Dynamic Features and Causes of Chaoshuidong Siphonal Spring
-
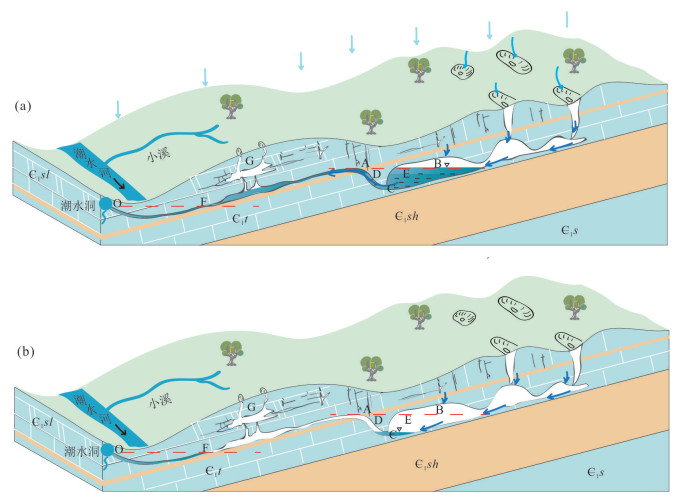
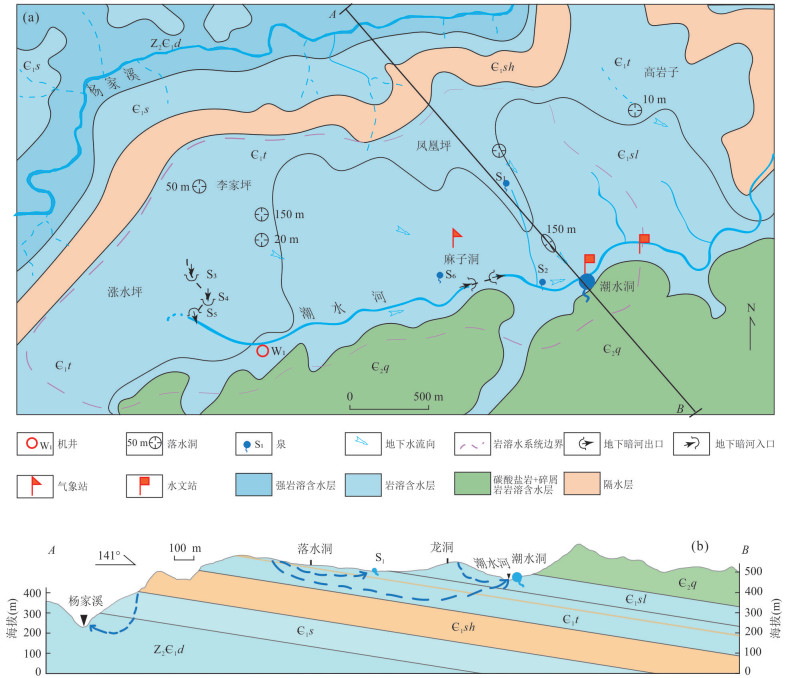
摘要: 潮水洞无降雨补给时仍有规律的间歇性流出,是典型的岩溶间歇泉,其流量、水化学动态规律及形成机制缺乏系统的研究.基于长期水文气象观测和水化学测试数据,分析了潮水洞不同时期流量、水温和电导率变化特征以及潮水洞岩溶水系统的水化学特征.潮水洞为多个岩溶水子系统的连接,其动态呈现为雨期和无雨期两个不同特征,且存在多个不稳定周期的间歇出流过程.通过c(Mg2+)/c(Ca2+)比值及水文动态特征辨识出间歇出流的地下水来源为天河板组灰岩含水层,随着过程流量的不断增加,深循环地下水占比最高达97%.结合水文地质条件概化出潮水洞岩溶水系统循环模式,天河板组灰岩含水层内虹吸管道的发育是间歇性动态特征的主要成因.Abstract: The Chaoshuidong Siphonal Spring () is in Yichang City, Hubei Province, which could still regularly intermittently flows out when there is no rain. Systematic research into the flow and hydrochemical dynamics and formation mechanisms of CSS is lacked. Based on long-term hydrological and meteorological observation data and hydrochemical test data, in this paper, it analyzes and summarizes the changes in the flow, water temperature and conductivity of the CSS at different times, and also analyzes the hydrochemical characteristics of the CSS karst water system. The CSS karst water system can be divided into the local water flow system of the Shilongdong Group and the intermediate water flow system of the Tianheban Group, and its dynamic characteristics can be divided into two distinct periods of rain and rain-free periods, which reflects the rapid response of karst water system to rainfall and the control function of karst siphon pipe to the intermediate water flow system of Tianheban Group, respectively.There are many intermittent flow out of multiple unstable cycles during the rain-free period. The source of intermittent discharge groundwater was identified by ion ratio method and the analysis of hydrodynamic features as the Tianheban Group rock aquifer, and with the increasing process flow, the proportion of deep-cycle groundwater reached 97%. Finally, combined with hydrogeological condition analysis, in the paper it summarizes the conceptual pattern map of water circulation in the CSS karst water system, and the development of the siphon pipe inside the gray rock aquifer of the Tianheban Group forms the characteristics of the water circulation during the rain and rain-free periodof the CSS.
-
图 2 (a) 潮水洞2018-9-20—2018-11-06动态变化特征;(b)潮水洞雨期和无雨期水文动态特征分析; (c) 2018-9-20—2018-11-6潮水洞间歇出流间隔回归分析结果
Fig. 2. (a) Dynamic change characteristics of CSS between September 20th and November 6th, 2018;(b) analysis of hydrodynamic features during the rain and free-rain periods of the CSS; (c) the results of the regression analysis of the intermittent outlet interval of the CSS between September 20th and November 6th, 2018
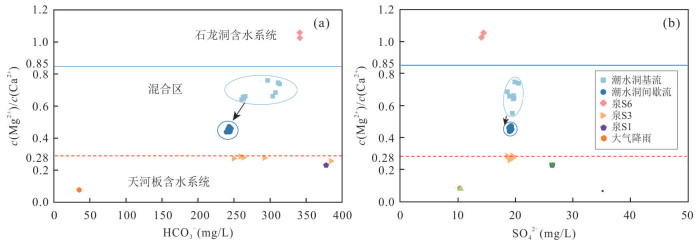
表 1 潮水洞岩溶水系统样品水化学分类
Table 1. Water chemistry classification of samples of karst water system of CSS
采样点类型 统计 离子(mg/L) TDS (mg/L) 水化学类型 Ca2+ Mg2+ Na++K+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- NO3- 潮水洞基流 平均值 73.74 29.40 3.74 3.62 19.68 279.77 17.77 243.82 HCO3-Ca-Mg 最大值 79.39 34.50 5.08 5.12 20.66 313.39 18.91 290.49 最小值 62.36 23.94 2.92 2.99 18.74 252.67 13.97 160.38 潮水洞间歇流 平均值 80.55 21.59 2.51 2.48 19.27 242.72 17.20 267.49 HCO3-Ca-Mg 最大值 88.92 23.36 2.78 2.72 19.47 246.08 17.42 275.78 最小值 64.28 18.02 2.05 2.34 19.05 239.49 16.99 247.64 天河板含水系统 平均值 96.03 15.22 1.58 2.19 17.75 304.35 10.08 195.18 HCO3-Ca 最大值 134.00 18.50 2.38 5.19 26.54 384.42 13.40 255.39 最小值 84.10 13.80 0.88 1.19 13.28 249.75 1.37 158.20 石龙洞含水系统 平均值 68.30 42.55 1.50 1.42 14.39 340.00 5.35 192.66 HCO3-Ca-Mg 最大值 70.80 44.70 1.54 1.50 14.58 340.00 5.81 192.80 最小值 65.80 40.40 1.46 1.34 14.20 340.00 4.89 192.52 表 2 潮水洞雨期和无雨期流量衰减分析结果
Table 2. The results of the analysis of flow attenuation of CSS during rain and rain-free periods
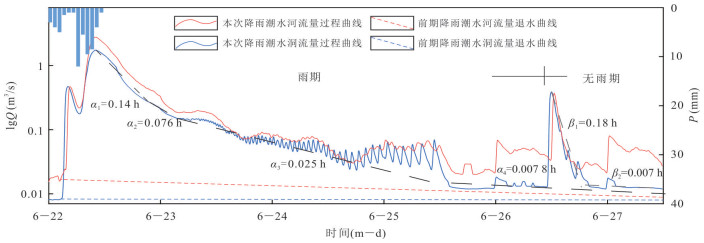
时期 日期(年-月-日) 降雨量P (mm) 第一衰减α1(h) 第二衰减α2(h) 第三衰减α3(h) 第四衰减α4(h) VP(104 m3) VI(104 m3) φ 雨期 2019-3-21 39.5 0.24 0.11 0.089 0.003 7 6.06 11.05 0.55 2019-3-31 21.5 0.18 0.088 0.032 0.004 2 2.07 5.10 0.41 2019-4-9 31.5 0.17 0.049 0.034 0.004 8 6.82 10.99 0.62 2019-5-6 65.5 0.16 0.080 0.026 0.007 5 3.67 5.10 0.72 2019-6-22 57.5 0.17 0.065 0.033 0.003 7 6.62 13.09 0.51 2019-6-28 54.0 0.26 0.059 0.033 0.002 2 6.97 15.96 0.44 2019-8-3 97.5 0.17 0.041 0.016 0.002 1 15.99 26.73 0.60 平均 0.193 0.070 0.038 0.004 0 6.89 12.57 0.55 无雨期 2018-10-9 0 0.12 0.005 2018-10-13 0 0.17 0.007 2019-1-7 0 0.17 0.007 2019-1-10 0 0.18 0.009 2019-6-26 0 0.18 0.007 2019-9-16 0 0.18 0.008 2019-9-21 0 0.20 0.008 平均 0 0.17 0.007 -
Bakalowicz, M., 2005.Karst Groundwater:A Challenge for New Resources.Hydrogeology Journal, 13(1):148-160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-004-0402-9 Cheng, X., Wan, J.W., Huang, K., et al., 2019.Experimental Study on the Interference of Fluorescent Tracer.Carsologica Sinica, 38(5):795-803(in Chinese with English abstract). Han, Y.F., 2010.Unscrambling of Huangnidong Karstic Geyser Generation.Coal Geology of China, 22(Suppl.1):54-55, 59(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGMT2010S1017.htm Jiang, Y., Zhou, Z.F., Tang, Y, T., et al., 2018.A Brief Analysis of the Hydrologic Process Variation Characteristics and Genesis of Chaojing Intermittent Spring.Collected Papers of Eco-Cultural Summit Forum on Chaojing in Changshun and Intermittent Kasrt Spring in Southern China, Guizhou, 5-11(in Chinese). Jiang, Z.C., Wang, R.J., Pei, J.G., et al., 2001.Epikarst Zone in South China and Its Regulation Function to Karst Water.Carsologica Sinica, 20(2):106-110(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/292707139_Epikarst_zone_in_south_China_and_its_regulation_function_to_karst_water Herman, E.K., Toran, L., White, W.B., 2009.Quantifying the Place of Karst Aquifers in the Groundwater to Surface Water Continuum:A Time Series Analysis Study of Storm Behavior in Pennsylvania Water Resources.Journal of Hydrology, 376(1-2):307-317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.07.043 Hurwitz, S., Kumar, A., Taylor, R., et al., 2008.Climate-Induced Variations of Geyser Periodicity in Yellowstone National Park, USA.Geology, 36(6):451-454. https://doi.org/10.1130/g24723a.1 Kalhor, K., Ghasemizadeh, R., Rajic, L., et al., 2019.Assessment of Groundwater Quality and Remediation in Karst Aquifers:A Review.Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 8:104-121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2018.10.004 Kansou, K., Bredeweg, B., 2014.Hypothesis Assessment with Qualitative Reasoning:Modelling the Fontestorbes Fountain.Ecological Informatics, 19:71-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoinf.2013.10.007 Karst Research Group, 1978.Karst Research of China.Science Press, Beijing. Long, X., Sun, Z.Y., Zhou, A.G., et al., 2015.Hydrogeochemical and Isotopic Evidence for Flow Paths of Karst Waters Collected in the Heshang Cave, Central China.Journal of Earth Science, 26(1):149-156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0522-2 Mangin, A., 1969.Etude Hydraulique du mécanisme d'intermittence de Fontestorbes (Bélesta, Ariège).Ann. Spéliol, 2(24):253-299. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288915344_Etude_hydraulique_du_mecanisme_d'intermittence_de_Fontestorbes_Belesta_Ariege Somaratne, N., 2014.Characteristics of Point Recharge in Karst Aquifers.Water, 6(9):2782-2807. doi: 10.3390/w6092782 Rudolph, M.L., Manga, M., Hurwitz, S., et al., 2012.Mechanics of Old Faithful Geyser, Calistoga, California.Geophysical Research Letters, 39(24):L24308. https://doi.org/10.1029/2012gl054012 Wang, Y., Luo, Z.H., Wu, Y., et al., 2019.Urbanization Factors of Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment in Karst Area:A Case Study of Shuicheng Basin.Earth Science, 44(9):2909-2919(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201909009.htm Wang, Y.L., Zhou, Z.F., Xue, B, Q., et al., 2018.A Brief Analysis of the Characteristics and Influencing Factors of CO2 Transformation in Water-Gas Process in Karst Spring under the Short Time Scale.Collected Papers of Eco-Cultural Summit Forum on Chaojing in Changshun and Intermittent Kasrt Spring in Southern China, Guizhou, 19-28(in Chinese). Williams, P.W., 1977.Hydrology of the Walkoropupu Springs:A Major Tidal Karst Resurgence in Northwest Nelson (New Zealand).Journal of Hydrology, 35(1-2):73-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(77)90078-6 Xue, B.Q., Zhou, Z.F., Wang, Y.L., et al., 2018.Chemical Characteristics and Genetic Analysis of Main Ions of Surface Karst Spring on Chaojing in Changshun.Collected Papers of Eco-Cultural Summit Forum on Chaojing in Changshun and Intermittent Kasrt Spring in Southern China, Guizhou, 29-35(in Chinese). Yang, Z.H., Song, X.Q., Su, W.C., 2019.Slope Runoff Process and Its Utilization Technology in Southwest Karst Area.Earth Science, 44(9):2931-2943(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201909012.htm Yin, D.C., Luo, M.M., Zhang, L., et al., 2016.Methods of Calculating Recharge Coefficient of Precipitation Event Based on Spring Recession Analyses.Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 43(3):11-16(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SWDG201603003.htm Yuan, D.X., Jiang, Y.J., Shen, L.C., et al., 2016.The Modern Karstology.Science Press, Beijing(in Chinese). Zhang, R.Q., Zhou, H., Chen, Z.H., et al., 1991.The Systematic Analysis of Guozhuang Spring Karst-Water System in Shanxi.Earth Science, 16(1):1-17(in Chinese with English abstract). http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=DQKX199101000&dbcode=CJFD&year=1991&dflag=pdfdown Zou, C.J., 1993.Developing Regularity and Dynamic Model Test Study of Karst Tidal Spring.Carsologica Sinica, 12(2):133-141(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199302006.htm 程烯, 万军伟, 黄琨, 等, 2019.荧光示踪剂的干扰实验研究.中国岩溶, 38(5):795-803. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201905019.htm 韩玉福, 2010.解读黄泥洞岩溶间歇泉的生成.中国煤炭地质, 22(增刊1):54-55, 59. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT2010S1017.htm 蒋翼, 周忠发, 汤云涛, 等, 2018.潮井间歇泉水文过程变化特征及成因浅析.贵州: 中国南方喀斯特间歇泉-长顺"潮井"生态文化高层论坛论文集, 5-11. 蒋忠诚, 王瑞江, 裴建国, 等, 2001.我国南方表层岩溶带及其对岩溶水的调蓄功能.中国岩溶, 20(2):106-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2001.02.005 汪炎林, 周忠发, 薛冰清, 等, 2018.短时间尺度下岩溶泉水-气CO2转化特征及影响因素浅析.贵州: 中国南方喀斯特间歇泉-长顺"潮井"生态文化高层论坛论文集, 19-28. 汪莹, 罗朝晖, 吴亚, 等, 2019.岩溶地下水脆弱性评价的城镇化因子:以水城盆地为例.地球科学, 44(9):2909-2919. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.135 薛冰清, 周忠发, 汪炎林, 等, 2018.长顺潮井表层岩溶泉水主要离子化学特征及成因分析.贵州: 中国南方喀斯特间歇泉-长顺"潮井"生态文化高层论坛论文集, 29-35. 杨振华, 宋小庆, 苏维词, 2019.西南喀斯特地区坡地产流过程及其利用技术.地球科学, 44(9):2931-2943. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.213 尹德超, 罗明明, 张亮, 等, 2016.基于流量衰减分析的次降水入渗补给系数计算方法.水文地质工程地质, 43(3):11-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201603003.htm 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 沈立成, 等, 2016.现代岩溶学.北京:科学出版社. 张人权, 周宏, 陈植华, 等, 1991.山西郭庄泉岩溶水系统分析.地球科学, 16(1):1-17. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.1991.01.002 邹成杰, 1993.岩溶多潮泉发育规律研究.中国岩溶, 12(2):133-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199302006.htm -









 下载:
下载: