Thermal History of Nianzha Gold Deposit: Constraints from Zircon U-Pb, (U-Th)/He and Apatite Fission Track Geochronology
-
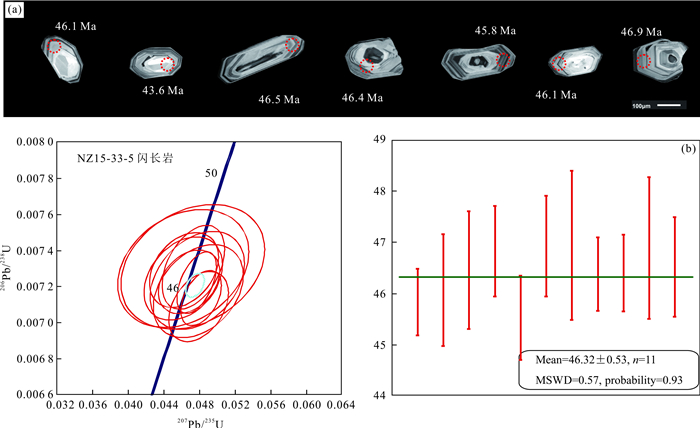
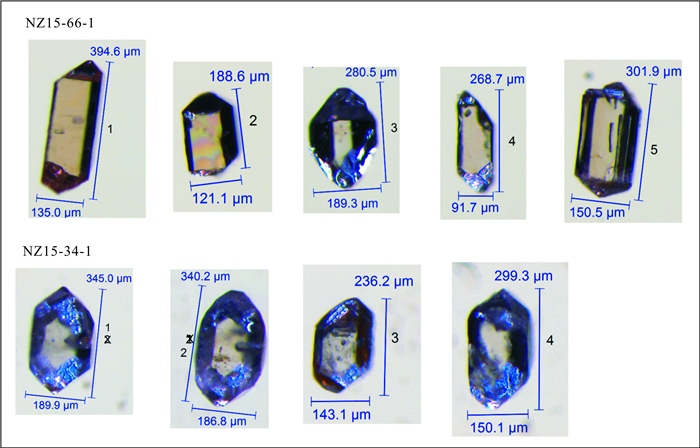
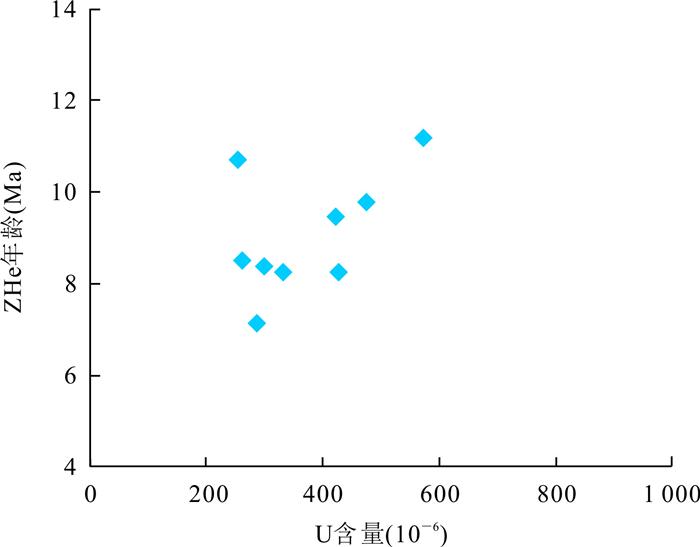
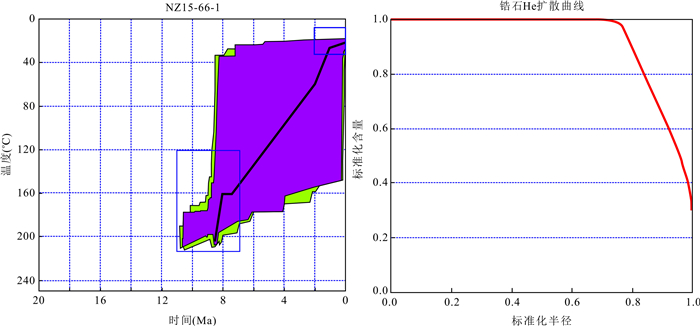
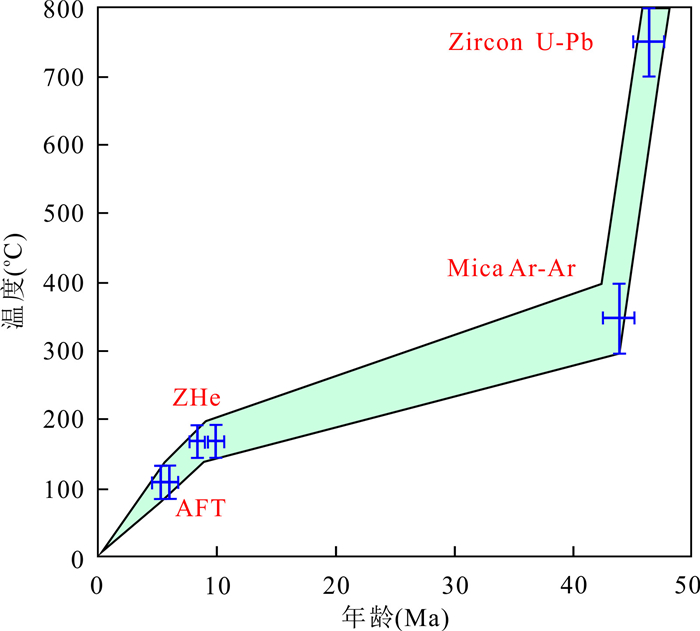
摘要: 念扎金矿床是近年来最新发现的位于雅鲁藏布江缝合带南侧仁布构造混杂岩带与蚀变闪长岩接触带的大型造山型金矿床.为约束念扎矿床的冷却及剥露历史,利用锆石的U-Pb、(U-Th)/He及磷灰石裂变径迹定年对新鲜及矿化闪长岩年龄进行测定.结果表明,新鲜闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为(46.32±0.53)Ma,(U-Th)/He年龄介于(7.14±0.24)Ma到(9.80±0.27)Ma,矿化闪长岩锆石(U-Th)/He年龄介于(8.38±0.24)Ma到(11.19±0.31)Ma之间,两件矿化闪长岩磷灰石裂变径迹年龄分别为(5.9±0.5)Ma和(5.3±1.0)Ma.念扎金矿床自闪长岩固结以来经历了两次快速冷却过程:第一次是从46.3 Ma开始持续到43.6 Ma,温度从750℃降至350℃,冷却速率高达约148℃/Ma;第二次为8.5~2.0 Ma,温度从约200℃降至30℃,冷却速率为26℃/Ma.念扎矿床成矿深度为9.7 km;在8.5 Ma时,矿床被抬升至4.6 km处;从8.5~5.6 Ma,矿床抬升至2.8 km;从5.6~2.0 Ma,念扎矿床被剥露至地表.Abstract: The Nianzha gold deposit, located in the central section of the Yurlung-Zangbo suture zone is a large orogenic gold deposit which occurred in a fracture zone bordered by altered diorite in the hanging wall to the north and the Renbu tectonic mélange in the footwall to the south. In this paper, it combines zircon U-Pb, (U-Th)/He and apatite fission track dating of the fresh and mineralized diorite in order to restrict the cooling and denudation history of the Nianzha deposit. The results show that the zircon U-Pb age of the fresh diorite is (46.32±0.53) Ma and zircon (U-Th)/He ages of fresh diorite is between (7.14 ±0.24) Ma and (9.80 ±0.27) Ma, and the zircon (U-Th)/He ages of the mineralized diorite are between (8.38±0.24) Ma and (11.19±0.31) Ma. The apatite fission track ages of two mineralization diorite are (5.9±0.5) Ma and (5.3±1.0) Ma respectively. Since the consolidation of the diorite, the Nianzha gold deposit has experienced two rapid cooling processes:the first process started from 46.3 Ma to 43.6 Ma, and the temperature dropped from 750℃ to 350℃ with the cooling rate of about 148℃/Ma, while the second process happened between 8.5~2.0 Ma with the temperature dropped from 200℃ to 30℃ with cooling rate of about 26℃/Ma. The mineralization depth of the Nianzha deposit is about 9.7 km; at 8.5 Ma, the deposit was uplifted to 4.6 km; from 8.5 to 5.6 Ma, the deposit are uplifted to 2.8 km; and from 5.6 to 2.0 Ma, the Nianzha deposit was exfoliated to the surface.
-
Key words:
- U-Pb dating /
- (U-Th)/He dating /
- fission track age /
- thermal history /
- Nianzha gold deposit /
- petrology
-
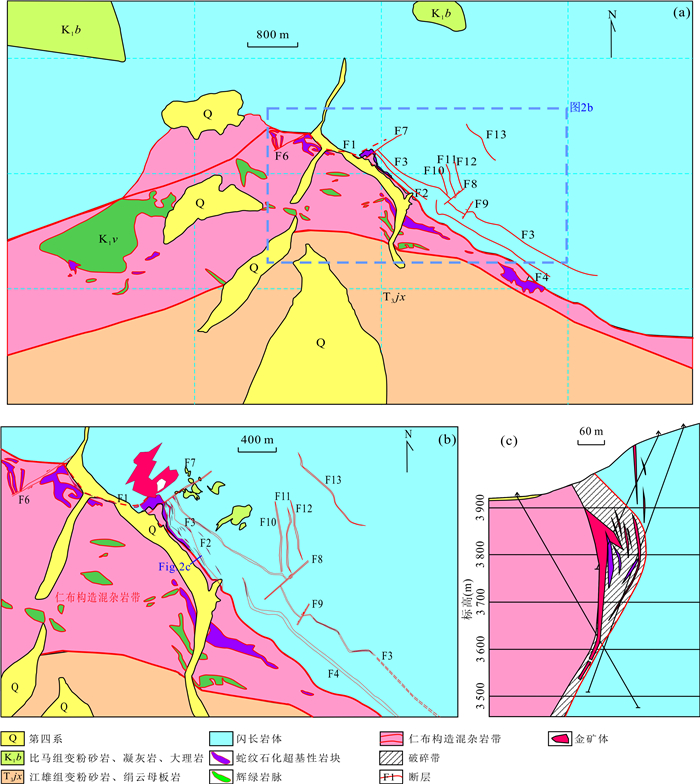
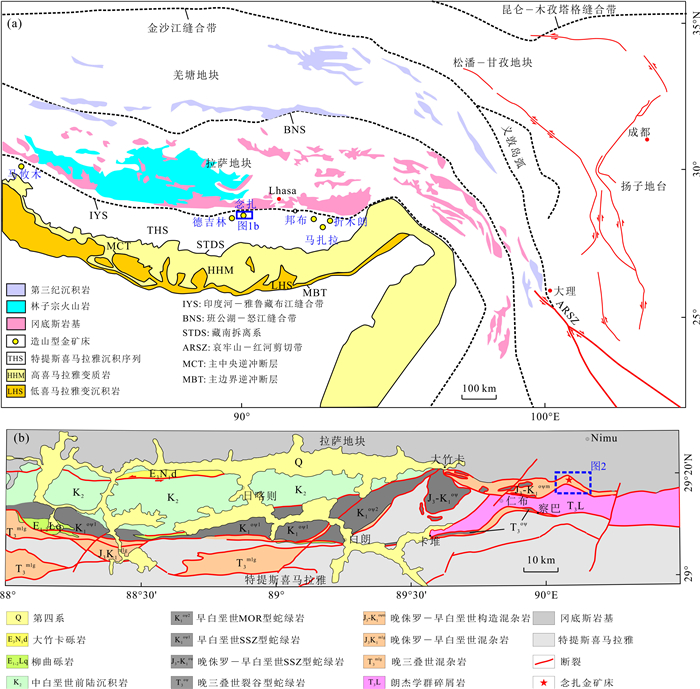
图 1 青藏高原造山型金成矿带(a)及日喀则-仁布区域地质简图(b)
a据侯增谦和王二七(2008)改编
Fig. 1. Geological maps of orogenic gold metallogenic belts in the Tibetan orogenic belt (a) and Xigaze-Renbu area, southern Tibet (b)
表 1 磷灰石裂变径迹分析结果
Table 1. The apatite fission track analysis results
实验号 原样号 颗粒数
(n)ρs(105/cm2)
(Ns)ρi(105/cm2)
(Ni)ρd(105/cm2)
(N)P(χ2)
(%)中值
t(Ma)
(±1σ)组合
t(Ma)
(±1σ)L(μm)
(N)1 ZK1206-31
硅化黄铁矿化闪长岩35 0.309
(64)8.476
(1 758)7.428
(5 949)98.2 5.3±1 5.3±1 13.1±1.8
(63)2 NZ15-3-2
褐铁矿化闪长岩35 1.042
(295)26.66
(7 545)7.672
(5 949)19.5 5.9±0.5 5.9±0.4 13.5±2.2
(82) -
Bellemans, F., De Cort, F., van Den Haute, P., 1995.Composition of SRM and CN U-Doped Glasses:Significance for Their Use as Thermal Neutron Fluence Monitors in Fission Track Dating.Radiation Measurements, 24(2):153-160. https://doi.org/10.1016/1350-4487(94)00100-f Belousova, E.A., Griffin, W.L., O'Reilly, S.Y., et al., 2002.Igneous Zircon: Trace Element Composition as an Indicator of Source Rock Type. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 143(5): 602-622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-002-0364-7 Chu, M. F., Chung, S. L., Song, B., et al., 2006. Zircon U-Pb and Hf Isotope Constraints on the Mesozoic Tectonics and Crustal Evolution of Southern Tibet.Geology, 34(9): 745. https://doi.org/10.1130/g22725.1 Copeland, P., Harrison, H.M., Kidd, W.S.F., et al., 1987.Rapid Early Miocene Acceleration of Uplift in the Gangdese Belt, Xizang (Southern Tibet), and Its Bearing on Accommodation Mechanisms of the India-Asia Collision.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 86(2-4):240-252. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(87)90224-X Dai, J.G., Wang, C.S., Hourigan, J., et al., 2013.Exhumation History of the Gangdese Batholith, Southern Tibetan Plateau:Evidence from Apatite and Zircon (U-Th)/He Thermochronology.The Journal of Geology, 121(2):155-172. doi: 10.1086/669250 Deng, X. G., Zeng, P., Zhang, Q. S., et al., 2012. Geological Characteristics and Prospecting Potential of a Gold Deposit in the Yarlung Zangbo Suture Zone.Acta Geologica Sichuan, 32(Suppl.2):51-53(in Chinese). Dodson, M. H., 1973. Closure Temperature in Cooling Geochronological and Petrological Systems.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 40(3):259-274. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00373790 Dong, G.C., Mo, X.X., Zhao, Z.D., et al., 2006.Magma Mixing in Middle Part of Gangdise Magma Belt: Evidences from Granitoid Complex.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(4): 835-844(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200604007.htm England, P., Molnar, P., 1990.Surface Uplift, Uplift of Rocks, and Exhumation of Rocks.Geology, 18(12):1173-1177. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1990)018<1173:SUUORA>2.3.CO;2 Fitzgerald, P.G., Baldwin, S.L., Webb, L.E., et al., 2006.Interpretation of (U-Th)/He Single Grain Ages from Slowly Cooled Crustal Terranes: A Case Study from the Transantarctic Mountains of Southern Victoria Land. Chemical Geology, 225(1-2):91-120. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.09.001 Flowers, R. M., 2009. Exploiting Radiation Damage Control on Apatite (U-Th)/He Dates in Cratonic Regions.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 277(1-2): 148-155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2008.10.005 Galbraith, R.F., 1981.On Statistical Models for Fission Track Counts. Journal of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, 13(6):471-478. https://doi.org/ 10.1007/bf01034498 Ge, Y.K., Dai, J.G., Wang, C.S., et al., 2017.Cenozoic Thermo-Tectonic Evolution of the Gangdese Batholith Constrained by Low-Temperature Thermochronology.Gondwana Research, 41:451-462.https://doi.org/10.1016/j. gr.2016.05.006 doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.05.006 Gleadow, A. J. W., Duddy, I. R., 1981. A Natural Long-Term Track Annealing Experiment for Apatite. Nuclear Tracks, 5(1-2): 169-174. https://doi.org/10.1016/ 0191-278x(81)90039-1 doi: 10.1016/0191-278x(81)90039-1 Gleadow, A., Harrison, M., Kohn, B., et al., 2015. The Fish Canyon Tuff:A New Look at an Old Low-Temperature Thermochronology Standard. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 424: 95-108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. epsl.2015.05.003 doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.05.003 Gong, W., Jiang, X. D., 2017. Thermal Evolution History and Its Genesis of the Ailao Shan-Red River Fault Zone in the Ailao Shan and Day Nui Con Voi Massif during Oligocene-Early Miocene.Earth Science, 42(2):224-239(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201702005 Green, P. F., 1986. On the Thermo-Tectonic Evolution of Northern England: Evidence from Fission Track Analysis.Geological Magazine, 123(5):493. doi: 10.1017/S0016756800035081 Grove, M., Harrison, T.M., 1996.40Ar Diffusion in Fe-Rich Biotite.American Mineralogist, 81(7-8):940-951. doi: 10.2138/am-1996-7-816 Harrison, T.M., Copeland, P., Kidd, W.S.F., et al., 1992.Raising Tibet. Science, 255(5052): 1663-1670. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.255.5052.1663 Harrison, T. M., Duncan, I., McDougall, I., 1985. Diffusion of 40Ar in Biotite:Temperature, Pressure and Compositional Effects. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49(11): 2461-2468. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(85)90246-7 Hou, Z. Q., Wang, E. Q., 2008. Metallogenesis of the Indo-Asian Collisional Orogen:New Advances.Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 29(3): 275-292(in Chinese with English abstract). Hurford, A. J., Green, P. F., 1982. A Users' Guide to Fission Track Dating Calibration. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 59(2):343-354. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821x(82)90136-4 Ketcham, R.A., 2005.Forward and Inverse Modeling of LowTemperature Thermochronometry Data.Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 58(1): 275-314. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2005.58.11 Li, H. Y., Zhong, S. L., Wang, Y. B., et al., 2007. Age, Petrogenesis and Geological Significance of the Linzizong Volcanic Successions in the Linzhou Basin, Southern Tibet: Evidence From Zircon U-Pb Dates and Hf Isotopes.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2):493-500(in Chinese with English abstract). Li, G. W., Kohn, B., Sandiford, M., et al., 2015. Constraining the Age of Liuqu Conglomerate, Southern Tibet:Implications for Evolution of the India-Asia Collision Zone. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 426: 259-266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.06.010 Li, G. W., Kohn, B., Sandiford, M., et al., 2016. Synorogenic Morphotectonic Evolution of the Gangdese Batholith, South Tibet: Insights from Low-Temperature Thermochronology. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 17(1): 101-112. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015gc006047 Li, G.W., Liu, X.H., Alex, P., et al., 2010.In-Situ Detrital Zircon Geochronology and Hf Isotopic Analyses from Upper Triassic Tethys Sequence Strata. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 297(3-4): 461-470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2010.06.050 Li, G.W., Liu, X.H., Wei, L.J., et al., 2011.Discovery of the Late Cretaceous Detrital Zircon in Renbu Tectonic Mélange, South Tibet, and Its Tectonic Significance.Acta Petrologic Sinica, 27(11):3328-3334(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201111014 Li, Y. L., Wang, C. S., Dai, J. G., et al., 2015. Propagation of the Deformation and Growth of the Tibetan-Himalayan Orogen:A Review.Earth-Science Reviews, 143:36-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2015.01.001 Liu, J.L., Chen, X.Y., Wu, W.B., et al., 2015.New Tectono-Geochronological Constraints on Timing of Shearing along the Ailao Shan-Red River Shear Zone:Implications for Genesis of Ailao Shan Gold Mineralization. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103: 70-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.006 Jiang, S.H., Nie, F.J., Hu, P., et al., 2009.Mayum:An Orogenic Gold Deposit in Tibet, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3): 160-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j. oregeorev.2009.03.006 doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.03.006 Ma, S. W., 2017. Structural Framework and the Relationship with Mineralization of Jiama Copper-Polymetallic Deposit, Southern Tibet(Dissertation).Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing(in Chinese with English abstract). Mo, X.X., Hou, Z.Q., Niu, Y.L., et al., 2007.Mantle Contributions to Crustal Thickening during Continental Collision: Evidence from Cenozoic Igneous Rocks in Southern Tibet.Lithos, 96(1-2):225-242.https://doi.org/10.1016/ j.lithos.2006.10.005 doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.005 Pan, G.T., Wang, L.Q., Li, R.S., et al., 2012.Tectonic Evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 53:3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.018 Reiners, P. W., Farley, K. A., 2001. Influence of Crystal Size on Apatite (U-Th)/He Thermochronology:An Example from the Bighorn Mountains, Wyoming.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 188(3-4): 413-420. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(01)00341-7 Reiners, P.W., Spell, T.L., Nicolescu, S., et al., 2004.Zircon (U-Th)/He Thermochronometry:He Diffusion and Comparisons with 40Ar/39Ar Dating.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(8):1857-1887.https://doi.org/10.1016/j. gca.2003.10.021 doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2003.10.021 Reiners, P.W., 2005.Zircon (U-Th)/He Thermochronometry. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 58(1): 151-179. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2005.58.6 Rohrmann, A., Kapp, P., Carrapa, B., et al., 2012. Thermochronologic Evidence for Plateau Formation in Central Tibet by 45 Ma. Geology, 40(2): 187-190. https://doi.org/10.1130/g32530.1 Shuster, D.L., Flowers, R.M., Farley, K.A., 2006.The Influence of Natural Radiation Damage on Helium Diffusion Kinetics in Apatite.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 249(3-4): 148-161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2006.07.028 Sun, J.B., Chen, W., Yu, S., et al., 2017.Study on Zircon (U-Th)/He Dating Technique. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33 (6):1947-1956(in Chinese with English abstract). Sun, Q. Z., Zheng, Y. C., Hou, Z. Q., et al., 2013. Genesis of Bangbu Orogenic Gold Deposit in Tibet:Constraints from Fluid Inclusions and Isotopic Composition. Mineral Deposits, 32(2):353-366(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201302011.htm Sun, X. M., Wei, H. X., Zhai, W., et al., 2016. Fluid Inclusion Geochemistry and Ar-Ar Geochronology of the Cenozoic Bangbu Orogenic Gold Deposit, Southern Tibet, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 74: 196-210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.11.021 Wu, Y.B., Zheng, Y.F., 2004.Genesis of Zircon and Its Constraints on Interpretation of U-Pb Age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15):1554-1569(in Chinese). doi: 10.1007/BF03184122 Yin, A., Harrison, T.M., 2000.Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28: 211-280. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 Yuan, W.M., Dong, J.Q., Bao, Z.K., et al., 2008.Apatite Fission Track Evidences for Neogene Tectono-Thermal History in Nimu Area, Southern Gangdese Terrane, Tibet Plateau.Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 42 (6):470-473(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YZJS200806023.htm Zhang, X., 2017. Mineralization of Orogenic Gold Deposits in the Indus-Yarlung Tsangpo Suture Zone of Tibetan Plateau(Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Beijing(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, X., Deng, X.G., Yang, Z.S., et al., 2017.Genesis of the Gold Deposit in the Indus-Yarlung Tsangpo Suture Zone, Southern Tibet: Evidence from Geological and Geochemical Data. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 91(3):947-970. doi: 10.1111/acgs.2017.91.issue-3 Zhang, X., Zhao, X.Y., Yang, Z.S., et al., 2018.Ar-Ar Dating on Muscovite of Nianzha Orogenic Gold Deposit in Yurlung-Zangbo Suture Zone and Its Geological Significance. Mineral Exploration, 9(5): 825-835(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ytgcj201805005 Zhang, Y., Chen, W., 2011. Study on the 4He Content Measurement. Geological Review, 57(2): 300-304(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZLP201102017.htm Zhao, X.Y., Yang, Z.S., Hou, Z.Q., et al., 2018.The Structural Deformation Characteristics and the Control of Gold Mineralization of the Upper Triassic Flysch (Langjiexue Group) in Tibetan Plateau. Geological Journal, 54(3): 1331-1342. https://doi.org/10.1002/gj.3230 Zhu, X.Q., Guo, X.W., Zhang, X.H., et al., 2018.Thermochronological Constraints on Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of South-Central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.Earth Science, 43 (6):1903-1920(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201806009 邓学国, 曾攀, 张庆松, 等, 2012.雅鲁藏布江缝合带某金矿地质特征及找矿潜力远景.四川地质学报, 32(增刊2):51-53. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8707722 董国臣, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等, 2006.冈底斯岩浆带中段岩浆混合作用:来自花岗杂岩的证据.岩石学报, 22(4):835-844. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200604007 宫伟, 姜效典, 2017.哀牢山-红河断裂带哀牢山-大象山段渐新世-早中新世热史演化及成因.地球科学, 42(2):224-239. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3430 侯增谦, 王二七, 2008.印度-亚洲大陆碰撞成矿作用主要研究进展.地球学报, 29(3):275-292. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.03.003 李皓扬, 钟孙霖, 王彦斌, 等, 2007.藏南林周盆地林子宗火山岩的时代、成因及其地质意义:锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据.岩石学报, 23(2):493-500. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98200702025 李广伟, 刘小汉, 韦利杰, 等, 2011.藏南仁布混杂岩带中晚白垩世碎屑锆石的发现及其启示.岩石学报, 27(11):3328-3334. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSXB201111014.htm 马士委, 2017.藏南甲玛铜多金属矿床构造格架与成矿的关系(博士学位论文).北京: 中国地质科学院. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-82501-1017055374.htm 孙敬博, 陈文, 喻顺, 等, 2017.锆石(U-Th)/He定年技术研究.岩石学报, 33(6):1947-1956. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201706020.htm 孙清钟, 郑远川, 侯增谦, 等, 2013.西藏邦布石英脉型金矿床的成因:流体包裹体及氢-氧同位素证据.矿床地质, 32(2):353-366. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2013.02.010 吴元保, 郑永飞, 2004.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约.科学通报, 49(15):1554–1569. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kxtb200416002 袁万明, 董金泉, 保增宽, 等, 2008.西藏冈底斯地块尼木地区新第三纪构造热历史的磷灰石裂变径迹约束.原子能科学技术, 42(6):470-473. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YZJS200806023.htm 张雄, 2017.青藏高原雅鲁藏布江缝合带造山型金矿成矿作用研究(博士学位论文).北京: 中国地质大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1017126728.htm 张雄, 赵晓燕, 杨竹森, 等, 2018.雅鲁藏布江缝合带念扎造山型金矿床白云母Ar-Ar年代学及其地质意义.矿产勘查, 9(5):825-835. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2018.05.005 张彦, 陈文, 2011.4He同位素含量测试技术研究.地质论评, 57(2):300-304. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzlp201102016 朱晓青, 郭兴伟, 张训华, 等, 2018.青藏高原中-南部新生代构造演化的热年代学制约.地球科学, 43(6):1903-1920. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3854 -
 dqkx-44-6-2039-Table.pdf
dqkx-44-6-2039-Table.pdf

-









 下载:
下载: