Petrographic Analysis and Classification of Sand and Sandstone
-
摘要: 定量的砂岩(砂)岩相学分析是重要的岩石学分析手段,有助于探讨沉积物的源区、背景和沉积盆地性质.在过去几十年中,科学家们对于砂岩(砂)的定量碎屑颗粒统计及其潜在地质意义(如沉积碎屑物与源区母岩的关系、沉积过程对碎屑组分的影响、碎屑组分与大地构造背景的关系等)取得了很多进展,但是对于定量的岩相分析方法和命名方案一直缺少系统的总结,导致一些实际工作中的波折和误区.在总结前人文献的基础上,系统描述了砂岩(砂)定量岩相分析的方法,并推荐最优的分类命名方案,希望建立统一的工作规范,本文提升砂岩(砂)碎屑颗粒统计结果的可靠性和数据的可对比性.同时,我们对砂岩构造背景判别图解的适用性进行了探讨,认为图解是展示砂岩碎屑组分统计结果的有效工具,但用于构造背景判断时则需谨慎,最好基于岩石本身的特征并结合其他资料综合探讨.Abstract: Quantitative petrographic analysis of sand and sandstone is an important way of petrology and it contributes to study the source area and background of sediments and the characteristic of sedimentary basin. In the past few decades, geologists have made a lot of progresses on quantitative debris particle statistics and its potential geological significance, such as the relationships between sedimentary debris and source rock, the effects of sedimentary process on debris compositions, the correlations between debris composition and tectonic setting. However, the systematic summary of quantitative petrographic analysis and classifications are scarce, which leads to misunderstandings or even mistakes in practice. Based on the previous literature, in the paper, it systematically describes the quantitative petrographic analysis of sand and sandstone and recommends the best classification naming scheme. This study intends to establish a uniform standard to promote the reliability of debris particle statistics and comparability of the data. Meanwhile, it also discusses applicability of sandstone tectonic background discrimination diagram. Although the diagrams are an effective way to show statistical results of sandstone debris components, it should be used with caution when applied to discriminate the tectonic setting. The best way to discriminate the tectonic setting is to conduct a comprehensive discussion based on the characteristics of the rock itself and other data.
-
Key words:
- sandstone petrography /
- Gazzi-Dickinson method /
- QFL diagram /
- source area /
- tectonic setting /
- petroleum geology
-
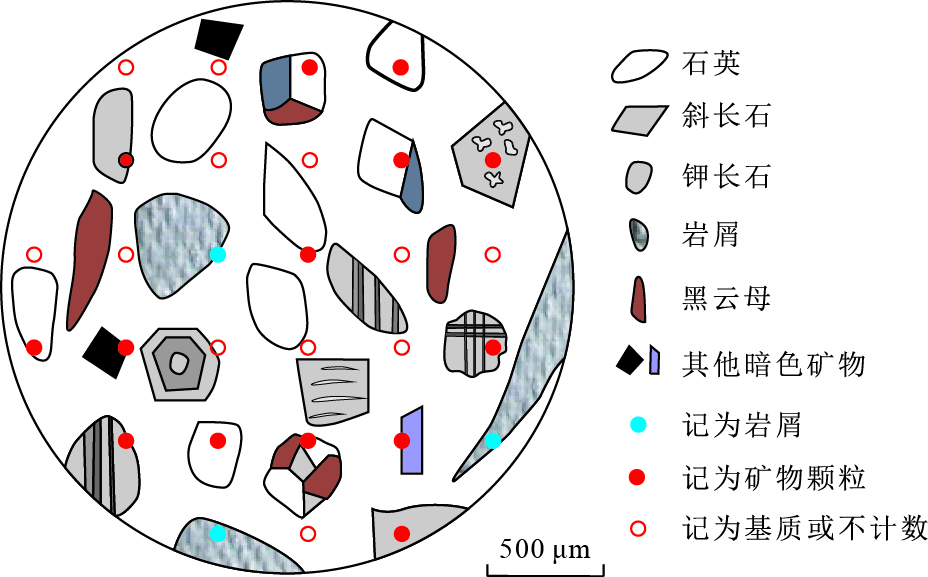
图 1 砂岩碎屑颗粒统计Gazzi-Dickinson计点法示意
据王建刚(2011)修改
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of statistical Gazzi-Dickinson point-counting method for sandstone clastic grain
图 2 不同种类的岩屑
沉积岩岩屑:a.灰岩; b.白云岩(瓦迪比, 阿曼北部);c.石膏(阿兹拉克沙漠, 约旦);d.燧石(罗曼达图, 意大利南部);e.由渐新世浊积岩改造的碎屑岩(加拉西亚, 大尼科巴岛).变质沉积岩碎屑:f.板岩(大竹河, 台湾);g.钙质片岩(菲施巴赫河, 奥地利);h.硅线石矽线石片岩(加德满都, 尼泊尔).火山岩碎屑:i.德干玄武岩(达布蒂河, 印度);j.安山岩(里奥格兰德, 阿根廷);k.流纹岩(利帕里岛, 意大利).变质火山岩碎屑:l.变质流纹岩(阿尔卑斯山南部, 意大利).变质基性岩颗粒:m.绿帘石绿片岩(拉巴河, 大高加索山脉西北部);n.绿帘石-蓝闪石蓝片岩(瓦拉伊塔河, 欧洲阿尔卑斯山西部).超基性岩碎屑:o.粒状蛇纹石岩(瓦迪汉, 阿曼北部);p.来自俯冲变质蛇绿岩的叶状蛇纹石岩(沃尔特里沙滩, 意大利).所有照片均拍摄于正交偏光下;蓝色的短条100 μm.据Garzanti(2019)
Fig. 2. Different kinds of rock fragments
图 3 泥质岩碎屑变质等级划分及显微特征
Lsp.泥质岩(未变质)(利古里亚阿尔卑斯山西部);Lmp1.板岩(发育弱劈理, 北高加索山脉西部);Lmp2.千枚岩岩屑(发育强劈理, 利古里亚阿尔卑斯山);Lmp3.云母片岩(阿尔卑斯山东部);Lmp4.白云母片岩(阿尔卑斯山西部);Rmp5.黑云母片岩(阿尔卑斯山中部; bi, 黑云母).图中白色圆圈的直径为62.5 μm, 所有照片均拍摄于正交偏光下.据Garzanti and Vezzoli(2003)
Fig. 3. Metamorphic rank and microscopic characteristics of metapelite grains
图 4 粉砂岩(长英质岩石)碎屑变质等级划分及显微特征
Lsp.粉砂岩(含碎屑云母, 未变质, 利古里亚阿尔卑斯山西部);Lmf1.变质粉砂岩(发育弱劈理, 特提斯喜马拉雅);Lmf2.石英-绢云母(重结晶)片岩(发育强劈理, 小喜马拉雅);Lmf3.石英-云母岩屑(片理发育, 阿尔卑斯山脉东部);Lmf4.白云母片麻岩(北高加索山脉中部);Rmf5.黑云母片麻岩(高喜马拉雅, bi, 黑云母).图中白色圆圈的直径为62.5 μm.所有照片均拍摄于正交偏光下.据Garzanti and Vezzoli(2003)
Fig. 4. Metamorphic rank and microscopic characteristics of metapsammite/metafelsite grains
图 5 碳酸盐岩碎屑变质等级划分及显微特征
Lsc.泥粒灰岩(含碎屑云母, 亚平宁山脉北部);Lmc1.变质灰岩(发育弱劈理, 轻微重结晶, 特提斯喜马拉雅);Lmc2.变质灰岩岩屑(发育强烈劈理, 明显重结晶, 阿尔卑斯山北部);Lmc3.大理岩(强烈重结晶, 含自生细粒白云母, 亚平宁山脉北部);Lmc4.白云母钙质片岩(阿尔卑斯山中部);Rmc5.黑云母钙质片岩(高喜马拉雅; bi.黑云母).图中白色圆圈的直径为62.5 μm.所有照片均拍摄于正交偏光下.据Garzanti and Vezzoli(2003)
Fig. 5. Metamorphic rank and microscopic characteristics of metacarbonate grains
图 6 基性岩碎屑变质等级划分及显微特征
Lv.玄武岩(阿曼蛇绿岩);Lmb1.变质玄武岩(塞浦路斯蛇绿岩);Lmb2.绿泥石片岩(利古里亚阿尔卑斯, chl.绿泥石);Lmb3.绿泥闪帘片岩(利古里亚阿尔卑斯, ep.绿帘石);Lmb4.蓝片岩岩屑(阿尔卑斯山西部, gl.蓝闪石);Rmb5.角闪岩岩屑(阿尔卑斯山中部, hb.普通角闪石).图中白色圆圈的直径为62.5 μm.所有照片均拍摄于正交偏光下.据Garzanti and Vezzoli(2003)
Fig. 6. Metamorphic rank and microscopic characteristics of metabasite grains
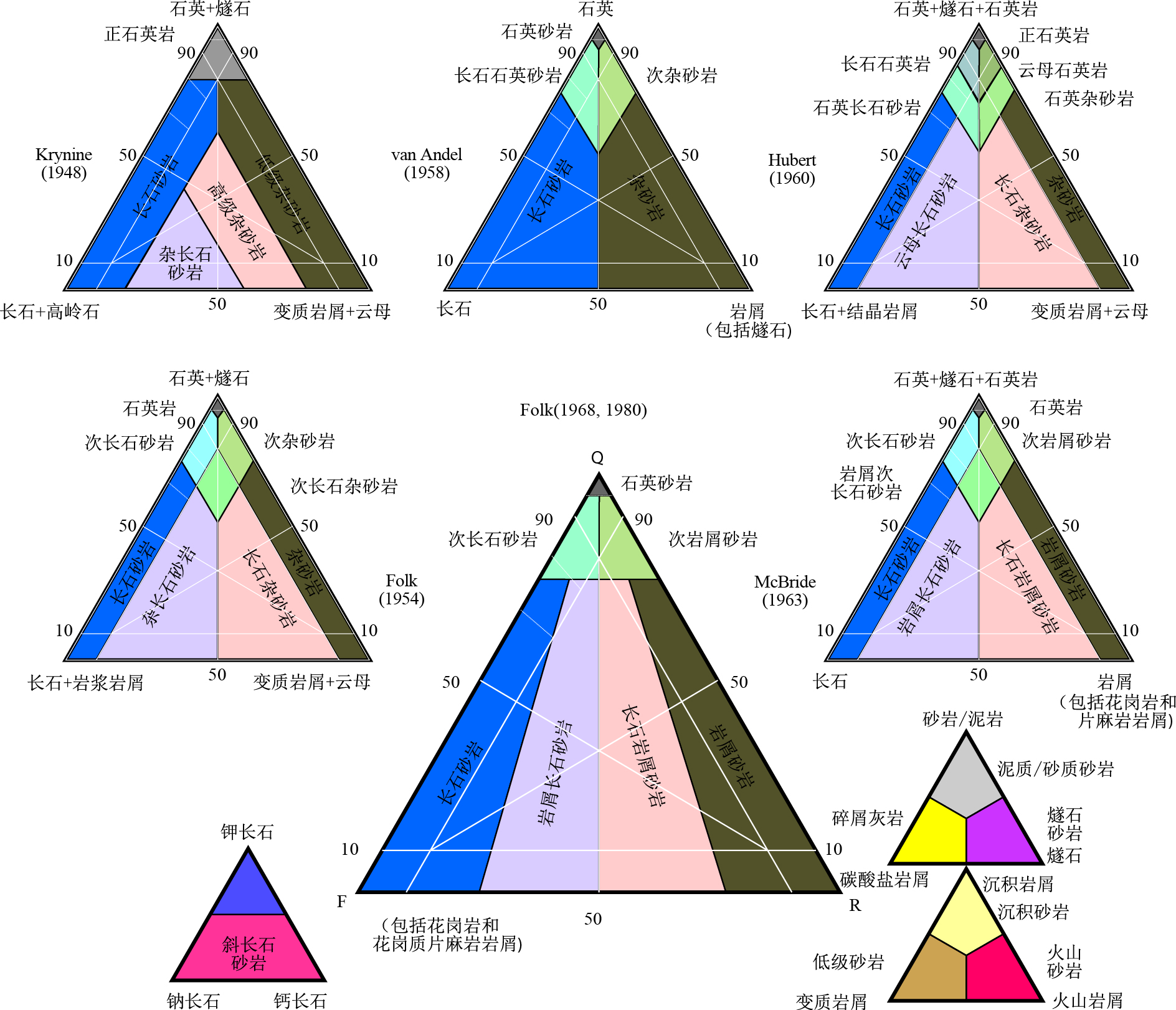
图 7 基于岩相组成的传统砂岩分类系统
据Krynine(1948);Folk(1954, 1968, 1980);van Andel(1958);Hubert(1960);McBride(1963)
Fig. 7. Traditional sandstone classifications based on petrographic composition
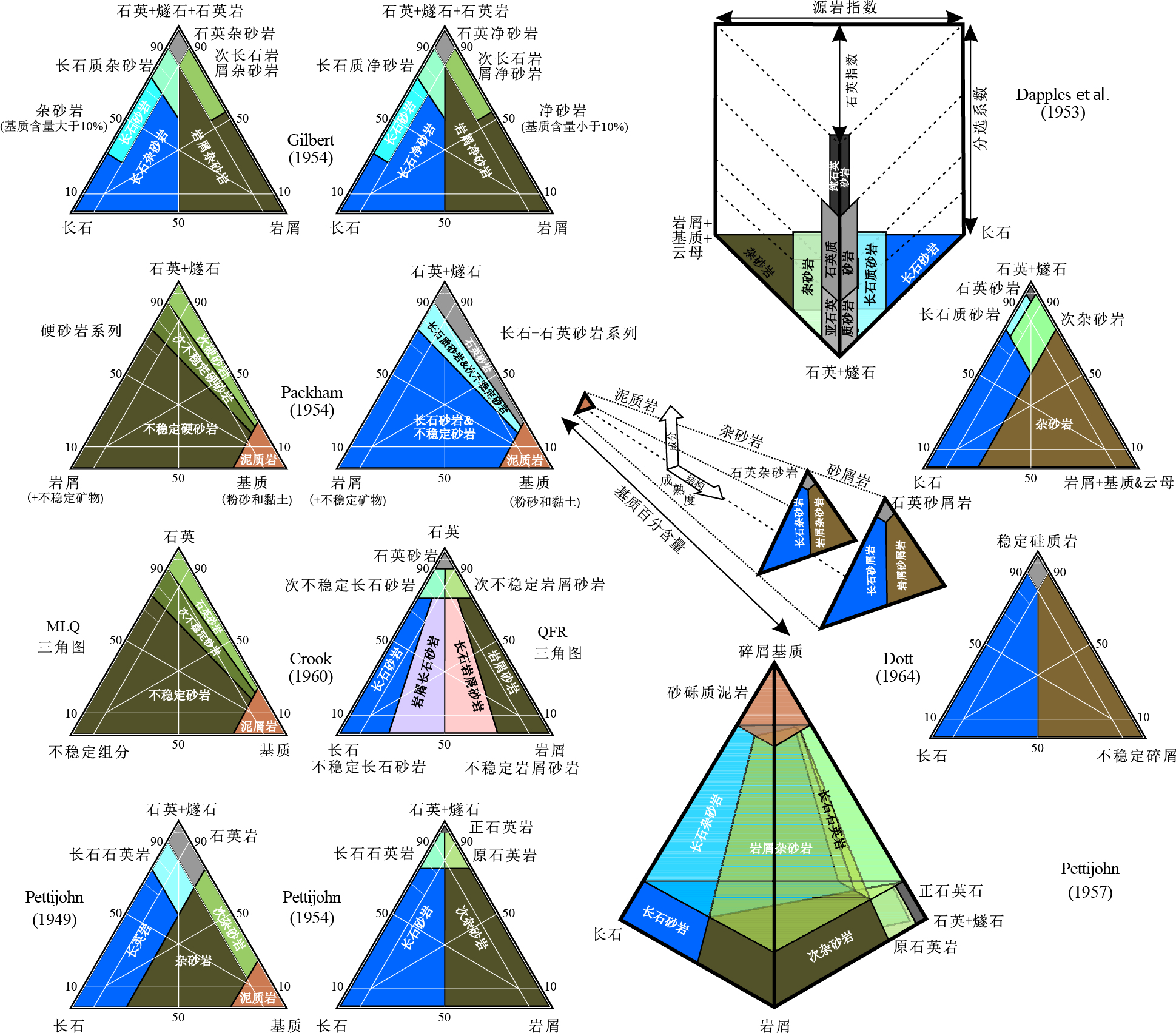
图 8 基于岩相组成和结构的传统砂岩系统
据Pettijohn(1949, 1954, 1957);Dapples et al.(1953);Gilbert(1954);Packham(1954);Crook(1960)和Dott(1964)
Fig. 8. Traditional sandstone classifications based on both petrographic composition and texture
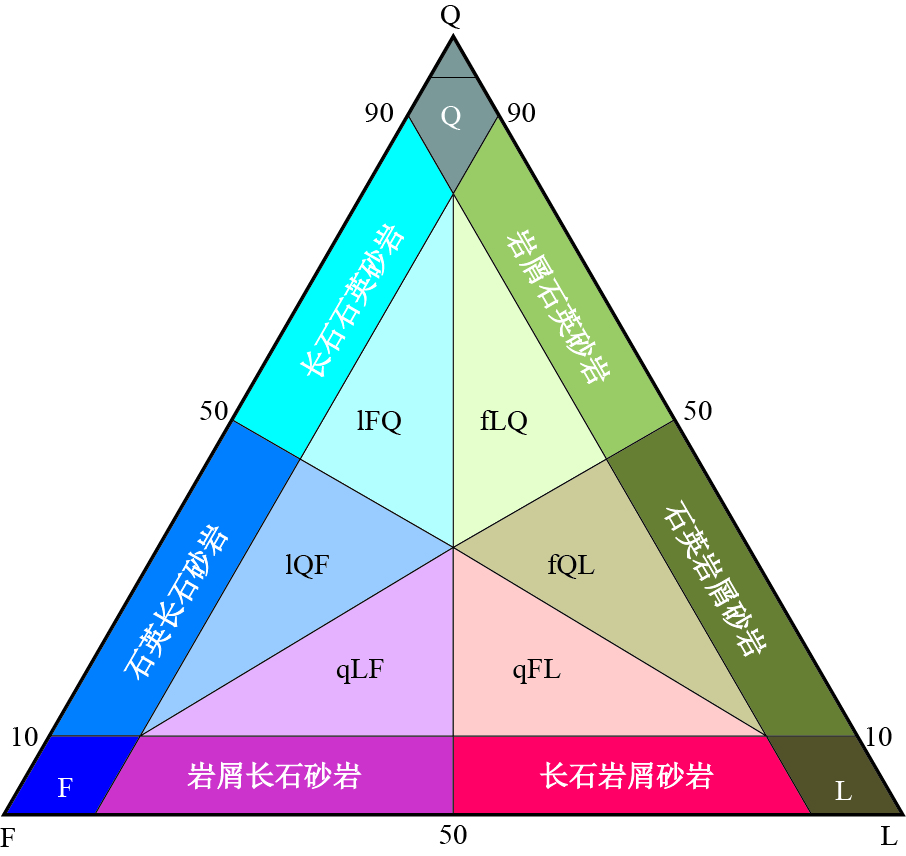
图 9 本文推荐的砂岩分类方案
Q.石英砂岩;F.长石砂岩;L.岩屑砂岩;lFQ.岩屑长石石英砂岩;lQF.岩屑石英长石砂岩;qLF.石英岩屑长石砂岩;qFL.石英长石岩屑砂岩;fQL.长石石英岩屑砂岩;fLQ.长石岩屑石英砂岩.据Garzanti(2016)
Fig. 9. The proposed classification of sand and sandstone
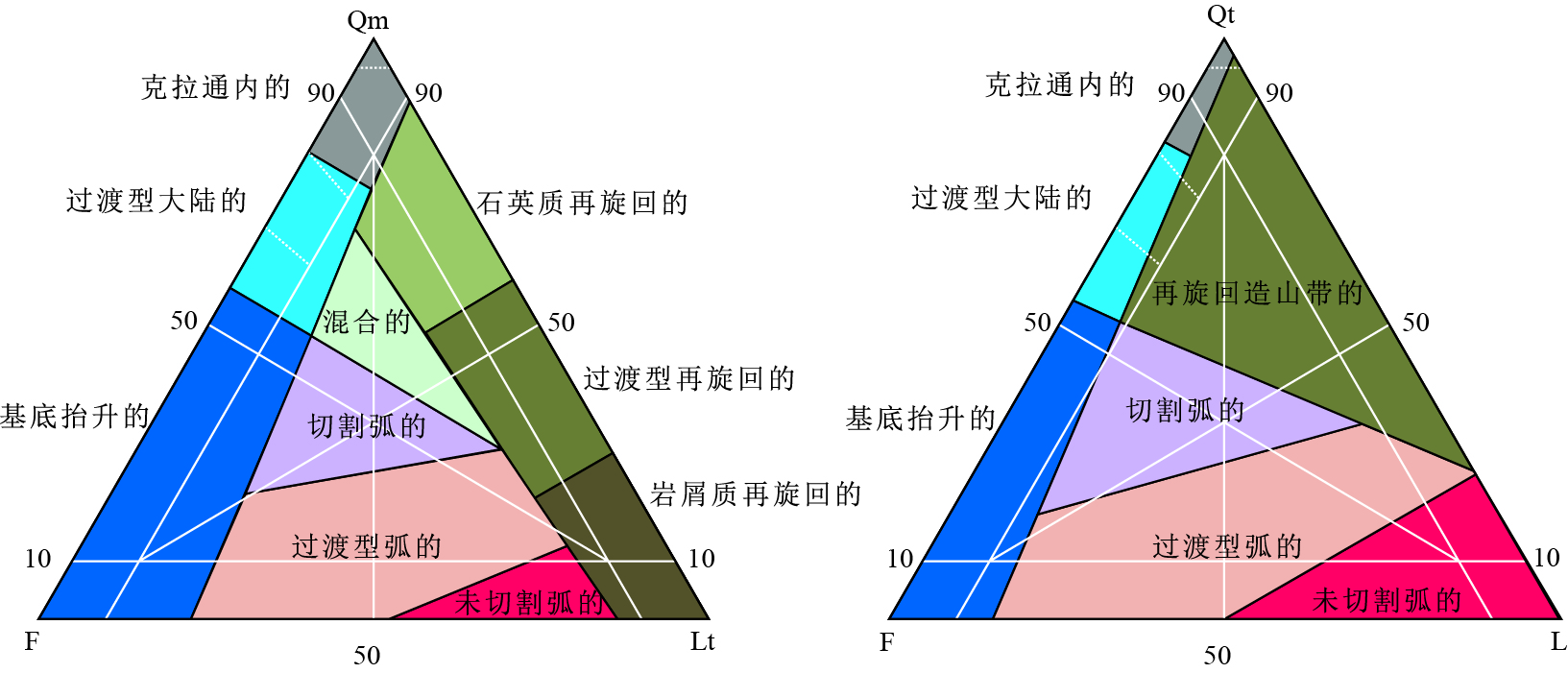
图 10 砂岩的QmFLt和QtFL构造判别图解
Fig. 10. The QmFLt and QtFL triangular diagrams of sandstones
-
Chen Y.F., Wang Y.W., Wang J.B., et al.2018.Greisenized Alteration-Mineralization Geochemistry of the Tin Deposit Related to A-Type Granite:Case Study on the Kamusite and Ganliangzi Deposits, Xinjiang.Earth Science, 43(9):3154-3168(in Chinese with English abstract). Crook K.A.W..1960.Classification of Arenites.American Journal of Science, 258(6):419-428. doi: 10.2475/ajs.258.6.419 Crook K.A.W..1974.Lithogenesis and Geotectonics:The Significance of Compositional Variation in Flysch Arenites (Graywackes).In:Dott R.H., Shaver R.H., eds., Modern and Ancient Geosynclinal Sedimentation.Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists, Special Publication, 19:304-310. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285323571_Lithogenesis_and_geotectonics_The_significance_of_compositional_variation_in_flysch_arenites_greywackes Cummins W.A..1962.The Greywacke Problem.Geological Journal, 3(1):51-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1002/gj.3350030105 Dapples E.C., Krumbein W.C., Sloss L.L..1953.Petrographic and Lithologic Attributes of Sandstones.The Journal of Geology, 61(4):291-317. doi: 10.1086/626098 Dickinson W.R..1970.Interpreting Detrital Modes of Graywacke and Arkose.Journal of Sedimentary Research, 40(2):695-707. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/250081783_Interpreting_Detrital_Modes_of_Graywacke_and_Arkose Dickinson W.R..1985.Interpreting Provenance Relations from Detrital Modes of Sandstones.In:Zuffa G.G., ed., Provenance of Arenites.Reidel, Dordrecht, NATO ASI Series, 148:333-361. doi: 10.1007%2F978-94-017-2809-6_15 Dickinson W.R., Suczek C.A..1979.Plate Tectonics and Sandstone Composition.American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin, 63:2164-2172. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cd2e9450770825a11349d2088338932f Dorsey R.J..1988.Provenance Evolution and Unroofing History of a Modern Arc-Continent Collision:Evidence from Petrography of Plio-Pleistocene Sandstones, Eastern Taiwan.Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 58(2):208-218. http://www.uvm.edu/~cmehrten/courses/earthhist/Dorsey1988.pdf Dott R.H..1964.Wacke, Graywacke and Matrix:What Approach to Immature Sandstone Classification? Journal of Sedimentary Research, 34(3):625-632. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/sepm/jsedres/article-abstract/34/3/625/95753 Folk R.L..1954.The Distinction between Grain Size and Mineral Composition in Sedimentary Rock Nomenclature.The Journal of Geology, 62(4):344-359. doi: 10.1086/626171 Folk R.L..1968.Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks.Hemphill Publishing, Austin. U.S.A., 170. Folk R.L..1980.Petrology of Sedimentary Rocks.Hemphill Publishing, Austin. U.S.A., 182. Frey M..1987.Very Low-Grade Metamorphism of Clastic Sedimentary Rocks.Low Temperature Metamorphism.Blackie and Son, London, 9-58. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304919935_Very_low-grade_metamorphism_of_clastic_sedimentary_rocks Galehouse.1971.Pipette Analysis.In:Carver R.E., ed., Procedures in Sedimentary Petrology.Wiley Interscience, Athens, GA, 650. Garzanti E..2016.From Static to Dynamic Provenance Analysis:Sedimentary Petrology Upgraded.Sedimentary Geology, 336:3-13. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.07.010 Garzanti E..2017.The Maturity Myth in Sedimentology and Provenance Analysis.Journal of Sedimentary Research, 87(4):353-365. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2017.17 Garzanti E..2019.Petrographic Classification of Sand and Sandstone.Earth-Science Reviews, 192:545-563. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.12.014 Garzanti E., Andò S., Limonta M., et al.2018.Diagenetic Control on Mineralogical Suites in Sand, Silt, and Mud (Cenozoic Nile Delta):Implications for Provenance Reconstructions.Earth-Science Reviews, 185:122-139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.010 Garzanti E., Andò S., Padoan M., et al.2015.The Modern Nile Sediment System:Processes and Products.Quaternary Science Reviews, 130:9-56. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2015.07.011 Garzanti E., Andò S., Scutellà M..2000.Actualistic Ophiolite Provenance:The Cyprus Case.The Journal of Geology, 108(2):199-218. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ027320346/ Garzanti E., Andò S., Vezzoli G..2009.Grain-Size Dependence of Sediment Composition and Environmental Bias in Provenance Studies.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 277(3):422-432. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f0a9e1bb833371ed30c2c45bee88bca2 Garzanti E., Andò S., Vezzoli G., et al.2012.Petrology of the Namib Sand Sea:Long-Distance Transport and Compositional Variability in the Wind-Displaced Orange Delta.Earth-Science Reviews, 112(3-4):173-189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2012.02.008 Garzanti E., Dinis P., Vermeesch P., et al.2017.Sedimentary Processes Controlling Ultralong Cells of Littoral Transport:Placer Formation and Termination of the Orange Sand Highway in Southern Angola.Sedimentology, 65(2):431-460. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=48d9085dac3a0a3424b82d4f137a2e2d Garzanti E., Doglioni C., Vezzoli G., et al.2007.Orogenic Belts and Orogenic Sediment Provenances.The Journal of Geology, 115(3):315-334. doi: 10.1086/512755 Garzanti E., Padoan M., Andò S., et al.2013.Weathering and Relative Durability of Detrital Minerals in Equatorial Climate:Sand Petrology and Geochemistry in the East African Rift.The Journal of Geology, 121(6):547-580. doi: 10.1086/673259 Garzanti E., Vermeesch P., Andò S., et al.2014a.Ultra-Long Distance Littoral Transport of Orange Sand and Provenance of the Skeleton Coast Erg (Namibia).Marine Geology, 357:25-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.margeo.2014.07.005 Garzanti E., Vermeesch P., Padoan M., et al.2014b.Provenance of Passive-Margin Sand (Southern Africa).The Journal of Geology, 122(1):17-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=164f9b009d3e84019eb44c458b00580a Garzanti E., Vezzoli G..2003.A Classification of Metamorphic Grains in Sands Based on Their Composition and Grade.Journal of Sedimentary Research, 73(5):830-837. doi: 10.1306/012203730830 Garzanti E., Vezzoli G., Andò S., et al.2001.Petrology of Rifted-Margin Sand (Red Sea and Gulf of Aden, Yemen).The Journal of Geology, 109(3):277-297. doi: 10.1086/319973 Garzanti E., Vezzoli G., Andò S..2002.Modern Sand from Obducted Ophiolite Belts (Oman, U.A.E.).The Journal of Geology, 110 (4):371-391. doi: 10.1086/340440 Gilbert C.M..1954.Sedimentary Rocks.In:Williams H., Turner F.J., Gilbert C.M., eds., Petrography.Freeman, San Francisco, 406. Hubert J.F..1960.Petrology of the Fountain and Lyons Formations, Front Range, Colorado (Dissertation).Colorado School of Mines, Colorado. Ingersoll R.V..1983.Petrofacies and Provenance of Late Mesozoic Forearc Basin, Northern and Central California.AAPG Bulletin, 67(7):1125-1142. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255934284_Petrofacies_and_Provenance_of_Late_Mesozoic_Forearc_Basin_Northern_and_Central_California Ingersoll R.V., Bullard T.F., Ford R.L., et al.1984.The Effect of Grain Size on Detrital Modes:A Test of the Gazzi-Dickinson Point-Counting Method.Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 54(1):103-116. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Raymond_Ingersoll/publication/260785669_The_effect_of_grain_size_on_detrital_modes_A_test_of_the_Gazzi-Dickinson_point_counting_method/links/55dddfef08ae7983897d09c4.pdf?origin=publication_detail Ingersoll R.V., Suczek C.A..1979.Petrology and Provenance of Neogene Sand from Nicobar and Bengal Fans, DSDP Sites 211 and 218.Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 49(4):1217-1228. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/sepm/jsedres/article-abstract/49/4/1217/97232/Petrology-and-provenance-of-Neogene-sand-from Klein G.D..1963.Analysis and Review of Sandstone Classifications in the North American Geological Literature, 1940-1960.Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 74(5):555-576. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1963)74[555:AAROSC]2.0.CO;2 Krynine P.D..1948.The Megascopic Study and Field Classification of Sedimentary Rocks.The Journal of Geology, 56(2):130-165. https://ci.nii.ac.jp/ncid/BA84011400 McBride E.F..1963.A Classification of Common Sandstones.Journal of Sedimentary Petrology, 33(3):664-669. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Earle_Mcbride/publication/240778409_A_Classification_of_Common_Sandstones/links/0c96053bfed33192e5000000.pdf Molinaroli E., Blom M., Basu A..1991.Methods of Provenance Determination Tested with Discriminant Function Analysis.Journal of Sedimentary Research, 61(6):900-908. https://core.ac.uk/display/53164325 Okada H..1971.Classification of Sandstone:Analysis and Proposal.The Journal of Geology, 79(5):509-525. doi: 10.1086/627673 Packham G.H..1954.Sedimentary Structures as An Important Factor in the Classification of Sandstones.American Journal of Science, 252(8):466-476. doi: 10.2475/ajs.252.8.466 Pettijohn F.J..1949.Sedimentary Rocks.Harper and Brothers, New York, 526. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201710002 Pettijohn F.J..1954.Classification of Sandstones.The Journal of Geology, 62(4):360-365. doi: 10.1086/626172 Pettijohn F.J..1957.Paleocurrents of Lake Superior Precambrian Quartzites.Bulletin of the Geological Society of America, 68(4):469-480. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1957)68[469:POLSPQ]2.0.CO;2 Powell C.M..1979.A Morphological Classification of Rock Cleavage.Tectonophysics, 58(1-2):21-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(79)90320-2 Qin Z.W., Ma C.Q., Fu J.M., et al.2018.The Origin of Mafic Enclaves in Xiangjia Granitic Pluton of East Kunlun Orogenic Belt:Evidence from Petrography and Geochemistry.Earth Science, 43(7):2420-2437(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201807016.htm Sorby H.C..1880.On the Structure and Origin of Non-Calcareous Stratified Rocks.Proceedings of the Geological Society London, 36:46-92. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285499252_On_the_structure_and_origin_of_noncalcareous_stratified_rocks van Andel T.H..1958.Origin and Classification of Cretaceous, Paleocene and Eocene Sandstones of Western Venezuela.AAPG Bulletin, 42(4):734-763. Völl G..1976.Recrystallization of Quartz, Biotite and Feldspars from Erstfeld to the Leventina Nappe, Swiss Alps, and Its Geological Significance.Schweiz. Mineral. Pertogr. Mitt., 56:641-647. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10003976886 Wang J.G..2011.Sedimentary Record and Basin Evolution of the Himalayan Orogen in Xigaze Area, Southern Tibet (Dissertation).Nanjing University, Nanjing(in Chinese with English abstract). Weltje G.J..2006.Ternary Sandstone Composition and Provenance:An Evaluation of the 'Dickinson Model'.Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 264(1):611-627. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/books/book/1637/chapter/107438592/Ternary-sandstone-composition-and-provenancean Weltje G.J..2012.Quantitative Models of Sediment Generation and Provenance:State of the Art and Future Developments.Sedimentary Geology, 280:4-20. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.03.010 Whetten J.T., Hawkins J.W..1970.Diagenetic Origin of Graywacke Matrix Minerals.Sedimentology, 15:347-361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.1970.tb02191.x White N.M., Pringle M., Garzanti E., et al.2002.Constraints on the Exhumation and Erosion of the High Himalayan Slab, NW India, from Foreland Basin Deposits.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 195(1-2):29-44. doi: 10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00565-9 Young S.W..1976.Petrographic Textures of Detrital Polycrystalline Quartz as an Aid to Interpreting Crystalline Source Rocks.SEPM Journal of Sedimentary Research, 46(3):595-603. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284034294_Petrographic_Textures_of_Detrital_Polycrystalline_Quartz_as_an_Aid_to_Interpreting_Crystalline_Source_Rocks Zhang Z.M., Kang D.Y., Ding H.X., et al.2018.Partial Melting of Himalayan Orogen and Formation Mechanism of Leucogranites.Earth Science, 43(1):82-98(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201801005 陈言飞, 王玉往, 王京彬, 等.2018.与A型花岗岩有关锡矿的云英岩化蚀变矿化地球化学:以新疆卡姆斯特和干梁子矿床为例.地球科学, 43(9):3154-3168. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.321 秦拯纬, 马昌前, 付建明, 等.2018.东昆仑香加花岗质岩体中镁铁质包体成因:岩相学及地球化学证据.地球科学, 43(7):2420-2437. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.549 王建刚.2011.西藏日喀则地区喜马拉雅造山带沉积记录与盆地演化(博士学位论文).南京:南京大学. 张泽明, 康东艳, 丁慧霞, 等.2018.喜马拉雅造山带的部分熔融与淡色花岗岩成因机制.地球科学, 43(1):82-98. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.005 -
 dqkx-45-6-2186-Table1-3.pdf
dqkx-45-6-2186-Table1-3.pdf

-










 下载:
下载: