Fe-Mg Isotopic Compositions of Altered Oceanic Crust and Subduction-Zone Fluids
-
摘要: 贫碳酸盐的蚀变洋壳具有与新鲜洋中脊玄武岩一致的Mg同位素组成,说明低温和高温洋壳蚀变不会导致Mg同位素分馏.大别山港河和花凉亭的早期变质脉比榴辉岩具有偏高的δ56Fe-δ26Mg值,而且早期到晚期变质脉的δ56Fe-δ26Mg值逐渐降低.这些结果说明,在流体-岩石反应和流体演化过程中,Fe-Mg同位素发生了显著的分馏,且矿物溶解-再沉淀是同位素分馏的控制因素.相比洋中脊玄武岩,蚀变洋壳和变质脉具有相似或偏高的δ56Fe-δ26Mg值,说明蚀变洋壳脱水产生的流体富集重Fe-Mg同位素,不能解释弧岩浆岩的轻Fe/重Mg同位素组成.因此,弧岩浆岩异常的Fe-Mg同位素组成是熔体提取和富集54Fe-26Mg的蛇纹岩流体交代地幔楔两个过程共同作用的结果.Abstract: The origin of the light Fe and heavy Mg isotope enrichments in arc lavas remains unclear because of the lack of constraints on the Fe-Mg isotope compositions of altered oceanic crust (AOC) and metamorphic fluids in subduction zones. Carbonate-barren AOC has Mg isotope compositions similar to those of fresh mid-ocean ridge basalts, suggesting that low-to-high temperature alteration of oceanic crust by seawater and hydrothermal fluids results in limited Mg isotope fractionation. Fe-Mg isotope measurements show that the early omphacite-epidote veins have higher δ56Fe and δ26Mg compared to the host eclogites and that the δ56Fe and δ26Mg gradually decrease from the early omphacite-epidote through epidote-quartz to the late kyanite-epidote-quartz veins. These results indicate significant Fe-Mg isotope fractionation during fluid-rock interaction and fluid evolution due to the dissolution-precipitation processes of minerals in subduction zones. Compared to mid-ocean ridge basalts, the similar or higher δ56Fe and δ26Mg of AOC and metamorphic veins suggest that AOC-derived fluids are probably enriched in heavy Fe-Mg isotopes. Thus, contribution from AOC-derived fluids is unlikely to explain the light Fe and heavy Mg isotope compositions of arc lavas. We propose that the Fe-Mg isotope anomaly of arc lavas may result from a combination of prior melt depletion and addition of serpentinite-derived 54Fe-26Mg-rich fluids into the overlying mantle wedge.
-
Key words:
- Fe-Mg isotopes /
- altered oceanic crust /
- eclogite /
- metamorphic fluids /
- fluid evolution /
- arc lavas /
- geochemistry
-
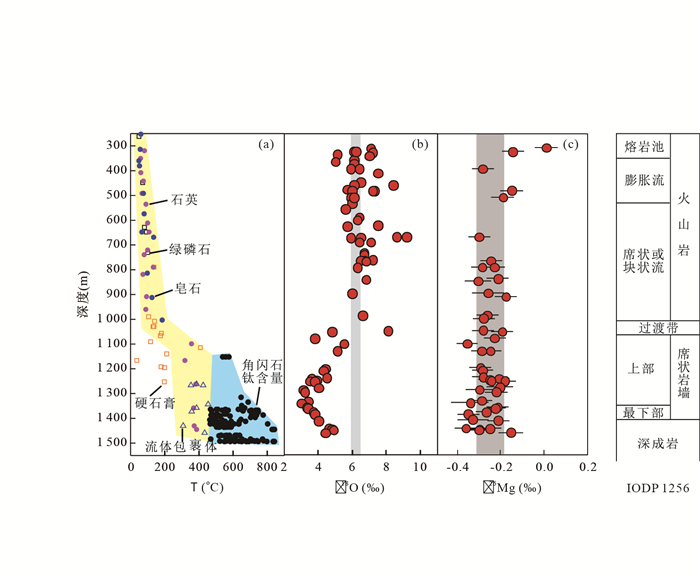
图 1 IODP 1256钻孔洋壳的蚀变温度(a),δ18O(b)和δ26Mg(c)的空间变化
蚀变温度、O和Mg同位素数据引自Alt et al.(2010)、Gao et al.(2012)和Huang et al.(2015).灰色条带表示新鲜洋中脊玄武岩的O和Mg同位素组成(Harmon and Hoefs, 1995;Teng et al., 2010)
Fig. 1. Down-hole variations in alteration temperatures, δ18O, and δ26Mg of oceanic crust from IODP site 1256
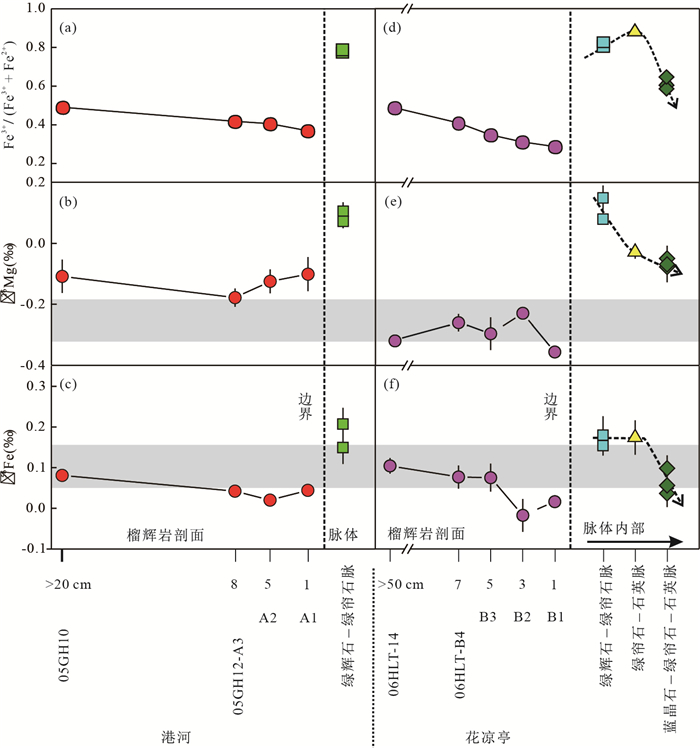
图 2 大别山港河和花凉亭榴辉岩和变质脉的Fe3+/ΣFe、δ26Mg和δ56Fe变化
据Huang et al.(2019).灰色条带表示新鲜洋中脊玄武岩的Fe-Mg同位素组成(Weyer and Ionov, 2007;Teng et al., 2010;Nebel et al., 2013)
Fig. 2. Fe3+/ΣFe、δ26Mg, and δ56Fe in ecoligites and veins at Ganghe and Hualiangting in the Dabie orogen
图 3 大别山港河和花凉亭超高压榴辉岩和变质脉中矿物的Fe-Mg同位素组成
据Huang et al.(2019).黑色正方形表示新鲜洋中脊玄武岩的Fe-Mg同位素组成(Weyer and Ionov, 2007;Teng et al., 2010;Nebel et al., 2013)
Fig. 3. δ26Mg and δ56Fe of minerals from ecoligites and veins at Ganghe and Hualiangting in the Dabie orogen
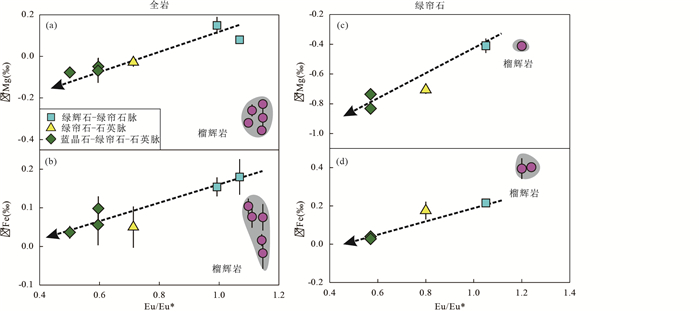
图 4 大别山花凉亭三期变质脉全岩(a, b)和绿帘石(c, d)的Eu/Eu*、δ26Mg和δ56Fe协变图解
Fig. 4. Eu/Eu*, δ26Mg, and δ56Fe in whole-rocks (a, b) and epidotes (c, d) of multi-stage veins at Hualiangting in the Dabie orogen
-
Alt, J.C., Laverne, C., Coggon, R.M., et al., 2010.Subsurface Structure of a Submarine Hydrothermal System in Ocean Crust Formed at the East Pacific Rise, ODP/IODP Site 1256.Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 11(10): Q10010. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010gc003144 Chen, Y.X., Schertl, H.P., Zheng, Y.F., et al., 2016.Mg-O Isotopes Trace the Origin of Mg-Rich Fluids in the Deeply Subducted Continental Crust of Western Alps.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 456:157-167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.09.010 Craddock, P.R., Warren, J.M., Dauphas, N., 2013.Abyssal Peridotites Reveal the Near-Chondritic Fe Isotopic Composition of the Earth.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 365:63-76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.01.011 Dauphas, N., Craddock, P.R., Asimow, P.D., et al., 2009.Iron Isotopes May Reveal the Redox Conditions of Mantle Melting from Archean to Present.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 288(1-2):255-267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2009.09.029 Dauphas, N., John, S.G., Rouxel, O., 2017.Iron Isotope Systematics.Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 82(1):415-510. https://doi.org/10.2138/rmg.2017.82.11 Debret, B., Bouilhol, P., Pons, L., et al., 2018.Carbonate Transfer during the Onset of Slab Devolatilization:New Insights from Fe and Zn Stable Isotopes.Journal of Petrology, 59(6):1145-1166. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egy057v Debret, B., Millet, M.A., Pons, M.L., et al., 2016.Isotopic Evidence for Iron Mobility during Subduction.Geology, 44(3):215-218. https://doi.org/10.1130/g37565.1 El Korh, A., Luais, B., Deloule, E., et al., 2017.Iron Isotope Fractionation in Subduction-Related High-Pressure Metabasites (Ile de Groix, France).Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 172:41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-017-1357-x Elliott, T., Plank, T., Zindler, A., et al., 1997.Element Transport from Slab to Volcanic Front at the Mariana Arc.Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 102(B7):14991-15019. doi: 10.1029/97JB00788 Feineman, M.D., Ryerson, F.J., DePaolo, D.J., et al., 2007.Zoisite-Aqueous Fluid Trace Element Partitioning with Implications for Subduction Zone Fluid Composition.Chemical Geology, 239(3-4):250-265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.01.008 Foden, J., Sossi, P.A., Nebel, O., 2018.Controls on the Iron Isotopic Composition of Global Arc Magmas.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 494:190-201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2018.04.039 Gao, Y.J., Vils, F., Cooper, K.M., et al., 2012.Downhole Variation of Lithium and Oxygen Isotopic Compositions of Oceanic Crust at East Pacific Rise, ODP Site 1256. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 13(10): Q10001. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012gc004207 Guo, S., Chen, Y., Ye, K., et al., 2015.Formation of Multiple High-Pressure Veins in Ultrahigh-Pressure Eclogite (Hualiangting, Dabie Terrane, China):Fluid Source, Element Transfer, and Closed-System Metamorphic Veining.Chemical Geology, 417:238-260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.10.006 Guo, S., Ye, K., Chen, Y., et al., 2012.Fluid-Rock Interaction and Element Mobilization in UHP Metabasalt:Constraints from an Omphacite-Epidote Vein and Host Eclogites in the Dabie Orogen.Lithos, 136-139:145-167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2011.11.008 Guo, S., Ye, K., Wu, T.F., et al., 2013.A Potential Method to Confirm the Previous Existence of Lawsonite in Eclogite:The Mass Imbalance of Sr and LREEs in Multistage Epidote (Ganghe, Dabie UHP Terrane).Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 31(4):415-435. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12027 Guo, S., Ye, K., Yang, Y.H., et al., 2014.In Situ Sr Isotopic Analyses of Epidote:Tracing the Sources of Multi-Stage Fluids in Ultrahigh-Pressure Eclogite (Ganghe, Dabie Terrane).Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 167(2):975. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-014-0975-9 Harmon, R.S., Hoefs, J., 1995.Oxygen Isotope Heterogeneity of the Mantle Deduced from Global 18O Systematics of Basalts from Different Geotectonic Settings.Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 120(1):95-114. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00311010 Huang, J., Guo, S., Jin, Q.Z., et al., 2019.Iron and Magnesium Isotopic Compositions of Subduction-Zone Fluids and Implications for Arc Volcanism.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2019.06.020 Huang, J., Ke, S., Gao, Y.J., et al., 2015.Magnesium Isotopic Compositions of Altered Oceanic Basalts and Gabbros from IODP Site 1256 at the East Pacific Rise.Lithos, 231:53-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.009 Inglis, E.C., Debret, B., Burton, K.W., et al., 2017.The Behavior of Iron and Zinc Stable Isotopes Accompanying the Subduction of Mafic Oceanic Crust:A Case Study from Western Alpine Ophiolites.Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 18(7):2562-2579. doi: 10.1002/2016GC006735 Li, S.G., Yang, W., Ke, S., et al., 2017.Deep Carbon Cycles Constrained by a Large-Scale Mantle Mg Isotope Anomaly in Eastern China.National Science Review, 4(1):111-120. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nww070 Li, Y.L., Zheng, Y.F., Fu, B., 2005.Mössbauer Spectroscopy of Omphacite and Garnet Pairs from Eclogites:Application to Geothermobarometry.American Mineralogist, 90(1):90-100. https://doi.org/10.2138/am.2005.1400 Martin, L.A.J., Wood, B.J., Turner, S., et al., 2011.Experimental Measurements of Trace Element Partitioning between Lawsonite, Zoisite and Fluid and Their Implication for the Composition of Arc Magmas.Journal of Petrology, 52(6):1049-1075. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egr018 Nebel, O., Arculus, R.J., Sossi, P.A., et al., 2013.Iron Isotopic Evidence for Convective Resurfacing of Recycled Arc-Front Mantle beneath Back-Arc Basins.Geophysical Research Letters, 40(22):5849-5853. https://doi.org/10.1002/2013gl057976 Nebel, O., Sossi, P.A., Bénard, A., et al., 2015.Redox-Variability and Controls in Subduction Zones from an Iron-Isotope Perspective.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 432:142-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.09.036 Pogge von Strandmann, P.A.E., Elliott, T., Marschall, H.R., et al., 2011.Variations of Li and Mg Isotope Ratios in Bulk Chondrites and Mantle Xenoliths.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(18):5247-5268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2011.06.026 Schmidt, M.W., Poli, S., 1998.Experimentally Based Water Budgets for Dehydrating Slabs and Consequences for Arc Magma Generation.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 163(1-4):361-379. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(98)00142-3 Scott, S.R., Sims, K.W.W., Frost, B.R., et al., 2017.On the Hydration of Olivine in Ultramafic Rocks:Implications from Fe Isotopes in Serpentinites.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 215:105-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2017.07.011 Sossi, P.A., Nebel, O., Foden, J., 2016.Iron Isotope Systematics in Planetary Reservoirs.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 452:295-308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2016.07.032 Teng, F.Z., Dauphas, N., Huang, S.C., et al., 2013.Iron Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 107:12-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2012.12.027 Teng, F.Z., Hu, Y., Chauvel, C., 2016.Magnesium Isotope Geochemistry in Arc Volcanism.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 113(26):7082-7087. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1518456113 Teng, F.Z., Li, W.Y., Ke, S., et al., 2010.Magnesium Isotopic Composition of the Earth and Chondrites.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(14):4150-4166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2010.04.019 Turner, S., Williams, H., Piazolo, S., et al., 2018.Sub-Arc Xenolith Fe-Li-Pb Isotopes and Textures Tell Tales of Their Journey through the Mantle Wedge and Crust.Geology, 46(11):947-950. https://doi.org/10.1130/g45359.1 Wang, S.J., Teng, F.Z., Li, S.G., et al., 2014.Magnesium Isotopic Systematics of Mafic Rocks during Continental Subduction.Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143:34-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2014.03.029 Wang, S.J., Teng, F.Z., Li, S.G., et al., 2017.Tracing Subduction Zone Fluid-Rock Interactions Using Trace Element and Mg-Sr-Nd Isotopes.Lithos, 290/291:94-103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2017.08.004 Weyer, S., Ionov, D.A., 2007.Partial Melting and Melt Percolation in the Mantle:The Message from Fe Isotopes.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 259(1-2):119-133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2007.04.033 Williams, H., Peslier, A., McCammon, C., et al., 2005.Systematic Iron Isotope Variations in Mantle Rocks and Minerals:The Effects of Partial Melting and Oxygen Fugacity.Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 235(1-2):435-452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.04.020 Zheng, Y.F., Fu, B., Gong, B., et al., 2003.Stable Isotope Geochemistry of Ultrahigh Pressure Metamorphic Rocks from the Dabie-Sulu Orogen in China:Implications for Geodynamics and Fluid Regime.Earth-Science Reviews, 62(1-2):105-161. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-8252(02)00133-2 -









 下载:
下载: