Large Perturbed Marine Carbon-Nitrogen-Sulfur Isotopes during Early Triassic
-
摘要: 早三叠世作为显生宙最大生物灭绝之后的一段特殊地质历史时期,不仅见证了海洋生物的迟缓复苏,而且记录了极其动荡的海洋环境变化,该时期异常的生物环境事件及其机制已经成为当前国际地质学者关注的重大科学问题之一.近些年来,研究学者在早三叠世的碳-氮-硫异常循环研究中取得了许多重要的进展,这对深入理解该时期的环境演变及其对生物复苏的影响十分重要.重点回顾近年来关于早三叠世古海洋碳-氮-硫循环方面的研究进展,对当前存在的科学问题及发展趋势进行分析和总结.Abstract: Early Triassic oceans recorded the delayed biotic recovery and the large perturbed environments. Hence, the environmental events and their mechanism became one of the key scientific topics for the geological scientists. In recent years, researchers have made many significant progresses in the marine carbon-nitrogen-sulfur cycles of the Early Triassic, which are important for understanding the co-evolution between the biotic recovery and environmental changes. The progress, problem and future development in the researches of carbon-nitrogen-sulfur cycles during the Early Triassic have been reviewed and summarized.
-
Key words:
- Early Triassic /
- carbon isotope /
- nitrogen isotope /
- sulfur isotope /
- ocean anoxia /
- stratigraphy
-
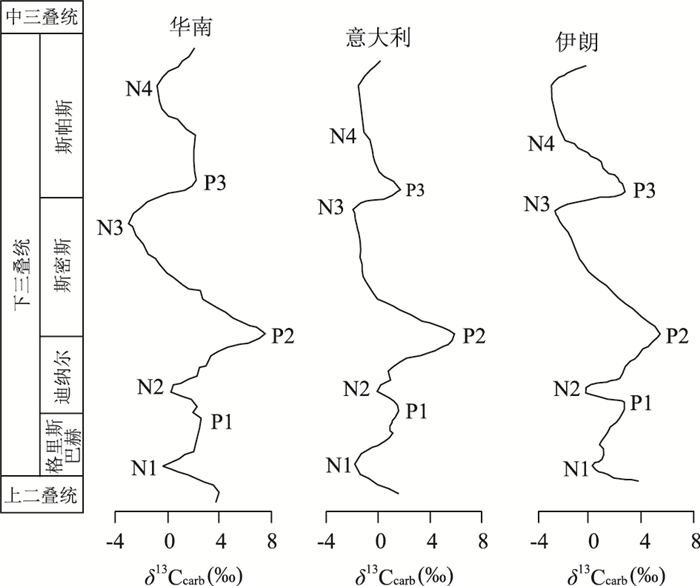
图 1 早三叠世碳同位素组成全球对比
δ13Ccarb结果均相对于VPDB;碳同位素分别引自:华南,Payne et al.(2004);意大利,Horacek et al.(2007a);伊朗,Horacek et al.(2007b);N代表碳同位素负偏事件,P代表碳同位素正漂事件
Fig. 1. Global correlation of the Early Triassic carbon isotope changes
图 3 打讲、上关刀、下关刀剖面早三叠世δ34SCAS, δ13Ccarb曲线
据Song et al.(2014);δ13Ccarb结果均相对于VPDB;δ34SCAS结果均相对于VCDT.C.=Clarkina; H.=Hindeodus parvus; I.s.=Isarcicella staeschi; I.i.=Isarcicella isarcica; Ns.=Neospathodus; Nv.= Novispathodus; T.=Triassospathodus; Cs.=Chiosella; Ni.=Nicoraella; Pg.=Paragondolella; Bv.=Budurovignathus
Fig. 3. Early Triassic δ34SCAS, δ13Ccarb curves from Dajiang, Lower and Upper Guandao sections
-
Algeo, T.J., Hannigan, R., Rowe, H., et al., 2007.Sequencing Events across the Permian-Triassic Boundary, Guryul Ravine (Kashmir, India).Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 252(1):328-346.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.11.050 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=4a9aa9f7a9edf8d3adeacf845149d477 Bernasconi, S.M., Meier, I., Wohlwend, S., et al., 2017.An Evaporite-Based High-Resolution Sulfur Isotope Record of Late Permian and Triassic Seawater Sulfate.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 204:331-349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2017.01.047 Berner, R.A., 2004.The Phanerozoic Carbon Cycle:CO2 and O2.Oxford University Press, New York. Berner, R.A., 2005.The Carbon and Sulfur Cycles and Atmospheric Oxygen from Middle Permian to Middle Triassic.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 69(13):3211-3217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.03.021 Berner, R.A., 2006.Geocarbsulf:A Combined Model for Phanerozoic Atmospheric O2 and CO2.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(23):5653-5664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2005.11.032 Berner, R.A., Kothavala, Z., 2001.Geocarb Ⅲ:A Revised Model of Atmospheric CO2 over Phanerozoic Time.American Journal of Science, 301(2):182-204. doi: 10.2475/ajs.301.2.182 Berner, R.A., Rao, J.L., 1994.Phosphorus in Sediments of the Amazon River and Estuary:Implications for the Global Flux of Phosphorus to the Sea.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 58(10):2333-2339. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(94)90014-0 Bottrell, S.H., Newton, R.J., 2006.Reconstruction of Changes in Global Sulfur Cycling from Marine Sulfate Isotopes.Earth-Science Reviews, 75(1):59-83. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d8174a3ba7587853b13dccac16f70afe Brühwiler, T., Goudemand, N., Galfetti, T., et al., 2009.The Lower Triassic Sedimentary and Carbon Isotope Records from Tulong (South Tibet) and Their Significance for Tethyan Palaeoceanography.Sedimentary Geology, 222(3-4):314-332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2009.10.003 Cao, C.Q., Love, G.D., Hays, L.E., et al., 2009.Biogeochemical Evidence for Euxinic Oceans and Ecological Disturbance Presaging the End-Permian Mass Extinction Event.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 281(3-4):188-201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.02.012 Cao, C.Q., Wang, W., Jing, Y., 2002.Carbon Isotope Changes near Permo-Triassic Boundary in Meishan, Zhejiang.Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(4):302-306 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/02tb9072 Caravaca, G., Thomazo, C., Vennin, E., et al., 2017.Early Triassic Fluctuations of the Global Carbon Cycle:New Evidence from Paired Carbon Isotopes in the Western USA Basin.Global and Planetary Change, 154:10-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2017.05.005 Chen, J.S., Chu, X.L., 1988.Sulfur Isotope Composition of Triassic Marine Sulfates of South China.Chemical Geology:Isotope Geoscience Section, 72(2):155-161. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9622(88)90063-2 Chen, J.S., Chu, X.L., Shao, M.R., 1986.Sulfur Isotope of the Triassic Sea.Scientia Geologica Sinica, 21(4):330-338 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX198604002.htm Chen, Z.Q., Benton, M.J., 2012.The Timing and Pattern of Biotic Recovery Following the End-Permian Mass Extinction.Nature Geoscience, 5(6):375-383. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1475 Clarkson, M.O., Richoz, S., Wood, R.A., et al., 2013.A New High-Resolution δ13C Record for the Early Triassic:Insights from the Arabian Platform.Gondwana Research, 24(1):233-242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2012.10.002 Clarkson, M.O., Wood, R.A., Poulton, S.W., et al., 2016.Dynamic Anoxic Ferruginous Conditions during the End-Permian Mass Extinction and Recovery.Nature Communications, 7:12236. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12236 Cortecci, G., Reyes, E., Berti, G., et al., 1981.Sulfur and Oxygen Isotopes in Italian Marine Sulfates of Permian and Triassic Ages.Chemical Geology, 34(1-2):65-79. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(81)90072-3 Fike, D.A., Bradley, A.S., Rose, C.V., 2015.Rethinking the Ancient Sulfur Cycle.Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 43(1):593-622. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-054802 Fike, D.A., Grotzinger, J.P., Pratt, L.M., et al., 2006.Oxidation of the Ediacaran Ocean.Nature, 444(7120):744-747. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05345 Galfetti, T., Bucher, H., Brayard, A., et al., 2007a.Late Early Triassic Climate Change:Insights from Carbonate Carbon Isotopes, Sedimentary Evolution and Ammonoid Paleobiogeography.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 243(3-4):394-411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.08.014 Galfetti, T., Hochuli, P.A., Brayard, A., et al., 2007b.Smithian-Spathian Boundary Event:Evidence for Global Climatic Change in the Wake of the End-Permian Biotic Crisis.Geology, 35(4):291.https://doi.org/10.1130/g23117a.1 doi: 10.1130/G23117A.1 Gill, B.C., Lyons, T.W., Young, S.A., et al., 2011.Geochemical Evidence for Widespread Euxinia in the Later Cambrian Ocean.Nature, 469(7328):80-83. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09700 Grasby, S.E., Beauchamp, B., Embry, A., et al., 2013.Recurrent Early Triassic Ocean Anoxia.Geology, 41(2):175-178.https://doi.org/10.1130/g33599.1 doi: 10.1130/G33599.1 Grasby, S.E., Beauchamp, B., Knies, J., 2016.Early Triassic Productivity Crises Delayed Recovery from World's Worst Mass Extinction.Geology, 44(9):779-782. doi: 10.1130/G38141.1 Holser, W.T., 1977.Catastrophic Chemical Events in the History of the Ocean.Nature, 267(5610):403-408. doi: 10.1038/267403a0 Horacek, M., Brandner, R., Abart, R., 2007a.Carbon Isotope Record of the P/T Boundary and the Lower Triassic in the Southern Alps:Evidence for Rapid Changes in Storage of Organic Carbon.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 252(1-2):347-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.11.049 Horacek, M., Richoz, S., Brandner, R., et al., 2007b.Evidence for Recurrent Changes in Lower Triassic Oceanic Circulation of the Tethys:The δ13C Record from Marine Sections in Iran.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 252(1-2):355-369. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.11.052 Horacek, M., Koike, T., Richoz, S., 2009.Lower Triassic δ13C Isotope Curve from Shallow-Marine Carbonates in Japan, Panthalassa Realm:Confirmation of the Tethys δ13C Curve.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 36(6):481-490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.05.005 Huang, K.K., Huang, S.J., Lan, Y.F., et al., 2013.Review of the Carbon Isotope of Early Triassic Carbonates.Advances in Earth Science, 28(3):357-365 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201303009.htm Huang, S.J., Huang, K.K., Lü, J., et al., 2012.Carbon Isotopic Composition of Early Triassic Marine Carbonates, Eastern Sichuan Basin, China.Science China Earth Sciences, 42(10):1508-1522 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/s11430-012-4440-1 Huang, Y.G., Chen, Z.Q., Wignall, P.B., et al., 2017.Latest Permian to Middle Triassic Redox Condition Variations in Ramp Settings, South China:Pyrite Framboid Evidence.Geological Society of America Bulletin, 129(1-2):229-243.https://doi.org/10.1130/b31458.1 doi: 10.1130/B31458.1 Jenkyns, H.C., Gröcke, D.R., Hesselbo, S.P., 2001.Nitrogen Isotope Evidence for Water Mass Denitrification during the Early Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event.Paleoceanography, 16(6):593-603.https://doi.org/10.1029/2000pa000558 doi: 10.1029/2000PA000558 Kaiho, K., Oba, M., Fukuda, Y., et al., 2012.Changes in Depth-Transect Redox Conditions Spanning the End-Permian Mass Extinction and Their Impact on the Marine Extinction:Evidence from Biomarkers and Sulfur Isotopes.Global and Planetary Change, 94-95:20-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.05.024 Kampschulte, A., Strauss, H., 2004.The Sulfur Isotopic Evolution of Phanerozoic Seawater Based on the Analysis of Structurally Substituted Sulfate in Carbonates.Chemical Geology, 204(3):255-286.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.11.013 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254103003747 Knies, J., Grasby, S.E., Beauchamp, B., et al., 2013.Water Mass Denitrification during the Latest Permian Extinction in the Sverdrup Basin, Arctic Canada.Geology, 41(2):167-170.https://doi.org/10.1130/g33816.1 doi: 10.1130/G33816.1 Knoll, A.H., Bambach, R.K., Payne, J.L., et al., 2007.Paleophysiology and End-Permian Mass Extinction.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 256(3-4):295-313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.02.018 Kump, L.R., Arthur, M.A., 1999.Interpreting Carbon-Isotope Excursions:Carbonates and Organic Matter.Chemical Geology, 161(1-3):181-198.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(99)00086-8 doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00086-8 Lei, L.D., 2017.Marine Redox Variability and Its Coupling with Oceanic C-N Biogeochemical Cycling across the Permian-Triassic Boundary in South China (Dissertation).China University of Geosciences, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, R., Jones, B., 2016.Diagenetic Overprint on Negative δ13C Excursions across the Permian/Triassic Boundary:A Case Study from Meishan Section, China.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 468:18-33.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2016.11.044 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0031018216307933 Luo, G.M., Algeo, T.J., Huang, J.H., et al., 2014.Vertical δ13Corg Gradients Record Changes in Planktonic Microbial Community Composition during the End-Permian Mass Extinction.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 396:119-131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2014.01.006 Luo, G.M., Junium, C.K., Izon, G., et al., 2018.Nitrogen Fixation Sustained Productivity in the Wake of the Palaeoproterozoic Great Oxygenation Event.Nature Communications, 9(1):69-78.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-03361-2 doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02477-1 Luo, G.M., Kump, L.R., Wang, Y.B., et al., 2010.Isotopic Evidence for an Anomalously Low Oceanic Sulfate Concentration Following End-Permian Mass Extinction.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 300(1):101-111.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2010.09.041 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=27834f35de4ea01ffe320ad6ce098a23 Luo, G.M., Wang, Y.B., Algeo, T.J., et al., 2011.Enhanced Nitrogen Fixation in the Immediate Aftermath of the Latest Permian Marine Mass Extinction.Geology, 39(7):647-650.https://doi.org/10.1130/g32024.1 doi: 10.1130/G32024.1 Marenco, P.J., Corsetti, F.A., Hammond, D.E., et al., 2008.Oxidation of Pyrite during Extraction of Carbonate Associated Sulfate.Chemical Geology, 247(1):124-132.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.10.006 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0009254107004421 McFadden, K.A., Huang, J., Chu, X., et al., 2008.Pulsed Oxidation and Biological Evolution in the Ediacaran Doushantuo Formation.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105(9):3197-3202. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0708336105 Meyer, K.M., Yu, M., Jost, A.B., et al., 2011.δ13C Evidence That High Primary Productivity Delayed Recovery from End-Permian Mass Extinction.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 302(3/4):378-384.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2010.12.033 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9e83b975bd7f08f4a8f24fb68895bc17 Meyer, K.M., Yu, M., Lehrmann, D., et al., 2013.Constraints on Early Triassic Carbon Cycle Dynamics from Paired Organic and Inorganic Carbon Isotope Records.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 361:429-435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2012.10.035 Minagawa, M., Wada, E., 1986.Nitrogen Isotope Ratios of Red Tide Organisms in the East China Sea:A Characterization of Biological Nitrogen Fixation.Marine Chemistry, 19(3):245-259. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-4203(86)90026-5 Newton, R.J., Pevitt, E.L., Wignall, P.B., et al., 2004.Large Shifts in the Isotopic Composition of Seawater Sulphate across the Permo-Triassic Boundary in Northern Italy.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 218(3):331-345.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(03)00676-9 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6e45e8319d1456f55968a0e8b2bef50c Payne, J., Kump, L., 2007.Evidence for Recurrent Early Triassic Massive Volcanism from Quantitative Interpretation of Carbon Isotope Fluctuations.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 256(1/2):264-277.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.01.034 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c90108bb89203fa367523f22f826668e Payne, J.L., Lehrmann, D.J., Wei, J., et al., 2004.Large Perturbations of the Carbon Cycle during Recovery from the End-Permian Extinction.Science, 305(5683):506-509. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1097023 Riccardi, A.L., Arthur, M.A., Kump, L.R., 2006.Sulfur Isotopic Evidence for Chemocline upward Excursions during the End-Permian Mass Extinction.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(23):5740-5752. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2006.08.005 Romano, C., Goudemand, N., Vennemann, T.W., et al., 2013.Climatic and Biotic Upheavals Following the End-Permian Mass Extinction.Nature Geoscience, 6(1):57-60. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo1667 Shen, J., Schoepfer, S.D., Feng, Q.L., et al., 2015.Marine Productivity Changes during the End-Permian Crisis and Early Triassic Recovery.Earth-Science Reviews, 149:136-162. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.11.002 Shen, S.Z., Crowley, J.L., Wang, Y., et al., 2011.Calibrating the End-Permian Mass Extinction.Science, 334(6061):1367-1372. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1213454 Shen, S.Z., Zhu, M.Y., Wang, X.D., et al., 2010.A Comparison of the Biological, Geological Events and Environmental Backgrounds between the Neoproterozoic-Cambrian and Permian-Triassic Transitions.Science China Earth Sciences, 40(9):1228-1244 (in Chinese). http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/resolve/reference/XREF?id=10.1007/s11430-010-4092-y Sigman, D.M., Casdotti, K.L., 2001.Nitrogen Isotopes in the Ocean.Academic Press, London. Song, H.J., Tong, J.N., 2016.Mass Extinction and Survival during the Permian-Triassic Crisis.Earth Science, 41(6):901-918 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201606001.htm Song, H.J., Wignall, P.B., Tong, J.N., et al., 2012.Geochemical Evidence from Bio-Apatite for Multiple Oceanic Anoxic Events during Permian-Triassic Transition and the Link with End-Permian Extinction and Recovery.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 353:12-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d9a213220876084fad58736e519e23ca Song, H.Y., Tong, J.N., Algeo, T.J., et al., 2013.Large Vertical δ13CDIC Gradients in Early Triassic Seas of the South China Craton:Implications for Oceanographic Changes Related to Siberian Traps Volcanism.Global and Planetary Change, 105:7-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.10.023 Song, H.Y., Tong, J.N., Algeo, T.J., et al., 2014.Early Triassic Seawater Sulfate Drawdown.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 128:95-113. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.12.009 Song, H.Y., Tong, J.N., Song, H.J., et al., 2010.Excursion of Sulfur Isotope Compositions in the Lower Triassic of South Guizhou, China.Journal of Earth Science, 21(S1):158-160. doi: 10.1007/s12583-010-0198-6 Sun, Y., Joachimski, M.M., Wignall, P.B., et al., 2012.Lethally Hot Temperatures during the Early Triassic Greenhouse.Science, 338(6105):366-370. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1224126 Sun, Y.D., Wignall, P.B., Joachimski, M.M., et al., 2015.High Amplitude Redox Changes in the Late Early Triassic of South China and the Smithian-Spathian Extinction.Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 427:62-78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.03.038 Thomazo, C., Vennin, E., Brayard, A., et al., 2016.A Diagenetic Control on the Early Triassic Smithian-Spathian Carbon Isotopic Excursions Recorded in the Marine Settings of the Thaynes Group (Utah, USA).Geobiology, 14(3):220-236.https://doi.org/10.1111/gbi.12174 doi: 10.1111/gbi.2016.14.issue-3 Tong, J.N., Qiu, H., Zhao, L., et al., 2002.Lower Triassic Inorganic Carbon Isotope Excursion in Chaohu, Anhui Province, China.Journal of Earth Science, 13(2):98-106. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx-e200202002 Tong, J.N., Yin, H.F., 2009.Advance in the Study of Early Triassic Life and Environment.Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 48(3):497-508 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gswxb200903020 Tong, J.N., Zuo, J.X., Chen, Z.Q., 2007.Early Triassic Carbon Isotope Excursions from South China:Proxies for Devastation and Restoration of Marine Ecosystems Following the End-Permian Mass Extinction.Geological Journal, 42(3-4):371-389.https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.1084 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1099-1034 Wada, E., Hattori, A., 1990.Nitrogen in the Sea:Forms, Abundance, and Rate Processes.CRC Press, Boca Raton. Wignall, P.B., Bond, D.P.G., Sun, Y.D., et al., 2016.Ultra-Shallow-Marine Anoxia in an Early Triassic Shallow-Marine Clastic Ramp (Spitsbergen) and the Suppression of Benthic Radiation.Geological Magazine, 153(2):316-331.https://doi.org/10.1017/s0016756815000588 doi: 10.1017/S0016756815000588 Zhou, G.S., 2003.Global Carbon Cycle.Meteorology Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Zuo, J.X., Tong, J.N., Qiu, H.O., et al., 2006.Carbon Isotope Composition of the Lower Triassic Marine Carbonates, Lower Yangtze Region, South China.Science in China (Series D), 49(3):225-241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-006-0225-8 曹长群, 王伟, 金玉玕, 2002.浙江煤山二叠-三叠系界线附近碳同位素变化.科学通报, 47(4):302-306. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2002.04.014 陈锦石, 储雪蕾, 邵茂茸, 1986.三叠纪海的硫同位素.地质科学, 21(4):330-338. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000368688 黄可可, 黄思静, 兰叶芳, 等, 2013.早三叠世海相碳酸盐碳同位素研究进展.地球科学进展, 28(3):357-365. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkxjz201303007 黄思静, 黄可可, 吕杰, 等, 2012.早三叠世海水的碳同位素组成与演化-来自四川盆地东部的研究.中国科学(D辑), 42(10):1508-1522. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK201204687033 雷丽丹, 2017.华南古中生代之交古海洋氧化(博士学位论文).武汉: 中国地质大学. 沈树忠, 朱茂炎, 王向东, 等, 2010.新元古代-寒武纪与二叠-三叠纪转折时期生物和地质事件及其环境背景之比较.中国科学, 40(9):1228-1240. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=JDXK201009013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ 宋海军, 童金南, 2016.二叠纪-三叠纪之交生物大灭绝与残存.地球科学, 41(6):901-918. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3307 童金南, 殷鸿福, 2009.早三叠世生物与环境研究进.古生物学报, 48(3):497-508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-6616.2009.03.020 周广胜, 2003.全球碳循环.北京:气象出版社. -









 下载:
下载:



