Characteristics of Quartz Overgrowth in Sandstones from Es3 Interval Central Anticlinal Belt in Dongying Depression and Its Significance
-
摘要: 石英次生加大是砂岩储层中常见且重要的成岩现象.本文通过对东营凹陷中央背斜带沙三段不同含油级别砂岩样品铸体薄片镜下观察、石英次生加大边宽度和含量的定量统计以及流体包裹体测温,分析了不同含油级别砂岩中石英次生加大边发育特征、期次和石英次生加大所需硅质的可能来源.砂岩样品中石英次生加大边最大宽度和加大边面积分布范围变化大,分别分布在4~90 μm和2.50~39 927.80 μm2之间.砂岩中与油气充注有关的石英次生加大主要有两期,结合埋藏-温度史图,该两期石英次生加大边发育时间分别为距今15~6 Ma和4~0 Ma.钾长石溶蚀和沙三段砂泥岩层中黏土矿物的转化是研究区不同含油级别砂岩石英次生加大边发育的主要硅质来源.东营凹陷中央背斜带沙三段不同含油级别砂岩石英次生加大边发育具有相似性和差异性两种特征:(1)不同含油级别砂岩中石英次生加大边最大宽度和单颗粒石英次生加大边面积整体统计分布特征具有相似性;(2)石英次生加大边宽度和单颗粒石英加大边面积普遍存在差异性.砂岩孔渗性、含烃流体充注造成的酸性水介质环境和油水分布特征是造成沙三段不同含油级别砂岩石英次生加大边发育相似性和差异性的主要原因,该区砂岩中石英次生加大可作为含烃流体充注的成岩示踪标志.Abstract: Quartz overgrowth is a common and important cementation in sandstone reservoirs. On the basis of micro-observation on different oil saturation sandstone thin sections from the Es3 interval of the Central Anticlinal Belt in Dongying depression, the width and the content of quartz overgrowth were quantified and the temperature of fluid inclusions were measured. Then the characteristics of quartz overgrowth, the stage of quartz overgrowth and the possible source of silica required for quartz overgrowth were analyzed. The width and the content of quartz overgrowth vary significantly with a range 4-90 μm and 2.50-39 927.80 μm2, respectively. There are two main stages of secondary quartz overgrowth related to oil and gas filling in sandstone. Combined with burial-temperature histories, the two stages of quartz overgrowth are 15-6 Ma and 4-0 Ma, respectively. The dissolution of potash feldspar and the transformation of clay minerals in sandstone and mudstone layers of the Es3 interval are the main siliceous sources for the quartz overgrowth. The characteristics of quartz overgrowth in different oil saturation sandstone can be concluded into the similarity and difference: (1) The overall distribution of maximum width of quartz overgrowth and the area of each quartz overgrowth in different oil saturation sandstone are the same; (2) the width and the area of quartz overgrowth are generally different from each other. Porosity and permeability of sandstone, acidic water environment caused by hydrocarbon-bearing fluid filling and oil-water distribution characteristics are the main reasons for the similarity and difference of quartz overgrowth in sandstones with different oil saturation. And the quartz overgrowth can be regarded as trace marker of hydrocarbon-bearing fluid filling.
-
Key words:
- Dongying depression /
- Central Anticlinal Belt /
- Es3 /
- oil saturation /
- quartz overgrowth /
- petroleum geology
-
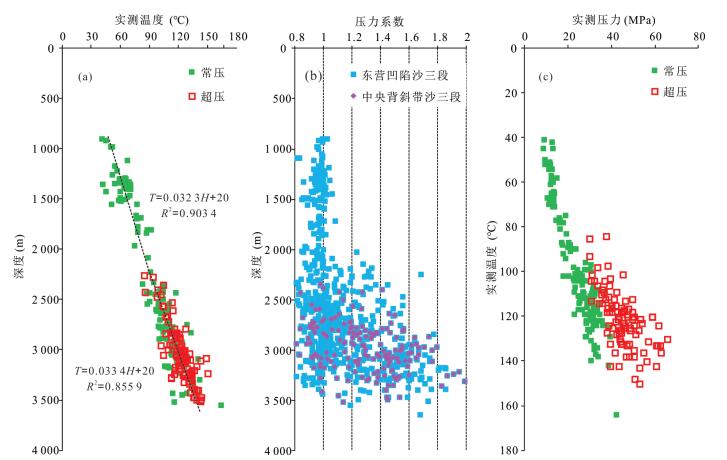
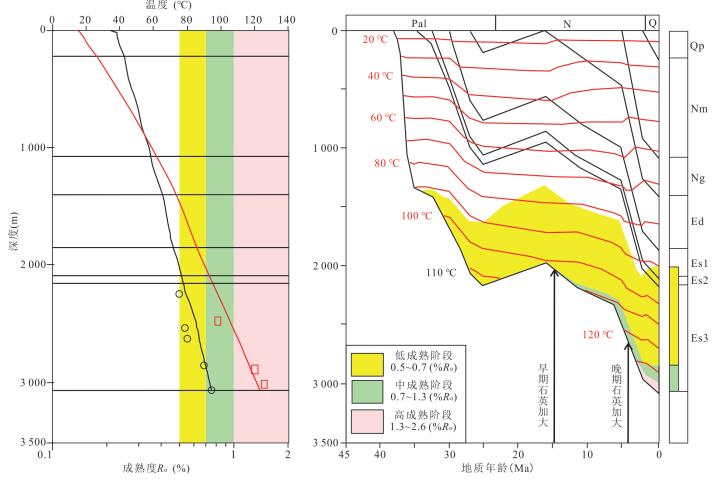
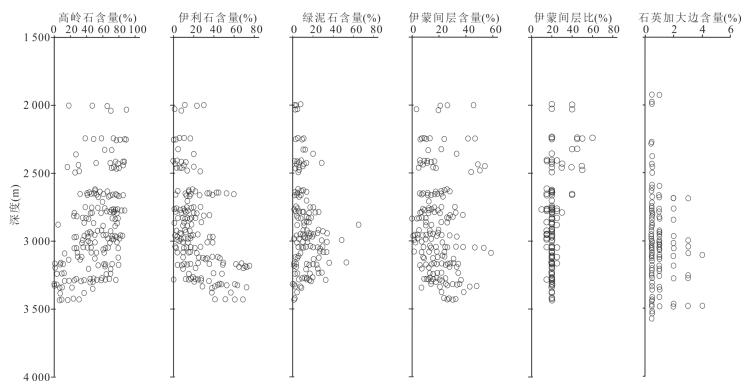
图 2 东营凹陷取样井和样品点纵向分布及超压顶面位置
剖面AB位置见图 1
Fig. 2. Cross section (AB) showing the distribution of core sample and the top of overpressure
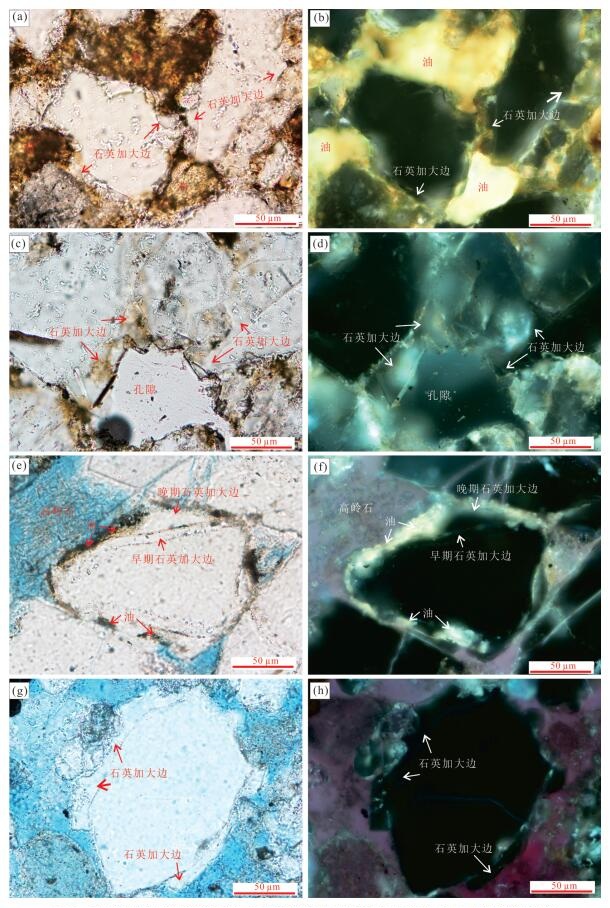
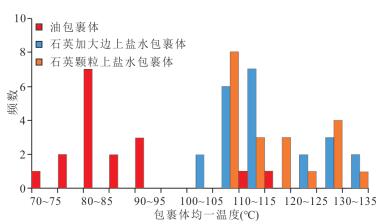
图 5 东营凹陷中央背斜带沙三段不同含油级别砂岩石英次生加大边发育特征
a~d.营691井2 860.94 m油浸细砂岩,孔隙度为23.50%;a和c为单偏光50-,B和D为荧光50UV;e、f.河144井2 698.1 m油斑粉砂岩,孔隙度15.10%,e为单偏光50-,f为荧光50UV;g、h.河144井2 703.95 m油斑粉砂岩,孔隙度13.10%,g为单偏光50-,h为荧光50UV
Fig. 5. The characteristics of quartz overgrowth in different oil saturation sandstones of Es3 interval in Central Anticlinal Belt Dongying depression
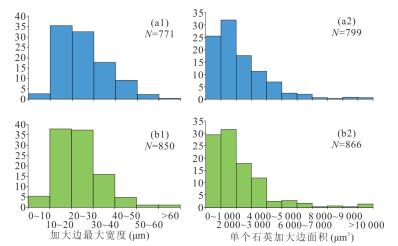
图 7 东营凹陷中央背斜带沙三段不同含油级别砂岩石英次生加大边宽度分布直方图
DY25,DY26,DY27,DY30,DY31,DY32,DY33,DY34为高含油砂岩样品;DY28,DY29,DY36,DY38,DY39,DY43,DY44,DY45为低含油砂岩样品,样品的详细信息见表 1和表 2
Fig. 7. The histogram for the maximum width of each quartz overgrowth of different oil saturation sandstone in Central Anticlinal Belt Dongying depression
表 1 东营凹陷中央背斜带砂岩样品基本信息和碎屑颗粒成分统计表
Table 1. The depths, mineral compositions, porosity, and permeability of sandstones in Central Anticlinal Belt Dongying depression
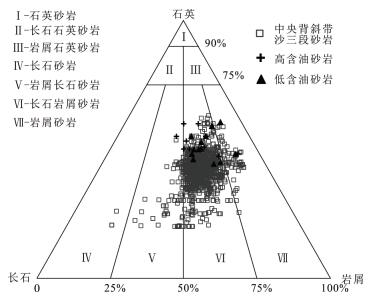
样品编号 井号 深度(m) 层位 岩性 石英 长石 岩屑 CMI 接触类型 孔隙度(%) 渗透率(mD) DY21-2◇ 营691 2455.23 Es3x 油斑灰质砂岩 38 15 23 2.50 点 2.30 0.22 DY22◆ 营691 2458.38 Es3x 富含油细砂岩 44 12 24 3.70 点-线 18.40 218.32 DY23◇ 营691 2630.43 Es3x 油斑细砂岩 35 12 20 3.00 点-线 3.30 0.12 DY24◇ 营691 2636.40 Es3x 泥质砂岩 36 14 31 2.50 点-线 5.30 0.09 DY25◆ 营691 2787.50 Es3x 富含油粉砂岩 42 21 21 2.00 点-线 22.40 8.43 DY26◆ 营691 2860.94 Es3x 油浸细砂岩 44 20 23 2.20 点-线 23.50 72.96 DY27◆ 营691 2878.88 Es3x 富含油细砂岩 44 19 20 2.40 点-线 24.10 13.02 DY28◇ 营691 2885.73 Es3x 油斑细砂岩 47 13 26 3.70 线 11.40 1.68 DY29◇ 营691 2888.99 Es3x 油斑细砂岩 36 12 32 3.00 点-线 11.60 0.18 DY30◆ 新营69 2959.60 Es3 油浸细砂岩 46 13 25 3.70 点-线 16.00 2.60 DY31◆ 新营69 2960.40 Es3 油浸细砂岩 53 18 18 3.00 点-线 22.30 35.00 DY32◆ 新营69 2963.60 Es3 油浸细砂岩 44 20 16 2.20 点-线 24.30 13.00 DY33◆ 新营69 2969.54 Es3 油浸细砂岩 51 13 21 4.00 点-线 22.60 10.00 DY34◆ 新营69 2973.41 Es3 油浸粉砂岩 41 15 19 2.80 点-线 / / DY36◇ 河130 2405.95 Es3s 油斑粉砂岩 39 19 23 2.10 点 34.30 59.70 DY37◇ 河130 2412.38 Es3s 灰质细砂岩 41 18 24 2.30 点 5.20 0.47 DY38◇ 河130 2412.58 Es3s 灰质细砂岩 39 15 24 2.70 点 18.70 5.08 DY39◇ 河130 2420.14 Es3s 粉砂岩 40 21 26 1.90 点 22.10 2.21 DY40◆ 河130 2782.40 Es3z 油浸粉砂岩 39 12 32 3.30 点-线 11.60 1.87 DY41◆ 河130 2784.20 Es3z 油浸粉砂岩 42 14 26 2.90 点-线 23.30 9.97 DY42◇ 河130 2791.65 Es3z 油斑粉砂岩 35 5 33 6.50 点-线 4.60 0.03 DY43◇ 河144 2695.35 Es3z 油斑粉砂岩 38 6 34 5.90 点-线 14.50 11.00 DY44◇ 河144 2698.10 Es3z 油斑粉砂岩 43 8 22 5.50 点-线 15.10 13.00 DY45◇ 河144 2703.95 Es3z 油斑粉砂岩 49 6 26 8.50 点-线 13.10 5.00 注:表中石英、长石和岩屑含量均为面积百分数,CMI=单晶石英/单晶长石;样品编号中◆代表高含油砂岩样品,◇代表低含油砂岩样品. 表 2 东营凹陷中央背斜带沙三段砂岩石英次生加大边宽度统计数据表
Table 2. Statistical data for the area and maximum width of quartz overgrowth, the solution pores of feldspar, and the oil saturation of sandstones
编号 岩石名称 石英加大边面积百分数(%) 石英加大边最大宽度范围(μm) 单颗粒石英加大边面积(μm2) 宽度统计点数 长石溶蚀面孔率(%) 含油饱和度(%) DY25◆ 富含油粉砂岩 0.27 7~47 194.50~6869.60 52 2.40 62.70 DY26◆ 油浸细砂岩 0.90 8~60 9.00~9212.70 191 2.98 / DY27◆ 富含油细砂岩 0.72 6~55 412.60~13434.50 176 2.53 52.80 DY30◆ 油浸细砂岩 0.67 11~51 2.50~12960.62 156 3.56 49.20 DY31◆ 油浸细砂岩 0.08 8~45 451.60~3888.20 56 2.29 47.70 DY32◆ 油浸细砂岩 0.43 10~72 599.40~13060.80 106 2.07 57.70 DY33◆ 油浸细砂岩 0.20 13~43 198.50~6362.10 41 2.64 59.70 DY34◆ 油浸粉砂岩 0.07 4~36 199.10~2507.50 21 2.01 / DY28◇ 油斑细砂岩 0.22 10~35 882.90~12876.40 39 0.17 / DY29◇ 油斑细砂岩 0.36 8~38 214.50~4609.70 91 0.81 / DY36◇ 油斑粉砂岩 0.78 10~54 4.80~39927.85 215 2.19 / DY38◇ 灰质细砂岩 0.46 10~67 1236.10~11567.10 118 0.39 / DY39◇ 粉砂岩 0.20 16~90 331.40~4998.40 62 1.29 / DY43◇ 油斑粉砂岩 0.03 14~22 541.30~2395.90 25 0.19 / DY44◇ 油斑粉砂岩 0.71 9~44 371.10~11600.50 162 1.16 / DY45◇ 油斑粉砂岩 0.64 7~76 3.00~9118.60 154 0.24 / 注:样品编号中◆代表高含油砂岩样品,◇代表低含油砂岩样品. -
BjØ rkum, P. A., Oelkers, E. H., Nadeau, P. H., et al., 1998. Porosity Prediction in Quartzose Sandstones as a Function of Time, Temperature, Depth, Stylolite Frequency, and Hydrocarbon Saturation. AAPG Bulletin, 82(4):637-648. https://doi.org/10.1306/1d9bc5cf-172d-11d7-8645000102c1865d Cai, J. G., Zhang, Z. H., Zhu, X. M., et al., 2003. Hydrocarbon Filling and Chemical Diagenesis Evolution of the Clastic Reservoir of the Paleogene in Dongying Sag. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 30(3):79-83 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf200303022 Cao, Y. C., Chen, L., Wang, Y. Z., et al., 2011. Diagenetic Evolution of Es3 Reservoir and Its Influence on Property in the Northern Minfeng Sub-Sag of Dongying Sag. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 35(5):6-13 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydxxb201105002 Carr, A. D., Petersen, H. I., 2004. Modelling of the Hydrocarbon Generation History and Volumetric Considerations of the Coal-Sourced Lulita Field, Danish North Sea. Petroleum Geoscience, 10(2):107-119. https://doi.org/10.1144/1354-079303-595 Gluyas, J., 1993. The Link between Petroleum Emplacement and Sandstone Cementation. Geological Society, 4:1395-1402. https://doi.org/10.1144/0041395 Guo, J., Zeng, J. H., Song, G. Q., et al., 2014. Response of Diagenesis to Hydrocarbon Fluid Flow in Central Uplift Belt of Dongying Depression. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 44(4):1123-1133 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201404006 Guo, X. W., He, S., Liu, K. Y., et al., 2010. Oil Generation as the Dominant Overpressure Mechanism in the Cenozoic Dongying Depression, Bohai Bay Basin, China. AAPG Bulletin, 94(12):1859-1881. https://doi.org/10.1306/05191009179 Guo, X. W., He, S., Song, G. Q., et al., 2011. Evidences of Overpressure Caused by Oil Generation in Dongying Depression. Erath Science, 36(6):1085-1094 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201106013 Hao, X. F., 2013. Overpressure Genesis and Evolution of Sandstone Reservoirs in the 3rd and 4th Members of Shahejie Formation, the Dongying Depression. Oil and Gas Geology, 34(2):167-173 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201302004 Haszeldine, R. S., Cavanagh, A. J., England, G. L., 2003. Effects of Oil Charge on Illite Dates and Stopping Quartz Cement:Calibration of Basin Models. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 78-79:373-376. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0375-6742(03)00151-1 He, S., Song, G. Q., Wang, Y. S., et al., 2012. Distribution and Major Control Factors of the Present-Day Large-Scale Overpressured System in Dongying Depression. Erath Science, 37(5):1029-1042 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201205015 Hendry, J. P., Trewin, N. H., 1995. Authigenic Quartz Microfabrics in Cretaceous Turbidites:Evidence for Silica Transformation Processes in Sandstones. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 65(2):380-392. https://doi.org/10.1306/d42680cc-2b26-11d7-8648000102c1865d Li, Z., Luo, W., Zeng, B. Y., et al., 2018. Fluid-Rock Interactions and Reservoir Formation Driven by Multiscale Structural Deformation in Basin Evolution. Earth Science, 43(10):3498-3510 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201810013 Marchand, A. M. E., Haszeldine, R. S., Macaulay, C. I., et al., 2000. Quartz Cementation Inhibited by Crestal Oil Charge:Miller Deep Water Sandstone, UK North Sea. Clay Minerals, 35(1):201-210. https://doi.org/10.1180/000985500546585 Marchand, A. M. E., Haszeldine, R. S., Smalley, P. C., et al., 2001. Evidence for Reduced Quartz-Cementation Rates in Oil-Filled Sandstones. Geology, 29(10):915-918. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2001)0290915:efrqcr>2.0.co; 2 doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)0290915:efrqcr>2.0.co;2 Marchand, A. M. E., Smalley, P. C., Haszeldine, R. S., et al., 2002. Note on the Importance of Hydrocarbon Fill for Reservoir Quality Prediction in Sandstones. AAPG Bulletin, 86(9):1561-1571. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-7753(02)00304-X McBride, E. F., 1989. Quartz Cement in Sandstones:A Review. Earth-Science Reviews, 26(1-3):69-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(89)90019-6 Molenaar, N., Cyziene, J., Sliaupa, S., et al., 2008. Lack of Inhibiting Effect of Oil Emplacement on Quartz Cementation:Evidence from Cambrian Reservoir Sandstones, Paleozoic Baltic Basin. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 120(9):1280-1295. https://doi.org/10.1130/B25979.1 Oelkers, E. H., Bjorkum, P. A., Murphy, W. M. A., 1996. A Petrographic and Computational Investigation of Quartz Cementation and Porosity Reduction in North Sea Sandstones. American Journal of Science, 296(4):420-452. https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.296.4.420 Oye, O. J., Aplin, A. C., Jones, S. J., et al., 2018. Vertical Effective Stress as a Control on Quartz Cementation in Sandstones. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 98:640-652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.09.017 Peltonen, C., Marcussen, ., Bj rlykke, K., et al., 2009. Clay Mineral Diagenesis and Quartz Cementation in Mudstones:The Effects of Smectite to Illite Reaction on Rock Properties. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 26(6):887-898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.01.021 Qiu, N. S., Jin, Z. J., Hu, W. X., 2000. Study on the Hydrocarbon Charge History in Dongying Depression by Evidence from Fluid Inclusions. Journal of China University of Petroleum (Edition of Natural Science), 24(4):95-97 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydxxb200004023 Ramm, M., 1992. Porosity-Depth Trends in Reservoir Sandstones:Theoretical Models Related to Jurassic Sandstones Offshore Norway. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 9(5):553-567. https://doi.org/10.1016/0264-8172(92)90066-n Robinson, A., Gluyas, J., 1992. Duration of Quartz Cementation in Sandstones, North Sea and Haltenbanken Basins. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 9(3):324-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/0264-8172(92)90081-o Vagle, G. B., Hurst, A., Dypvik, H., 1994. Origin of Quartz Cements in some Sandstones from the Jurassic of the Inner Moray Firth (UK). Sedimentology, 41(2):363-377. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.1994.tb01411.x Walderhaug, O., 1994. Temperatures of Quartz Cementation in Jurassic Sandstones from the Norwegian Continental Shelf:Evidence from Fluid Inclusions. Journal of Sedimentary Research, A64(2):311-323. https://doi.org/10.1306/d4267d89-2b26-11d7-8648000102c1865d Wang, B. J., 2012. Overpressure Distribution and Evolution, Dynamical Mechanism of Oil and Gas, Dongying Depression (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, J. F., 2005. Sedimentary Facies of the Shahejie Formation of Paleogene in Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression. Journal of Palaeogeography, 7(1):45-58 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb200501005 Weibel, R., Friis, H., Kazerouni, A. M., et al., 2010. Development of Early Diagenetic Silica and Quartz Morphologies:Examples from the Siri Canyon, Danish North Sea. Sedimentary Geology, 228(3-4):151-170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2010.04.008 Wilkinson, M., Haszeldine, R. S., Ellam, R. M., et al., 2004. Hydrocarbon Filling History from Diagenetic Evidence:Brent Group, UK North Sea. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 21(4):443-455. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0264-8172(03)00092-8 Worden, R. H., Bukar, M., Shell, P., 2018. The Effect of Oil Emplacement on Quartz Cementation in a Deeply Buried Sandstone Reservoir. AAPG Bulletin, 102(1):49-75. https://doi.org/10.1306/02071716001 Worden, R. H., Morad, S., 2000. Quartz Cementation in Oil Field Sandstones:A Review of the Key Controversies. In:Worden, R. H., Morad, S., eds., Quartz Cementation in Oil Field Sandstones. Blackwell Publishing Ltd., Oxford, Worden, R. H., Oxtoby, N. H., Smalley, P. C., 1998. Can Oil Emplacement Prevent Quartz Cementation in Sandstones?. Petroleum Geoscience, 4(2):129-137. https://doi.org/10.1144/petgeo.4.2.129 Yang, Z., He, S., Zhou, C. N., et al., 2010. Coupling Relationship between Reservoir Diagenesis and Natural Gas Accumulation of Daniudi Gas Field in North Ordos Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 31(3):373-378 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201003005 Yuan, G. H., Cao, Y. C., Gluyas, J., et al., 2018. Petrography, Fluid-Inclusion, Isotope, and Trace-Element Constraints on the Origin of Quartz Cementation and Feldspar Dissolution and the Associated Fluid Evolution in Arkosic Sandstones. AAPG Bulletin, 102(5):761-792. https://doi.org/10.1306/0608171616017066 Yuan, G. H., Cao, Y. C., Jia, Z. Z., et al., 2015. Selective Dissolution of Feldspars in the Presence of Carbonates:The Way to Generate Secondary Pores in Buried Sandstones by Organic CO2. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 60(5):105-119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2014.11.001 Zhang, Q. Q., Cao, Y. C., Liu, K. Y., et al., 2017. Sedimentary Characteristics of Re-Transported Gravity Flow Deposits and Their Distribution:Influence of Deltaic Sedimentation in Dongying Sag. Earth Science, 42(11):2025-2039 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201711013.htm Zhou, X., He, S., Chen, Z. Y., et al., 2016. Diagenesis and Diagenetic Facies of Low Porosity and Permeability Sandstone in Member 8 of the Yanchang Formation in Daijiaping Area, Ordos Basin. Oil and Gas Geology, 37(2):155-164 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201602002 蔡进功, 张枝焕, 朱筱敏, 等, 2003.东营凹陷烃类充注与储集层化学成岩作用.石油勘探与开发, 30(3):79-83. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf200303022 操应长, 陈林, 王艳忠, 等, 2011.东营凹陷民丰北带古近系沙三段成岩演化及其对储层物性的影响.中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 35(5):6-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydxxb201105002 郭佳, 曾溅辉, 宋国奇, 等, 2014.东营凹陷中央隆起带烃类流体活动在成岩作用上的响应.吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(4):1123-1133. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201404006 郭小文, 何生, 宋国奇, 等, 2011东营凹陷生油增压成因证据.地球科学, 36(6):1085-1094. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201106013 郝雪峰, 2013.东营凹陷沙三-沙四段砂岩储层超压成因与演化.石油与天然气地质, 34(2):167-173. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95357X/20132/45594896.html 何生, 宋国奇, 王永诗, 等, 2012.东营凹陷现今大规模超压系统整体分布特征及主控因素.地球科学, 37(5):1029-1042. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201205015 李忠, 罗威, 曾冰艳, 等, 2018.盆地多尺度构造驱动的流体-岩石作用及成储效应.地球科学, 43(10):3498-3510. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201810013 邱楠生, 金之钧, 胡文喧, 2000.东营凹陷油气充注历史的流体包裹体分析.中国石油大学学报(自然科学版), 24(4):95-97. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sydxxb200004023 王冰洁, 2012.东营凹陷超压特征及演化与油气驱动机制(博士学位论文).武汉: 中国地质大学. 王居峰, 2005.济阳坳陷东营凹陷古近系沙河街组沉积相.古地理学报, 7(1):45-58. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=gdlxb200501005 杨智, 何生, 邹才能, 等, 2010.鄂尔多斯盆地北部大牛地气田成岩成藏耦合关系.石油学报, 31(3):373-378. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb201003005 张青青, 操应长, 刘可禹, 等, 2017.东营凹陷滑塌型重力流沉积分布特征及三角洲沉积对其影响.地球科学, 42(11):2025-2039. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201711013 周翔, 何生, 陈召佑, 等, 2016.鄂尔多斯盆地代家坪地区延长组8段低孔渗砂岩成岩作用及成岩相.石油与天然气地质, 37(2):155-164. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201602002 -










 下载:
下载: