Genetic Mechanism of Xiwenzhuang Geothermal Field in Taiyuan Basin
-
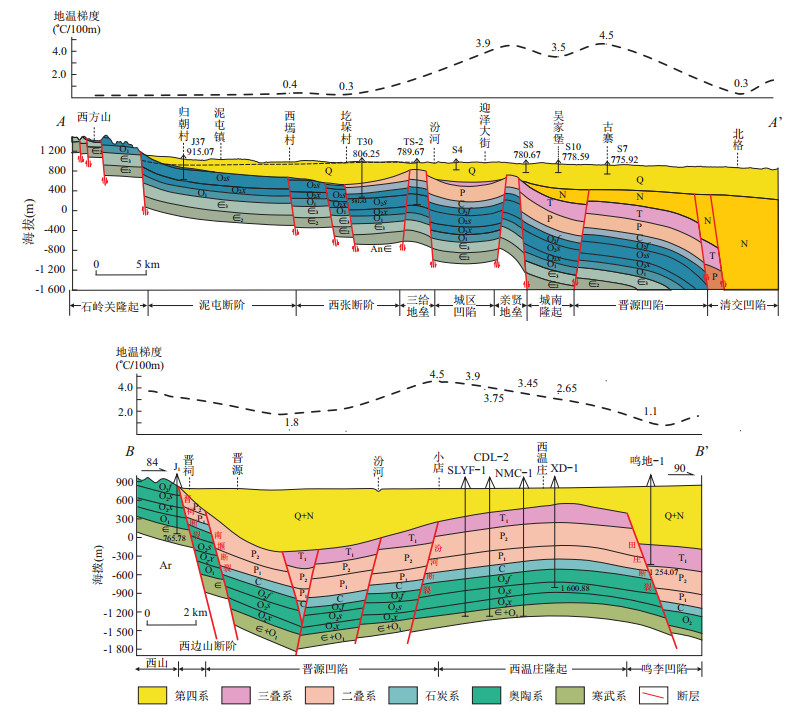
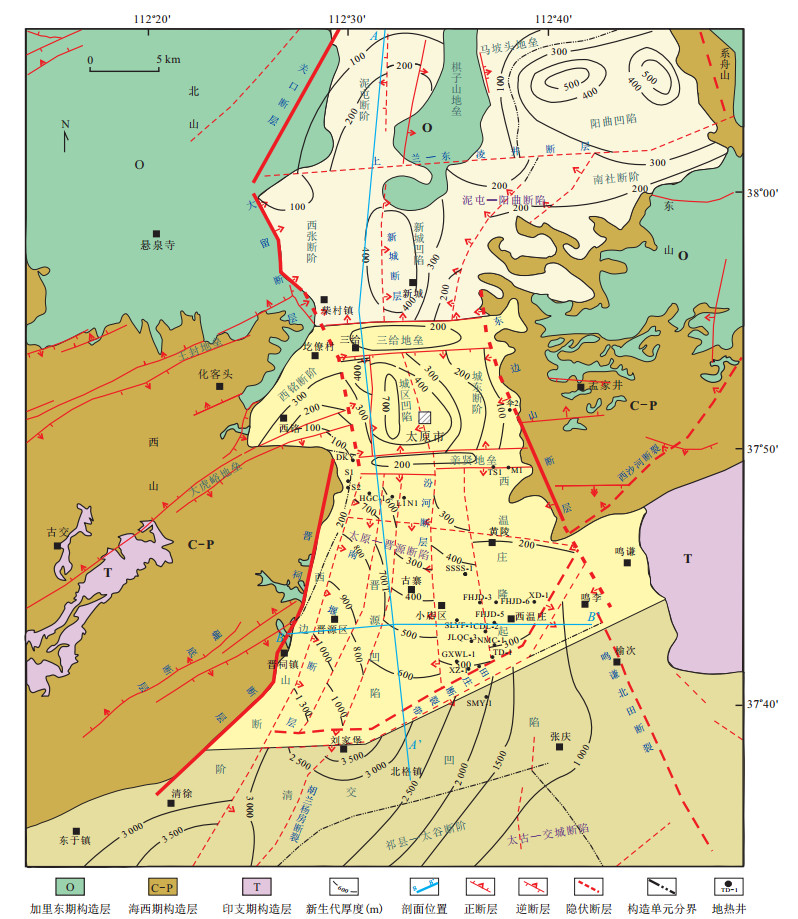
摘要: 地热田成因机制的研究是地热田资源量精细评价与有效开发的依据.在综合前人研究成果与最新地热钻井资料的基础上,通过对太原盆地岩溶热储地热系统的"源、储、通、盖"主要因素分析,建立了西温庄地热田形成的概念模型,并精细评价了地热资源量.西温庄地热田是一个在非对称性裂谷盆地的高大地热流值背景下,来自东、西山奥陶系岩溶储层裸露区的大气降水,沿着岩溶不整合面和断裂这个运移通道,从东山和西山双向补给,经盆地边界断裂进入盆地深部热储,吸热、增温后逐步在盆地中部西温庄隆起的碳酸盐岩岩溶储集层中富集、承压而形成的中低温传导型地热系统.西温庄地热田的岩溶地热系统具有封盖性能好、主力储集层段多、补给速度较快、盖层地温梯度较高等特征.表现为奥陶系岩溶热储上覆盖层包括石炭系、二叠系、三叠系与第四系,顶面埋深800~1 700 m;从上至下依次发育了峰峰组下段-上马家沟组上段、上马家沟组下段、下马家沟组上段和亮甲山组4套主力含水层段,热储层平均有效厚度累计184.6 m;地热水从补给区至盆地承压区的运移时间约2 000 a;奥陶系热储上覆岩层的平均地温梯度为3.0~4.0℃/100 m,地热水温度范围为55~75℃.西温庄地热田奥陶系岩溶热储的地热资源量精细评价结果表明,热储总量合计33.53×108 GJ,折合标煤1.14×108 t.年开采地热资源量可满足607×104m2的供暖面积,开发潜力巨大.Abstract: The study of the genetic mechanism of geothermal field is beneficial to the fine evaluation and effective development of geothermal field resources.On the basis of previous research results and the latest geothermal drilling data, the conceptual model of the formation of Xiwenzhuang geothermal field is established through analysis of main factors of "source, reservoir, migration channel and cover" of the karst geothermal system in Taiyuan Basin, and geothermal resources are carefully evaluated.It is considered that the Xiwenzhuang geothermal field formatted a middle-low temperature conducting geothermal system whose heat source results from the high terrestrial heat flow of asymmetric rift basin, whose recharge water source comes from the atmospheric precipitation in the exposed area of Ordovician karst reservoir in Dongshan and Xishan, and whose migration channels are the karst unconformity surface and fractures by which karst water migrated through the boundary faults of Dongshan and Xishan into the deep geothermal reservoir of the basin from Dongshan and Xishan bidirectional recharge, and after endothermic and temperature-increasing, gradually enriched and confined in the Ordovician karst reservoir of the Xiwenzhuang uplift in the central part of the basin.This geothermal system is characterized by better sealing performance, more aquifers of geothermal reservoir, faster recharge speed and higher geothermal gradient.In detail, the Ordovician karstic reservoir's cap rocks resulting in the buried depth of 800-1 700 m constitute of Carboniferous, Permian, Triassic and Quaternary.From top to bottom, the four main aquifers of Fengfeng Formation, Upper Majiagou Formation, Lower Majiagou Formation and Liangjiashan Formation are developed in turn.The average effective thickness of the thermal reservoir is 184.6 m in total, the migration age from the recharge source area to the confined area of basin is about 2 000 a, the average geothermal gradient of the overlying strata of the Ordovician geothermal reservoir is 3.0-4.0℃/100 m, and the geothermal water temperature range is 55-75℃.According to the fine evaluation results of geothermal resources of Ordovician karstic reservoir, the total geothermal reserve is 33.53×108 GJ, which is equivalent to 1.14×108 t of standard coal.The annual exploitation of geothermal resources can meet the demand of indoor heating area of 6.07 million square meters with huge potential for development.
-
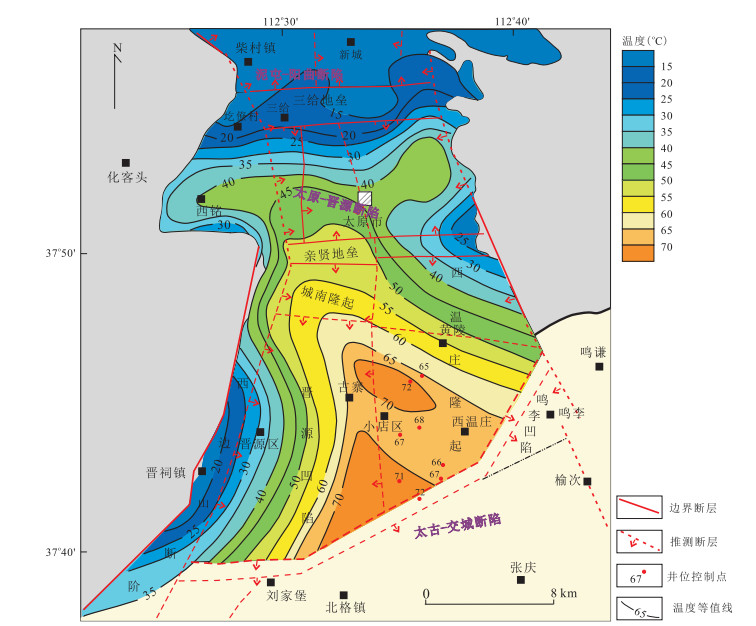
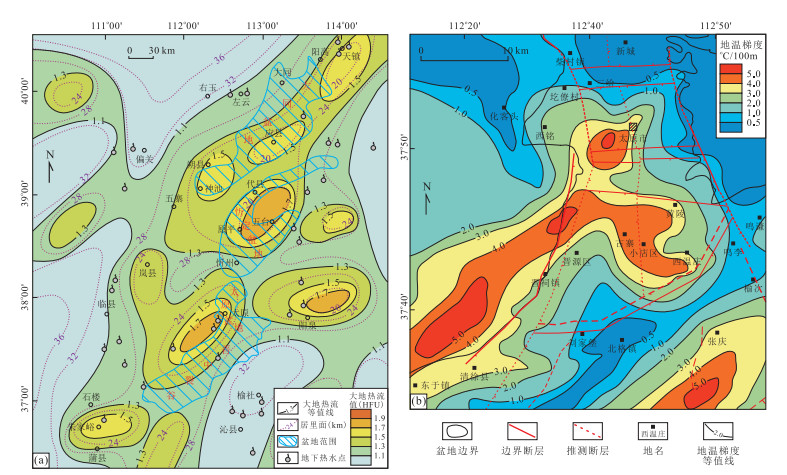
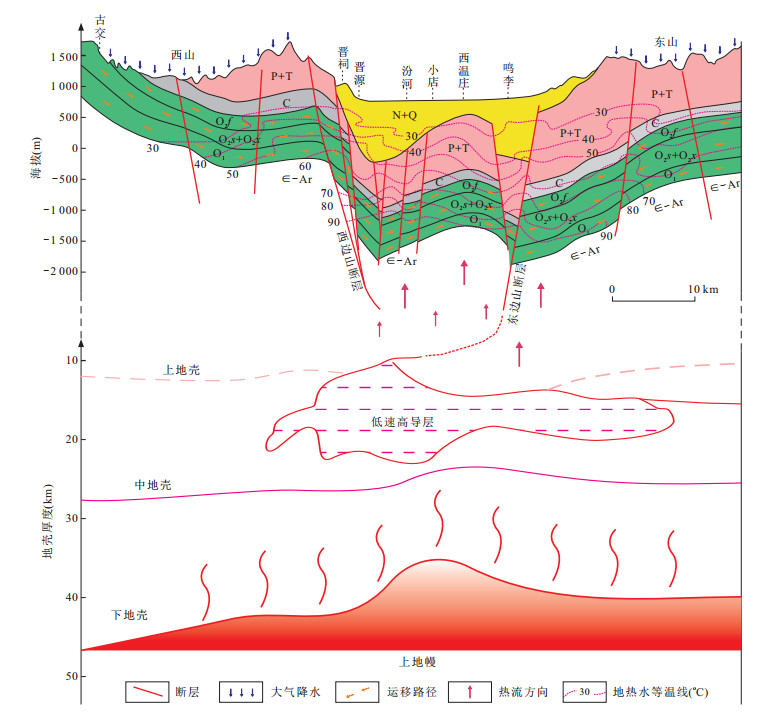
图 6 太原盆地及邻区深部地温场(a)与浅部地温场(b)分布
图a据李世忠等(1994);图b据马瑞(2007)修改
Fig. 6. Distribution of deep (a) and shallow (b) geothermal fields in Taiyuan Basin and adjacent areas
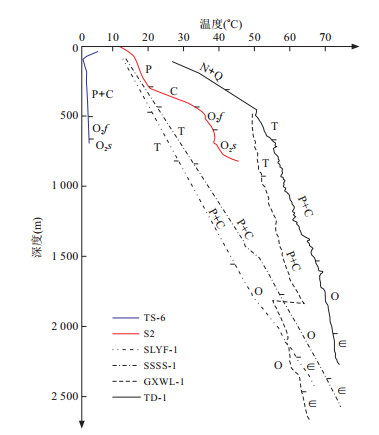
图 7 太原盆地地热井地层温度-深度关系
TS-6井、S2井数据来源据马瑞(2007)
Fig. 7. Relationship between formation temperature and depth of geothermal wells in Taiyuan Basin
表 1 太原盆地典型地热钻孔测试数据
Table 1. Test data of typical geothermal boreholes in Taiyuan Basin
序号 井号 地名 构造单元 完井年份 取水层段
(m)热储层位 井口水温(℃) 单井水量
(m3/h)SiO2含量
(mg/L)热储温度
Tr(℃)G盖 1 TS1 统计学校 亲贤地垒 1991 495~1 166.75 O2s 32 25 1.76 2 S1 神堂沟 西边山断阶 1995 410~603.71 O2f+O2s 43 60 20 5.61 3 S2 神堂沟 西边山断阶 1995 385~801.18 O2f+O2s 40 100 3.71 4 DKY 地勘院 西边山断阶 2004 875~1 339.21 O2x+O2s 51 82.9 3.01 5 N1 农展馆 城南隆起 2004 1 245~1 690.5 O2f+O2s 50 78.75 2.30 6 L1 丽华苑 城南隆起 2005 1 287~1 803.35 O2f+O2s 62.5 250 2.87 7 伞2 伞儿树村 城东断阶 2005 725~1 250.35 O2f+O2s 32 33.75 20 1.64 8 M1 煤炭学院 亲贤地垒 2005 755~1 300 O2f+O2s 33 30 1.65 9 XD-1 西温庄乡 西温庄隆起 2007 1 296~1 600.88 O2f+O2s 53 32 28 2.63 10 XZ-1 西攒村 西温庄隆起 2007 1 580~2 200 O2s+ O2x 65 62.74 2.45 11 HGC-1 化工厂 城南隆起 2014 1 145~1 701.66 O2s+ O2x 64 100 3.46 12 TD-1 太原大学 西温庄隆起 2014 1 550.13~2 260 O+∈3f 68 120 28.52 81 3.71 13 SLYF-1 双良研发 西温庄隆起 2015 1 618.0~2 464.8 O+∈3f 74 102 33.42 87 4.26 14 FHJD-3 孵化基地 西温庄隆起 2015 1 682~2 525.7 O+∈3f 65 100 29.35 82 3.40 15 FHJD-5 孵化基地 西温庄隆起 2015 1 638~2 526 O+∈3f 66 156 28.92 82 3.41 16 FHJD-6 孵化基地 西温庄隆起 2015 1 699~2 479 O+∈3f 61 154 30.93 84 3.52 17 NMC-1 农牧场 西温庄隆起 2016 1 512~2 219.7 O+∈3f 72 147 29.24 82 3.85 18 CDL-2 昌达隆 西温庄隆起 2016 1 648~2 357 O+∈3f 72 83 30.24 83 4.44 19 JLQC-3 江铃汽车 西温庄隆起 2016 1 790~2 624 O+∈3f 67 129 29.71 83 4.08 20 QGY-1 青干院 西温庄隆起 2017 1 586~2 435 O+∈3f 65 45 25.08 77 3.30 注:编号1~8马瑞(2007);9~10据陈光平(2011).热储温度Tr根据地热水测试出的硅温标SiO2计算得出,公式为Tr=1 522/(5.75-lg(SiO2))-273.15;G盖表示钻孔上覆盖层的平均地温梯度(℃/100m),据恒温层厚60 m、基准温度为12.5 ℃计算得到. 表 2 太原盆地TD-1井测井解释
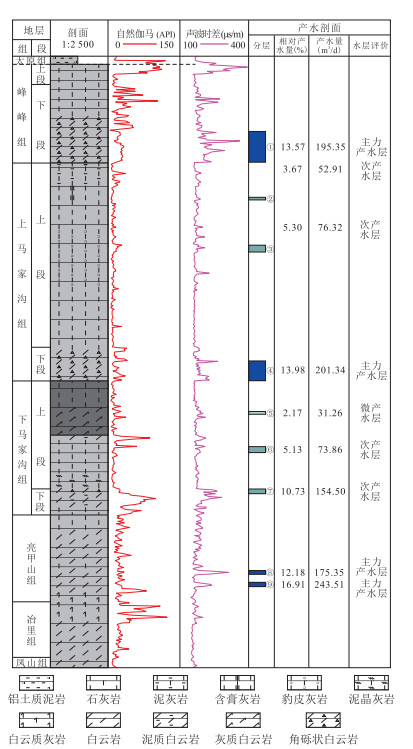
Table 2. Log interpretation of Well TD-1 in Taiyuan Basin
层号 产水层位 产水井段
(m)厚度
(m)温度差
(℃)热导率
(W/m·℃)相对产能
(%)层位岩性 下部岩性 解释评价 综合产能 1 峰峰下段 1 599.30~1 631.50 32.20 1.11 2.06 13.57 角砾状白云岩 泥灰岩 主力产水层 22.54% 2 上马上段 1 667.70~1 670.00 2.30 0.042 5 3.84 3.67 豹皮灰岩 灰岩 次产水层 3 上马上段 1 717.10~1 723.80 6.70 0.147 3.24 5.30 豹皮灰岩 灰岩 次产水层 13.98% 4 上马下段 1 836.10~1 856.60 20.50 0.384 3.79 13.98 角砾状白云岩 灰岩 主力产水层 5 下马上段 1 888.30~1 891.30 3.00 0.061 3.49 2.17 灰质白云岩 泥质白云岩 微产水层 18.03% 6 下马上段 1 924.70~1 930.50 5.80 0.073 4 5.61 5.13 灰岩 泥晶灰岩 次产水层 7 下马下段 1 968.30~1 973.00 4.70 0.146 2.29 10.73 角砾状白云岩 泥质白云岩 次产水层 8 亮甲山组 2 052.40~2 056.00 3.60 0.057 3 4.46 12.18 白云岩 白云质灰岩 主力产水层 29.09% 9 亮甲山组 2 064.20~2 069.00 4.80 0.096 4 3.54 16.91 白云岩 白云质灰岩 主力产水层 10 凤山组 2 185.30~2 190.00 4.70 0.120 2.78 9.79 砾屑白云岩 细晶白云岩 次产水层 11 凤山组 2 192.10~2 194.00 1.90 0.048 6 2.78 6.57 粗晶白云岩 细晶白云岩 次产水层 16.36% 表 3 西温庄地热田岩溶水水化学分析数据
Table 3. Chemical analysis data of karst water in Xiwenzhuang geothermal field
序号 井名 井深 水位 TDS
(mg/L)pH K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- 水化学类型 (m) (mg/L) 1 TD-1 2 260 20.4 1 892.0 7.4 28.0 47.2 373.6 84.8 47.3 1 210.9 162.7 SO4-Ca 2 TD-2 2 556 20.4 2 108.0 7.0 30.2 53.0 437.1 73.7 79.8 1 297.4 174.6 SO4-Ca 3 FHJD-1 2 500 17.5 1 898.0 7.1 23.8 47.2 419.0 61.2 215.7 970.6 196.6 SO4-Ca 3 FHJD-2 2 919 16.5 2 050.0 7.5 22.6 61.5 304.0 62.5 58.6 1 160.0 117.0 SO4-Ca 5 GXWL-1 2 690 26.1 2 112.0 8.3 30.9 71.9 350.6 142.9 124.1 1 232.5 189.9 SO4-Ca·Mg 6 GXWL-2 2 494 19.6 2 104.1 7.1 24.4 54.6 421.8 85.7 71.1 1 282.9 149.8 SO4-Ca 7 GXWL-3 2 681 20.1 2 102.0 7.9 34.3 61.2 473.6 73.9 65.4 1 398.6 184.8 SO4-Ca 8 GXWL-4 2 711 3.7 2 382.0 7.9 50.1 90.0 469.8 89.6 152.5 1 328.4 194.9 SO4-Ca 9 SLYF-1 2 467 12.3 2 122.0 7.3 31.2 63.8 312.6 151.4 62.1 1 315.9 194.9 SO4-Ca·Mg 10 SLYF-2 2 735 14.5 2 120.0 7.2 31.2 63.8 312.6 151.5 62.0 1 314.6 193.9 SO4-Ca·Mg 11 SSSS-1 2 467 13.0 1 984.0 7.7 31.9 48.0 398.3 75.3 128.0 1 145.9 228.8 SO4-Ca 12 SSSS-2 2 735 14.7 2 122.0 7.3 31.2 63.8 312.6 151.4 62.1 1 315.9 194.9 SO4-Ca·Mg 13 SSSS-3 2 698 -15.0 2 004.0 7.3 31.1 52.2 422.2 80.0 136.3 1 210.2 130.0 SO4-Ca 14 SSSS-5 2 308 3.2 2 007.0 7.7 33.0 50.2 410.2 80.3 135.0 1 200.1 136.2 SO4-Ca 15 SSSS-9 2 470 2.5 1 812.0 8.3 56.6 260.1 187.4 41.8 60.4 1 069.5 210.6 SO4-Ca·Na 16 TZMJ-1 2 335 -13.4 1 976.0 7.7 32.1 48.0 400.0 76.8 128.1 1 146.1 228.8 SO4-Ca 17 TZMJ-2 2 575 -12.7 1 983.0 7.7 32.1 48.0 400.1 76.8 128.1 1 146.4 228.6 SO4-Ca 注:本次研究的采样工作主要集中在2017年2月的供暖季进行,全部为地热井封闭采灌循环系统下的地热水水样.采样点分布如图 1所示,井号前代码相同的地热井为同一供暖项目使用,岩溶热储的取水段顶部相距500~600 m.样品的测试分析工作委托国土资源部地下水矿泉水及环境监测中心完成. 表 4 西温庄地热田地热资源评价参数取值与计算结果
Table 4. Evaluation parameters and calculation results of geothermal resources in Xiwenzhuang geothermal field
层位 评价单元面积(km2) 热储层顶板埋深(m) 平均有效厚度(m) 平均温度
(℃)平均孔隙度
(%)地热资源量
(108 GJ)地热资源量
(108t标煤)峰峰组 124.94 1 565 37.5 56.4 7.0 5.524 98 0.188 6 上马家沟组 124.94 1 689.9 58.2 62.4 6.0 9.596 593 0.327 5 下马家沟组 124.94 1 883.9 46.8 71.3 5.0 9.109 051 0.310 9 亮甲山组 124.94 2 040 26.3 75.8 4.5 5.642 322 0.192 6 冶里组 124.94 2 127.5 15.8 78.4 4.0 3.660 673 0.124 9 合计 184.6 33.533 6 1.144 5 -
Arnórsson, S., 1995.Geothermal Systems in Iceland:Structure and Conceptual Models-I.High-Temperature Areas.Geothermics, 24(5-6):561-602. https://doi.org/10.1016/0375-6505(95)00025-9 Chen, G.P., 2011.Thermal Analysis of Geological Conditions of Xiwenzhuang Geothermal Fields in Taiyuan Basin.Huabei Land and Resources, (3):5-7 (in Chinese). Deng, Q.D., Chen, S.P., Min, W., et al., 1999.Discussion on Cenozoic Tectonics and Dynamics of Ordos Block.Journal of Geomechanics, 5(3):13-21 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb199903003 Guan, Y.B., Li, H.M., 2001.The Structural Framework and Evolution of Taiyuan Area.Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science), 20(1):32-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=lngcjsdxxb200101010 Guo, S.Y., Li, X.J., 2013.Reservoir Stratum Characterstics and Geothermal Resources Potential of Rongcheng Uplift Geothermal Field in Baoding, Hebei.Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 48(3):922-931 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx201303026 Ha, C.Y., Tang, B.Y., Lu, R.A., et al., 1989.Characteristics of Fissure Karst in the Middle Ordovician Limestone and Groundwater Natural Resources in the West Mountain of Taiyuan, Shanxi Province.Carsologica Sinica, 8(1):41-46 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198901006.htm Haakon, F., 2010.Structural Geology.Cambridge University Press, New York, 333-353. Han, D.M., Xu, H.L., Liang, X., 2006.Demarcation of Groundwater System of Big Karst Spring:A Case Study of Eastern and Western Mountain Areas, Taiyuan Basin.Earth Science, 31(6):885-890 (in Chinese with English abstract). He, Y., 2010.Geological Features of Xiwenzhuang Uplift Geothermal Field in Taiyuan Basin.Shanxi Coking Coal Science & Technology, 34(6):47-49, 56 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sxjmkj201006016 He, Z.L., Feng, J.Y., Zhang, Y., et al., 2017.A Tentative Discussion on an Evaluation System of Geothermal Unit Ranking and Classification in China.Earth Science Frontiers, 24(3):168-179 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201703015 Hou, Y.X., 2002.Research on the Geothermal Resources of Border Mount Fracture Zone in Taiyuan Region.Coal Geology of China, 14(4):38-41 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgmtdz200204016 Li, C.S., Wu, X.C., Sun, B., et al., 2018.Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Geothermal Water in Northern Ji'nan.Earth Science, 43(S1):313-325 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.206 Li, J.X., Guo, Q.H., Yu, Z.Y., 2017.Impact of Clay Mineral Formation in High-Temperature Geothermal System on Accuracy of Na-K and K-Mg Geothermometers.Earth Science, 42(1):142-154 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.011 Li, S.Z., Lu, R.A., Xu, S.Z., et al., 1994.Analysis of Formation Mechanism of Thermal Mineral Water in Shanxi Province.Geological Review, 40(3):221-228 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/OA000003056 Li, X.Q., Hou, X.W., Zhang, H.D., et al., 2006.Study on the Geochemistry-Isotope Characteristics of the Groundwater Systems in Taiyuan Basin.Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 20(5):109-114 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ghqzyyhj200605022 Ma, R., 2007.Water-Rock Interaction and Genesis of Low-Medium Temperature Thermal Groundwater in Carbonate Reservoir: A Case Study of Taiyuan, Shanxi (Dissertation).China University of Geosciences, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Ma, R., Wang, Y.X., Sun, Z.Y., et al., 2011.Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater in Carbonate Aquifers in Taiyuan, Northern China.Applied Geochemistry, 26(5):884-897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.02.008 Ma, T., Wang, Y.X., Guo, Q.H., et al., 2005.Karst Water System Evolution and Global Environmental Changes-A Case Study in Shanxi Province.China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan (in Chinese). Ma, T., Wang, Y.X., Guo, Q.H., et al., 2009.Hydrochemical and Isotopic Evidence of Origin of Thermal Karst Water at Taiyuan, Northern China.Journal of Earth Science, 20(5):879-889. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-009-0074-4 Ma, T., Wang, Y.X., Ma, R., et al., 2012.Evolution of Middle-Low Temperature Carbonate Geothermal System in Taiyuan, Northern China.Earth Science, 37(2):229-237 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2012.023 Mao, X.P., Wang, X.W., Li, K.W., et al., 2018.Sources of Heat and Control Factors in Geothermal Field.Earth Science, 43(11):4256-4266 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.210 Song, D.N., 2001.Re-Recognization of Huaiyuan Movement.Geology of Shandong, 17(1):19-23, 51 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sddz200101004 Sun, L.F., Wang, Y.X., Ma, T., et al., 1997.Evolution of the Niangziguan Karst Springs in View of Travertines' Environmental Record and Groundwater Flow System Development.Earth Science, 22(6):648-651 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX706.018.htm Wang, J.Y., 2015.Geothermics and Its Application.Science Press, Beijing, 1-6 (in Chinese). Yan, Z.W., 2008.Influences of SO42- on the Solubility of Calcite and Dolomite.Carsologica Sinica, 27(1):24-31 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgyr200801005 Yan, Z.W., Liu, H.L., Zhang, Z.W., 2009.Influences of Temperature and PCO2 on the Solubility of Calcite and Dolomite.Carsologica Sinica, 28(1):7-10, 41 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgyr200901002 Yang, J.L., Liu, F.T., Jia, Z., et al., 2018.The Hydrochemical and δ2H-δ18O Characteristics of Two Geothermal Fields in Niutuozhen of Hebei Province and Tianjin and Their Environmental Significance.Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 39(1):71-78 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqxb201801008 Yang, J.Z., 2010.Talking about the Structural Environment of Xiwenzhuang Area in Taiyuan City and Xiwenzhuang Geothermal Resources.Sci-Tech Information Development & Economy, 20(1):163-165 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kjqbkfyjj201001079 Zeng, J.Y., Li, Z.H., Chen, W., et al., 2016.Preliminary Study on Exploration and Activity of East Segment of Tianzhuang Fault in Taiyuan Basin.Journal of Seismological Research, 39(2):261-269 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzyj201602012 Zhang, H.W., Deng, Q.D., 1992.A Study on the Mechanism of the Asymmetry Basin-A Case of the Weihe Basin.Earthquake Research in China, 8(1):26-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGZD199201003.htm Zhang, S.Q., 1990.The Study on Karst Hydrogeological Structure System in Taiyuan Area, Shanxi Province.Scientia Geologica Sinica, (2):173-182 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000368837 Zhang, S.Q., Li, C.H., Sun, W.Y., et al., 2008.Construction of the Conceptual Model of Thermal Reservoir Structure of the Xining Basin, China.Geological Bulletin of China, 27(1):126-136 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz200801012 Zhang, Y., Feng, J.Y., He, Z.L., et al., 2017.Classification of Geothermal Systems and Their Formation Key Factors.Earth Science Frontiers, 24(3):190-198 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201703017 Zhang, Y., Liu, Z., 2009.Application of an Integrated Approach to Determine the Scope of Yinchuan Basin Geothermal Field.Ningxia Engineering Technology, 8(3):247-249 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=nxgcjs200903013 陈光平, 2011.太原盆地西温庄地热田地热地质条件分析.华北国土资源, (3):5-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7487.2011.03.002 邓起东, 程绍平, 闵伟, 等, 1999.鄂尔多斯块体新生代构造活动和动力学的讨论.地质力学学报, 5(3):13-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.1999.03.003 关英斌, 李海梅, 2001.太原地区构造格局及其演化.辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 20(1):32-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-0562.2001.01.010 郭世炎, 李小军, 2013.河北保定容城凸起地热田储层属性与资源潜力.地质科学, 48(3):922-931. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0563-5020.2013.03.026 哈承佑, 汤邦义, 鲁荣安, 1989.太原西山岩溶发育特征及地下水天然资源的研究.中国岩溶, 8(1):41-46. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198901006.htm 韩冬梅, 徐恒力, 梁杏, 2006.北方岩溶大泉地下水系统的圈划:以太原盆地东西山地区为例.地球科学, 31(6):885-890. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2006.06.020 贺鹰, 2010.太原盆地西温庄隆起地热田地质特征.山西焦煤科技, 34(6):47-49, 56. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0652.2010.06.016 何治亮, 冯建赟, 张英, 等, 2017.试论中国地热单元分级分类评价体系.地学前缘, 24(3):168-179. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201703015 侯玉新, 2002.太原边山断裂带地热资源研究.中国煤田地质, 14(4):38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2002.04.016 李常锁, 武显仓, 孙斌, 等, 2018.济南北部地热水水化学特征及其形成机理.地球科学, 43(S1):313-325. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.206 李洁祥, 郭清海, 余正艳, 2017.高温地热系统中粘土矿物形成对Na-K和K-Mg地球化学温标准确性的影响.地球科学, 42(1):142-154. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.011 李世忠, 鲁荣安, 许绍倬, 等, 1994.山西省热矿水形成机制分析.地质论评, 40(3):221-228. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1994.03.005 李向全, 侯新伟, 张宏达, 等, 2006.太原盆地地下水系统水化学-同位素特征研究.干旱区资源与环境, 20(5):109-114. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7578.2006.05.022 马瑞, 2007.碳酸盐岩热储隐伏型中低温热水的成因与水-岩相互作用研究(博士学位论文).武汉: 中国地质大学. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/article/cdmd-10491-2007142827.htm 马腾, 王焰新, 郭清海, 等, 2005.岩溶水系统演化与全球变化研究——以山西岩溶大泉为例.武汉:中国地质大学出版社. 马腾, 王焰新, 马瑞, 等, 2012.太原盆地区碳酸盐岩中-低温地热系统演化.地球科学, 37(2):229-237. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2012.023 毛小平, 汪新伟, 李克文, 等, 2018.地热田热量来源及形成主控因素.地球科学, 43(11):4256-4266. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.210 宋奠南, 2001.对怀远运动的再认识.山东地质, 17(1):19-23, 51. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sddz200101004 孙连发, 王焰新, 马腾, 等, 1997.应用泉钙华环境记录和地下水流动系统探讨娘子关泉群演变历史.地球科学, 22(6):648-651. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=569 汪集旸, 2015.地热学及其应用.北京:科学出版社, 1-6. 闫志为, 2008.硫酸根离子对方解石和白云石溶解度的影响.中国岩溶, 27(1):24-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2008.01.005 闫志为, 刘辉利, 张志卫, 2009.温度及CO2对方解石、白云石溶解度影响特征分析.中国岩溶, 28(1):7-10, 41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2009.01.002 杨吉龙, 柳富田, 贾志, 等, 2018.河北牛驼镇与天津地热田水化学和氢氧同位素特征及其环境指示意义.地球学报, 39(1):71-78. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqxb201801008 杨建中, 2010.太原市西温庄一带构造环境与西温庄地热.科技情报开发与经济, 20(1):163-165. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6033.2010.01.079 曾金艳, 李自红, 陈文, 等, 2016.太原盆地田庄断裂东段探测和活动性初步研究.地震研究, 39(2):261-269. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2016.02.012 张宏卫, 邓起东, 1992.不对称盆地形成机制探讨——以渭河盆地为例.中国地震, 8(1):26-35. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGZD199201003.htm 张寿全, 1990.山西省太原地区的岩溶水文地质结构系统.地质科学, (2):173-182. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK000000368837 张森琦, 李长辉, 孙王勇, 等, 2008.西宁盆地热储构造概念模型的建立.地质通报, 27(1):126-136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2008.01.012 张英, 冯建赟, 何治亮, 等, 2017.地热系统类型划分与主控因素分析.地学前缘, 24(3):190-198. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201703017 张宇, 刘峥, 2009.综合方法圈定银川盆地地热田范围.宁夏工程技术, 8 (3):247-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7244.2009.03.013 -









 下载:
下载: