Provenance of Clay-Sized Detrital Sediments and Its Paleoenvironmental Implications at Site U1456 in the Eastern Arabian Sea since 30 ka
-
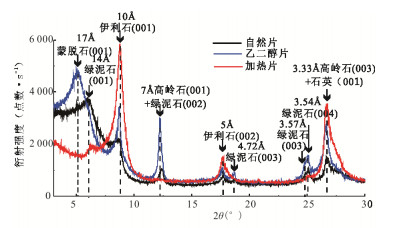
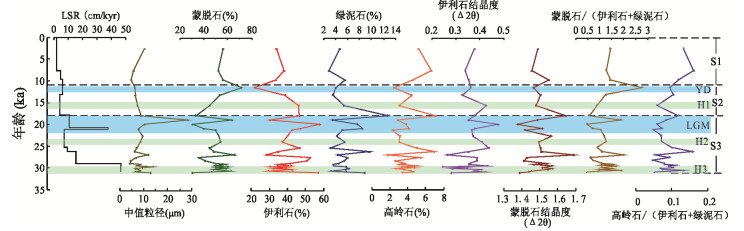
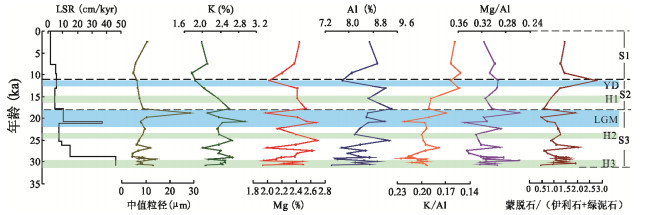
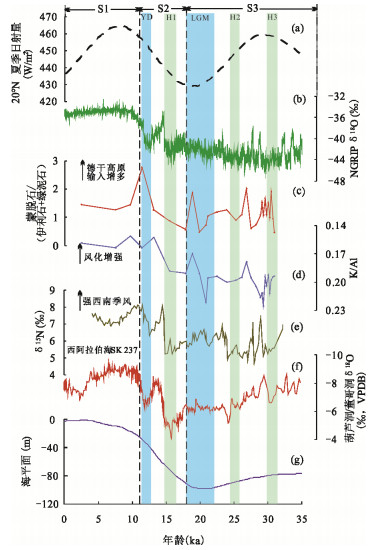
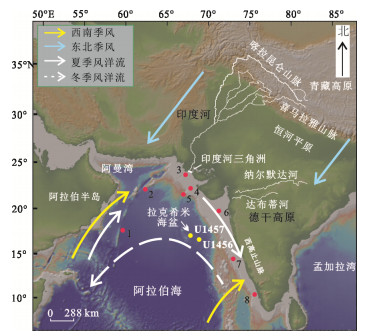
摘要: 通过对国际大洋发现计划U1456站位沉积物AMS 14C年代、粘土矿物、常量元素及粒度组成的综合分析,探讨了东阿拉伯海粘土粒级碎屑沉积物的源-汇过程及其古环境指示意义.30 ka以来U1456站位的粘土矿物组合以蒙脱石和伊利石为主,并含有少量的绿泥石和高岭石.物源分析结果表明粘土粒级碎屑沉积物主要来自于印度河与德干高原.30 ka以来西南季风很可能是影响喜马拉雅山脉以及印度大陆风化剥蚀的重要因素.在西南季风减弱的阶段,印度河物源端元对研究区的输入量减少,这可能与此时热带辐合带的南移及末次冰盛期喜马拉雅山脉冰川覆盖面积的增加有关,从而导致印度河径流量及喜马拉雅山脉可供风化剥蚀的区域减少.K/Al比值指示的源区大陆化学风化作用强度与前人重建的西南季风记录间较为同步,在东阿拉伯海可以作为晚第四纪以来西南季风演化的有效重建指标.Abstract: AMS 14C dating, clay minerals, major elements and grain size at site U1456 from International Ocean Discovery Program were analyzed, in order to constrain the source-to-sink processes of clay-sized detrital sediments and their paleoenvironmental significance in the eastern Arabian Sea. The clay mineral assemblages at site U1456 since 30 ka are dominated by smectite and illite, with minor chlorite and kaolinite. Provenance analysis results suggest that clay-sized detrital sediments are primarily derived from the Indus River and Deccan Trap. Southwest Asian monsoon probably is the main factor affecting the weathering and erosion in the western Himalaya and the Indian subcontinent since 30 ka. Relatively reduced contribution from the Indus River to the study area during weak southwest Asian monsoon intervals should correlate with the southward migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone and the extension of glacial cover over the Himalayas during the Last Glacial Maximum, and thus reduction in the Indus River runoff as well as available exposure area for erosion and weathering over the Himalayas. The weathering and erosion on the continent revealed by K/Al ratio show coherent variations to the previous southwest Asian monsoon records, indicating the efficiency of K/Al ratio for tracking the regional climate signal in the eastern Arabian Sea since the late Quaternary.
-
Key words:
- eastern Arabian Sea /
- clay mineral /
- major elements /
- provenance /
- erosion and weathering /
- southwest Asian monsoon
-
表 1 U1456站位C孔AMS14C年代数据
Table 1. AMS14C age, calibrated calendar age, and sedimentation rate of site U1456
层位(cm) AMS 14C年龄(a) 日历年龄(cal. a; ±2σ) 沉积速率(cm/ka) 测试材料 12 6 550±30 7 652~7 480 1.64 Globigeriniodes sacculifer 22 8 510±30 9 865~9 549 4.74 42 1 110±40 13 272~13 035 5.86 62 1 456±50 18 091~17 705 4.21 92 17 120±60 21 080~20 622 10.33 102 17 330±70 21 412~20 869 37.45 132 20 760±80 25 542~25 012 7.32 142 21 810±80 26 424~25 948 9.24 182 24 680±100 29 185~28 596 15.01 192 24 910±100 29 438~28 802 46.51 表 2 东阿拉伯海U1456站位常量元素含量(%)间相关性
Table 2. Correlation of major elements at site U1456 in the eastern Arabian Sea a)
Al Ca Fe K Mg Mn Na P Ti Al 1.00 Ca -0.26 1.00 Fe -0.07 -0.20 1.00 K 0.45* 0.17 -0.13 1.00 Mg 0.66* -0.24 -0.06 0.48* 1.00 Mn 0.26 0.21 -0.04 0.58* 0.48* 1.00 Na -0.24 0.24 -0.15 -0.39* -0.29 -0.05 1.00 P -0.26 0.43* -0.12 0.30 -0.10 0.29 0.30 1.00 Ti -0.05 0.18 0.30 -0.34 -0.42* -0.23 0.31 0.21 1.00 注:*代表在0.05水平上显著相关 表 3 东阿拉伯海潜在物源的粘土矿物组合对比(a)
Table 3. Comparison among the clay mineral assemblages of potential provenances for the eastern Arabian Sea
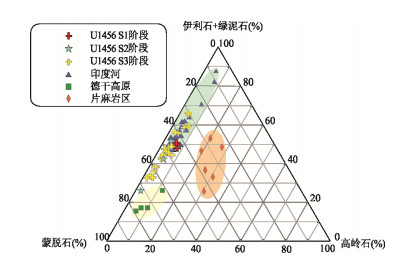
阶段 潜在物源 数据来源 蒙脱石(%) 伊利石(%) 高岭石(%) 绿泥石(%) 伊利石结晶度 晚更新世 印度河 SK 148/22(c) 7.00 70.00 5.00 18.00 — SK 148/21(c) 9.00 61.00 6.00 23.00 Keti Bandar(b) 40.50±3.74 46.25±2.76 4.13±1.36 9.12±0.83 0.30±0.03 德干高原 SK 148/38(c) 62.00 21.00 12.00 5.00 — 片麻岩区 GC 3 34.00±3.20 32.00±6.92 19.00±4.81 14.00±2.86 0.45±0.13 GC 5 24.00±6.80 31.00±7.21 27.00±5.32 17.00±2.65 全新世 印度河 SK 148/22(c) 34.00 44.00 4.00 18.00 — SK 148/21(c) 31.00 48.00 5.00 16.00 Keti Bandar(b) 45.11±3.40 40.47±2.14 4.42±1.43 9.68±2.52 0.31±0.03 Indus-23 40.05±3.88 49.38±3.95 3.08±0.53 7.85±1.44 0.34±0.02 德干高原 SK 148/38(c) 76.00 12.00 7.00 5.00 — 坎贝湾(c) 73.00 7.00 10.00 10.00 片麻岩区 GC 3 27.00±2.44 41.00±6.28 20.00±3.37 12.00±1.77 0.41±0.13 GC 5 36.00±8.24 16.00±8.54 31.00±3.85 17.00±2.79 注:a.潜在物源的粘土矿物组合据文献(Rao and Rao, 1995; Thamban et al., 2002 ;Kessarkar et al., 2003 ;Alizai et al., 2012 ;Limmer et al., 2012a );b.位于印度河三角洲(图 1);c.粘土矿物组合为多个样品平均值 -
Ali, S., Hathorne, E. C., Frank, M., et al., 2015. South Asian Monsoon History over the Past 60 kyr Recorded by Radiogenic Isotopes and Clay Mineral Assemblages in the Andaman Sea. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 16(2): 505-521. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014gc005586 Alizai, A., Carter, A., Clift, P. D., et al., 2011. Sediment Provenance, Reworking and Transport Processes in the Indus River by U-Pb Dating of Detrital Zircon Grains. Global and Planetary Change, 76(1-2): 33-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2010.11.008 Alizai, A., Hillier, S., Clift, P. D., et al., 2012. Clay Mineral Variations in Holocene Terrestrial Sediments from the Indus Basin. Quaternary Research, 77(3): 368-381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2012.01.008 Altabet, M. A., Higginson, M. J., Murray, D. W., 2002. The Effect of Millennial-Scale Changes in Arabian Sea Denitrification on Atmospheric CO2. Nature, 415(6868): 159-162. https://doi.org/10.1038/415159a Beaumont, C., Jamieson, R. A., Nguyen, M. H., et al., 2001. Himalayan Tectonics Explained by Extrusion of a Low-Viscosity Crustal Channel Coupled to Focused Surface Denudation. Nature, 414(6865): 738-742. https://doi.org/10.1038/414738a Biscaye, P. E., 1965. Mineralogy and Sedimentation of Recent Deep-Sea Clay in the Atlantic Ocean and Adjacent Seas and Oceans. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 76(7): 803-831. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1965)76[803:MASORD]2.0.CO;2 Broccoli, A. J., Dahl, K. A., Stouffer, R. J., 2006. Response of the ITCZ to Northern Hemisphere Cooling. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(1):1-4. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005gl024546 Cabarcos, E., Flores, J. A., Singh, A. D., et al., 2014. Monsoonal Dynamics and Evolution of the Primary Productivity in the Eastern Arabian Sea over the Past 30 ka. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 411(1): 249-256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.07.006 Chamely, 1989. Clay Sedimentology. Springer, Berlin, 1-623. Chauhan, O. S., Gujar, A. R., 1996. Surficial Clay Mineral Distribution on the Southwestern Continental Margin of India: Evidence of Input from the Bay of Bengal. Continental Shelf Research, 16(3): 321-333. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-4343(95)00015-S Chauhan, O. S., Patil, S. K., Suneethi, J., 2004. Fluvial Influx and Weathering History of the Himalayas since Last Glacial Maxima-Isotopic, Sedimentological and Magnetic Records from the Bay of Bengal. Current Science, 87(4): 509-515. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Open J-Gate000000983663 Chauhan, O. S., Sukhija, B. S., Gujar, A. R., et al., 2000. Late-Quaternary Variations in Clay Minerals Along the Sw Continental Margin of India: Evidence of Climatic Variations. Geo-Marine Letters, 20(2): 118-122. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003670000043 Chen, ,Z., Yan, W., 2000. Advance of the Studies on Clay Minerals in Marine Sediments and Its Response to Evolution of Paleoclimate and Paleoenvironment. Marine Sciences, 24(2): 25-27. (in Chinese) Cheng, H., Edwards, R. L., Broecker, W. S., et al., 2009. Ice Age Terminations. Science, 326(5950): 248-252. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1177840 Clift, P. D., 2002. A Brief History of the Indus River. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 195(1):237-258. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.2002.195.01.13 Clift, P. D., Giosan, L., Blusztajn, J., et al., 2008a. Holocene Erosion of the Lesser Himalaya Triggered by Intensified Summer Monsoon. Geology, 36(1): 79-82. https://doi.org/10.1130/g24315a.1 Clift, P. D., Hodges, K. V., Heslop, D., et al., 2008b. Correlation of Himalayan Exhumation Rates and Asian Monsoon Intensity. Nature Geoscience, 1(12): 875-880. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo351 Clift, P. D., Wan, S., Blusztajn, J., 2014. Reconstructing Chemical Weathering, Physical Erosion and Monsoon Intensity since 25 Ma in the Northern South China Sea: A Review of Competing Proxies. Earth-Science Reviews, 130(3): 86-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.01.002 Das, S. S., Rai, A. K., Akaram, V., et al., 2013. Paleoenvironmental Significance of Clay Mineral Assemblages in the Southeastern Arabian Sea During Last 30 Ka. Journal of Earth System Science, 122(1): 173-185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-012-0251-1 Dou, Y. G., Yang, S. Y., Liu, Z. X., et al., 2010. Clay Mineral Evolution in the Central Okinawa Trough since 28 ka: Implications for Sediment Provenance and Paleoenvironmental Change. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 288(1-4): 108-117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.01.040 Ferrier, K. L., Mitrovica, J. X., Giosan, L., et al., 2015. Sea-Level Responses to Erosion and Deposition of Sediment in the Indus River Basin and the Arabian Sea. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 416(3): 12-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.01.026 Fleitmann, D., Burns, S. J., Mangini, A., 2007. Holocene ITCZ and Indian Monsoon Dynamics Recorded in Stalagmites from Oman and Yemen (Socotra). Quaternary Science Review, 26(1-2): 170-188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.04.012 Garcin, Y., Vincens, A., Williamson, D., et al., 2007. Abrupt Resumption of the African Monsoon at the Yonger Dryas-Holocene Climatic Transition. Quaternary Science Reviews, 26(5-6): 690-704. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2006.10.014 Gebregiorgis, D., Hathorne, E. C., Sijinkumar, A. V., et al., 2016. South Asian Summer Monsoon Variability During the Last ~54 ka Inferred from Surface Water Salinity and River Runoff Proxies. Quaternary Science Reviews, 138: 6-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.02.012 Goswami, V., Singh, S. K., Bhushan, R., et al., 2012. Temporal Variations in 87Sr/86Sr and εNd in Sediments of the Southeastern Arabian Sea: Impact of Monsoon and Surface Water Circulation. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 13(1):1-3. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011gc003802 Griffin, J. J., Hent, W., Dorris, G. E., 1968. The Distribution of Clay Minerals in the World Ocean. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 15(4):433-459. doi: 10.1016/0011-7471(68)90051-X Haug, G. H., Hughen, K. A., Sigman, D. M., et al., 2001. Southward Migration of the Intertropical Convergence Zone through the Holocene. Science. 293(5533): 1304-1308. doi: 10.1126/science.1059725 Hu, D. K., Böning, P., Köhler, C. M., et al., 2012. Deep Sea Records of the Continental Weathering and Erosion Response to East Asian Monsoon Intensification since 14 ka in the South China Sea. Chemical Geology, 326-327(11): 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.07.024 Huang, J. B., Wang, S. W., Wen, X. Y., et al., 2008. Progress in Studies of the Climate of Humid Period and the Impacts of Changing Precession in Early-Mid Holocene. Progress in Natural Science, 18(12): 1459-1464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2008.05.011 John, S., Michaele, K., Michel, F., et al., 2002. Marine Reservoir Corrections for the Indian Ocean and Southeast Asia. Radiocarbon, 44(1): 167-180. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200064778 Joussain, R., Colin, C., Liu, Z., et al., 2016. Climatic Control of Sediment Transport from the Himalayas to the Proximal Ne Bengal Fan During the Last Glacial-Interglacial Cycle. Quaternary Science Reviews, 148: 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2016.06.016 Kageyama, M., Mignot, J., Swingedouw, D., et al., 2009. Glacial Climate Sensitivity to Different States of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation: Results from the IPSL Model. Climate of the Past, 5: 551-570. https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-5-551-2009 Kessarkar, P. M., Purnachadra Rao, V., Naqvi, S. W. A., et al., 2013. Variation in the Indian Summer Monsoon Intensity During the Bølling-Ållerød and Holocene. Paleoceanography, 28(3): 413-425. https://doi.org/10.1002/palo.20040 Kessarkar, P. M., Rao, V. P., Ahmad, S. M., et al., 2003. Clay Minerals and Sr-Nd Isotopes of the Sediments along the Western Margin of India and Their Implication for Sediment Provenance. Marine Geology, 202(1-2): 55-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-3227(03)00240-8 Kolla, V., Kosteckl, J. A., Robinson, F., et al., 1981. Distributions and Origins of Clay Minerals and Quartz in Surface Sediments of the Arabian Sea. Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 51(2): 563-569. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=uKgrngbN7OVFvtoiU0iRSNUFqFbP19jhJM+LacK+Ihs= Kong, W. L., Li, S. Y., Wan, Q., et al. 2011. Differentiation and Discrimination of Marine Clay Minerals as Indicators of Paleoenvironment. Journal of Anhui University (Natural Science Edition), 35(5): 100-108(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ahdxxb201105020 Kotlia, B. S., Sanwal, J., Phartiyal, B., et al., 2010. Late Quaternary Climatic Changes in the Eastern Kumaun Himalaya, India, as Deduced from Multi-Proxy Studies. Quaternary International, 213(1-2): 44-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2009.09.002 Lan, X. H., Li, R. H., Mi, B. B., et al., 2016. Distribution Characteristics of Rare Earth Elements in Surface Sediment and Their Provenance Discrimination in the Eastern Bohai and Northern Yellow Seas. Earth Science, 31(4): 463-474(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201603013 Laskar, J., Robutel, P., Joutel, F., et al., 2004. A Long-Term Numerical Solution for the Isolation Quantities Of the Earth. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 428(1): 261-285. https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20041335 Limmer, D. R., Boning, P., Giosan, L., et al., 2012a. Geochemical Record of Holocene to Recent Sedimentation on the Western Indus Continental Shelf, Arabian Sea. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 13(1): 1-26. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011gc003845 Limmer, D. R., Kolher, C. M., Hillier, S., et al., 2012b. Chemical Weathering and Provenance Evolution of Holocene-Recent Sediments from the Western Indus Shelf, Northern Arabian Sea Inferred from Physical and Mineralogical Properties. Marine Geology, 326-328(9): 101-115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2012.07.009 Li, J. R., Liu, S. F., Feng, X. L., et al., 2017. Major and Trace Element Geochemistry of the Mid-Bay of Bengal Surface Sediments: Implications for Provenance. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 36(3): 82-90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1041-z Liu, Z. F., 2010. Clay Mineral Assemblages in Sediments of the South China Sea: East Asian Monsoon Evolution Proxies? Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 28(5): 1012-1019. (in Chinese with English Abstract) http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=aebb71b1619fb1c98d3daabc52799637&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Liu, Z. F., Colin, C., Li, X. J., et al., 2010. Clay Mineral Distribution in Surface Sediments of the Northeastern South China Sea and Surrounding Fluvial Drainage Basins: Source and Transport. Marine Geology, 277(1-4):48-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2010.08.010 Liu, Z. F., Colin, C., Trentesaux, A., et al., 2005. Late Quaternary Climatic Control on Erosion and Weathering in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau and the Mekong Basin. Quaternary Research, 63(3): 316-328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2005.02.005 Liu, Z. F., Colin, C., Trentesaux, A., et al., 2004. Erosional History of the Eastern Tibetan Plateau Since 190 kyr ago: Clay Mineralogical and Geochemical Investigations from the Southwestern South China Sea. Marine Geology, 209(1-8): 1-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2004.06.004 Liu, Z. F., Trentesaux, A., Clemens, S. C., et al., 2003. Clay Mineral Assemblages in the Northern South China Sea: Implications for East Asian Monsoon Evolution over the Past 2 Million Years. Marine Geology, 201(1-3): 133-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-3227(03)00213-5 Milliman, J. D., Farnsworth, K. L., 2011. River Discharge to the Coastal Ocean——A Global Synthesis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1-384. Mulitza, S., Prange, M., Stuut, J. B., et al. 2008. Shale Megadrought Triggered by Glacial Slowdowns of Atlantic Meridional Overturning. Paleoceanography, 23(4):1-11. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008PA001637 Naidu, P. D., Malmgren, B. A., 1996. A High-Resolution Record of Late Quaternary Upwelling along the Oman Margin, Arabian Sea Based on Planktonic Foraminifera. Paleoceanography, 11(1): 129-140. https://doi.org/10.1029/95pa03198 Oliva, P., Viers, J., Dupré, B., 2003. Chemical Weathering in Granitic Environments. Chemical Geology, 202(3-4):225-256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2002.08.001 Owen, L. A., Finkel, R. C., Caffee, M. W., 2002. A Note on the Extent of Glaciation Throughout the Himalaya During the Global Last Glacial Maximum. Quaternary Science Reviews, 21(1-3): 147-157. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0277-3791(01)00104-4 Pandarinath, K., 2009. Clay Minerals in SW Indian Continental Shelf Sediment Cores as Indicators of Provenance and Palaeomonsoonal Conditions: A Statistical Approach. International Geology Review, 51(2): 145-165. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206810802622112 Pandey, D. K., Clift, P. D., Kulhanek, D. K., et al., 2015. Expedition 355 Preliminary Report: Arabian Sea Monsoon. International Ocean Discovery Program. https: //doi.org/10.14379/iodp.pr.355.2015 Pattan, J. N., Parthiban, G., Garg, A., et al., 2017. Intense Reducing Conditions during the Last Deglaciation and Heinrich Events (H1, H2, H3) in Sediments from the Oxygen Minimum Zone off Goa, Eastern Arabian Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 84: 243-256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.03.034 Phillips, S. C., Johnson, J. E., Underwood, M. B., et al., 2014. Long-Timescale Variation in Bulk and Clay Mineral Composition of Indian Continental Margin Sediments in the Bay of Bengal, Arabian Sea, and Andaman Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 58: 117-138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.06.018 Prins, M. A., Postma, G., 2000. Effects of Climate, Sea Level, and Tectonics Unraveled for Last Deglaciation Turbidite Records of the Arabian Sea. Geology, 28(4): 375-378. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<375:eocsla>2.0.co;2 doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<375:eocsla>2.0.co;2 Rao, V. P., Rao, B. R., 1995. Provenance and Distribution of Clay Minerals in the Sediments of Clay Minerals in the Sediments of the Western Continental Shelf and Slope of India. Continental Shelf Research, 15(14): 1757-1771 doi: 10.1016/0278-4343(94)00092-2 Rohling, E. J., Foster, G. L., Grant, K. M., et al., 2014. Sea-Level and Deep-Sea-Temperature Variability over the Past 5.3 Million Years. Nature, 508(7497): 477-482. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13230 Saraswat, R., Lea, D. W., Nigam, R., et al., 2013. Deglaciation in the Tropical Indian Ocean Driven by Interplay between the Regional Monsoon and Global Teleconnections. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 375: 166-175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.05.022 Sarkar, A., Ramesh, R., Somayajulu, B. L. K., et al., 2000. High Resolution Holocene Monsoon Record from the Eastern Arabian Sea. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 177(3-4): 209-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821x(00)00053-4 Singh, A. D., Jung, S. J. A., Darling, K., et al., 2011. Productivity Collapses in the Arabian Sea During Glacial Cold Phases. Paleoceanography, 26(3): 1318-1323. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009pa001923 Sinha, A., Cannariato, K. G., Stott, L. D., et al., 2005. Variability of Southwest Indian Summer Monsoon Precipitation During the Bølling-Ållerød. Geology, 33(10): 813-816. https://doi.org/10.1130/g21498.1 Stager, J. C., Ryves, D. B., Chase, B. M., et al., 2011. Catastrophic Drought in the Afro-Asian Monsoon Region During Heinrich Event 1. Science, 33: 1299-1302. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1198322 Stoll, H. M., Vance, D., Arevalos, A., 2007. Records of the Nd Isotope Composition of Seawater from the Bay of Bengal: Implications for the Impact of Northern Hemisphere Cooling on Itcz Movement. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 255(1-2): 213-228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2006.12.016 Stuiver, M., Reimer, P. J., Reimer, R., 1993. Extended 14C Database and Revised Calib Radiocarbon Calibration Program. Radiocarbon, 35(1): 215-230. doi: 10.1017/S0033822200013904 Svensson, A., Andersen, K. K., Bigler, M., et al., 2008. A 60 000 Year Greenland Stratigraphic Ice Core Chronology. Climate of the Past, 4(1): 47-57. https://doi.org/10.5194/cp-4-47-2008 Thamban, M., Rao, V. P., and Schneider, R. R., 2002. Reconstruction of Late Quaternary Monsoon Oscillations Based on Clay Mineral Proxies Using Sediment Cores from the Western Margin of India. Marine Geology, 186(3-4): 527-539. https://doi.org/PiiS0025-3227(02)00268-2 doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(02)00268-2 Thiry, M., 2000. Palaeoclimatic Interpretation of Clay Minerals in Marine Deposits: An Outlook from the Continental Origin. Earth-Science Reviews, 49(1-4): 201-221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-8252(99)00054-9 Tripathy, G. R., Singh, S. K., Ramaswamy, V., 2014. Major and Trace Element Geochemistry of Bay of Bengal Sediments: Implications to Provenances and Their Controlling Factors. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 397: 20-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.04.012 Wan, S. M., Clift, P. D., Li, A. C., et al., 2012. Tectonic and Climatic Controls on Long-Term Silicate Weathering in Asia since 5 Ma. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(15): 151-155. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012gl052377 Wan, S. M., Clift, P. D., Zhao, D. B., et al., 2017. Enhanced Silicate Weathering of Tropical Shelf Sediments Exposed during Glacial Lowstands: A Sink for aAtmospheric CO2. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 200: 123-144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2016.12.010 Wang, Y. Y., Huang, S. B., Zhao, L., et al., 2017. Evolution of Quaternary Sedimentary Environment in Shallow Aquifers, at Shahu Area, Jianghan Plain. Earth Science, 42(5): 751-760. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.063 (in Chinese with English abstract) Wei, G. J., Li, Liu, Y.X. H., et al., 2006. Geochemical Record of Chemical Weathering and Monsoon Climate Change since the Early Miocene in the South China Sea. Paleoceanography, 24(4): 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006PA001300 Xu, Z. K., Chang, F. M., Li, T. G., et al., 2012a. Provenance of Sediments in the Northern Okinawa trough over the Last 24 ka: High Resolution Record from Major Elements. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 32(4):73-82(in Chinese with English abstract). http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ba0a91bd18c113a882dd13e3a87e2159&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn Xu, Z. K., Li, T. G., Wan, S. M., et al., 2012b. Evolution of East Asian Monsoon: Clay Mineral Evidence in the Western Philippine Sea over the Past 700 kyr. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 60: 188-196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.08.018 Xu, Z. K., Li, T. G., Clift, P. D., et al., 2017. Sediment Provenance and Paleoenvironmental Change in the Middle Okinawa Trough During the Last 18.5 ka: Clay Mineral and Geochemical Evidence. Quaternary International, 440: 139-149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quaint.2016.07.058 Xu, Z. K., Li, T. G., Yu, X. K., et al., 2013. Sediment Provenance and Evolution of the East Asian Winter Monsoon since 700 ka Recorded by Major Elements in the West Philippine Sea. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(9): 1044-1052, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-012-5538-8 Yu, Z. J., Wan, S. M., Colin, C., et al., 2016. Co-Evolution of Monsoonal Precipitation in East Asia and the Tropical Pacific Enso System since 2.36 Ma: New Insights from High-Resolution Clay Mineral Records in the West Philippine Sea. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 446:45-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.04.022 Zorzi, C., Sanchez Goni, M. F., Anupama, K., et al., 2015. Indian Monsoon Variations during Three Contrasting Climate Periods: The Holocene, Heinrich Stadial 2 and the Last Interglacial-Glacial Transition. Quaternary Science Reviews, 125: 50-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirew.2015.06.009 陈忠, 颜文, 2000.海洋沉积粘土矿物与古气候, 古环境演化响应的研究进展.海洋科学, 24(2): 25-27. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hykx200002009 孔为伦, 李双应, 万秋, 等, 2011.海洋粘土矿物的古环境含义辨析.安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 35(5): 100-108. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2162.2011.05.020 蓝先洪, 李日辉, 密蓓蓓, 等, 2016.渤海东部和黄海北部表层沉积物稀土元素的分布特征与物源判别.地球科学, 41(3): 463-474. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3272 刘志飞, 2010.南海沉积物中的黏土矿物:指示东亚季风演化历史?沉积学报, 28(5):1012-1019. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb200704013 王妍妍, 黄爽兵, 赵龙, 等, 2017.江汉平原沙湖地区浅层含水层第四纪沉积环境演化.地球科学, 42(5): 751-760. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3573 徐兆凯, 常凤鸣, 李铁刚, 等, 2012.24 ka来冲绳海槽背部沉积物来源的高分辨率常量元素记录.海洋地质与第四纪地质, 32(4):73-82. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96122X/201204/43148733.html -









 下载:
下载: