Paleoclimatic Implications of Oxygen Isotope from Authigenic Carbonates in Loess Deposit of Northeastern Tibetan Plateau
-
摘要: 黄土中含有较为丰富的碳酸盐,其中次生碳酸盐记录了成壤时期的气候和环境,可以用来重建古气候.测试了末次盛冰期和全新世早期青藏高原东北部乐都、中国东北和新疆巴音布鲁克黄土中次生碳酸盐的δ18O值,结果显示高原东北部这两个时期的δ18O值分别为-1.38‰和-5.58‰,比该地区现代季风气候条件下次生碳酸盐δ18O理论值分别高5.74‰和1.54‰.温度的差异不足以导致次生碳酸盐δ18O值如此幅度的变化.同时,末次盛冰期和全新世早期乐都地区黄土中次生碳酸盐的δ18O值比同时期黄土高原和东北地区等东亚季风区明显偏正约2.0‰~6.2‰,但其与新疆等西风区次生碳酸盐的δ18O相近.这些不同时期黄土中次生碳酸盐的δ18O值的分布特征及空间差异,可能反映东亚夏季风夹带的水汽可能不是青藏高原东北部末次盛冰期和全新世早期降水最重要的来源,而西风降水和(或)局部水汽蒸发循环对该地区的降水可能有重要贡献.青藏高原东北部黄土次生碳酸盐的δ18O值从末次盛冰期到全新世早期逐渐降低,这可能是由于气候由干冷向暖湿转变、有效湿度增加而导致的.有限的数据表明不同气候带(青藏高原东北部、东亚季风区和西风带)的黄土中次生碳酸盐氧同位素存在明显差异,它所代表的气候意义值得进一步的深入研究.Abstract: The carbonate in loess deposit records the pedogenic environment, especially the moisture information, and can be used to qualitatively and/or quantitatively reconstruct paleoclimate. The δ18O values of the pedogenic carbonate in loess of LGM and Early Holocene, from Ledu (northeastern Tibetan plateau), Northeast China and Bayanbulak basin in Xingjiang, were measured. It showns that the δ18O values of the pedogenic carbonate in loess of LGM and Early Holocene from northeastern Tibetan plateau are -1.38 ‰ and -5.58 ‰, which are 5.74‰ and 1.54‰ respectively higher than the theoretical values of δ18O under the condition of modern monsoon climate. However, the temperature difference was not enough to cause this significant magnitude change of the δ18O values in the pedogenic carbonate. Compared with that in East Asian monsoon region including the Chinese Loess plateau and the Northeast China, the values of the δ18O of the pedogenic carbonate in loess from Ledu during LGM and the Early Holocene are ~2.0‰-6.2‰ higher obviously, but similar to those in the westerly regions such as Xinjiang. The distribution characteristics and spatial differences of the δ18O values of the pedogenic carbonate in loess in different periods may reflect that the East Asian summer monsoon was not the controlling factor of the precipitation during the LGM and early Holocene in the northeastern Tibetan plateau (NETP), while the westerly rainfall and/or local vapor evaporation cycle had an important impact in this period. The climate changing from dry and cold to warm and humid, with higher temperature but less evaporation, could be the reason for the gradual decrease of the δ18O values of the pedogenic carbonate in the loess from LGM to Early Holocene in NETP. The δ18O values of the pedogenic carbonate in the loess from different climatic zones (NETP, the East Asian monsoon region and the westerly zone), revealed by limited data in this study, are significantly different, with which climatic indication is worth further investigation.
-
Key words:
- authigenic carbonate /
- oxygen isotope /
- geochemistry /
- paleoclimate /
- northeastern Tibetan plateau
-
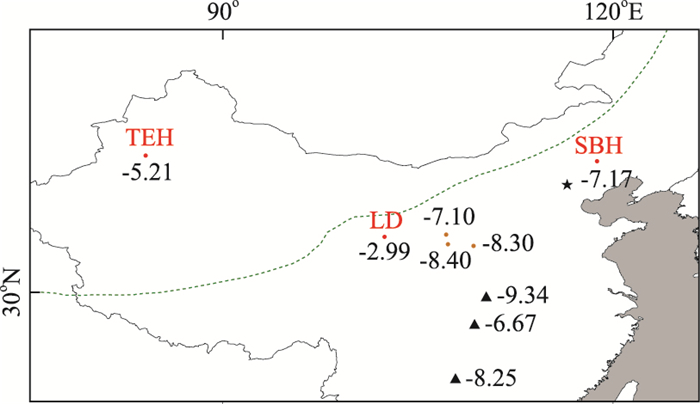
图 1 采样点位置及各地的δ18O值比较
Hu et al.(submitted);其他地区数据引自Sheng et al.(2008);石笋δ18O数据引自Wang et al.(2008)和Zhang et al.(2013);黑色数字表示δ18O值.TEH.天鹅湖剖面;SBH.三把火黄土剖面;LD.乐都黄土剖面.虚线是指现代东亚夏季风的边缘
Fig. 1. The locations and the comparison of oxygen isotope values (the black number) from the studied region
表 1 乐都、新疆、东北等地黄土样品年代及次生碳酸盐δ18O值
Table 1. The ages of the studied samples and the results of the oxygen isotope measurements from Ledu, Xinjiang and northeast China
样品号 采样点经纬度 年代(ka) δ18OPDB(‰) LD-60 36.45°N,102.58°E 9.4±0.6 -5.58 LD-180 15.8±1.0 -1.53 LD-310 20.9±1.4 -1.23 TEH6-5 42.71°N,84.21°E 6.9±0.82 -5.80 TEH6-6 4.3±0.26 -5.46 TEH6-7 2.3±0.36 -4.67 TEH6-8 1.4±0.35 -4.89 SBH-2-20 42.28°N,118.92°E 14.4±0.8 -6.76 SBH-2-80 20.9±1.3 -7.58 注:东都、新疆、东北的样品年代数据分别引自 Wang et al.(2015) ,Long et al.(2017) ,Yi et al.(2015) . -
Bayat, O., Karimi, A., Khademi, H., 2017.Stable Isotope Geochemistry of Pedogenic Carbonates in Loess-Derived Soils of Northeastern Iran:Paleoenvironmental Implications and Correlation across Eurasia.Quaternary International, 429:52-61. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1040618216000720 Caves, J.K., Winnick, M.J., Graham, S.A., et al., 2015.Role of the Westerlies in Central Asia Climate over the Cenozoic.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 428:33-43. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.07.023 Cerling, T.E., 1984.The Stable Isotopic Composition of Modern Soil Carbonate and Its Relationship to Climate.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 71(2):229-240. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(84)90089-X Cerling, T.E., Wang, Y., Quade, J., 1993.Expansion of C4 Ecosystems as an Indicator of Global Ecological Change in the Late Miocene.Nature, 361(6410):344-345. doi: 10.1038/361344a0 Chen, J., An, Z., Wang, H., et al., 1996.An Study of the S1 Paleosol Carbonates from the Central Loess Plateau of North China.Chinese Science Bulletin, 41(18):1542-1545. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/86894X/199618/4001157409.html Chen, J., Qiu, G., Yang, J.D., 1997.Sr Isotopic Composition of Loess Carbonate and the Identification of the Lithogenic Carbonates and Pedogenic Carbonates.Progress in Natural Science, 7(6):731-734 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZKJY199705010.htm Chen, Z., Ma, H.Z., Cao, G.C., et al., 2006.Study on Carbonates in Loess:A Review.Journal of Salt Lake Research, 14(4):66-72 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yhyj200604013 Cheng, H., Edwards, R.L., Broecker, W.S., et al., 2009.Ice Age Terminations.Science, 326(5950):248-252. doi: 10.1126/science.1177840 Clemens, S.C., Prell, W.L., Sun, Y.B., 2010.Orbital-Scale Timing and Mechanisms Driving Late Pleistocene Indo-Asian Summer Monsoons:Reinterpreting Cave Speleothem δ18O.Paleoceanography, 25(4):PA4207. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010pa001926 Dansgaard, W., 1953.The Abundance of δ18O in Atmospheric Water and Water Vapour.Tellus, 5(4):461-469. doi: 10.3402/tellusa.v5i4.8697 Dansgaard, W., 1964.Stable Isotopes in Precipitation.Tellus, 16(4):436-468. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_eccac9b506cf02a199ddb09f26be29ac Dykoski, C.A., Edwards, R.L., Cheng, H., et al., 2005.A High-Resolution, Absolute-Dated Holocene and Deglacial Asian Monsoon Record from Dongge Cave, China.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(1):71-86. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c81cb5ec937567176b6373900b59e7e4 Fang, Q., Hong, H.L., Zhao, L.L., et al., 2018.Climatic Implication of Authigenic Minerals Formed during Pedogenic Weathering Processes.Earth Science, 43(3):753-769 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201803007 Gu, Z.Y., 1991.Isotopic Compositions of the Loess-Paleosoil Sequence Carbonate and Paleoclimatic Changes.Chinese Science Bulletin, 36(10):767-770 (in Chinese). Han, J.M., Jiang, W.Y., Liu, D.S., 1996.Carbonate Isotopic Records of Paleoclimatic Changes in Loess.Science in China (Series D), 26(5):399-404 (in Chinese). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=902e7fef12fab1f41473d5120de17a58 Han, J.M., Jiang, W.Y., Lü, H.Y., 1995a.Carbon and Oxygen Isotopes of Calcium Nodules in Loess (Ⅱ.) Carbon Isotope and Its Paleo-Environmental Significance.Quaternary Sciences, 15(4):367-377 (in Chinese with English abstract). Han J.M., Jiang, W., Wu N.Q., et al., 1995b.Carbon and Oxygen Isotopes of Calcium Nodules in Loess (Ⅰ.) Oxygen Isotope and Its Paleo-Environmental Significance.Quaternary Sciences, 15(2):130-137 (in Chinese with English abstract). He, T., Chen, Y., Balsam, W., et al., 2012.Distribution and Origin of Protodolomite from the Late Miocene-Pliocene Red Clay Formation, Chinese Loess Plateau.Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 13(6):Q06004. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012gc004039 Ji, J, Shen, J, Balsam, W., et al., 2005.Asian Monsoon Oscillations in the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since the Late Glacial as Interpreted from Visible Reflectance of Qinghai Lake Sediments.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(1-2):61-70. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.025 Ji, J.F., Ge, Y., Balsam, W., et al., 2009.Rapid Identification of Dolomite Using a Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometer (FTIR):A Fast Method for Identifying Heinrich Events in IODP Site U1308.Marine Geology, 258(1):60-68. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025322708003101 Jiang, W.Y., Han, J.M., Liu, D.S., 2001.Aridification and Its Influence on Carbon Isotope Composition of Pedogenic Carbonate.Quaternary Sciences, 21(5):427-435 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DSJJ200105005.htm Khademi, H., Mermut, A.R., 1999.Submicroscopy and Stable Isotope Geochemistry of Carbonate and Associated Palygorskite in Iranian Aridisols.European Journal of Soil Science, 50(2):207-216. http://europepmc.org/abstract/AGR/IND22070992 Kim, S.T., O'Neil, J.R., 1997.Equilibrium and Nonequilibrium Oxygen Isotope Effects in Synthetic Carbonates.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 61(16):3461-3475. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00169-5 Li, G.J., Chen, J., Chen, Y., et al., 2007.Dolomite as a Tracer for the Source Regions of Asian Dust.Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 112:D17201. https://doi.org/10.1029/2007jd008676 Li, T., Liu, F., Abels, H.A., et al., 2016.Continued Obliquity Pacing of East Asian Summer Precipitation after the Mid-Pleistocene Transition.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 457:181-190. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=725dc232057ca5c89afe8cb9446fc362 Li, Y., Wang N.A., Zhou, X.H., et al., 2014.Synchronous or Asynchronous Holocene Indian and East Asian Summer Monsoon Evolution:A Synthesis on Holocene Asian Summer Monsoon Simulations, Records and Modern Monsoon Indices.Global and Planetary Change, 116(2):30-40. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921818114000423 Liu, D.S., 1997.Quaternary Environment.Science Press, Beijing, 25-36 (in Chinese). Liu, W., Li, X., Zhang, L., et al., 2009.Evaluation of Oxygen Isotopes in Carbonate as an Indicator of Lake Evolution in Arid Areas:The Modern Qinghai Lake, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Chemical Geology, 268(1):126-136. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254109003453 Liu, Z., Bowen, G.J., Welker, J.M., 2010.Atmospheric Circulation is Reflected in Precipitation Isotope Gradients over the Conterminous United States.Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 115:D22120. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010jd014175 Liu, Z.F., Christophe, C., Alain, T., 2005.Application of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy in Quantitative Mineralogy of the South China Sea:Example of Core MD01-2393.Earth Science, 30(1):25-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX200501002.htm Liu, Z.Y., Wen, X.Y., Brady, E.C., et al., 2014.Chinese Cave Records and the East Asia Summer Monsoon.Quaternary Science Reviews, 83(1):115-128. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379113004150 Long, H., Shen, J., Chen, J., et al., 2017.Holocene Moisture Variations over the Arid Central Asia Revealed by a Comprehensive Sand-Dune Record from the Central Tian Shan, NW China.Quaternary Science Reviews, 174:13-32. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2017.08.024 Lu, H., Zhao, C., Mason, J., et al., 2010.Holocene Climatic Changes Revealed by Aeolian Deposits from the Qinghai Lake Area (Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau) and Possible Forcing Mechanisms.Holocene, 21(21):297-304. Lu, Y.C., An, Z.S., 1979.A Series of Physical Environment Changes in the Loess Plateau in the Past 700 000 Years.Chinese Science Bulletin, 24(5):221-224 (in Chinese). Meng, X., Liu, L., Balsam, W., et al., 2016.Dolomite Abundance in Chinese Loess Deposits:A New Proxy of Monsoon Precipitation Intensity.Geophysical Research Letters, 42(23):10391-10398. doi: 10.1002/2015GL066681/pdf Meng, X., Liu, L., Wang, X., et al., 2018.Mineralogical Evidence of Reduced East Asian Summer Monsoon Rainfall on the Chinese Loess Plateau during the Early Pleistocene Interglacials.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 486:61-69. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.12.048 Michalski, G., Rech, J., Thiemens, M., 2005.The Onset of Hyper-Aridity in the Atacama Desert:Nitrate δ17O as a Tracer of Soil Moisture.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69:A444. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2005GeCAS..69..444M Mix, H.T., Winnick, M.J., Mulch, A., et al., 2013.Grassland Expansion as an Instrument of Hydrologic Change in Neogene Western North America.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 377(5):73-83. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X1300407X Porter, S.C., Singhvi, A., An, Z.S., et al., 2010.Luminescence Age and Palaeoenvironmental Implications of a Late Pleistocene Ground Wedge on the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau.Permafrost and Periglacial Processes, 12(2):203-210. doi: 10.1002/ppp.386/pdf Qiang, M.R., Chen, F.H., Song, L., et al., 2013.Late Quaternary Aeolian Activity in Gonghe Basin, Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China.Quaternary Research, 79(3):403-412. http://journals.cambridge.org/abstract_S0033589400003586 Railsback, L.B., Xiao, H., Liang, F., et al., 2014.A Stalagmite Record of Abrupt Climate Change and Possible Westerlies-Derived Atmospheric Precipitation during the Penultimate Glacial Maximum in Northern China.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 393(2):30-44. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031018213004690 Ricketts, R.D., Johnson, T.C., Brown, E.T., et al., 2001.The Holocene Paleolimnology of Lake Issyk-Kul, Kyrgyzstan:Trace Element and Stable Isotope Composition of Ostracodes.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 176(1):207-227. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S003101820100339X Salomons, W., Mook, W.G., 1976.Isotope Geochemistry of Carbonate Dissolution and Reprecipitation in Soils.Soil Science, 122(1):15-24. doi: 10.1097/00010694-197607000-00003 Sheng, X.F., Chen, J., Ji, J.F., 2008.Morphological Characters and Multi-Element Isotopic Signatures of Carbonates from Chinese Loess-Paleosol Sequences.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(17):4323-4337. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703708003967 Sheng, X.F., Chen, J., Yang, J.D., et al., 2002.Carbon and Oxygen Isotopic Composition of Carbonate in Different Grain Size Fractions from Loess-Paleosol Sequences, China.Geochimica, 31(2):105-112 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQHX200202000.htm Tian, L., Yao, T., Macclune, K., et al., 2007.Stable Isotopic Variations in West China:A Consideration of Moisture Sources.Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 112(D10):D10112. doi: 10.1029-2006JD007718/ Tian, L.D., Yao, T.D., Numaguti, A., et al., 2001.Stable Isotope Variations in Monsoon Precipitation on the Tibetan Plateau.Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan, 79(5):959-966. doi: 10.2151/jmsj.79.959 Turpin, M., Gressier, V., Bahamonde, J.R., et al., 2014.Component-Specific Petrographic and Geochemical Characterization of Fine-Grained Carbonates along Carboniferous and Jurassic Platform-to-Basin Transects.Sedimentary Geology, 300(1):62-85. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0037073813002078 Vandenberghe, J., Renssen, H., Huissteden, K.V., et al., 2006.Penetration of Atlantic Westerly Winds into Central and East Asia.Quaternary Science Reviews, 25(17/18):2380-2389. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379106001260 Wang, F., Ge, W., Luo, H., et al, 2016.Oxygen-17 Anomaly in Soil Nitrate:A New Precipitation Proxy for Desert Landscapes.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 438:103-111. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2016.01.002 Wang, X., Vandenberghe, D., Yi, S.W., et al., 2013.Late Quaternary Paleoclimatic and Geomorphological Evolution at the Interface between the Menyuan Basin and the Qilian Mountains, Northeastern Tibetan Plateau.Quaternary Research, 80(3):534-544. doi: 10.1016/j.yqres.2013.08.004 Wang, X., Yi, S.W., Lu, H., et al., 2015.Aeolian Process and Climatic Changes in Loess Records from the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau:Response to Global Temperature Forcing since 30 ka.Paleoceanography, 30(6):612-620. doi: 10.1002/2014PA002731 Wang, Y.J., Cheng, H., Edwards, R.L., et al., 2008.Millennial- and Orbital-Scale Changes in the East Asian Monsoon over the Past 224 000 Years.Nature, 451(7182):1090-1093. doi: 10.1038/nature06692 Wen, Q.Z., 1989.Geochemistry of Loess in China.Science Press, Beijing, 115-169 (in Chinese). Yao, T.D., Masson-Delmotte, V., Gao, J., et al., 2013.A Review of Climatic Controls on δ18O in Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau:Observations and Simulations.Reviews of Geophysics, 51(4):525-548. doi: 10.1002/rog.v51.4 Yi, S., Buylaert, J.P., Murray, A.S., et al., 2015.High Resolution OSL and Post-IR IRSL Dating of the Last Interglacial-Glacial Cycle at the Sanbahuo Loess Site (Northeastern China).Quaternary Geochronology, 30:200-206. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2015.02.013 Zeng, F.M., 2016.Provenance of the Late Quaternary Loess Deposit in the Qinghai Lake Region.Earth Science, 41(1):131-138 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201601011.htm Zeng, M.X., Song, Y.G., 2013.Carbonate Minerals of Zhaosu Loess Section in Westerly Area and Their Paleoenvironmental Significance.Quaternary Sciences, 33(3):424-436 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201303005.htm Zhang, C., Tang, Q., Chen, D., 2016.Recent Changes in the Moisture Source of Precipitation over the Tibetan Plateau.Journal of Climate, 30(5):1807-1819. Zhang, H., Yu, K., Zhao, J., et al., 2013.East Asian Summer Monsoon Variations in the Past 12.5 ka:High-Resolution δ18O Record from a Precisely Dated Aragonite Stalagmite in Central China.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 73(8):162-175. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_393e94d7e6f20227ed38f03aaaa3d6d1 Zhang, Z.K., Li, G.J., Yan, H., et al., 2018.Microcodium in Chinese Loess as a Recorder for the Oxygen Isotopic Composition of Monsoonal Rainwater.Quaternary International, 464:364-369. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2017.10.050 陈骏, 仇刚, 杨杰东, 1997.黄土碳酸盐Sr同位素组成与原生和次生碳酸盐识别.自然科学进展, 7(6):731-734. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.1997.06.015 陈忠, 马海州, 曹广超, 等, 2006.黄土碳酸盐的研究.盐湖研究, 14(4):66-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-858X.2006.04.013 方谦, 洪汉烈, 赵璐璐, 等, 2018.风化成土过程中自生矿物的气候指示意义.地球科学, 43(3):753-769. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3766 顾兆炎, 1991.黄土-古土壤序列碳酸盐同位素组成与古气候变化.科学通报, 36(10):767-770. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94252X/199110/552649.html 韩家懋, 姜文英, 刘东生, 1996.黄土碳酸盐中古气候变化的同位素记录.中国科学(D辑), 26(5):399-404. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.05.001 韩家懋, 姜文英, 吕厚远, 1995a.黄土中钙结核的碳氧同位素研究(二)碳同位素及其古环境意义.第四纪研究, 15(4):367-377. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ504.012.htm 韩家懋, 姜文英, 吴乃琴, 等, 1995b.黄土中钙结核的碳氧同位素研究(一)氧同位素及其古环境意义.第四纪研究, 15(2):130-137. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ502.004.htm 姜文英, 韩家懋, 刘东生, 2001.干旱化对成土碳酸盐碳同位素组成的影响.第四纪研究, 21(5):427-435. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2001.05.006 刘东生, 1997.第四纪环境.北京:科学出版社, 25-36. 刘志飞, Christophe, C., Alain, T., 2005.傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)方法在南海定量矿物学研究中的应用:以MD01-2393孔为例.地球科学, 30(1):25-29. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=1449 卢演俦, 安芷生, 1979.约70万年以来黄土高原自然环境变化系列探讨.科学通报, 24(5):221-224. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=KXTB197905008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 盛雪芬, 陈骏, 杨杰东, 等, 2002.不同粒级黄土-古土壤中碳酸盐碳氧稳定同位素组成及其古环境意义.地球化学, 31(2):105-112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2002.02.001 文启忠, 1989.中国黄土地球化学.北京:科学出版社, 115-169. 曾方明, 2016.青海湖地区晚第四纪黄土的物质来源.地球科学, 41(1):131-138. http://www.earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3226 曾蒙秀, 宋友桂, 2013.西风区昭苏黄土剖面中碳酸盐矿物组成及其古环境意义辨识.第四纪研究, 33(3):424-436. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2013.03.03 -









 下载:
下载: