地质模型参数及反演搜索范围
Table 2. Model B: a two-layer model characterized by S-wave velocities increasing with depth and search space in the inversion
层序号 模型参数 搜索范围 VS(m/s) VP(m/s) ρ(g/cm3) h(m) VS(m/s) h(m) 1 150 298 1.8 5 100~300 1~10 均匀半空间 450 802 2.1 ∞ 200~3 000 ∞ 表 3 模型C:四层含低速软夹层地质模型参数及反演搜索范围
Table 3. Model C: a four-layer model with a soft layer trapped between two stiff layers and search space in the inversion
层序号 模型参数 搜索范围 VS(m/s) VP(m/s) ρ(g/cm3) h(m) VS(m/s) h(m) 1 200 490 2.0 5 120~300 2~8 2 160 392 2.0 5 100~300 2~8 3 260 637 2.0 5 100~500 2~8 均匀半空间 380 931 2.0 ∞ 200~800 ∞ 表 4 模型D:六层含高速硬夹层地质模型参数及反演搜索范围
Table 4. Model D: a six-layer model with a stiff layer sandwiched between two soft layers and search space in the inversion
层序号 模型参数 搜索范围 VS(m/s) VP(m/s) ρ(g/cm3) h(m) VS(m/s) h(m) 1 200 490 2.0 2.5 150~400 0.1~5 2 260 637 2.0 2.5 10~400 0.1~5 3 120 294 2.0 2.5 50~600 0.1~5 4 240 588 2.0 3 100~600 0.1~5 5 260 637 2.0 3 150~600 0.1~5 6 370 906 2.0 ∞ 200~600 ∞ -
Cui, J.W., 2004.An Improved Global Optimization Method and Its Application to the Inversion of Surface Wave Dispersion Curves. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(3):521-527(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s11803-007-0592-y Dal Moro, G., Pipan, M., Gabrielli, P., 2007.Rayleigh Wave Dispersion Curve Inversion via Genetic Algorithms and Marginal Posterior Probability Density Estimation. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 61(1):39-55.doi:10.10 16/j.jappgeo.2006.04.002 Fan, Y.H., Liu, J.Q., Xiao, B.X., 2002.Fast Vector-Transfer Algorithm for Computation of Rayleigh Wave Dispersion Curves. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Sciences Edition), 29(5):25-30(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007%2Fs11770-014-0430-8.pdf Feng, H.J., Zhou, A.G., Yu, J.J., et al., 2016.A Comparative Study on Plum-Rain-Triggered Landslide Susceptibility Assessment Models in West Zhejiang Province. Earth Science, 41(3):403-415 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1186/s40677-017-0078-9 Foti, S., Comina, C., Boiero, D., et al., 2009.Non-Uniqueness in Surface-Wave Inversion and Consequences on Seismic Site Response Analyses. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 29(6):982-993.doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2008.11.004 Gao, L., Xia, J., Pan, Y., 2014.Misidentification Caused by Leaky Surface Wave in High-Frequency Surface Wave Method. Geophysical Journal International, 199(3):1452-1462.doi: 10.1093/gji/ggu337 Haskell, N.A., 1953.The Dispersion of Surface Waves on Multi-Layered Media. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 43(1):86-103.doi: 10.1029/SP030p0086 He, Y.F., Chen, W.T., Chen, X.F., 2006.Normal Mode Computation by the Generalized Reflection-Transmission Coefficient Method in Planar Layered Half Space. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(4):1074-1081(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200604019.htm Hu, J.F., Duan, Y.K., Hu, Y.L., et al., 1999.Inversion of Shear-Wave Velocity Structure in Shallow Soil from Rayleigh Waces. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 42(3):393-400(in Chinese with English abstract). http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/EN/Y1999/V42/I03/393 Huang, F.M., Yin, K.L., Zhang, G.R., et al., 2015.Landslide Groundwater Level Time Series Prediction Based on Phase Space Reconstruction and Wavelet Analysis-Support Vector Machine Optimized by PSO Algorithm. Earth Science, 40(7):1254-1265(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dqkx201507013.aspx Huang, Z.X., Li, H.Y., Xu, Y., 2014.Lithospheric S-wave Velocity Structure of West China and Neighboring Areas from Surface Wave Tomography. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(12):3994-4004(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQWX201412013.htm Li, Q.C., Shao, G.Z., Liu, J.L., et al., 2006.Past, Present and Future of Rayleigh Surface Wave Exploration. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 28(3):74-77(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s10712-011-9134-2 Li, X.Y., Zhu, P.M., Zhou, Q., et al., 2014.S-Wave Velocity Structure of Upper Crust in Three Gorges Reservoir Region of the Yangtze River. Earth Science, 39(12):1842-1850(in Chinese with English abstract). http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2014AGUFM.S23C4516L Lin, C.P., Chang, C.C., Chang, T.S., 2004.The Use of MASW Method in the Assessment of Soil Liquefaction Potential. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 24(9-10):689-698.doi: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2004.06.012 Liu, X.F., Fan, Y.H., 2012.On the Characteristics of High-Frequency Rayleigh Waves in Stratified Half-Space. Geophysical Journal International, 190(2):1041-1057.doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246x.2012.05479.x Liu, X.F., Fan, Y.H., Chen, X.F., 2009.Research on the Cross of the Dispersion Curves of Rayleigh Waves and Multi-Modes Coupling Phenomnon. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(9):2302-2309(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200909016.htm Liu, X.M., Fan, Y.H., Zhai, J.Y., et al., 2009.Numerical Simulation of Rayleigh Wave Zigzag Dispersion Curves of Four Typical Strata. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(12):3042-3050(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1569103 Lu, L.Y., Zhang, B.X., Wang, C.H., 2006.Experiment and Inversion Studies on Rayleigh Wave Considering Higher Modes. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(4):1082-1091(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200604020.htm Pan, J.T., Li, Y.H., Wu, Q.J., et al., 2014.3-D S-wave Velocity Structure of Crust and Upper-Mantle beneath the Northeast China. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(7):2077-2087(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQWX201407005.htm Pei, D.H., Louie, J.N., Pullammanappallil, S.K., 2007.Application of Simulated Annealing Inversion on High-Frequency Fundamental-Mode Rayleigh Wave Dispersion Curves. Geophysics, 72(5):R77-R85.doi: 10.1190/1.2752529 Poli, R., Kennedy, J., Blackwell, T., 2007.Particle Swarm Optimization. Swarm Intelligence, 1(1):33-57.doi: 10.1007/s11721-007-0002-0 Shi, Y.L., Jin, W., 1995.Genetic Algorithms Inversion of Lithospheric Structure from Surface Wave Dispersion. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 38 (2):189-198(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX502.006.htm Shirazi, H., Abdallah, I., Nazarian, S., 2009.Developing Artificial Neural Network Models to Automate Spectral Analysis of Surface Wave Method in Pavements. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering, 21(12):722-729.doi: 10.1061/(asce)0899-1561(2009)21:12(722) Song, X.H., Tang, L., Lv, X.C., et al., 2012.Application of Particle Swarm Optimization to Interpret Rayleigh Wave Dispersion Curves. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 84:1-13.doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2012.05.011 Tan, K., Zhang, Q.Q., Cao, Q., et al., 2015.Hyperspectral Retrieval Model of Soil Organic Matter Content Based On Particle Swarm Optimization-Support Vector Machines. Earth Science, 40(8):1339-1345(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/9/1/28/html Tillmann, A., 2005.An Unsupervised Wavelet Transform Method for Simultaneous Inversion of Multimode Surface Waves. Journal of Environmental & Engineering Geophysics, 10(3):287-294.doi: 10.2113/jeeg10.3.287 Xia, J.H., Miller, R.D., Park, C.B., 1999.Estimation of Near-Surface Shear-Wave Velocity by Inversion of Rayleigh Waves. Geophysics, 64(3):691-700.doi: 10.1190/1.1444578 Xia, J., Chen, C., Li, P.H., et al., 2004.Delineation of a Collapse Feature in a Noisy Environment Using a Multichannel Surface Wave Technique. Géotechnique, 54(1):17-27.doi: 10.1680/geot.54.1.17.36326 Zhang, B.X., Lu, L.Y., Bao, G.S., 2002.A Study on Zigzag Dispersion Curves in Rayleigh Wave Exploration. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 45(2):263-274(in Chinese with English abstract). http://manu39.magtech.com.cn/Geophy/EN/Y2002/V45/I02/263 Zhang, B.X., Xiao, B.X., Yang, W.J., et al., 2000.Mechanism of Zigzag Dispersion Curves in Rayleigh Exploration and Its Inversion Study. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 43(4):557-567(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200004016.htm Zhang, S.X., Chan, L.S., 2003.Possible Effects of Misidentified Mode Number on Rayleigh Wave Inversion. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 53(1):17-29.doi: 10.1016/s0926-9851(03)00014-4 Zhou, Z.S., Liu, X.L., Xiong, X.Y., 2007.A Study of Richardson Number and Instability in Moist Saturated Flow. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(2):567-573(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dqwlxb200702007.aspx 崔建文, 2004.一种改进的全局优化算法及其在面波频散曲线反演中的应用.地球物理学报, 47(3):521-527. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200403025.htm 凡友华, 刘家琦, 肖柏勋, 2002.计算瑞利波频散曲线的快速矢量传递算法.湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 29(5):25-30. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNDX200205005.htm 冯杭建, 周爱国, 俞剑君, 等, 2016.浙西梅雨滑坡易发性评价模型对比.地球科学, 41(3):403-415. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3259 何耀锋, 陈蔚天, 陈晓非, 2006.利用广义反射-透射系数方法求解含低速层水平层状介质模型中面波频散曲线问题.地球物理学报, 49(4):1074-1081. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200604019.htm 胡家富, 段永康, 胡毅力, 等, 1999.利用Rayleigh波反演浅土层的剪切波速度结构.地球物理学报, 42(3):393-400. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX199903011.htm 黄发明, 殷坤龙, 张桂荣, 等, 2015.基于相空间重构和小波分析-粒子群向量机的滑坡地下水位预测.地球科学, 40(7):1254-1265. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3113 黄忠贤, 李红谊, 胥颐, 2014.中国西部及邻区岩石圈S波速度结构面波层析成像.地球物理学报, 57(12):3994-4004. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201412013.htm 李庆春, 邵广周, 刘金兰, 等, 2006.瑞雷面波勘探的过去、现在和未来.地球科学与环境学报, 28(3):74-77. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XAGX200603016.htm 李小勇, 朱培民, 周强, 等, 2014.三峡库区上地壳横波速度结构.地球科学, 39(12):1842-1850. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3000 刘雪峰, 凡友华, 陈晓非, 2009.Rayleigh波频散曲线"交叉"及多模式耦合作用研究.地球物理学报, 52(9):2302-2309. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200909016.htm 刘雪明, 凡友华, 翟佳羽, 等, 2009.四种典型地层的瑞雷波"之"字型频散曲线数值模拟研究.地球物理学报, 52(12):3042-3050. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200912014.htm 鲁来玉, 张碧星, 汪承灏, 2006.基于瑞利波高阶模式反演的实验研究.地球物理学报, 49(4):1082-1091. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200604020.htm 潘佳铁, 李永华, 吴庆举, 等, 2014.中国东北地区地壳上地幔三维S波速度结构.地球物理学报, 57(7):2077-2087. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201407005.htm 石耀霖, 金文, 1995.面波频散反演地球内部构造的遗传算法.地球物理学报, 38(2):189-198. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX502.006.htm 谭琨, 张倩倩, 曹茜, 等, 2015.基于粒子群优化支持向量机的矿区土壤有机质含量高光谱反演.地球科学, 40(8):1339-1345. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201508009.htm 张碧星, 鲁来玉, 鲍光淑, 2002.瑞利波勘探中"之"字形频散曲线研究.地球物理学报, 45(2):263-274. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200202012.htm 张碧星, 肖柏勋, 杨文杰, 等, 2000.瑞利波勘探中"之"形频散曲线的形成机理及反演研究.地球物理学报, 43(4):557-567. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200004016.htm 周竹生, 刘喜亮, 熊孝雨, 2007.弹性介质中瑞雷面波有限差分法正演模拟.地球物理学报, 50(2):567-573. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX200702029.htm -









 下载:
下载: