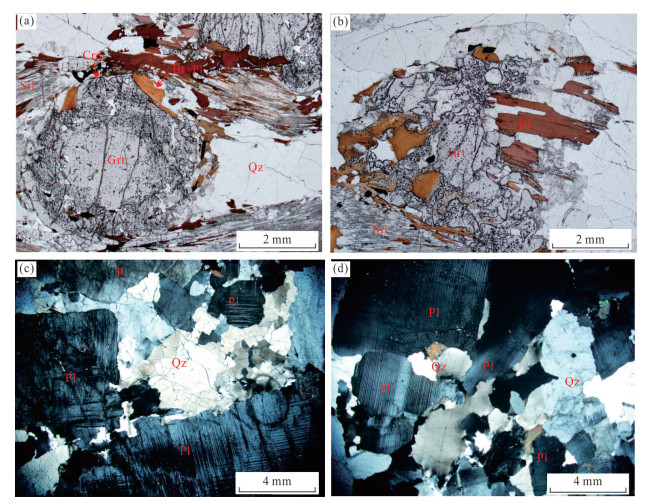
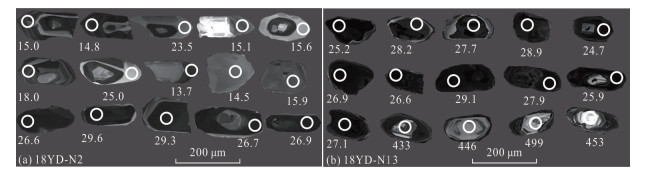
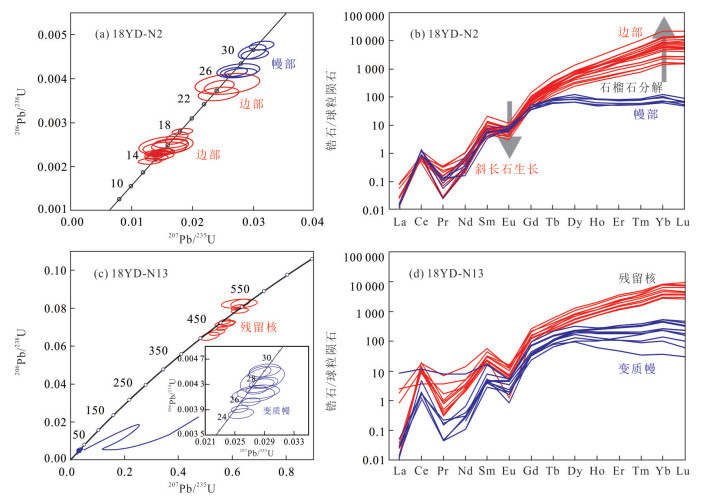
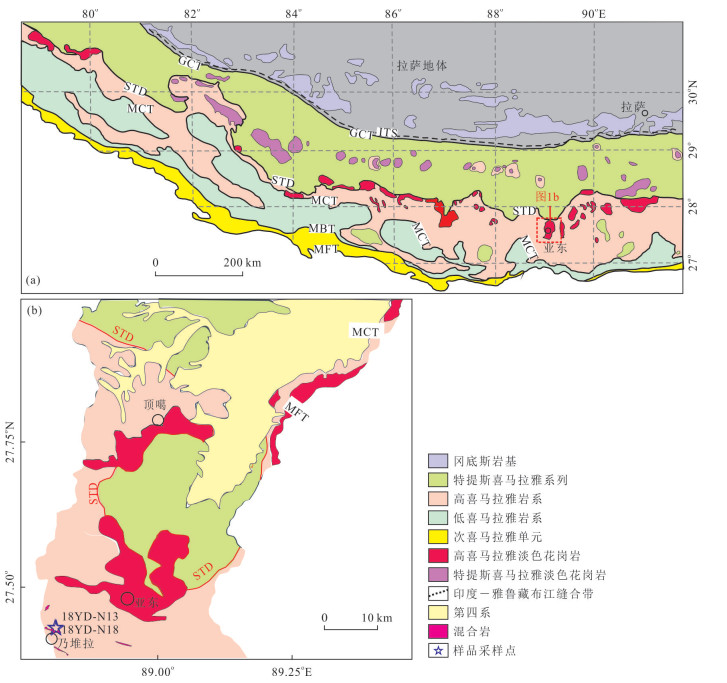
Timescales of Partial Melting in Yadong Region of Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence: Constraints from Zircon U-Pb Geochronology of Naiduila Migmatites
-
摘要: 高喜马拉雅结晶岩系由中-高级变质岩和淡色花岗岩组成,是研究喜马拉雅造山带形成与演化的天然实验室.高喜马拉雅结晶岩系混合岩和淡色花岗岩中锆石和独居石的定年结果往往是分散的,对这些定年结果的解释还存在争议,严重制约了对高喜马拉雅结晶岩系变质、部分熔融作用的起始时间和持续过程的理解.对造山带中段亚东地区高喜马拉雅结晶岩系上部构造层位的乃堆拉混合岩进行了锆石U-Pb年代学研究.研究结果显示,乃堆拉混合岩暗色体给出了29.1~24.7 Ma的进变质和部分熔融的时间,混合岩浅色体获得了25.0~13.7 Ma的退变质和熔体结晶的时间,表明亚东地区高喜马拉雅结晶岩系的部分熔融作用大约开始于30 Ma并持续到13 Ma,暗示它是一个长期、持续的过程.亚东地区高喜马拉雅结晶岩系发生部分熔融的时间明显早于藏南拆离系和主中央断裂开始活动的时间,部分熔融可能在高喜马拉雅结晶岩系俯冲过程中就已经发生了.相关成果为建立造山带构造演化模型提供了新信息.Abstract: The Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence is composed mainly of middle-high grade metamorphic rocks and leucogranites, forming a natural laboratory for studying the formation and evolution of the Himalayan orogen. However, the geological significance of the U-Pb ages remains controversial because zircons and monazites of the migmatites and leucogranites from the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence commonly have yielded variable U-Pb ages, which significantly restricts our understanding of timing and duration of metamorphism, partial melting and melt crystallization of the orogen.Here it presents zircon U-Pb geochronological study of the Naiduila migmatites in Yadong region from the upper structural level of the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence, middle Himalaya. The results show that zircons from the melanosomes of the migmatites in Naiduila area have variable U-Pb ages ranging from 29.1 to 24.7 Ma, and zircons from the leucosomes of the migmatites yield various U-Pb ages of 25.0-13.7 Ma. The former may be interpreted as the timing and duration of prograde metamorphism and partial melting, and the latter represents timescales of retrogressive metamorphism and melt crystallization.Therefore, it is proposed that the partial melting of the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence in the Yadong region initiated at ca.30 Ma and lasted to ca.13 Ma, indicating that it is a long-term and sustained process. The study also indicates that the timing of partial melting of the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence is earlier than the starting activation of the South Tibetan detachment and the Main Central Thrust. This may further indicates that the partial melting occurred during subduction. The study provides new information on the structural evolution model of the orogen.
-
Key words:
- Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence /
- partial melting /
- duration /
- migmatite /
- zircon U-Pb /
- geochronology
-
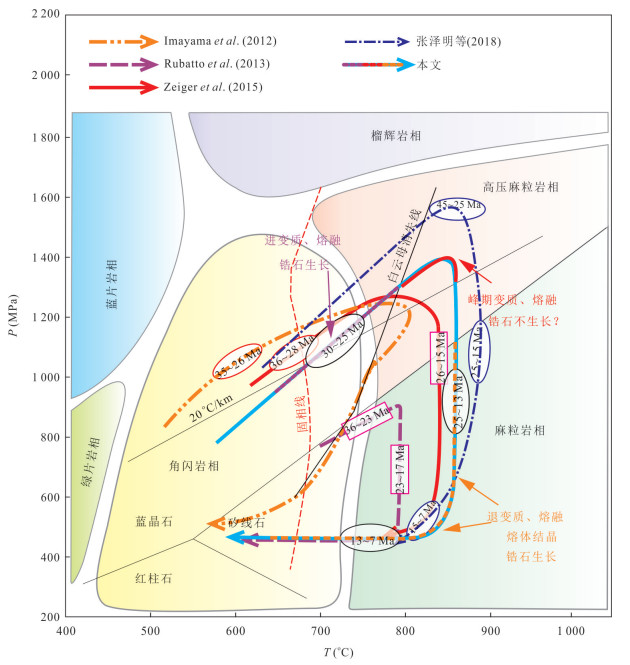
图 6 高喜马拉雅结晶岩系变质作用P-T-t轨迹和部分熔融的时间及持续过程
据Gou et al.(2016)和张泽明等(2017)修改
Fig. 6. Metamorphic P-T-t path of the Higher Himalayan crystalline sequence, showing the time and duration of partial melting
-
Ambrose, T. K., Larson, K. P., Guilmette, C., et al., 2015. Lateral Extrusion, Underplating, and Out-of-Sequence Thrusting within the Himalayan Metamorphic Core, Kanchenjunga, Nepal. Lithosphere, 7(4):441-464. https://doi.org/10.1130/l437.1 Bea, F., Pereira, M. D., Stroh, A., 1994. Mineral/Leucosome Trace-Element Partitioning in a Peraluminous Migmatite (a Laser Ablation-ICP-MS Study). Chemical Geology, 117(1-4):291-312. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)90133-3 Carosi, R., Montomoli, C., Langone, A., et al., 2015. Eocene Partial Melting Recorded in Peritectic Garnets from Kyanite-Gneiss, Greater Himalayan Sequence, Central Nepal. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 412(1):111-129. https://doi.org/10.1144/sp412.1 Corfu, F., Hanchar, J.M., Hoskin, P.W.O., et al., 2003. Atlas of Zircon Textures. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1):469-500. https://doi.org/10.2113/0530469 Corrie, S. L., Kohn, M. J., 2011. Metamorphic History of the Central Himalaya, Annapurna Region, Nepal, and Implications for Tectonic Models. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 123(9-10):1863-1879. https://doi.org/10.1130/b30376.1 Cottle, J. M., Searle, M. P., Horstwood, M. S. A., et al., 2009. Timing of Midcrustal Metamorphism, Melting, and Deformation in the Mount Everest Region of Southern Tibet Revealed by U(-Th)-Pb Geochronology. The Journal of Geology, 117(6):643-664. https://doi.org/10.1086/605994 Cui, H.J., Gou, Z.B., Liu, H., et al., 2019. The Petrogenesis and Tectonic Significance of the Late Early Cretaceous Granodiorites in the Nyixung Area, Western Lhasa Block, Xizang. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 39(1):1-13 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl201901001 Ding, H.X., Zhang, Z.M., Li, M.M., et al., 2017. Metamorphism and Tectonic Significance of the Greater Himalayan Crystalline Sequence in Cona Region, Eastern Himalaya. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(8):2357-2376 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201708003 Fu, J.G., Li, G.M., Wang, G.H., et al., 2018. Timing of E-W Extension Deformation in North Himalaya:Evidences from Ar-Ar Age in the Cuonadong Dome, South Tibet. Earth Science, 43(8):2638-2650 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201808008.htm Godin, L., Grujic, D., Law, R. D., et al., 2006. Channel Flow, Ductile Extrusion and Exhumation in Continental Collision Zones:An Introduction. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 268(1):1-23. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.2006.268.01.01 Gou, Z. B., Dong, X., Wang, B. D., 2019. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of the Paiku Leucogranites, Northern Himalaya. Journal of Earth Science, 30(3):525-534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-019-1219-8 Gou, Z. B., Zhang, Z. M., Dong, X., et al., 2016. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of the Yadong Leucogranites, Southern Himalaya. Lithos, 256-257:300-310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2016.04.009 Groppo, C., Rolfo, F., Indares, A., 2012. Partial Melting in the Higher Himalayan Crystallines of Eastern Nepal:The Effect of Decompression and Implications for the 'Channel Flow' Model. Journal of Petrology, 53(5):1057-1088. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egs009 Groppo, C., Rubatto, D., Rolfo, F., et al., 2010. Early Oligocene Partial Melting in the Main Central Thrust Zone (Arun Valley, Eastern Nepal Himalaya). Lithos, 118(3-4):287-301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2010.05.003 Guilmette, C., Indares, A., Hébert, R, 2011. High-Pressure Anatectic Paragneisses from the Namche Barwa, Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis:Textural Evidence for Partial Melting, Phase Equilibria Modeling and Tectonic Implications. Lithos, 124(1-2):66-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2010.09.003 Iaccarino, S., Montomoli, C., Carosi, R., et al., 2015. Pressure-Temperature-Time-Deformation Path of Kyanite-Bearing Migmatitic Paragneiss in the Kali Gandaki Valley (Central Nepal):Investigation of Late Eocene-Early Oligocene Melting Processes. Lithos, 231:103-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.005 Imayama, T., Takeshita, T., Yi, K., et al., 2012. Two-Stage Partial Melting and Contrasting Cooling History within the Higher Himalayan Crystalline Sequence in the Far-Eastern Nepal Himalaya. Lithos, 134-135:1-22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2011.12.004 Kali, E., Leloup, P. H., Arnaud, N., et al., 2010. Exhumation History of the Deepest Central Himalayan Rocks, Ama Drime Range:Key Pressure-Temperature-Deformation-Time Constraints on Orogenic Models. Tectonics, 29:TC2014. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009tc002551 Kohn, M. J., Corrie, S. L., 2011. Preserved Zr-Temperatures and U-Pb Ages in High-Grade Metamorphic Titanite:Evidence for a Static Hot Channel in the Himalayan Orogen. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 311(1-2):136-143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.09.008 Li, W.C., Zhang, Z.M., Xiang, H., et al., 2015. Metamorphism and Anatexis of the Himalayan Orogen:Petrology and Geochronology of HP Pelitic Granulites from the Yadong Area, Southern Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(5):1219-1234 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201505003.htm Liu, Y.S., Gao, S., Hu, Z.C., et al., 2010. Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycling-Induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons from Mantle Xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2):537-571. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egp082 Ludwig, K.R., 2003. ISOPLOT: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publication, Berkeley. Pan, G.T., Wang, L.Q., Li, X.Z., et al., 2001. The Tectonic Framework and Spatial Allocation of the Archipelagic Arc Basin Systems on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 21(3):1-26 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl200103001 Patiño Douce, A. E., Harris, N., 1998. Experimental Constraints on Himalayan Anatexis. Journal of Petrology, 39(4):689-710. https://doi.org/10.1093/petroj/39.4.689 Regis, D., Warren, C. J., Mottram, C. M., et al., 2016. Using Monazite and Zircon Petrochronology to Constrain the P-T-t Evolution of the Middle Crust in the Bhutan Himalaya. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 34(6):617-639. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12196 Rubatto, D., Chakraborty, S., Dasgupta, S., 2013. Timescales of Crustal Melting in the Higher Himalayan Crystallines (Sikkim, Eastern Himalaya) Inferred from Trace Element-Constrained Monazite and Zircon Chronology. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 165(2):349-372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-012-0812-y Sawyer, E.W., 2008. Atlas of Migmatites. NRC Research Press, Ottawa. Searle, M. P., Godin, L., 2003. The South Tibetan Detachment and the Manaslu Leucogranite:A Structural Reinterpretation and Restoration of the Annapurna-Manaslu Himalaya, Nepal. The Journal of Geology, 111(5):505-523. https://doi.org/10.1086/376763 Streule, M. J., Searle, M. P., Waters, D. J., et al., 2010. Metamorphism, Melting, and Channel Flow in the Greater Himalayan Sequence and Makalu Leucogranite:Constraints from Thermobarometry, Metamorphic Modeling, and U-Pb Geochronology. Tectonics, 29:TC5011. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009tc002533 Wang, J. M., Zhang, J. J., Wang, X. X., 2013. Structural Kinematics, Metamorphic P-T Profiles and Zircon Geochronology across the Greater Himalayan Crystalline Complex in South-Central Tibet:Implication for a Revised Channel Flow. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 31(6):607-628. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmg.12036 Wang, J. M., Rubatto, D., Zhang, J. J., 2015. Timing of Partial Melting and Cooling across the Greater Himalayan Crystalline Complex (Nyalam, Central Himalaya):In-Sequence Thrusting and Its Implications. Journal of Petrology, 56(9):1677-1702. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egv050 Wang, J. M., Zhang, J. J., Liu, K., et al., 2016. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Tectonometamorphic Discontinuities in the Central Himalaya:Constraints from P-T Paths and Geochronology. Tectonophysics, 679:41-60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.04.035 Wang, L.Q., Pan, G.T., Li, D.M., et al., 2000. The Evolution and Mineralization of the Jomda-Weixi Continental Marginal Volcanic Arc, Southwestern China. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 20(2):1-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl200002001 Waters, D. J., 2001. The Significance of Prograde and Retrograde Quartz-bearing Intergrowth Microstructures in Partially Melted Granulite-Facies Rocks. Lithos, 56(1):97-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-4937(00)00061-x Wu, Y.B., Zheng, Y.F., 2004. Genesis of Zircon and Its Constraints on Interpretation of U-Pb Age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(16):1589-1604 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb2004-49-16-1589 Vannay, J. C., Hodges, K. V., 1996. Tectonometamorphic Evolution of the Himalayan Metamorphic Core between the Annapurna and Dhaulagiri, Central Nepal. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 14(5):635-656. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-1314.1996.00426.x Viskupic, K., Hodges, K. V., Bowring, S. A., 2005. Timescales of Melt Generation and the Thermal Evolution of the Himalayan Metamorphic Core, Everest Region, Eastern Nepal. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 149(1):1-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-004-0628-5 Yin, A., Harrison, T. M., 2000. Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28(1):211-280. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 Zeiger, K., Gordon, S. M., Long, S. P., et al., 2015. Timing and Conditions of Metamorphism and Melt Crystallization in Greater Himalayan Rocks, Eastern and Central Bhutan:Insight from U-Pb Zircon and Monazite Geochronology and Trace-Element Analyses. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 169(5):47. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-015-1143-6 Zhang, L.K., Zhang, Z., Li, G.M., et al., 2018. Rock Assemblage, Structural Characteristics and Genesis Mechanism of the Cuonadong Dome, Tethys Himalaya. Earth Science, 43(8):2664-2683 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201808010 Zhang, Z.M., Dong, X., Ding, H.X., et al., 2017. Metamorphism and Partial Melting of the Himalayan Orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(8):2313-2341 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-YSXB201708001.htm Zhang, Z.M., Kang, D.Y., Ding, H.X., et al., 2018. Partial Melting of Himalayan Orogen and Formation Mechanism of Leucogranites. Earth Science, 43(1):82-98 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201801005 崔浩杰, 苟正彬, 刘函, 等, 2019.拉萨地块西段尼雄地区早白垩世晚期花岗闪长岩的成因及构造意义.沉积与特提斯地质, 39(1):1-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl201901001 丁慧霞, 张泽明, 李梦梅, 等, 2017.喜马拉雅造山带东段错那地区高喜马拉雅结晶岩系的变质作用与构造意义.岩石学报, 33(8):2357-2376. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201708003 付建刚, 李光明, 王根厚, 等, 2018.北喜马拉雅E-W向伸展变形时限:来自藏南错那洞穹隆Ar-Ar年代学证据.地球科学, 43(8):2638-2650. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.530 李旺超, 张泽明, 向华, 等, 2015.喜马拉雅造山带核部的变质作用与部分熔融:亚东地区高压泥质麻粒岩的岩石学与年代学研究.岩石学报, 31(5):1219-1234. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/ysxb98201505003 潘桂棠, 王立全, 李兴振, 等, 2001.青藏高原区域构造格局及其多岛弧盆系的空间配置.沉积与特提斯地质, 21(3):1-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl200103001 王立全, 潘桂棠, 李定谋, 等, 2000.江达-维西陆缘火山弧的形成演化及成矿作用.沉积与特提斯地质, 20(2):1-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxgdl200002001 吴元保, 郑永飞, 2004.锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约.科学通报, 49(16):1589-1604. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb200416002 张林奎, 张志, 李光明, 等, 2018.特提斯喜马拉雅错那洞穹隆的岩石组合、构造特征与成因.地球科学, 43(8):2664-2683. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.141 张泽明, 董昕, 丁慧霞, 等, 2017.喜马拉雅造山带的变质作用与部分熔融.岩石学报, 33(8):2313-2341. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ysxb98201708001 张泽明, 康东艳, 丁慧霞, 等, 2018.喜马拉雅造山带的部分熔融与淡色花岗岩成因机制.地球科学, 43(1):82-98. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.005 -
 dqkx-45-8-2894-Table1-2.doc
dqkx-45-8-2894-Table1-2.doc

-









 下载:
下载: