Genesis of Chambishi Copper Deposit in Copperbelt Province of Zambia: Evidence from Fluid Inclusions and H-O-S Isotope Geochemisty
-
摘要: 为揭示谦比希铜矿床的成矿流体性质、成矿物质来源及其演化特征,对其矿石和脉石矿物展开了流体包裹体和H-O-S同位素地球化学研究.结果显示,热液型脉状矿化石英流体包裹体均一温度变化于100~350 ℃,盐度变化于11%~19%NaCleqv;δDV-SMOW值为-64.0‰~-52.6‰,δ18OH2O值为1.57‰~2.97‰.热液型脉状和沉积型层状铜矿体δ34SCDT值分别变化于5.5‰~12.1‰和6.0‰~21.0‰.分析表明,热液型成矿流体属Cl-Na-Ca型水溶液,属中低密度流体;成矿流体受幔源和壳源岩浆混合,导致铜发生沉淀.沉积型层状矿化硫主要来自成岩硫化物和海水硫酸盐,硫酸盐以热化学还原为主,导致SO42-较彻底的变为H2S.整体看来,谦比希铜矿床热液型脉状矿化与新元古代中期岩浆活动密切相关,沉积型层状矿化主要与新元古代晚期大规模造山运动和区域变质作用有关.Abstract: Fluid inclusions study and H-O-S isotopic geochemical analysis of ore and vein minerals were carried out in this study in order to reveal the characteristics of ore-forming fluid and material of the Chambishi copper deposit. The results of microscopic measurement of temperature show that the homogenization temperature and salinity of the fluid inclusions from hydrothermal fluid filling deposit mainly range from 100 to 350 ℃ and 11% to 19% NaCleqv, respectively. Analyses of H-O isotopic composition of the hydrothermal fluid filling deposit show that the values of δDV-SMOW and δ18OH2O are -64.0‰ to -52.6‰ and 1.57‰ to 2.97‰, respectively. Analyses of S isotopic composition show that the values of δ34SCDT from hydrothermal fluid filling orebodies and depositional orebodies are 5.5‰ to 12.1‰ and 6.0‰ to 21.0‰, respectively. The above data indicate that the ore-forming fluid of the hydrothermal fluid filling deposit is of medium-low temperature, low-middle salinity and density, and belongs to Cl-Na-Ca-type aqueous solution. The fluid is a mix of mantle and crust-derived magmas. Fluid mixing is the main reason for copper precipitation. Sulfur of the hydrothermal fluid filling deposit is similar to those of mantle-derived sulfur, whereas the sulfur of the depositional ore deposit is mainly sourced from diagenetic sulphide and seawater sulfate. The mechanism of sulfate reduction for both deposits is thermochemical reduction which resulted in the change of sulfur from SO42- to H2S. The mixed sources of ore-forming fluid and material indicate that mineralization of the hydrothermal fluid filling deposit is closely related to the middle Neoproterozoic magmatism, whereas mineralization of the depositional ore deposit is mainly related to the strong Late Neoproterozoic orogenesis and regional metamorphism.
-
Key words:
- fluid inclusion /
- H-O-S isotope /
- ore-forming fluid /
- Chambishi copper deposit /
- Zambia /
- ore deposit
-
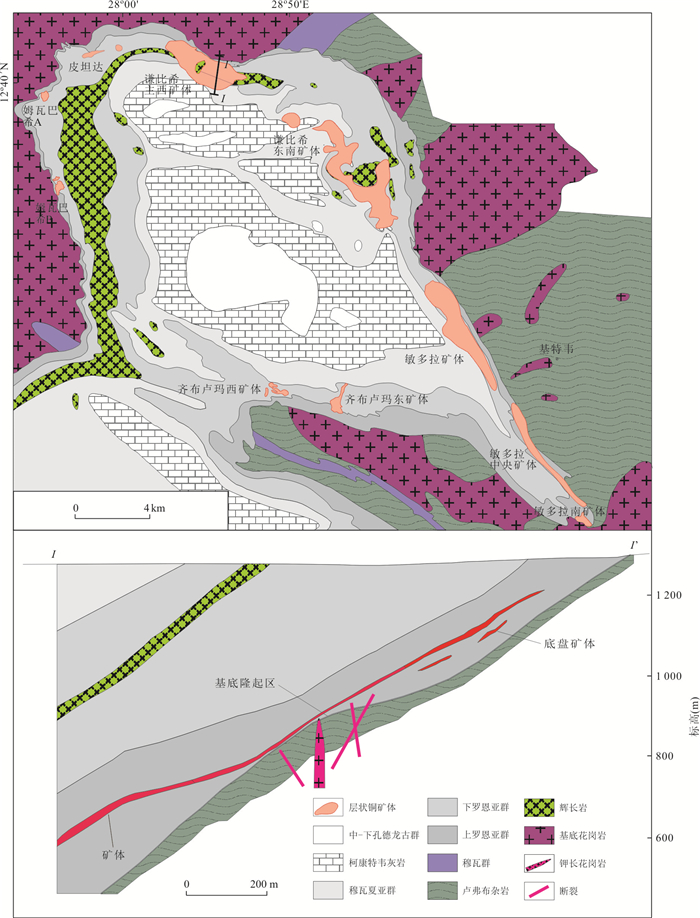
图 1 赞比亚铜带省构造纲要图
Fig. 1. Simplified tectonic map of the copperbelt province, Zambia
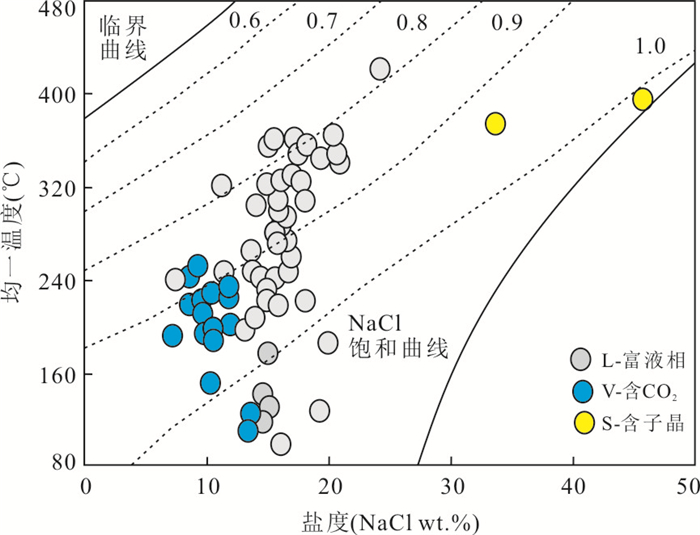
图 8 谦比希铜矿床热液型石英流体包裹体均一温度和盐度关系图
底图据Bodnar(1983)
Fig. 8. Plot of homogenization temperature and salinity of hydrothermal fluid inclusions from the Chambishi copper deposit
图 9 谦比希铜矿床与区带矿床硫同位素数据对比图
Fig. 9. Comparison of sulfur isotope data among the Chambishi copper deposit and other deposits in the region
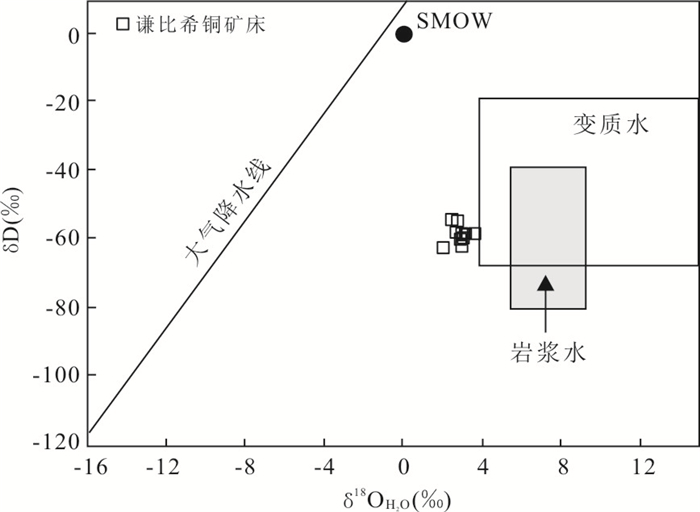
图 10 谦比希铜矿床石英流体包裹体的氢氧关系图
底图据Taylor(1974)
Fig. 10. Plot of δ18OH2O versus δD of fluid inclusions from the Chambishi copper deposit
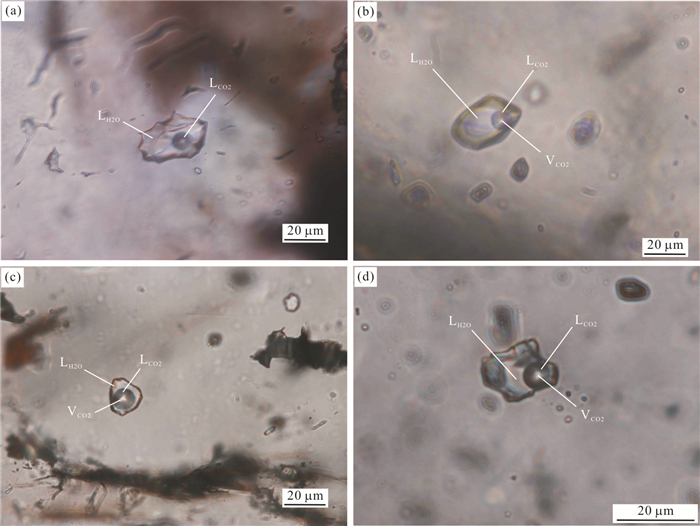
表 1 谦比希铜矿床热液型石英流体包裹体主要类型及特征
Table 1. Major types of hydrothermal fluid inclusions from the Chambishi copper deposit
类型 相态 含量 形态 大小(μm) 主要特征 Ⅰ型 富液相、气液两相原生流体包裹体(LH2O+ LCO2) > 75% 以扁圆状和椭圆状为主,少量呈似六边形负晶或不规则状 10~25 呈孤立状随机分布,或呈群状、带状分布在矿物的生长环带中 Ⅱ型 含CO2三相包裹体(LH2O+LCO2+VCO2) < 10% 以椭圆形为主 10~15 呈孤立状产出,液相CO2相体积约占包裹体总体积的15%~25%.在均一化过程中,部分CO2包裹体发生爆裂 Ⅲ型 含子矿物多相包裹体(S+LH2O+LCO2+VCO2) < 5% 以六边形负晶和椭圆形为主 15 单个包裹体中可见一个子晶,且子晶的种类有石盐、钾盐等.石盐子晶颗粒大,晶形好,呈立方体;钾盐子晶颗粒小,呈浑圆状 注:LH2O代表液体相水;LCO2代表液体相二氧化碳;VCO2代表气体相二氧化碳;S代表子晶矿物. 表 2 谦比希铜矿床热液型石英包裹体氢氧同位素测试结果
Table 2. Hydrogen and oxygen isotopic compositions of hydrothermal fluid inclusions from the Chambishi copper deposit
样品号 矿物 δDV-SMOW(‰) δ18OV-SMOW(‰) δ18OH2O(‰) QES560-01 石英 -52.6 12.0 2.07 QES560-02 石英 -57.7 12.3 2.37 QES680-01 石英 -58.6 12.9 2.97 QES680-02 石英 -53.0 12.4 2.47 ES680C8-1 石英 -63.5 12.6 2.67 ES680C8-2 石英 -60.5 12.5 2.57 QES560-03 石英 -60.0 12.7 2.77 QES560-04 石英 -58.5 12.8 2.87 QES680-03 石英 -58.4 12.6 2.67 QES680-04 石英 -58.6 13.4 3.47 ES680C8-3 石英 -64.0 11.5 1.57 表 3 谦比希铜矿床硫同位素测试结果
Table 3. Sulfur isotopic compositions of chalcopyrite and bornite from the Chambishi copper deposit
样品号 样品描述 测试矿物 δ34SCDT(‰) w232m6-1 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 10.4 w232m6-2-H 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 8.9 w232m6-2-B 层状铜矿体 斑铜矿 8.2 w184m4-1-H 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 7.0 w184m4-1-B 层状铜矿体 斑铜矿 6.8 w184m3-2-H 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 7.3 w184m3-2-B 层状铜矿体 斑铜矿 7.4 w184m4-2 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 7.2 w184m3-2-1 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 6.6 w184m4-h7-B 层状铜矿体 斑铜矿 6.0 se980-9-H 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 19.2 se980-9-B 层状铜矿体 斑铜矿 21.0 se980-16 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 11.5 se980-10-H 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 13.8 se980-10-B 层状铜矿体 斑铜矿 14.1 es98004-4 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 12.3 es98004-5 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 12.1 es98004-3 层状铜矿体 黄铜矿 11.9 w184m4-h7-H 脉状铜‒钼矿体 黄铜矿 6.1 mob-1-H 脉状铜‒钼矿体 黄铜矿 8.4 mob-1-B 脉状铜‒钼矿体 斑铜矿 12.1 mob-2 脉状铜‒钼矿体 黄铜矿 6.1 mob-3-H 脉状铜‒钼矿体 黄铜矿 5.6 mob-3-B 脉状铜‒钼矿体 斑铜矿 5.5 mob-4 脉状铜‒钼矿体 黄铜矿 5.7 -
Armstrong, R. A., Master, S., Robb, L. J., 2005. Geochronology of the Nchanga Granite, and Constraints on the Maximum Age of the Katanga Supergroup, Zambian Copperbelt. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 42: 32-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2005.08.012 Armstrong, R. A., Robb, L. J., Masters, S., et al., 1999. New U-Pb Age Constraints on the Katangan Sequence, Central African Copperbelt. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 28 (4A): 6-7. Bodnar, R. J., 1983. A Method of Calculating Fluid Inclusion Volumes Based on Vapor Bubble Diameters and PVTX Properties of Inclusion Fluids. Economic Geology, 78: 535-542. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.78.3.535 Cailteux, J., Binda, P. L., Katekesha, W. M., et al., 1994. Lithostratigraphical Correlation of the Neoproterozoic Roan Supergroup from Shaba (Zaire) and Zambia, in the Central African Copper-Cobalt Metallogenic Province. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 19: 265-278. doi: 10.1016/0899-5362(94)90014-0 Chaussidon, M., Albarède, F., Sheppard, S. M. F., 1989. Sulphur Isotope Variations in the Mantle from Ion Microprobe Analyses of Micro-Sulphide Inclusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 92(2): 144-156. doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(89)90042-3 Clayton, R. N., O'Neil, J. R., Mayeda, T. K., 1972. Oxygen Isotope Exchange between Quartz and Water. Journal of Geophysical Research, 77: 3057-3067. doi: 10.1029/JB077i017p03057 Fang, K., Hu, Q.F., Li, M.J., et al., 2019. Characteristics of Molybdenum Mineralization in the Southeast Orebody of Chambishi Copper Deposit in Copperbelt Province of Zambia. Mineral Resources and Geology, 33(6): 987-994 (in Chinese with English abstract). Freeman, P. V., 1988. Description of Mineral Deposits on the Copperbelt. Zambia Consolidated Copper Mines Ltd., Unpublished Company Report, Lukasa, 1095. Greyling, L.N., Robb, L.J., Master, S., et al., 2005. The Nature of Early Basinal Fluids in the Zambian Copperbelt: A Case Study from the Chambishi Deposit. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 42(1): 159-172. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1464343X05000932 Guo, W, Lin, X, Hu, S.H., 2020. Advances in LA-ICP-MS Analysis for Individual Fluid Inclusions and Applications. Earth Sicence, 45(4): 1362-1374 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hitzman, M., Kirkham, R., Broughton, D., et al., 2005. The Sediment-Hosted Stratiform Copper Ore System. Economic Geology, 100: 609-642. Hoefs, J., 1997. Stable Isotope Geochemistry. Springer, Berlin, 1-281. Kampunzu, A.B., Cailteux, J., 1999. Tectonic Evolution of the Lufilian Arc (Central Africa Copperbelt) during Neoproterozoic Pan African Orogenesis. Gondwana Research, 2: 401-421. doi: 10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70279-3 Kampunzu, A. B., Cailteux, J. L. H., Kamona, A. F., et al., 2009. Sediment-Hosted Zn-Pb-Cu Deposits in the Central African Copperbelt. Ore Geology Reviews, 35(3-4): 263-297. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2009.02.003 Key, R. M., Liyugu, A. K., Njamu, F. M., 2001. The Western Arm of the Lufilian are in NW Zambia and Its Potential for Copper Mineralization. Journal of Africa Earth Science, 33: 503-528. doi: 10.1016/S0899-5362(01)00098-7 Li, X.Q., Mao, J.W., Yan, Y.L., et al., 2009. Regional Geology and Characteristics of Ore Deposits in Katangan Copper-Cobalt Belt within Congo (Kinshasa), Central Africa. Mineral Deposits, 28(3): 366-380 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, B., Duan, G.X., 1987. The Density and Isochoric Formulae for NaCl-H2O Fluid Inclusions (Salinity 25 wt%) and Their Applications. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 7(4): 345-352 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, J.C., 2016. Geological Characteristics and Genesis Discussion of Chambishi Copper Deposits in Copperbelt Province, Zambia (Dissertaiton). Guilin University of Technology, Guilin (in Chinese with English abstract). Lu, H.Z., Fan, H.R., Ni, P., et al., 2004. Fluid Inclusion. Science Press, Beijing, 1-487 (in Chinese). Machel, H.G., 2001. Bacterial and Thermochemical Sulfate Reduction in Diagenetic Settings: Old and New Insights. Sedimentary Geology, 140: 143-175. doi: 10.1016/S0037-0738(00)00176-7 Meshoulam, A., Ellis, G.S., Said Ahmad, et al., 2016. Study of Thermochemical Sulfate Reduction Mechanism Using Compound Specific Sulfur Isotope Analysis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 188: 73-92. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.05.026 Mo, X.X., 2019. Magmatism and Deep Geological Process. Earth Sicence, 44(5): 1487-1493 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201905007.htm Ohmoto, H., Rye, R. O., 1979. Isotopes of Sulfur and Carbon. In: Geochemistry of Hydrothermal Ore Deposits. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 509-567. Polya, D. A., Foxford, K. A., Stuart, F., et al. 2000. Evolution and Paragenetic Context of Low Delta D Hydrothermal Fluids from the Panasqueira W-Sn Deposit, Portugal: New Evidence from Microthermometric, Stable Isotope, Noble Gas and Halogen Analyses of Primary Fluid Inclusions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64: 3357-3371. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(00)00459-2 Qin, P., Hao, B., Fang, K., et al., 2019. The Geological Significance for Re-Os Isotopic Dating of Cu-Mo Ore in the Lower Footwall of Chambishi Copper Deposit within Copperbelt Province of Zambia. Mineral Resources and Geology, 33(3): 377-384 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-KCYD201903002.htm Rainaud, C., Master, S., Armstrong, R.A., et al., 2005. Geochronology and Nature of the Palaeoproterozoic Basement in the Central African Copperbelt (Zambia and the Democratic Republic of Congo), with Regional Implications. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 42: 1-31. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1464343X0500097X Ren, J.P., Wang, J., Zhang, D.H., et al., 2018. Reactivation of Lufilian Arc in Zambia: Zircon and Apatite Fission Track Chronology. Earth Sicence, 43(6): 1850-1860 (in Chinese with English abstract). Roedder, E., 1976. Fluid Inclusion Evidence on the Genesis of Ores in Sedimentary and Volcanic Rocks. Hand Book of Stratabound and Stratiform Ore Deposits, 3(1): 67-110. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444414021500072 Rye, R. O., Ohmoto, H., 1974. Sulfur and Carbon Isotopes and Ore Genesis: A Review. Economic Geology, 69(6): 826-842. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.826 Selley, D., Broughton, D., Scott, R., et al., 2005. A New Look at the Geology of the Zambian Copperbelt. In: Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume. Society of Economic Geology, Littleton, 965-1000. Taylor, H. P., 1974. The Application of Oxygen and Hydrogen Isotope Studies to Problems of Hydrothermal Alteration and Ore Deposition. Economic Geology, 69(6): 843-883. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.69.6.843 Truche, L., Bazarkina, E.F., Barré, G., et al., 2014. The Role of S3- Ion in Thermochemical Sulphate Reduction: Geological and Geochemical Implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 396: 190-200. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.04.018 Wagner, T., Mlynarczyk, M. S. J., Williams-Jones, A. E., et al., 2009. Stable Isotope Constraints on Ore Formation at the San Rafael Tin-Copper Deposit, Southeast Peru. Economic Geology, 104(2): 223-248. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.104.2.223 Wei, Y.B., Liu, X.C., 2012. Geological Characteristics and Prospecting Potential of Kalulushi Copper Deposits in Copperbelt Province, Zambia. Journal of East China Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 35(4): 364-370 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HDDZ201204012.htm Yan, P., Liu, W.C., 2006. Mineralization Characteristics and Genesis of Chambishi Copper Deposit in Zambia. China Mine Engineering, 35(1): 1-4, 8 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yuan, S.D., Chou, I.M., Burruss, R.C., et al., 2013. Disproportionation and Thermochemical Sulfate Reduction Reactions in S-H2O-CH4 and S-D2O-CH4 Systems from 200 to 340 ℃ at Elevated Pressures. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 118: 263-275. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2013.05.021 Zhang, D.H., 1992. Aqueous Phase Composition Characteristics of Mineral Fluid Inclusion and Its Signification in Ore Genesis. Earth Science, 12(6): 49-55 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=721142 Zhao, X.G., 2010. Geological Characteristics of Chambishi Copper Deposit in Zambia. Geology and Exploration, 46(1): 183-190 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201001027.htm Zheng, Y.F., Xu, B.L., Zhou, G.T., 2000. Geochemistry of Stable Isotopes of Minerals. Earth Science Frontiers, 7(2): 299-320 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, H.B., Zhang, D.H., Xiao, B., et al., 2016. Geological Characteristics and Genesis of Chambishi Copper Deposit in Copperbelt of Zambia. Mineral Resources and Geology, 30(1): 19-23, 28 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=KCYD201601003&dbcode=CJFD&year=2016&dflag=pdfdown 方科, 胡乔帆, 李明君, 等, 2019. 赞比亚铜带省谦比希铜矿床东南矿区钼矿化特征. 矿产与地质, 33(6): 987-994. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2019.06.007 郭伟, 林贤, 胡圣虹, 2020. 单个流体包裹体LA-ICP-MS分析及应用进展. 地球科学, 45(4): 1362-1374. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.199 李向前, 毛景文, 闫艳玲, 等, 2009. 中非刚果(金)加丹加铜钴矿带主要矿化类型及特征. 矿床地质, 28(3): 366-380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.03.012 刘斌, 段光贤, 1987. NaCl-H2O溶液包裹体的密度式和等容式及其应用. 矿物学报, 7(4): 345-352. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.1987.04.010 刘俊辰, 2016. 赞比亚铜带省谦比希铜矿地质特征和成因探讨(硕士学位论文). 桂林: 桂林理工大学. 卢焕章, 范宏瑞, 倪培, 等, 2004. 流体包裹体. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-487. 莫宣学, 2019. 岩浆作用与地球深部过程. 地球科学, 44(5): 1487-1493. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.972 覃鹏, 郝波, 方科, 等, 2019. 赞比亚铜带省谦比希铜矿床下盘铜钼矿化Re-Os年龄测定及地质意义. 矿产与地质, 33(3): 377-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201903002.htm 任军平, 王杰, 张东红, 等, 2018. 赞比亚卢弗里安弧构造带再活化的证据: 锆石和磷灰石裂变径迹年代学. 地球科学, 43(6): 1850-1860. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.610 魏元泵, 刘湘成, 2012. 赞比亚铜带省卡卢鲁西铜矿区地质特征及找矿前景探讨. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 35(4): 364-370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2012.04.010 颜平, 刘文成, 2006. 赞比亚谦比西铜矿矿床特征及成因. 中国矿山工程, 35(1): 1-4, 8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-609X.2006.01.002 张德会, 1992. 矿物流体包裹体液相成分特征及其矿床成因意义. 地球科学, 17(6): 677-688. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX199206006.htm 赵兴国, 2010. 赞比亚谦比希铜矿床地质特征. 地质与勘探, 46(1): 183-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201001027.htm 郑永飞, 徐宝龙, 周根陶, 2000. 矿物稳定同位素地球化学研究. 地学前缘, 7(2): 299-320. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2000.02.001 朱海宾, 张东红, 肖波, 等, 2016. 赞比亚铜带省谦比希铜矿地质及矿床成因研究. 矿产与地质, 30(1): 19-23, 28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2016.01.004 -
 dqkxzx-46-5-1554-附表1.pdf
dqkxzx-46-5-1554-附表1.pdf

-










 下载:
下载: