Marine Electrical Resistivity Tomography Research in Pearl River Estuary of Greater Bay Area
-
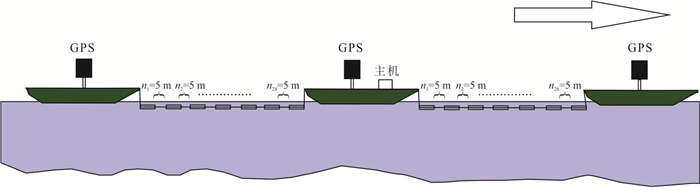
摘要: 海域环境对高密度电阻率法在仪器设备、测量技术和反演解译等方面提出了更高要求,开展海上高密度电法的数值模拟和实测研究将进一步丰富近岸海域地质、资源和环境等问题的勘查手段.基于数值模拟和野外实测,深入研究了偶极-偶极、温纳、斯贝等不同装置对近岸海域典型地电模型的分辨能力和空间定位效果,并详细分析了海水导电性的影响,最后在珠江口伶仃洋海域开展了国内首次2条长剖面的实际测量.结果表明海水电导率对不同测量装置在探测深度和精度方面存在差异化影响,井中电缆利用浮力材料固定后,进行水面拖缆式偶极-偶极测量能大幅降低海底沉缆式测量的施工风险,实现复杂海域环境下高密度电法探测效果、深度与效率的优化折中.Abstract: Applying the electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) technique in the marine environment claims higher levels in the aspects of instrument, measurement techniques, inversion and interpretation methods and so on. The exploration approaches on issues of geology, natural resources and environment will be further enriched by numerical simulations and actual measurement research of the marine ERT in the coastal area. Based on numerical simulations and field measurements, in this paper it focuses on the research of the resolution and spatial location of the typical geo-electrical models in the offshore area with different arrays such as dipole-dipole, Wenner and Schlumberger. It also studied the effects of seawater conductivity and first conducted two long profile measurements at the site of Pearl River Estuary in the Lingdingyang area. It shows that the detection depth and resolution with different configurations would be differentially influenced by the conductivity of the seawater. And the construction risk of applying the boat-towed electrode arrays floating on the water and pulled behind a boat with borehole electrode cables and buoyant materials is much lower than a pulled-array on the seafloor. This will achieve a balance among the effect, depth and the efficiency for the ERT in the complex marine environment and finally promote the development and maturity of ERT technology.
-
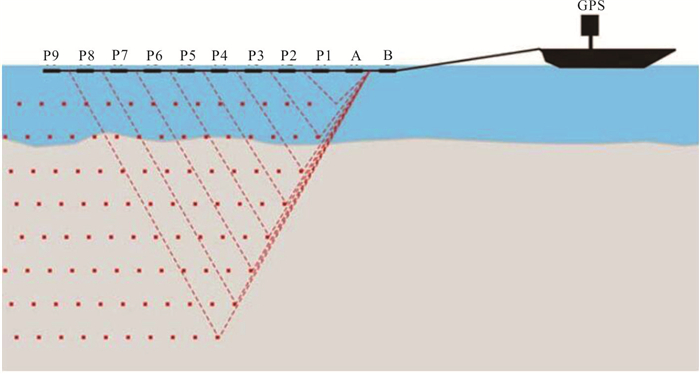
图 1 高密度电阻率法工作示意图(据Loke et al., 2013)
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of a multi-electrode system, and a possible sequence of measurements to create a 2-D pseudosection(after Loke et al., 2013)
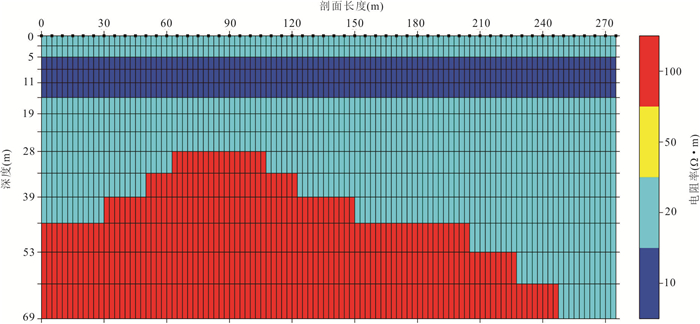
表 1 基岩界面模型参数
Table 1. The parameters of bedrock interface model
介质层 厚度(m) 电阻率值(Ω.m) 上覆水层 5(0~5) 20 淤泥层 10(5~15) 10 砂层 54(15~69) 20 风化基岩层 41(28~69) 100 表 2 层状地层模型参数
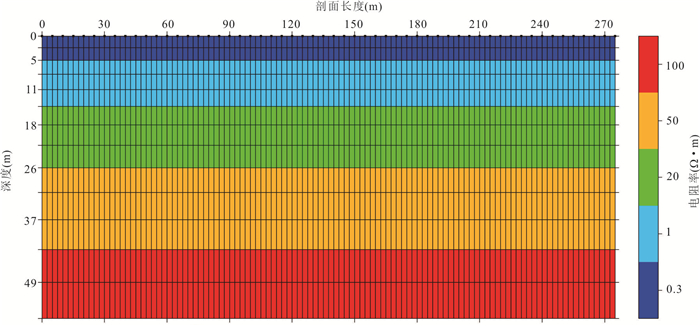
Table 2. The parameters of layered earth model
介质层 厚度(m) 电阻率值(Ω.m) 上覆水层 5(0~5) 0.3/20/50 淤泥层 9(5~14) 1 低阻砂层 12(14~26) 20 高阻砂层 17(26~43) 50 风化基岩层 14(43~57) 100 -
AGI, 2009.Instruction Manual for EarthImager 2D Version 2.4.0.Advanced Geosciences, Inc., Austin, Texas, 139. Amidu, S.A., Dunbar, J.A., 2008.An Evaluation of the Electrical-Resistivity Method for Water-Reservoir Salinity Studies.Geophysics, 73(4):G39-G49. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2938994 Baumgartner, F., 1996.A New Method for Geoelectrical Investigations Underwater.Geophysical Prospecting, 44(1):71-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2478.1996.tb00140.x Carretero, S., Rapaglia, J., Perdomo, S., et al., 2019.A Multi-Parameter Study of Groundwater-Seawater Interactions along Partido de La Costa, Buenos Aires Province, Argentina.Environmental Earth Sciences, 78(16):513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-019-8532-5 Day-Lewis, F.D., White, E.A., Johnson, C.D., et al., 2006.Continuous Resistivity Profiling to Delineate Submarine Groundwater Discharge:Examples and Limitations.The Leading Edge, 25(6):724-728. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2210056 Fu, L.K., 1959.Several Theory Problems of Underwater DC Resistivity Method.Earth Science, 3(3):12-25(in Chinese with English abstract). Ge, W.Z., 1994.The Forward Solution of the Electrical Field Due to a Point Source in Layered Media and Its Applications.Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 37(Suppl.2):534-541(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX4S2.059.htm Giampaolo, V., Capozzoli, L., Grimaldi, S., et al., 2016.Sinkhole Risk Assessment by ERT:The Case Study of Sirino Lake (Basilicata, Italy).Geomorphology, 253:1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2015.09.028 He, Z.X., Yu, G., 2008.Marine EM Survey Technology and Its New Advances.Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 31(1):2-9(in Chinese with English abstract). Henderson, R.D., Day-Lewis, F.D., Abarca, E., et al., 2010.Marine Electrical Resistivity Imaging of Submarine Groundwater Discharge:Sensitivity Analysis and Application in Waquoit Bay, Massachusetts, USA.Hydrogeology Journal, 18(1):173-185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-009-0498-z Hu, X.Y., Kim, K., 2018.A Trial for Introducing 6-Element Tensor Impedance in Magnetotelluric Method and Its Application.Earth Science, 43(10):3399-3406(in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2018.317 Huang, J.G., Ruan, B.Y., Bao, G.X., 2004.DC Resistivity Numerical Modeling Underwater.Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 26(2):136-140(in Chinese with English abstract). Kwon, H.S., Kim, J.H., Ahn, H.Y., et al., 2005.Delineation of a Fault Zone beneath a Riverbed by an Electrical Resistivity Survey Using a Floating Streamer Cable.Exploration Geophysics, 36(1):50-58. https://doi.org/10.1071/eg05050 Loke, M.H., Chambers, J.E., Rucker, D.F., et al., 2013.Recent Developments in the Direct-Current Geoelectrical Imaging Method.Journal of Applied Geophysics, 95:135-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jappgeo.2013.02.017 Liu, C., Dai, G.Q., Wang, J., 2017.Reservoir Deposition Exploration Based on Electrical Resistivity Imaging over Water.Western Resources, (6):94-95(in Chinese). Mao, Y.H., Zhao, Z.X., Sun, Z., 2020.Extensional Thinning Mechanism of the Western Continental Margin of the Pearl River Mouth Basin.Earth Science, 45(5):1622-1635(in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2019.160 Ni, L., Chen, D.H., Xu, H.W., et al., 2012.Electrical Exploration on Water Region Used in the Geophysical Prospecting Cross the River and Lake.Progress in Geophysics, 27(6):2710-2715(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201206051.htm O'Connell, Y., Daly, E., Henry, T., et al., 2018.Terrestrial and Marine Electrical Resistivity to Identify Groundwater Pathways in Coastal Karst Aquifers.Near Surface Geophysics, 16(2):164-175. https://doi.org/10.3997/1873-0604.2017062 Redhaounia, B., Ilondo, B.O., Gabtni, H., et al., 2016.Electrical Resistivity Tomography (ERT) Applied to Karst Carbonate Aquifers:Case Study from Amdoun, Northwestern Tunisia.Pure and Applied Geophysics, 173(4):1289-1303. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00024-015-1173-z Ren, G.X., Guo, X.J., Jiang, F.W., et al., 2015.A Navigated Underwater DC Resistivity Survey System Developed and Used in Detecting.Progress in Geophysics, 30(3):1430-1436(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQWJ201503058.htm Rucker, D.F., Noonan, G.E., Greenwood, W.J., 2011.Electrical Resistivity in Support of Geological Mapping along the Panama Canal.Engineering Geology, 117(1-2):121-133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.10.012 Song, S.H., Cho, I.K., 2009.Application of a Streamer Resistivity Survey in a Shallow Brackish-Water Reservoir. Exploration Geophysics, 40(2):206-213. http://www.cabdirect.org/abstracts/20093199689.html Tao, Z., Wang, Y.X., Wang, J.L., 1998.The Experiment and Research of the Axial Even Permutation Electrical Sounding in Marine.China Offshore Oil and Gas(Geology), 12(5):346-348(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199805016.htm Wang, J., Zhang, S.M., Ma, X.C., 2012.Application of Water Multi-Electrode Resistivity Method in Oil-Gas Pipeline Projects.Jilin Geology, 31(2):76-79(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JLDZ201202022.htm Xia, Z., 2015.Comprehensive Research of Marine Geological Environment in the Nearshore of Pearl River Mouth.Science Press, Beijing, 17(in Chinese). Xu, D., Hu, X.Y., Shan, C.L., et al., 2016.Landslide Monitoring in Southwestern China via Time-Lapse Electrical Resistivity Tomography.Applied Geophysics, 13(1):1-12. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yydqwl201601001 Yang, C.H., You, J.I., Lin, C.P., 2002.Delineating Lake Bottom Structure by Resistivity Image Profiling on Water Surface. Terrestrial Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 13(1):39-52. doi: 10.3319/TAO.2002.13.1.39(T) Yang, Z.L., Yin, C.C., Zhang, B., et al., 2018.3-D Arbitrarily Anisotropic Modeling for Towed Marine DC Resistivity Method in Deep Ocean.Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 48(6):1845-1853(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201806022.htm Zhu, D.B., Yang, Y.C., Tian, Z.H., 2014.Underway Electrical Rapid Prospecting Technology.Progress in Geophysics, 29(3):1377-1383(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQWJ201403052.htm 傅良魁, 1959.水下电法勘探方法的几个理论问题.地球科学, 3(3):12-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX195903002.htm 葛为中, 1994.层状介质点源电场正演解析及其应用.地球物理学报, 37(增刊2):534-541. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX4S2.059.htm 何展翔, 余刚, 2008.海洋电磁勘探技术及新进展.勘探地球物理进展, 31(1):2-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTDQ200801003.htm 胡祥云, 金钢燮, 2018.大地电磁六元素张量阻抗理论及其应用.地球科学, 43(10):3399-3406. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.317 黄俊革, 阮百尧, 鲍光淑, 2004.水下直流电阻率法数值模拟.物探化探计算技术, 26(2):136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTHT200402011.htm 刘成, 戴国强, 王俊, 2017.基于水上高密度的水库淤积勘查应用.西部资源, (6):94-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBZY201706038.htm 毛云华, 赵中贤, 孙珍, 2020.珠江口盆地西部陆缘伸展-减薄机制.地球科学, 45(5):1622-1635. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.160 倪亮, 陈大红, 徐华文, 等, 2012.水域电法在江、湖穿越工程中应用.地球物理学进展, 27(6):2710-2715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201206051.htm 任广欣, 郭秀军, 蒋甫伟, 等, 2015.走航式水下多道电阻率探测系统研制与应用.地球物理学进展, 30(3):1430-1436. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201503058.htm 陶忠, 王一新, 王家林, 1998.海洋轴向偶极电测深法的试验研究.中国海上油气(地质), 12(5):346-348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD199805016.htm 王剑, 张赛民, 马晓成, 2012.水上高密度电法在油气管道工程中应用.吉林地质, 31(2):76-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLDZ201202022.htm 夏真, 2015.珠江口近岸海洋地质环境综合研究.北京:科学出版社, 17. 杨志龙, 殷长春, 张博, 等, 2018.全拖曳式深海直流电阻率法三维任意各向异性正演模拟.吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 48(6):1845-1853. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201806022.htm 朱德兵, 杨益成, 田忠涵, 2014.走航式电法快速探测技术.地球物理学进展, 29(3):1377-1383. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201403052.htm -










 下载:
下载: