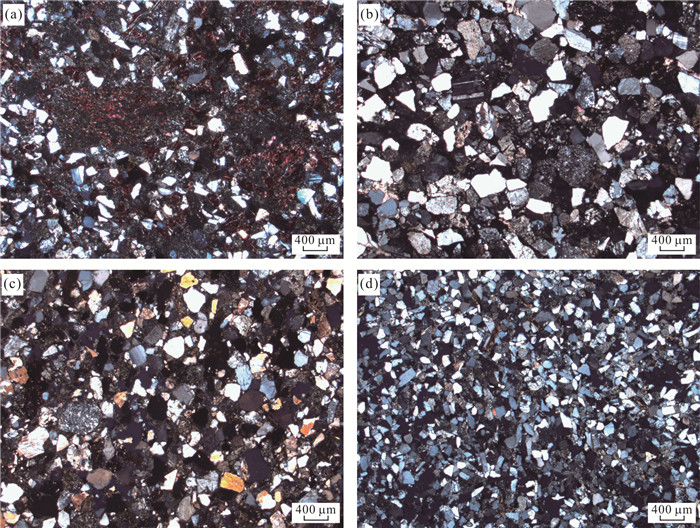
Geochemical Characteristics and Signatures of Mesozoic Sandstones from Huanghua Depression
-
摘要: 中生代黄骅坳陷位于华北克拉通汇聚与破坏的中心,为各物源的汇集地,记录了华北中生代盆地的构造及物源演化.对研究区中生界砂岩进行了主、微量元素测试分析,结果显示,样品SiO2、Al2O3、Na2O、K2O和Fe2O3T平均含量分别为66.98%、13.65%、2.74%、3.03%和3.26%,砂岩为岩屑砂岩、长石砂岩和杂砂岩.砂岩CIA和ICV的平均值分别为56.12和0.94,均经历了一定的化学风化及再旋回作用.砂岩的母岩为长英质火成岩和再旋回沉积岩,并混杂少量基性火成岩.由三叠纪到白垩纪,中生界砂岩物源逐渐由华北北缘大陆弧演化为燕山造山带和黄骅坳陷内的岩浆作用及古隆起.Abstract: In Mesozoic, the Huanghua Depression was located in the center of the convergence and destruction of the North China Craton and was the sink place of all source areas. It recorded the evolution of the tectonic and provenance of the Mesozoic basins in North China. The main and trace elements of Mesozoic sandstones from the study area were examined. It is found that the average contents of SiO2, Al2O3, Na2O, K2O, and Fe2O3T are 66.98%, 13.65%, 2.74%, 3.03%, and 3.26%, respectively. The sandstones are litharenites, arkoses, and greywackes. The average CIA and ICV values are 56.12 and 0.94, and the sandstones experienced some chemical weathering and recycling. The parent rocks of the sandstones are feldspathic igneous rocks and recycling sedimentary rocks, mixed with a small amount of basic igneous rocks. From the Triassic to the Cretaceous, the source of Mesozoic sandstones gradually evolved from continental arc in the northern margin of North China to the paleo-uplift and the interplate magmatic area of the Yanshan orogenic belt and the Huanghua Depression.
-
Key words:
- weathering /
- provenance /
- tectonic setting /
- Mesozoic /
- Huanghua Depression /
- geochemistry
-
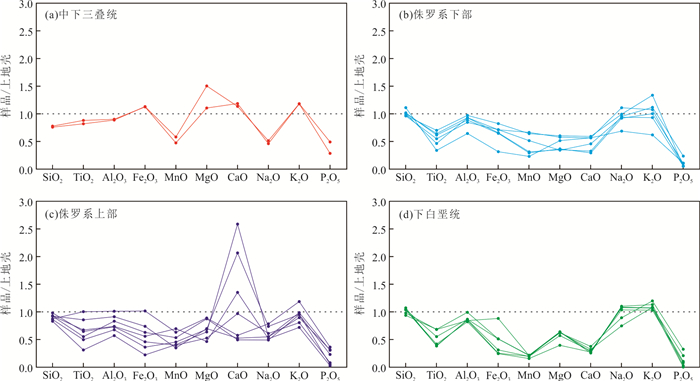
图 4 中生界砂岩主量元素平均上地壳标准化蛛网图(上地壳标准值据Hu and Gao, 2008)
Fig. 4. Major elements spider diagram normalized to average UCC for Mesozoic sandstones(normalized values from Hu and Gao, 2008)
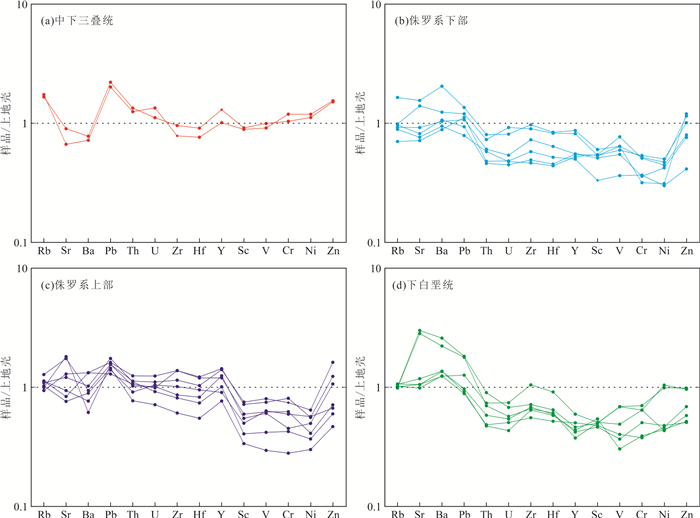
图 6 中生界砂岩微量元素平均上地壳标准化蛛网图(上地壳标准值据Hu and Gao, 2008)
Fig. 6. Trace elements spider diagram normalized to average UCC for Mesozoic sandstones(normalized values from Hu and Gao, 2008)
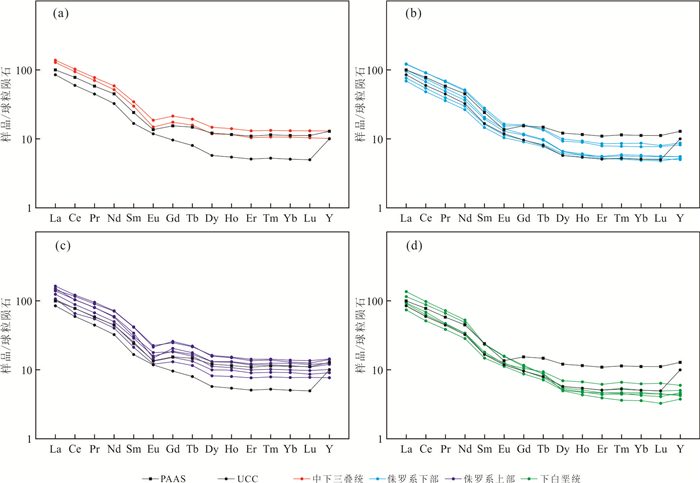
图 7 中生界砂岩稀土元素球粒陨石标准化蛛网图
球粒陨石标准化数据据Boynton(1984);PAAS数据据McLennan and Taylor(1991);UCC数据据Hu and Gao(2008)
Fig. 7. REE spider diagram normalized to chondrite for Mesozoic sandstones
图 9 中生界砂岩风化条件图解
a.据Nesbitt and Young(1984),平均上地壳数据(UCC)据Hu and Gao(2008);b.碱性金属和碱土金属在风化过程中的迁移性对比图(Garzanti et al., 2013),αAlE值根据平均上地壳数据标准化(Hu and Gao, 2008)
Fig. 9. Weathering condition plots for Mesozoic sandstones
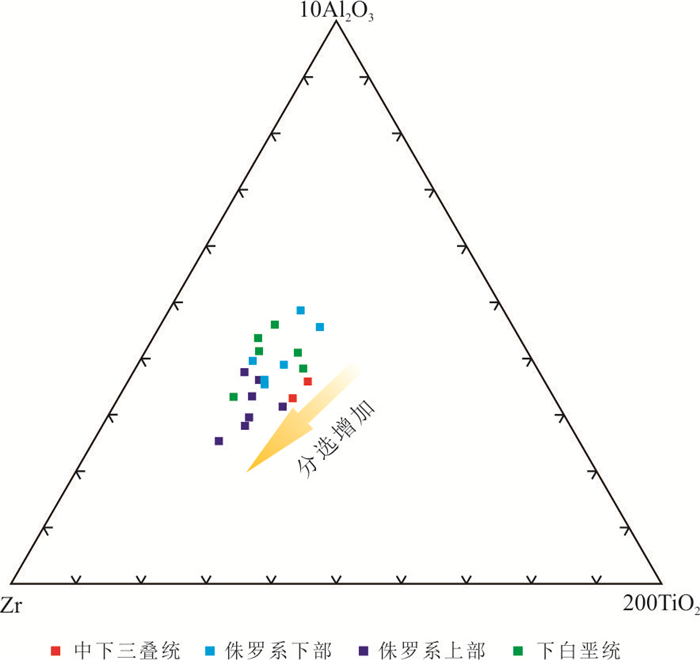
图 10 中生界砂岩Al2O3-Zr-TiO2三角图(Garcia et al., 1991)
Fig. 10. Al2O3-Zr-TiO2 ternary plot for Mesozoic sandstones(Garcia et al., 1991)
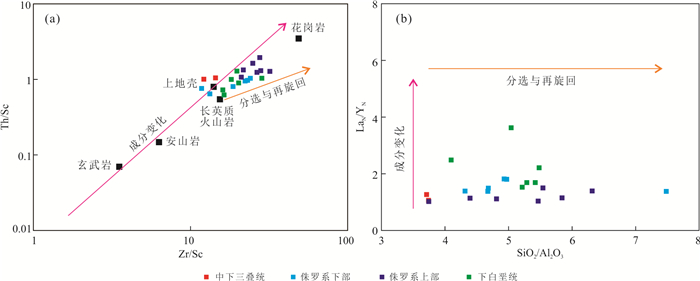
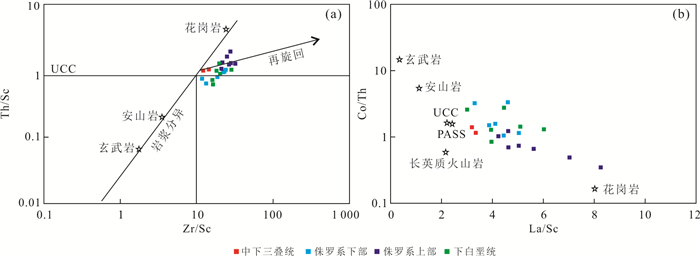
图 11 中生界砂岩成分及分选与再旋回变化
a. 据McLennan et al.(1993),紫色箭头表示由岩浆分异导致的成分变化,黄色箭头表示由锆石增多导致的分选与再旋回变化,黑色方块的玄武岩、安山岩、长英质火山岩及花岗岩数据据Condie(1993),平均上地壳标准值据Hu and Gao(2008);b. 据Roser and Korsch(1999),N表示平均上地壳标准化
Fig. 11. Variations of composition, sorting and recycling for Mesozoic sandstones
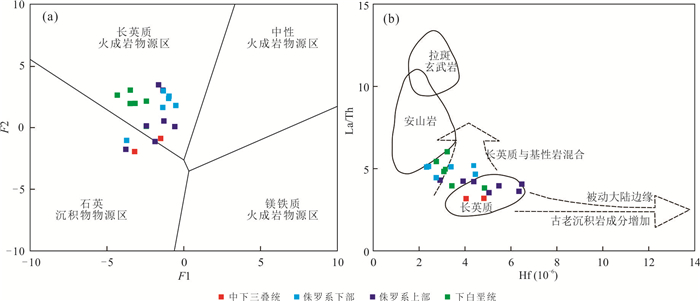
图 12 中生界砂岩物源判别图
a. 据Roser and Korsch(1988),其中F1 =-1.773TiO2+0.607Al2O3+0.760Fe2O3T-1.500MgO+0.616CaO+0.509Na2O-1.224K2O-9.090,F2 = 0.445TiO2+0.070Al2O3-0.250Fe2O3T-1.142MgO+0.438CaO+1.475Na2O+1.426K2O-6.861;b. 据Floyd and Leveridge(1987)
Fig. 12. Provenance discrimination diagrams for Mesozoic sandstones
图 13 中生界砂岩物源判别图
a. 据McLennan et al.(1993);b. 据Gu et al.(2002)
Fig. 13. Provenance discrimination diagrams for the Mesozoic sandstones
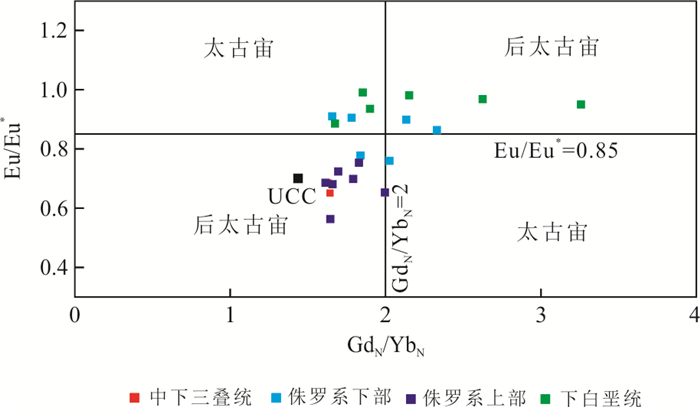
图 14 中生界砂岩Eu/Eu*-GdN/YbN图解(McLennan and Taylor, 1991)
Fig. 14. Eu/Eu* versus GdN/YbN plot for Mesozoic sandstones(McLennan and Taylor, 1991)
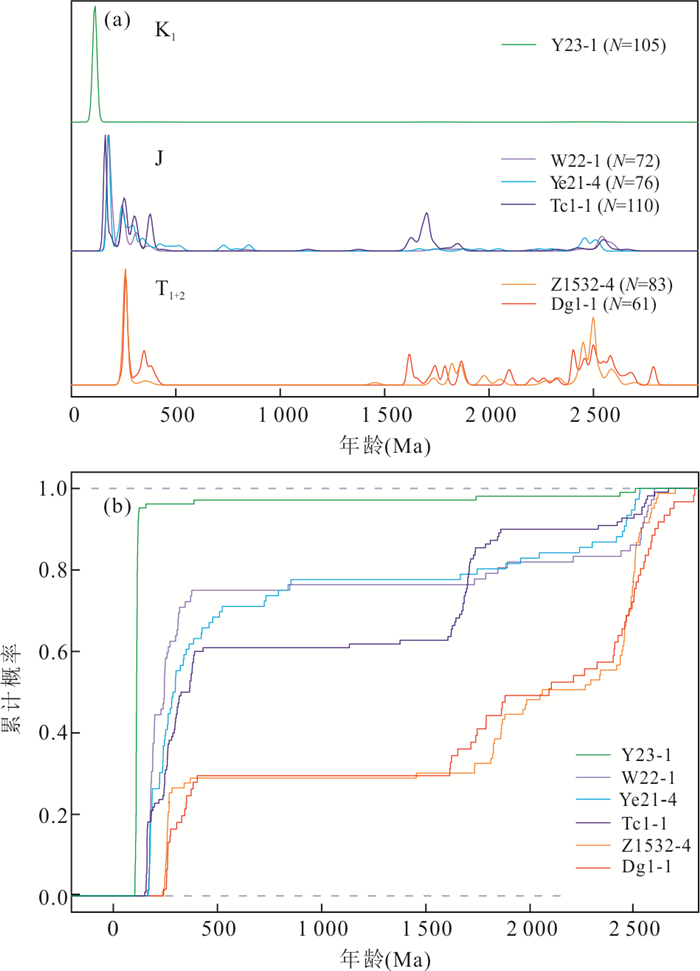
图 15 中生界砂岩碎屑锆石年龄概率分布
a.中生界砂岩碎屑锆石年龄概率曲线;b. 中生界砂岩碎屑锆石年龄累计概率曲线. 数据来自Li et al.(2013)和朱吉昌等(2020)
Fig. 15. Probability distribution of detrital zircon ages for Mesozoic sandstones
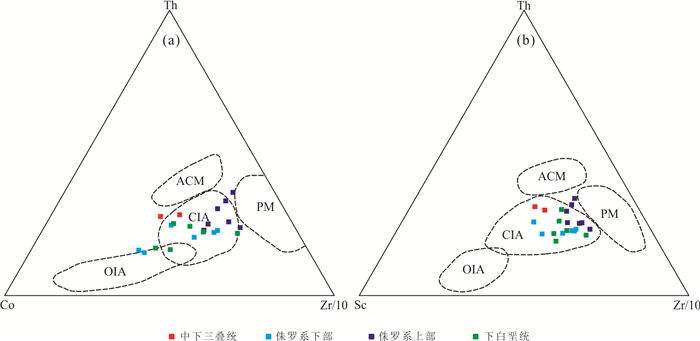
图 16 中生界砂岩构造环境判别图
and Crook(1986). ACM. 主动大陆边缘;PM. 被动大陆边缘;OIA. 大洋岛弧:CIA. 大陆岛弧
Fig. 16. Tectonic setting discrimination plots of Mesozoic sandstones
表 1 中生界砂岩元素比值物源特征
Table 1. Provenance characteristics of the element ratio of Mesozoic sandstones
微量元素比值 中生界砂岩元素比值范围 中生界砂岩元素比值平均值 长英质物源元素比值 镁铁质物源元素比值 平均上地壳元素比值 Eu/Eu* 0.56~0.99 0.81 0.40~0.94 0.71~0.95 0.70 (La/Lu)N 1.18~4.66 1.84 3.00~27.00 1.10~7.00 10.38 La/Sc 3.01~8.25 4.66 2.50~16.30 0.43~0.86 2.20 Th/Sc 0.62~1.95 1.08 0.84~20.50 0.05~0.22 0.75 Th/Co 0.30~2.88 0.98 0.04~3.25 0.04~1.40 0.61 Cr/Th 2.65~6.95 5.18 4.00~15.00 25.00~500.00 8.76 La/Co 1.33~12.20 4.20 1.80~13.80 0.14~0.38 1.79 注:长英质物源及镁铁质物源数据据Cullers and Pidkovyrov(2000);平均上地壳数据据Hu and Gao(2008). -
Aitchison, J., 1986. The Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data. Chapman and Hall, London. Bhatia, M. R., Crook, K. A. W., 1986. Trace Element Characteristics of Graywackes and Tectonic Setting Discrimination of Sedimentary Basins. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 92(2): 181-193. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00375292 Boynton, W. V., 1984. Cosmochemistry of the Rare Earth Elements: Meteorite Studies. In: Henderson, P., ed., Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-42148-7.50008-3 Cao, X. Z., Flament, N., Müller, D., et al., 2018. The Dynamic Topography of Eastern China since the Latest Jurassic Period. Tectonics, 37(5): 1274-1291. https://doi.org/10.1029/2017tc004830 Condie, K. C., 1993. Chemical Composition and Evolution of the Upper Continental Crust: Contrasting Results from Surface Samples and Shales. Chemical Geology, 104(1-4): 1-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(93)90140-e Cox, R., Lowe, D. R., Cullers, R. L., 1995. The Influence of Sediment Recycling and Basement Composition on Evolution of Mudrock Chemistry in the Southwestern United States. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(14): 2919-2940. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(95)00185-9 Cullers, R. L., Podkovyrov, V. N., 2000. Geochemistry of the Mesoproterozoic Lakhanda Shales in Southeastern Yakutia, Russia: Implications for Mineralogical and Provenance Control, and Recycling. Precambrian Research, 104(1-2): 77-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-9268(00)00090-5 Dong, S.W., Zhang, Y.Q., Chen, X.H., et al., 2008. The Formation and Deformational Characteristics of East Asia Multi-Direction Convergent Tectonic System in Late Jurassic. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 29(3): 306-317 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200803006.htm Floyd, P. A., Leveridge, B. E., 1987. Tectonic Environment of the Devonian Gramscatho Basin, South Cornwall: Framework Mode and Geochemical Evidence from Turbiditic Sandstones. Journal of the Geological Society, 144(4): 531-542. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsjgs.144.4.0531 Filzmoser, P., Hron, K., Reimann, C., 2009. Principal Component Analysis for Compositional Data with Outliers. Environmetrics, 20(6): 621-632. https://doi.org/10.1002/env.966 Garcia, D., Coelho, J., Perrin, M., 1991. Fractionation between TiO2 and Zr as a Measure of Sorting within Shale and Sandstone Series (Northern Portugal). European Journal of Mineralogy, 3(2): 401-414. https://doi.org/10.1127/ejm/3/2/0401 Garzanti, E., Padoan, M., Setti, M., et al., 2013. Weathering Geochemistry and Sr-Nd Fingerprints of Equatorial Upper Nile and Congo Muds. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 14(2): 292-316. https://doi.org/10.1002/ggge.20060 Gu, X. X., Liu, J. M., Zheng, M. H., et al., 2002. Provenance and Tectonic Setting of the Proterozoic Turbidites in Hunan, South China: Geochemical Evidence. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 72(3): 393-407. https://doi.org/10.1306/081601720393 Hu, Z. C., Gao, S., 2008. Upper Crustal Abundances of Trace Elements: A Revision and Update. Chemical Geology, 253(3-4): 205-221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.05.010 Huang, D. Y., 2019. Jurassic Integrative Stratigraphy and Timescale of China. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 49(1): 227-256 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N072017-00443 Li, H. Y., Xu, Y. G., Liu, Y. M., et al., 2013. Detrital Zircons Reveal No Jurassic Plateau in the Eastern North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 24(2): 622-634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2012.12.007 Li, S. Z., Jahn, B. M., Zhao, S. J., et al., 2017. Triassic Southeastward Subduction of North China Block to South China Block: Insights from New Geological, Geophysical and Geochemical Data. Earth-Science Reviews, 166: 270-285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.01.009 Li, S.Z., Suo, Y.H., Dai, L.M., et al., 2010. Development of the Bohai Bay Basin and Destruction of the North China Craton. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(4): 64-89 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/284685931_Development_of_the_Bohai_Bay_Basin_and_destruction_of_the_North_China_Craton Lindsey, D.A., 1999. An Evaluation of Alternative Chemical Classifications of Sandstones (Open-File Report). U.S. Geological Survey, Denver. McLennan, S. M., Hemming, S., McDaniel, D. K., et al., 1993. Geochemical Approaches to Sedimentation, Provenance, and Tectonics. In: Johnsson, M.J., Basu, A., eds., Processes Controlling the Composition of Clastic Sediments. Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, 284: 21-40. https://doi.org/10.1130/spe284-p21 McLennan, S. M., Taylor, S. R., 1991. Sedimentary Rocks and Crustal Evolution: Tectonic Setting and Secular Trends. The Journal of Geology, 99(1): 1-21. https://doi.org/10.1086/629470 Nesbitt, H. W., Young, G. M., 1982. Early Proterozoic Climates and Plate Motions Inferred from Major Element Chemistry of Lutites. Nature, 299(5885): 715-717. https://doi.org/10.1038/299715a0 Nesbitt, H. W., Young, G. M., 1984. Prediction of Some Weathering Trends of Plutonic and Volcanic Rocks Based on Thermodynamic and Kinetic Considerations. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 48(7): 1523-1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(84)90408-3 Pettijohn, F.J., Potter, P.E., 1972. Sand and Sandstone. Springer, New York. Roser, B. P., Korsch, R. J., 1988. Provenance Signatures of Sandstone-Mudstone Suites Determined Using Discriminant Function Analysis of Major-Element Data. Chemical Geology, 67(1-2): 119-139. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(88)90010-1 Roser, B. P., Korsch, R. J., 1999. Geochemical Characterization, Evolution and Source of a Mesozoic Accretionary Wedge: The Torlesse Terrane, New Zealand. Geological Magazine, 136(5): 493-512. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0016756899003003 Song, G.Z., Xu, M., Li, L., et al., 2019. Yanshanian Tectonic Inversion and the Response of Sequence Stratigraphic Patterns in Eastern Yihezhuang Salient, Jiyang Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Earth Science, 44(2): 489-503 (in Chinese with English abstract). Taylor, S.R., McLennan, S.M., 1985. The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. Templ, M., Hron, K., Filzmoser, P., 2011. RobCompositions: An R-Package for Robust Statistical Analysis of Compositional Data. In: Pawlowsku-Glahn, V., Buccianti, A., eds., Compositional Data Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, London. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119976462.ch25 van de Kamp, P. C., Leake, B. E., 1985. Petrography and Geochemistry of Feldspathic and Mafic Sediments of the Northeastern Pacific Margin. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh: Earth Sciences, 76(4): 411-449. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0263593300010646 von Eynatten, H., Critelli, S., Ingersoll, R. V., et al., 2012. Introduction to the Special Issue "Actualistic Models of Sediment Generation". Sedimentary Geology, 280: 1-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.07.020 Wang, C.S., Hu, X.M., 2005. Cretaceous World and Oceanic Red Beds. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(2): 11-21 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200502001.htm Wu, F.Y., Yang, J.H., Liu, X.M., 2005. Geochronological Framework of the Mesozoic Granitic Magmatism in the Liaodong Peninsula, Northeast China. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(3): 305-317 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286695037_Geochronological_framework_of_the_Mesozoic_granitic_magmatism_in_the_Liaodong_Peninsula_Northeast_China Wu, Q.X., Wei, A.J., Wang, Y.C., et al., 2018. Tectonic Difference and Genetic Mechanism of Buried Hill in Southern Bohai Area. Earth Science, 43(10): 3698-3708 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/329983802_Tectonic_Difference_and_Genetic_Mechanism_of_Buried_Hill_in_Southern_Bohai_Area Yi, Z. Y., Liu, Y. Q., Meert, J. G., 2019. A True Polar Wander Trigger for the Great Jurassic East Asian Aridification. Geology, 47(12): 1112-1116. https://doi.org/10.1130/g46641.1 Zhang, F.P., Wu, Z.P., Li, W., et al., 2019. Structural Characteristics and Its Tectonic Evolution of Huanghua Depression during the Indosinian-Yanshanian. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 48(4): 842-857 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGKD201904017.htm Zhang, S. H., Zhao, Y., Song, B., et al., 2007. Carboniferous Granitic Plutons from the Northern Margin of the North China Block: Implications for a Late Palaeozoic Active Continental Margin. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(2): 451-463. https://doi.org/10.1144/0016-76492005-190 Zhu, J. C., Feng, Y. L., Meng, Q. R., et al., 2020. Late Mesozoic Tectonostratigraphic Division and Correlation of the Bohai Bay Basin: Implications for the Yanshanian Orogeny. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 50(1): 28-49 (in Chinese). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/60111X/201911/7100270184.html Zhu, R. X., Xu, Y. G., 2019. The Subduction of the West Pacific Plate and the Destruction of the North China Craton. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 49(9): 1346-1356 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/N072018-00282 董树文, 张岳桥, 陈宣华, 等, 2008. 晚侏罗世东亚多向汇聚构造体系的形成与变形特征. 地球学报, 29(3): 306-317. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.03.005 黄迪颖, 2019. 中国侏罗纪综合地层和时间框架. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49(1): 227-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201901011.htm 李三忠, 索艳慧, 戴黎明, 等, 2010. 渤海湾盆地形成与华北克拉通破坏. 地学前缘, 17(4): 64-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201004009.htm 宋广增, 徐蒙, 李磊, 等, 2019. 济阳坳陷义和庄凸起东部燕山期构造负反转及层序地层样式响应. 地球科学, 44(2): 489-503. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.519 王成善, 胡修棉, 2005. 白垩纪世界与大洋红层. 地学前缘, 12(2): 11-21. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.02.003 吴福元, 杨进辉, 柳小明, 2005. 辽东半岛中生代花岗质岩浆作用的年代学格架. 高校地质学报, 11(3): 305-317. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2005.03.003 吴庆勋, 韦阿娟, 王粤川, 等, 2018. 渤海南部地区潜山构造差异与成因机制. 地球科学, 43(10): 3698-3708. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.578 张飞鹏, 吴智平, 李伟, 等, 2019. 黄骅坳陷印支-燕山期构造特征及其演化过程. 中国矿业大学学报, 48(4): 842-857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201904017.htm 朱吉昌, 冯有良, 孟庆任, 等, 2020. 渤海湾盆地晚中生代构造地层划分及对比: 对燕山运动的启示. 中国科学: 地球科学, 50(1): 28-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK202001002.htm 朱日祥, 徐义刚, 2019. 西太平洋板块俯冲与华北克拉通破坏. 中国科学: 地球科学, 49(9): 1346-1356. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201909003.htm -
 dqkxzx-46-8-2903-附表.xlsx
dqkxzx-46-8-2903-附表.xlsx

-










 下载:
下载: