Comparison of Microbial Community in Topsoil among Different Habitats in Dajiuhu, Hubei Province: Evidence from Phospholipid Fatty Acids
-
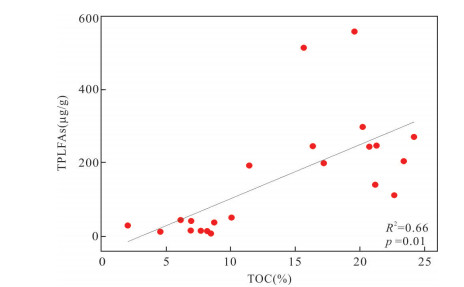
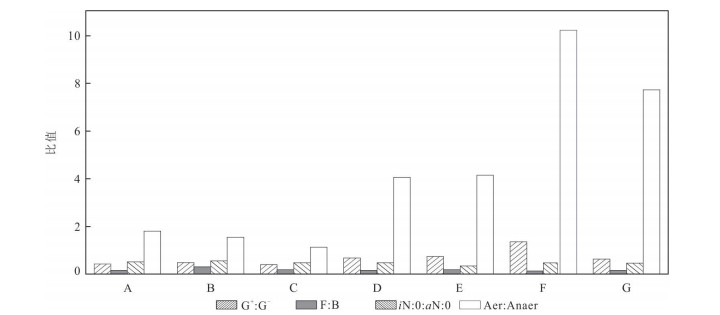
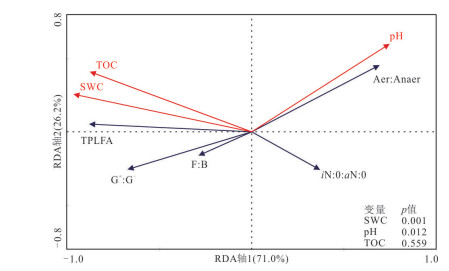
摘要: 磷脂脂肪酸(phospholipid fatty acid,PLFAs)是活体微生物细胞膜的重要组成部分,微生物通过改变细胞膜中PLFA组成,快速响应环境变化.目前,表土PLFAs研究主要集中于季节和植被群落变化对微生物群落结构影响,对于不同生境下表土PLFAs揭示的微生物群落结构的差异性尚不明确.基于此,对神农架大九湖7种不同生境表土进行PLFAs研究.结果表明,表土样品PLFAs集中分布于C14到C19;除湿生泥炭沼泽和湿生半退化沼泽生境外,其他生境以n16:0为主峰.不同生境的PLFAs含量差异较大,沼泽生境TPLFAs含量是草甸及阔叶林生境下的3~8倍.PLFAs组成还揭示出生境间主要受到pH和含水率的影响,微生物群落结构存在差异.不同生境下表层土壤PLFAs揭示的微生物丰度和群落结构具有一定的相似性及差异性.运用PLFAs对微生物量及微生物群落结构的划分将有助于更好的了解区域生态系统中微生物群落结构的变化,为研究微生物参与碳循环及古生态研究奠定基础.Abstract: As an important component of microbial cell membrane,phospholipid fatty acid (PLFAs) can respond sensitively to environmental changes,PLFAs can be altered by microorganisms changing their cell membrane composition by changing their metabolic or nutrient pathways. The current researches on soil PLFAs mainly focus on how changes in seasons and vegetation community affect microbial community structure. It is still not clear how habitats mediate the structure of soil microbial community revealed by topsoil PLFAs. In this study,soil PLFAs compositions were investigated among different habitats (including Sphagnum peat,herb peat,degraded peat,hygrophyte-mesophyte meadow,mesophyte-xeric meadow,xeric meadow,and deciduous broad-leaved forest) in Dajiuhu,Shennongjia. The results show that totally 26 PLFAs with carbon numbers ranging from C14 to C19 are common in the topsoil of the seven habitats. The concentration of total PLFAs in peats is 3-8 times higher than that in meadows. Because of pH and SWC (soil water content) PLFAs also reveal that microbial community structures are different among habitats. The microbial abundance and microbial community structure are similar and different in topsoil under different habitats. The results in this study shed light to better understand the changes of microbial community structure in regional ecosystem,and to facilitate the study of microbe's role in carbon cycle,paleoecology.
-
Key words:
- phospholipid fatty acid /
- habitat /
- microbial biomass /
- microbial community structure /
- topsoil /
- geobiology
-
表 1 不同生境下表土的物理化学性质
Table 1. Physical and chemical properties of topsoil collected from different habitats
生境类型 SWC pH NH3-N NO3--N C/N TOC T (%) (mg/L) (mg/L) (%) (℃) 湿生泥炭沼泽(n=4) 94.0 4.1±0.1 2.9±0.7 0.2±0.1 15.5±2.6 19.8±2.0 17.5±3.7 湿生草本沼泽(n =5) 84.0±0.1 4.1±0.3 2.6±0.9 0.1±0.1 18.6±2.0 19.7±3.0 16.6±2.9 湿生半退化沼泽(n =3) 76.0±0.1 3.9±0.2 3.4±1.3 0.2±0.1 16.8±0.6 18.8±5.4 17.7±0.5 湿生-中生草甸(n =3) 51.0±0.1 4.6±0.1 2.5±0.9 0.2±0.2 18.8±5.0 5.7±2.7 18.7±1.7 中生-旱生草甸(n =2) 34.0±0.1 4.7±0.1 3.0±0.3 1.0±0.6 15.4±4.4 6.9±0.8 19.5±0.6 旱生草甸(n =2) 36.0 4.6±0.1 3.4±0.2 1.0±0.4 16.6±6.2 5.8±1.1 20.0 落叶阔叶林(n =3) 48.0 4.8±1.0 3.5±1.6 0.1±0.1 25.2±6.9 9.1±0.7 18.0 -
Andersen, R., Grasset, L., Thormann, M.N., et al., 2010.Changes in Microbial Community Structure and Function Following Sphagnum Peatland Restoration.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42(2):291-301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.11.006 Anderson, J.P.E., Domsch, K.H., 1973.Quantification of Bacterial and Fungal Contributions to Soil Respiration.Archives of Microbiology, 93:113-127. doi: 10.1007-BF00424942/ Borga, P., Nilsson, M., Tunlid, A., 1994.Bacterial Communities in Peat in Relation to Botanical Composition as Revealed by Phospholipid Fatty Acid Analysis.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 26(7):841-848. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(94)90300-x Börjesson, J., Menichetti, L., Thornton, B., et al., 2016.Seasonal Dynamics of the Soil Microbial Community:Assimilation of Old and Young Carbon Sources in a Long-Term Field Experiment as Revealed by Natural 13C Abundance.European Journal of Soil Science, 67:79-89. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejss.12309 Ding, X., Chen, S., Zhang, B., et al., 2019.Warming Increases Microbial Residue Contribution to Soil Organic Carbon in an Alpine Meadow.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 15:13-19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.04.004 Eberlein, C., Baumgarten, T., Starke, S., et al., 2018.Immediate Response Mechanisms of Gram-Negative Solvent-Tolerant Bacteria to Cope with Environmental Stress:Cis-Trans Isomerization of Unsaturated Fatty Acids and Outer Membrane Vesicle Secretion.Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 102:2583-2593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8832-9 Fanina, N., Kardola, P., Farrellc, M., et al., 2019.The Ratio of Gram-Positive to Gram-Negative Bacterial PLFA Markers as an Indicator of Carbon Availability in Organic Soils.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 128:111-114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2018.10.010 Findlay, R.H., King, G.M., Watling, L., 1989.Efficacy of Phospholipid Analysis Determining Microbial Biomass in Sediments.Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 55(11):2888-2893. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_203186 Frostegård, A., Tunlid, A., Bååth, E., 1991.Microbial Biomass Measured as Total Lipid Phosphate in Soils of Different Organic Content.Journal of Microbiological Methods, 14(3):151-163. doi: 10.1016-0167-7012(91)90018-L/ Hooper, D.U., Bignell, D.E., Brown, V.K., et al., 2000.Interactions between Aboveground and Belowground Biodiversity in Terrestrial Ecosystems.Bioscience, 50(12):1049-1061. doi: 10.1641/0006-3568(2000)050[1049:IBAABB]2.0.CO;2 Huang, X., Wang, C., Xue, J., et al., 2010.Occurrence of Diploptene in Moss Species from the Dajiuhu Peatland in Southern China.Organic Geochemistry, 41:321-324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.09.008 Huang, X.Y., Zhang, Z.Q., Wang, H.M., et al., 2017.Overview on Critical Zone Observatory at Dajiuhu Peatland, Shennongjia.Earth Science, 42(6):1026-1038(in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dpkx.2017.081 Jaatinen, K., Tuittila, E.S., Laine, J., et al., 2005.Methane-Oxidizing Bacteria in a Finnish Raised Mire Complex:Effects of Site Fertility and Drainage.Microbial Ecology, 50(3):429-439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-005-0219-7 Kourtev, P.S., Ehrenfeld, J.G., Häggblom, M.H., 2003.Experimental Analysis of the Effect of Exotic and Native Plant Species on the Structure and Function of Soil Microbial Communities.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 35(7):895-905. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00120-2 Lauber, C.L., Strickland, M.S., Bradford, M.A., et al., 2008.The Influence of Soil Properties on the Structure of Bacterial and Fungal Communities across Land-Use Types.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40(9):2407-2415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.05.021 Li, J.X., Li, J., Dang, H.S., et al., 2007.Vegetation and Conservation Strategy of Dajiuhu Wetland Park in Shennongjia Region.Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 25(6):605-611(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20083053494.html Li, X.Y., Sun, J., Wang, H.H., et al., 2017.Changes in the Soil Microbial Phospholipid Fatty Acid Profile with Depth in Three Soil Types of Paddy Fields in China.Geoderma, 290:69-74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2016.11.006 Li, Y.Y., Ge, J.W., Peng, F.J., et al., 2017.Characteristics of Methane Flux and Their Effect Factor on Dajiuhu Peatland of Shennongjia.Earth Science, 42(5):832-842(in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2017.071 Liang, C., Schimel, J.P., Jastrow, J.D., 2017.The Importance of Anabolism in Microbial Control over Soil Carbon Storage.Nature Microbiology, 2:17105. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2017.105 Lipson, D.A., Schmidt, S.K., Monson, R.K., 2000.Carbon Availability and Temperature Control the Post-Snowmelt Decline of Microbial Biomass in an Alpine Soil.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32:441-448. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0038-0717(99)00068-1 Liu, H.Y, Gu, Y.S., Lun, Z.J., et al., 2018.Phytolith-Inferred Transfer Function for Paleohydrological Reconstruction of Dajiuhu Peatland, Central China.The Holocene, 28:1623-1630. https://doi.org/10.1177/0959683618782590 Luo, T., Lun, Z.J., Gu, Y.S., et al., 2015.Plant Community Survey and Ecological Protection of Dajiuhu Wetlands in Shengnongjia Area.Wetland Science, 13(2):153-160(in Chinese with English abstract). Miltner, A., Bombach, P., Schmidt-Brücken, B., et al., 2012.SOM Genesis:Microbial Biomass as a Significant Source.Biogeochemistry, 111(1-3):41-55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10533-011-9658-z Miura, T., Makotoa, K., Niwab, S., et al., 2017.Comparison of Fatty Acid Methyl Ester Methods for Characterization of Microbial Communities in Forest and Arable Soil:Phospholipid Fraction (PLFA) versus Total Ester Linked Fatty Acids (EL-FAME).Pedobiologia Journal of Soil Ecology, 63:14-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2017.04.002 Moore-Kucera, J., Dick, R.P., 2008.PLFA Profiling of Microbial Community Structure and Seasonal Shifts in Soils of a Douglas-Fir Chronosequence.Microbial Ecology, 55(3):500-511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-007-9295-1 Mutabaruka, R., Hairiah, K., Cadisch, G., 2007.Microbial Degradation of Hydrolysable and Condensed Tannin Polyphenol-Protein Complexes in Soils from Different Land-Use Histories.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 39:1479-1492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2006.12.036 Olsson, S., Alström, S., 2000.Characterisation of Bacteria in Soils under Barley Monoculture and Crop Rotation.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 32(10):1443-1451. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0038-0717(00)00062-6 Qin, Y.M., Gong, J., Gu, Y.S., et al., 2018.Ecological Monitoring and Environmental Significance of Testate Amoebae in Subalpine Peatlands in West Hubei Province, China.Earth Science, 43(11):4036-4045(in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.599 Rousk, J., Brookes, P.C., Bååth, E., 2010a.Investigating the Mechanisms for the Opposing pH Relationships of Fungal and Bacterial Growth in Soil.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42:926-934. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.02.009 Rousk, J., Brookes, P.C., Bååth, E., 2010b.The Microbial PLFA Composition as Affected by pH in an Arable Soil.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 42:516-520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.11.026 Sundh, I., Borgå, P., Nilsson, M., et al., 1995.Estimation of Cell Numbers of Methanotrophic Bacteria in Boreal Peatlands Based on Analysis of Specific Phospholipid Fatty Acids.FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 18:103-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-6496(95)00046-d Wagner, D., Eisenhauer, N., Cesarz, S., 2015.Plant Species Richness does not Attenuate Responses of Soil Microbial and Nematode Communities to a Flood Event.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 89:135-149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.07.001 Wickland, K.P., Striegl, R.G., Mast, M.A., et al., 2001.Carbon Gas Exchange at a Southern Rocky Mountain Wetland, 1996-1998.Global Biogeochemical Cycle, 15:321-335. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000GB001325 Wu, Y., Ma, B., Zhou, L., et al., 2009.Changes in the Soil Microbial Community Structure with Latitude in Eastern China, Based on Phospholipid Fatty Acid Analysis.Applied Soil Ecology, 43(1-2):234-240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2009.08.002 Xie, S.C., Evershed, R.P., Huang, X.Y., et al., 2013.Concordant Monsoon-Driven Postglacial Hydrological Changes in Peat and Stalagmite Records and Their Impacts on Prehistoric Cultures in Central China.The Geological Society of America, 41(8):827-830. https://doi.org/10.1130/g34318.1 Yu, S.F., She, G.H., Ye, S.M., et al., 2018.Characteristics of Soil Microbial Biomass and Community Composition in Pinus Yunnanensis var.Tenuifolia Secondary Forests.Journal of Sustainable Forestry, 20:1-19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10549811.2018.1483250 Zelles, L., 1997.Phospholipid Fatty Acid Profiles in Selected Members of Soil Microbial Communities.Chemosphere, 35:275-294. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(97)00155-0 Zelles, L., 1999.Fatty Acid Patterns of Phospholipids and Lipopolysaccharides in the Characterisation of Microbial Communities in Soil:A Review.Biology and Fertility of Soils, 29(2):111-129. http://www.bioone.org/servlet/linkout?suffix=i0277-5212-29-1-353-Zelles2&dbid=16&doi=10.1672%2F08-114.1&key=10.1007%2Fs003740050533 Zhang, G., Zheng, C.Y., Wang, Y., et al., 2015.Soil Organic Carbon and Microbial Community Structure Exhibit Different Responses to Three Land Use Types in the North China Plain.Acta Agriculture Scandinavica, 65(4):341-349. https://doi.org/10.1080/09064710.2015.1011223 Zhang, Y.Y., Zheng, N.G., Wang, J., et al., 2019.High Turnover Rate of Free Phospholipids in Soil Confirms the Classic Hypothesis of PLFA Methodology.Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 135:323-330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2019.05.023 Zogg, P.G., Zak, D.R., Ringelberg, D.B., et al., 1997.Compositional and Functional Shifts in Microbial Communities Due to Soil Warming.Soil Science Society of America Journal, 61(2):475-481. https://doi.org/10.2136/sssaj1997.03615995006100020015x 黄咸雨, 张志麒, 王红梅, 等, 2017.神农架大九湖泥炭湿地关键带监测进展.地球科学, 42(6):1026-1038. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.081 李静霞, 李佳, 党海山, 等, 2007.神农架大九湖湿地公园的植被现状与保护对策.武汉植物学研究, 25(6):605 -611. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whzwxyj200706016 李艳元, 葛继稳, 彭凤娇, 等, 2017.神农架大九湖泥炭湿地CH4通量特征及影响因子.地球科学, 42(5):832-842. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.071 罗涛, 伦子健, 顾延生, 等, 2015.神农架大九湖湿地植物群落调查与生态保护研究.湿地科学, 13(2):153-160. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=shidkx201502003 秦养民, 巩静, 顾延生, 等, 2018.鄂西亚高山泥炭地有壳变形虫生态监测及对水位的指示意义.地球科学, 43(11):4036-4045. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.599 -










 下载:
下载: