Mazhala Gold-Antimony Deposit in Southern Tibet: The Characteristics of OreForming Fluids and The Origin of Gold and Antimony
-
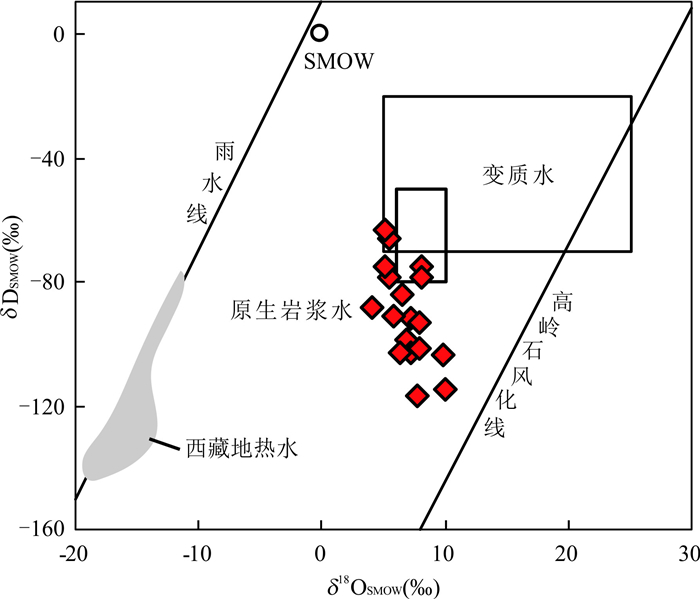
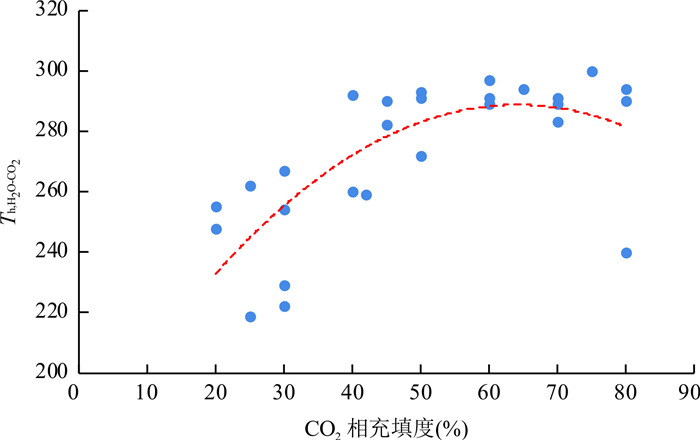
摘要: 马扎拉金-锑矿床是藏南巨型金-锑成矿带的重要组成部分,其矿床成因目前仍存在不同认识.通过主要矿石和蚀变围岩的岩相学、矿相学、流体包裹体和稳定同位素分析,探讨了马扎拉金-锑矿床的成矿流体性质、矿质迁移和沉淀机制.结果表明,马扎拉金-锑矿床成矿流体主要来自岩浆水,主成矿期流体为中温(约255℃)、低盐度(2.8%~3.5% NaCleqv)、富CO2流体,成矿压力约150 MPa,流体演化过程中的CO2与水的不混溶是造成矿质沉淀的主要原因,成矿金属主要来源于地层,特别是区域广泛分布的海相火山岩地层.Abstract: The genesis of Mazhala Au-Sb deposit, which is one of the most important Au-Sb deposits in South Tibet Au-Sb metallogenic belt, is still open to debate. Based on field observation, petrography, microscopy, fluid inclusions, and stable isotopic results, in this paper, it discusses the characteristics of ore-forming fluid, the transportation, and the precipitation mechanism of Au and Sb. It can be concluded that the ore-formng fluid has a dominant magmatic origin, and is of moderate temperature (ca.255℃), low salinity (ca.2.8%-3.5% NaCleqv) and rich in CO2. The estimated ore-forming pressure is about 150 MPa. The unmixing between CO2 and aqueous during the fluid evolution leads to the ore precipitation. The Au, Sb may have been sourced from wall rocks, especially the submarine volcanic rock of them.
-
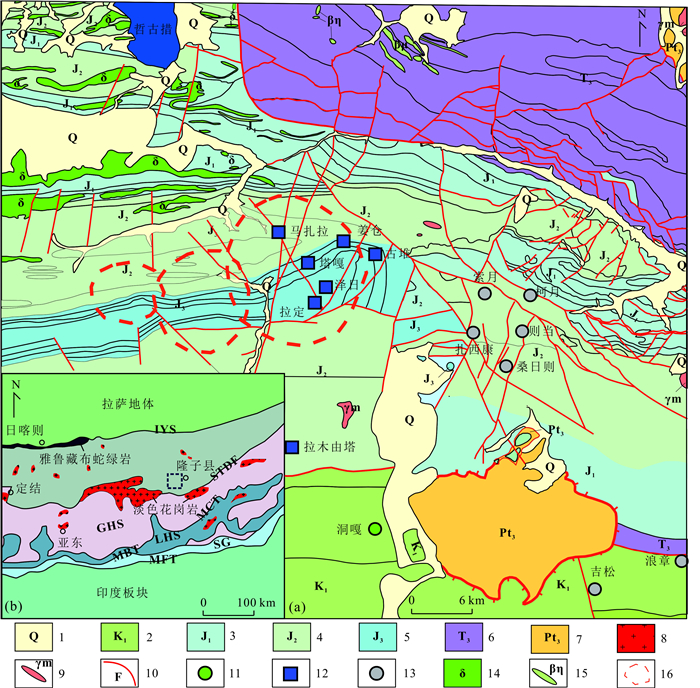
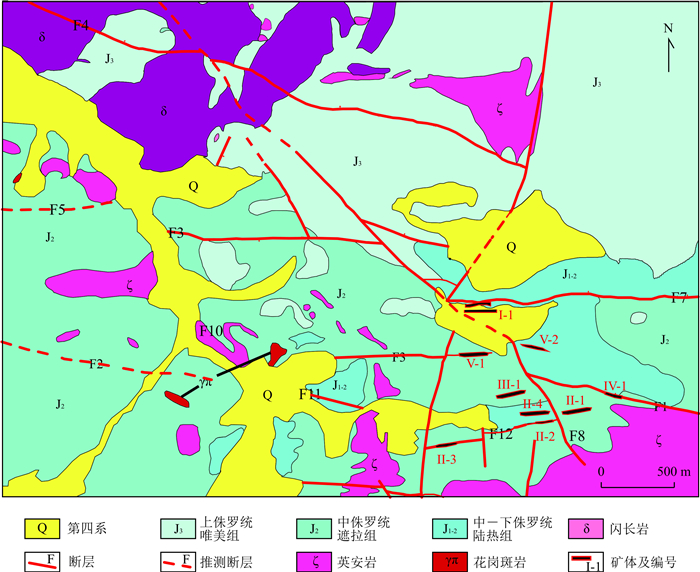
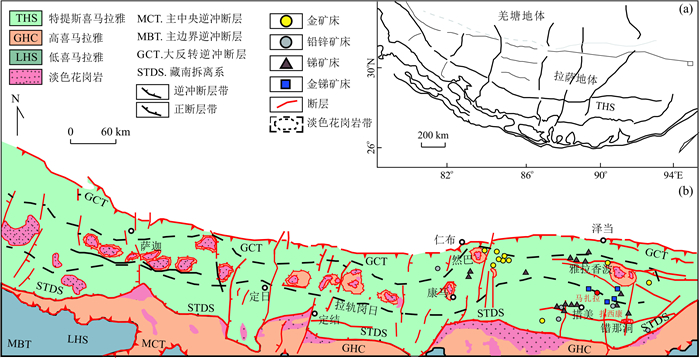
图 2 区域地质图及矿床(点)分布
据李应栩等(2018)修改;1.第四系;2.下白垩统拉康组;3.下侏罗统日当组、陆热组;4.中侏罗统遮拉组;5.上侏罗统桑秀组、唯美组;6.三叠统聂如组;7.二叠统曲德贡组;8.淡色花岗岩;9.花岗岩脉;10.断层;11.W-Sn矿点;12. Au-Sb矿点;13.Pb-Zn矿点;14.闪长岩;15.辉绿岩脉;16.遥感解译推测的环形构造;THS:特提斯喜马拉雅;GHS:高喜马拉雅;LHS:低喜马拉雅;SG:北印度沉积岩系;IYS:雅鲁藏布江缝合带;STDS:藏南拆离系;MCT.主中央逆冲断裂;MBT.边界逆冲断裂;MFT.前锋逆冲断裂
Fig. 2. Regional geological map and the distribution of deposits
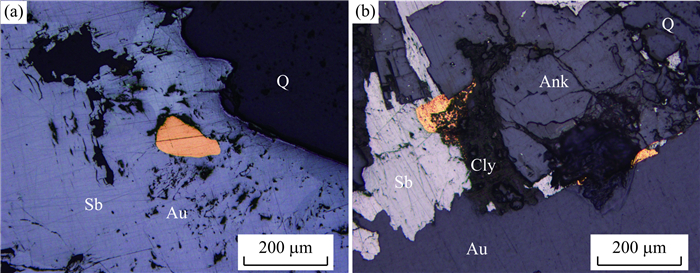
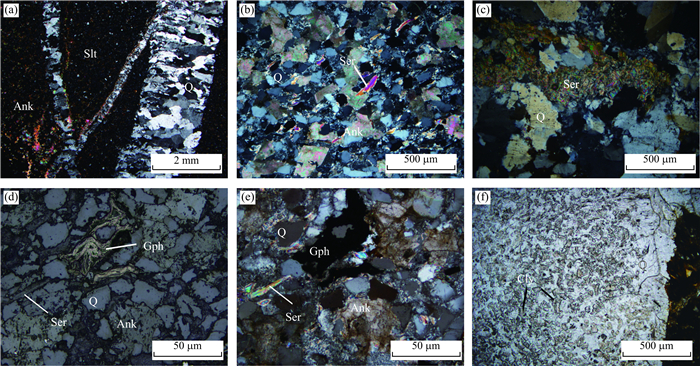
图 7 矿区主要蚀变的显微镜下照片
a.蚀变围岩中的石英-铁白云石脉及边部的碳酸盐化蚀变;b.石英-绢云母化蚀变;c.围岩中的浸染状绢云母和铁白云石;d.围岩中浸染状绢云母、石墨和铁白云石;e.图 7d的透射光下照片;f.围岩中石英-粘土矿物团块;a~c、e为透射光正交偏光,d为反射光单偏光,f为透射光单偏光;Q.石英;Ser.绢云母;Ank.铁白云石;Gph.石墨;Cly.粘土矿物;Slt.板岩
Fig. 7. Microscopic photos of typical alterations in Mazhala deposits
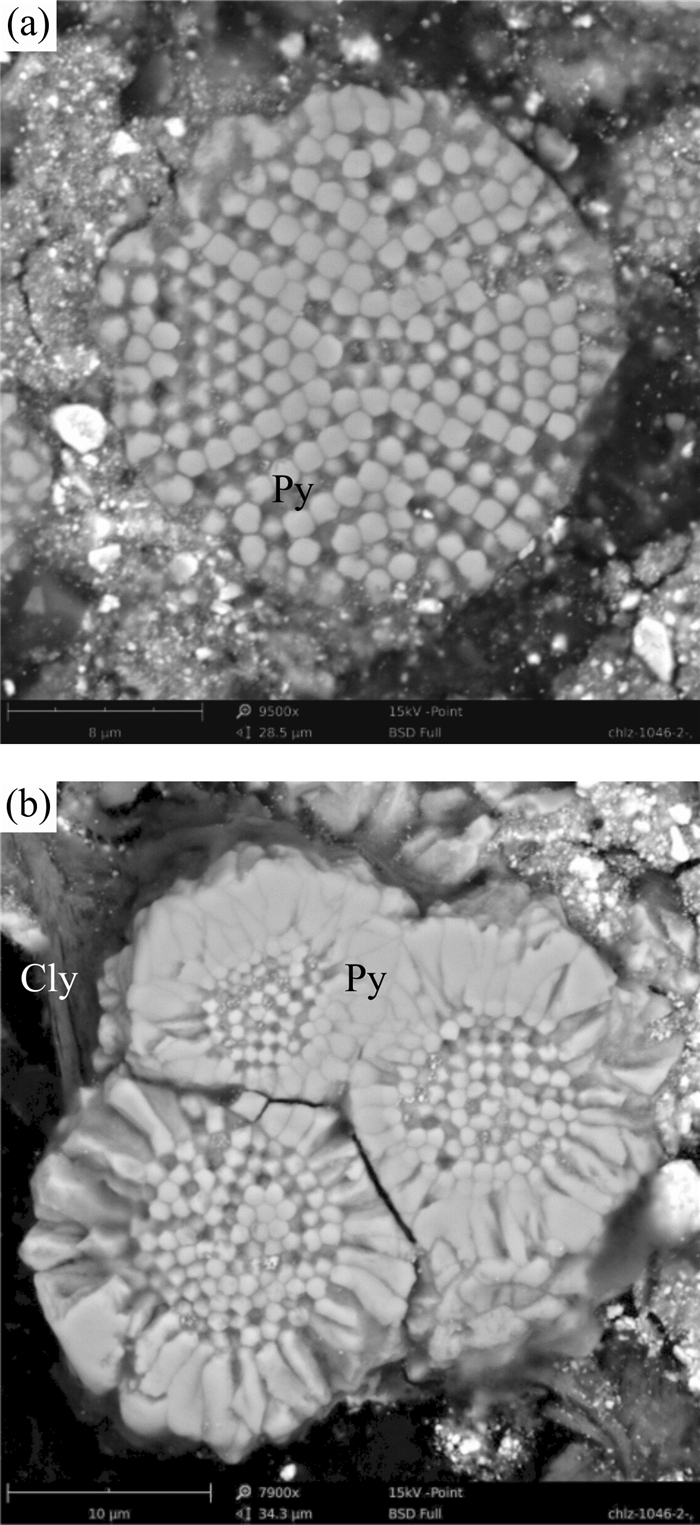
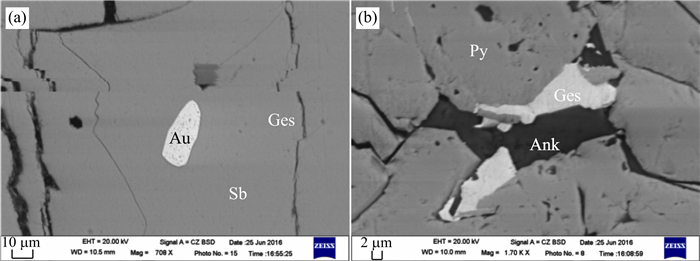
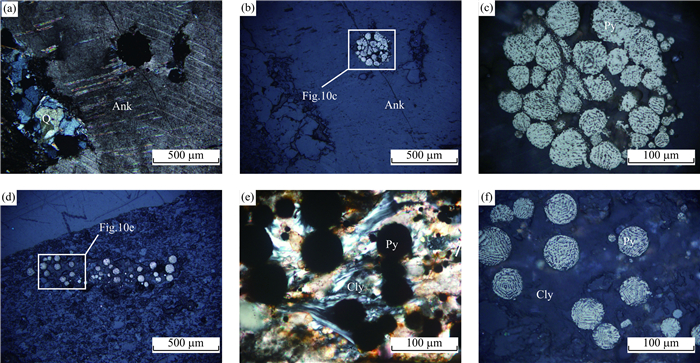
图 9 围岩中黄铁矿和毒砂的显微镜下照片
a.蚀变围岩中具环带的自形黄铁矿和自形毒砂;b.葵花状黄铁矿,中部为草霉状黄铁矿群;c.图 9b的局部放大照片;d.黄铁矿中包裹自形毒砂;Py.黄铁矿;Apy.毒砂;反射光,单偏光
Fig. 9. Microscopic photos of pyrite and arsenopyrite in altered country rock
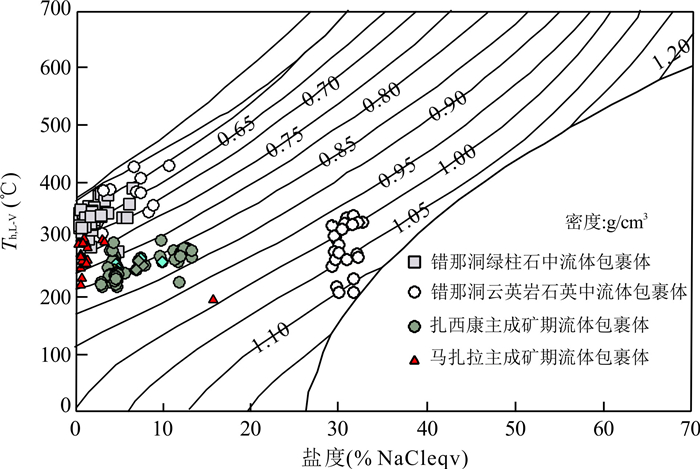
图 14 马扎拉金锑矿床主成矿阶段流体包裹体温度-盐度图解
错那洞和扎西康数据引自Xie et al.(2017)
Fig. 14. The temperature-salinity diagram of fluid inclusions for main ore-forming stage in Mazhala Au-Sb deposit
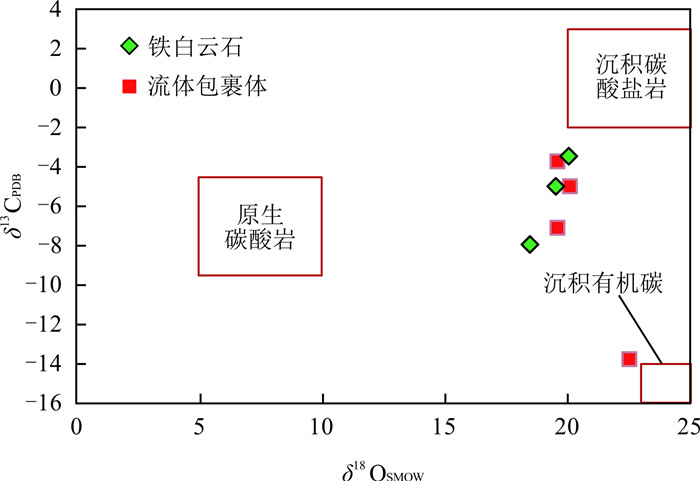
图 17 马扎拉金矿铁白云石和石英流体包裹体中CO2的C-O同位素图解
沉积碳酸盐C-O同位素范围引自Baker and Fallick(1989);原生碳酸岩的C-O同位素范围引自Deines and Gold(1973);沉积有机碳的C-O同位素范围引自Anderson and Arthur(1983)
Fig. 17. C-O isotopic diagram of ankerite and CO2 in fluid inclusions hosted in quartz
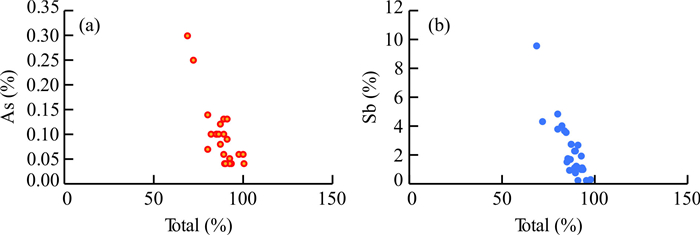
表 1 藏南马扎拉金锑矿床碳酸盐矿物和石英中流体包裹体中CO2碳同位素测试结果
Table 1. Carbon isotope results of CO2 in fluid inclusion hosted in quartz for Mazhala Au-Sb deposit
样品号 矿物 样品描述 δ13CV-PDB
(‰)δ18OV-SMOW
(‰)MZL-2025 石英 石英碳酸盐 -5.0 20.1 MZL-1039-2 石英 石英碳酸盐脉 -3.7 19.6 MZL-1008 石英 石英脉 -7.1 19.6 MZL-B127 石英 石英晶簇 -13.8 22.5 表 2 藏南马扎拉金锑矿床铁白云石的碳同位素测试结果
Table 2. Carbon isotope results of ankerite in Mazhala Au-Sb deposit
样品号 矿物 样品描述 δ13CV-PDB
(‰)δ18OV-SMOW
(‰)MZL-2025 铁白云石 石英碳酸盐脉 -7.7 18.3 MZL-1039 铁白云石 石英碳酸盐脉 -3.5 20 MZL-1008 铁白云石 石英碳酸盐脉 -5.0 19.5 表 3 藏南马扎拉金锑矿床硫同位素测试值
Table 3. Result of sulfur isotope assay in Mazhala Au-Sb deposit
样品号 矿物 样品描述 δ34SV-CDT(%) MZL-B124 黄铁矿 地层 -26.9 MZL-B112 黄铁矿 地层 -34.4 MZL-1008 辉锑矿 石英辉锑矿脉 0.7 MZL-B127 辉锑矿 石英辉锑矿脉 1.9 -
Aikman, A.B., Harrison, T.M., Lin, D., 2008.Preliminary Results from the Yala-Xiangbo Leucogranite Dome, SE Tibet.Himalayan Journal of Sciences, 2(4):91. doi: 10.3126/hjs.v2i4.809 Anderson, T.F., Arthur, M.A., 1983.Stable Isotopes of Oxygen and Carbon and Their Application to Sedimentologic and Paleoenvironmental Problems. In: Anderson, T. F., Arthur, M.A., eds., Stable Isotopes in Sedimentary Geology.Society for Sedimentary Geology, Tulsa, Oklahoma. Baker, A.J., Fallick, A.E., 1989.Evidence from Lewisian Limestones for Isotopically Heavy Carbon in Two-Thousand-Million-Year-Old Sea Water.Nature, 337:352-354. doi: 10.1038/337352a0 Boyle, R.W., Jonasson, I.R., 1984. The Geochemistry of Antimony and Its Use as an Indicator Element in Geochemical Prospecting.Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 20(3):223-302. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(84)90071-2 Burg, J.P., Chen, G.M., 1984.Tectonics and Structural Zonation of Southern Tibet, China.Nature, 311:219-223. doi: 10.1038/311219a0 Craig, H., 1961. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science, 133(3465):1702-1703. doi: 10.1126/science.133.3465.1702 Deines, P., Gold, D. P., 1973. The Isotopic Composition of Carbonatite and Kimberlite Carbonates and Their Bearing on the Isotopic Composition of Deep-Seated Carbon.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 37(7):1709-1733. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(73)90158-0 Diedesch, T. F., Jessup, M. J., Cottle, J. M., et al., 2016. Tectonic Evolution of the Middle Crust in Southern Tibet from Structural and Kinematic Studies in the Lhagoi Kangri Gneiss Dome.Lithosphere, 8(5):480-504. doi: 10.1130/L506.1 Dong, L., Li, G. M., Li, Y. X., et al., 2016. Basalts from the Mazhala Area in Southern Xizang:Geochemistry, Petrogenesis and Geological Implications.Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 36(3):16-24(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-TTSD201603003.htm Fu, J.G., Li, G.M., Wang, G.H., et al., 2017.First Field Identification of the Cuonadong Dome in Southern Tibet:Implications for EW Extension of the North Himalayan Gneiss Dome. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 106(5):1581-1596. doi: 10.1007/s00531-016-1368-2 Gehrels, G.E., Yin, A., Wang, X.F., 2003.Magmatic History of the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau.Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 108(B9). https://doi.org/10.1029/2002jb001876 Guo, Z. F., Wilson, M., 2012. The Himalayan Leucogranites:Constraints on the Nature of Their Crustal Source Region and Geodynamic Setting. Gondwana Research, 22(2):360-376. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.07.027 Hall, D.L., Sterner, S.M., Bodnar, R.J., 1988.Freezing Point Depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O Solutions.Economic Geology, 83(1):197-202. Harris, N., Massey, J., 1994. Decompression and Anatexis of Himalayan Metapelites.Tectonics, 13(6):1537-1546. doi: 10.1029/94TC01611 Harris, N., Massey, J., Inger, S., 1993. The Role of Fluids in the Formation of High Himalayan Leucogranites.Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 74(1):391-400. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1993.074.01.26 Harrison, M.T., Grove, M., Mckeegan, K.D., et al., 1999.Origin and Episodic Emplacement of the Manaslu Intrusive Complex, Central Himalaya.Journal of Petrology, 40(1):3-19. doi: 10.1093/petroj/40.1.3 Hou, Z. Q., Cook, N. J., Zaw, K., 2009. Metallogenesis of the Tibetan Collisional Orogen. Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3):1. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.07.002 Hou, Z.Q., Mo, X.X., Yang, Z.M., et al., 2006a.Metallogeneses in the Collisional Orogen of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau:Tectonic Setting, Tempo-Spatial Distribution and Ore Deposit Types. Geology in China, 33(2):340-351(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200602013.htm Hou, Z.Q., Yang, Z.S., Xu, W.Y., et al., 2006b.Metallogenesis in Tibetan Collisional Orogenic Belt:Ⅰ. Mineralization in Main Collisional Orogenic Setting.Mineral Deposits, 25(4):337-358 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hou, Z.Q, Qu, X.M, Yang, Z.S, et al., 2006c.Metallogenesis in Tibetan Collisional Orogenic Belt:Ⅲ. Mineralization in Post-Collisional Extension Setting.Mineral Deposits, 25(6):629-651 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hou, Z.Q., Zhang, H.R., 2015.Geodynamics and Metallogeny of the Eastern Tethyan Metallogenic Domain.Ore Geology Reviews, 70:346-384. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.026 Hou, Z.Q., Zheng, Y.C., Zeng, L.S., et al., 2012.Eocene-Oligocene Granitoids in Southern Tibet:Constraints on Crustal Anatexis and Tectonic Evolution of the Himalayan Orogen.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 349-350:38-52. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2012.06.030 Jeffrey, L., Hacker, B.R., Dinklage, W.S., et al., 2000.Evolution of the Kangmar Dome, Southern Tibet:Structural, Petrologic, and Thermochronologic Constraints.Tectonics, 19(5):872-895. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999tc001147 Jiang, S.H., Nie, F.J., Hu, P., et al., 2009.Mayum:An Orogenic Gold Deposit in Tibet, China.Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3):160-173. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.03.006 Jochum, K. P., Hofmann, A. W., 1997. Constraints on Earth Evolution from Antimony in Mantle-Derived Rocks. Chemical Geology, 139(1-4):39-49. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00032-6 Jochum, K.P., Verma, S.P., 1996.Extreme Enrichment of Sb, Tl and Other Trace Elements in Altered MORB.Chemical Geology, 130(3-4):289-299. doi: 10.1016/0009-2541(96)00014-9 Kali, E., Leloup, P. H., Arnaud, N., et al., 2010. Exhumation History of the Deepest Central Himalayan Rocks, Ama Drime Range:Key Pressure-Temperature-Deformation-Time Constraints on Orogenic Models.Tectonics, 29(2): https://doi.org/10.1029/2009tc002551 Li, G.M., Rui, Z.Y., 2004.Diagenetic and Mineralization Ages for the Porphyry Copper Deposits in the Gangdise Metallogenic Belt, Southern Xizang.Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 28(2):165-170(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200402008 Li, G.M., Zeng, Q.G., Yong, Y.Y., et al., 2005.Discovery of Epithermal Au-Sb Deposits in Gangdese Metallogenic Belt of Tibet and Its Significance:Case Study of Longruri Au-Sb Deposit. Mineral Deposits, 24(6):595-602(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KCDZ200506002.htm Li, G.M., Zhang, L.K., Jiao, Y.J., et al., 2017.First Discovery and Implications of Cuonadong Superlarge Be-W-Sn Polymetallic Deposit in Himalayan Metallogenic Belt, Southern Tibet. Mineral Deposits, 36(4):1003-1008(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kcdz201704014 Li, J.G., Wang, Q.H., Chen, J.K., et al., 2002.Study of Metallogenic and Prospecting Models for the Shalagang Antimony Deposit, Gyangze, Tibet.Journal of Chengdu Universityof Technology, 29(5):533-538(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb200205011 Li, Y.X., Li, G.M., Dong, L., et al., 2018.Geology and Exploration Potential of the Mazhala Gold Deposit, Cuomei, Xizang:An Approach. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 38(3):90-100(in Chinese with English abstract). Lin, B., Tang, J. X., Zheng, W. B., et al., 2016. Geochemical Characteristics, Age and Genesis of Cuonadong Leucogranite, Tibet. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 35(3):391-406 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yskwxzz201603002 Liu, H.B., Jin, G.S., Li, J.J., et al., 2013.Determination of Stable Isotope Composition in Uranium Geological Samples.World Nuclear Geoscience, 30(3):174-179(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sjhdzkx201303009 Matsuhisa, Y., Goldsmith, J.R., Clayton, R.N., 1979.Oxygen Isotopic Fractionation in the System Quartz-Albite-Anorthite-Water. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 43(7):1131-1140. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(79)90099-1 Mo, R. W., Sun, X. M., Zhai, W., et al., 2013. Ore-Forming Fluid Geochemistry and Metallogenic Mechanism from Mazhala Gold-Antimony Deposit in Southern Tibet, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4):1427-1438(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201304025 Nie, F.J., Hu, P., Jiang, S.H., et al., 2005.Type and Temporal-Spatial Distribution of Gold and Antimony Deposits(Prospects) in Southern Tibet, China.Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(3):373-385(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200503009 Pearson, O.N., DeCelles, P.G., 2005.Structural Geology and Regional Tectonic Significance of the Ramgarh Thrust, Himalayan Fold-Thrust Belt of Nepal. Tectonics, 24(4). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003tc001617 Qing, C.S., Ding, J., Li, Y.X., et al., 2014.Element Combination Anomalies and Prospecting Direction in Mazhala Gold-Antimony Deposit. Metal Mine, (12):134-137(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsks201412029 Raymond, J., Williams-Jones, A.E., Clark, J.R., 2005.Mineralization Associated with Scale and Altered Rock and Pipe Fragments from the Berlín Geothermal Field, El Salvador; Implications for Metal Transport in Natural Systems.Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 145(1-2):81-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2005.01.003 Reyes, A.G., Trompetter, W.J., Britten, K., et al., 2003.Mineral Deposits in the Rotokawa Geothermal Pipelines, New Zealand. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 119(1-4):215-239. doi: 10.1016/S0377-0273(02)00355-4 Robb, L., 2007.Introduction to Ore-Forming Processes. Blackwell Publishing, England. Spycher, N.F., Reed, M.H., 1989.As (Ⅲ) and Sb (Ⅲ) Sulfide Complexes:An Evaluation of Stoichiometry and Stability from Existing Experimental Data.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 53(9):2185-2194. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(89)90342-6 Sun, X. M., Zhang, Y., Xiong, D. X., et al., 2009. Crust and Mantle Contributions to Gold-Forming Process at the Daping Deposit, Ailaoshan Gold Belt, Yunnan, China.Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3):235-249. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.05.002 Taylor, H.P., 1974.The Application of Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Studies to Problems of Hydrothermal Alteration and Ore Deposition.Economic Geology, 69(6):843-883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843 Visonà, D, Lombardo, B., 2002. Two-Mica and Tourmaline Leucogranites from the Everest-Makalu Region (Nepal-Tibet). Himalayan Leucogranite Genesis by Isobaric Heating? Lithos, 62(3-4):125-150. doi: 10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00112-3 Wagner, T., Lee, J., Hacker, B.R., et al., 2010.Kinematics and Vorticity in Kangmar Dome, Southern Tibet:Testing Midcrustal Channel Flow Models for the Himalaya.Tectonics, 29(6). https://doi.org/10.1029/2010tc002746 Wang, J.H., Yin, A., Harrison, T.M., et al., 2001.A Tectonic Model for Cenozoic Igneous Activities in the Eastern Indo-Asian Collision Zone. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 188(1-2):123-133. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(01)00315-6 Wilson, N., Webster-Brown, J., Brown, K., 2007.Controls on Stibnite Precipitation at Two New Zealand Geothermal Power Stations.Geothermics, 36(4):330-347. doi: 10.1016/j.geothermics.2007.04.001 Wu, F.Y., Liu, Z.C., Liu, X.C., et al., 2015.Himalayan Leucogranite:Petrogenesis and Implications to Orogenesis and Plateau Uplift. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1):1-36(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201501001 Wu, Z.H., Ye, P.S., Wu, Z.H., et al., 2014.LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb Ages of Tectonic-Thermal Events in the Yalaxiangbo Dome of Tethys Himalayan belt. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(5):595-605. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgqydz201405001 Xie, Y.L., Hou, Z., Goldfarb, R.J., et al., 2016.Rare Earth Element Deposits in China.Society of Economic Geologists, 18:115-136. Xie, Y.L., Li, L.M., Wang, B.G., et al., 2017.Genesis of the Zhaxikang Epithermal Pb-Zn-Sb Deposit in Southern Tibet, China:Evidence for a Magmatic Link. Ore Geology Reviews, 80:891-909. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.08.007 Xie, Y. L., Wang, B. G., Guo, X., et al., 2014. Fluid Inclusion Study of Pegmatite in Zhaxikang Pb-Zn-Sb Polymetallic Deposit, Tibet, China. Acta Geologica Sinica(English Edition), 88(Suppl.2):1183-1185. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=WFHYXW592465 Yang, Z. M., Cook, D. R., 2019. Porphyry Copper Deposits in China.Economic Geology, Special Publication(in press). Yang, Z. S., Hou, Z. Q., Gao, W., et al., 2006. Metallogenic Characteristics and Genetic Model of Antimony and Gold Deposits in South Tibetan Detachment System.Acta Geologica Sinica, 80(9):1377-1391(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200609013 Yang, Z. S., Hou, Z. Q., Meng, X. J., et al., 2009. Post-Collisional Sb and Au Mineralization Related to the South Tibetan Detachment System, Himalayan Orogen.Ore Geology Reviews, 36(1-3):194-212. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.03.005 Yin, A., 2006.Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Himalayan Orogen as Constrained by along-Strike Variation of Structural Geometry, Exhumation History, and Foreland Sedimentation.Earth-Science Reviews, 76(1-2):1-131. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.05.004 Yin, A., Harrison, T.M., 2000.Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28(1):211-280. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 Zakaznova-Iakovleva, V. P., Migdisov, A. A., Zakaznova-Iakovlevaa, V. P., et al., 2001. An Experimental Study of Stibnite Solubility in Gaseous Hydrogen Sulphide from 200 to 320℃.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(2):289-298. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00523-8 Zhai, W., Sun, X.M., Yi, J.Z., et al., 2014.Geology, Geochemistry, and Genesis of Orogenic Gold-Antimony Mineralization in the Himalayan Orogen, South Tibet, China.Ore Geology Reviews, 58:68-90. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.11.001 Zhai, W., Zheng, S.Q., Sun, X.M., et al., 2018.He-Ar Isotope Compositions of Orogenic Mazhala Au-Sb and Shalagang Sb Deposits in Himalayan Orogeny, Southern Tibet:Constrains to Ore-Forming Fluid Origin.Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(12):3525-3538(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB201812005.htm Zhang, H. F., Harris, N., Parrish, R., et al., 2005. Geochemistry of North Himalayan Leucogranites:Regional Comparison, Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications. Earth Science, 30(3):275-288(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dqkx200503003.htm Zhang, J.F., Zheng, Y.Y., Zhang, G.Y., et al., 2011.Geologic Characteristic and Mineralization of Mazhala Gold-Antimony Deposit in Northern Himalaya.Gold, 32(1):20-24(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=huangj201101005 Zhang, J. Y., Liao, Q. A., Li, D. W., et al., 2003. Laguigangri Leucogranites and Its Relation with Laguigangri Metamorphic Core Complex in Sajia, South Tibet.Earth Science, 28(6):695-701 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200306018 Zhang, L. K., Zhang, Z., Li, G. M., et al., 2018. Rock Assem-blage, Structural Characteristics and Genesis Mechanism of the Cuonadong Dome, Tethys Himalaya.Earth Science, 43(8):2664-2683(in Chinese with English abstract). Zheng, Y.Y., Sun, X., Tian, L.M., et al., 2014.Mineralization, Deposit Type and Metallogenic Age of the Gold Antimony Polymetallic Belt in the Eastern Part of North Himalayan. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 38(1):108-118(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201401011 董磊, 李光明, 李应栩, 等, 2016.藏南马扎拉地区玄武岩地球化学特征、成因及其地质意义.沉积与特提斯地质, 36(3):16-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2016.03.003 侯增谦, 莫宣学, 杨志明, 等, 2006a.青藏高原碰撞造山带成矿作用:构造背景、时空分布和主要类型.中国地质, 33(2):340-351. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi200602013 侯增谦, 曲晓明, 杨竹森, 等, 2006c.青藏高原碰撞造山带:Ⅲ.后碰撞伸展成矿作用.矿床地质, 25(6):629-651. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200604001 侯增谦, 杨竹森, 徐文艺, 等, 2006b.青藏高原碰撞造山带:Ⅰ.主碰撞造山成矿作用.矿床地质, 25(4):337-358. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz200604001 李光明, 芮宗瑶, 2004.西藏冈底斯成矿带斑岩铜矿的成岩成矿年龄.大地构造与成矿学, 28(2):165-170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2004.02.008 李光明, 张林奎, 焦彦杰, 等, 2017.西藏喜马拉雅成矿带错那洞超大型铍锡钨多金属矿床的发现及意义.矿床地质, 36(4):1003-1008. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz201704014 李光明, 曾庆贵, 雍永源, 等, 2005.西藏冈底斯成矿带浅成低温热液型金锑矿床的发现及其意义:以西藏弄如日金锑矿床为例.矿床地质, 24(6):595-602. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2005.06.003 李金高, 王全海, 陈健坤, 等, 2002.西藏江孜县沙拉岗锑矿床成矿与找矿模式的初步研究.成都理工学院学报, 29(5):533-538. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2002.05.011 李应栩, 李光明, 董磊, 等, 2018.西藏马扎拉金矿区外围地质特征与找矿方向.沉积与特提斯地质, 38(3):90-100. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yxgdl201803010 林彬, 唐菊兴, 郑文宝, 等, 2016.西藏错那洞淡色花岗岩地球化学特征、成岩时代及岩石成因.岩石矿物学杂志, 35(3):391-406. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2016.03.002 刘汉彬, 金贵善, 李军杰, 等, 2013.铀矿地质样品的稳定同位素组成测试方法.世界核地质科学, 30(3):174-179. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2013.03.009 莫儒伟, 孙晓明, 翟伟, 等, 2013.藏南马扎拉金锑矿床成矿流体地球化学和成矿机制.岩石学报, 29(4):1427-1438. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201304025 聂凤军, 胡朋, 江思宏, 等, 2005.藏南地区金和锑矿床(点)类型及其时空分布特征.地质学报, 79(3):373-385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2005.03.009 卿成实, 丁俊, 李应栩, 等, 2014.马扎拉金锑矿元素组合异常及找矿方向.金属矿山, (12):134-137. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsks201412029 吴福元, 刘志超, 刘小驰, 等, 2015.喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩.岩石学报, 31(1):1-36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx200503003 杨竹森, 侯增谦, 高伟, 等, 2006.藏南拆离系锑金成矿特征与成因模式.地质学报, 80(9):1377-1391. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2006.09.013 翟伟, 郑思琦, 孙晓明, 等, 2018.藏南喜马拉雅造山带造山型马扎拉Au-Sb矿床和沙拉岗Sb矿床流体包裹体He-Ar同位素组成:对成矿流体来源的制约.岩石学报, 34(12):3525-3538. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ysxb98201812005 张宏飞, Harris, N., Parrish, R., 等, 2005.北喜马拉雅淡色花岗岩地球化学:区域对比、岩石成因及其构造意义.地球科学, 30(3):275-288. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=1410 张建芳, 郑有业, 张刚阳, 等, 2011.西藏北喜马拉雅马扎拉金锑矿床地质特征及成矿作用.黄金, 32(1):20-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1277.2011.01.005 张金阳, 廖群安, 李德威, 等, 2003.藏南萨迦拉轨岗日淡色花岗岩特征及与变质核杂岩的关系.地球科学, 28(6):695-701. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2003.06.018 张林奎, 张志, 李光明, 等, 2018.特提斯喜马拉雅错那洞穹隆的岩石组合、构造特征与成因.地球科学, 43(8):2664-2683. http://earth-science.net/WebPage/Article.aspx?id=3904 郑有业, 孙祥, 田立明, 等, 2014.北喜马拉雅东段金锑多金属成矿作用、矿床类型与成矿时代.大地构造与成矿学, 38(1):108-118. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/ddgzyckx201401011 -
 dqkx-44-6-1998-Table.pdf
dqkx-44-6-1998-Table.pdf

-









 下载:
下载: