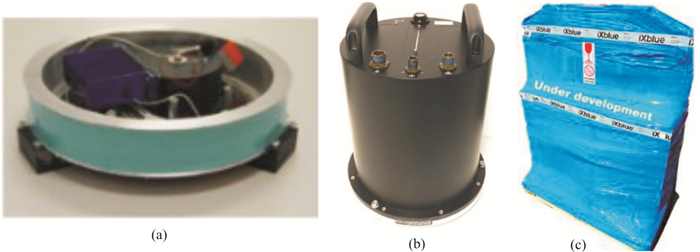
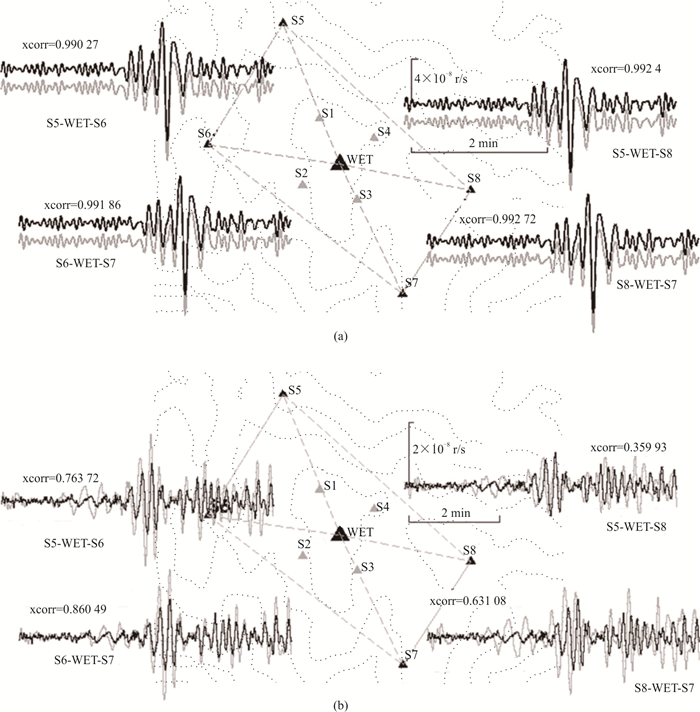
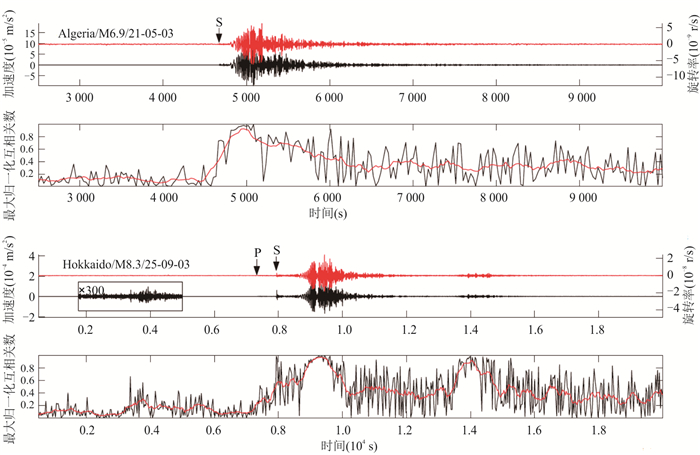
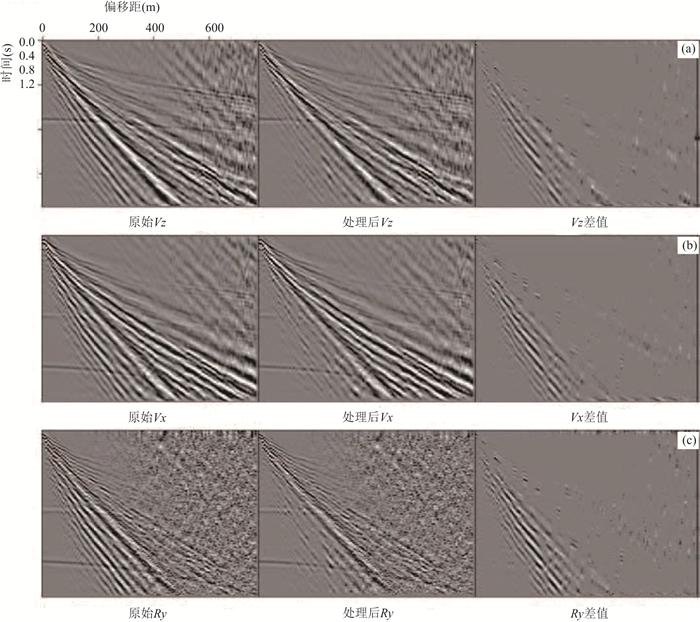
Progress in Rotational Seismology
-
摘要: 系统调研了地震波旋转运动的理论研究、仪器研制、实际观测和应用,总结了地震波旋转运动的研究成果.首先介绍了旋转分量的定义及间接地通过平动分量求取旋转分量的方法,以及从不同应用角度对旋转分量展开的研究;其次介绍了旋转地震仪的分类及其原理,对比了不同类型旋转地震仪的优缺点及其目前可以达到的技术参数指标;最后讨论了旋转分量观测及其在天然地震以及勘探地震中的应用,包括建筑工程领域的尝试.调研发现国内外旋转运动的研究差距较大,国内仍处于探索阶段.其中,不同震源与介质类型所产生的各种地震波在旋转分量上的特征差异一直是领域关注的焦点;如何制造高精度、高灵敏度、宽频带的旋转地震仪是国外同行攻关的热点;如何在地震学及相关工程中应用旋转分量,联合平动分量反演地下介质精细结构和震源性质的新特性参数是旋转运动学发展的重点.Abstract: Based on the extensive investigation of rotational motion with its theory, seismometers, practical observations and their engineering applications, the researches and developments on rotational motion are summarized. The definition of the rotational component and the method of calculating the rotational component indirectly through the translational component are introduced in detail. On the basis of introducing some real observations of the rotational motions, in this paper it focuses on the classification of rotational seismograph with its respective principle, advantages and disadvantages. Also, the examples of rotational-component observation are presented. Moreover, the applications of rotational components in natural earthquake and exploration seismology are discussed. Our investigation demonstrates that the research of rotational motion is still in the experimental and initial stage, especially in China, and that the difference of seismic wave fields under different sources and different media should be the hotspots of the field research. And the development trend is to manufacture equipment with high precision and sensitivity with wider frequency band. The superiorities of the six-component observations need to be elaborated to reverse the fine structure of underground medium and earthquake sources in seismology and engineering through jointly utilizing of the rotational and translational components.
-
Key words:
- rotation /
- translation /
- seismometer /
- six components /
- seismology
-
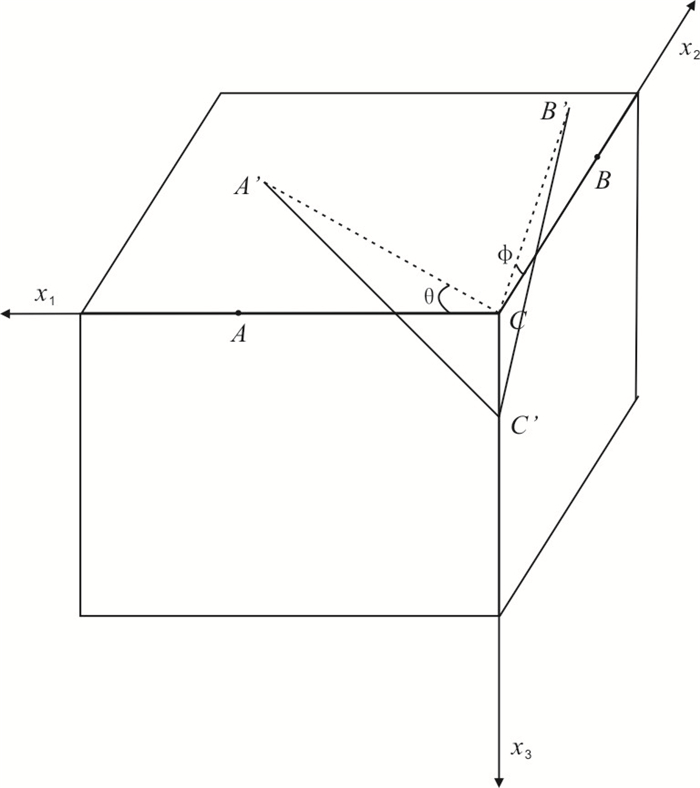
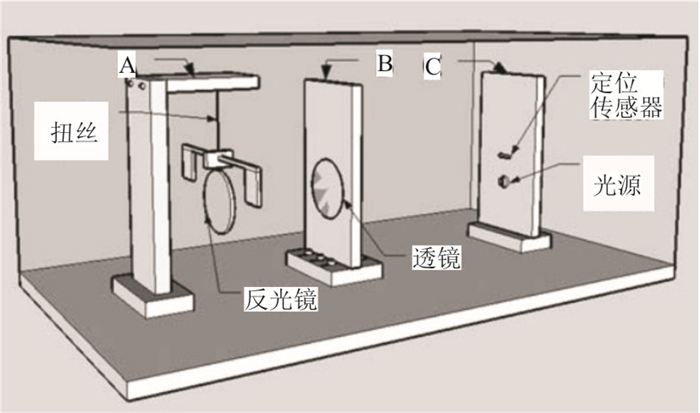
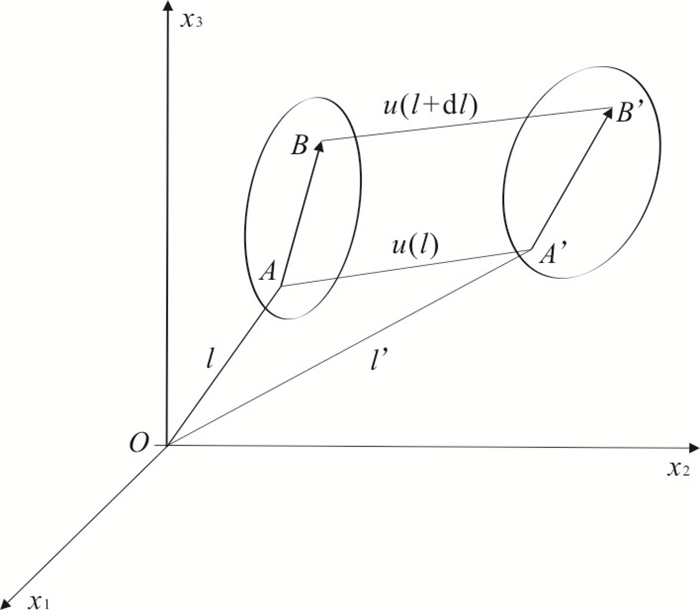
图 2 两点差分法示意图(吴其伟, 2013)
Fig. 2. Schematic diagram of two-point difference method
表 1 各种旋转地震观测仪器的性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison of various rotational seismometers
技术分类 测量等效分辨率 动态范围(dB) 测量频带(Hz) 装置型号 研究机构 阵列间接测量法 1.67×10-8 r/s 100 1~100 3DOF 捷克查理大学 2.16×10-9 r/s 120 2~60 6DOF 捷克查理大学 1.1×10-6 r/s@0.5 Hz 80 0.2~25.0 S-5-SR 俄罗斯科学院 非光学直接测量 电磁换能式 10-7 r/s 120 0.7~50.0 TAPS 波兰华沙军事科学院 机电结构电容式 6×10-8 r/s/rtHz 110 0.03~50.00 R2 德国慕尼黑大学 55 mr/s@1 Hz
230 mr/s@4 Hz— 1~25 LQ.RP.P.H2O 加州圣克鲁斯地质勘探局地震科学中心 57 mr/s@1 Hz
22 mr/s@4 Hz— 1~35 LQS.RP.P.HH2O 加州圣克鲁斯地质勘探局地震科学中心 光学直接测量 光学扭秤式 10-7 r/s/rtHz@10 mHz — 0.01~10.00 IFRS 美国华盛顿大学 激光陀螺仪 9×10-11 r/s/rtHz 280 0.003~10.000 G-Ring 德国慕尼黑工业大学 10-11 r/s@0.01~1 Hz — 300s~5 GINGERino 意大利核子物理国家研究院 光纤陀螺仪 2×10-8 r/s/rtHz 180 DC~328.12 FOSREM 波兰华沙军事科学院 2×10-8 r/s/rtHz 135 0.01~60.00 blueSeis-3A 法国ixBlue公司 1×10-9 r/s/rtHz — 0.01~100.00 blueSeis-1X 法国ixBlue公司 ~1×10-9 r/s — — — 北京航空航天大学 ~5×10-9 r/s — ~10-3~10 — 北京大学 -
Barak, O., Herkenhoff, F., Dash, R., et al., 2014. Six-Component Seismic Land Data Acquired with Geophones and Rotation Sensors: Wave-Mode Selectivity by Application of Multicomponent Polarization Filtering. The Leading Edge, 33(11): 1224-1232. doi: 10.1190/tle33111224.1 Båth, M., 1979. Introduction to Seismology. Birkhäuser, Basel. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-0348-5283-8 Belfi, J., Beverini, N., Carelli, G., et al., 2012. Horizontal Rotation Signals Detected by "G-Pisa" Ring Laser for the Mw=9.0, March 2011, Japan Earthquake. Journal of Seismology, (16): 767-776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-012-9276-9 Bernauer, F., Wassermann, J., Igel, H., 2012. Rotational Sensors: A Comparison of Different Sensor Types. Journal of Seismology, 16(4): 595-602. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-012-9286-7 Bernauer, M., Fichtner, A., Igel, H., 2009. Inferring Earth Structure from Combined Measurements of Rotational and Translational Ground Motions. Geophysics, 74(6): WCD41-WCD47. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.3211110 Brokešová, J., Málek, J., 2013. Rotaphone, a Self-Calibrated Six-Degree-of-Freedom Seismic Sensor and Its Strong-Motion Records. Seismological Research Letters, 84(5): 737-744. https://doi.org/10.1785/0220120189 Brokešová, J., Málek, J., 2015. Six-Degree-of-Freedom Near-Source Seismic Motions II: Examples of Real Seismogram Analysis and S-Wave Velocity Retrieval. Journal of Seismology, 19(2): 511-539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-015-9480-5 Brokešová, J., Málek, J., Kolínský, P., 2012. Rotaphone, a Mechanical Seismic Sensor System for Field Rotation Rate Measurements and Its In Situ Calibration. Journal of Seismology, 16(4): 603-621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-012-9274-y Cai, N.C., Fu, Z.Z., 2009. Manufacture of Rotation Seismograph. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 31(3): 347-352(in Chinese with English abstract). http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2009BuSSA..99.1443J Chen, Q.J., Yin, J.M., Yang, Y.S., 2014. Time-Frequency Characteristic Analysis of Six-Degree-Freedom Ground Motion Records. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 35(3): 499-506(in Chinese with English abstract). Cochard, A., Igel, H., Schuberth, B., et al., 2009.Rotational Motions in Seismology: Theory, Observation, Simulation. In: Teisseyre, R., Takeo, M., Majewski, E., eds., Earthquake Source Asymmetry, Structural Media and Rotation Effects. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 391-412. Driel, M.V., Wassermann, J., Nader, M.F., et al., 2012. Strain Rotation Coupling and Its Implications on the Measurement of Rotational Ground Motions. Journal of Seismology, 16(4): 657-668. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-012-9296-5 Droste, Z., Teisseyre, R., 1976. Rotational and Displacemental Components of Ground Motion as Deduced from Data of the Azimuth System of Seismograph. Publ. Inst. Geophys. Pol. Acad. Sci. 97: 157-167. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/291981429_Rotational_and_displacemental_components_of_ground_motion_as_deduced_from_data_of_the_azimuth_system_of_seismograph Dunn, R.W., Mahdi, H.H., Al-Shukri, H.J., 2009. Design of a Relatively Inexpensive Ring Laser Seismic Detector. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(2B): 1437-1442. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120080092 Evans, J.R., Kozak, J.T., Jedlicka, P., et al., 2016. Developments in New Fluid Rotational Seismometers: Instrument Performance and Future Directions. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 106(6): 2865-2876. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120150265 Feng, X., Fehler, M., Brown, S., et al., 2018. Short-Period Nonlinear Viscoelastic Memory of Rocks Revealed by Copropagating Longitudinal Acoustic Waves. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(5): 3993-4006. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017jb015012 Ferrari, G., 2006. Note on the Historical Rotation Seismographs, in Earthquake Source Asymmetry, Structural Media and Rotation Effects. Springer Verlag, Heidelberg, 367-376. Fichtner, A., Igel, H., 2009. Sensitivity Densities for Rotational Ground-Motion Measurements. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(2B): 1302-1314. http://dx.doi.org/10.1785/0120080064 Graizer, V.M., 1991. Inertial Seismometry Methods. Izvestiya of the USSR Academy of Sciences. Physics of the Solid Earth, 27(1): 51-61. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10020498703 Gu, H. D., Chen, Y. T., 1988. Significance of Rotation in Seismology. Northeastern Seismological Research, 1(2): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DDYJ198802000.htm Guyer, R. A., McCall, K. R., Boitnott, G. N., 1995. Hysteresis, Discrete Memory, and Nonlinear Wave Propagation in Rock: A New Paradigm. Physical Review Letters, 74(17): 3491-3494. https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.74.3491 He, C., Luo, Q. F., Hong, Z., 2011. Brief Discussion on the Study of the Seismic Rotational Components. Journal of Seismological Research, 34(1): 81-87(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZYJ201101014.htm Hong, Z., Cui, T.C., 2012. Research of Rotation Component of Ground Motion. Shanxi Architecture, 38(8): 39-40(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-jzsx201208023.htm Hu, D. S., 1989. The Theory of Elastic Dynamics. Geological Publishing House, Beijing(in Chinese). Igel, H., Cochard, A., Wassermann, J., et al., 2007. Broad-Band Observations of Earthquake-Induced Rotational Ground Motions. Geophysical Journal International, 168(1): 182-196. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246x.2006.03146.x Jaroszewicz, L., Kurzych, A., Krajewski, Z., et al., 2016. Review of the Usefulness of Various Rotational Seismometers with Laboratory Results of Fibre-Optic Ones Tested for Engineering Applications. Sensors (Basel), 16(12): 2161. https://doi.org/10.3390/s16122161 Jaroszewicz, L.R., Krajewski, Z., Teisseyre, K.P., 2012. Usefulness of AFORS-Autonomous Fibre-Optic Rotational Seismograph for Investigation of Rotational Phenomena. Journal of Seismology, 16(4): 573-586. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-011-9258-3 Jaroszewicz, L.R., Krajewski, Z., Teisseyre, R., et al., 2005. Usefulness of the Fiber-Optic Interferometer for the Investigation of the Seismic Rotation Waves. Optica Applicata, 34(2): 383-394. https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-2370(94)00841-n Kharin, D.A., Simonov, L.I., 1969. VBPP Seismometer for Sepa- Rate Registration of Translational Motion and Rotations. Seismic Instruments, 5: 51-66 (in Russian). Kurzych, A., Jaroszewicz, L.R., Krajewski, Z., et al., 2014. Fibre Optic System for Monitoring Rotational Seismic Phenomena. Sensors (Basel), 14(3): 5459-5469. https://doi.org/10.3390/s140305459 Kurzych, A., Jaroszewicz, L.R., Krajewski, Z.J., et al., 2018. Fibre-Optic Sagnac Interferometer in a FOG Minimum Configuration as Instrumental Challenge for Rotational Seismology. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 36 (4): 879-884. https://doi.org/10.1109/jlt.2017.2769136 Langston, C.A., Lee, W.H.K., Lin, C.J., et al., 2009. Seismic-Wave Strain, Rotation, and Gradiometry for the 4 March 2008 TAIGER Explosions. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(2B): 1287-1301. http://dx.doi.org/10.1785/0120080200 Lai, X. L., Sun, Y., 2017. Three Component Rotational Ground Motion Obtained from Explosive Source Data. Earth Science, 42(4): 645-651(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201704014.htm Lee, C.E.B., Celebi, M., Todorovska, M.I., et al., 2007.Rotational Seismology and Engineering Applications—Proceedings for the First International Workshop, Menlo Park, California, U.S.A.-September 18 to 19, 2007. United States Geological Survey-Publications, Palo Alto, California. Lee, W.H.K., Igel, H., Trifunac, M.D., 2009. Recent Advances in Rotational Seismology. Seismological Research Letters, 80 (3): 479-490. http://dx.doi.org/10.1785/gssrl.80.3.479 Li, X.P., 2012. Determination Method and Engineering Characteristics of Rotational Component in Earthquake Ground Motion. Chongqing University, Chongqing(in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y., Luo, R., Chen, F., et al., 2016. A Fiber Optic Gyroscope Prototype with High Bias Stability for Rotational Seismology Phenomena Measurement. 4th IWGoRS Workshop, Germany. Lin, C., Huang, H., Dinh, P.N., et al., 2011. Rotational Motions for Teleseismic Surface Waves. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(15): 532-560. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011gl047959 Liu, L.F., Chen, G., Jin, G.L., 2007. Principle and Classification of Optic Fiber Gyroscope. Modern Defence Technology, 35(2): 59-64(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XDFJ200702014.htm Lyubushin, A.A., Kaláb, Z., Lednická, M., et al., 2015. Coherence Spectra of Rotational and Translational Components of Mining Induced Seismic Events. Acta Geodaetica et Geophysica, 50(4): 391-402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40328-015-0099-3 Madziwa-Nussinov, T., Wagoner, K., Shore, P., et al., 2012. Characteristics and Response of a Rotational Seismometer to Seismic Signals. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 102 (2): 563-573. http://dx.doi.org/10.1785/0120110166 McLeod, D.P., Stedman, G.E., Webb, T.H., et al., 1998. Comparison of Standard and Ring Laser Rotational Seismograms. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 88(6): 1495-1503. Newmark, N.M., Rosenblueth, E., 1971. Fundamentals of Earthquake Engineering. Journal of Applied Mechanics, 39(2): 366. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.3422685 Nigbor, R., 1994. Six-Degree-of-Freedom Ground-Motion Measurement. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(5): 1665-1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(95)93429-s Nigbor, R.L., Evans, J.R., Hutt, C.R., 2009. Laboratory and Field Testing of Commercial Rotational Seismometers. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(2B): 1215-1227. https://doi.org/10.1785/0120080247 Ning, I.L.C., Sava, P., 2017. High-Resolution Multicomponent Distributed Acoustic Sensing. 2017 SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, Houston, Texas. Ning, I.L.C., Sava, P., 2018. Multicomponent Distributed Acoustic Sensing: Concept and Theory. Geophysics, 83(2): P1-P8. https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2017-0327.1 Oliveira, C.S., Bolt, B.A., 1989. Rotational Components of Surface Strong Ground Motion. Earthquake Engineering & Structural Dynamics, 18(4): 517-526. https://doi.org/10.1002/eqe.4290180406 Pham, N.D., Igel, H., Puente, J.D.L., et al., 2010. Rotational Motions in Homogeneous Anisotropic Elastic Media. Geophysics, 75(5): D47-D56. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.3479489 Reinwald, M., Bernauer, M., Igel, H., et al., 2016. Improved Finite-Source Inversion through Joint Measurements of Rotational and Translational Ground Motions: A Numerical Study. Solid Earth, 7(5): 1467-1477. doi: 10.5194/se-7-1467-2016 Renaud, G., Le Bas, P.Y., Johnson, P.A., 2012. Revealing Highly Complex Elastic Nonlinear (Anelastic) Behavior of Earth Materials Applying a New Probe: Dynamic Acoustoelastic Testing. Journal of Geophysical Research (Solid Earth), 117(B6): B06202. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011jb009127. Sbaa, S., Hollender, F., Perron, V., et al., 2017. Analysis of Rotation Sensor Data from the SINAPS @ Kefalonia (Greece) Post‑Seismic Experiment-Link to Surface Geology and Wavefield Characteristics. Earth Planets and Space, 69: 124-129. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40623-017-0711-6 Schreiber, K.U., Hautmann, J.N., Velikoseltsev, A., et al., 2009. Ring Laser Measurements of Ground Rotations for Seismology. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(2B): 1190-1198. http://dx.doi.org/10.1785/0120080171 Simonelli, A., Belfi, J., Beverini, N., et al., 2016. First Deep Underground Observation of Rotational Signals from an Earthquake at Teleseismic Distance Using a Large Ring Laser Gyroscope. Annals of Geophysics, 59: 1-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.4401/ag-6970 Solarz, L., Krajewski, Z., Jaroszewicz, L.R., 2004. Analysis of seismic Rotations Detected by Two Antiparallel Seismometers: Spine Function Approximation of Rotation and Displacement Velocities. Acta Geophysica Polonica, 52(2): 198-217. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/266594038_Analysis_of_seismic_rotations_detected_by_two_antiparallel_seismometers_Spline_function_approximation_of_rotation_and_displacement_velocities Sun, L., Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., 2018. Six-Component Elastic-Wave Simulation and Analysis. EGU General Assembly 2018, Geophysical Research Abstracts, 20. Suryanto, W., Igel, H., Wassermann, J., et al., 2006. First Comparison of Array-Derived Rotational Ground Motions with Direct Ring Laser Measurements. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 96(6): 2059-2071. doi: 10.1785/0120060004 Teisseyre, R., 2010. Tutorial on New Developments in the Physics of Rotational Motions. Translated World Seismology, 99(2B): 1028-1039. http://dx.doi.org/10.1785/0120080089 Teisseyre, R., Suchcicki, J., Teisseyre, K.P., et al., 2003. Seismic Rotation Waves: Basic Elements of the Theory and Recordings. Annals of Geophysics, 46(4), 671-685. http://dx.doi.org/10.4401/ag-4375 TenCate, J.A., Malcolm, A.E., Feng, X., et al., 2016. The Effect of Crack Orientation on the Nonlinear Interaction of a PWave with an S Wave. Geophysical Research Letters, 43(12): 6146-6152. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/2016gl069219. Trifunac, M.D., 2009. Review: Rotations in Structural Response. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 99(2B): 968-979. http://dx.doi.org/10.1785/0120080068 Velikoseltsev, A., Schreiber, K. U., Yankovsky, A., et al., 2012. On the Application of Fiber Optic Gyroscopes for Detection of Seismic Rotations. Journal of Seismology, 16(4): 623-637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-012-9282-y Wang, C., Wang, Y., 2017. Ground Roll Attenuation Using Polarization Analysis in the T-f-k Domain. Geophysical Journal International, 210(1): 240-254. https://doi.org/10.1093/gji/ggx152 Wang, C., Wang, Y., Sun, P.Y., et al., 2019. Discussions on the Processing of the Multi-Component Seismic Vector Field. Applied Sciences, 9(9): 1770. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091770 Wang, C., Wang, Y., Wang, X.K., et al., 2016. Multicomponent Seismic Noise Attenuation with Multivariate Order Statistic Filers. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 133: 70-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2016.07.023 Wang, H. W., 2001. Optical Fiber Sensing Techniques and Applications. National Defense Industry Press, Beijing(in Chinese). Wang, J.J., 1995. The Effects of Tilts on Thin-Walled Cylindrical Shell Structure. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 17(2): 217-222(in Chinese). Wang, J.J., Hu, Y.X., 1991. A Study on Rotational Components of Surface Ground Motion. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 11(2): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, Q. W., 2013. Determination Method and Response to Structure of Tilt Component in Earthquake Ground Motion(Dissertation). Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan(in Chinese with English abstract). Xun, C., Wang, C., Wang, Y., 2016. The Application of Multi-Directional Vector Media Filtering in Multi-Component Seismic Data. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 55(5): 703-710(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYWT201605011.htm Yan, Y. Y., 2017. Seismic Response Analysis of High-Rise Building under Different Types of Multi-Dimensional Earthquake Ground Motions(Dissertation). Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan(in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, Y.H., Wang, Z., Yi, X.S., et al., 2005. High Precision Fiber Optic Gyroscope Based on Er-Doped Superfluorescent Fiber Source. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 31(11): 1159-1162(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/298474106_High_precision_fiber_optic_gyroscope_based_on_Er-doped_superfluorescent_fiber_source Zembaty, Z., Kokot, S., Bobra, P., 2013. Application of Rotation Rate Sensors in an Experiment of Stiffness Reconstruction. Smart Mater and Structures, 22(7): 077001. https://doi.org/10.1088/0964-1726/22/7/077001 Zhang, J., Li, J.B., Ruan, A.G., et al., 2018. Application of Converted S-Waves from the Active-Source Ocean Bottom Seismometer Experiment. Earth Science, 43(10): 3778-3791(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201810037.htm Zhao, M.H., Du, F., Wang, Q., et al., 2018. Current Status and Challenges for Three-Dimensional Deep Seismic Survey in the South China Sea. Earth Science, 43(10): 3749-3761(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/329984216_Current_Status_and_Challenges_for_Three-Dimensional_Deep_Seismic_Survey_in_the_South_China_Sea Zhu, Z.X., 1983. On the Nonlinear Strain Measures. Advances in Mechanics, 13(3): 259-272(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-LXJZ198303000.htm 蔡乃成, 付子忠, 2009. 旋转地震仪的研制. 地震学报, 31(3): 347-352. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-3782.2009.03.011 陈清军, 殷建明, 杨永胜, 2014. 六分量地震动实测记录的时频特征分析. 力学季刊, 35(3): 499-506. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SHLX201403015.htm 顾浩鼎, 陈运泰, 1988. 旋转在地震学中的意义. 东北地震研究, 1(2): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DDYJ198802000.htm 何超, 罗奇峰, 洪钟, 2011. 关于地震动转动分量的研究. 地震研究, 34(1): 81-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0666.2011.01.013 洪钟, 崔太成, 2012. 地震动转动分量研究. 山西建筑, 38(8): 39-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2012.08.023 胡德绥, 1989. 弹性波动力学. 北京: 地质出版社. 赖晓玲, 孙译, 2017. 利用爆炸震源资料获得三分量旋转地震动. 地球科学, 42(4): 645-651. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.052 李旭鹏, 2012. 地震动扭转分量的确定方法及工程特性研究(硕士学位论文). 重庆: 重庆大学. 刘兰芳, 陈刚, 金国良, 2007. 光纤陀螺仪基本原理与分类. 现代防御技术, 35(2): 59-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086X.2007.02.015 王惠文, 2001. 光纤传感技术与应用. 北京: 国防工业出版社. 王君杰, 1995. 地震动扭转分量对薄壁柱壳结构的影响. 地震学报, 17(2): 217-222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXB502.010.htm 王君杰, 胡聿贤, 1991. 地震动旋转分量的研究. 地震工程与工程振动, 11(2): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGGC199102000.htm 吴其伟, 2013. 地震动摇摆分量的确定方法及对结构响应研究(硕士学位论文). 武汉: 武汉理工大学. 寻超, 汪超, 王赟, 2016. 多方向矢量中值滤波在多分量地震数据中的应用. 石油物探, 55(5): 703-710. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1441.2016.05.009 严艳艳, 2017. 不同类型多维地震动作用下高层建筑结构的地震响应分析(硕士学位论文). 武汉: 武汉理工大学. 杨远洪, 王峥, 伊小素, 等, 2005, 基于掺铒超荧光光纤光源的高精度光纤陀螺. 北京航空航天大学学报, 31(11): 1159-1162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2005.11.001 张洁, 李家彪, 阮爱国, 等, 2018. 海底地震仪(OBS)主动源转换横波的应用. 地球科学, 43(10): 3778-3791. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.534 赵明辉, 杜峰, 王强, 等, 2018. 南海海底地震仪三维深地震探测的进展及挑战. 地球科学, 43(10): 3749-3761. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.573 朱兆祥, 1983. 论非线性应变. 力学进展, 13(3): 259-272. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LXJZ198303000.htm -









 下载:
下载: