Stable Isotopic Characteristics of Precipitation and Moisture Recycling in Badain Jaran Desert
-
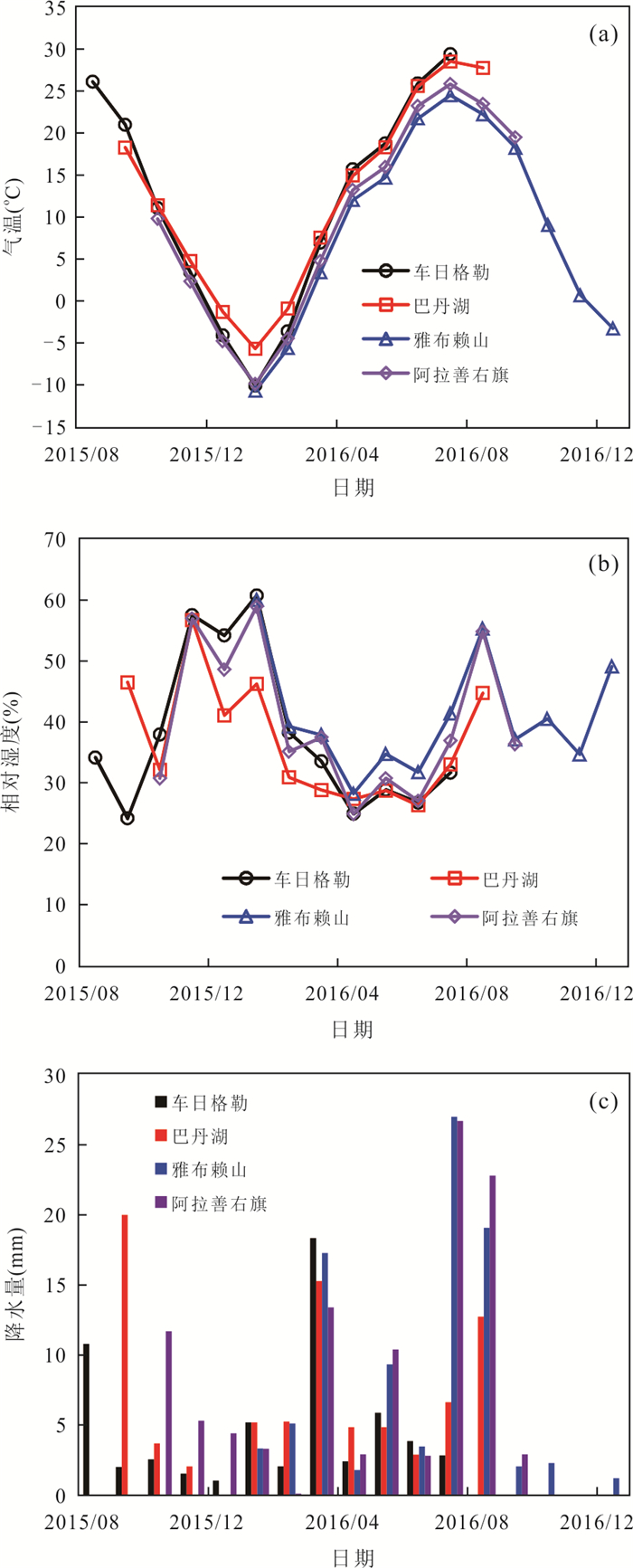
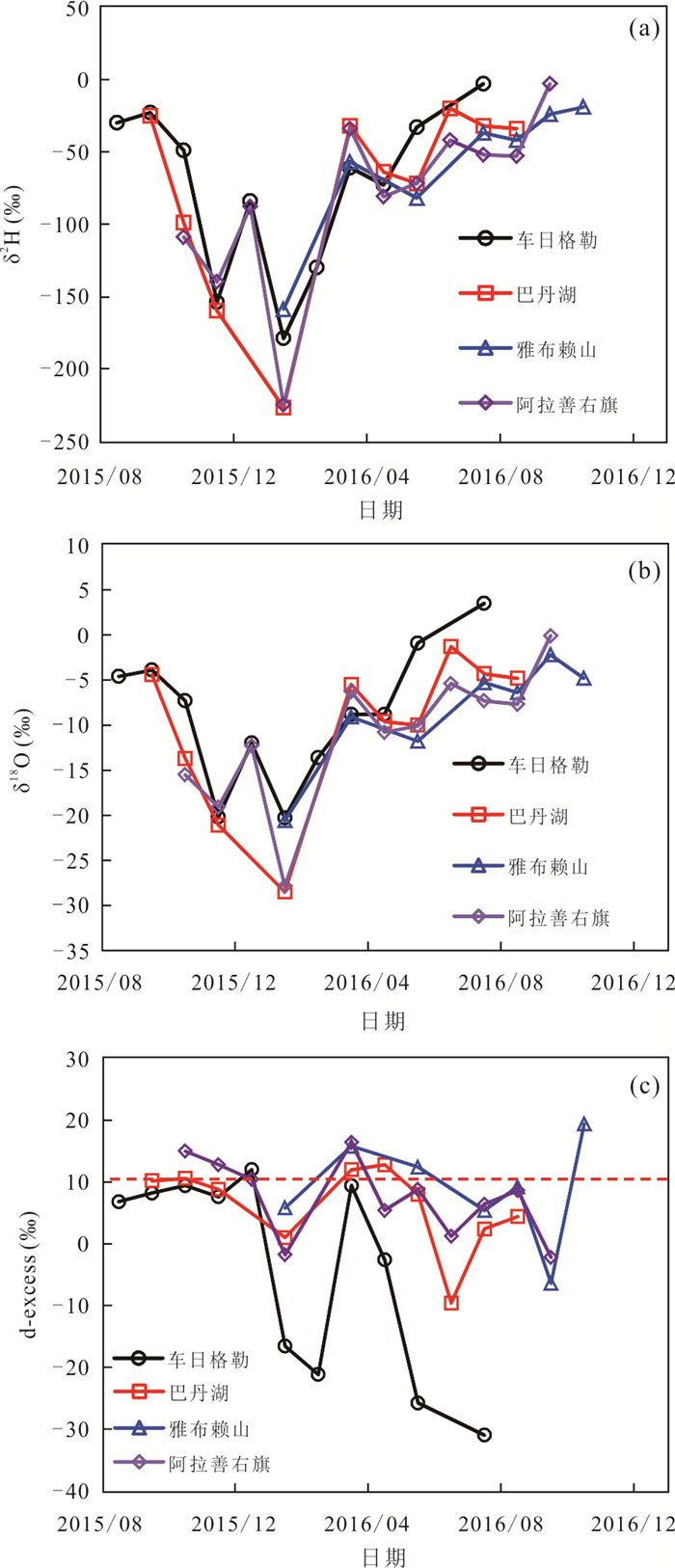
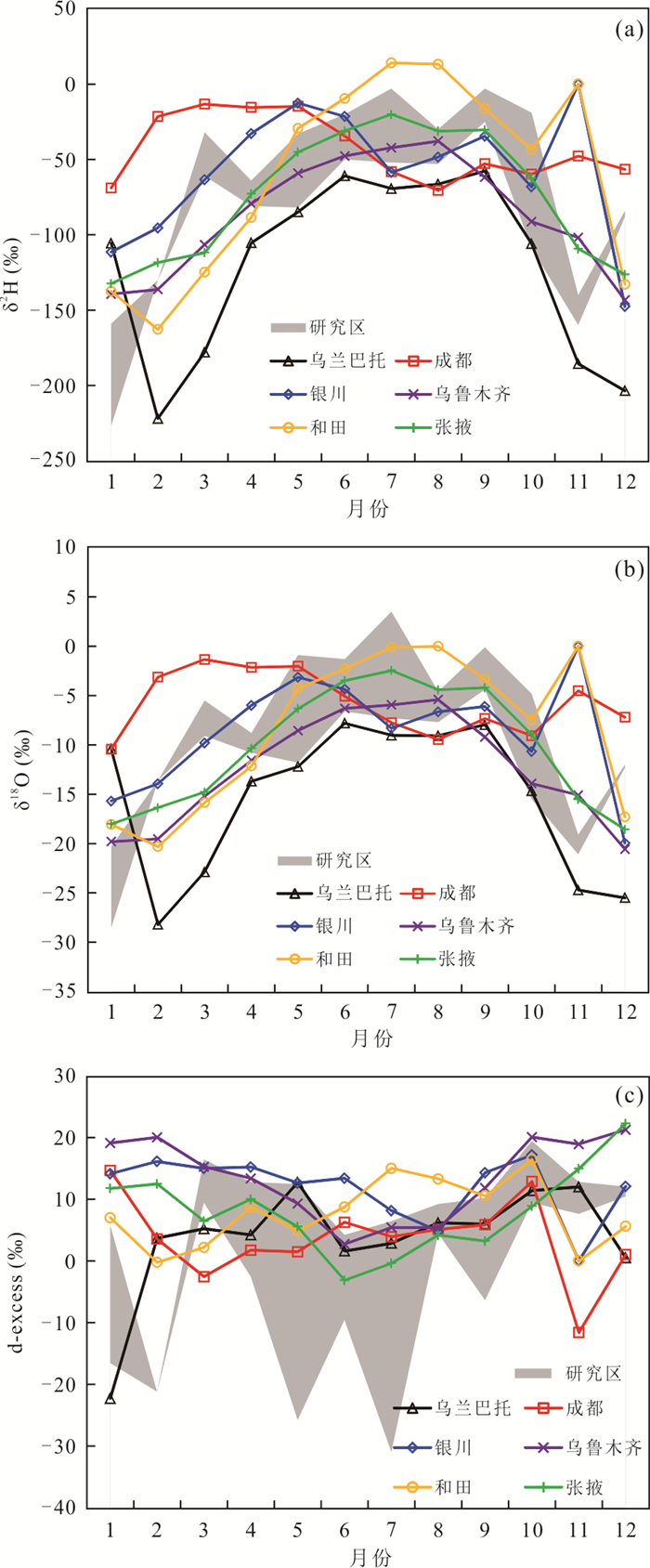
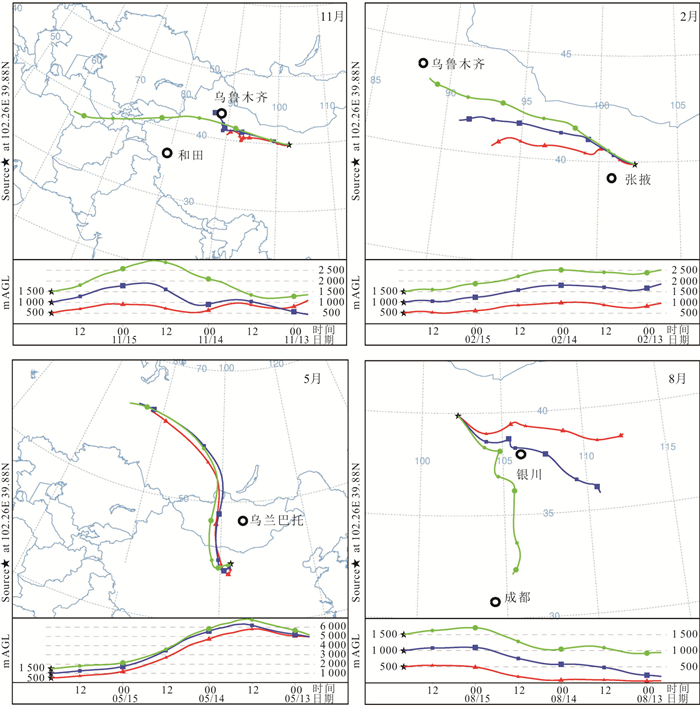
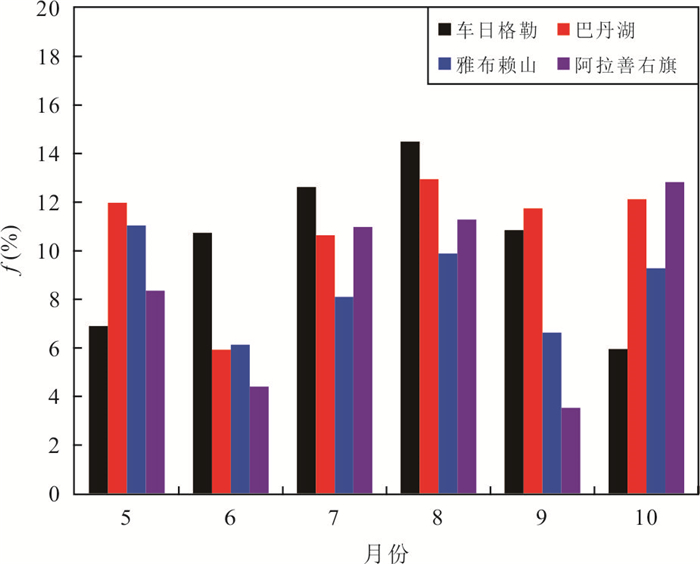
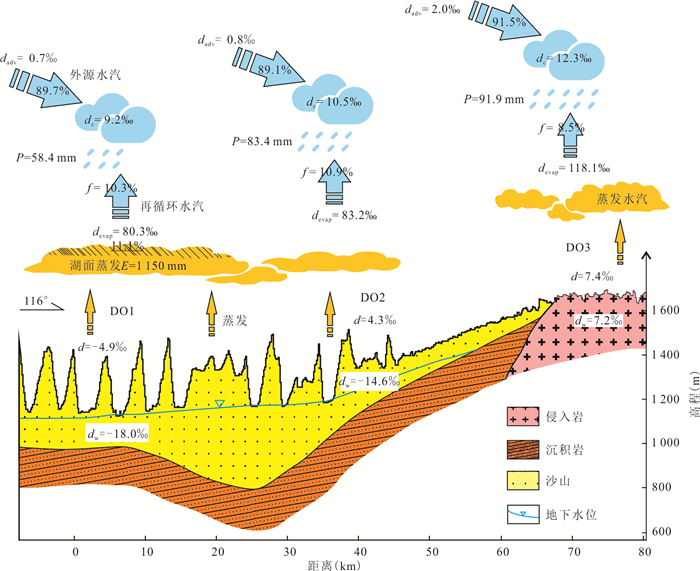
摘要: 了解沙漠降水稳定同位素特征,有助于研究干旱区水循环过程.根据2015-2016年取自巴丹吉林沙漠4个站点的降水样品,分析了δ2H、δ18O的时空分布特征及影响因素;借助后向气团轨迹模型分析了降水水汽来源;采用氘盈余模型计算了水汽再循环比.结果显示,降水δ2H、δ18O均表现出季节效应,夏高冬低;沙漠腹地较外围山区δ2H、δ18O偏正,d-excess偏负,反映出腹地降水的蒸发程度更高.年内降水主要来自西风水汽,夏季部分受东南季风影响.沙漠湖泊区再循环比为10.3%~10.9%,略大于山区的8.5%;再循环水汽在总蒸发量中占比11.1%,反映出沙漠强烈的蒸发对本地降水的贡献较为有限.Abstract: Understanding the isotopic characteristics of precipitation in desert is helpful to study the water cycle process in arid areas. According to the precipitation samples from 4 stations in the Badain Jaran Desert from 2015 to 2016, the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics and influencing factors of δ2H and δ18O were analyzed. The source of precipitation moisture was analyzed with the backward air mass trajectory model and the recycled moisture fractions were calculated with deuterium excess. The results show that the precipitations of δ2H and δ18O show seasonal effect, which are higher in summer and lower in winter. The precipitations of δ2H and δ18O in the hinterland of desert are more positive and d-excess is more negative than that in the surrounding mountainous areas, reflecting the stronger evaporation of precipitation in the hinterland. The annual precipitation is mainly from the westerly moisture, and the summer precipitation is affected by the southeast monsoon. The recycled moisture fraction in desert is 10.3%-10.9%, which is slightly larger than 8.5% of mountainous area; the recycled moisture accounts for 11.1% of the total evaporation, which reflects that the contribution of strong evaporation in desert to local precipitation is relatively limited.
-
Key words:
- precipitation /
- stable isotope /
- d-excess /
- moisture recycling /
- Badain Jaran Desert /
- atmospheric science
-
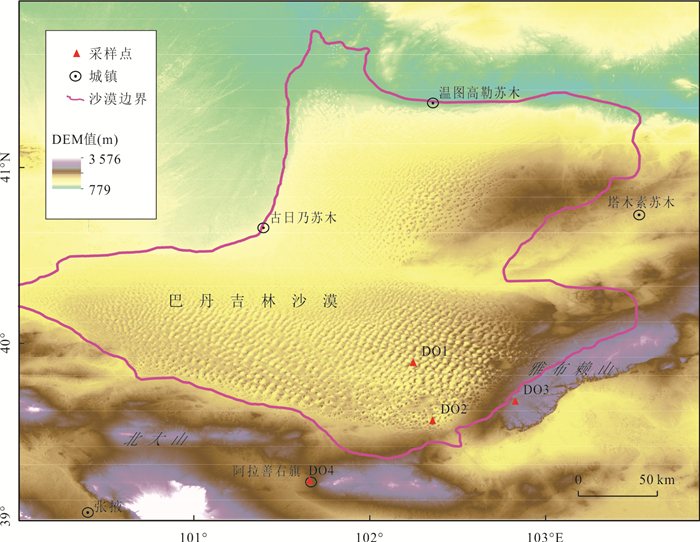
表 1 取样点基本信息
Table 1. The information of sampling points
编号 采样点 经度(E) 纬度(N) 取样时段 Google Earth高程(m) 取样数(个) DO1 车日格勒 102.26° 39.88° 2015/08—2016/07 1 168 11 DO2 巴丹湖 102.37° 39.55° 2015/09—2016/08 1 217 10 DO3 雅布赖山 102.84° 39.66° 2016/01—2016/12 1 696 7 DO4 阿拉善右旗 101.67° 39.21° 2015/01—2016/09 1 503 11 表 2 采样点同位素特征
Table 2. Isotopic characteristics of sampling points
编号 采样点 年均气温
T(℃)年均空气湿度
h(%)年降水量
P(mm)年均值(‰) 雨量加权值(‰) d-excess
年均值(‰)δ18O δ2H δ18O δ2H DO1 车日格勒 11.7 37.7 58.4 -8.8 -72.4 -7.4 -60.1 -3.4 DO2 巴丹湖 12.4 36.9 83.4 -10.3 -76.5 -7.2 -50.6 6.1 DO3 雅布赖山 8.9 40.8 91.9 -8.6 -60.8 -6.7 -45.4 7.7 DO4 阿拉善右旗 9.9 39.9 106.7 -11.1 -81.7 -9.7 -68.5 7.4 表 3 采样点大气降水线方程
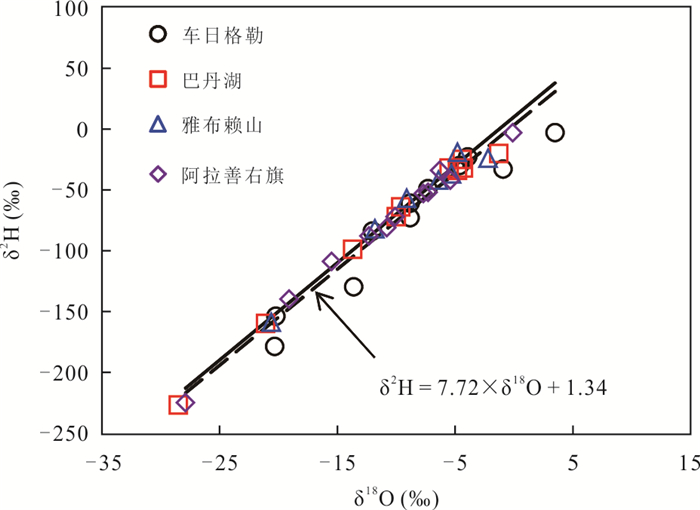
Table 3. Local meteoric water line in the different sampling sites
站点编号 位置 LMWL R2 n P DO1 车日格勒 δ2H = 7.39×δ18O-9.32 0.92 12 < 0.01 DO2 巴丹湖 δ2H = 7.90×δ18O+5.02 0.99 10 < 0.01 DO3 雅布赖山 δ2H = 7.79 × δ18O+7.03 0.97 9 < 0.01 DO4 阿拉善右旗 δ2H = 7.96 × δ18O+6.93 0.99 11 < 0.01 DO1+DO2 沙漠区 δ2H = 7.61 × δ18O-2.93 0.95 21 < 0.01 DO1+DO2+DO3 沙漠及山区 δ2H = 7.67 × δ18O-0.31 0.95 28 < 0.01 DO1+DO2+DO3+DO4 全部 δ2H = 7.72× δ18O+1.34 0.97 42 < 0.01 表 4 稳定同位素与影响因子相关性分析
Table 4. Correlation analysis of stable isotopes and influencing factors
δ2H δ18O d-excess T h P δ2H 1 δ18O 0.981 1 d-excess 0.118 -0.068 1 T 0.795 0.802 -0.020 1 h -0.465 -0.478 0.053 -0.433 1 P 0.259 0.217 0.231 0.368 0.237 1 -
An, W. L., Hou, S. G., Zhang, Q., et al., 2017. Enhanced Recent Local Moisture Recycling on the Northwestern Tibetan Plateau Deduced from Ice Core Deuterium Excess Records. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 122(23): 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017jd027235 Araguás-Araguás, L., Froehlich, K., Rozanski, K., 1998. Stable Isotope Composition of Precipitation over Southeast Asia. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 103(D22): 28721-28742. https://doi.org/10.1029/98jd02582 Best, A. C., 1950. Empirical Formulae for the Terminal Velocity of Water Drops Falling through the Atmosphere. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 76(329): 302-311. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49707632905 Chen, J. S., Li, L., Wang, J. Y., et al., 2004. Groundwater Maintains Dune Landscape. Nature, 432(7016): 459-460. https://doi.org/10.1038/432459a Chen, Z. Y., Qi, J. X., Zhang, Z. J., et al., 2010. Application of Isotope Hydrogeology Method in Typical Basins of North China. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Clark, I. D., Fritz, P., 1997. Environmental Isotopes in Hydrogeology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin. Craig, H., 1961. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science, 133(3465): 1702-1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702 Dansgaard, W., 1964. Stable Isotopes in Precipitation. Tellus, 16(4): 436-468. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2153-3490.1964.tb00181.x Froehlich, K., Kralik, M., Papesch, W., et al., 2008. Deuterium Excess in Precipitation of Alpine Regions-Moisture Recycling. Isotopes in Environmental and Health Studies, 44(1): 61-70. https://doi.org/10.1080/10256010801887208 Gat, J. R., Bowser, C. J., Kendall, C., 1994. The Contribution of Evaporation from the Great Lakes to the Continental Atmosphere: Estimate Based on Stable Isotope Data. Geophysical Research Letters, 21(7): 557-560. https://doi.org/10.1029/94gl00069 Gates, J. B., Edmunds, W. M., Darling, W. G., et al., 2008. Conceptual Model of Recharge to Southeastern Badain Jaran Desert Groundwater and Lakes from Environmental Tracers. Applied Geochemistry, 23(12): 3519-3534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.07.019 Han, P.F., Wang, X.S., Hu, X.N., et al., 2018. Dynamic Relationship between Lake Surface Evaporation and Meteorological Factors in the Badain Jaran Desert. Arid Zone Research, 35(5): 1012-1020 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, G. L., Nie, Z. L., Liu, Z., et al., 2021. OSL Ages and Its Hydrological Implications of Alluvial-Diluvia Deposits from the Southern Margin of Badain Jaran Desert. Earth Science, 46(5): 1829-1839 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jin, K., Rao, W. B., Tan, H. B., et al., 2018. H-O Isotopic and Chemical Characteristics of a Precipitation-Lake Water-Groundwater System in a Desert Area. Journal of Hydrology, 559: 848-860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.03.005 Kinzer, G. D., Gunn, R., 1951. The Evaporation, Temperature and Thermal Relaxation-Time of Freely Falling Waterdrops. Journal of Meteorology, 8(2): 71-83. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0469(1951)0080071:tetatr>2.0.co;2 doi: 10.1175/1520-0469(1951)0080071:tetatr>2.0.co;2 Kong, Y. L., Pang, Z. H., Froehlich, K., 2013. Quantifying Recycled Moisture Fraction in Precipitation of an Arid Region Using Deuterium Excess. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 65(1): 19251. https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v65i0.19251 Li, Z. J., Li, Z. X., Yu, H. C., et al., 2019. Environmental Significance and Zonal Characteristics of Stable Isotope of Atmospheric Precipitation in Arid Central Asia. Atmospheric Research, 227: 24-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2019.04.022 Li, Z. X., Feng, Q., Wang, Q. J., et al., 2016. Contributions of Local Terrestrial Evaporation and Transpiration to Precipitation Using δ18O and d-Excess as a Proxy in Shiyang Inland River Basin in China. Global and Planetary Change, 146: 140-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2016.10.003 Ma, N., Wang, N. A., Zhao, L. Q., et al., 2014. Observation of Mega-Dune Evaporation after Various Rain Events in the Hinterland of Badain Jaran Desert, China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(2): 162-170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-013-0050-3 Peng, H. D., Mayer, B., Norman, A. L., et al., 2005. Modelling of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Compositions for Local Precipitation. Tellus B: Chemical and Physical Meteorology, 57(4): 273-282. https://doi.org/10.3402/tellusb.v57i4.16545 Peng, T. R., Liu, K. K., Wang, C. H., et al., 2011. A Water Isotope Approach to Assessing Moisture Recycling in the Island-Based Precipitation of Taiwan: A Case Study in the Western Pacific. Water Resources Research, 47(8): W08507. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010wr009890 Rao, W. B., Zhang, W. B., Yong, B., et al., 2018. Identifying the Source of Atmospheric Moisture over Arid Deserts Using Stable Isotopes (2H and 18O) in Precipitation. Hydrological Processes, 32(3): 436-449. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.11431 Stein, A. F., Draxler, R. R., Rolph, G. D., et al., 2015. NOAA's HYSPLIT Atmospheric Transport and Dispersion Modeling System. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 96(12): 2059-2077. https://doi.org/10.1175/bams-d-14-00110.1 Stewart, M. K., 1975. Stable Isotope Fractionation Due to Evaporation and Isotopic Exchange of Falling Waterdrops: Applications to Atmospheric Processes and Evaporation of Lakes. Journal of Geophysical Research, 80(9): 1133-1146. https://doi.org/10.1029/jc080i009p01133 Sun, C. J., Chen, W., Chen, Y. N., et al., 2020. Stable Isotopes of Atmospheric Precipitation and Its Environmental Drivers in the Eastern Chinese Loess Plateau, China. Journal of Hydrology, 581: 124404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.124404 Trenberth, K. E., 1999. Atmospheric Moisture Recycling: Role of Advection and Local Evaporation. Journal of Climate, 12(5): 1368-1381. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1999)0121368:amrroa>2.0.co;2 doi: 10.1175/1520-0442(1999)0121368:amrroa>2.0.co;2 Wang, N.A., Ma, N., Chen, H.B., et al., 2013. A Preliminary Study of Precipitation Characteristics in the Hinterland of Badain Jaran Desert. Advances in Water Science, 24(2): 153-160 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, S. J., Zhang, M. J., Che, Y. J., et al., 2016. Influence of Below-Cloud Evaporation on Deuterium Excess in Precipitation of Arid Central Asia and Its Meteorological Controls. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 17(7): 1973-1984. https://doi.org/10.1175/jhm-d-15-0203.1 Wang, X. S., Hu, X. N., Jin, X. M., et al., 2019. Hydrogeological Conditions and Groundwater Circulation Model of the Badain Jaran Desert. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Wang, X. S., Zhou, Y. Y., 2018. Investigating the Mysteries of Groundwater in the Badain Jaran Desert, China. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(2): 1639-1655. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1750-1 Yu, W. S., Yao, T. D., Tian, L. D., et al., 2006. Relationships between δ18O in Summer Precipitation and Temperature and Moisture Trajectories at Muztagata, Western China. Science China Earth Sciences, 49(1): 27-35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-004-5097-1 Zhao, L. J., Liu, X. H., Wang, N. L., et al., 2019. Contribution of Recycled Moisture to Local Precipitation in the Inland Heihe River Basin. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 271: 316-335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2019.03.014 Zhao, L. J., Yin, L., Xiao, H. L., et al., 2011. Isotopic Evidence for the Moisture Origin and Composition of Surface Runoff in the Headwaters of the Heihe River Basin. Chinese Science Bulletin, 56(4-5): 406-415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-010-4278-x Zhou, Y.Y., Wang, X.S., 2019. Numerical Simulation of Groundwater Evaporation in the Badain Jaran Desert of China. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 46(5): 44-54 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SWDG201905008.htm Zhu, G. F., Guo, H. W., Qin, D. H., et al., 2019. Contribution of Recycled Moisture to Precipitation in the Monsoon Marginal Zone: Estimate Based on Stable Isotope Data. Journal of Hydrology, 569: 423-435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.014 陈宗宇, 齐继祥, 张兆吉, 等, 2010. 北方典型盆地同位素水文地质学方法应用. 北京: 科学出版社. 韩鹏飞, 王旭升, 胡晓农, 等, 2018. 巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊水面蒸发与气象要素的动态关系. 干旱区研究, 35(5): 1012-1020. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHQJ201805002.htm 姜高磊, 聂振龙, 刘哲, 等, 2020. 巴丹吉林沙漠南缘冲洪积物的光释光年代及其水文学意义. 地球科学, 46(5): 1829-1839. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.148 王乃昂, 马宁, 陈红宝, 等, 2013. 巴丹吉林沙漠腹地降水特征的初步分析. 水科学进展, 24(2): 153-160. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201302000.htm 王旭升, 胡晓农, 金晓媚, 等, 2019. 巴丹吉林沙漠的水文地质条件及地下水循环模式. 北京: 科学出版社. 周燕怡, 王旭升, 2019. 巴丹吉林沙漠潜水蒸发的数值模拟研究. 水文地质工程地质, 46(5): 44-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201905008.htm -









 下载:
下载: