PRB Thickness and Influence Based on 1D PCE Chain Degradation
-
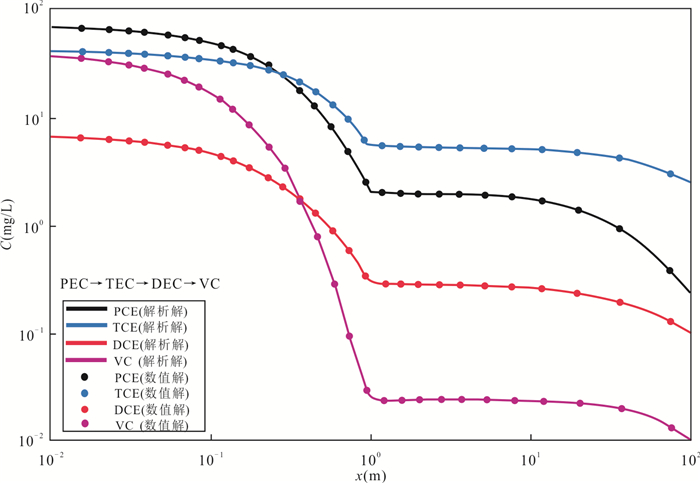
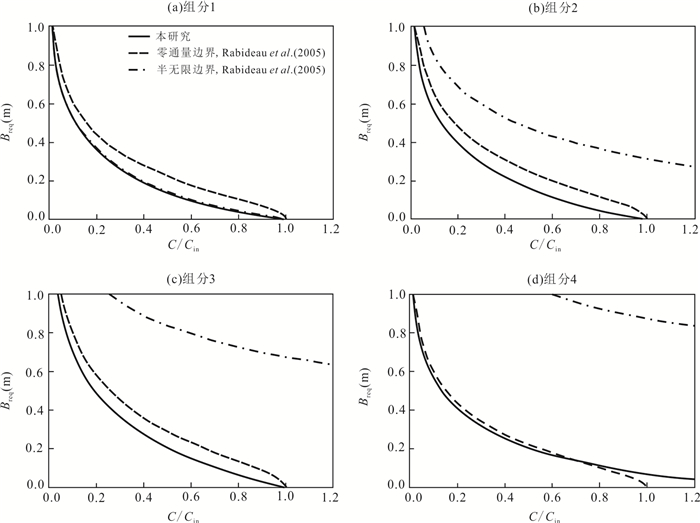
摘要: 可渗透反应墙(Permeable Reactive Barrier,PRB)技术是原位地下水或者土壤修复中最受瞩目的技术之一,该技术设计和安装的首要关键问题就是反应墙的厚度计算.现有的反应墙设计方法大部分只考虑了单一污染物或者反应墙本身,很少考虑多种污染物的存在以及含水层水力性质的实际情况.聚焦于可渗透反应墙中的PCE(四氯乙烯)链式降解过程,基于可渗透反应墙-含水层的多域多组分污染物的体系建立了一维条件下的对流弥散方程,通过借鉴相关文献提出的转换算法得出方程解析解,并由此推导出适合多组分污染物体系的反应墙厚度公式,利用软件COMSOL建立了数值模型验证了其正确性.对比已有的Rabideau模型发现:计算反应墙厚度时不能完全忽略含水层的自然衰减反应,尤其当达标面远离反应墙出口处时;对于多种组分皆来源于同一种母源反应物的污染物,计算反应墙厚度时边界条件十分关键.本文模型的解析解可以为可渗透反应墙的设计和安装提供建设性的意见,还可以快速分析多组分污染物的分布和预测,为地下水的修复工程、风险评估、后期监测控制提供了计算的支撑.Abstract: Permeable Reactive Barrier (PRB) technology is one of the most popular technologies for in-situ groundwater or soil remediation. A key task of design and installation is to calculate the thickness of the PRB. Most of the existing models of calculating the PRB thickness only consider the single species or the reaction barrier itself, with little consideration of a variety of contaminants and the combination of the aquifers. The response to PRB and aquifer multi-domain system, the convection dispersion equation of multi-species under one-dimensional condition was established. The analytical solution of the equation was obtained by using a conversion algorithm proposed by related literature, and the formula of the new PRB thickness was deduced at the same time, and then the numerical model was built based on the software COMSOL to validate this analytical solution. After comparing the required PRB thickness calculated from this study and previously developed Rabideau models, the aquifer reaction capability is found to be non-negligible for the determination of the required thickness of the PRB especially when the compliance plane becoming far from the PRB exit face. For the remediation multiple species sharing a single parental species, the correctness in the boundary and the domain conditions are crucial to estimate the effective thickness of a PRB. The proposed analytical solution provides meaningful designing insights for the PRB design and installation.
-
Key words:
- Permeable Reactive Barrier (PRB) /
- 1D flow /
- PCE /
- analytical solution /
- PRB thickness /
- environmental science
-
表 1 模型所需参数
Table 1. Required model parameters
参数 值 参数 值 nB 0.5 nL 0.1 uB (m/d) q/nB uL (m/d) q/nL DB (m2/d) 0.1uB C1b (mg/L) 100 DL (m2/d) 10uL C2b (mg/L) 50 B (m) 1 C3b (mg/L) 10 q (m/d) 0.3 C4b (mg/L) 80 λΒ1 (1/d) 3.61a yB1 1.0a λΒ2 (1/d) 5.73a yB2 0.4a λΒ3 (1/d) 2.97a yB3 0.02a λΒ4 (1/d) 3.61a yB4 0.01a λL1 (1/d) 0.005b yL1 1.0b λL2 (1/d) 0.003b yL2 0.792 0b λL3 (1/d) 0.002b yL3 0.737 7b λL4 (1/d) 0.001b yL4 0.644 5b 注:上标a代表数据引自ETI (2005);上标b代表数据引自Alvarez and Illman (2006). -
Alvarez, P. J. J., Illman, W. A., 2006. Bioremediation and Natural Attenuation: Process Fundamentals and Mathematical Models. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken. https://doi.org/10.1002/047173862x Clement, T. P., 2001. Generalized Solution to Multispecies Transport Equations Coupled with a First-Order Reaction Network. Water Resources Research, 37(1): 157-163. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000wr900239 ETI, 2005. First-Order Kinetic Degradation Models. Technical Note 2.06. Environmental Technologies Inc., Waterloo. Eykholt, G. R., Elder, C. R., Benson, C. H., 1999. Effects of Aquifer Heterogeneity and Reaction Mechanism Uncertainty on a Reactive Barrier. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 68(1-2): 73-96. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3894(99)00032-1 Gavaskar, A. R., 1999. Design and Construction Techniques for Permeable Reactive Barriers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 68(1-2): 41-71. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3894(99)00031-x Gavaskar, A.R., Gupta, N., Sass, B.M., et al., 1998. Permeable Barriers for Groundwater Remediation: Design Construction and Monitoring. Battelle Press, Columbus. https://doi.org/10.21236/ada379980 Huang, R.Z., Gao, Y.J., Liu, R., et al., 2016. Review of Permeable Reactive Barriers for Groundwater Remediation. Journal of Liaoning University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 36(4): 240-244 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-LNGX201604008.htm Li, J.J., Cai, W.T., Zhang, T., et al., 2019. Study on the Remediation of High Concentration Cr(Ⅵ) Contaminated Groundwater by Mixed Medium of Cast Iron and Coconut Shell Activated Carbon. Environmental Pollution & Control, 41(5): 551-555, 578 (in Chinese with English abstract). Park, E., Zhan, H. B., 2009. One-Dimensional Solute Transport in a Permeable Reactive Barrier-Aquifer System. Water Resources Research, 45(7): W07502. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008wr007155 Rabideau, A. J., Suribhatla, R., Craig, J. R., 2005. Analytical Models for the Design of Iron-Based Permeable Reactive Barriers. Journal of Environmental Engineering, 131(11): 1589-1597. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9372(2005)131:11(1589) Sun, Y., Petersen, J. N., Clement, T. P., et al., 1999. Development of Analytical Solutions for Multispecies Transport with Serial and Parallel Reactions. Water Resources Research, 35(1): 185-190. https://doi.org/10.1029/1998wr900003 Tan, Y., Liang, J., Zeng, G.M., et al., 2016. Effects of PRB Design Based on Numerical Simulation and Response Surface Methodology. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 10(2): 655-661 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201602023.htm Tratnyek, P. G., Johnson, T. L., Scherer, M. M., et al., 1997. Remediating Ground Water with Zero-Valent Metals: Chemical Considerations in Barrier Design. Groundwater Monitoring & Remediation, 17(4): 108-114. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6592.1997.tb01270.x van Genuchten, M.T., Alves, W.J., 1983. Analytical Solutions of the One-Dimensional Convective-Dispersive Solute Transport Equation. Technical Bulletin U.S. Department of Agriculture, 1661: 149. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-3774(84)90020-9 Wang, H.Q., 2020. Study on Permeable Reactive Barrier Technology for the Remediation of Polluted Groundwater. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 10(2): 251-259 (in Chinese with English abstract). 黄润竹, 高艳娇, 刘瑞, 等, 2016. 应用可渗透反应墙进行地下水修复的综述. 辽宁工业大学学报(自然科学版), 36(4): 240-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LNGX201604008.htm 李敬杰, 蔡五田, 张涛, 等, 2019. 铸铁和椰壳活性炭混合介质修复高浓度Cr(Ⅵ)污染地下水研究. 环境污染与防治, 41(5): 551-555, 578. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR201905011.htm 谭勇, 梁婕, 曾光明, 等, 2016. 基于数值模拟和响应面法的PRB设计影响研究. 环境工程学报, 10(2): 655-661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJJZ201602023.htm 王泓泉, 2020. 污染地下水可渗透反应墙(PRB)技术研究进展. 环境工程技术学报, 10(2): 251-259. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKWZ202002020.htm -










 下载:
下载: