Distribution and Paleoclimate Implication of Microbial Tetraether Lipids in Wushan Loess
-
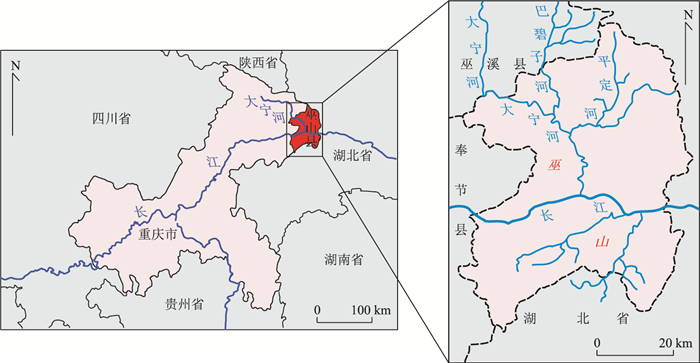
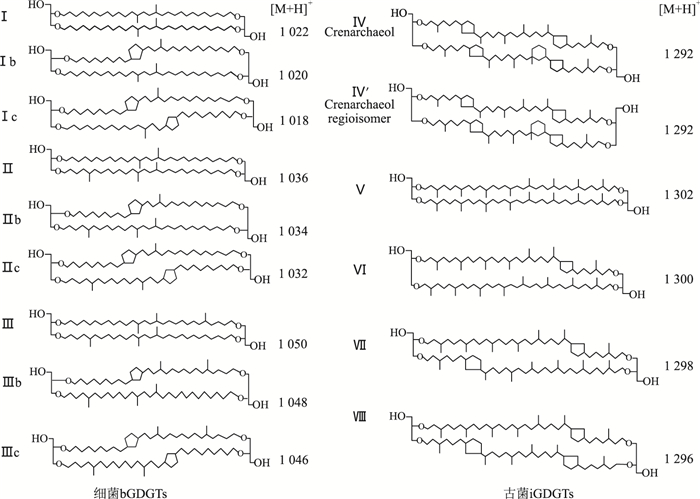
摘要: "巫山黄土"是指分布于长江三峡地区的黄土状堆积物,是中国黄土的重要组成部分,具有重要的古气候环境意义.微生物四醚膜脂是反演古气候环境的灵敏指标,为了进一步理解巫山黄土中蕴含的古气候意义,通过测定巫山黄土中微生物醚类化合物(glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers,GDGTs)并分析其分布特征,基于支链GDGTs(bGDGTs)的甲基化指数(methylation index of branched tetraethers,MBT)和环化指数(cyclization ration of branched tetraethers,CBT)重建该地44.4~22.8 ka.BP的古温度年平均气温(mean annual air temperature,MAAT),MAAT与频率磁化率曲线和北大西洋沉积物有孔虫曲线对比,其变化趋势具有一致性,反映了其指标的可靠性.巫山黄土的陆源输入指数(BIT值,bGDGTs vs.crenarchaeol)在0.5~1.0之间,大部分值接近于1.0,但有几个极低值,分析为干旱事件.根据MAAT和BIT指标,巫山地区在冰期气候有剧烈的波动,在36.2±3.6 ka.BP、26.0±2.7 ka.BP、23.7±2.3 ka.BP时相对比较干旱,推测可能分别对应着H4、H3和H2事件,表明该区气候变化响应全球气候变化.Abstract: "Wushan loess", regarded as the southern boundary of Chinese Loess, is distributed in the Three Gorges area in the Yangtze River, which contains rich paleoclimatic information attracting attentions of many scholars in paleoclimate. In order to further reveal its causes and better understand the paleoclimatic significance contained in Wushan loess, the glycerol dialkyl glycerol tetraethers (GDGTs) extracted from Wushan loess section were investigated. Comparing the mean annual air temperature (MAAT) reconstructed based on branched GDGTs (bGDGTs) with frequency-dependent magnetic susceptibility and North Atlantic sediments, it is found that the three curves are analogous in climate evolution patterns. These similarities show that climatic changes in Wushan region respond to global climatic changes. The BIT values range from 0.5-1.0 and most BIT (bGDGTs vs. crenarchaeol) values are close to 1. The low BIT values suggest that it was very dry at 36.2 ka.BP, 30.2 ka.BP and 23.5 ka.BP. Based on MAAT and BIT values, it is found that it was relatively cold when it was very dry. It is proposed that the three periods correspond to H4, H3, H2 climate events, respectively.
-
图 4 巫山黄土剖面GDGTs各参数的变化及bGDGTs重建的温度与频率磁化率、北大西洋V23-81钻孔沉积物有孔虫曲线对比
Fig. 4. Variations of GDGT proxies in Wushan loess section and comparison of bGDGT-derived MAAT with frequency-dependent magnetic susceptibility and North Atlantic Core V23-81 N. Pachyderma
表 1 巫山黄土剖面OSL测年结果
Table 1. OSL dating results of the samples from Wushan loess section
采样深度(m) 估计光释光年龄(ka.BP) 2 26.4±2.3 4 28.2±2.5 6 31.9±2.9 10 44.4±4.2 -
An, Z.S., 2000.The History and Variability of the East Asian Paleomonsoon Climate.Quaternary Science Reviews, 19(1-5):171-187.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0277-3791(99)00060-8 doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00060-8 Bond, G., Heinrich, H., Broecker, W., et al., 1992.Evidence for Massive Discharges of Icebergs into the North Atlantic Ocean during the Last Glacial Period.Nature, 360(6401):245-249. https://doi.org/10.1038/360245a0 Buckles, L.K., Weijers, J.W.H., Tran, X.M., et al., 2014.Provenance of Tetraether Membrane Lipids in a Large Temperate Lake (Loch Lomond, UK):Implications for Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraether (GDGT)-Based Palaeothermometry.Biogeosciences, 11(19):5539-5563. doi: 10.5194/bg-11-5539-2014 Coffinet, S., Huguet, A., Williamson, D., et al., 2015.Occurrence and Distribution of Glycerol Dialkanol Diethers and Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers in a Peat Core from SW Tanzania.Organic Geochemistry, 83-84:170-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2015.03.013 Dang, X.Y., Yang, H., Naafs, B.D.A., et al., 2016.Evidence of Moisture Control on the Methylation of Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers in Semi-Arid and Arid Soils.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 189:24-36. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.06.004 Dirghangi, S.S., Pagani, M., Hren, M.T., et al., 2013.Distribution of Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers in Soils from Two Environmental Transects in the USA.Organic Geochemistry, 59:49-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.03.009 Günther, F., Thiele, A., Gleixner, G., et al., 2014.Distribution of Bacterial and Archaeal Ether Lipids in Soils and Surface Sediments of Tibetan Lakes:Implications for GDGT-Based Proxies in Saline High Mountain Lakes.Organic Geochemistry, 67:19-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.11.014 Hao, Q.Z., Oldfield, F., Bloemendal, J., et al., 2008.The Magnetic Properties of Loess and Paleosol Samples from the Chinese Loess Plateau Spanning the Last 22 Million Years.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 260(3-4):389-404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.11.010 Heinrich, H., 1988.Origin and Consequences of Cyclic Ice Rafting in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean during the Past 130, 000 Years.Quaternary Research, 29(2):142-152. https://doi.org/10.1016/0033-5894(88)90057-9 Herfort, L., Schouten, S., Boon, J.P., et al., 2006.Characterization of Transport and Deposition of Terrestrial Organic Matter in the Southern North Sea Using the BIT Index.Limnology and Oceanography, 51(5):2196-2205. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2006.51.5.2196 Hopmans, E.C., Weijers, J.W.H., Schefuβ, E., et al., 2004.A Novel Proxy for Terrestrial Organic Matter in Sediments Based on Branched and Isoprenoid Tetraether Lipids.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 224(1-2):107-116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2004.05.012 Huang, Z., Wang, J.L., Wang, Y., 2010.Grain-Size Features of Quaternary Sediments in Changjiang Three Gorge Reservoir of the Wushan Area.Tropical Geography, 30(1):30-33, 39 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=rddl201001006 Huguet, A., Wiesenberg, G.L.B., Gocke, M., et al., 2012.Branched Tetraether Membrane Lipids Associated with Rhizoliths in Loess:Rhizomicrobial Overprinting of Initial Biomarker Record.Organic Geochemistry, 43:12-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.11.006 Kang, S.G., Lu, Y.C., Wang, X.L., 2011.Closely-Spaced Recuperated OSL Dating of the Last Interglacial Paleosol in the Southeastern Margin of the Chinese Loess Plateau.Quaternary Geochronology, 6(5):480-490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quageo.2011.04.004 Kim, J.H., Ludwig, W., Schouten, S., et al., 2007.Impact of Flood Events on the Transport of Terrestrial Organic Matter to the Ocean:A Study of the Têt River (SW France) Using the BIT Index.Organic Geochemistry, 38(10):1593-1606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2007.06.010 Lai, Z.P., Wintle, A.G., Thomas, D.S.G., 2007.Rates of Dust Deposition between 50 ka and 20 ka Revealed by OSL Dating at Yuanbao on the Chinese Loess Plateau.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 248(3-4):431-439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.12.013 Li, C.A., Zhang, Y.F., Yuan, S.Y., et al., 2010.Grain Size Characteristics and Origin of the "Wushan Loess" at Wushan Area.Earth Science, 35(5):879-884 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201005018 Li, G.H., Xia, D.S., Jin, M., et al., 2015.Magnetic Characteristics of Loess-Paleosol Sequences in Tacheng, Northwestern China, and Their Paleoenvironmental Implications.Quaternary International, 372:87-96.https://doi.org/10.13039/501100001809 doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.08.002 Li, T.G., Chen, J.X., Zhang, D.Y., et al., 2006.Sedimentary Record of Millennial-Scale Paleoceanography Evolution since the Last Glaciation in the Okinawa Trough.Studia Marina Sinica, 47(4):16-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HKJK200600001.htm Liu, X.M., Liu, D.S., Heller, F., et al., 1990.Frequency-Dependent Susceptibility of Loess and Quaternary Paleoclimate.Quaternary Sciences, 10(1):42-50 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000269607 Lu, B., Chen, R.H., Wang, Z.P., et al., 2001.Long-Chain Alkenones and Their Application Study on the Paleo-Temperature of U37k Values in the Arctic Ocean.Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 23(5):49-57 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.hyxb.org.cn/aos/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20010506 Lü, X.X., Yang, H., Song, J.M., et al., 2014.Sources and Distribution of Isoprenoid Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers (GDGTs) in Sediments from the East Coastal Sea of China:Application of GDGT-Based Paleothermometry to a Shallow Marginal Sea.Organic Geochemistry, 75:24-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2014.06.007 Peterse, F., van der Meer, J., Schouten, S., et al., 2012.Revised Calibration of the MBT-CBT Paleotemperature Proxy Based on Branched Tetraether Membrane Lipids in Surface Soils.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 96:215-229.https://doi.org/10.13039/501100000781 doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2012.08.011 Schouten, S., Hopmans, E.C., Schefuβ, E., et al., 2002.Distributional Variations in Marine Crenarchaeotal Membrane Lipids:A New Tool for Reconstructing Ancient Sea Water Temperatures? Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 204(1-2):265-274.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(02)00979-2 doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00979-2 Schreuder, L.T., Beets, C.J., Prins, M.A., et al., 2016.Late Pleistocene Climate Evolution in Southeastern Europe Recorded by Soil Bacterial Membrane Lipids in Serbian Loess.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 449:141-148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.02.013 Sinninghe Damsté, J.S., 2016.Spatial Heterogeneity of Sources of Branched Tetraethers in Shelf Systems:The Geochemistry of Tetraethers in the Berau River Delta (Kalimantan, Indonesia).Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 186:13-31. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.04.033 Sun, D.H., Su, R.X., Bloemendal, J., et al., 2008.Grain-Size and Accumulation Rate Records from Late Cenozoic Aeolian Sequences in Northern China:Implications for Variations in the East Asian Winter Monsoon and Westerly Atmospheric Circulation.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 264(1-2):39-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.03.011 Tang, C.Y., Yang, H., Dang, X.Y., et al., 2017.Comparison of Paleotemperature Reconstructions Using Microbial Tetraether Thermometers of the Chinese Loess-Paleosol Sequence for the Past 350 000 Years.Science China Earth Sciences, 60(6):1159-1170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-016-9035-y Tierney, J.E., Russell, J.M., 2009.Distributions of Branched GDGTs in a Tropical Lake System:Implications for Lacustrine Application of the MBT/CBT Paleoproxy.Organic Geochemistry, 40(9):1032-1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.04.014 Wang, H., Liu, W., Zhang, C.L., 2014.Dependence of the Cyclization of Branched Tetraethers on Soil Moisture in Alkaline Soils from Arid-Subhumid China:Implications for Palaeorainfall Reconstructions on the Chinese Loess Plateau.Biogeosciences, 11(23):6755-6768. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-11-6755-2014 Wang, H.Y., Liu, W.G., Zhang, C.L., et al., 2013.Branched and Isoprenoid Tetraether (BIT) Index Traces Water Content along Two Marsh-Soil Transects Surrounding Lake Qinghai:Implications for Paleo-Humidity Variation.Organic Geochemistry, 59:75-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.03.011 Wang, S.W., 2011.D/O Cycles and H Events.Advances in Climate Change Research, 7(6):458-460 (in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=qhbhyjjz201106013 Wang, Y.X., Yang, J.D., Chen, J., et al., 2007.The Sr and Nd Isotopic Variations of the Chinese Loess Plateau during the Past 7 Ma:Implications for the East Asian Winter Monsoon and Source Areas of Loess.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 249(3-4):351-361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.02.010 Wei, H.Z., Lei, F., Jiang, S.Y., et al., 2015.Implication of Boron Isotope Geochemistry for the Pedogenic Environments in Loess and Paleosol Sequences of Central China.Quaternary Research, 83(1):243-255. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2014.09.004 Weijers, J.W.H., Schouten, S., Hopmans, E.C., et al., 2006a.Membrane Lipids of Mesophilic Anaerobic Bacteria Thriving in Peats have Typical Archaeal Traits.Environmental Microbiology, 8(4):648-657.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00941.x doi: 10.1111/emi.2006.8.issue-4 Weijers, J.W.H., Schouten, S., Spaargaren, O.C., et al., 2006b.Occurrence and Distribution of Tetraether Membrane Lipids in Soils:Implications for the Use of the TEX86 Proxy and the BIT Index.Organic Geochemistry, 37(12):1680-1693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.07.018 Weijers, J.W.H., Schouten, S., van den Donker, J.C., et al., 2007.Environmental Controls on Bacterial Tetraether Membrane Lipid Distribution in Soils.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(3):703-713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2006.10.003 Weijers, J.W.H., Steinmann, P., Hopmans, E.C., et al., 2011.Bacterial Tetraether Membrane Lipids in Peat and Coal:Testing the MBT-CBT Temperature Proxy for Climate Reconstruction.Organic Geochemistry, 42(5):477-486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2011.03.013 Wu, K., Peng, H.X., Shi, R., et al., 2014.Analysis on the Characteristics and Their Origin of the Grain-Size of Wushan Loess in the Three Gorges Area, China.Journal of Huazhong Normal University (Natural Sciences), 48(2):284-289 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HZSZ201402026.htm Xie, S.C., Evershed, R.P., Huang, X.Y., et al., 2013.Concordant Monsoon-Driven Postglacial Hydrological Changes in Peat and Stalagmite Records and Their Impacts on Prehistoric Cultures in Central China.Geology, 41(8):827-830.https://doi.org/10.1130/g34318.1 doi: 10.1130/G34318.1 Yang, G.F., Zhang, C.L., Xie, S.C., et al., 2013.Microbial Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers from River Water and Soil near the Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River.Organic Geochemistry, 56:40-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2012.11.014 Yang, H., Ding, W.H., Wang, J.X., et al., 2012.Soil pH Impact on Microbial Tetraether Lipids and Terrestrial Input Index (BIT) in China.Science China Earth Sciences, 55(2):236-245. doi: 10.1007/s11430-011-4295-x Yang, H., 2014.The Paleoclimate Reconstruction Based on Microbial Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers in Terrestrial Environments: Modern Process and Its Application in Chinese Loess-Paleosol and Stalagmite (Dissertation).China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 55-57 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, H., Pancost, R.D., Tang, C.Y., et al., 2014.Distributions of Isoprenoid and Branched Glycerol Dialkanol Diethers in Chinese Surface Soils and a Loess-Paleosol Sequence:Implications for the Degradation of Tetraether Lipids.Organic Geochemistry, 66:70-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.11.003 Yao, L.K., Xue, B., Yao, M., et al., 2007.By Using U37K Index to Study Sea Surface Paleotemperatures in South China Sea since the Last Glacial Maximum.Journal of Marine Sciences, 25(4):24-31 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DHHY200704002.htm Zhang, Y.F., Li, C.A., Shao, L., et al., 2010.Magnetic Fabric Characteristics and Implications for Its Origin of "Wushan Loess".Earth Science, 35(5):885-890 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201005019 Zhou, H., Hu, J., Ming, L., et al., 2011.Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers and Paleoenvironmental Reconstruction in Zoig Peat Sediments during the Last 150 Years.Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(23):2456-2463. doi: 10.1007/s11434-011-4594-9 黄臻, 王建力, 王勇, 2010.长江三峡巫山第四纪沉积物粒度分布特征.热带地理, 30(1):30-33, 39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2010.01.006 李长安, 张玉芬, 袁胜元, 等, 2010."巫山黄土"粒度特征及其对成因的指示.地球科学, 35(5):879-884. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=2033 李铁刚, 陈金霞, 张德玉, 等, 2006.冲绳海槽末次冰期以来千年尺度古海洋演化的沉积记录.海洋科学集刊, 47(4):16-28. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=HKJK200600001&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 刘秀铭, 刘东生, Heller, F., 等, 1990.黄土频率磁化率与古气候冷暖变换.第四纪研究, 10(1):42-50. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1990.01.005 卢冰, 陈荣华, 王自磐, 等, 2001.长链烯酮及U37k值在北极海洋古温度的应用研究.海洋学报, 23(5):49-57. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2001.05.006 王绍武, 2011.D/O循环与H事件.气候变化研究进展, 7(6):458-460. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1719.2011.06.013 吴可, 彭红霞, 时冉, 等, 2014.长江三峡地区黄土粒度特征及其成因分析.华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 48(2):284-289. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hzsfdxxb201402026 杨欢, 2014.陆相微生物脂类GDGTs的古气候重建: 现代过程及其在黄土-古土壤和石笋中的应用(博士学位论文).武汉: 中国地质大学, 55-57. 姚龙奎, 薛斌, 姚梅, 等, 2007.U37K指标在南海末次盛冰期表层海水古温度研究中的应用.海洋学研究, 25(4):24-31. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_dhhy200704003.aspx 张玉芬, 李长安, 邵磊, 等, 2010."巫山黄土"的磁组构特征及成因.地球科学, 35(5):885-890. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=2034 -









 下载:
下载: