Petrogenesis of Early Paleocene Dengtong Volcanic-Plutonic Complex in Central Lhasa Terrane and Evolution of Crustal High-Silica Magma
-
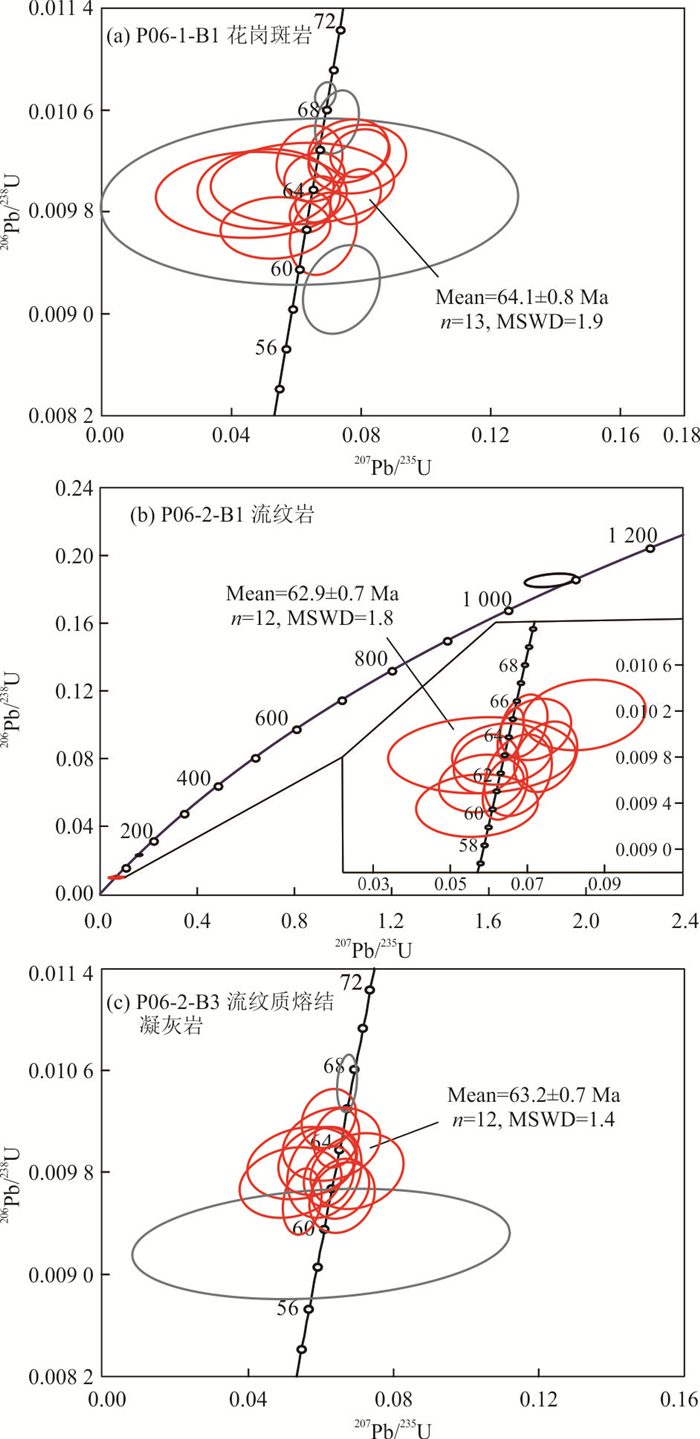
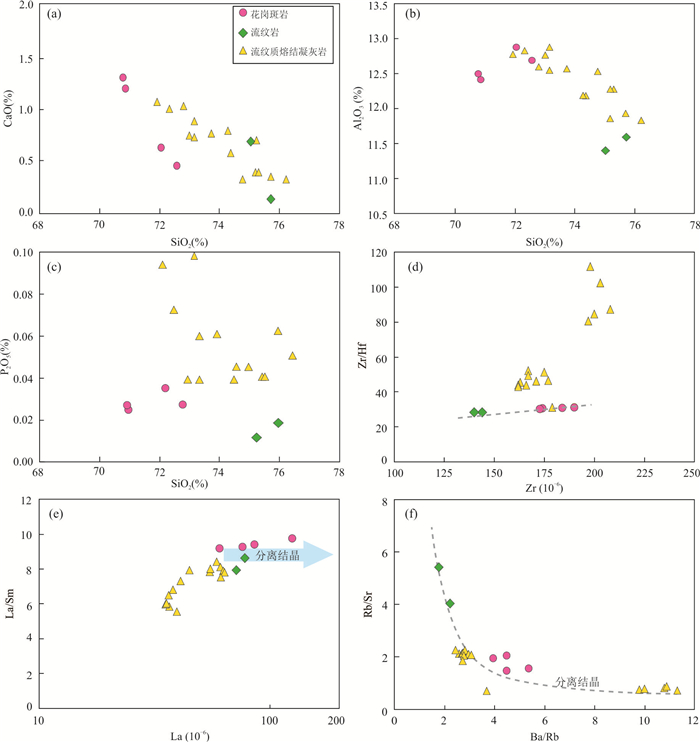
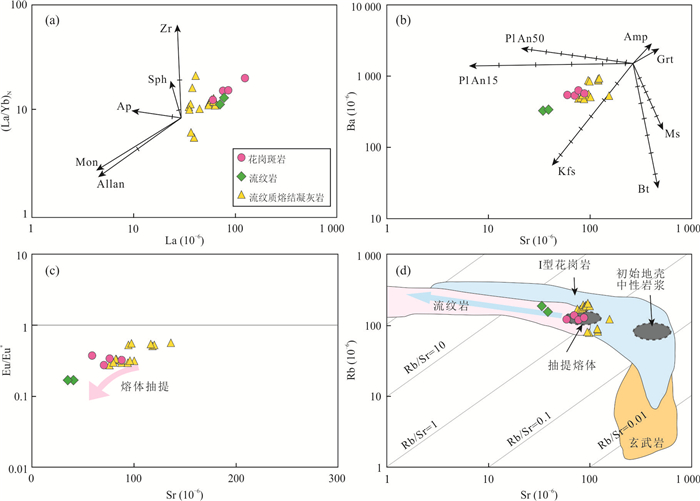
摘要: 花岗岩-流纹岩的成因研究是认识地壳演化机制的重要途径.通过岩石学、地球化学和同位素地质学方法,对拉萨地体中部措麦地区灯垌破火山机构的火山-侵入杂岩进行了成因研究.灯垌火山-侵入杂岩主要由花岗斑岩、流纹岩和流纹质熔结凝灰岩组成,锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄分别为64.1±0.8 Ma、62.9±0.7 Ma和63.2±0.7 Ma,形成时代一致.他们同属高钾钙碱性准铝质-过铝质岩浆岩,亏损高场强元素、富集大离子亲石元素,轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素平坦,具有一致的锆石δ18O值(6.15‰~7.34‰),为同源岩浆演化的产物.流纹岩与花岗斑岩亏损Ba、Sr、P和Ti元素,具显著的负Eu异常,是岩浆发生不同程度分异演化的产物,前者代表晶粥体分离的熔体相,而后者是晶粥体富矿物相部分的产物.流纹质熔结凝灰岩轻重稀土元素分异程度相对较弱,具中等-弱的Eu负异常,是晶粥体自身被活化喷发的产物.结合前人研究成果,认为灯垌火山-侵入杂岩可能形成于古新世新特提斯洋北向俯冲于拉萨地体之下的过程中,俯冲带流体进入地幔楔并使其部分熔融,形成的幔源物质上涌,使地壳部分熔融形成的中酸性岩浆侵入或喷发而形成侵入岩或火山岩.Abstract: Genetic study on the granite-rhyolite associations is an essential way to uncover the mechanism of crustal evoltion. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb dating, and oxygen isotopes of the Dengtong volcanic-plutonic complex in the central Lhasa Terrane are reported in this paper. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb ages for the granite porphyry, rhyolite and rhyolitic ignimbrite samples are 64.1±0.8 Ma, 62.9±0.7 Ma and 63.2±0.7 Ma, respectively. These rocks display similar geochemical characterstics. They are high K calc-alkaline and weakly peraluminous, exhibit HFSE depletion, LILE and LREE enrichment, and flat HREE, with consistent zircon oxygen isotopic composition (δ18O=6.15‰-7.34‰), suggesting consecutive magma evolution of cognate origin. The rhyolite and granite porphyry are depleted in Ba, Sr, P and Ti with significant negative Eu anomaly, indicating conspicuous fractionation. The rhyolite presents the extracted melt from the mush enriched in mineral phases, while the granite porphyry generated from the mush by fractional crystallization. The rhyolitic ignimbrite displays relatively weak negative Eu anomaly, and was generated by the eruption of the residual magma mush. Considering the temporal and spatial distribution of the Paleocene magmatic rocks along the central Lhasa Terrane, it is proposed that the roll-back of the Yarlung-Zangbo Neo-Tethyan oceanic lithosphere subducted beneath the Lhasa Terrane was responsible for the geodynamic regime of the Dengtong volcanic-plutonic complex. The upwelling of the asthenosphere material caused partial melting of lower crust, and resulted in intrusive or volcanic rocks.
-
Key words:
- magma evolution /
- volcanic-plutonic complex /
- zircon U-Pb-O isotopes /
- Lhasa Terrane /
- geochronology /
- geochemistry
-
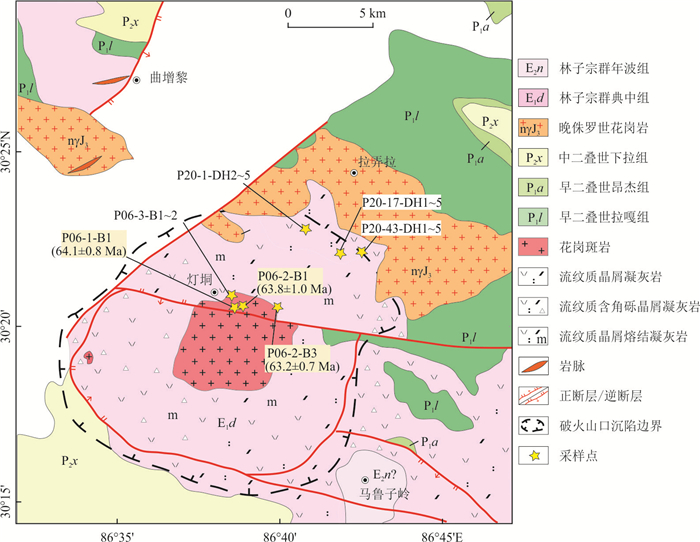
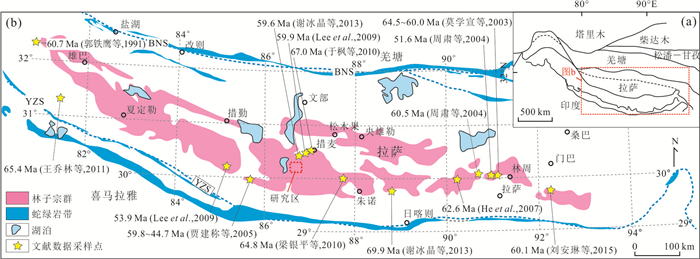
图 1 青藏高原构造单元划分(a)据和拉萨地体林子宗群火山岩分布(b)
图a据Zhang and Zhang (2017);图b据莫宣学等(2003)修改,BNS.班公湖-怒江缝合带,YZS.雅鲁藏布江缝合带
Fig. 1. Tectonic framework of the Tibet Plateau (a) and distribution of the Linzizong Group volcanic rocks at the Lhasa Terrane(b)
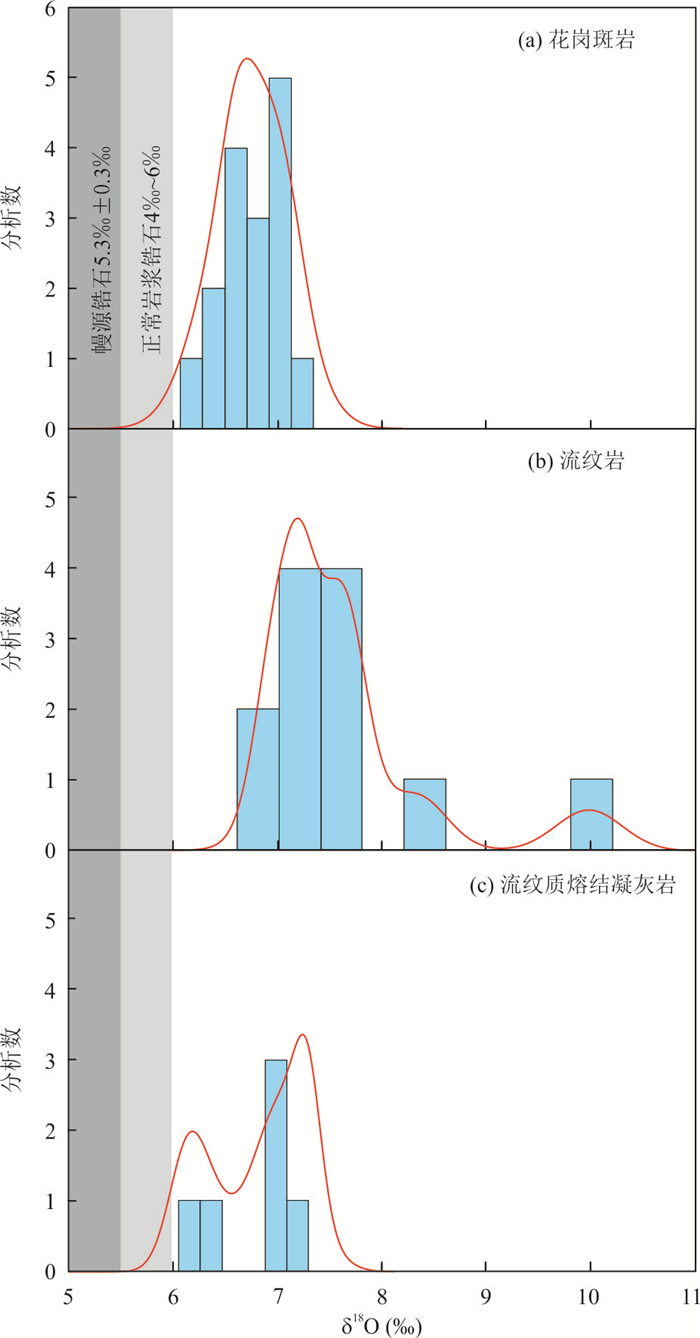
图 5 锆石δ18O值频数分布
幔源锆石δ18O平均值据Valley et al.(1998);正常岩浆锆石δ18O值据Blum et al.(2016)
Fig. 5. Histograms of zircon δ18O values
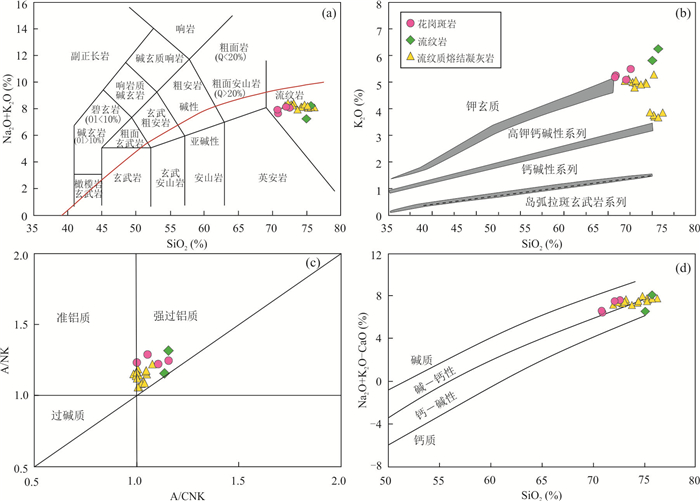
图 6 地球化学分类图解
图a据Irvine and Baragar (1971);图b据Peccerillo and Taylor (1976);图c据Maniar and Piccoli (1989);图d据Frost et al. (2001)
Fig. 6. Geochemical classification diagrams
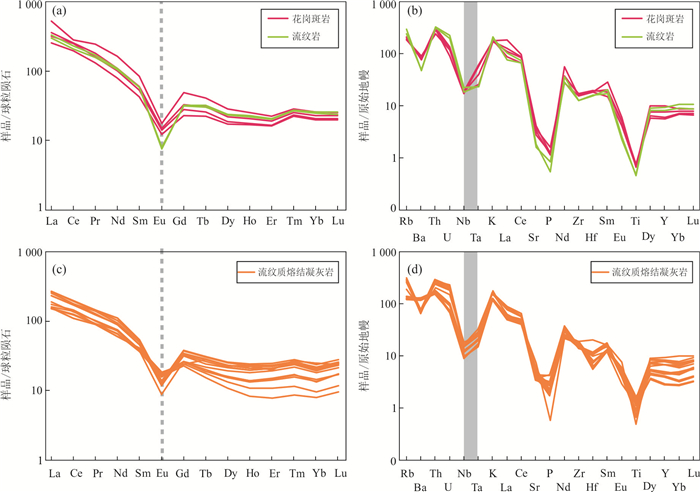
图 7 稀土元素球粒陨石标准化图解(a、c)和微量元素原始地幔标准化图解(b、d) (标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Fig. 7. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, c) and primitive mantle-normalized trace elements spider diagrams (b, d) (normalized values after Sun and McDonough, 1989)
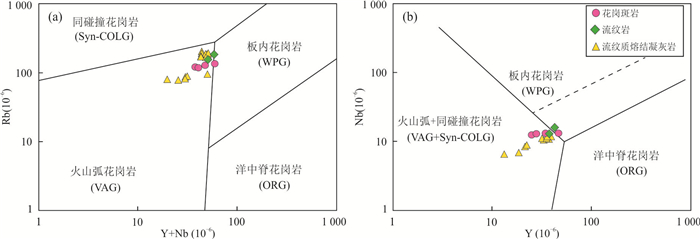
图 10 构造判别图解(据Pearce et al., 1984)
Fig. 10. Tectonic discrimination diagrams (after Pearce et al., 1984)
-
Bachmann, O., Bergantz, G. W., 2004. On the Origin of Crystal-Poor Rhyolites: Extracted from Batholithic Crystal Mushes. Journal of Petrology, 45(8): 1565-1582. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egh019 Bachmann, O., Huber, C., 2016. Silicic Magma Reservoirs in the Earth's Crust. American Mineralogist, 101(11): 2377-2404. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2016-5675 Bindeman, I. N., Ponomareva, V. V., Bailey, J. C., et al., 2004. Volcanic Arc of Kamchatka: A Province with High-δ18O Magma Sources and Large-Scale 18O/16O Depletion of the Upper Crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(4): 841-865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2003.07.009 Blum, T. B., Kitajima, K., Nakashima, D., et al., 2016. Oxygen Isotope Evolution of the Lake Owyhee Volcanic Field, Oregon, and Implications for the Low-δ18O Magmatism of the Snake River Plain-Yellowstone Hotspot and Other Low-δ18O Large Igneous Provinces. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 171(11): 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-016-1297-x Burgisser, A., Bergantz, G. W., 2011. A Rapid Mechanism to Remobilize and Homogenize Highly Crystalline Magma Bodies. Nature, 471(7337): 212-215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09799 Chappell, B. W., White, A. J. R., Williams, I. S., et al., 1999. Discussion and Reply: Evaluation of Petrogenetic Models for Lachlan Fold Belt Granitoids: Implications for Crustal Architecture and Tectonic Models. Australian Journal of Earth Sciences, 46(5): 827-836. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-0952.1999.00742.x Condie, K. C., 2001. Mantle Plumes and Their Record in Earth History. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511810589 Dong, G. C., Mo, X. X., Zhao, Z. D., et al., 2005. A New Understanding of the Stratigraphic Successions of the Linzizong Volcanic Rocks in the Lhünzhub Basin, Northern Lhasa, Tibet, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 24(6): 549-557(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/313201746_A_new_understanding_of_the_stratigraphic_successions_of_the_Lingzizong_volcanic_rocks_in_the_Lh_nzhub_basin_northern_Lhasa_Tibet Frost, B. R., Barnes, C. G., Collins, W. J., et al., 2001. A Geochemical Classification for Granitic Rocks. Journal of Petrology, 42(11): 2033-2048. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033 Gualda, G. A. R., Ghiorso, M. S., 2013. Low-Pressure Origin of High-Silica Rhyolites and Granites. The Journal of Geology, 121(5): 537-545. https://doi.org/10.1086/671395 Guo, T. Y., Liang, D. Y., Zhang, Y. Z., 1991. Ali Geology, Tibet. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press (in Chinese). He, S. D., Kapp, P., DeCelles, P. G., et al., 2007. Cretaceous-Tertiary Geology of the Gangdese Arc in the Linzhou Area, Southern Tibet. Tectonophysics, 433(1-4): 15-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2007.01.005 Hoskin, P. W. O., Schaltegger, U., 2003. The Composition of Zircon and Igneous and Metamorphic Petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27-62. https://doi.org/10.2113/0530027 Hu, X. M., Garzanti, E., Moore, T., et al., 2015. Direct Stratigraphic Dating of India-Asia Collision Onset at the Selandian (Middle Paleocene, 59±1 Ma). Geology, 43(10): 859-862. https://doi.org/10.1130/g36872.1 Ickert, R. B., Hiess, J., Williams, I. S., et al., 2008. Determining High Precision, In Situ, Oxygen Isotope Ratios with a SHRIMP II: Analyses of MPI-DING Silicate-Glass Reference Materials and Zircon from Contrasting Granites. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 114-128. https://doi.org/10.2113/0530027 Irvine, T. N., Baragar, W. R. A., 1971. A Guide to the Chemical Classification of the Common Volcanic Rocks. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8(5): 523-548. https://doi.org/10.1139/e71-055 Jia, J. C., Wen, C. S., Wang, G. H., et al., 2005. Geochemical Characteristics and Geodynamic Significance of the Linzizong Group Volcanic Rocks in the Gangdise Area. Chinese Geology, 32(3): 396-404(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200503007.htm Kemp, A. I. S., Hawkesworth, C. J., Foster, G. L., et al., 2007. Magmatic and Crustal Differentiation History of Granitic Rocks from Hf-O Isotopes in Zircon. Science, 315(5814): 980-983. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1136154 Lee, C. T. A., Morton, D. M., 2015. High Silica Granites: Terminal Porosity and Crystal Settling in Shallow Magma Chambers. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 409: 23-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2014.10.040 Lee, H. Y., Chung, S. L., Lo, C. H., et al., 2009. Eocene Neotethyan Slab Breakoff in Southern Tibet Inferred from the Linzizong Volcanic Record. Tectonophysics, 477(1-2): 20-35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2009.02.031 Lee, H. Y., Chung, S. L., Wang, Y. B., et al., 2007. Age, Petrogenesis and Geological Significance of the Linzizong Volcanic Successions in the Linzhou Basin, Southern Tibet: Evidence from Zircon U-Pb Dates and Hf Isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 493-500(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702026.htm Li, Y., Zhang, S. Z., Li, F. Q., et al., 2018. Zircon U-Pb Ages and Implications of the Dianzhong Formation in Chazi Area, Middle Lhasa Block, Tibet. Earth Science, 43(8): 2755-2766(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201808017.htm Li, Z. H., Zheng, L. L., Li, J. M., et al., 2009. 40Ar-39Ar Dating of Linzizong Volcanic Rocks in the Central Gangdise Area and Its Geological Implication. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 28(3): 223-227(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200903002.htm Liang, Y. P., Zhu, J., Ci, Q., et al., 2010. Zircon U-Pb Ages and Geochemistry of Volcanic Rock from Linzizong Group in Zhunuo Area in Middle Gangdise Belt, Tibet Plateau. Earth Science, 35(2): 211-223(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201002004.htm Linnen, R. L., Samson, I. M., Williams-Jones, A. E., et al., 2014. Geochemistry of the Rare-Earth Element, Nb, Ta, Hf, and Zr Deposits. In: Holland, H.D., Turekian, K.K., eds., Treatise on Geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-08-095975-7.01124-4 Liu, A. L., Zhu, D. C., Wang, Q., et al., 2015. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Age and Origin of the Linzizong Volcanic Rocks from Milashan, Southern Tibet. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(5): 826-833(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/282680271_LA-ICP-MS_zircon_U-Pb_age_and_origin_of_the_Linzizong_volcanic_rocks_from_Milashan_southern_Tibet Maniar, P. D., Piccoli, P. M., 1989. Tectonic Discrimination of Granitoids. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 101(5): 635-643. https://doi.org/10.1130/0016-7606(1989)1010635:tdog>2.3.co;2 doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1989)1010635:tdog>2.3.co;2 McDonough, W. F., Sun, S. S., 1995. The Composition of the Earth. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 223-253. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4 Mo, X. X., Hou, Z. Q., Niu, Y. L., et al., 2007. Mantle Contributions to Crustal Thickening during Continental Collision: Evidence from Cenozoic Igneous Rocks in Southern Tibet. Lithos, 96(1-2): 225-242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.005 Mo, X. X., Zhao, Z. D., Deng, J. F., et al., 2003. Response of Volcanism to the India-Asia Collision. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(3): 135-148(in Chinese with English abstract). http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10026542218 Moyen, J. F., 2009. High Sr/Y and La/Yb Ratios: The Meaning of the "Adakitic Signature". Lithos, 112(3-4): 556-574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.001 Pearce, J. A., Harris, N. B. W., Tindle, A. G., 1984. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 Peccerillo, A., Taylor, S. R., 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene Calc-Alkaline Volcanic Rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00384745 Ruprecht, P., Bachmann, O., 2010. Pre-Eruptive Reheating during Magma Mixing at Quizapu Volcano and the Implications for the Explosiveness of Silicic Arc Volcanoes. Geology, 38(10): 919-922. https://doi.org/10.1130/g31110.1 Simon, L., Lécuyer, C., 2005. Continental Recycling: The Oxygen Isotope Point of View. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 6(8): Q08004. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005gc000958 Streck, M. J., 2014. Evaluation of Crystal Mush Extraction Models to Explain Crystal-Poor Rhyolites. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 284: 79-94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2014.07.005 Sun, S. S., McDonough, W. F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1989.042.01.19 Taylor, R. M., 1968. The Association of Manganese and Cobalt in Soils: Further Observations. Journal of Soil Science, 19(1): 77-80. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2389.1968.tb01522.x Valley, J. W., Kinny, P. D., Schulze, D. J., et al., 1998. Zircon Megacrysts from Kimberlite: Oxygen Isotope Variability among Mantle Melts. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 133(1-2): 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050432 Wang, Q. L., 2011. Geochemistry and Zircon U-Pb Chronology of Linzizong Group Volcanic Rocks in Western Gangdese, Tibet (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, F. Y., Ji, W. Q., Wang, J. G., et al., 2014. Zircon U-Pb and Hf Isotopic Constraints on the Onset Time of India-Asia Collision. American Journal of Science, 314(2): 548-579. https://doi.org/10.2475/02.2014.04 Xie, B. J., Zhou, S., Xie, G. G., et al., 2013. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Data and Regional Contrasts of Geochemical Characteristics of Linzizong Volcanic Rocks from Konglong and Dinrenle Region, Middle Gangdese Belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11): 3803-3814(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286481126_Zircon_SHRIMP_U-Pb_data_and_regional_contrasts_of_geochemical_characteristics_of_Linzizong_volcanic_rocks_from_Konglong_and_Dinrenle_region_middle_Gangdese_belt Yang, H., Xiang, S. Y., Wang, X., et al., 2013. Age and Tectonic Setting of Dianzhong Formation in the Maxiang Area, Tibet, China. Geological Science and Technology Information, 32(4): 89-96(in Chinese with English abstract). Yu, F., Li, Z. G., Zhao, Z. D., et al., 2010. Geochemistry and Implication of the Linzizong Volcanic Succession in Cuomai Area, Central-Western Gangdese, Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2217-2225(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_ysxb98201007022.aspx Zhang, K. J., Zhang, Y. X., Tang, X. C., et al., 2012. Late Mesozoic Tectonic Evolution and Growth of the Tibetan Plateau Prior to the Indo-Asian Collision. Earth-Science Reviews, 114(3-4): 236-249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.06.001 Zhang, Y. X., Zhang, K. J., 2017. Early Permian Qiangtang Flood Basalts, Northern Tibet, China: A Mantle Plume That Disintegrated Northern Gondwana? Gondwana Research, 44: 96-108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2016.10.019 Zhou, S., Mo, X. X., Dong, G. C., et al., 2004. 40Ar/39Ar Ages of Linzizong Igneous Rocks in Linzhou Basin, Tibet. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(20): 2095-2103(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-20-2095 Zhu, D. C., Zhao, Z. D., Pan, G. T., et al., 2009. Early Cretaceous Subduction-Related Adakite-Like Rocks of the Gangdese Belt, Southern Tibet: Products of Slab Melting and Subsequent Melt-Peridotite Interaction? Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(3): 298-309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.05.003 Zou, J. Q., Yu, H. X., Wang, B. D., et al., 2018. Petrogenesis and Geological Implications of Early Jurassic Granodiorites in Renqinze Area, Central Part of Southern Lhasa Subterrane. Earth Science, 43(8): 2795-2810(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201808020.htm 董国臣, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 等, 2005. 拉萨北部林周盆地林子宗火山岩层序新议. 地质通报, 24(6): 549-557. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD200506012.htm 郭铁鹰, 梁定益, 张宜智, 1991. 西藏阿里地质. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社. 贾建称, 温长顺, 王根厚, 等, 2005. 冈底斯地区林子宗群火山岩岩石地球化学特征及地球动力学意义. 中国地质, 32(3): 396-404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200503007.htm 李皓扬, 钟孙霖, 王彦斌, 等, 2007. 藏南林周盆地林子宗火山岩的时代、成因及其地质意义: 锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素证据. 岩石学报, 23(2): 493-500. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200702026.htm 李勇, 张士贞, 李奋其, 等, 2018. 拉萨地块中段查孜地区典中组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地质意义. 地球科学, 43(8): 2755-2766. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.593 李再会, 郑来林, 李军敏, 等, 2009. 冈底斯中段林子宗火山岩40Ar-39Ar年龄及其意义. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 28(3): 223-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH200903002.htm 梁银平, 朱杰, 次邛, 等, 2010. 青藏高原冈底斯带中部朱诺地区林子宗群火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄和地球化学特征. 地球科学, 35(2): 211-223. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2010.021 刘安琳, 朱弟成, 王青, 等, 2015. 藏南米拉山地区林子宗火山岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄和起源. 地质通报, 34(5): 826-833. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201505003.htm 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 邓晋福, 等, 2003. 印度-亚洲大陆主碰撞过程的火山作用响应. 地学前缘, 10(3): 135-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200303019.htm 王乔林, 2011. 冈底斯西段林子宗群火山岩的地球化学特征及锆石年代学研究(硕士学位论文). 北京: 中国地质大学. 谢冰晶, 周肃, 谢国刚, 等, 2013. 西藏冈底斯中段孔隆至丁仁勒地区林子宗群火山岩锆石SHRIMP年龄和地球化学特征的区域对比. 岩石学报, 29(11): 3803-3814. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201311013.htm 杨辉, 向树元, 王欣, 等, 2013. 西藏马乡地区典中组年龄厘定及其构造背景. 地质科技情报, 32(4): 89-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201304015.htm 于枫, 李志国, 赵志丹, 等, 2010. 西藏冈底斯带中西部措麦地区林子宗火山岩地球化学特征及意义. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2217-2225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201007023.htm 周肃, 莫宣学, 董国臣, 等, 2004. 西藏林周盆地林子宗火山岩40Ar/39Ar年代格架. 科学通报, 49(20): 2095-2103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200420013.htm 邹洁琼, 余红霞, 王保弟, 等, 2018. 南拉萨地块中部早侏罗世仁钦则花岗闪长岩成因及其地质意义. 地球科学, 43(8): 2795-2810. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.589 -









 下载:
下载: