Water of Garnet in Eclogite from Jinheqiao Area in the Dabie Orogen
-
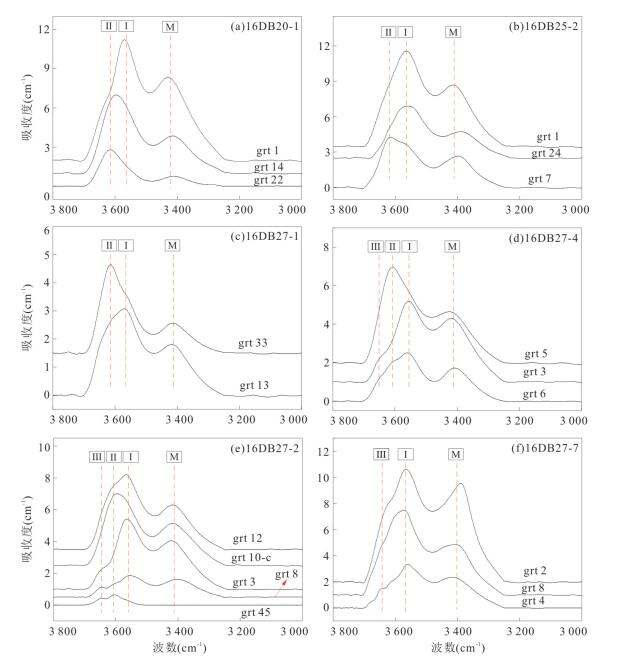
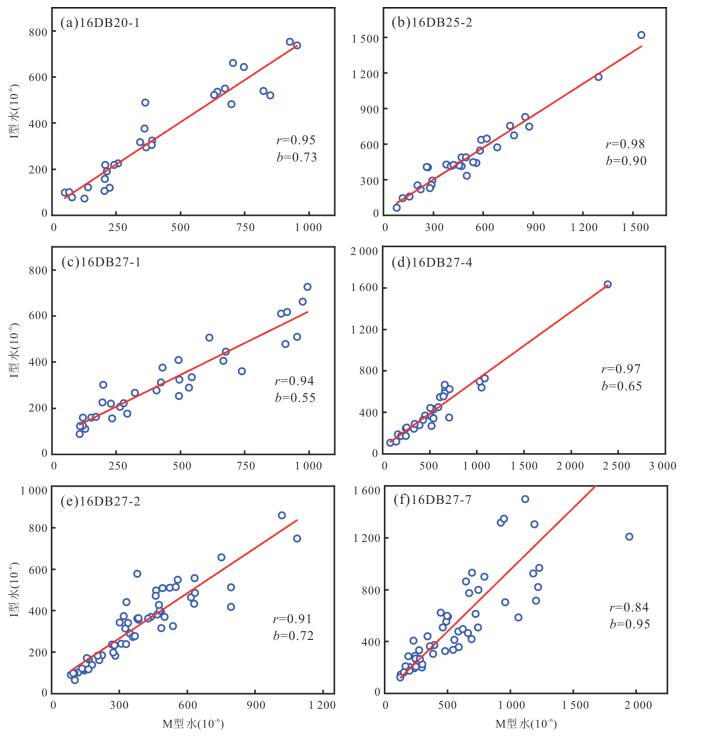
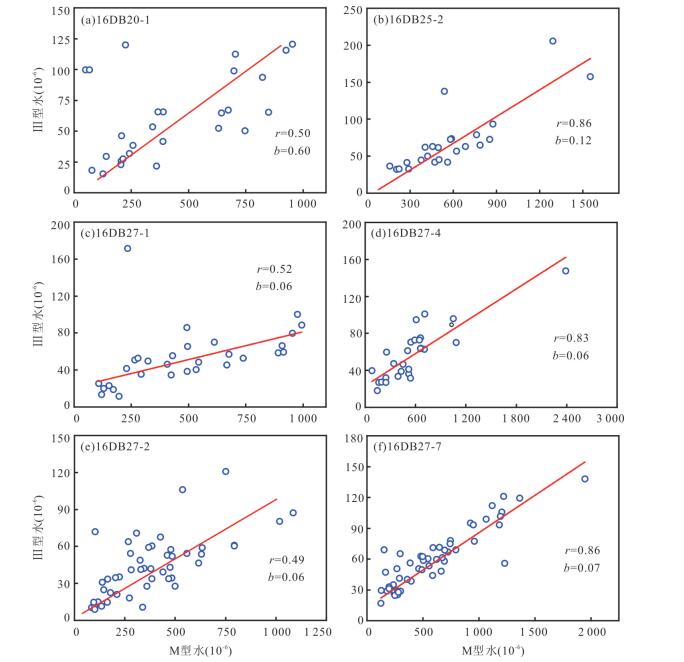
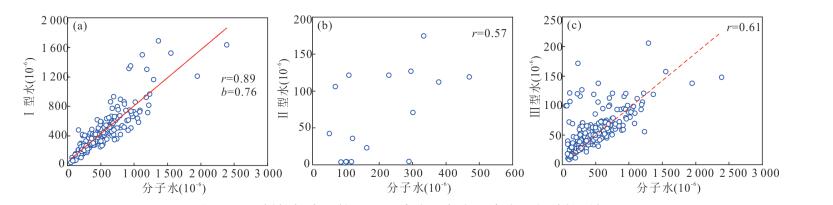
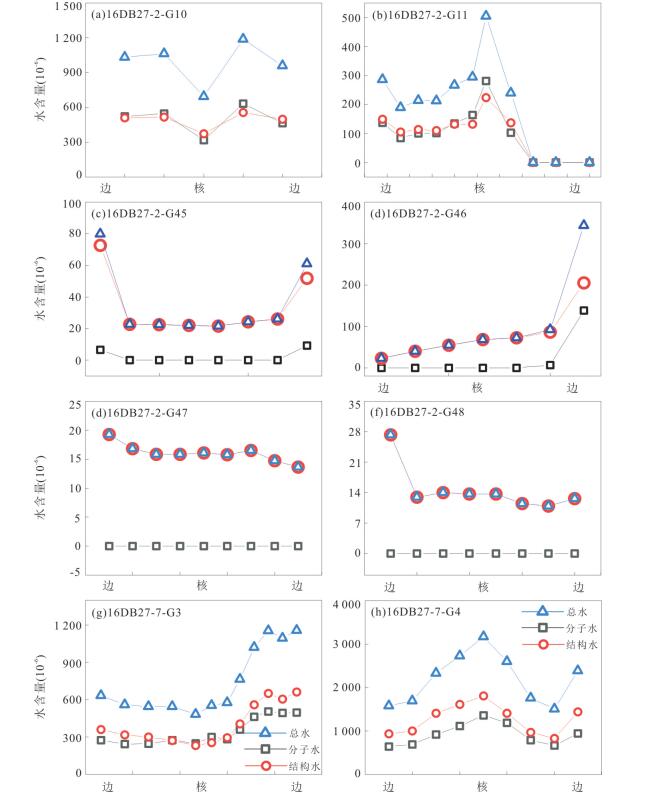
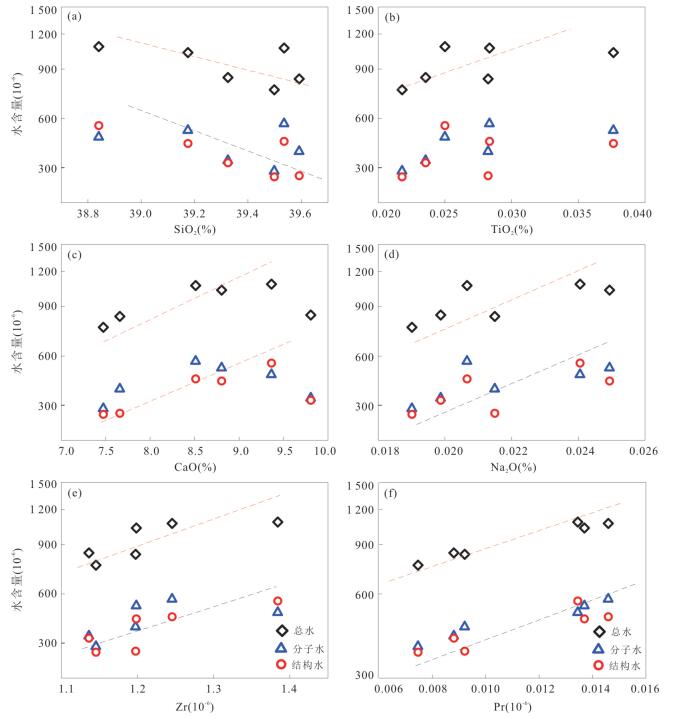
摘要: 名义上无水矿物的水含量研究对于认识俯冲带流体活动和地球动力学具有重要意义.对大别山金河桥榴辉岩中石榴石进行了傅里叶变换红外光谱分析和主微量元素分析,结果表明石榴石含有分子水和结构羟基,分别为 < 1×10-6~1 946×10-6和< 1×10-6~1 347×10-6.石榴石羟基含量与Ca、Na、Ti、Zr和Pr正相关,而与Si负相关,表明羟基结合机制以水榴石替代为主并伴有其他机制.分子水主要为初始水或折返过程中羟基转化形成.石榴石总水含量为 < 1×10-6~3 293×10-6,最大值对应于峰期超高压石榴石水储存能力.水在峰期石榴石中可达到饱和.石榴石变化的水含量受原岩性质、流体可获得性、压力和温度等多种因素控制,但主要由折返过程中降压脱水导致.石榴石平均总水含量为749×10-6~1 164×10-6,是俯冲板片向地幔水传输的重要介质.Abstract: Nominally anhydrous minerals (NAMs) are major components of the subducted continental slab and thus regarded as important water reservoir in continental subduction zone. The water contents of NAMs are critical for understanding of fluid action and geodynamics of subduction zones. In this study,Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) as well as major and trace element analyses were carried out on garnets in Jinheqiao eclogites from the Dabie orogen. The results demonstrate that garnet grains contain molecular water and hydroxyl (OH) with the contents of < 1×10-6 to 1 946×10-6 and < 1×10-6 to 1 347×10-6,respectively. Contents of hydroxyl are positively correlated with Ca,Na,Ti,Zr and Pr,but negatively correlated with Si for garnets in most samples,indicating that the incorporation of OH in garnet is dominated by hydrogarnet substitution. Molecular water is primary or transformed from hydroxyl during exhumation,implying molecular water an internal origin in eclogite. Garnet has total water contents varying from < 1×10-6 to 3 293×10-6,with the highest water content corresponding to the garnet's capacity for water storage under peak UHP metamorphism. Water can be saturated in peak metamorphic garnet. The variable water contents in garnet have been controlled by several factors including protolith nature,fluid availability,pressure and temperature,which however,have been dominated by decompression dehydration during exhumation. Garnets in the Jinheqiao eclogites have average total water contents ranging from 749×10-6 to 1 164×10-6,suggesting that they have similar capacity for water storage as omphacite and thus are important media for subducted slab to transport water into deep mantle.
-
Key words:
- eclogite /
- garnet /
- nominally anhydrous minerals /
- water /
- fluid action /
- subduction zone /
- petrology
-
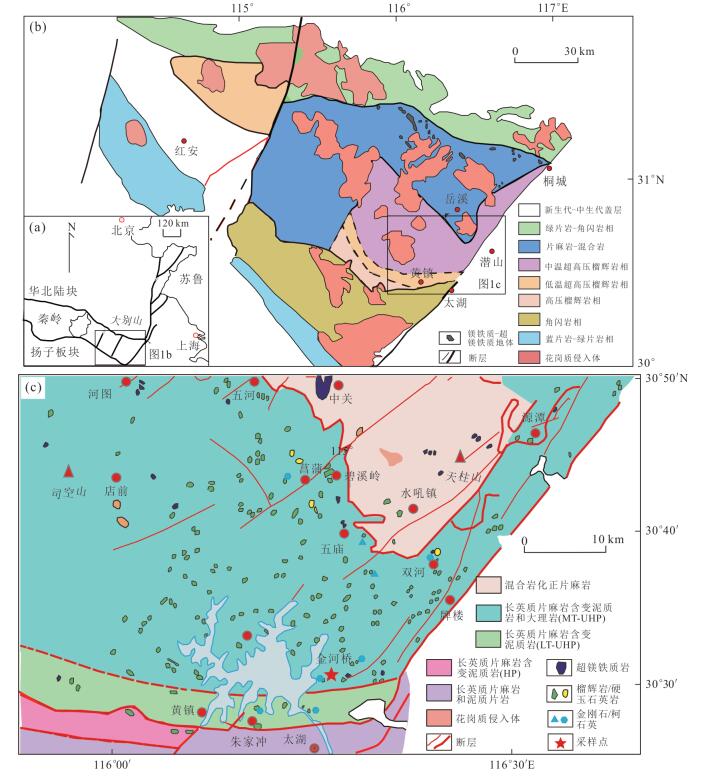
图 1 大别山地质简图及采样位置
据Lin et al. (2009)和Wei et al. (2013)修改
Fig. 1. Geological maps of Dabie orogen (a, b) and study area (c) with sample location
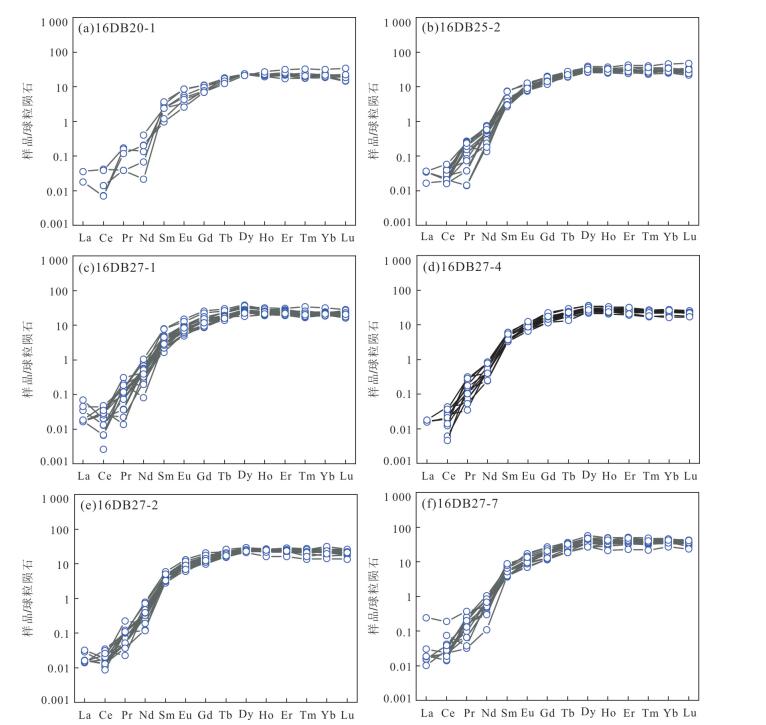
图 5 金河桥榴辉岩中石榴石稀土元素配分图解
球粒陨石标准化值来自Sun and McDonough (1989)
Fig. 5. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of garnets for Jinheqiao eclogite
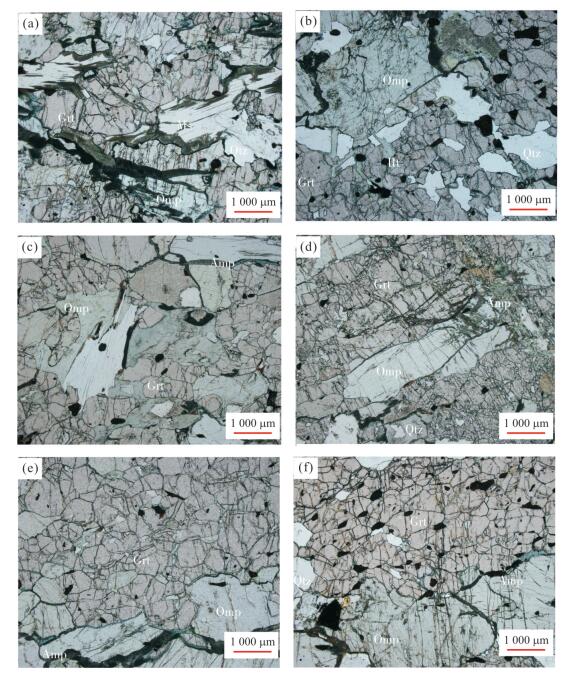
表 1 金河桥榴辉岩矿物含量(%)
Table 1. Contents of minerals in Jinheqiao eclogite(%)
样品编号 构造 绿辉石 石榴石 白云母 石英 角闪石 金红石 帘石 锆石 磷灰石 后成合晶 16DB20-1 块状 50 35 4 2 1 1 1 < 1 < 1 4 16DB25-2 块状 58 27 2 5 1 1 0 < 1 < 1 4 16DB27-1 块状 56 37 1 1 1 1 0 < 1 < 1 1 16DB27-4 块状 50 37 1 2 3 1 0 < 1 < 1 4 16DB27-2 条带状 35 54 2 3 2 1 0 < 1 < 1 1 16DB27-7 条带状 20 54 1 20 1 1 0 < 1 < 1 1 表 2 金河桥榴辉岩石榴石代表性主量元素组成
Table 2. Representative garnet major element compositions for Jinheqiao eclogite
Sample 16DB27-4 16DB27-2 16DB27-7 Spot Grt3 Grt8 Grt19 Grt22 Grt26 Grt1 Grt13 Grt18 Grt22 Grt29 Grt1 Grt18 Grt24 Grt27 Grt39 SiO2 39.30 38.94 40.05 38.68 38.17 39.02 38.77 38.67 38.87 39.36 40.04 38.74 39.55 39.40 38.98 TiO2 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.03 0.05 0.00 0.03 0.04 0.00 0.02 0.00 Al2O3 22.21 22.42 21.80 22.49 23.85 22.30 22.47 22.44 22.23 22.53 22.33 24.22 22.63 22.26 22.37 Cr2O3 0.07 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.06 0.03 0.05 0.05 0.03 0.04 0.05 0.09 FeO 19.23 18.93 19.56 18.59 17.54 20.13 18.97 19.88 18.75 19.45 18.99 18.95 19.91 18.91 20.79 MnO 0.42 0.40 0.38 0.37 0.37 0.44 0.32 0.42 0.41 0.35 0.42 0.41 0.35 0.39 0.39 MgO 7.93 8.81 9.41 9.20 8.95 9.18 8.27 8.52 9.15 9.56 9.56 9.73 10.21 10.73 9.46 CaO 10.46 9.93 8.64 10.13 9.86 8.29 10.09 9.46 9.86 8.60 8.49 7.66 7.01 7.48 7.62 Total 99.63 99.43 99.85 99.50 98.81 99.43 98.98 99.47 99.33 99.90 99.92 99.77 99.71 99.22 99.71 Atom per 12 O Si 3.00 2.96 3.03 2.94 2.90 2.97 2.97 2.95 2.96 2.98 3.02 2.90 2.99 2.98 2.97 Ti 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Al iv 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.06 0.10 0.03 0.03 0.05 0.04 0.02 0.00 0.10 0.01 0.02 0.03 Al vi 1.99 1.98 1.94 1.96 2.04 1.98 2.00 1.98 1.96 1.99 1.98 2.05 2.00 1.97 1.97 Cr 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01 Fe2+ 1.22 1.19 1.21 1.15 1.17 1.27 1.22 1.25 1.16 1.22 1.20 1.26 1.26 1.17 1.30 Fe3+ 0.00 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.02 0.03 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.02 Mn 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.02 Mg 0.90 1.00 1.06 1.04 1.01 1.04 0.94 0.97 1.04 1.08 1.07 1.09 1.15 1.21 1.07 Ca 0.85 0.81 0.70 0.83 0.80 0.68 0.83 0.77 0.80 0.70 0.68 0.61 0.57 0.61 0.62 Total 8.00 8.02 7.99 8.04 8.05 8.02 8.01 8.02 8.02 8.01 7.99 8.04 8.01 8.01 8.02 Almandine 40.5 38.1 39.6 35.7 36.6 41.2 39.6 40.0 36.9 39.7 40.1 40.5 41.8 38.2 42.0 Andradite 0.20 0.95 1.30 1.73 0.00 0.75 0.00 0.82 1.69 0.54 0.00 0.00 0.00 1.16 1.0 Grossular 28.1 26.4 22.4 26.3 27.5 21.8 27.7 25.2 25.4 22.7 22.8 21.1 18.9 19.0 19.7 Pyrope 30.1 33.7 35.9 35.5 35.0 35.1 31.8 32.9 35.1 36.2 36.0 37.4 38.5 40.6 36.2 Spessartine 0.91 0.86 0.82 0.80 0.82 0.96 0.71 0.92 0.89 0.75 0.91 0.89 0.75 0.84 0.8 Uvarovite 0.22 0.00 0.02 0.07 0.19 0.21 0.24 0.18 0.09 0.15 0.15 0.10 0.13 0.14 0.3 Sample 16DB27-4 16DB27-2 16DB27-7 Spot Grt3 Grt8 Grt19 Grt22 Grt26 Grt1 Grt13 Grt18 Grt22 Grt29 Grt1 Grt18 Grt24 Grt27 Grt39 SiO2 38.99 39.72 39.45 39.93 39.41 39.41 39.37 39.33 39.09 38.77 39.35 38.87 39.20 39.35 39.04 TiO2 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.02 0.04 0.02 0.00 0.03 Al2O3 22.52 22.70 22.52 22.53 22.63 22.72 22.62 22.34 22.51 22.33 21.98 22.36 21.54 21.90 21.94 Cr2O3 0.03 0.07 0.06 0.08 0.01 0.04 0.06 0.07 0.04 0.05 0.05 0.03 0.03 0.00 0.06 FeO 18.00 17.72 19.81 18.17 19.66 19.34 18.83 19.24 21.48 21.84 21.34 21.60 23.56 22.04 21.65 MnO 0.39 0.39 0.38 0.37 0.39 0.35 0.39 0.39 0.46 0.53 0.42 0.37 0.44 0.41 0.38 MgO 9.55 10.10 9.18 10.13 9.60 10.38 11.04 10.03 9.68 8.79 7.70 7.75 6.23 7.29 7.77 CaO 9.61 8.57 8.24 8.66 7.56 7.44 6.80 8.10 6.31 7.50 8.68 8.25 9.03 9.20 8.76 Total 99.07 99.27 99.65 99.90 99.25 99.69 99.13 99.49 99.58 99.81 99.54 99.27 100.04 100.19 99.63 Atom per 12 O Si 2.96 2.99 2.99 3.00 2.99 2.97 2.98 2.98 2.98 2.96 3.01 2.98 3.02 3.01 2.99 Ti 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Al iv 0.04 0.01 0.01 0.00 0.01 0.03 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.04 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.01 Al vi 1.98 2.01 2.00 1.99 2.01 2.00 1.99 1.98 2.00 1.98 1.98 2.01 1.96 1.97 1.98 Cr 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 Fe2+ 1.13 1.14 1.27 1.14 1.27 1.22 1.19 1.20 1.37 1.38 1.37 1.40 1.50 1.39 1.37 Fe3+ 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.02 0.01 Mn 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 Mg 1.08 1.13 1.04 1.13 1.08 1.17 1.24 1.13 1.10 1.00 0.88 0.89 0.72 0.83 0.89 Ca 0.78 0.69 0.67 0.70 0.61 0.60 0.55 0.66 0.52 0.61 0.71 0.68 0.75 0.75 0.72 Total 8.02 8.00 8.00 8.00 8.00 8.01 8.01 8.01 8.01 8.02 7.99 8.01 7.99 8.00 8.00 Almandine 36.3 38.0 42.1 38.1 42.3 39.7 38.8 39.1 44.8 44.3 45.7 46.7 49.7 46.0 45.5 Andradite 0.63 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.04 0.05 0.90 0.00 0.97 0.00 0.00 0.78 0.86 0.71 Grossular 25.7 23.0 22.2 23.0 20.5 20.1 18.3 21.0 17.2 19.6 23.7 22.6 24.3 24.4 23.1 Pyrope 36.5 38.0 34.7 37.8 36.3 39.3 41.8 38.0 36.9 33.8 29.5 29.7 24.2 27.8 29.7 Spessartine 0.84 0.83 0.82 0.79 0.83 0.75 0.83 0.84 0.99 1.16 0.91 0.80 0.96 0.90 0.82 Uvarovite 0.10 0.20 0.19 0.23 0.03 0.13 0.18 0.20 0.13 0.14 0.16 0.09 0.09 0.00 0.19 -
An, S.C., Li, S.G., Liu, Z., et al., 2018. Modification of the Sm-Nd Isotopic System in Garnet Induced by Retrogressive Fluids. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 36(8): 1039-1048.https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12426 Bell, D.R., Ihinger, P.D., Rossman, G.R., 1995. Quantitative Analysis of Trace OH in Garnet and Pyroxenes. American Mineralogist, 80(5-6): 465-474.https://doi.org/10.2138/am-1995-5-607 Bell, D.R., Rossman, G.R., 1992a. The Distribution of Hydroxyl in Garnets from the Subcontinental Mantle of Southern Africa. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 111(2): 161-178.https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00348949 Bell, D.R., Rossman, G.R., 1992b. Water in Earth's Mantle: The Role of Nominally Anhydrous Minerals. Science, 255(5050): 1391-1397.https://doi.org/10.1126/science.255.5050.1391 Chen, R.X., Zheng, Y.F., Gong, B., 2011. Mineral Hydrogen Isotopes and Water Contents in Ultrahigh-Pressure Metabasite and Metagranite: Constraints on Fluid Flow during Continental Subduction-Zone Metamorphism. Chemical Geology, 281(1-2): 103-124.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2007.02.012 Chen, Y.X., Zhou, K., Zheng, Y.F., et al., 2015. Garnet Geochemistry Records the Action of Metamorphic Fluids in Ultrahigh-Pressure Dioritic Gneiss from the Sulu Orogen. Chemical Geology, 398: 46-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.01.021 Demouchy, S., Bolfan-Casanova, N., 2016. Distribution and Transport of Hydrogen in the Lithospheric Mantle: A Review. Lithos, 240-243: 402-425.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2015.11.012 Gao, X.Y., Zheng, Y.F., Chen, Y.X., 2011. U-Pb Ages and Trace Elements in Metamorphic Zircon and Titanite from UHP Eclogite in the Dabie Orogen: Constraints on P-T-t Path. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 29(7): 721-740.https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.2011.00938.x Geiger, C.A., Stahl, A., Rossman, G.R., 2000. Single-Crystal IR- and UV/VIS-Spectroscopic Measurements on Transition-Metal-Bearing Pyrope: The Incorporation of Hydroxide in Garnet. European Journal of Mineralogy, 12(2): 259-271. https://doi.org/10.1127/0935-1221/2000/0012-0259 Gose, J., Schmädicke, E., 2018. Water Incorporation in Garnet: Coesite versus Quartz Eclogite from Erzgebirge and Fichtelgebirge. Journal of Petrology, 59(2): 207-232.https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egy022 Katayama, I., Nakashima, S., Yurimoto, H., 2006. Water Content in Natural Eclogite and Implication for Water Transport into the Deep Upper Mantle. Lithos, 86(3-4): 245-259.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2005.06.006 Koch-Müller, M., Matsyuk, S.S., Wirth, R., 2004. Hydroxyl in Omphacites and Omphacitic Clinopyroxenes of Upper Mantle to Lower Crustal Origin beneath the Siberian Platform. American Mineralogist, 89(7): 921-931. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2004-0701 Li, Q. L., Li, S. G., Zheng, Y.F., et al., 2003. A High Precision U-Pb Age of Metamorphic Rutile in Coesite-Bearing Eclogite from the Dabie Mountains in Central China: A New Constraint on the Cooling History. Chemical Geology, 200(3-4): 255-265. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(03)00194-3 Li, Q. L., Li, S. G., Zheng, Y. F., et al., 2003. O-Nd-Pb Isotopic Systems in Eclogite Minerals at Jinheqiao in Dabieshan and Constraints on Their Relative Diffusivity. Geological Journal of China Universities, 9(2):218-226 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gxdzxb200302007 Li, Z.H., Yang, S.T., Liu, M.Q., et al., 2019. Aqueous Fluid Activity and Its Effects in the Subduction Zones:A Systematic Numerical Modelling Study. Earth Science, 44(12):3984-3992(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264370711000664 Lin, W., Shi, Y. H., Wang, Q. C., 2009. Exhumation Tectonics of the HP-UHP Orogenic Belt in Eastern China: New Structural-Petrological Insights from the Tongcheng Massif, Eastern Dabieshan. Lithos, 109(3-4): 285-303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2008.10.007 Liu, F.L., Xu, Z.Q., Liou, J.G., 2004. Tracing the Boundary between UHP and HP Metamorphic Belts in the Southwestern Sulu Terrane, Eastern China: Evidence from Mineral Inclusions in Zircons from Metamorphic Rocks. International Geology Review, 46(5): 409-425. https://doi.org/10.2747/0020-6814.46.5.409 Liu, X.W., Xie, Z.J., Wang, L., et al., 2016. Water Incorporation in Garnets from Ultrahigh Pressure Eclogites at Shuanghe, Dabieshan. Mineralogical Magazine, 80(6): 959-975.https://doi.org/10.1180/minmag.2016.080.034 Liu, Y.S., Hu, Z.C., Gao, S., et al., 2008. In Situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by LA-ICP-MS without Applying an Internal Standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 Lu, R., Keppler, H., 1997. Water Solubility in Pyrope to 100 kbar. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 129(1): 35-42.https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050321 Maldener, J., Hosch, A., Langer, K., et al., 2003. Hydrogen in Some Natural Garnets Studied by Nuclear Reaction Analysis and Vibrational Spectroscopy. Physics and Chemistry of Minerals, 30(6): 337-344.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00269-003-0321-7 Matsyuk, S. S., Langer, K., Hösch, A., 1998. Hydroxyl Defects in Garnets from Mantle Xenoliths in Kimberlites of the Siberian Platform. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 132(2): 163-179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050414 Mookherjee, M., Karato, S. I., 2010. Solubility of Water in Pyrope-Rich Garnet at High Pressures and Temperature. Geophysical Research Letters, 37(3): L03310. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009gl041289 Schmädicke, E., Gose, J., 2017. Water Transport by Subduction: Clues from Garnet of Erzgebirge UHP Eclogite. American Mineralogist, 102(5): 975-986. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-2017-5920 Sheng, Y.M., Xia, Q.K., Dallai, L., et al., 2007. H2O Contents and D/H Ratios of Nominally Anhydrous Minerals from Ultrahigh-Pressure Eclogites of the Dabie Orogen, Eastern China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(8): 2079-2103.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2007.01.018 Shi, Y.H., Wang, Q.C., 2006. Variation in Peak P-T Conditions across the Upper Contact of the UHP Terrane, Dabieshan, China: Gradational or Abrupt?. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 24(9): 803-822. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.2006.00670.x Su, W., You, Z. D., Cong, B. L., et al., 2002. Cluster of Water Molecules in Garnet from Ultrahigh-Pressure Eclogite. Geology, 30(7): 611-614. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0611:cowmig>2.0.co;2 Sun, S. S., McDonough, W.F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1989.042.01.19 Wang, L.P., Zhang, Y.X., Essene, E.J., 1996. Diffusion of the Hydrous Component in Pyrope. American Mineralogist, 81(5-6): 706-718. https://doi.org/10.2138/am-1996-5-618 Wang, L., Wang, S.J., Brown, M., et al., 2017. On the Survival of Intergranular Coesite in UHP Eclogite. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 36(2): 173-194.https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12288 Wei, C.J., Qian, J.H., Tian, Z.L., 2013. Metamorphic Evolution of Medium-Temperature Ultra-High Pressure (MT-UHP) Eclogites from the South Dabie Orogen, Central China: An Insight from Phase Equilibria Modeling. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 31(7): 755-774.https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12043 Withers, A.C., Wood, B.J., Carroll, M.R., 1998. The OH Content of Pyrope at High Pressure. Chemical Geology, 147(1), 161-171.https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(97)00179-4 Wu, Y.N., Wang, Y.F., 2018. An FTIR Study of Kyanite in the Maobei Kyanite-Bearing Eclogites from the Sulu Orogenic Belt, Eastern China. Journal of Earth Science, 29(1): 21-29.https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-017-0774-0 Xia, Q.K., Cheng, H., Liu, J., et al., 2017.The Distribution of the Early Cretaceous Hydrous Lithospheric Mantle in the North China Craton:Constraints from Water Content in Peridotites of Tietonggou.Earth Science, 42(6):853-861(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.nature.com/articles/ncomms8700 Xia, Q.K., Liu, J., Kovács, I., et al., 2019. Water in the Upper Mantle and Deep Crust of Eastern China:Concentration, Distribution and Implications. National Science Review, 6(1):125-144. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwx016 Xia, Q.K., Sheng, Y.M., Yang, X.Z., et al., 2005. Heterogeneity of Water in Garnets from UHP Eclogites, Eastern Dabieshan, China. Chemical Geology, 224(4): 237-246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.08.003 Xiao, Y. L., Hoefs, J., van den Kerkhof, A.M., et al., 2000. Fluid History of UHP Metamorphism in Dabie Shan, China: A Fluid Inclusion and Oxygen Isotope Study on the Coesite-Bearing Eclogite from Bixiling. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 139(1): 1-16.https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050570 Zheng, Y.F., 2009. Fluid Regime in Continental Subduction Zones: Petrological Insights from Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphic Rocks. Journal of the Geological Society, 166(4): 763-782.https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-76492008-016r Zheng, Y.F., Chen, R.X., Xu, Z., et al., 2016. The Transport of Water in Subduction Zones. Science China:Earth Sciences, 46(3):253-286(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_3637742 Zheng, Y.F., Chen, R. X., Zhao, Z. F., 2009. Chemical Geodynamics of Continental Subduction-Zone Metamorphism: Insights from Studies of the Chinese Continental Scientific Drilling (CCSD) Core Samples. Tectonophysics, 475(2): 327-358.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2008.09.014 Zheng, Y.F., Chen, Y.X., 2019. Crust-Mantle Interaction in Continental Subduction Zones. Earth Science, 44(12):3961-3983 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201912001 Zheng, Y.F., Fu, B., Gong, B., et al., 2003. Stable Isotope Geochemistry of Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphic Rocks from the Dabie-Sulu Orogen in China: Implications for Geodynamics and Fluid Regime. Earth-Science Reviews, 62(1-2): 105-161.https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-8252(02)00133-2 Zheng, Y.F., Hermann, J., 2014. Geochemistry of Continental Subduction-Zone Fluids. Earth, Planets and Space, 66(1): 93.https://doi.org/10.1186/1880-5981-66-93 李秋立, 李曙光, 郑永飞, 等, 2003.大别山金河桥榴辉岩矿物O-Nd-Pb同位素体系及其对扩散速率的制约.高校地质学报, 9(2):218-226. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.02.007 李忠海, 杨舒婷, 刘明启, 等, 2019.板块俯冲水流体活动及其效应的定量化数值模拟.地球科学, 44(12):3984-3992. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.232?viewType=HTML 夏群科, 程徽, 刘佳, 等, 2017.山东铁铜沟橄榄岩的水含量:华北克拉通早白垩世富水岩石圈的分布.地球科学, 42(6):853-861. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201706001 郑永飞, 陈仁旭, 徐峥, 等, 2016.俯冲带中的水迁移.中国科学:地球科学, 46(3):253-286. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201603001 郑永飞, 陈伊翔, 2019.大陆俯冲带壳幔相互作用.地球科学, 44(12):3961-3983. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201912001 -
 dqkx-45-4-1168-Table1-2.pdf
dqkx-45-4-1168-Table1-2.pdf

-









 下载:
下载: