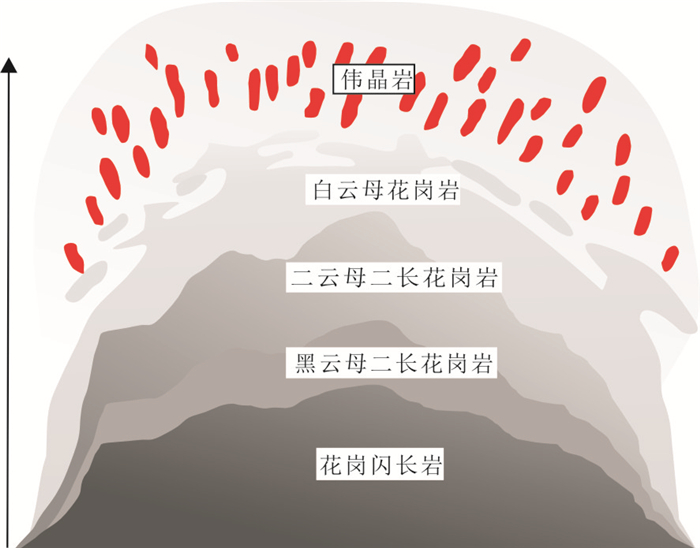
Petrogenesis and Rare-Metal Mineralization of the Mufushan Granitic Pegmatite, South China: Insights from in Situ Mineral Analysis
-
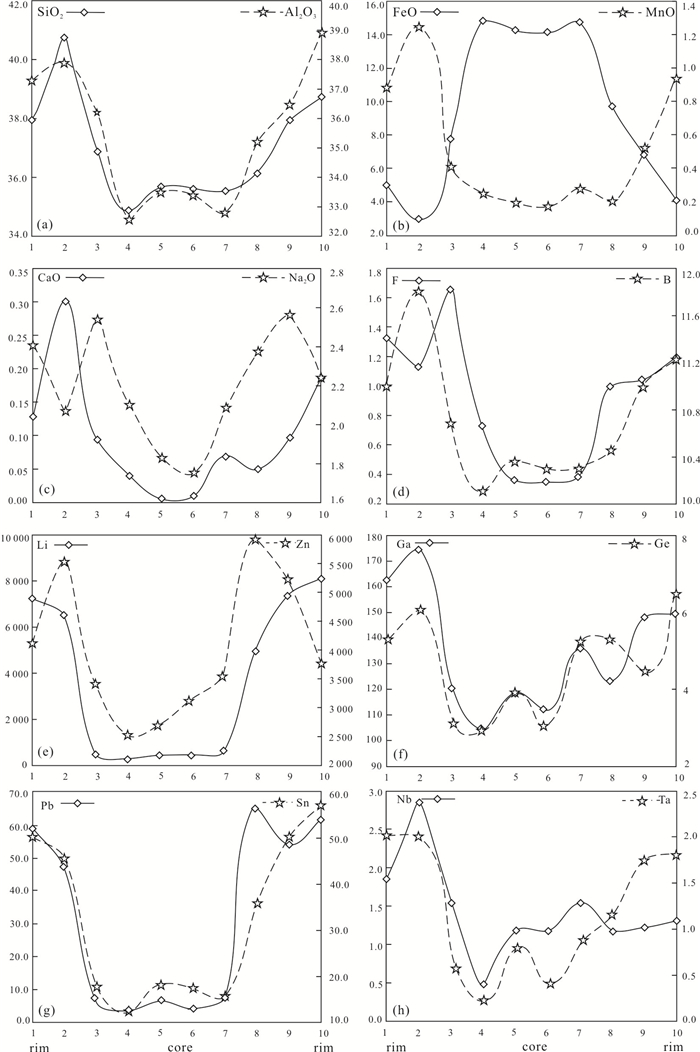
摘要: 华南晚中生代幕阜山花岗复式岩基内部及周缘广泛发育花岗伟晶岩脉,部分岩脉富含Li-Nb-Ta等元素,形成大型-超大型稀有金属矿床.本文以幕阜山北缘断峰山地区贫锂伟晶岩类和南缘仁里地区新发现的富锂伟晶岩为主要研究对象,通过详细的岩相学和主要及特征矿物(长石、云母、电气石、石榴子石、绿柱石、铌钽铁矿)的微区原位EPMA和LA-ICP-MS主微量元素地球化学的对比分析,深入探讨了伟晶岩的分类、成因演化及成矿潜力.按照特征矿物组合将伟晶岩划分为断峰山地区电气石伟晶岩、电气石-绿柱石伟晶岩、绿柱石伟晶岩、铌钽铁矿-绿柱石伟晶岩和仁里地区的锂电气石-锂云母伟晶岩5类.5类岩脉中的长石、云母、电气石和/或石榴子石的化学成分记录了不同程度花岗伟晶岩脉的演化阶段,按岩浆演化程度由低至高依次为电气石伟晶岩→电气石-绿柱石伟晶岩→绿柱石伟晶岩→铌钽铁矿-绿柱石伟晶岩→锂电气石-锂云母伟晶岩,并分别对应伟晶岩稀有金属富集程度分类中的无矿→(含Be)→富Be→富Be、Nb、Ta→富Li、Be、Nb、Ta阶段.这一结果表明仁里地区伟晶岩已演化至晚期富集多种稀有金属元素阶段,具有Li-Nb-Ta多金属成矿潜力,而断峰山地区的伟晶岩演化程度相对较低.断峰山电气石-绿柱石伟晶岩中的色带电气石晶体发育强烈成分环带,由内向外可明显分为5环,自核部至边部,Li、Zn、Ga、Ge、Nb、Ta、Sn、Pb等不相容元素和金属元素含量逐渐升高,清晰记录了正常岩浆演化序列及稀有金属富集过程.结合前人有关幕阜山花岗岩类的研究资料,本文认为幕阜山伟晶岩为该地区晚中生代巨量花岗质岩浆经历长期结晶分异作用晚期的分异产物.Abstract: Granitic pegmatites are widely distributed in the inner and adjacent region of the Late Mesozoic Mufushan granitic complex in South China. Some of them are rich in Li-Nb-Ta and related elements, forming large-ultra-large rare metal deposits. This study focuses on the lithium-poor pegmatites from Duanfengshan area in the northern Mufushan and the newly discovered lithium-rich pegmatite from Renli area in the south. Hereby we provided detailed petrographic and in situ EPMA and LA-ICP-MS geochemical analysis of major and characteristic minerals (feldspar, mica, tourmaline, garnet, beryl, columbite-tantalite) from the Mufushan pegmatites, aiming to constrain the classification, evolution and mineralization of the investigated pegmatites. Based on the combination of the characteristics minerals, the Mufushan pegmatites have been divided into five groups:Tur-pegmatite, Tur-Brl-pegmatite, Brl-pegmatite, Col-Brl-pegmatite in Duanfengshan area and Elb-Lpd-pegmatite in Renli area. Compositional variation of feldspar, mica, tourmaline and garnet from the studied pegmatites display continuous magmatic evolution sequence. From low to high evolution degrees, the Mufushan pegmatites are Tur-pegmatite→Tur-Brl-pegmatite→Brl-pegmatite→Col-Brl-pegmatite→Elb-Lpd-pegmatite, corresponding to the mineralization stages of metal barren→(Be-bearing)→Be-rich→Be, Nb, Ta-rich→Li, Be, Nb, Ta-rich, respectively. This result indicates that the Renli pegmatites have evolved to a relatively late-stage with various rare metal enrichment, which thus has higher potential of Li-Nb-Ta polymetallic mineralization. In contrast, the evolutionary degrees of Duanfengshan pegmatites are relatively low. A strongly zoned tourmaline crystal has been observed in the Tur-Brl-pegmatite from Duanfengshan area, in which five compositional zones from inside to outside can be divided. The content of incompatible elements such as Li, Zn, Ga, Ge, Nb, Ta, Sn, Pb gradually increased from inner to outter, which clearly recording the normal magmatic evolution sequences and the rare metal enrichment processes. Combined with previous studies, our work suggests that the Mufushan pegmatites are generated by extremely prolonged fractional crystallization of the Mufushan massive granitic magma, representing the final-stage product of granitic magma.
-
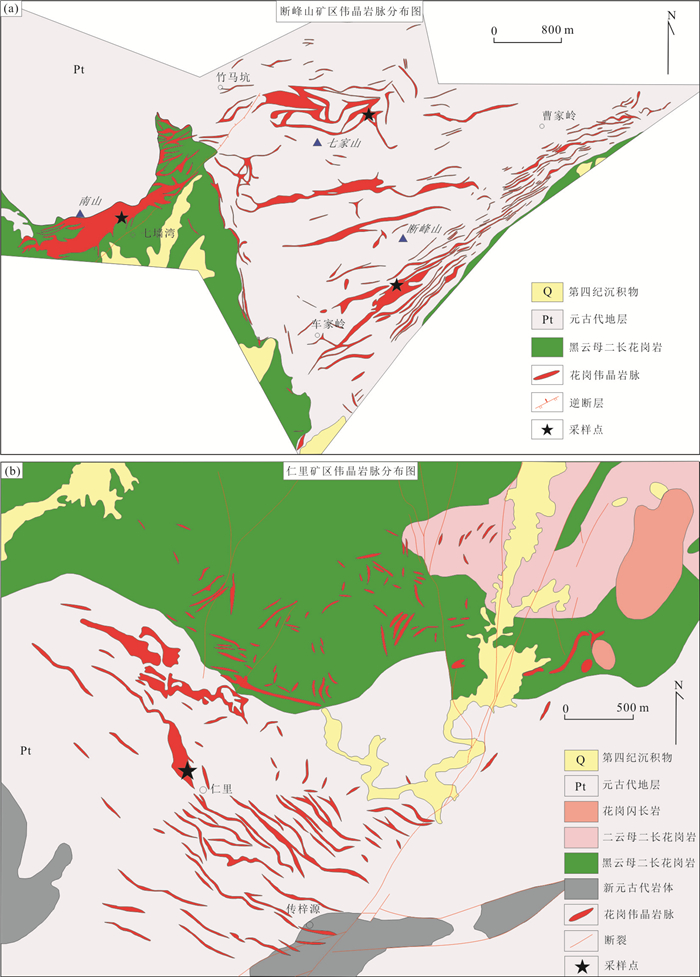
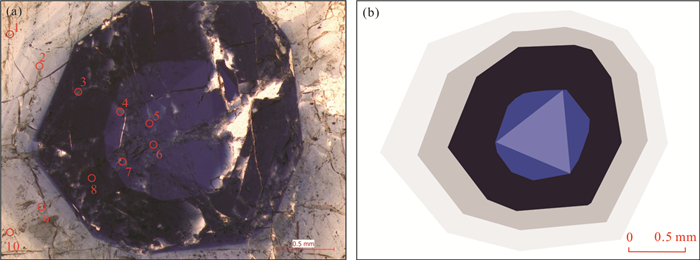
图 3 断峰山矿区和仁里矿区伟晶岩特征性矿物
a. Tur-伟晶岩中生长于白云母中的黑电气石;b. Tur-伟晶岩中生长于石英中的黑电气石c. Tur-Brl-伟晶岩中黑电气石;d. Tur-Brl-伟晶岩中色带电气石;e. Tur-Brl-伟晶岩中簇状绿柱石集合体;f. Brl-伟晶岩中绿柱石单晶;g. Col-Brl-伟晶岩中绿柱石巨晶;h. Col-Brl-伟晶岩中铌钽铁矿颗粒;i. Elb-Lpd-伟晶岩中锂电气石;j.锂电气石镜下照片,正交偏光;k. Elb-Lpd-伟晶岩中锂云母;l.锂云母镜下照片,正交偏光;Elb.锂电气石;Lpd.锂云母
Fig. 3. Characteristic minerals of the pegmatite in Duanfengshan and Renli diggings
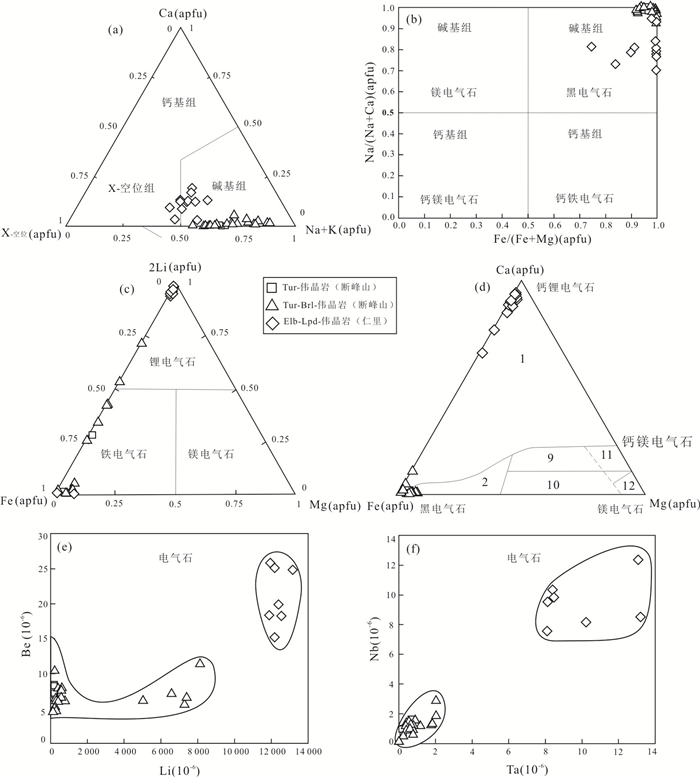
图 4 幕阜山伟晶岩中电气石分类命名(a~c)、成岩环境(d)和微量元素特征(e、f)
电气石化学成分与成岩环境判别图d引自Henry and Guidotti(1985).图中1、2区分别表示富Li和贫Li的花岗岩和伟晶岩、细晶岩;9区代表富Ca的变质泥岩、砂岩和钙硅酸盐;10区代表贫Ca的变质泥岩、砂岩和石英-电气石岩;11区代表变质碳酸盐岩;12区代表变质镁铁质岩
Fig. 4. Classification of tourmaline (a-c), Ca-Fe-Mg diagram for tourmaline from various rock types (d) and characteristics (e, f) of trace elements in Mufushan pegmatites
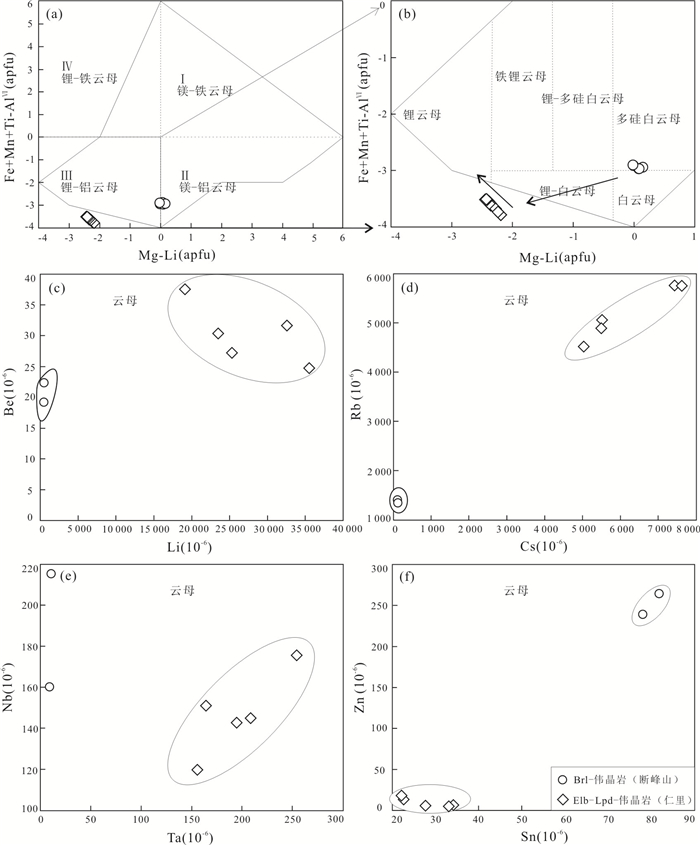
图 5 幕阜山伟晶岩云母化学成分演化图和微量元素特征
Fig. 5. Chemical composition evolution of mica and characteristics of trace elements in Mufushan pegmatite
图 7 幕阜山伟晶岩电气石Fe⁃Al和Al/(Al+Fe)⁃Na/(Na+X⁃空位)图解
Fig. 7. Fe⁃Al and Al/(Al+Fe)⁃Na/(Na+X⁃vac) diagram of tourmaline of pegmatite in Mufushan
图 8 幕阜山伟晶岩云母(a)、长石(b)、石榴子石(c)演化图解
底图数据据Selway et al.(2005)
Fig. 8. Evolution diagrams for mica (a), K-feldspar (b), garnet (c) in Mufushan pegmatites
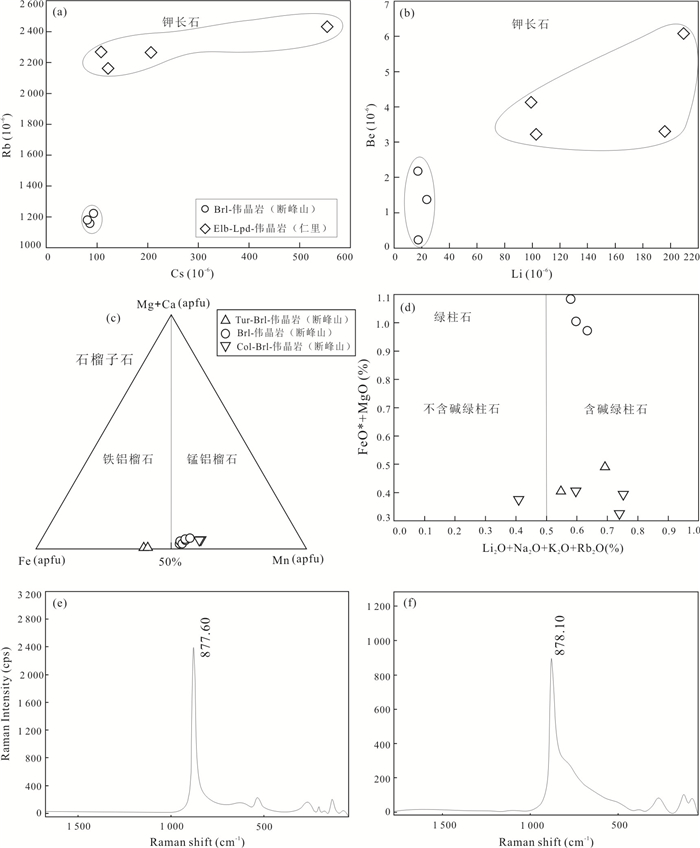
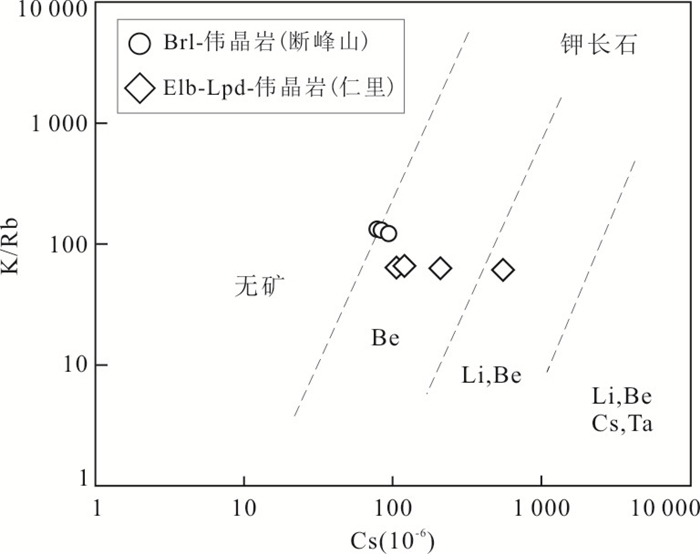
图 12 幕阜山伟晶岩钾长石K/Rb-Cs与化学演化图解
Fig. 12. K/Rb-Cs and chemical evolution of K-feldspar in Mufushan pegmatites
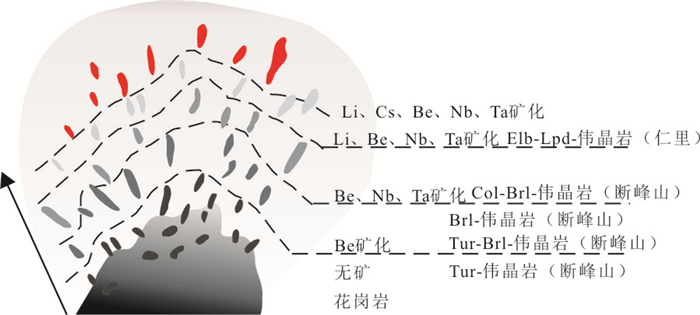
表 1 幕阜山伟晶岩脉分类
Table 1. Classification of pegmatite dykes in Mufushan
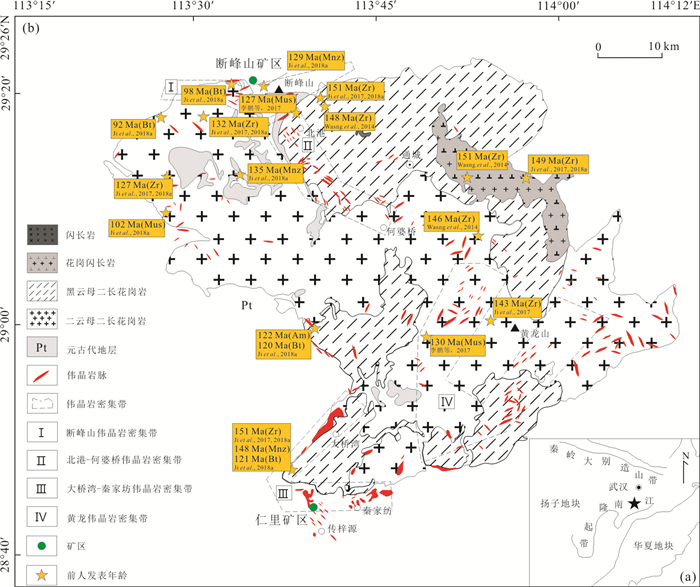
矿区 岩脉名称 岩脉类型 矿物组合 断峰山 电气石伟晶岩 Tur-伟晶岩 钾长石、钠长石、白云母、石英、石榴子石、电气石 电气石-绿柱石伟晶岩 Tur-Brl-伟晶岩 钾长石、钠长石、白云母、石英、石榴子石、绿柱石、电气石 绿柱石伟晶岩 Brl-伟晶岩 钾长石、钠长石、白云母、石英、石榴子石、绿柱石 铌钽铁矿-绿柱石伟晶岩 Col-Brl-伟晶岩 钾长石、钠长石、石英、白云母、绿柱石、石榴子石、铌钽铁矿 仁里 锂电气石-锂云母伟晶岩 Elb-Lpd-伟晶岩 钾长石、钠长石、石英、绿柱石、石榴子石、锂电气石、锂云母 -
Černý, P., 1991. Rare-Element Granitic Pegmatites. Part Ⅱ:Regional and Global Environments and Petrogenesis. Geoscience Canada, 18(2):68-81. Dutrow, B. L., Henry, D. J., 2011. Tourmaline:A Geologic DVD. Elements, 7(5):301-306. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.7.5.301 Henry, D.J., Guidotti, C.V., 1985. Tourmaline as a Petrogenetic Indicator Mineral-An Example from the Staurolite-Grade Metapelites of NW Maine. American Mineralogist, 70(1):1-15. doi: 10.1093-cvr-cvr203/ Henry, D. J., Novak, M., Hawthorne, F. C., et al., 2011. Nomenclature of the Tourmaline-Supergroup Minerals. American Mineralogist, 96(5/6):895-913. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2011.3636 Hu, Z. C., Liu, Y. S., Gao, S., et al., 2012. A "Wire" Signal Smoothing Device for Laser Ablation Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Spectrochimica Acta Part B:Atomic Spectroscopy, 78:50-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sab.2012.09.007 Ji, W. B., Faure, M., Lin., W., et al., 2018a. Multiple Emplacement and Exhumation History of the Late Mesozoic Dayunshan-Mufushan Batholith in Southeast China and Its Tectonic Significance:1. Structural Analysis and Geochronological Constraints. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 123(1):689-710. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017jb014597 Ji, W. B., Faure, M., Lin.W., et al., 2018b. Multiple Emplacement and Exhumation History of the Late Mesozoic Dayunshan-Mufushan Batholith in Southeast China and Its Tectonic Significance:2. Magnetic Fabrics and Gravity Survey. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 123(1):711-731. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017jb014598 Ji, W. B., Lin, W., Faure, M., et al., 2017. Origin of the Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous Peraluminous Granitoids in the Northeastern Hunan Province (middle Yangtze Region), South China:Geodynamic Implications for the Paleo-Pacific Subduction. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 141:174-193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.07.005 Li, J. K., Zou, T. R., Liu, X. F., et al., 2015. The Metallogenetic Regularities of Lithium Deposits in China. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 89(2):652-670. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.12453 Li, P., Li, J. K., Pei, R. F., et al., 2017. Multistage Magmatic Evolution and Cretaceous Peak Metallogenic Epochs of Mufushan Composite Granite Mass:Constrains from Geochronological Evidence. Earth Science, 42(10):1684-1696 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.114 Liu, L. J., Wang, ,D. H., Liu, X. F., et al., 2017. The Main Types, Distribution Features and Present Situation of Exploration and Development for Domestic and Foreign Lithium Mine. Geology in China, 44(2):263-278 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201702004 Liu, X., Zhou, F. C., Huang, Z. B., et al., 2018. Discovery of Renli Superlarge Pegmatite-Type Nb-Ta Polymetallic Deposit in Pingjiang, Hunan Province and Its Significances. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 42(2):235-243 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201802004 Liu, Y. S., Hu, Z. C., Gao, S., et al., 2008. In Situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by LA-ICP-MS without Applying an Internal Standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2):34-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 London, D., Morgan, G. B., Hervig, R. L., 1989. Vapor-Undersaturated Experiments with Macusani Glass+H2O at 200 MPa, and the Internal Differentiation of Granitic Pegmatites. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 102(1):1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf01160186 Monier, G., Robert, J. L., 1986. Evolution of the Miscibility Gap between Muscovite and Biotite Solid Solutions with Increasing Lithium Content:An Experimental Study in the System K2O-Li2O-MgO-FeO-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O-HF at 600℃, 2 kbar PH2O:Comparison with Natural Lithium Micas. Mineralogical Magazine, 50(358):641-651. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1986.050.358.09 Rao, C., Wang, R. C., Zhang, A. C., et al., 2012. The Corundum Plus Tourmaline Nodules Related to Hydrothermal Alteration of Spodumene in the Nanping No. 31 Pegmatite Dyke, Fujian Province, Southeastern China. Canadian Mineralogist, 50(6), 1623-1635. https://doi.org/10.3749/canmin.50.6.1623 Samadi, R., Miller, N. R., Mirnejad, H., et al., 2014. Origin of Garnet in Aplite and Pegmatite from Khajeh Morad in Northeastern Iran:A Major, Trace Element, and Oxygen Isotope Approach. Lithos, 208-209:378-392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.08.023 Selway, J. B., 2005. A Review of Rare-Element (Li-Cs-Ta) Pegmatite Exploration Techniques for the Superior Province, Canada, and Large Worldwide Tantalum Deposits. Exploration and Mining Geology, 14(1-4):1-30. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsemg.14.1-4.1 Shearer, C. K., Papike, J. J., Jolliff, B. L., 1992. Petrogenetic Links among Granites and Pegmatites in the Harney Peak Rare-Element Granite-Pegmatite System, Black Hills, South Dakota. Canadian Mineralogist, 30(3):785-809. Tindle, A. G., Webb, P. C., 1990. Estimation of Lithium Contents in Trioctahedral Micas Using Microprobe Data:Application to Micas from Granitic Rocks. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2(5):595-610. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/2/5/0595 Tischendorf, G., Gottesmann, B., Förster, H. J., et al., 1997. On Li-Bearing Micas:Estimating Li from Electron Microprobe Analyses and an Improved Diagram for Graphical Representation. Mineralogical Magazine, 61(409):809-834. https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.1997.061.409.05 Trueman, D., Černý, P., 1982. Exploration for Rare-Element Granitic Pegmatites. In: Černý, P., ed., Granitic Pegmatites in Science and Industry. Mineralogical Association of Canada, Québec. Wang, D. H., Wang, R. J., Li, J. K., et al., 2013. The Progress in the Strategic Research and Survey of Rare Earth, Rare Metal and Rare-Scattered Elements Mineral Resources. Geology in China, 40(2):361-370 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201302002.htm Wang, D. H., Zhao, T., He, H. H., et al., 2016. Review of Three Rare Mineral Resources Investigation and Progress in Central-South China. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 36(1):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=glgxy201601001 Wang, H., Li, P., Ma, H. D., et al., 2017. Discovery of the Bailongshan Superlarge Lithium-Rubidium Deposit in Karakorum, Hetian, Xinjiang, and Its Prospecting Implication. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 41(6):1053-1062 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201706005 Wang, L. X., Ma, C. Q., Zhang, C., et al., 2014. Genesis of Leucogranite by Prolonged Fractional Crystallization:A Case Study of the Mufushan Complex, South China. Lithos, 206-207:147-163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.07.026 Wang, P., Pan, Z. L., Weng, L. B., et al., 1982. System Mineralogy (Middle). Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 155 (in Chinese). Wang, R., C., Che, X. D., Zhang, W. L., et al., 2009. Geochemical Evolution and Late Re-Equilibration of Na-Cs-Rich Beryl from the Koktokay #3 Pegmatite (Altai, NW China). European Journal of Mineralogy, 21(4):795-809. https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2009/0021-1936 Wang, Z. P., Liu, S. B., Ma, S. C., et al., 2018. Metallogenic Regularity, Deep and Periphery Prospecting of Dangba Superlarge Spodumene Deposit in Aba, Sichuan Province. Earth Science, 43(6):2029-2041 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.604 Wen, C. H., Chen, J. F., Luo, X, Y., et al., 2016. Geochemical Features of the Chuanziyuan Rare Metal Pegmatite in Northeastern Hunan, China. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 35(1):171-177 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201601020 Xiong, Q., Zheng, J. P., Griffin, W. L., et al., 2011. Zircons in the Shenglikou Ultrahigh-Pressure Garnet Peridotite Massif and Its Country Rocks from the North Qaidam Terrane (Western China):Meso-Neoproterozoic Crust-Mantle Coupling and Early Paleozoic Convergent Plate-Margin Processes. Precambrian Research, 187(1-2):33-57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.precamres.2011.02.003 Xu, Z. Q., Wang, Q. C., Zhao, Z. B., et al., 2018. On the Structural Backgrounds of the Large-Scale "Hard-Rock Type" Lithium Ore Belts in China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(6):1091-1106 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201806001 Yang, S. Y., Jiang, S. Y., 2012. Chemical and Boron Isotopic Composition of Tourmaline in the Xiangshan Volcanic- Intrusive Complex, Southeast China:Evidence for Boron Mobilization and Infiltration during Magmatic- Hydrothermal Processes. Chemical Geology, 312-313:177-189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.04.026 Yang, S. Y., Jiang, S. Y., Palmer, M. R., 2015a. Chemical and Boron Isotopic Compositions of Tourmaline from the Nyalam Leucogranites, South Tibetan Himalaya:Implication for Their Formation from B-Rich Melt to Hydrothermal Fluids. Chemical Geology, 419:102-113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.10.026 Yang, S. Y., Jiang, S. Y., Zhao, K. D., et al., 2015b. Tourmaline as a Recorder of Magmatic-Hydrothermal Evolution:An in Situ Major and Trace Element Analysis of Tourmaline from the Qitianling Batholith, South China. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 170(5-6):42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-015-1195-7 Yang, Y. Q., Ni, Y. X., Guo, Y. Q., et al., 1987. Rock- Rorming and Ore Forming Characteristics of the Xikeng Granitic Pegmatites in Fujian Province. Mineral Deposits, 6(3):12-23 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, A. C., Wang, R. C., Jiang, S. Y., et al., 2008. Chemical and Textural Features of Tourmaline from the Spodumene-Subtype Koktokay No. 3 Pegmatite, Altai, Northwestern China:A Record of Magmatic to Hydrothermal Evolution. Canadian Mineralogist, 46(1):41-58. https://doi.org/10.3749/canmin.46.1.41 Zhang, R. X., Yang, S. Y., 2016. A Mathematical Model for Determining Carbon Coating Thickness and Its Application in Electron Probe Microanalysis. Microscopy and Microanalysis, 22(6):1374-1380. https://doi.org/10.1017/s143192761601182x Zhu, J.C., Wu, C. N., Liu, C. S., et al., 2000. Magmatic-Hydrothermal Evolution and Genesis of Koktokay No.3 Rare Metal Pegmatite Dyke, Altai, China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 6(1):40-52 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb200001006 Zou, T. R., Xu, J. G., 1975. On the Origin and Classification of Granite Pegmatites. Geochimica, 4(3):161-174 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000257704 李鹏, 李建康, 裴荣富, 等, 2017.幕阜山复式花岗岩体多期次演化与白垩纪稀有金属成矿高峰:年代学依据.地球科学, 42(10):1684-1696. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3668 刘丽君, 王登红, 刘喜方, 等, 2017.国内外锂矿主要类型、分布特点及勘查开发现状.中国地质, 44(2):263-278. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201702004 刘翔, 周芳春, 黄志飚, 等, 2018.湖南平江县仁里超大型伟晶岩型铌钽多金属矿床的发现及其意义.大地构造与成矿学.42(2):235-243. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201802004 王登红, 王瑞江, 李建康, 等, 2013.中国三稀矿产资源战略调查研究进展综述.中国地质, 40(2):361-370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.02.001 王登红, 赵汀, 何晗晗, 等, 2016.中南地区三稀矿产资源调查研究及开发利用进展综述.桂林理工大学学报, 36(1):1-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-9057.2016.01.001 王核, 李沛, 马华东, 等, 2017.新疆和田县白龙山超大型伟晶岩型锂铷多金属矿床的发现及其意义.大地构造与成矿学, 41(6):1053-1062. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201706005 王濮, 潘兆橹, 翁玲宝, 等, 1982.系统矿物学(中).北京:地质出版社, 155. 王子平, 刘善宝, 马圣钞, 等, 2018.四川阿坝州党坝超大型锂辉石矿床成矿规律及深部和外围找矿方向.地球科学, 43(6):2029-2041. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3864 文春华, 陈剑锋, 罗小亚, 等, 2016.湘东北传梓源稀有金属花岗伟晶岩地球化学特征.矿物岩石地球化学通报, 35(1):171-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2016.01.020 许志琴, 王汝成, 赵中宝, 等, 2018.试论中国大陆"硬岩型"大型锂矿带的构造背景.地质学报, 92(6):1091-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.06.001 杨岳清, 倪云翔, 郭永泉, 等, 1987.福建西坑花岗伟晶岩成岩成矿特征.矿床地质, 6(3):12-23. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ198703002.htm 朱金初, 吴长年, 刘昌实, 等, 2000.新疆阿尔泰可可托海3号伟晶岩脉岩浆-热液演化和成因.高校地质学报, 6(1):40-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2000.01.006 邹天人, 徐建国, 1975.论花岗伟晶岩的成因和类型的划分.地球化学, 4(3):161-174. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1975.03.001 -









 下载:
下载: