Study on Spatial Distribution and Key Influencing Factors of Landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir Area
-
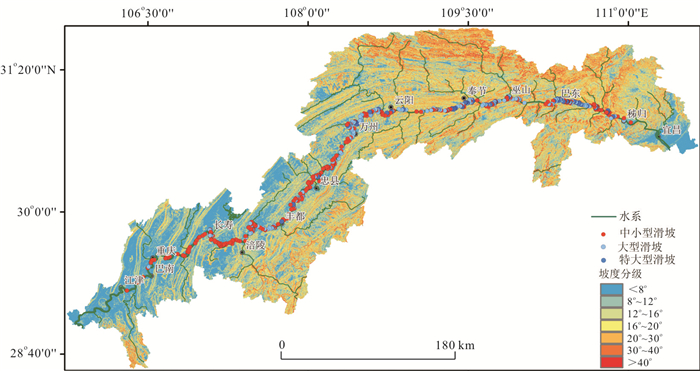
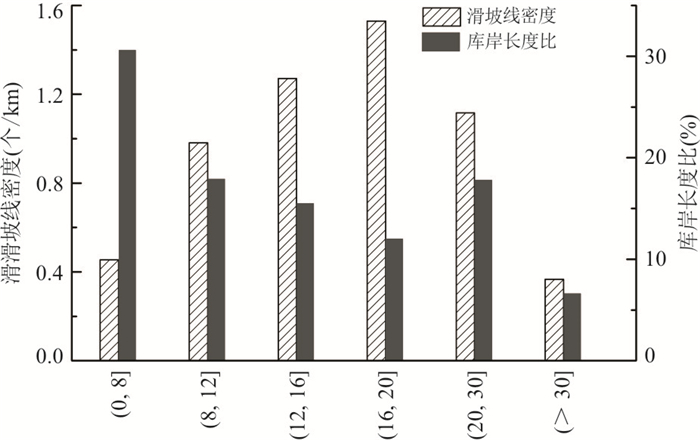
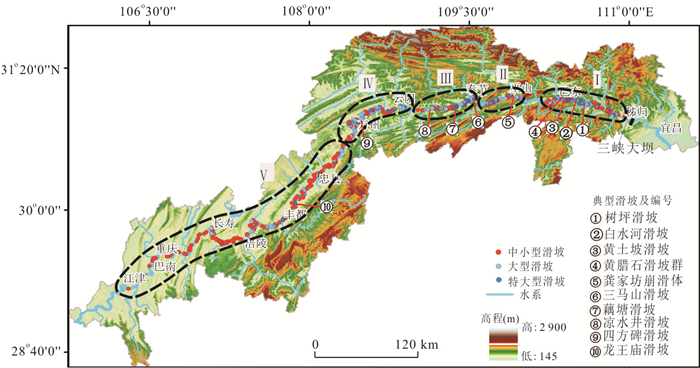
摘要: 三峡库区涉水滑坡众多,目前库岸滑坡空间发育规律及其影响因素尚不明确.收集三峡大坝至库尾江津长江两岸593处滑坡相关资料,选取地层岩性、斜坡结构、高程与坡度作为滑坡关键控制因素及库水作用这一诱发因素.沿三峡大坝追溯至库尾,根据不同影响因子把干流库岸进行分段研究,统计滑坡在各影响因子中的分布特征,分析其分布规律及内在机理,可得以下结论:(1)受不同岩组的工程地质性质差异,干流库岸稳定性差异较大,造成滑坡在空间分布上呈显著区域差异性与分带性特征;(2)在同一岩组的左、右两岸或上下游段滑坡发育密度呈明显局部差异性,其主要受斜坡结构影响,顺向坡中发育密度明显高于横向坡与逆向坡;(3)由于地形地貌条件及库水作用影响,滑坡后缘高程与坡度由库首至库尾逐渐降低,而前缘主要集中于100~175 m,滑坡复活变形的最主要诱发因素为库水位升降作用,当水位作用于滑坡中前部时影响效果最明显,影响时效随着滑坡逐年变形应力调整后逐渐减弱.研究结果为三峡库区滑坡防治提供了一定依据.Abstract: There are many wading landslides in Three Gorges reservoir area, however, the spatial distribution and influencing factors of these landslides are not yet clear. The relevant data of 593 landslides along the Yangtze River from Three Gorges Dam to Jiangjin city were collected in this study. The lithology, slope structure, elevation and slopes angle were selected as the key control factors and reservoir water was selected as inducing factor. The reservoir bank slope on both sides of the Yangtze River was divided into several sections according to different factors. The spatial distribution characteristics and its internal mechanism of landslides were analyzed. The results could be summarized as follows:(1) The macroscopic spatial distribution of landslides presents significant regional differences and zonation characteristics because of the engineering geological properties of different rock groups. (2) It also shows obvious local differences in the left and right sides or the upstream and downstream in the same rock group. This may be related to the slope structure. The density of landslides in the consequent slope is much higher than transverse slope or converse slope. (3) Due to the topographic conditions and the influence of the reservoir water, the elevation of trailing and slopes angle of the landslides are gradually reduced from the head to tail region. Landslides front elevation were mainly focused on 100-175 m. The main inducing factor of landslide deformation was the fluctuation of reservoir water level. The effect was most significant when the water level fluctuated in front and middle of the landslide. The effect of the fluctuation of reservoir water level to landslide decreases gradually with the adjustment of deformation. The research results can facilitate the future prevention and controlling of landslides in Three Gorges reservoir area.
-
表 1 三峡库区工程地质岩组划分
Table 1. Landslides distribution characteristics in different slope structures
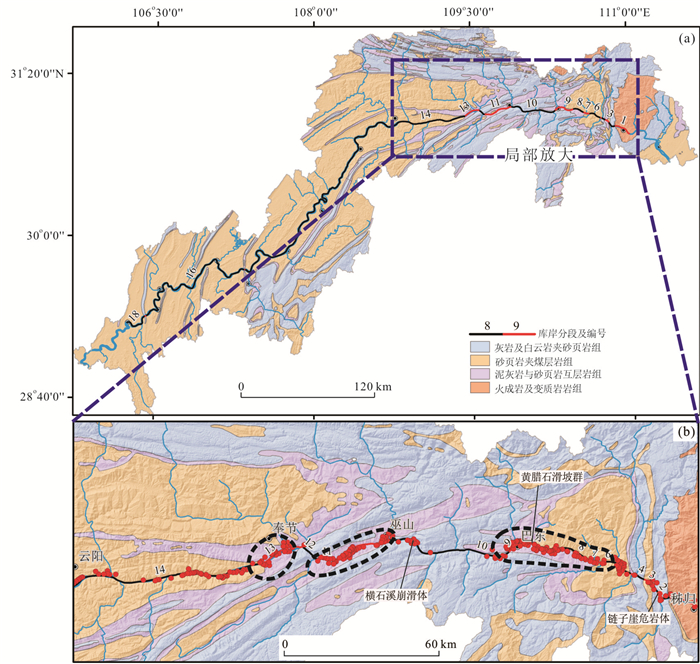
岩组 地层单元 主要岩性简述 灰岩及白云岩夹砂页岩组(LDS) Z、∈、O、S1-2、T1-2j、T1d、T3xj、T3j 以石灰岩、白云岩、角砾状灰岩、泥质灰岩以及硅质灰岩等碳酸岩盐类为主,间夹砂岩、页岩 砂页岩夹煤层岩组(SC) J1z、J1-2z、J1t、J2s、J1b、J2x、J3p、J3s、K1-2 主要由中厚-厚层状或块状长石砂岩、长石石英砂岩、粉砂岩等与厚层不等的页岩呈互层状,夹泥岩、碎屑灰岩及煤层 泥灰岩与砂泥岩互层岩组(SM) T2b、T2l、D2c、P、C1-2 以石灰岩、泥质灰岩与泥岩和砂页岩类成互层为主,夹煤层、铝土层、磁铁矿和磷矿层等 火成岩及变质岩岩组(IM) Pt、Ar、Nh 主要由花岗-闪长岩、片麻岩等岩浆岩与变质杂岩组成,主要分布与黄陵背斜及其周边 表 2 不同工程地质岩组滑坡分布特征
Table 2. Landslides distribution characteristics in different engineering geological petrofabric
岩组 岸坡长度(km) 库岸长度比例(%) 滑坡数量(个) 滑坡数量比例(%) 滑坡线密度(个/km) 灰岩及白云岩夹砂页岩组(LDS) 62.7 9.4 26 4.4 0.415 砂页岩夹煤层岩组(SC) 514 76.7 405 68.3 0.788 泥灰岩与砂页岩互层岩组(SM) 77.4 11.5 154 26 1.989 火成岩及变质岩岩组(IM) 16.2 2.4 8 1.3 0.495 表 3 不同斜坡结构滑坡分布特征
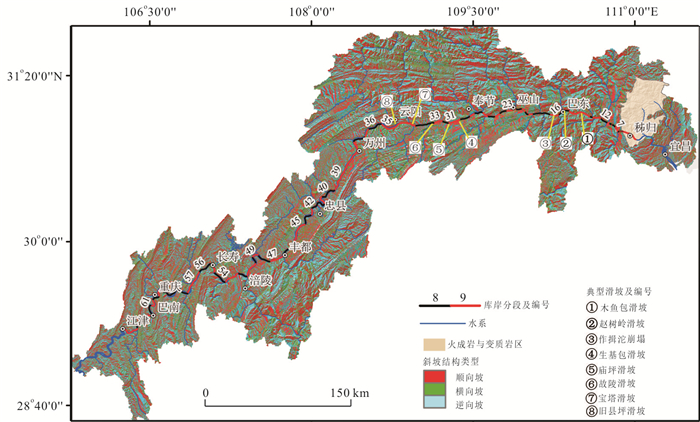
Table 3. Landslides distribution characteristics in different slope structures
斜坡结构 岸坡长度(km) 库岸长度比例(%) 滑坡数量(个) 滑坡数量比例(%) 滑坡线密度(个/km) 顺向坡 605.9 46.4 336 57.5 0.556 横向坡 257.5 19.7 106 18.2 0.412 逆向坡 441.9 33.9 142 24.3 0.321 -
Bai, S. B., Wang, J., Lü, G. N., et al., 2010. GIS-Based Logistic Regression for Landslide Susceptibility Mapping of the Zhongxian Segment in the Three Gorges Area, China. Geomorphology, 115(1-2):23-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.09.025 Chai, B., Yin, K. L., Du, J., et al., 2013. Correlation between Incompetent Beds and Slope Deformation at Badong Town in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 69(1):209-223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1948-9 Chen, G. J., Li, C. A., Chen, S., et al., 2013. Landslide Development and the Geological Process of Watercourse Evolution in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Earth Science, 38(2):411-416 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201302019 Deng, Q. L., Ke, Y. Y., Guo, F., 2008. Abnormal Carbonic Clay and Its Significance in Relation to Geological Hazards in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, Yangtze River. Earth Science, 33(3):405-410 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200803016 Deng, Q. L., Fu, M., Ren, X. W., et al., 2017. Precedent Long-Term Gravitational Deformation of Large Scale Landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Engineering Geology, 221:170-183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.02.017 Huang, B. L., Yin, Y. P., Du, C. L., 2016. Risk Management Study on Impulse Waves Generated by Hongyanzi Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir of China on June 24, 2015. Landslides, 13(3):603-616. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-016-0702-x Huang, B. L., Yin, Y. P., Liu, G. N., et al., 2012. Analysis of Waves Generated by Gongjiafang Landslide in Wu Gorge, Three Gorges Reservoir, on November 23, 2008. Landslides, 9(3):395-405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-012-0331-y Huang, R. Q., 2007. Large-Scale Landslides and Their Sliding Mechanisms in China since the 20th Century. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 26(3):433-454 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb200703001 Jian, W. X., Wang, Z. J., Yin, K. L., 2009. Mechanism of the Anlesi Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Engineering Geology, 108(1-2):86-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2009.06.017 Jiang, J. W., Xiang, W., Zeng, W., et al., 2012. Water-Rock(Soil) Interaction Mechanism of Huangtupo Riverside Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 34(7):1209-1216 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c9517c11253493dd98db3c9a9bfc49b5 Liu, C. Z., Li, T. F., Wen, M. S., et al., 2004. Assessment and Early Warning on Geo-Hazards in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region of Changjiang River. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 31(4):9-19 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=swdzgcdz200404002 Liu, G. R., Yan, E. C., Lian, C., 2002. Discussion on Classification of Landslides. Journal of Engineering Geology, 10(4):339-342 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ200204000.htm Miao, H. B., Wang, G. H., Yin, K. L., et al., 2014. Mechanism of the Slow-Moving Landslides in Jurassic Red-Strata in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Engineering Geology, 171:59-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.12.017 Miao, H. B., Yin, K. L., Wang, G. H., 2016. Dynamic Mechanism of Intermittent Reactivation of Deep-Seated Reservoir Ancient Landslide. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 37(9):2645-2653 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201609029 Xia, M., Ren, G. M., Ma, X. L., 2013. Deformation and Mechanism of Landslide Influenced by the Effects of Reservoir Water and Rainfall, Three Gorges, China. Natural Hazards, 68(2):467-482. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-013-0634-x Pradhan, B., Lee, S., 2010. Landslide Susceptibility Assessment and Factor Effect Analysis:Backpropagation Artificial Neural Networks and Their Comparison with Frequency Ratio and Bivariate Logistic Regression Modelling. Environmental Modelling & Software, 25(6):747-759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2009.10.016 Shi, J. S., Xu, R. C., Shi, L., et al., 2007. ETM+ Imagery and GIS-Based Landslide Susceptibility Mapping for the Regional Area of Geheyan Reservoir on the Qingjiang River, Hubei Province, China. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(6):119-128 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy200706015 Wang, F. W., Zhang, Y. M., Huo, Z. T., et al., 2004. The July 14, 2003 Qianjiangping Landslide, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides, 1(2):157-162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-004-0020-6 Wang, F. W., Zhang, Y. M., Huo, Z. T., et al., 2008. Movement of the Shuping Landslide in the First Four Years after the Initial Impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam Reservoir, China. Landslides, 5(3):321-329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-008-0128-1 Wang, N. T., Peng, K., Li, Q. H., et al., 2012. Quantitative Evaluation of Geological Disaster Liability Based on RS & GIS Analysis:A Case Study of Wufeng County, Hubei Province. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(6):221-229 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201206026 Xiao, S. R., Lu, S. S., Guan, H. F., et al., 2013. Study of Geomechanical Model of Liangshuijing Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 34(12):3534-3542 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ytlx201312029 Xu, G. L., Li, W. N., Yu, Z., et al., 2015. The 2 September 2014 Shanshucao Landslide, Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Landslides, 12(6):1169-1178. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-015-0652-8 Xu, Q., 2012. Theoretical Studies on Prediction of Landslides Using Slope Deformation Process Data. Journal of Engineering Geology, 20(2):145-152 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcdzxb201202001 Xu, Q., Tang, M. G, Xu, K. X., et al., 2008. Research on Space-Time Evolution Laws and Early Warning-Prediction of Landslides. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 27(6):1104-1112 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb200806003 Yin, Y.P., Hu, R.L., 2004. Engineering Geological Characteristics of Purplish-Red Mudstone of Middle Tertiary Formation at the Three Gorges Reservoir. Journal of Engineering Geology, 12(2):124-135 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gcdzxb200402003 Yin, Y. P., Tang, H. M., Li, X., et al., 2004. Major Geologic Hazard and Prevention on the Relocation Site at the Three Gorges. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Yin, Y. P., Huang, B. L., Wang, W. P., et al., 2016. Reservoir-Induced Landslides and Risk Control in Three Gorges Project on Yangtze River, China. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 8(5):577-595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.08.001 Zhang, F., Wang, K. W., Luo, X. Q., et al., 2007. Relationship between Landslides and Structural Featurein Three Gorges Reservoir. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(1):38-46 (in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200701006 Zhang, Z. Y., Wang, S. T., Wang, L. S., et al., 2009. Engineering Geological Analysis Principle. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Zhu, D.P., 2010. Revival Mechanism and Deformation Prediction of Typical Accumulative Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 1-5 (in Chinese with English abstract). 陈国金, 李长安, 陈松, 等, 2013.长江三峡库区滑坡发育与河道演变的地质过程分析.地球科学, 38(2):411-416. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2013.040 邓清禄, 柯于义, 郭锋, 2008.长江三峡非正常含炭粘土沉积及其地质灾害意义.地球科学, 33(3):405-410. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2008.03.016 黄润秋, 2007. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制.岩石力学与工程学报, 26(3):433-454. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001 江洎洧, 项伟, 曾雯, 等, 2012.三峡库区黄土坡临江滑坡体水岩(土)相互作用机理.岩土工程学报, 34(7):1209-1216. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTGC201207007.htm 刘传正, 李铁锋, 温铭生, 等, 2004.三峡库区地质灾害空间评价预警研究.水文地质工程地质, 31(4):9-19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2004.04.002 刘广润, 晏鄂川, 练操, 2002.论滑坡分类.工程地质学报, 10(4):339-342. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2002.04.001 缪海波, 殷坤龙, 王功辉, 2016.库岸深层老滑坡间歇性复活的动力学机制研究.岩土力学, 37(9):2645-2653. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201609029 石菊松, 徐瑞春, 石玲, 等, 2007.基于RS和GIS技术的清江隔河岩库区滑坡易发性评价与制图.地学前缘, 14(6):119-128. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.06.015 王宁涛, 彭轲, 黎清华, 等, 2012.基于RS和GIS的地质灾害易发性定量评价——以湖北省五峰县为例.地学前缘, 19(6):221-229. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201206026 肖诗荣, 卢树胜, 管宏飞, 等, 2013.三峡库区凉水井滑坡地质力学模型研究.岩土力学, 34(12):3534-3542. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytlx201312029 许强, 2012.滑坡的变形破坏行为与内在机理.工程地质学报, 20(2):145-152. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.02.001 许强, 汤明高, 徐开祥, 等, 2008.滑坡时空演化规律及预警预报研究.岩石力学与工程学报, 27(6):1104-1112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.06.003 殷跃平, 胡瑞林, 2004.三峡库区巴东组(T2b)紫红色泥岩工程地质特征研究.工程地质学报, 12(2):124-135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2004.02.003 殷跃平, 唐辉明, 李晓, 等, 2004.长江三峡库区移民迁建新址重大地质灾害及防治研究.北京:地质出版社. 张帆, 王孔伟, 罗先启, 等, 2007.长江三峡库区构造特征与滑坡分布关系.地质学报, 81(1):38-46. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200701006 张倬元, 王士天, 王兰生, 等, 2009.工程地质分析原理.北京:地质出版社. 朱大鹏, 2010.三峡库区典型堆积层滑坡复活机理及变形预测研究(博士学位论文).武汉: 中国地质大学, 1-5. -









 下载:
下载: