Zircon U-Pb Ages and Petrogenesis of Ore-Bearing Porphyry for Qingcaoshan Porphyry Cu-Au Deposit, Tibet
-
摘要: 西藏青草山Cu-Au矿床是班公湖-怒江缝合带北侧新发现的具有大型远景的斑岩型矿床,但该矿床含矿斑岩的年龄、成因及源区一直未得到有效的约束.对青草山花岗闪长岩以及含矿花岗岩闪长斑岩进行了锆石年代学、Hf同位素以及岩石地球化学研究.结果显示,花岗闪长岩与含矿花岗闪长斑岩的侵入时代分别为131.2±0.3 Ma与117.9±0.8 Ma,代表了班公湖-怒江缝合带早期的成岩作用以及斑岩Cu-Au成矿作用.二者具有相似的地球化学特征,表明二者可能具有相同的岩浆源区,是不同时期同源岩浆活动的产物.结合含矿花岗闪长斑岩锆石Hf同位素组成,认为青草山含矿斑岩形成于班公湖-怒江洋壳向北俯冲过程中,是下地壳部分熔融的产物,受到了少量地幔物质的混合.Abstract: The Qingcaoshan porphyry Cu-Au deposit, located in the northern Bangong Co-Nujiang belt, is a newly discovered porphyry deposit with huge potential.However, the age, origin and source area of the ore-bearing porphyry have not been effectively constrained.In this paper, we present the zircon geochronology, Hf isotope, and geochemistry of Qingcaoshan granodiorite and granodiorite porphyry.The analysis results show that the ages of granodiorite porphyry and granodiorite are 117.9±0.8 Ma and 131.2±0.3 Ma, respectively, which represent porphyry mineralization of Bangong Co-Nujiang metallogenic belt.They also exhibit relatively uniform in-situ zircon Hf isotopic compositions.In conclusion, Qingcaoshan ore-bearing porphyries were derived from the partial melting of mafic lower crust, which were induced by the subduction of the Bangong Co-Nujiang ocean crust, and they were also mixed by a small amount of enriched lithospheric mantle.
-
Key words:
- petrogenesis /
- zircon U-Pb age /
- porphyry Cu-Au deposit /
- Qingcaoshan /
- Bangong Co-Nujiang metallogenic belt /
- Tibet /
- geochemistry /
- geochronology
-
图 4 青草山花岗闪长斑岩和花岗闪长岩主量元素图解
图a据Wilson(1989);图b据Peccerillo and Taylor(1976).多不杂与波龙矿床的花岗闪长斑岩数据分别来源于佘宏全等(2009)及陈华安等(2013)
Fig. 4. Discrimination diagrams for the Qingcaoshan granodiorite porphyry and granodiorite
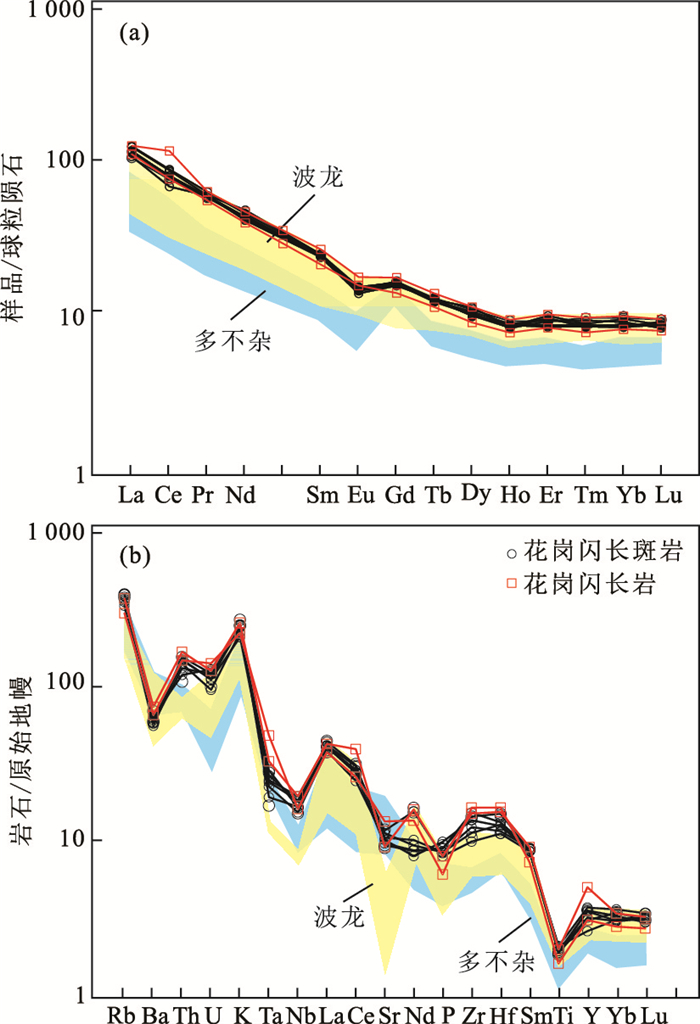
图 5 青草山花岗闪长斑岩和花岗闪长岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分模式(a)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b)
标准化数值据Sun and McDonough(1989).多不杂与波龙矿床的花岗闪长斑岩数据分别来源于佘宏全等(2009)及陈华安等(2013)
Fig. 5. Chondrite-normalized rare earth element pattern (a) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagram (b) for the Qingcaoshan granodiorite porphyry and granodiorite
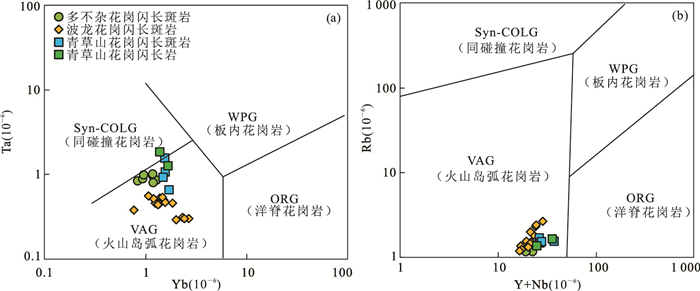
图 6 青草山花岗闪长斑岩和花岗闪长岩的构造判别图解
图b据Pearce et al.(1984).多不杂与波龙矿床的花岗闪长斑岩数据分别来源于佘宏全等(2009)及陈华安等(2013);VAG.火山岛弧花岗岩;WPG.板内花岗岩;Syn-COLG.同碰撞花岗岩;ORG.洋脊花岗岩
Fig. 6. Discrimination diagrams for the Qingcaoshan granodiorite porphyry and granodiorite
图 7 草山花岗闪长斑岩和花岗闪长岩的La/Sm-La图解
多不杂与波龙矿床的花岗闪长斑岩数据分别来源于佘宏全等(2009)及陈华安等(2013)
Fig. 7. La/Sm-La diagram for the Qingcaoshan granodiorite porphyry and granodiorite
图 8 青草山花岗闪长斑岩锆石εHf(t)-t图解
波龙花岗闪长斑岩与多龙矿集区成矿斑岩数据分别来源于陈华安等(2013)
Fig. 8. εHf(t)-t diagram for the Qingcaoshan granodiorite porphyry
表 1 青草山花岗闪长斑岩与花岗闪长岩LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb分析结果
Table 1. LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dating data of the Qingcaoshan granodiorite porphyry and granodiorite
测点号 含量(10-6) Th/U 同位素比值 年龄(Ma) Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 花岗闪长斑岩 QCS-B3-1 92 639 0.14 0.050 0 0.001 7 0.130 6 0.004 3 0.018 9 0.000 2 118 3.65 118 1.02 QCS-B3-2 76 600 0.13 0.045 2 0.001 5 0.115 6 0.003 7 0.018 6 0.000 2 112 3.48 117 1.05 QCS-B3-3 78 581 0.13 0.049 4 0.001 6 0.128 5 0.004 2 0.018 9 0.000 2 120 3.68 119 1.06 QCS-B3-4 131 670 0.20 0.047 1 0.001 6 0.133 2 0.004 7 0.020 5 0.000 2 123 3.37 128 1.15 QCS-B3-5 188 786 0.24 0.048 7 0.001 3 0.135 9 0.003 5 0.020 2 0.000 2 128 3.23 128 1.12 QCS-B3-6 121 686 0.18 0.047 0 0.001 5 0.126 4 0.004 0 0.019 5 0.000 2 120 3.85 122 1.21 QCS-B3-7 187 785 0.24 0.046 7 0.001 4 0.133 8 0.003 9 0.020 8 0.000 2 128 3.42 132 1.07 QCS-B3-8 136 732 0.19 0.045 6 0.001 3 0.129 6 0.003 8 0.020 6 0.000 2 126 3.43 132 0.94 QCS-B3-10 131 536 0.24 0.048 0 0.001 9 0.122 0 0.004 5 0.018 6 0.000 2 119 4.13 118 1.19 QCS-B3-11 309 1 017 0.30 0.048 5 0.001 3 0.134 8 0.003 6 0.020 1 0.000 2 125 3.15 128 0.97 QCS-B3-12 139 671 0.21 0.048 2 0.001 6 0.130 3 0.004 4 0.019 5 0.000 2 122 3.97 123 1.07 QCS-B3-13 234 878 0.27 0.047 8 0.001 2 0.136 8 0.003 5 0.020 7 0.000 2 130 3.10 132 1.10 QCS-B3-14 78 588 0.13 0.047 8 0.001 6 0.126 3 0.004 2 0.019 3 0.000 2 117 3.58 118 1.12 QCS-B3-15 102 653 0.16 0.049 1 0.001 7 0.125 9 0.004 1 0.018 6 0.000 2 118 3.69 118 1.21 QCS-B3-16 101 675 0.15 0.051 5 0.001 7 0.138 6 0.004 7 0.019 6 0.000 2 122 4.32 122 1.24 QCS-B3-17 174 797 0.22 0.048 0 0.001 4 0.138 5 0.003 9 0.020 9 0.000 2 130 3.73 132 1.14 QCS-B3-18 109 407 0.27 0.050 3 0.002 2 0.124 7 0.005 1 0.018 1 0.000 2 118 4.63 117 1.32 QCS-B3-19 108 449 0.24 0.045 9 0.001 8 0.115 7 0.004 6 0.018 3 0.000 2 114 4.14 117 1.10 QCS-B3-20 118 650 0.18 0.046 5 0.001 6 0.124 0 0.004 3 0.019 4 0.000 2 120 4.06 121 1.10 花岗闪长岩 QCS-B9-1 206 784 0.26 0.047 2 0.001 3 0.135 2 0.003 6 0.020 8 0.000 2 128 3.3 131 1.0 QCS-B9-2 258 1 113 0.23 0.049 9 0.001 6 0.141 6 0.004 4 0.020 9 0.000 4 127 3.1 130 1.0 QCS-B9-3 309 1 033 0.30 0.050 6 0.001 5 0.147 8 0.004 8 0.021 1 0.000 2 133 4.0 131 1.5 QCS-B9-4 263 970 0.27 0.050 0 0.001 4 0.143 6 0.004 0 0.020 8 0.000 2 131 3.6 130 1.4 QCS-B9-7 281 1 146 0.25 0.048 6 0.001 3 0.141 3 0.004 0 0.021 0 0.000 2 131 3.5 131 1.5 QCS-B9-9 307 1 084 0.28 0.046 9 0.001 2 0.131 1 0.003 2 0.020 2 0.000 2 125 3.0 131 1.1 QCS-B9-10 113 774 0.15 0.052 4 0.001 7 0.149 3 0.004 7 0.020 7 0.000 2 138 4.0 130 1.2 QCS-B9-14 235 1 022 0.23 0.049 7 0.001 3 0.147 9 0.003 9 0.021 4 0.000 2 136 3.4 133 1.2 QCS-B9-15 310 771 0.40 0.048 2 0.001 6 0.142 4 0.004 7 0.021 4 0.000 2 132 4.1 134 1.3 QCS-B9-16 206 789 0.26 0.047 0 0.001 4 0.139 6 0.004 1 0.021 5 0.000 2 132 3.7 134 1.4 QCS-B9-17 130 647 0.20 0.053 1 0.001 5 0.159 8 0.004 9 0.021 6 0.000 3 139 4.8 132 1.8 QCS-B9-18 472 1 098 0.43 0.049 7 0.001 3 0.139 1 0.003 5 0.020 3 0.000 2 131 3.3 130 0.9 QCS-B9-19 239 817 0.29 0.049 1 0.001 3 0.141 6 0.003 8 0.020 8 0.000 2 133 3.4 131 1.1 表 2 青草山花岗闪长斑岩锆石原位Hf同位素数据
Table 2. In-situ zircon Hf isotope data of the Qingcaoshan granodiorite porphyry
测点号 t (Ma) 176Yb/177Hf 176Lu/177Hf 176Hf/177Hf ±σ εHf(t) ±1σ tDM2(Hf) fLu/Hf QCS-B3-3 120.8 0.021 689 0.000 797 0.282 707 0.000 379 0.27 0.57 1 029 -0.98 QCS-B3-1 121.0 0.019 219 0.000 697 0.282 712 0.000 340 0.48 0.57 1 018 -0.98 QCS-B3-18 117.0 0.018 597 0.000 679 0.282 719 0.000 174 1.10 0.61 997 -0.98 QCS-B3-4 130.5 0.020 163 0.000 737 0.282 694 0.000 232 0.02 0.61 1 051 -0.98 QCS-B3-5 129.0 0.021 672 0.000 798 0.282 702 0.000 122 0.30 0.62 1 034 -0.98 QCS-B3-7 132.7 0.024 334 0.000 899 0.282 712 0.000 209 0.72 0.58 1 014 -0.97 QCS-B3-8 131.2 0.019 496 0.000 706 0.282 675 0.000 425 -0.61 0.58 1 087 -0.98 QCS-B3-10 119.1 0.033 375 0.001 241 0.282 725 0.000 176 0.85 0.60 996 -0.96 QCS-B3-11 128.3 0.024 251 0.000 899 0.282 681 0.000 235 -0.47 0.58 1 077 -0.97 QCS-B3-12 124.6 0.019 970 0.000 730 0.282 689 0.000 357 -0.27 0.62 1 063 -0.98 QCS-B3-13 132.0 0.022 365 0.000 816 0.282 711 0.000 191 0.65 0.61 1 017 -0.98 QCS-B3-16 124.9 0.031 567 0.001 255 0.282 703 0.000 614 0.19 0.75 1 037 -0.96 QCS-B3-14 123.1 0.017 094 0.000 644 0.282 693 0.000 161 -0.14 0.59 1 054 -0.98 QCS-B3-15 119.1 0.017 330 0.000 643 0.282 690 0.000 069 -0.35 0.58 1 063 -0.98 QCS-B3-17 133.6 0.020 659 0.000 744 0.282 701 0.000 108 0.37 0.57 1 034 -0.98 注:εHf(t) = 10 000×{[(176Hf/177Hf)S-(176Lu/177Hf)S×(eλt-1)]/[(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0-(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR×(eλt-1)]-1};tDM =1/λ×ln{1+[(176Hf/177Hf)S-(176Hf/177Hf)DM]/[(176Lu/177Hf)S-(176Lu/177Hf)DM]};tDMC=tDM-(tDM-t)×[(fcc-fLu/Hf)/(fcc-fDM)];fLu/Hf =(176Lu/177Hf)S/(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR-1;λ=1.867×10-11a-1 ( Söderlund et al., 2004 ); (176Lu/177Hf)S和(176Hf/177Hf)S是样品的测量值;(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR =0.033 2,(176Hf/177Hf)CHUR, 0 =0.282 772;(176Lu/177Hf)DM = 0.038 4,(176Hf/177Hf)DM = 0.283 25(Griffin et al., 2000 ); (176Lu/177Hf)地壳=0.015;fcc= [(176Lu/177Hf)地壳/(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR]-1;fDM =[(176Lu/177Hf)DM/(176Lu/177Hf)CHUR]-1.表 3 青草山岩体主量(%)、微量(10-6)及稀土元素(10-6)分析结果
Table 3. Major elements (%), trace elements (10-6) and rare earth elements (10-6) compositions of intrusions from Qingcaoshan porphyry Cu-Au deposit
样品 花岗闪长斑岩 花岗闪长岩 QCS-B3 QCS-B4 QCS-B5 QCS-B6 QCS2015-1 QCS2015-2 QCS2015-3 QCS2015-4 QCS2015-5 QCS-B9 QCS-B10 SiO2 66.30 67.51 67.77 67.14 67.23 66.90 67.13 67.45 66.87 69.17 67.97 TiO2 0.44 0.40 0.42 0.42 0.41 0.45 0.42 0.41 0.45 0.35 0.43 Al2O3 15.59 14.68 15.11 15.50 15.94 15.33 15.44 15.39 15.20 14.76 15.43 Fe2O3 1.35 1.42 1.62 1.38 1.46 1.45 1.57 1.51 1.67 0.93 1.82 FeO 1.65 1.30 1.40 1.13 1.29 1.34 1.62 1.46 1.51 1.37 0.73 MnO 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.03 0.02 MgO 1.64 1.41 1.24 1.44 1.54 1.45 1.42 1.41 1.56 1.10 0.75 CaO 1.62 1.31 1.82 1.42 1.66 1.75 1.64 1.57 1.50 2.21 1.34 Na2O 2.05 1.48 2.13 2.19 2.11 2.03 2.09 2.23 2.12 2.17 1.55 K2O 6.95 7.60 5.87 6.91 6.99 6.78 7.01 6.95 6.28 6.24 7.26 P2O5 0.20 0.18 0.17 0.19 0.19 0.21 0.18 0.19 0.18 0.13 0.17 H2O+ 1.60 1.52 1.52 1.48 1.57 1.49 1.56 1.54 1.45 1.10 1.51 CO2 0.22 0.75 0.60 0.40 0.56 0.66 0.34 0.37 0.49 0.18 0.70 Total 99.63 99.58 99.69 99.61 100.96 99.86 100.44 100.5 99.29 99.74 99.68 Mg# 50.49 49.35 43.60 51.96 51.46 49.56 45.62 47.27 48.13 47.03 36.07 Na2O+K2O 9.00 9.08 8.00 9.10 9.10 8.81 9.10 9.18 8.40 8.41 8.81 Na2O/K2O 3.39 5.14 2.76 3.16 3.31 3.34 3.35 3.12 2.96 2.88 4.68 La 24.7 29.2 27.0 27.2 26.8 25.1 26.4 28.9 27.4 24.7 27.9 Ce 46.4 53.7 49.0 48.7 47.1 41.8 49.1 52.9 52.0 44.5 66.9 Pr 5.51 5.99 5.64 5.65 5.56 5.67 5.55 5.70 5.62 5.03 5.73 Nd 20.1 21.5 20.4 20.5 20.0 19.5 20.3 22.6 20.9 17.9 21.0 Sm 3.82 3.86 3.72 3.77 3.79 3.72 3.90 3.88 3.73 3.17 3.97 Eu 0.891 0.861 0.898 0.867 0.905 0.829 0.866 0.912 0.883 0.884 1.00 Gd 3.50 3.32 3.36 3.40 3.45 3.29 3.50 3.43 3.48 2.81 3.52 Tb 0.499 0.486 0.473 0.496 0.488 0.491 0.479 0.477 0.502 0.416 0.509 Dy 2.86 2.63 2.67 2.66 2.96 2.61 2.78 2.73 2.59 2.26 2.84 Ho 0.539 0.491 0.509 0.513 0.499 0.521 0.517 0.488 0.500 0.433 0.523 Er 1.57 1.65 1.45 1.47 1.71 1.49 1.62 1.58 1.54 1.36 1.66 Tm 0.255 0.222 0.225 0.228 0.234 0.229 0.231 0.246 0.243 0.196 0.243 Yb 1.70 1.55 1.48 1.54 1.67 1.51 1.49 1.60 1.76 1.37 1.66 Lu 0.248 0.223 0.230 0.227 0.229 0.236 0.241 0.219 0.250 0.200 0.237 Y 16.1 24.8 14.4 15.4 13.9 11.8 15.8 16.0 16.7 13.9 22.5 Li 37.0 36.4 31.7 36.9 34.6 35.8 0.8 33.5 38.1 21.8 15.8 Be 1.70 1.42 1.92 1.62 1.55 1.67 1.78 1.85 1.59 1.87 1.69 Sc 7.53 6.43 6.99 6.80 6.45 6.09 7.13 6.84 6.76 4.98 6.15 Cr 8.78 10.10 12.00 7.24 8.98 7.77 10.34 9.79 10.50 11.00 9.57 Co 7.71 10.10 8.30 7.18 7.89 8.97 9.02 9.45 8.34 4.77 7.63 Cu 1 767 2 931 1 287 1 921 1 367 1 786 1 573 1 005 2 450 541 1 257 Zn 72.4 134 46.2 65.2 56.7 99.0 76.5 121.0 90.2 60.9 57.6 Ga 18.0 18.4 17.1 17.9 17.8 19.0 18.2 16.8 16.4 17.4 19.0 Ge 1.30 1.35 1.33 1.21 1.18 1.40 1.37 1.26 1.24 1.25 1.11 Rb 232 230 197 201 221 218 208 233 213 176 218 Cs 9.51 9.69 10.70 9.23 9.76 9.45 9.99 10.43 9.82 9.44 10.90 Pb 49.4 551 12.5 14.1 78.0 47.0 17.0 32.0 23.0 26.2 14.4 Th 10.1 8.6 12.0 12.3 12.4 11.8 10.5 9.5 11.2 11.8 13.4 U 2.45 1.98 2.19 2.64 2.40 2.23 2.38 2.55 1.89 2.78 2.50 Ni 9.8 13.5 10.0 13.2 9.0 14.1 11.3 13.7 12.5 8.9 13.9 Sr 243 186 240 225 194 209 231 199 216 275 189 V 75.0 63.5 68.0 63.3 67.1 69.3 71.2 64.8 73.0 43.2 47.0 Zr 115 151 109 4 383 157 148 134 166 123 179 164 Nb 10.4 12.7 12.6 12.6 11.4 10.6 12.4 11.5 13.4 11.1 13.4 Ba 460 398 371 433 89 403 386 428 415 436 491 Hf 3.40 4.38 3.37 87.40 4.50 3.76 3.48 3.97 3.84 4.92 4.62 Ta 0.67 1.09 0.95 1.59 1.13 0.89 1.05 0.76 0.98 1.89 1.29 As 3.89 7.93 1.55 3.90 3.76 3.09 4.03 3.82 3.97 4.49 6.76 Hg 0.031 0.019 0.020 0.018 0.017 0.023 0.030 0.025 0.016 0.014 0.017 Bi 24.3 58.1 6.43 24.2 54.3 45.7 37.8 32.4 5.9 3.92 14.7 Sb 0.50 0.65 0.27 0.29 0.76 0.43 0.54 0.38 0.62 0.28 2.07 Mo 16.9 294 6.21 5.77 20.1 7.97 8.04 6.83 4.73 13.3 6.67 W 10.4 73.6 3.6 10.1 15.1 13.5 16.8 9.8 9.4 14.1 9.1 Sn 9.07 9.57 7.24 9.58 9.87 9.03 8.78 8.02 9.45 7.38 7.52 Ag 1.78 4.09 1.09 2.18 2.09 2.34 1.89 1.73 1.99 0.761 1.45 Au 166 137 76.8 218 156 139 189 167 187 11.4 67.7 ∑REE 112 125 117 117 129 119 133 142 138 105 137 LREE/HREE 9.1 10.9 10.2 10.1 9.3 9.3 9.8 10.7 10.2 10.6 11.3 Sr/Y 15.1 7.5 16.7 14.6 14.0 17.7 14.6 12.4 12.9 19.7 8.4 La/Yb 14.6 18.8 18.2 17.7 16.0 16.6 17.7 18.1 15.6 18.0 16.9 (La/Yb)N 10.5 13.5 13.1 12.7 11.5 11.9 12.7 13.0 11.2 12.9 12.1 Dy/Yb 1.70 1.70 1.80 1.70 1.69 1.69 1.80 1.73 1.77 1.65 1.71 δEu 0.73 0.72 0.76 0.73 0.75 0.71 0.70 0.75 0.74 0.89 0.80 注:Mg#=100×Mg/(Mg+ Fe)(原子个数比);TFeO=FeO+0.89×Fe2O3;A/CNK=摩尔Al2O3/(CaO+Na2O+K2O);δEu=2×EuN/(SmN+GdN). 表 4 班公湖-怒江成矿带主要矿床的年代学特征
Table 4. Ages of deposits in Bangong Co-Nujiang metallogenic belt
矿区 岩性 测试对象 方法 年龄(Ma) 资料来源 尕尔穷 石英闪长岩 锆石 LA-ICPMS U-Pb 87.1±0.4 姚晓峰等(2012) 花岗斑岩 83.2±0.7 姚晓峰等(2013) 石英闪长岩 辉钼矿 Re-Os等时线 86.87±0.5 李志军等(2011) 嘎拉勒 花岗闪长岩 锆石 LA-ICPMS U-Pb 86.52±0.41 闪长玢岩 88.59±0.45 吕立娜等(2011) 88.09±0.41 矽卡岩 白云母 40Ar-39Ar 91.48±0.68 汪傲等(2014) 多不杂 花岗闪长斑岩 锆石 SHRIMP U-Pb 120.9±2.4 佘宏全等(2009) 121.6±1.9 李金祥等(2008) 116.7±1.7 Li et al.(2011) 辉钼矿 Re-Os等时线 118.0±1.5 佘宏全等(2009) 绢云母 40Ar-39Ar 115.2±1.2 Li et al.(2011) 钾长石 115.2±1.1 波龙 花岗闪长斑岩 锆石 LA-ICPMS U-Pb 120.2±2.0 119.5±0.9 陈华安等(2013) 119.3±1.3 SHRIMP U-Pb 121.1±1.7 Li et al.(2011) SIMS U-Pb 117.5±1.0 118.0±1.0 118.5±1.0 Li et al.(2014) 石英闪长玢岩 118.4±1.1 118.6±1.0 花岗闪长斑岩 辉钼矿 Re-Os等时线 119.4±1.5 祝向平等(2011) 拿若 花岗闪长斑岩 锆石 SHRIMP U-Pb 119.5±0.6 吕立娜(2012) 铁格龙 英云闪长斑岩 锆石 SHRIMP U-Pb 119.7±0.6 吕立娜(2012) 尕尔勤 英云闪长斑岩 锆石 SHRIMP U-Pb 122.5±0.6 吕立娜(2012) 青草山 花岗闪长斑岩 锆石 LA-ICPMS U-Pb 114.6±1.2 周胜金等(2013) 117.9±0.8 本文 花岗闪长岩 131.2±0.3 -
Chen, H.A., Zhu, X.P., Ma, D.F., et al., 2013.Geochronology and Geochemistry of the Bolong Porphyry Cu-Au Deposit, Tibet and Its Mineralizing Significance.Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(10):1593-1611(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb201310009 Ding, S., Tang, J.X., Zheng, W.B., et al., 2017.Geochronology and Geochemistry of Naruo Porphyry Cu (Au) Deposit in Duolong Ore-Concentrated Area, Tibet, and Their Geological Significance.Earth Science, 42(1):1-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.001 Du, D.D., Qu, X, M., Wang, G.H., et al., 2011.Bidirectional Subduction of the Middle Tethys Oceanic Basin in the West Segment of Bangonghu-Nujiang Suture, Tibet:Evidence from Zircon U-Pb LAICPMS Dating and Petrogeochemistry of Arc Granites.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7):1993-2002 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201107008 Furman, T., Graham, D., 1999.Erosion of Lithospheric Mantle beneath the East African Rift System:Geochemical Evidence from the Kivu Volcanic Province.Lithos, 48(1):237-262. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-4937(99)00031-6 Gao, S., Rudnick.R., Richard, W., et al., 2003.Removal of Lithospheric Mantle in the North China Craton:Re-Os Isotopic Evidence for Coupled Crust-Mantle Growth.Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3):61-67 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200303006.htm Griffin, W.L., Pearson, N.J., Belousova, E., et al., 2000.The Hf Isotope Composition of Cratonic Mantle:LAM-MC-ICPMS Analysis of Zircon Megacrysts in Kimberlites.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1):133-147. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0016-7037(99)00343-9 Hou, K.J., Li, Y.H., Xie, G.Q., 2007.LA-MC-ICP-MS Technique for Hf Isotope Microanalysis of Zircon.Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 28(Suppl.):26-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200710025 Hu, Z.C., Liu, Y.S., Gao, S., et al., 2012.Improved in Situ Hf Isotope Ratio Analysis of Zircon Using Newly Designed X Skimmer Cone and Jet Sample Cone in Combination with the Addition of Nitrogen by Laser Ablation Multiple Collector ICP-MS.Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 27(9):1391-1399. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2ja30078h Huang, J.Q., Chen B.W., 1987.The Evolution of the Tethys in China and Adjacent Regions.Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Li, G.M., Duan, Z.M., Liu, B., et al., 2011.The Discovery of Jurassic Accretionary Complexes in Duolong Area, Northern Bangong Co-Nujiang Suture Zone, Tibet, and Its Geologic Significance.Geologcal Bulletin of China, 30(8):1256-1260 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201108012 Li, J.X., Li, G.M., Qin, K.Z., et al., 2008.Geochemistry of Porphyries and Volcanic Rocks and Ore-Forming Geochronology of Duobuza Gold-Rich Porphyry Copper Deposit in Bangonghu Belt, Tibet:Constraints on Metallogenic Tectonic Settings.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(3):531-543 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200803013.htm Li, J.X., Qin, K.Z., Li, G.M., et al., 2011.Magmatic-Hydrothermal Evolution of the Cretaceous Duolong Gold-Rich Porphyry Copper Deposit in the Bangongco Metallogenic Belt, Tibet:Evidence From U-Pb and 40Ar/39Ar Geochronology.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(6):525-536. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.008 Li, J.X., Qin, K.Z., Li, G.M., et al., 2014.Petrogenesis of Cretaceous Igneous Rocks From the Duolong Porphyry Cu-Au Deposit, Central Tibet:Evidence From Zircon U-Pb Geochronology, Petrochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf Isotope Characteristics.Geological Journal, 51(2):285-307. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/269727338_Petrogenesis_of_Cretaceous_igneous_rocks_from_the_Duolong_porphyry_Cu-Au_deposit_central_Tibet_Evidence_from_zircon_U-Pb_geochronology_petrochemistry_and_Sr-Nd-Pb-Hf_isotope_characteristics Li, Z.J., Tang, J.X., Yao, X.F., et al., 2011.Re-Os Isotope Age and Geological Significance of Molybdenite in the Gaerqiong Cu-Au Deposit of Geji, Tibet, China.Journal of Chengdu University of Technology(Science & Technology Edition), 38(6):678-683 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb201106013 Liu, Y.S., Gao, S., Hu, Z.C., et al., 2010.Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycling-Induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons from Mantle Xenoliths.Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2):537-571. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egp082 Lü, L. N., 2012. Metallogenic Model of Rich Iron and Copper (Gold) Deposit in Western Part of Bangong Co-Nujiang Metallogenic Belt, Tibet (Dissertation). Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Lü, L.N., Cui, Y.B., Song, L., et al., 2011.Geochemical Characteristics and Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb Dating of Galale Skarn Gold(Copper) Deposit, Tibet and Its Significance.Earth Science Frontiers, 18(5):224-242 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201105022 Mungall, J.E., 2002.Roasting the Mantle:Slab Melting and the Genesis of Major Au and Au-Rich Cu Deposits.Geology, 30(10):915-918.https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0915:rtmsma>2.0.co;2 doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0915:rtmsma>2.0.co;2 Oyarzun, R., Márquez, A., Lillo, J., et al., 2001.Giant Versus Small Porphyry Copper Deposits of Cenozoic Age in Northern Chile:Adakitic Versus Normal Calc-Alkaline Magmatism.Mineralium Deposita, 36(8):794-798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001260100205 Pan, G.T., Mo, X.X., Hou, Z.Q., et al., 2006.Spatial-Temporal Framework of the Gangdese Orogenic Belt and Its Evolution.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3):521-533 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98200603001 Pearce, J.A., Harris, N.B.W., Tindle, A.G., 1984.Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks.Journal of Petrology, 25(4):956-983. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 Peccerillo, A., Taylor, S.R., 1976.Geochemistry of Eocene Calc-Alkaline Volcanic Rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1):63-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00384745 Qiu, R.Z., Zhou, S., Deng, J.F., et al., 2004.Dating of Gabbro in the Shemalagou Ophiolite in the Western Segment of the Bangong Co-Nujiang Ophiolite Belt, Tibet-With a Discussion of the Age of the Bangong Co-Nujiang Ophiolite Belt.Chinese Geology, 31(3):262-268 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi200403004 Qu, X.M., Xin, H.B., 2006.Ages and Tectonic Environment of the Bangong Co Porphyry Copper Belt in Western Tibet, China.Geologcal Bulletin of China, 25(7):792-799 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200607004 Qu, X.M., Xin, H.B., Du, D.D., et al., 2012.Ages of Post-Collisional A-Type Granite and Constraints on the Closure of the Oceanic Basin in the Middle Segment of the Bangonghu-Nujiang Suture, the Tibetan Plateau.Geochimica, 41(1):1-14 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx201201001 She, H.Q., Li, J.W., Ma, D.F., et al., 2009.Molybdenite Re-Os and SHRIMP Zircon U-Pb Dating of Duobuza Porphyry Copper Deposit in Tibet and Its Geological Implications.Mineral Deposits, 28(6):737-746 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz200906003 Shi, R.D., 2007.The Bangong Lake Ophiolite (NW Tibet) and Its Bearing on the Tectonic Evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone.Chinese Science Bulletin, 52(2):223-227 (in Chinese). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1367912007002283 Sun, S.S., McDonough, W.F., 1989.Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts:Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes.Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1):313-345. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1989.042.01.19 Söderlund, U., Patchett, P.J., Vervoort, J.D., et al., 2004.The 176Lu Decay Constant Determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb Isotope Systematics of Precambrian Mafic Intrusions.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4):311-324. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(04)00012-3 Taylor, S.R., McLennan, S.M., 1985.The Continental Crust:Its Composition and Evolution.Blackwell Scientific Publication, Boston. Wang, A., Zhao, Y.Y., Xu, H., et al., 2014.40Ar/39Ar Age of Muscovite from the Galale Skarn Type Copper-Gold Deposit in Tibet and Its Geological Significance.Geological Bulletin of China, 33(7):1008-1014 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201407008 Wilson, M.1989.Igneous Petrogenesis:A Global Tectonic Approach.Chapman & Hall, London. Wu, F.Y., Li, X.H., Zheng, Y.F., et al., 2007.Lu-Hf Isotopic Systematic and Their Applications in Petrology.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2):185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.oalib.com/paper/1492671 Xin, H.B., Qu, X.M., Wang, R.J., et al., 2009.Geochemistry and Pb, Sr, Nd Isotopic Features of Ore-Bearing Porphyries in Bangong Lake Porphyry Copper Belt, Western Tibet.Mineral Deposits, 28(6):785-792 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz200906007 Yao, X.F., Tang, J.X., Li, Z.J., et al., 2012.Magma Origin of Two Plutons from Gaerqiong Copper-Gold Deposit and Its Geological Significance, Western Bangonghu-Nujiang Metallogenic Belt, Tibet:Implication from Hf Isotope Characteristics.Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 42(S2):188-197 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ2012S2022.htm Yao, X.F., Tang, J.X., Li, Z.J., et al., 2013.The Redefinition of the Ore-Forming Porphyry's Age in Gaerqiong Skarn-Type Gold Copper Deposit, Western Bangong Lake——Nujiang River Metallogenic Belt, Xizang (Tibet).Geological Review, 59(1):193-200 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201301027.htm Zhang, Z., Song, J.L., Tang, J.X., et al., 2017.Petrogenesis, Diagenesis and Mineralization Ages of Galale Cu-Au Deposit, Tibet:Zircon U-Pb Age, Hf Isotopic Composition and Molybdenite Re-Os Dating.Earth Science, 42(6):862-880 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.523 Zheng, Y.Y., Ci, Q., Wu, S., et al., 2017.The Discovery and Significance of Rongga Porphyry Mo Deposit in the Bangong-Nujiang Metallogenic Belt, Tibet.Earth Science, 42(9):1441-1453 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.109 Zhou, J.S., Meng, X.J., Zang, W.S., et al., 2013.Zircon U-Pb Geochronology and Trace Element Geochemistry of the Ore-Bearing Porphyry in Qingcaoshan Porphyry Cu-Au Deposit, Tibet, and Its Geological Significance.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11):3755-3766 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201311009 Zhu, D.C., Pan, G.T., Mo, X.X., et al., 2006a.Identification for the Mesozoic OIB-Type Basalts in Central Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau:Geochronology, Geochemistry and Their Tectonic Setting.Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(9):1312-1328 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200609008.htm Zhu, D.C., Pan, G.T., Mo, X.X., et al., 2006b.Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous Geodynamic Setting in Middle-Northern Gangdese:New Insights from Volcanic Rocks.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3):534-546 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200603002.htm Zhu, D.C., Zhao, Z.D., Pan, G.T., et al., 2009.Early Cretaceous Subduction-Related Adakite-Like Rocks of the Gangdese Belt, Southern Tibet:Products of Slab Melting and Subsequent Melt-Peridotite Interaction?Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(3):298-309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.05.003 Zhu, X.P., Chen, H.A., Ma, D.F., et al., 2011.Re-Os Dating for the Molybdenite from Bolong Porphyry Copper-Gold Deposit in Tibet, China and Its Geological Significance.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7):2159-2164 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201107023 陈华安, 祝向平, 马东方, 等, 2013.西藏波龙斑岩铜金矿床成矿斑岩年代学、岩石化学特征及其成矿意义.地质学报, 87(10):1593-1611. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201310009 丁帅, 唐菊兴, 郑文宝, 等, 2017.西藏拿若斑岩型铜(金)矿含矿岩体年代学、地球化学及地质意义.地球科学, 42(1):1-23. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.001 杜德道, 曲晓明, 王根厚, 等, 2011.西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带西段中特提斯洋盆的双向俯冲:来自岛弧型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和元素地球化学的证据.岩石学报, 27(7):1993-2002. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201107008 高山, Rudnick.R., Richard, W., 等, 2003.华北克拉通岩石圈地幔置换作用和壳幔生长耦合的Re-Os同位素证据.地学前缘, 10(3):61-67. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.03.005 侯可军, 李延河, 谢桂青, 2007.锆石Hf同位素的LA-MC-ICP-MS分析方法.质谱学报, 28(增刊):26-28. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/6529982 黄汲清, 陈炳蔚, 1987.中国及邻区特提斯海的演化.北京:地质出版社. 李光明, 段志明, 刘波, 等, 2011.西藏班公湖-怒江结合带北缘多龙地区侏罗纪增生杂岩的特征及意义.地质通报, 30(8):1256-1260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.08.012 李金祥, 李光明, 秦克章, 等, 2008.班公湖带多不杂富金斑岩铜矿床斑岩-火山岩的地球化学特征与时代:对成矿构造背景的制约.岩石学报, 24(3):531-543. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200803013 李志军, 唐菊兴, 姚晓峰, 等, 2011.班公湖-怒江成矿带西段尕尔穷铜金矿床辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其地质意义.成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 38(6):678-683. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2011.06.013 吕立娜, 崔玉斌, 宋亮, 等, 2011.西藏嘎拉勒夕卡岩型金(铜)矿床地球化学特征与锆石的LA-ICP-MS定年及意义.地学前缘, 18(5):224-242. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201105022 吕立娜, 2012. 西藏班公湖-怒江成矿带西段富铁与铜(金)矿床模型(硕士学位论文). 北京: 中国地质科学院. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-82501-1012371246.htm 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 等, 2006.冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化.岩石学报, 22(3):521-533. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603001 邱瑞照, 周肃, 邓晋福, 等, 2004.西藏班公湖-怒江西段舍马拉沟蛇绿岩中辉长岩年龄测定——兼论班公湖-怒江蛇绿岩带形成时代.中国地质, 31(3):262-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2004.03.004 曲晓明, 辛洪波, 2006.藏西班公湖斑岩铜矿带的形成时代与成矿构造环境.地质通报, 25(7):792-799. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2006.07.004 曲晓明, 辛洪波, 杜德道, 等, 2012.西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带中段碰撞后A型花岗岩的时代及其对洋盆闭合时间的约束.地球化学, 41(1):1-14. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqhx201201001 佘宏全, 李进文, 马东方, 等, 2009.西藏多不杂斑岩铜矿床辉钼矿Re-Os和锆石U-Pb SHRIMP测年及地质意义.矿床地质, 28(6):737-746. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.06.003 史仁灯, 2007.班公湖SSZ型蛇绿岩年龄对班-怒洋时限的制约.科学通报, 52(2):223-227. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2007.02.016 汪傲, 赵元艺, 许虹, 等, 2014.西藏嘎拉勒夕卡岩型铜金矿白云母40Ar-39Ar年龄及其地质意义.地质通报, 33(7):1008-1014. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2014.07.008 吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 等, 2007.Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用.岩石学报, 23(2):185-220. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200702001 辛洪波, 曲晓明, 王瑞江, 等, 2009.藏西班公湖斑岩铜矿带成矿斑岩地球化学及Pb、Sr、Nd同位素特征.矿床地质, 28(6):785-792. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.06.007 姚晓峰, 唐菊兴, 李志军, 等, 2012.班怒带西段尕尔穷铜金矿两套侵入岩源区及其地质意义——来自Hf同位素特征的指示.吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 42(S2):188-197. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201205935397 姚晓峰, 唐菊兴, 李志军, 等, 2013.班公湖-怒江带西段尕尔穷矽卡岩型铜金矿含矿母岩成岩时代的重新厘定及其地质意义.地质论评, 59(1):193-200. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0371-5736.2013.01.021 张志, 宋俊龙, 唐菊兴, 等, 2017.西藏嘎拉勒铜金矿床的成岩成矿时代与岩石成因:锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素组成及辉钼矿Re-Os定年.地球科学, 42(6):862-880. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.523 郑有业, 次琼, 吴松, 等, 2017.西藏班公湖-怒江成矿带荣嘎斑岩型钼矿床的发现及意义.地球科学, 42(9):1441-1453. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.109 周金胜, 孟祥金, 臧文栓, 等, 2013.西藏青草山斑岩铜金矿含矿斑岩锆石U-Pb年代学、微量元素地球化学及地质意义.岩石学报, 29(11):3755-3766. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201311009 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等, 2006a.青藏高原中部中生代OIB型玄武岩的识别:年代学、地球化学及其构造环境.地质学报, 80(9):1312-1328. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb200609008 朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 等, 2006b.冈底斯中北部晚侏罗世-早白垩世地球动力学环境:火山岩约束.岩石学报, 22(3):534-546. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200603002 祝向平, 陈华安, 马东方, 等, 2011.西藏波龙斑岩铜金矿床的Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义.岩石学报, 27(7):2159-2164. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201107023 -










 下载:
下载: