Identification of Degradation Process of Chenhu Wetland over Last 50 Years
-
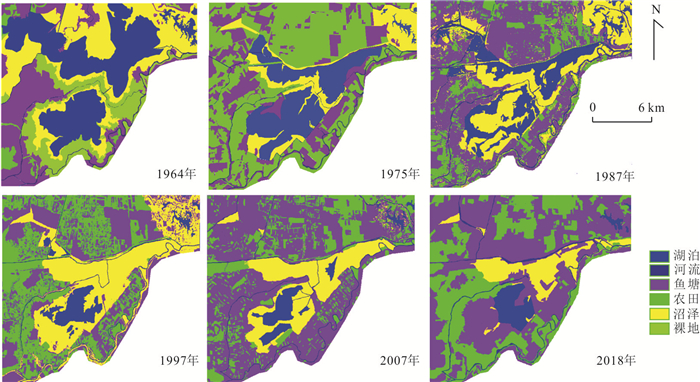
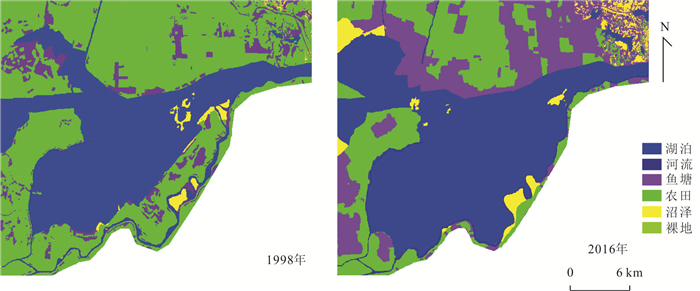
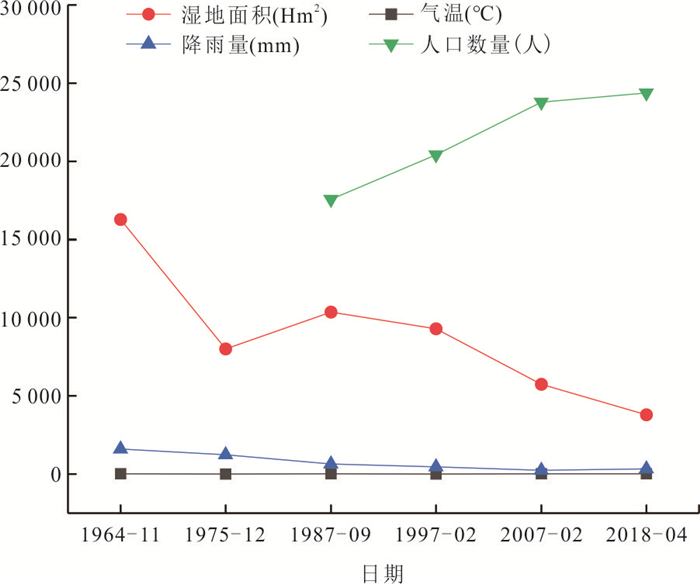
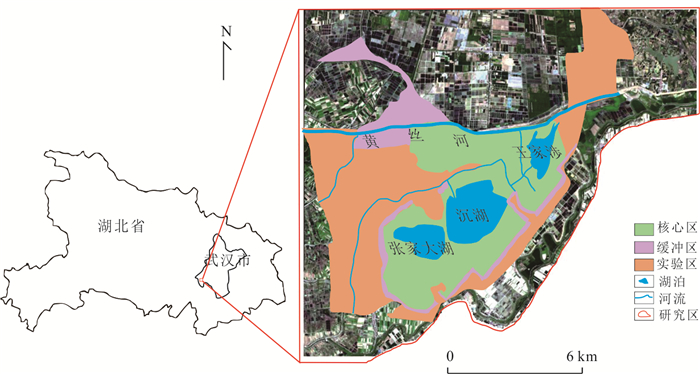
摘要: 沉湖湿地作为长江中下游平原典型湖泊湿地,1960s以来退化严重.收集1964、1975、1987、1997、1998、2007、2016、2018年8期航拍照片或遥感影像,运用遥感技术、动态度模型和转移矩阵模型分析,揭示武汉市沉湖湿地近50年退化过程及机理.结果表明,1964~2018年沉湖湿地由北向南退缩为鱼塘及耕地,总湿地面积缩小77%;湿地退化过程可分为3个阶段,1964~1975年围湖活动主导湿地湖泊向耕地退化,耕地面积以141%的年变幅扩张,1975~1997年湖泊改造工程迫使湖泊向沼泽退化,1997~2018年由湖泊退化而来的沼泽被进一步开垦为耕地或鱼塘;人口数量的增加及土地利用政策改变导致湿地生态服务功能退化,包括洪水调蓄、自净化功能衰退及生物多样性锐减,其退化模式可为长江中下游平原乃至全国湖泊湿地的退化提供类比参考.Abstract: Chenhu wetland is a typical freshwater lake-type wetland in the Middle-Lower Yangtze Plain, and has severely degraded since 1960s. In this study, aerial photographs or remote sensing images captured at eight different stages (i.e. 1964, 1975, 1987, 1997, 1998, 2007, 2016 and 2018) were analyzed to reveal the degradation processes and mechanisms of the Chenhu wetland in Wuhan over the past 50 years by the aid of remote sensing, dynamic degree models and transition matrix models.Our investigation reveals that the Chenhu wetland was gradually altered to fish ponds or agricultural lands from north to south, shrunk up to 77% in total between 1964 and 2018. Degradation of the Chenhu wetland by human impacts during this period can be divided into three stages: (i) between 1964 and 1975, degradation was dominated by filling of lakes into agricultural lands, with the rate of agricultural lands expansion exceeding 141%; (ii) between 1975 and 1994, artificial lake reconstruction projects has altered large areas of lakes into marshes; (iii) between 1997 and 2018, new marshes altered from lakes were further cultivated into agricultural lands or reserved as fish ponds. In general, population expansion and changes in land use policies have caused the degradation of ecosystem services, including impaired capacity in flood regulation and storage, natural self-purification and biodiversity losses. The degradation modes uncovered for the Chenhu wetland can also shed light on similar investigations on the degradation of other lake-type wetlands in Middle-Lower Yangtze Plain and even the whole China.
-
表 1 沉湖湿地用地类型分类
Table 1. Wetland cover types used in image classification and interpretation with their definitions
编号 名称 含义 航拍照片解译标志 卫星图像解译标志 1 湖泊 自然湖泊水域 2 河流 自然河流水域 3 沼泽 地表过湿,有常年薄层或季节性积水区域 4 耕地 指种植农作物的土地,包括熟耕地、新开垦地、闲置地、农林用地等类别 5 鱼塘 指发展水产品的土地,包括湖泊、沼泽围网区及水产养殖地等 6 裸地 生长有自然植物但还未利用的土地 表 2 精度样点验证
Table 2. The site for precision verification of interpretation
编号 地类 坐标 分类是否准确 2 耕地 113.861 9°E, 30.298 6°N 是 5 耕地 113.865 9°E, 30.284 9°N 是 6 湖泊 113.837 1°E, 30.329 4°N 是 8 沼泽 113.832 1°E, 30.336 4°N 是 10 鱼塘 113.869 2°E, 30.321 5°N 是 11 河流 113.871 1°E, 30.292 9°N 是 15 河流 113.868 2°E, 30.270 9°N 是 22 耕地 113.845 1°E, 30.281 2°N 是 26 鱼塘 113.815 6°E, 30.325 1°N 否 27 鱼塘 113.854 8°E, 30.336 7°N 是 表 3 1964~2018年沉湖湿地土地类型面积(Hm2)变化
Table 3. Land cover (Hm2) change of Chenhu Wetland in 1964-2018
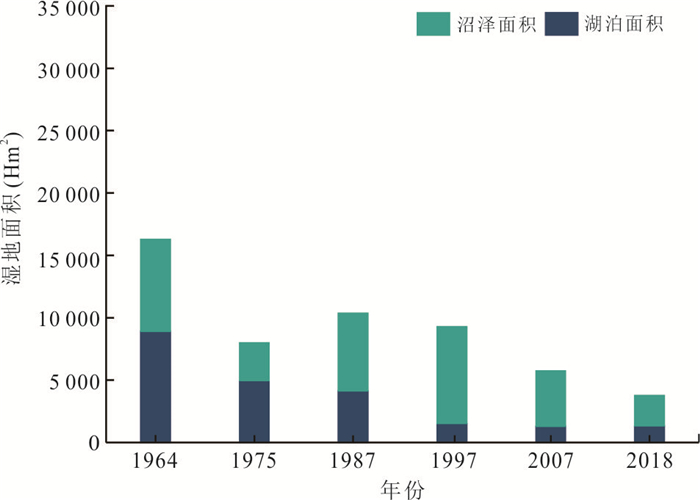
年份 湖泊 沼泽 鱼塘 耕地 河流 湿地(包含湖泊、沼泽) 研究区总面积 1964 8 903.7 7 382.1 5 585.9 726.6 535.6 16 285.8 26 968.6 1975 4 966.5 3 037.7 6 354.5 11 997.5 656 8 004.2 1987 4 143.4 6 218.5 11 058.5 4 198.1 1 074.7 10 361.9 1997 1 534.4 7 747.5 8 155.6 9 065.8 480.1 9 281.9 1998 9 431.6 404.2 2 476.3 14 050 620.9 9 835.8 2007 1 299.1 4 445.6 14 941 5 737.5 555.8 8 744.7 2016 12 783.2 1 125.4 6 090.9 6 544.1 438.6 13 908.6 2018 1 332.7 2 451.5 13 843.2 8 688.6 677.1 3 784.2 表 4 1964~2018年沉湖湿地各土地类型的动态度
Table 4. Land type dynamics of Chenhu wetland in 1964-2018
研究时段 湖泊 沼泽 鱼塘 耕地 河流 1964~1975年 -4.02% -5.35% 1.25% 141.02% 2.04% 1975~1987年 -1.38% 8.73% 6.17% -5.42% 5.32% 1987~1997年 -6.30% 2.46% -2.63% 11.60% -5.53% 1997~2007年 -1.53% -4.26% 8.32% -3.67% 1.58% 2007~2018年 0.24% -4.08% -0.67% 4.68% 1.98% -
Basommi, L. P. , Guan, Q. F. , Cheng, D. D. , et al. , 2016. Dynamics of Land Use Change in a Mining Area: A Case Study of Nadowli District, Ghana. Journal of Mountain Science, 13(4): 633-642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-015-3706-4 Cai, Z. Q. , Tian, Y. L. , Wang, Z. M. , et al. , 2018. Dynamic Changes of Wetland Distribution in Daqing City of Heilongjiang Province Based on Landsat. Wetland Science & Management, 14(2): 33-37 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-LKGL201802010.htm Chen, J. , 2008. Protection and Restoration of Chenhu Wetland. Wetland Science & Management, 4(3): 34-36 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-LKGL200803017.htm Cheng, S. P. , Luo, S. , Hu, H. X. , et al. , 2009. Features of Water Bird Diversity and the Relationships with Habitat Factors in Wuhan Wetlands. Journal of Huazhong Normal University (Natural Sciences), 43(3): 456-462 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HZSZ200903028.htm Cui, L. J. , Gao, C. J. , Zhao, X. S. , et al. , 2013. Dynamics of the Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River Basin, China, since Late Nineteenth Century. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 185(5): 4005-4018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-012-2845-0 Du, Y. , Xue, H. P. , Wu, S. J. , et al. , 2011. Lake Area Changes in the Middle Yangtze Region of China over the 20th Century. Journal of Environmental Management, 92(4): 1248-1255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2010.12.007 Gao, Z. Y. , Zhang, H. F. , Yang, X. N. , et al. , 2019. Assessing the Impacts of Ecological-Living-Productive Land Changes on Eco-Environmental Quality in Xining City on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions, 11(3): 194-207. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1226.2019.00194 Gong, H. , 2007. Three Times into the Chenhu Wetland. Wuhan Literature and History Materials, (2): 32-34 (in Chinese). He, X. F. , Wu, F. Q. , Zhou, Q. H. , et al. , 2015. Research on Water Birds Community Feature and Its Relationship with the Eutrophication in Chenhu Wetland. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 24(9): 1499-1506 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201509009.htm Hu, H. X. , Kang, H. L. , Gong, G. H. , et al. , 2005. Biodiversity of Winter Waterbirds in Hubei, China. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 14(4): 422-428 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY200504005.htm Hu, S. J. , Niu, Z. G. , Chen, Y. F. , et al. , 2017. Global Wetlands: Potential Distribution, Wetland Loss, and Status. Science of the Total Environment, 586: 319-327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.02.001 Kang, H. L., 2005. Study on the Relationship between Bird Community and Habitat and Its Protection in Chenhu Wetland of Wuhan (Dissertation). Wuhan University, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Lamsal, P. , Atreya, K. , Ghosh, M. K. , et al. , 2019. Effects of Population, Land Cover Change, and Climatic Variability on Wetland Resource Degradation in a Ramsar Listed Ghodaghodi Lake Complex, Nepal. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 191(7): 415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-019-7514-0 Li, J. B. , Qin, J. X. , Wang, K. L. , et al. , 2004. The Response of Environment System Changes of Dongting Lake to Hydrological Situation. Acta Geographica Sinica, 59(2): 239-248 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, D. Z. , Li, S. S. , Fu, D. Y. , et al. , 2018. Remote Sensing Analysis of Mangrove Distribution and Dynamics in Zhanjiang from 1991 to 2011. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 36(5): 1597-1603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-018-7004-1 Ma, T. , Shen, S. , Deng, Y. M. , et al. , 2020. Theoretical Approaches of Survey on Earth's Critical Zone in Basin: An Example from the Jianghan Plain, Central Yangtze River. Earth Science, 1-16 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2020.274 Meng, X. R. , Zhang, S. Q. , Zang, S. Y. , 2018. Remote Sensing Classification of Wetland Communities Based on Convolutional Neural Networks and High Resolution Images: A Case Study of the Honghe Wetland. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 38(11): 1914-1923 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DLKX201811019.htm Shen, G. , Yang, X. C. , Jin, Y. X. , et al. , 2019. Remote Sensing and Evaluation of the Wetland Ecological Degradation Process of the Zoige Plateau Wetland in China. Ecological Indicators, 104: 48-58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.04.063 Subira, M. , Graham, J. , 2019. Degradation of Kilombero Valley Ramsar Wetlands in Tanzania. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 112(S1): 216-227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2019.03.008 Tao, S. L. , Fang, J. Y. , Ma, S. H. , et al. , 2019. Changes in China's Lakes: Climate and Human Impacts. National Science Review, nwz103. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwz103 Tao, Y., 2018. Research on the Change of the Concept of Disaster Reporting in People's Daily since the 1990s (Dissertation). Anhui University, Hefei (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Y. J. , Zhou, W. , 1989. The Effect of Hunting on the Number of Wintering White Carp in Chenhu Lake. Chinese Wildlife, 10(4): 16-17 (in Chinese). Wu, X.K., 2016.Research on Wetland Protection in China Based on Ecological Compensation Perspective (Dissertation).Hubei University, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Xie, C. , Huang, X. , Mu, H. Q. , et al. , 2017. Impacts of Land-Use Changes on the Lakes across the Yangtze Floodplain in China. Environmental Science & Technology, 51(7): 3669-3677. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.6b04260 Yang, J. F. , Du, D. , Tian, S. S. , et al. , 2017. Biodiversity Assessment of Typical Lake Wetlands in Hubei Province. Journal of Hydroecology, 38(3): 15-22 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SCAN201703003.htm Yang, Y. , Lin, G. J. , Wang, L. L. , et al. , 2019. Analysis on Current Status and Protection Countermeasures of Wetlands in Middle Reaches of Changjiang River. Yangtze River, 50(7): 59-63, 70 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-RIVE201907009.htm Yu, S. C. , Li, C. A. , Yu, D. Q. , et al. , 2020. Land Cover Change on Beach of Dongting Lake's Beach. Earth Science, 45(6): 1918-1927 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, J. , Yu, Z. W. , Pang, H. D. , 2018. Discussion on Engineering Measures for Protection and Restoration of Shenhu Wetland in Caidian District. Hubei Forestry Science and Technology, 47(5): 56-58, 82 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, X. X. , Tuia, D. , Mou, L. C. , et al. , 2017. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review and List of Resources. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 5(4): 8-36. https://doi.org/10.1109/mgrs.2017.2762307 蔡卓岐, 田艳林, 王宗明, 等, 2018. 基于Landsat的黑龙江省大庆市湿地分布时空动态研究. 湿地科学与管理, 14(2): 33-37. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LKGL201802010.htm 陈君, 2008. 沉湖湿地的保护与恢复. 湿地科学与管理, 4(3): 34-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LKGL200803017.htm 成水平, 罗莎, 胡鸿兴, 等, 2009. 武汉湿地水鸟多样性特征及其与几种生境因子的关系. 华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 43(3): 456-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZSZ200903028.htm 龚皓, 2007. 三进沉湖湿地. 武汉文史资料, (2): 32-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHWS200702006.htm 何小芳, 吴法清, 周巧红, 等, 2015. 武汉沉湖湿地水鸟群落特征及其与富营养化关系研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 24(9): 1499-1506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201509009.htm 胡鸿兴, 康洪莉, 贡国鸿, 等, 2005. 湖北省湿地冬季水鸟多样性研究. 长江流域资源与环境, 14(4): 422-428. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY200504005.htm 康洪莉, 2005. 武汉沉湖湿地鸟类群落与生境之关系及保护研究(硕士学位论文). 武汉: 武汉大学. 李景保, 秦建新, 王克林, 等, 2004. 洞庭湖环境系统变化对水文情势的响应. 地理学报, 59(2): 239-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLXB200402010.htm 马腾, 沈帅, 邓娅敏, 等, 2020. 流域地球关键带调查理论方法: 以长江中游江汉平原为例. 地球科学, 1-16. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2020.274 孟祥锐, 张树清, 臧淑英, 2018. 基于卷积神经网络和高分辨率影像的湿地群落遥感分类: 以洪河湿地为例. 地理科学, 38(11): 1914-1923. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201811019.htm 陶颖, 2018.90年代以来《人民日报》灾难报道理念转变研究(硕士学位论文). 合肥: 安徽大学. 王勇军, 周伟, 1989. 狩猎对沉湖越冬白鹳数量变动的影响. 野生动物, 10(4): 16-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSDW198904004.htm 吴欣锴, 2016. 基于生态补偿视角的我国湿地保护研究(硕士学位论文). 武汉: 湖北大学. 杨杰峰, 杜丹, 田思思, 等, 2017. 湖北省典型湖泊湿地生物多样性评价研究. 水生态学杂志, 38(3): 15-22. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCAN201703003.htm 杨龑, 林国俊, 王伶俐, 等, 2019. 长江中游区湿地现状及保护对策分析. 人民长江, 50(7): 59-63, 70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201907009.htm 余姝辰, 李长安, 余德清, 等, 2020. 洞庭湖区湖泊洲滩地表覆盖变化. 地球科学, 45(6): 1918-1927. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.205 张俊, 余振维, 庞宏东, 2018. 蔡甸区沉湖湿地保护与修复工程措施探讨. 湖北林业科技, 47(5): 56-58, 82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FBLI201805015.htm -









 下载:
下载: