Two Contrasting Eclogite Types in the Himalayan Orogen and Differential Subduction of Indian Continent
-
摘要: 印度与亚洲大陆新生代碰撞-俯冲形成的喜马拉雅造山带核部由高压和超高压变质岩组成.超高压榴辉岩分布在喜马拉雅造山带西段,由石榴石、绿辉石、柯石英、多硅白云母、帘石、蓝晶石和金红石组成.超高压榴辉岩的峰期变质条件为2.6~2.8 GPa和600~620℃,其经历了角闪岩相退变质作用和低程度熔融.超高压榴辉岩的进变质、峰期和退变质年龄分别为~50 Ma、45~47 Ma和35~40 Ma,指示一个快速俯冲与快速折返过程.高压榴辉岩产出在喜马拉雅造山带中-东段,由石榴石、绿辉石、多硅白云母、石英和金红石组成.高压榴辉岩的峰期变质条件为> 2.1 GPa和> 750℃,叠加了高温麻粒岩相退变质作用与强烈部分熔融.高压榴辉岩的峰期和退变质年龄可能分别是~38 Ma和14~17 Ma,很可能经历了一个缓慢俯冲与缓慢折返过程.喜马拉雅造山带两种不同类型榴辉岩的存在表明,印度与亚洲大陆约在51~53 Ma碰撞后,印度大陆地壳的西北缘陡俯冲到了地幔深度,导致表壳岩石经历了超高压变质作用,而印度大陆地壳的东北缘平缓俯冲到亚洲大陆之下,导致表壳岩石经历了高压变质作用.Abstract: The core of the Himalayan orogen, resulting from the Cenozoic collision between the Indian and Asian continents, consists of high-pressure (HP) and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks. The ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) eclogites occur in the western segment of the Himalayan orogen, and contain garnet, omphacite, coesite, phengite, zoisite/epidote, kyanite and rutile. The UHP eclogites record a peak metamorphic condition of 2.6-2.8 GPa and 600-620℃, and a late stage of amphibolite-facies retrogression and slight partial melting. The prograde, peak and retrograde metamorphic times of the UHP eclogites are~50 Ma, ~45-47 Ma and~35-40 Ma, respectively, indicating that the UHP eclogites underwent a rapid subduction and rapid exhumation. The HP eclogites occur in the east-central segment of the Himalayan orogen, and contain garnet, omphacite, phengite, quartz and rutile. The HP eclogites have a peak metamorphic condition of > 2.1 GPa and > 750℃, and experienced a late stage of granulite-facies retrogression and extensive anataxis. The peak and retrograde metamorphic times of the HP eclotites are~38 Ma and~14-17 Ma, respectively, indicating that the HP eclogites underwent a slow subduction and slow exhumation. The presence of two contrasting eclogite types in the Himalayan orogen shows that, after the India collided with Asia at around 51-53 Ma, the north-western margin of Indian continental crust deeply subducted into the mantle, and underwent UHP metamorphism, and while the north-eastern margin of Indian continental crust shallowly subducted beneath the Asian continent, and experienced HP metamorphism.
-
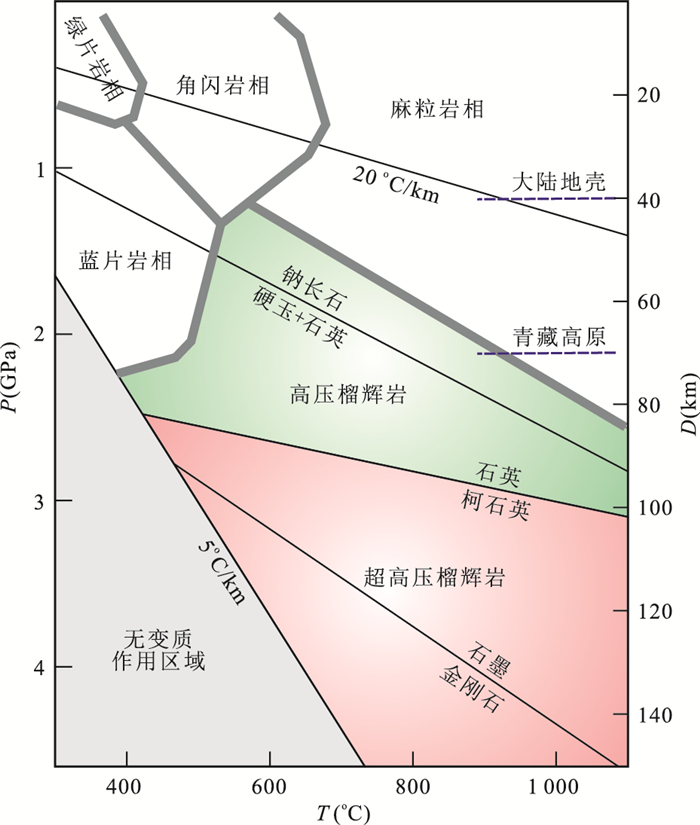
图 1 高压和超高榴辉岩形成条件与深度
Fig. 1. Metamorphic conditions and related depths of high- and ultrahigh-pressure eclogites
图 2 喜马拉雅造山带与高压和超高压变质岩分布
据Ding et al.(2016a)和张泽明等(2017, 2018)修改.MFT.主前缘逆冲断裂;MBT.主边界逆冲断裂;MCT.主中央逆冲断裂;STD.藏南拆离系.图中标注了较深入研究的中压、高压和超高压变质岩的地点与变质年龄,资料来源:Ama Drime (Kellett et al., 2014), Annapurna (Kohn and Corrie, 2011), Everest (Cottle et al., 2009), Gianbul (Horton et al., 2014), Jomolhari (Regis et al., 2014), Kaghan (Kaneko et al., 2003), Kali Gandaki (Iaccarino et al., 2015), Mabja dome (Lee and Whitehouse, 2007), Namche Barwa Syntaxis (Zhang et al., 2015), Nyalam (Wang et al., 2015), Sikkim (Rubatto et al., 2012), Tso Morari (Donaldson et al., 2013), Yadong (Zhang et al., 2017)和Yardoi dome (Ding et al., 2016b).变质作用类型:MP.中压;HP.高压;UHP.超高压
Fig. 2. Geological map of the Himalayan orogen, showing distributions of representative medium-, high- and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks
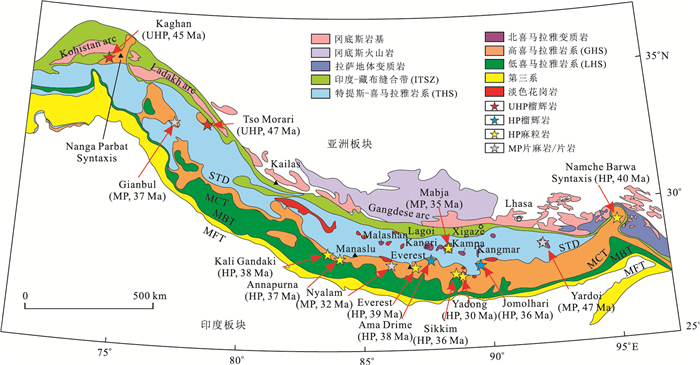
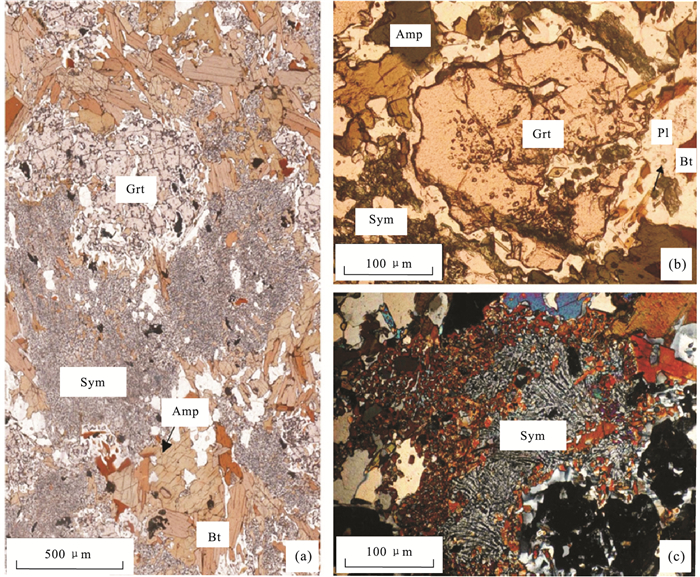
图 3 喜马拉雅造山带西段Kaghan超高压榴辉岩显微照片
据Rehman et al.(2007, 2013).a.超高压榴辉岩由石榴石、绿辉石和绿帘石组成,部分绿辉石边缘被角闪石,或由单斜辉石+角闪石+石英组成的合晶替代;b.超高压榴辉岩由石榴石、绿辉石、绿帘石、金红石、钛铁矿和柯石英组成.柯石英呈包裹体产于绿辉石中,发育放射状裂纹.部分石榴石和绿辉石被单斜辉石+角闪石+石英合晶替代;c.超高压榴辉岩,由石榴石、绿辉石和榍石组成,部分绿辉石被单斜辉石+角闪石+石英合晶冠状体替代;d.超高压榴辉岩绿辉石中的柯石英包体以及沿包体向外发育的放射状裂纹.注意绿辉石中含有出溶的石英棒或页片.矿物代号:Amp.角闪石;Coe.柯石英;Ep.绿帘石;Grt.石榴石;Ilm.钛铁矿;Omp.绿辉石;Qtz.石英;Rt.金红石;Sym.后成合晶;Tt.榍石;Zo.黝帘石
Fig. 3. Photomicrographs of ultrahigh-pressure eclogites from the Kaghan Valley, the western Himalaya
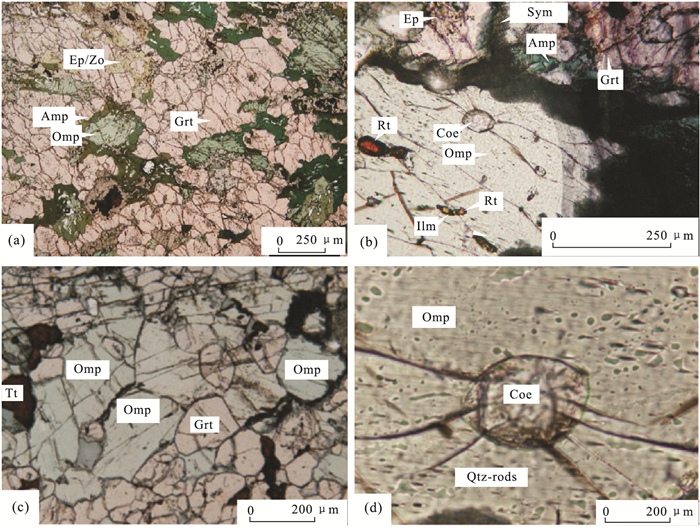
图 4 喜马拉雅造山带高压和超高压榴辉岩变质作用P-T-t轨迹
图中的数字为年龄(Ma),其中Groppo et al.(2007)P-T轨迹上的38 Ma峰压力年龄和15 Ma退变质年龄分别为Kellett et al.(2014)获得的石榴石Lu-Hf等时线年龄和锆石U-Pb年龄.变质相:AM.角闪岩相;Amp-Ec.角闪石榴辉岩相;BS.蓝片岩相;Dry-Ec.干榴辉岩相;EA.绿帘角闪岩相;Ep-Ec.绿帘石榴辉岩相;G.麻粒岩相;GS.绿片岩相;HG.高压麻粒岩相;Lw-Ec.硬柱石榴辉岩相;WGS.湿的花岗岩固相线.Coe.柯石英;Qtz.石英
Fig. 4. Metamorphic P-T-t paths of the high- and ultrahigh-pressure eclogites in the Himalayan orogen
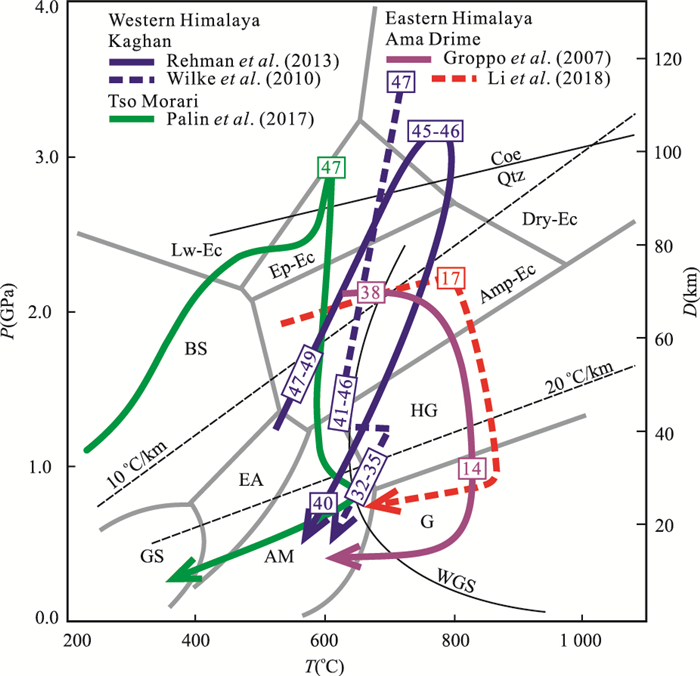
图 5 喜马拉雅造山带西段Tso Morari地块超高压榴辉岩显微照片
据Jonnalagadda et al.(2017).a.超高压榴辉岩由石榴石、绿辉石、多硅白云母和石英组成.注意,石榴石核部含石英和多硅白云母包体,而石榴石边缘含柯石英包体.部分绿辉石边缘被由极细的角闪石+斜长石合晶组合的冠状体替代;b.超高压榴辉岩石榴石变斑晶中的角闪石包体定向分布;c.超高压榴辉岩由石榴石、绿辉石、多硅白云母、绿帘石和方解石组成;d.超高压榴辉岩中的绿辉石含有近平行分布的出溶页片.矿物代号:Amp.角闪石;Cc.方解石;Coe.柯石英;Grt.石榴石;Omp.绿辉石;Phe.多硅白云母;Qtz.石英
Fig. 5. Photomicrographs of ultrahigh-pressure eclogites from the Tso Morari massif of the western Himalaya
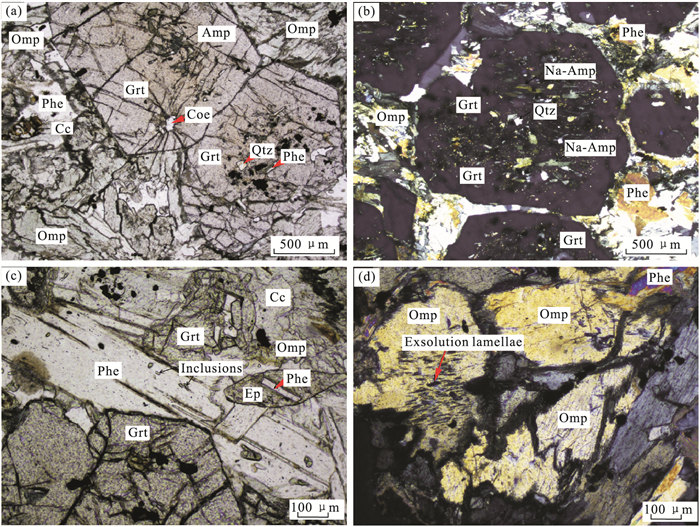
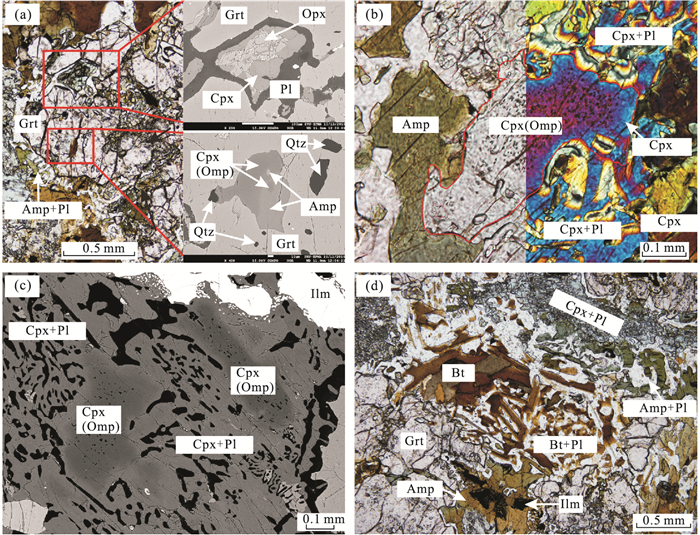
图 6 喜马拉雅造山带中东段Ama Drime麻粒岩化高压榴辉岩显微照片
据Kellett et al.(2014).a.麻粒岩化榴辉岩由石榴石、单斜辉石、角闪石、黑云母、斜长石和石英组成.绿辉石全部被由细粒斜长石+单斜辉石组成的合晶替代;b.榴辉岩石榴石核部含细小的矿物包体,其边缘被由斜长石+角闪石+斜方辉石+黑云母组成的合晶冠状体替代;c.榴辉岩中的绿辉石被由斜长石+角闪石+单斜辉石+斜方辉石组成的合晶替代.矿物代号:Amp.角闪石;Bt.黑云母;Grt.石榴石;Pl.斜长石;Sym.后成合晶
Fig. 6. Photomicrographs of granulitized high-pressure eclogites from the Ama Drime massif of the eastern Himalaya
图 7 喜马拉雅造山带中东段Thongmön高压榴辉岩显微照片
据Li et al.(2018).a.高压榴辉岩由石榴石和包含的单斜辉石(绿辉石)、角闪石和石英组成,石榴石被由单斜辉石、斜长石和斜方辉石,或角闪石和斜长石组成的合晶冠状体替代;b.高压榴辉岩的单斜辉石(绿辉石)发育由单斜辉石和斜长石组成的冠状体,或被角闪石部分替代;c.高压榴辉岩中残余的单斜辉石(绿辉石)被单斜辉石和斜长石合晶部分替代;d.高压榴辉岩中的多硅白云母被黑云母+斜长石合晶替代,单斜辉石+斜长石替代绿辉石,角闪石+斜长石合晶替代石榴石.矿物代号:Amp.角闪石;Bt.黑云母;Cpx.单斜辉石;Grt.石榴石;Ilm.钛铁矿;Omp.绿辉石;Opx.斜方辉石;Pl.斜长石;Qtz.石英
Fig. 7. Photomicrographs of granulitized high-pressure eclogites from the Thongmön of the eastern Himalaya
-
Aitchison, J.C., Ali, J.R., Davis, A.M., 2007.When and Where did India and Asia Collide?.Journal of Geophysical Research, 112(B5):423. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006jb004706 Ambrose, T.K., Larson, K.P., Guilmette, C., et al., 2015.Lateral Extrusion, Underplating, and Out-of-Sequence Thrusting within the Himalayan Metamorphic Core, Kanchenjunga, Nepal.Lithosphere, 7(4):441-464. https://doi.org/10.1130/l437.1 Bouilhol, P., Jagoutz, O., Hanchar, J.M., et al., 2013.Dating the India-Eurasia Collision through Arc Magmatic Records.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 366:163-175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.01.023 Burchfiel, B.C., Chen, Z.L., Hodges, K.V., et al., 1992.The South Tibetan Detachment System, Himalayan Orogen:Extension Contemporaneous with and Parallel to Shortening in a Collisional Mountain Belt.Geological Society of America Special Papers, 269:1-41. doi: 10.1130/SPE269 Burg, J.P., Guiraud, M., Chen, G.M., et al., 1984.Himalayan Metamorphism and Deformations in the North Himalayan Belt (Southern Tibet, China).Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 69(2):391-400.https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821x (84)90197-3 doi: 10.1016/0012-821x(84)90197-3 Chopin, C., 1984.Coesite and Pure Pyrope in High-Grade Blueschists of the Western Alps:A First Record and Some Consequences.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 86(2):107-118. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00381838 Chopin, C., 2003.Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism:Tracing Continental Crust into the Mantle.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 212(1-2):1-14.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x (03)00261-9 doi: 10.1016/s0012-821x(03)00261-9 Chu, M.F., Chung, S.L., O'Reilly, S.Y., et al., 2011.India's Hidden Inputs to Tibetan Orogeny Revealed by Hf Isotopes of Transhimalayan Zircons and Host Rocks.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 307(3-4):479-486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.05.020 Corrie, S.L., Kohn, M.J., Vervoort, J.D., 2010.Young Eclogite from the Greater Himalayan Sequence, Arun Valley, Eastern Nepal:P-T-t Path and Tectonic Implications.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 289(3-4):406-416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.11.029 Cottle, J.M., Jessup, M.J., Newell, D.L., et al., 2009.Geochronology of Granulitized Eclogite from the Ama Drime Massif:Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of the South Tibetan Himalaya.Tectonics, 28(1):TC1002. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008tc002256 Dasgupta, S., Chakraborty, S., Neogi, S., 2009.Petrology of an Inverted Barrovian Sequence of Metapelites in Sikkim Himalaya, India:Constraints on the Tectonics of Inversion.American Journal of Science, 309(1):43-84. https://doi.org/10.2475/01.2009.02 Dasgupta, S., Ganguly, J., Neogi, S., 2004.Inverted Metamorphic Sequence in the Sikkim Himalayas:Crystallization History, P-T Gradient and Implications.Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 22(5):395-412. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.2004.00522.x DeCelles, P.G., Kapp, P., Gehrels, G.E., et al., 2014.Paleocene-Eocene Foreland Basin Evolution in the Himalaya of Southern Tibet and Nepal:Implications for the Age of Initial India-Asia Collision.Tectonics, 33(5):824-849. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014tc003522 de Sigoyer, J., Chavagnac, V., Blichert-Toft, J., et al., 2000.Dating the Indian Continental Subduction and Collisional Thickening in the Northwest Himalaya:Multichronology of the Tso Morari Eclogites.Geology, 28(6):487-490.https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2000)028<0487:dticsa>2.3.co;2 doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)028<0487:dticsa>2.3.co;2 de Sigoyer, J., Guillot, S., Dick, P., 2004.Exhumation of the Ultrahigh-Pressure Tso Morari Unit in Eastern Ladakh (NW Himalaya):A Case Study.Tectonics, 23(3):TC3003. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002tc001492 de Sigoyer, J.D., Guillot, S., Lardeaux, J.M., et al., 1997.Glaucophane-Bearing Eclogites in the Tso Morari Dome (Eastern Ladakh, NW Himalaya).European Journal of Mineralogy, 9(5):1073-1084. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/9/5/1073 Ding, H.X., Zhang, Z.M., Dong, X., et al., 2016a.Early Eocene (ca.50 Ma) Collision of the Indian and Asian Continents:Constraints from the North Himalayan Metamorphic Rocks, Southeastern Tibet.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 435:64-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.12.006 Ding, L., Qasim, M., Jadoon, I.A.K., et al., 2016b.The India-Asia Collision in North Pakistan:Insight from the U-Pb Detrital Zircon Provenance of Cenozoic Foreland Basin.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 455:49-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.09.003 Ding, L., Maksatbek, S., Cai, F.L., et al., 2017.Processes of Initial Collision and Suturing between India and Asia.Science in China (Series D:Earth Sciences), 47(3):293-309(in Chinese). Donaldson, D.G., Webb, A.A.G., Menold, C.A., et al., 2013.Petrochronology of Himalayan Ultrahigh-Pressure Eclogite.Geology, 41(8):835-838. https://doi.org/10.1130/g33699.1 Epard, J.L., Steck, A., 2008.Structural Development of the Tso Morari Ultra-High Pressure Nappe of the Ladakh Himalaya.Tectonophysics, 451(1-4):242-264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.050 Ferrando, S., Rolfo, F., Lombardo, B., 2007.Fluid Evolution from Metamorphic Peak to Exhumation in Himalayan Granulitised Eclogites, Ama Drime Range, Southern Tibet.European Journal of Mineralogy, 19(4):439-461. https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2007/0019-1748 Gao, R., Lu, Z.W., Klemperer, S.L., et al., 2016.Crustal-Scale Duplexing beneath the Yarlung Zangbo Suture in the Western Himalaya.Nature Geoscience, 9(7):555-560. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2730 Ghazanfar, M., Chaudhry, M.N., 1986.Reporting MCT in Northwest Himalaya, Pakistan.University of Punjab Geological Bulletin, 21:10-18. Ghazanfar, M., Chaudhry, M.N., 1987, Geology, Structure and Geomorphology of Upper Kaghan Valley, Northwest Himalaya, Pakistan.University of Punjab Geological Bulletin, 22:13-56. Gibbons, A.D., Zahirovic, S., Müller, R.D., et al., 2015.A Tectonic Model Reconciling Evidence for the Collisions between India, Eurasia and Intra-Oceanic Arcs of the Central-Eastern Tethys.Gondwana Research, 28(2):451-492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.01.001 Gilotti, J.A., 2013.The Realm of Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism.Elements, 9(4):255-260. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.9.4.255 Groppo, C., Lombardo, B., Rolfo, F., et al., 2007.Clockwise Exhumation Path of Granulitized Eclogites from the Ama Drime Range (Eastern Himalayas).Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 25(1):51-75. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.2006.00678.x Groppo, C., Rolfo, F., Indares, A., 2012.Partial Melting in the Higher Himalayan Crystallines of Eastern Nepal:The Effect of Decompression and Implications for the'Channel Flow'Model.Journal of Petrology, 53(5):1057-1088. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egs009 Grujic, D., Warren, C.J., Wooden, J.L., 2011.Rapid Synconvergent Exhumation of Miocene-Aged Lower Orogenic Crust in the Eastern Himalaya.Lithosphere, 3(5):346-366. https://doi.org/10.1130/l154.1 Guillot, S., de Sigoyer, J., Lardeaux, J.M., et al., 1997.Eclogitic Metasediments from the Tso Morari Area (Ladakh, Himalaya):Evidence for Continental Subduction during India-Asia Convergence.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 128(2-3):197-212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050303 Guillot, S., Garzanti, E., Baratoux, D., et al., 2003.Reconstructing the Total Shortening History of the NW Himalaya.Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 4(7):1064. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002gc000484 Guillot, S., Mahéo, G., de Sigoyer, J., et al., 2008.Tethyan and Indian Subduction Viewed from the Himalayan High-to Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphic Rocks.Tectonophysics, 451(1-4):225-241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.059 Guillot, S., Replumaz, A., Hattori, K.H., et al., 2007.Initial Geometry of Western Himalaya and Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphic Evolution.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 30(3-4):557-564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2007.01.004 Guilmette, C., Indares, A., Hébert, R., 2011.High-Pressure Anatectic Paragneisses from the Namche Barwa, Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis:Textural Evidence for Partial Melting, Phase Equilibria Modeling and Tectonic Implications.Lithos, 124(1-2):66-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2010.09.003 Guo, X.Y., Gao, R., Zhao, J.M., et al., 2018.Deep-Seated Lithospheric Geometry in Revealing Collapse of the Tibetan Plateau.Earth-Science Reviews, 185:751-762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.07.013 Hermann, J., Zheng, Y.F., Rubatto, D., 2013.Deep Fluids in Subducted Continental Crust.Elements, 9(4):281-287. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.9.4.281 Honegger, K., Le Fort, P., Mascle, G., et al., 1989.The Blueschists along the Indus Suture Zone in Ladakh, NW Himalaya.Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 7(1):57-72. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.1989.tb00575.x Horton, F., Lee, J., Hacker, B., et al., 2014.Himalayan Gneiss Dome Formation in the Middle Crust and Exhumation by Normal Faulting:New Geochronology of Gianbul Dome, Northwestern India.Geological Society of America Bulletin, 127(1-2):162-180. https://doi.org/10.1130/b31005.1 Hu, X.M., Garzanti, E., Wang, J.G., et al., 2016.The Timing of India-Asia Collision Onset-Facts, Theories, Controversies.Earth-Science Reviews, 160:264-299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.07.014 Iaccarino, S., Montomoli, C., Carosi, R., et al., 2015.Pressure-Temperature-Time-Deformation Path of Kyanite-Bearing Migmatitic Paragneiss in the Kali Gandaki Valley (Central Nepal):Investigation of Late Eocene-Early Oligocene Melting Processes.Lithos, 231:103-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.005 Imayama, T., Takeshita, T., Yi, K., et al., 2012.Two-Stage Partial Melting and Contrasting Cooling History within the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence in the Far-Eastern Nepal Himalaya.Lithos, 134-135:1-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2011.12.004 Jagoutz, O., Royden, L., Holt, A.F., et al., 2015.Anomalously Fast Convergence of India and Eurasia Caused by Double Subduction.Nature Geoscience, 8(6):475-478. https://doi.org/10.1038/ngeo2418 Ji, W.Q., Wu, F.Y., Chung, S.L., et al., 2014.The Gangdese Magmatic Constraints on a Latest Cretaceous Lithospheric Delamination of the Lhasa Terrane, Southern Tibet.Lithos, 210-211:168-180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.10.001 Jonnalagadda, M.K., Karmalkar, N.R., Duraiswami, R.A., 2017.Geochemistry of Eclogites of the Tso Morari Complex, Ladakh, NW Himalayas:Insights into Trace Element Behavior during Subduction and Exhumation.Geoscience Frontiers. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2017.05.013 Kali, E., Leloup, P.H., Arnaud, N., et al., 2010.Exhumation History of the Deepest Central Himalayan Rocks, Ama Drime Range:Key Pressure-Temperature-Deformation-Time Constraints on Orogenic Models.Tectonics, 29(2):TC2014. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009tc002551 Kaneko, Y., Katayama, I., Yamamoto, H., et al., 2003.Timing of Himalayan Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism:Sinking Rate and Subduction Angle of the Indian Continental Crust beneath Asia.Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 21(6):589-599. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1314.2003.00466.x Kellett, D.A., Cottle, J.M., Smit, M., 2014.Eocene Deep Crust at Ama Drime, Tibet:Early Evolution of the Himalayan Orogen.Lithosphere, 6(4):220-229. https://doi.org/10.1130/l350.1 Kohn, M.J., 2014.Himalayan Metamorphism and Its Tectonic Implications.Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 42(1):381-419. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-earth-060313-055005 Kohn, M.J., Corrie, S.L., 2011.Preserved Zr-Temperatures and U-Pb Ages in High-Grade Metamorphic Titanite:Evidence for a Static Hot Channel in the Himalayan Orogen.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 311(1-2):136-143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.09.008 Lee, J., Whitehouse, M.J., 2007.Onset of Mid-Crustal Extensional Flow in Southern Tibet:Evidence from U/Pb Zircon Ages.Geology, 35(1):45. https://doi.org/10.1130/g22842a.1 Leech, M., Singh, S., Jain, A., et al., 2005.The Onset of India-Asia Continental Collision:Early, Steep Subduction Required by the Timing of UHP Metamorphism in the Western Himalaya.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 234(1-2):83-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.038 Leech, M.L., Singh, S., Jain, A.K., 2007.Continuous Metamorphic Zircon Growth and Interpretation of U-Pb SHRIMP Dating:An Example from the Western Himalaya.International Geology Review, 49(4):313-328. https://doi.org/10.2747/0020-6814.49.4.313 Li, D.W., 2003.SHRIMP U-Pb Zircon Geochronology of Granulites at Rimana (Southern Tibet) in the Central Segment of Himalayan Orogen.Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(23):2647. https://doi.org/10.1360/03wd0080 Li, J.T., Song, X.D., 2018.Tearing of Indian Mantle Lithosphere from High-Resolution Seismic Images and Its Implications for Lithosphere Coupling in Southern Tibet.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(33):8296-8300. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717258115 Li, Q.Y., Zhang, L.F., Fu, B., et al., 2018.Petrology and Zircon U-Pb Dating of Well-Preserved Eclogites from the Thongmön Area in Central Himalaya and Their Tectonic Implications.Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 37(2):203-226. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12457 Liou, J.G., Ernst, W.G., Zhang, R.Y., et al., 2009.Ultrahigh-Pressure Minerals and Metamorphic Terranes-The View from China.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 35(3-4):199-231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.10.012 Lombardo, B., Pertusati, P., Rolfo, F., et al., 1998.First Report of Eclogites from the Eastern Himalaya:Implications for the Himalayan Orogeny.Memorie di Scienze Geologichedell' Universitá di Padova, 50:67-68. Lombardo, B., Rolfo, F., 2000.Two Contrasting Eclogite Types in the Himalayas:Implications for the Himalayan Orogeny.Journal of Geodynamics, 30(1-2):37-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0264-3707(99)00026-5 Lombardo, B., Rolfo, F., Compagnoni, R., 2000.Glaucophane and Barroisite Eclogites from the Upper Kaghan Nappe:Implications for the Metamorphic History of the NW Himalaya.Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 170(1):411-430. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.2000.170.01.22 Lombardo, B., Rolfo, F., McClelland, W., 2016.A Review of the First Eclogites Discovered in the Eastern Himalaya.European Journal of Mineralogy, 28(6):1099-1109. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/2016/0028-2553 Meng, J., Wang, C.S., Zhao, X.X., et al., 2012.India-Asia Collision was at 24°N and 50 Ma:Palaeomagnetic Proof from Southernmost Asia.Scientific Reports, 2(1):925. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00925 Mukherjee, B.K., Sachan, H.K., 2001.Discovery of Coesite from the Indian Himalaya:A Record of Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphism in Indian Continental Crust.Current Science, 81:1358-1361. Mukherjee, B.K., Sachan, H.K., Ogasawara, Y., et al., 2003.Carbonate-Bearing UHPM Rocks from the Tso-Morari Region, Ladakh, India:Petrological Implications.International Geology Review, 45(1):49-69. https://doi.org/10.2747/0020-6814.45.1.49 Najman, Y., Appel, E., Boudagher-Fadel, M., et al., 2010.Timing of India-Asia Collision:Geological, Biostratigraphic, and Palaeomagnetic Constraints.Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(B12):416. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010jb007673 O'Brien, P.J., Zotov, N., Law, R., 1999.First Discovery of Coesite in the Kaghan Eclogites (Pakistan); Implications for Himalayan Evolution.Terra Nova, 2:109-111. O'Brien, P.J., Zotov, N., Law, R., et al., 2001.Coesite in Himalayan Eclogite and Implications for Models of India-Asia Collision.Geology, 29(5):435-438.https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0435:ciheai>2.0.co;2 doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0435:ciheai>2.0.co;2 Palin, R.M., Reuber, G.S., White, R.W., et al., 2017.Subduction Metamorphism in the Himalayan Ultrahigh-Pressure Tso Morari Massif:An Integrated Geodynamic and Petrological Modelling Approach.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 467:108-119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2017.03.029 Parrish, R.R., Gough, S.J., Searle, M.P., et al., 2006.Plate Velocity Exhumation of Ultrahigh-Pressure Eclogites in the Pakistan Himalaya.Geology, 34(11):989-992. https://doi.org/10.1130/g22796a.1 Peng, M., Jiang, M., Li, Z.H., et al., 2016.Complex Indian Subduction Style with Slab Fragmentation beneath the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis Revealed by Teleseismic P-Wave Tomography.Tectonophysics, 667:77-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2015.11.012 Pognante, U., Spencer, D.A., 1991.First Report of Eclogites from the Himalayan Belt, Kaghan Valley (Northern Pakistan).European Journal of Mineralogy, 3(3):613-618. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/3/3/0613 Ravikant, V., Wu, F.Y., Ji, W.Q., 2009.Zircon U-Pb and Hf Isotopic Constraints on Petrogenesis of the Cretaceous-Tertiary Granites in Eastern Karakoram and Ladakh, India.Lithos, 110(1-4):153-166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2008.12.013 Regis, D., Warren, C.J., Young, D., et al., 2014.Tectono-Metamorphic Evolution of the Jomolhari Massif:Variations in Timing of Syn-Collisional Metamorphism across Western Bhutan.Lithos, 190-191:449-466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.01.001 Rehman, H.U., Kobayash, K., Tsujimori, T., et al., 2013.Ion Microprobe U-Th-Pb Geochronology and Study of Micro-Inclusions in Zircon from the Himalayan High-and Ultrahigh-Pressure Eclogites, Kaghan Valley of Pakistan.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 63:179-196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.04.025 Rehman, H.U., Yamamoto, H., Kaneko, Y., et al., 2007.Thermobaric Structure of the Himalayan Metamorphic Belt in Kaghan Valley, Pakistan.Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 29(2-3):390-406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2006.06.002 Rehman, H.U., Yamamoto, H., Khalil, M.A.K., et al., 2008.Metamorphic History and Tectonic Evolution of the Himalayan UHP Eclogites in Kaghan Valley, Pakistan.Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 103(4):242-254. https://doi.org/10.2465/jmps.080222 Rolfo, F., McClelland, W., Lombardo, B., 2005.Geochronological Constraints on the Age of the Eclogite-Facies Metamorphism in the Eastern Himalaya.Geologie Alpine, Memoire H.S.44, 20th Himalaya-Karakorum-Tibet Workshop, Abstract Volume, 170. Rubatto, D., Chakraborty, S., Dasgupta, S., 2012.Timescales of Crustal Melting in the Higher Himalayan Crystallines (Sikkim, Eastern Himalaya) Inferred from Trace Element-Constrained Monazite and Zircon Chronology.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 165(2):349-372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-012-0812-y Schertl, H.P., O'Brien, P.J., 2013.Continental Crust at Mantle Depths:Key Minerals and Microstructures.Elements, 9(4):261-266. https://doi.org/10.2113/gselements.9.4.261 Searle.M.P., 2007.Diagnostic Features and Processes in the Construction and Evolution of Oman-Zagros-, Himalayan-, Karakoram-, and Tibetan-Type Orogenic Belts.In: Hatcher, R.D., Jr., Carlson, M.P., McBride, J.H., et al., eds., 4-D Framework of Continental Crust.Geological Society of America Memoir, 200: 41-61. Shams, F.A., 1972.Glaucophane-Bearing Rocks from near Topsin, Swat:First Record from Pakistan.Pakistan Journal of Scientific Research, 24:343-345. Singh, P., Saikia, A., Pant, N.C., et al., 2013.Insights into the P-T Evolution Path of Tso Morari Eclogites of the North-Western Himalayas:Constraints on the Geodynamic Evolution of the Region.Journal of Earth System Science, 122(3):677-698. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0307-x Smith, D.C., 1984.Coesite in Clinopyroxene in the Caledonides and Its Implications for Geodynamics.Nature, 310(5979):641-644. https://doi.org/10.1038/310641a0 Sobolev, N.V., Shatsky, V.S., 1990.Diamond Inclusions in Garnets from Metamorphic Rocks:A New Environment for Diamond Formation.Nature, 343(6260):742-746. https://doi.org/10.1038/343742a0 Spencer, D.A., Gebauer, D., 1996.SHRIMP Evidence for a Permian Protolith Age and a 44 Ma Metamorphic Age for the Himalayan Eclogites Upper Kaghan, Pakistan: Implications for the Subduction of Tethys and the Subdivision Terminology of the NW Himalaya.11th Himalaya-Karakorum-Tibet Workshop, Abstract Volume, 147. Spencer, D.A., Ramsay, J., Spencer-Cervato, C., et al., 1990.High Pressure (Eclogite Facies) Metamorphism in the Indian Plate, Northwestern Himalaya, Pakistan.Proceedings of the Second Pakistan Geological Congress, Geological Bulletin University of Peshawar, 23:87-100. Spencer, D.A., Tonarini, S., Pognante, U., 1995.Geochemical and Sr-Nd Isotopic Characterisation of Higher Himalayan Eclogites (and Associated Metabasites).European Journal of Mineralogy, 7(1):89-102. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/7/1/0089 St-Onge, M.R., Rayner, N., Palin, R.M., et al., 2013.Integrated Pressure-Temperature-Time Constraints for the Tso Morari Dome (Northwest India):Implications for the Burial and Exhumation Path of UHP Units in the Western Himalaya.Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 31(5):469-504. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12030 Thanh, N.X., Sajeev, K., Itaya, T., et al., 2011.Multiple Garnet Growth in Garnet-Kyanite-Staurolite Gneiss, Pangong Metamorphic Complex, Ladakh Himalaya:New Constraints on Tectonic Setting.Lithos, 127(3-4):552-563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2011.09.023 Tonarini, S., Villa, I.M., Oberli, F., et al., 1993.Eocene Age of Eclogite Metamorphism in Pakistan Himalaya:Implications for India-Eurasia Collision.Terra Nova, 5(1):13-20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3121.1993.tb00221.x Wang, J.M., Rubatto, D., Zhang, J.J., 2015.Timing of Partial Melting and Cooling Across the Greater Himalayan Crystalline Complex (Nyalam, Central Himalaya):In-Sequence Thrusting and Its Implications.Journal of Petrology, 56(9):1677-1702. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egv050 Wang, J.M., Zhang, J.J., Liu, K., et al., 2016.Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Tectonometamorphic Discontinuities in the Central Himalaya:Constraints from P-T Paths and Geochronology.Tectonophysics, 679:41-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.04.035 Wang, J.M., Zhang, J.J., Wang, X.X., 2013.Structural Kinematics, Metamorphic P-T Profiles and Zircon Geochronology across the Greater Himalayan Crystalline Complex in South-Central Tibet:Implication for a Revised Channel Flow.Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 31(6):607-628. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12036 Wang, Y.H., Zhang, L.F., Zhang, J.J., et al., 2017.The Youngest Eclogite in Central Himalaya:P-T Path, U-Pb Zircon Age and Its Tectonic Implication.Gondwana Research, 41:188-206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.013 Warren, C.J., Grujic, D., Kellett, D.A., et al., 2011.Probing the Depths of the India-Asia Collision:U-Th-Pb Monazite Chronology of Granulites from NW Bhutan.Tectonics, 30(2):46. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010tc002738 Wilke, F.D.H., O'Brien, P.J., Altenberger, U., et al., 2010.Multi-Stage Reaction History in Different Eclogite Types from the Pakistan Himalaya and Implications for Exhumation Processes.Lithos, 114(1-2):70-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2009.07.015 Wilke, F.D.H., O'Brien, P.J., Schmidt, A., et al., 2015.Subduction, Peak and Multi-Stage Exhumation Metamorphism:Traces from one Coesite-Bearing Eclogite, Tso Morari, Western Himalaya.Lithos, 231:77-91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.007 Wu, F.Y., Liu, Z.C., Liu, X.C., et al., 2015.Himalayan Leucogranite:Petrogenesis and Implications to Orogenesis and Plateau Uplift.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1):1-36(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201501001 Xu, Q., Zhao, J.M., Yuan, X.H., et al., 2015.Mapping Crustal Structure beneath Southern Tibet:Seismic Evidence for Continental Crustal Underthrusting.Gondwana Research, 27(4):1487-1493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2014.01.006 Xu, S.T., Okay, A.I., Ji, S.Y., et al., 1992.Diamonds from the Dabie Shan Metamorphic Rocks and Its Implication for Tectonic Setting.Science, 256:80-82. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5053.80 Yin, A., Harrison, T.M., 2000.Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen.Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28(1):211-280. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 Zeiger, K., Gordon, S.M., Long, S.P., et al., 2015.Timing and Conditions of Metamorphism and Melt Crystallization in Greater Himalayan Rocks, Eastern and Central Bhutan:Insight from U-Pb Zircon and Monazite Geochronology and Trace-Element Analyses.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 169(5):1-19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-015-1143-6 Zhang, J.J., Santosh, M., Wang, X.X., et al., 2012.Tectonics of the Northern Himalaya since the India-Asia Collision.Gondwana Research, 21(4):939-960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.004 Zhang, Z.M., Ding, H.X., Dong, X., et al., 2018.High-Temperature Metamorphism, Anataxis and Tectonic Evolution of a Mafic Granulite from the Eastern Himalayan Orogen.Journal of Earth Science, 29(5):1010-1025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-018-0852-y Zhang, Z.M., Ding, H.X., Dong, X., et al., 2019.Formation and Evolution of the Gangdese Magmatic Arc, Southern Tibet.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(2):275-294(in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.18654/1000-0569/2019.02.01 Zhang, Z.M., Dong, X., Ding, H.X., et al., 2017.Metamorphism and Partial Melting and the Himalayan Orogen.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(8):2313-2341(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201505003 Zhang, Z.M., Kang, D.Y., Ding, H.X., et al., 2018.Partial Melting of Himalayan Orogen and Formation Mechanism of Leucogranites.Earth Science, 43(1):82-98(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201801005 Zhang, Z.M., Xiang, H., Dong, X., et al., 2015.Long-Lived High-Temperature Granulite-Facies Metamorphism in the Eastern Himalayan Orogen, South Tibet.Lithos, 212-215:1-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2014.10.009 Zhang, Z.M., Xiang, H., Dong, X., et al., 2017.Oligocene HP Metamorphism and Anatexis of the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence in Yadong Region, East-Central Himalaya.Gondwana Research, 41:173-187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2015.03.002 Zhao, W.L., Morgan, W.J., 1985.Uplift of Tibetan Plateau.Tectonics, 4(4):359-369. https://doi.org/10.1029/tc004i004p00359 Zhao, W.J., Nelson, K.D., Che, J., et al., 1993.Deep Seismic Reflection Evidence for Continental Underthrusting beneath Southern Tibet.Nature, 366(6455):557-559. https://doi.org/10.1038/366557a0 Zheng, Y.F., Xia, Q.X., Chen, R.X., et al., 2011.Partial Melting, Fluid Supercriticality and Element Mobility in Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphic Rocks during Continental Collision.Earth-Science Reviews, 107(3-4):342-374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.04.004 Zhu, D.C., Wang, Q., Cawood, P.A., et al., 2017.Raising the Gangdese Mountains in Southern Tibet.Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth), 122(1):214-223. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016jb013508 Zhu, D.C., Wang, Q., Zhao, Z.D., et al., 2015.Magmatic Record of India-Asia Collision.Scientific Reports, 5(1):14289. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep14289 Zhuang, G.S., Najman, Y., Guillot, S., et al., 2015.Constraints on the Collision and the Pre-Collision Tectonic Configuration between India and Asia from Detrital Geochronology, Thermochronology, and Geochemistry Studies in the Lower Indus Basin, Pakistan.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 432:363-373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.10.026 丁林, Maksatbek, S., 蔡福龙, 等, 2017.印度与欧亚大陆初始碰撞时限、封闭方式和过程.中国科学(D辑:地球科学), 47(3):293-309. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201703003.htm 吴福元, 刘志超, 刘小驰, 等, 2015.喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩.岩石学报, 31(1):1-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200503003 张泽明, 董昕, 丁慧霞, 等, 2017.喜马拉雅造山带的变质作用与部分熔融.岩石学报, 33(8):2313-2341. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201708001 张泽明, 丁慧霞, 董昕, 田作林, 2019.冈底斯岩浆弧的形成与演化.岩石学报, 35(2):275-294. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201902001 张泽明, 康东艳, 丁慧霞, 等, 2018.喜马拉雅造山带的部分熔融与淡色花岗岩成因机制.地球科学, 43(1):82-98. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3726 -









 下载:
下载: