Pore Structure Characteristics of Shale Reservoir of the Lower Qian 4 Member in the Wangchang Anticline of the Qianjiang Sag
-
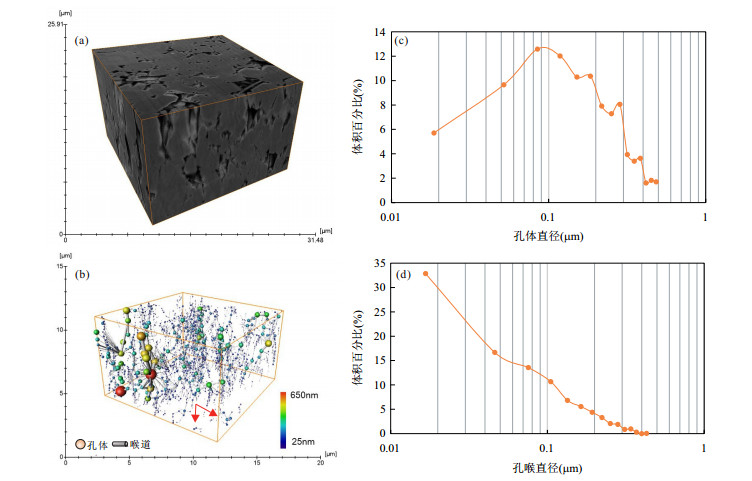
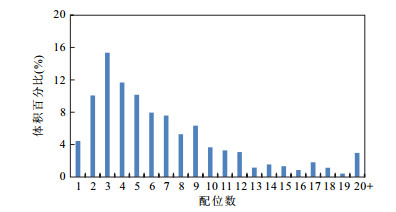
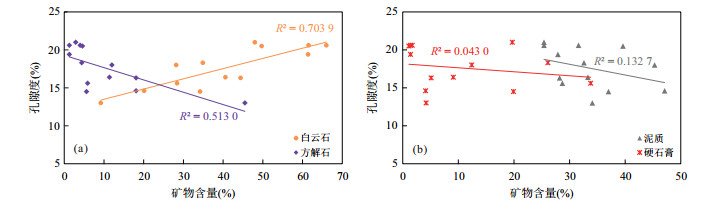
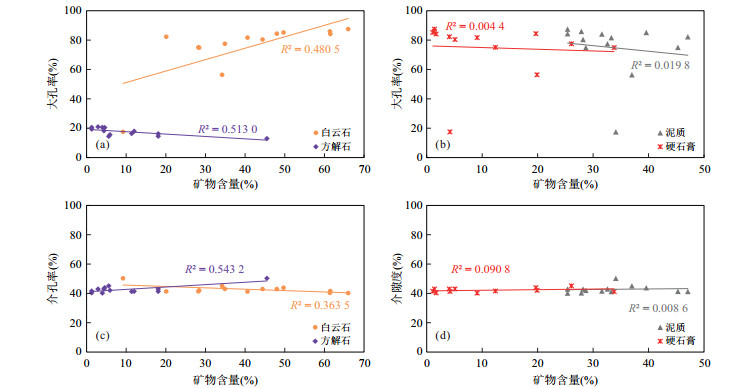
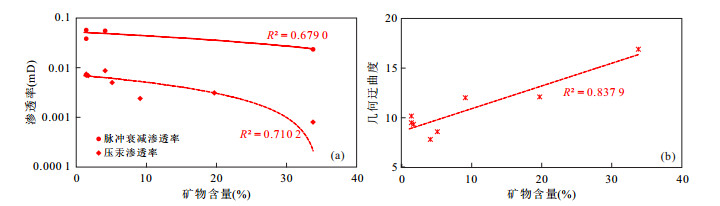
摘要: 为了解潜江凹陷王场背斜潜四下段14号韵律层页岩储层孔隙结构特征及探讨岩石物性优越性的受控因素,开展了X射线粉晶全岩、岩石物性、高压压汞、氮气吸附、微米CT扫描及聚集离子束扫描等分析.研究显示:储层主要由白云石(平均40.5%)、方解石(平均10.4%);长石(平均16.5%)、黏土矿物(平均11.2%)、硬石膏(平均10.8%)及石英(5.9%)构成;岩石为"高-中孔(平均17.6%),特低渗(平均0.043 6 mD)"储层类型;各岩性(除泥质灰岩)中大孔率高(平均79.7%)的特点促成了孔隙性的优良,白云石及方解石含量与大介孔率的相关性指示白云石化与大孔形成密切相关;白云石化协同方解石沉积带来的细小孔喉奠定了渗透性差的基础,硬石膏含量与几何迂曲度的正相关性指示硬石膏化对孔喉空间复杂度的加强及对渗透性的恶化,配位数少(主峰3个)及退汞效率低(平均40%)反映的连通性较差对渗透性亦有一定的影响.Abstract: The analyses of X-ray powder diffraction,porosity and permeability,high pressure mercury,nitrogen adsorption,Micro-CT scanning,and FIB-SEM were performed,aiming to understand the pore structure characteristics of the shale reservoir and discuss the controlling factors of the superiority of rock physical property of of different lithologies of the 14th cyclotherm of the Lower Qian4 Member in the Wangchang anticline of the Qianjiang sag. Studies show that the reservoir consists mainly of dolomite (40.5% on average),calcite (10.4% on average),feldspar (16.5% on average),clay minerals (11.2% on average),anhydrite (10.8% on average),and quartz (5.9% on average); the rock is "high-medium porosity (average 17.6%) and very low permeability (average 0.043 6 mD)" type; high macropore rate (79.7% on average) within each lithology (except argillaceous limestone) contributes to excellent porosity,and the correlation between dolomite and calcite content and macopore and micropore rate indicates that dolomitization is closely related to the formation of macropore. Dolomiticzation along with calcite precipiatation lays the foundation of poor permeability,and the positive correlation between anhydrite content and geometrical tortuosity indicates the enhancement of the space complexity of the pore throat and the deterioration of permeability. The less connecting number (main peak at 3) and the low efficiency of mercury withdrawal (40% on average) reflect poor connectivity which also has a certain effect on permeability.
-
Key words:
- Qianjiang Sag /
- Lower Qian4 Member /
- cyclotherm /
- shale /
- pore structure /
- oil-gas geology
-
图 1 研究区地质图
a.潜江凹陷潜四下段底面构造图;b.潜江凹陷古近系地层简图,据Fang et al. (2006),有修改
Fig. 1. Geological maps of research area
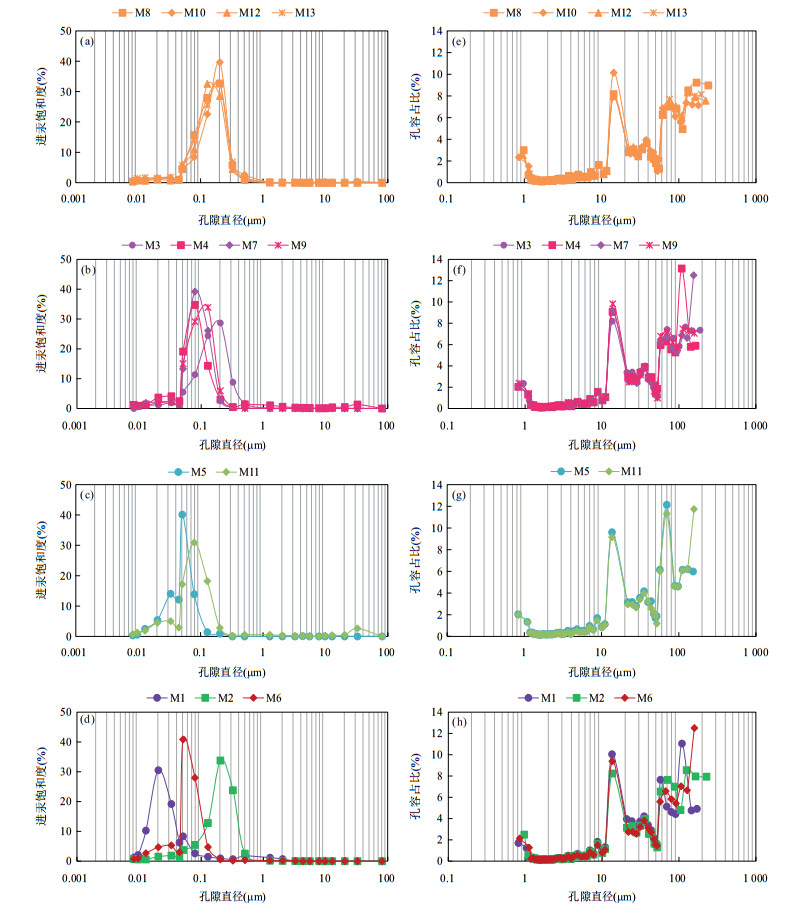
图 4 潜江凹陷王场背斜潜四下段14号韵律层各岩性高压压汞(a~d)及氮气吸附(e~h)孔隙直径分布图
a, e.泥质白云岩;b, f.泥质白云岩,含灰(M3和M7)及含硬石膏(M4和M9);c, g.白云质泥岩,含灰(M11)及含硬石膏(M5);d, h.泥质灰岩(M1)、含灰-云泥岩(M2)及云―泥质硬石膏岩(M6)
Fig. 4. Distribution of pore diameter from different lithologies of the 14th cyclotherm of the lower Qian4 Member in the Wangchang Anticline of the Qianjiang Sag by mecury injection and gas adsortion analysis
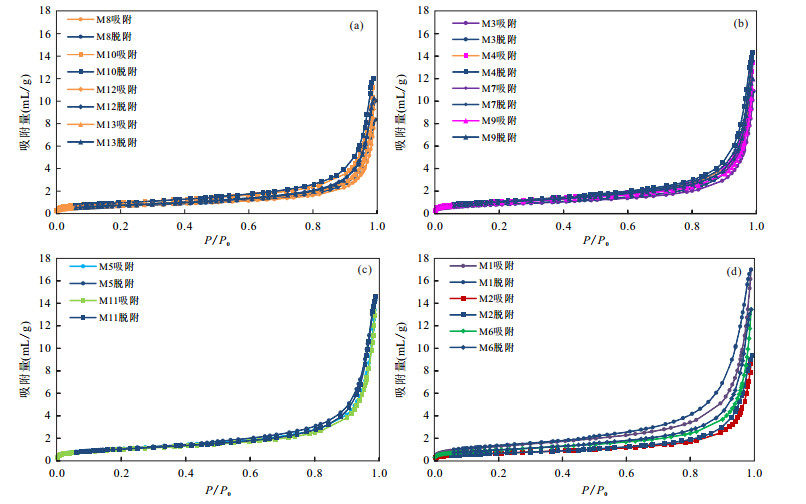
图 5 潜江凹陷王场背斜潜四下段14号韵律层各岩性低温氮气吸-脱附曲线
a.泥质白云岩;b.泥质白云岩,含灰(M3和M7)及含硬石膏(M4和M9);c.白云质泥岩,含灰(M11)及含硬石膏(M5);d.泥质灰岩(M1)、含灰-云泥岩(M2)及云-泥质硬石膏岩(M6)
Fig. 5. Adsorption-desorption isotherms of N2 at liquid N2(-197.3 ℃) temperature of different lithologies of the 14th cyclotherm of the lower Qian4 Member in the Wangchang Anticline of the Qianjiang Sag
表 2 国内外主要页岩油产层储层地质参数统计表
Table 2. Geological data of major pay zones of the shale oil at home and abroad
构造单元 Williston盆地 Western Gulf盆地 Permian盆地 沁阳凹陷 地层 Bakken中段 Eagle Ford组 Wolfcamp组 核桃园组 埋深(m) 3 155.7~3 203.1 2 409.4~2 849.9 \ 2 414~2 452 岩性 白云质粉砂,粉砂质白云岩 泥灰岩 钙质页岩、硅质页岩 灰质页岩,粉砂质页岩 参数 范围 平均 范围 平均 范围 平均 范围 平均 碳酸盐类型及含量 方解石(%) 0~7 1.4 8~83 53 \ \ 1~42 10 白云石(%) 39~63 53 0~2.0 0.5 \ \ 2~26 17 岩石物性 孔隙度(%) 4.0~11.0 7.0 1.6~14.0 4.8 9.0~12.2 10.3 2.7~5.8 4.3 脉充衰减渗透率(μD) \ \ \ \ 0.068~1.010 0.250 \ \ 高压压汞 压汞孔隙度(%) \ \ 0.32~10.27 4.7 \ \ \ \ 压汞渗透率(μD) \ \ 0.002 6~0.864 7 0.247 7 0.004 4~0.775 0 0.190 0 \ \ 中值孔喉(μm) \ \ 0.007 3~0.013 5 0.009 9 0.004 0 \ \ \ 介孔率(%) 4~99 \ 94~100 \ 99 \ \ \ 大孔率(%) < 1~96 \ 0~6 \ < 1 \ \ \ 氮气吸附 微孔率(%) \ \ \ \ \ \ 20.56~34.73 26.5 介孔率(%) \ \ \ \ \ \ 58.76~70.00 62.1 大孔率(%) \ \ \ \ \ \ 5.45~16.37 11.4 备注 大、介孔率由文中图 2.17中读取 大、介孔率由文中附录A图A中读取 大、介孔率由文中图 10读取 孔隙度为核磁孔隙度 数据来源 Nandy (2017) Ramiro-Ramirez (2016) Rafatian and Capsan (2015) 张文昭(2014) -
Bai, J.X., Shi, W.Z., He, Y., 2014. Controlling Factors and Sequence Models of the Lower 4th Member of Qianjiang Formation in Northern Area of Qianjiang Sag. China Petroleum Exploration, 19(1):22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsykt201401003 Fang, Z.X., Chen, K.Y., Chen, F.L., et al., 2006.The Filling Models of Jianghan Salt Lake Basin. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, 1-16 (in Chinese). Guo, F.F., Chang, Y., Zhang, B.S., et al., 2012. Characteristics of Hydrocarbon Migration and Accumulation in Lower Member of Eq4 in Qianjiang Depression. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 19(5):554-558 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkyqt201205003 Guo, L.B., Fu, Y.X., Zhang, L., 2013. The Emphatic Area of E2ql4 Reservoir Exploration in Qianjiang Depression. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 35(8):45-48 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hou, Y. G., Wang, F. R., He, S., et al., 2017. Properties and Shale Oil Potential of Saline Lacustrine Shales in the Qianjiang Depression, Jianghan Basin, China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 86: 1173-1190. https://doi.org/ 10. 1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.008 doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.008 Hu, Q.H., Zhang, Y.X., Meng, X.H., et al., 2017. Characterization of Micro-Nano Pore Networks in Shale Oil Reservoirs of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag of Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 44(5):681-690 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201705003 Kuila, U., Prasad, M., 2013. Specific Surface Area and Pore-Size Distribution in Clays and Shales. Geophysical Prospecting, 61(2): 341-362. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2478.12028 Lai, J., Wang, G. W., Wang, Z. Y., et al., 2018. A Review on Pore Structure Characterization in Tight Sandstones. Earth-Science Reviews, 177: 436-457. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.12.003 Lei, H., He, L., Li, R. S., et al., 2019. Effects of Boundary Layer and Stress Sensitivity on the Performance of Low-Velocity and One-Phase Flow in a Shale Oil Reservoir: Experimental and Numerical Modeling Approaches. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 180: 186-196. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.petrol.2019.05.025 Li, L., Wang, Z.X., Zheng, Y.H., et al., 2019. Mechanism of Shale Oil Enrichment from the Salt Cyclotherm in Qian3 Member of Qianjiang Sag, Jianghan Basin.Earth Science, 44(3):1012-1023(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201903027 Long, Y.M., Chen, M.F., Chen, F.L., et al., 2019. Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Inter-Salt Shale Oil Reservoirs in Qianjiang Formation, Qianjiang Sag. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 26(1):1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yqdzycsl201901007 Loucks, R. G., Reed, R. M., Ruppel, S. C., et al., 2012. Spectrum of Pore Types and Networks in Mudrocks and a Descriptive Classification for Matrix-Related Mudrock Pores. AAPG Bulletin, 96(6): 1071-1098. https://doi.org/10.1306/08171111061 Lu, S.F., Li, J.Q., Zhang, P.F., et al., 2018.Classification of Microscopic Pore-Throats and the Grading Evaluation on Shale Oil Reservoirs.Petroleum Exploration and Development, 45(3):1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201803008 Lu, S.F., Xue, H.T., Wang, M., et al., 2016.Several Key Issues and Research Trends in Evaluation of Shale Oil.Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(10):1309-1322 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201610012 Lu, Z., Wang, Y.P., Li, L., et al., 2018. Control Effect of Pore Throat Radius on Quality of Extra-Low and Ultra-Low Permeability Reservoir in Member 1 of Qingshankou Formation, Southern Songliao Basin. Earth Science, 43(11):4204-4214 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201811034 Murray, R.C., 1964.Origin and Diagenesis of Gypsum and Anhydrite. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 34(3):512-523. https://doi.org/10.1306/74d710d2-2b21-11d7-8648000102c1865d Nandy, D., 2017. Dolomitization and Porosity Evolution of Middle Bakken Member, Elm Coulee Field and Facies Characterization, Chemostratigraphy and Organic-Richness of Upper Bakken Shale, Williston Basin(Dissertation). Colorado School of Mines, Golden. Nelson, P. H., 2009. Pore-Throat Sizes in Sandstones, Tight Sandstones, and Shales. AAPG Bulletin, 93(3): 329-340. https://doi.org/10.1306/10240808059 Pu, X.G., Qi, Z.X., Zheng, X.L., et al., 2002. Basic Petroleum Geological Characteristics and Resource Potential of Inter-Salt Non-Sandstone Reservoir. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 29(5):28-30+36 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf200205009 Purser, B.H., Brown, A., Aissaoui, D.M., 1994. Nature, Origins and Evolution of Porosity in Dolomites. In: Purser, B., Tucker, M., Zenger, D., eds. Dolomites, Blackwell Scientific Publications, London. Rafatian, N., Capsan, J., 2015. Petrophysical Characterization of the Pore Space in Permian Wolfcamp Rocks. Petrophysics, 56(1):45-57. Ramiro-Ramirez, S., 2016. Petrographic and Petrophysical Characterization of the Eagle Ford Shale in La Salle and Gonzales Counties, Gulf Coast Region, Texas(Dissertation). Colorado School of Mines, Golden, 51-53. Sing, K.S.W., Everett, D.H., Haul, R.A.W., et al., 1985. Reporting Physisorption Data for Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 57(4):603-619. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac198557040603 Sondhi, N., 2011. Petrophysical Characterization of Eagle Ford Shale(Dissertation). University of Oklahoma, Norman, 67-108. Wang, D.F., Wang, S.Z., 1998.Geology of Saline Lacustrine Facies Oilfield. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, 156 (in Chinese). Wang, F.R., He, S., Zheng, Y.H., et al., 2016. Mineral Composition and Brittleness Characteristics of the Inter-Salt Shale Oil Reservoirs in the Qianjiang Formation, Qianjiang Sag. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 38(2):211-218 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201602010 Wang, G.L., Zhang, Y.S., Yang, Y.Q., et al., 2004. Evaluation of Nonsandstone Reservoirs between Salt Beds of the Paleogene Qiangjiang Formation in the Qianjiang Depression of the Jianghan Basin. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 26(5):462-468 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Q.S., Tang, D.Z., Peng, M.X., et al., 2010. Well Logging Response Features and Identification of Non-Sandstone Reservoirs in Jianghan Basin. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 32(2):73-77 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jhsyxyxb201002017 Wu, S.Q., Tang, X.S., Du, X.J., et al., 2013. Geologic Characteristics of Continental Shale Oil in the Qianjiang Depression, Jianghan Salt Lake Basin. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 36(3):282-286 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hddzxyxb201303006 Xia, H.F., Zhai, S.Q., Feng, H.C., et al., 2013. Experimental Research on Pore and Coordination Number of Cores Based on Ct Scanning Technique. Experimental Technology and Management, 30(4):20-23+50 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syjsygl201304006 Xie, T.J., Qi, Z.M., Zhu, Z.D., 1983. Salt Structures in Jianghan Basin and Their Control to Oil and Gas Accumulation. Petroleum Exploration and Development, (6):1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xiong, S.C., Chu, S.S., Pi, S.H., et al., 2017. Micro-Pore Characteristics and Recoverability of Tight Oil Reservoirs. Earth Science, 42(8):1379-1385 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201708016 Xiong, Z.Y., Wu, S.Q., Wang, Y., et al., 2015. Geological Characteristics and Practice for Intersalt Argillaceous Dolomites Reservoir in the Qianjiang Depression of Jianghan Salt Lake Basin. Geological Science and Technology Information, 34(2):181-187 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201502026 Yang, F., Ning, Z. F., Wang, Q., et al., 2016. Pore Structure Characteristics of Lower Silurian Shales in the Southern Sichuan Basin, China: Insights to Pore Development and Gas Storage Mechanism. International Journal of Coal Geology, 156: 12-24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2015.12.015 Yao, J., Tao, J., Li, A.F., 2007. Research on Oil-Water Two-Phase Flow Using 3d Random Network Model. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 28(2):94-97+101 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, S.W., 2007. Reservior Prediction Technology and Sedimentary Charicteristics of Salt Lake in the Qianjiang. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 29(5):36-40 (in Chinese). Zhang, W.Z., 2014. Characteristics and Evaluation Factors of Shale Oil Reservoir of the Third Member of Hetaoyuan Formation, Palaeogene in Biyang Depression (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Beijing, 70-90(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, L.H., Gang, P.X., Xiao, D.Q., et al., 2018. Geological Conditions for Shale Oil Formation and the Main Controlling Factors for the Enrichment of the 2nd Member of Kongdian Formation in the Cangdong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin.Natural Gas Geoscience, 29(9):1323-1332 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201809010 Zou, C.N., Tao, S.Z., Bai, B., et al., 2015. Differences and Relations between Unconventional and Conventional Oil and Gas. China Petroleum Exploration, 20(1):1-16 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsykt201501001 Zou, C.N., Zhu, R.K., Bai, B., et al., 2015. Significance, Geologic Characteristics, Resource Potential and Future Challenges of Tight Oil and Shale Oil. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 34(01):3-17+11-12 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kwysdqhxtb201501002 柏建新, 石万忠, 何勇, 2014.潜江凹陷潜北地区潜四下段盐湖层序控制因素及层序模式.中国石油勘探, 19(1):22-30. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsykt201401003 方志雄, 陈开远, 陈凤玲, 等, 2006.江汉盆地盐湖沉积充填模式.北京:石油工业出版社, 1-16. 郭飞飞, 常悦, 张本书, 等, 2012.潜江凹陷潜四下亚段油气运聚特征.断块油气田, 19(5):554-558. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dkyqt201205003 郭丽彬, 付宜兴, 张亮, 2013.潜江凹陷潜四下亚段油藏勘探值得关注的领域.石油天然气学报, 35(8):45-48. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jhsyxyxb201308009 胡钦红, 张宇翔, 孟祥豪, 等, 2017.渤海湾盆地东营凹陷古近系沙河街组页岩油储集层微米—纳米级孔隙体系表征.石油勘探与开发, 44(5):681-690. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201705003 李乐, 王自翔, 郑有恒, 等, 2019.江汉盆地潜江凹陷潜三段盐韵律层页岩油富集机理.地球科学, 44(3):1012-1023. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.389 龙玉梅, 陈曼霏, 陈风玲, 等, 2019.潜江凹陷潜江组盐间页岩油储层发育特征及影响因素.油气地质与采收率, 26(1):1-6. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yqdzycsl201901007 卢双舫, 李俊乾, 张鹏飞, 等, 2018.页岩油储集层微观孔喉分类与分级评价.石油勘探与开发, 45(3):1-9. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf201803008 卢双舫, 薛海涛, 王民, 等, 2016.页岩油评价中的若干关键问题及研究趋势.石油学报, 37(10):1309-1322. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb201610012 吕洲, 王玉普, 李莉, 等, 2018.孔喉半径对松辽盆地南部青一段特低-超低渗透储层质量的控制作用.地球科学, 43(11):4204-4214. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.578 蒲秀刚, 漆智先, 郑晓玲, 等, 2002.盐间非砂岩油藏基本石油地质特征及资源潜力.石油勘探与开发, 29(5):28-30+36. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syktykf200205009 王典敷, 汪仕忠, 1998.盐湖油田地质.北京:石油工业出版社, 156. 王芙蓉, 何生, 郑有恒, 等, 2016.江汉盆地潜江凹陷潜江组盐间页岩油储层矿物组成与脆性特征研究.石油实验地质, 38(2):211-218. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz201602010 王国力, 张永生, 杨玉卿, 等, 2004.江汉盆地潜江凹陷古近系潜江组盐间非砂岩储层评价.石油实验地质, 26(5):462-468. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz200405011 王庆胜, 汤达祯, 彭美霞, 等, 2010.江汉盆地盐间非砂岩储层测井响应特征与识别.石油天然气学报, 32(2):73-77. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jhsyxyxb201002017 吴世强, 唐小山, 杜小娟, 等, 2013.江汉盆地潜江凹陷陆相页岩油地质特征.东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 36(3):282-286. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hddzxyxb201303006 夏惠芬, 翟上奇, 冯海潮, 等, 2013.基于ct扫描技术的岩心孔隙配位数实验研究.实验技术与管理, 30(4):20-23+50. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syjsygl201304006 谢泰俊, 祁左明, 朱振东, 1983.江汉盆地的盐构造及其对油气的控制作用.石油勘探与开发, (6):1-8. 熊生春, 储莎莎, 皮淑慧, 等, 2017.致密油藏储层微观孔隙特征与可动用性评价.地球科学, 42(8):1379-1385. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.550 熊智勇, 吴世强, 王洋, 等, 2015.江汉盐湖盆地盐间泥质白云岩油藏地质特征与实践.地质科技情报, 34(2):181-187. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8177142 姚军, 陶军, 李爱芬, 2007.利用三维随机网络模型研究油水两相流动.石油学报, 28(2):94-97+101. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syxb200702018 张士万, 2007.潜江盐湖沉积特征及储层预测技术.石油天然气学报, 29(05):36-40. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jhsyxyxb200705008 张文昭, 2014.泌阳凹陷古近系核桃园组三段页岩油储层特征及评价要素(硕士学位论文).北京: 中国地质大学, 70-90. 周立宏, 蒲秀刚, 肖敦清, 等, 2018.渤海湾盆地沧东凹陷孔二段页岩油形成条件及富集主控因素.天然气地球科学, 29(9):1323-1332. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/trqdqkx201809010 邹才能, 陶士振, 白斌, 等, 2015a.论非常规油气与常规油气的区别和联系.中国石油勘探, 20(1):1-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgsykt201501001 邹才能, 朱如凯, 白斌, 等, 2015b.致密油与页岩油内涵、特征、潜力及挑战.矿物岩石地球化学通报, 34(1):3-17+11-12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb201501002 -
 dqkx-45-2-602-Table1-2.pdf
dqkx-45-2-602-Table1-2.pdf

-










 下载:
下载: