Thickening Mechanism and Reservoir Formation Model of Bozhong 29-6 Oilfield in Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin
-
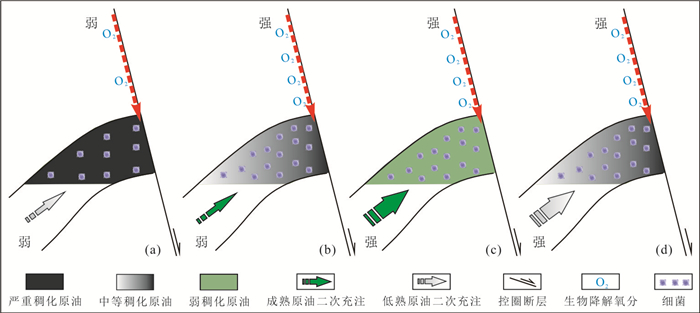
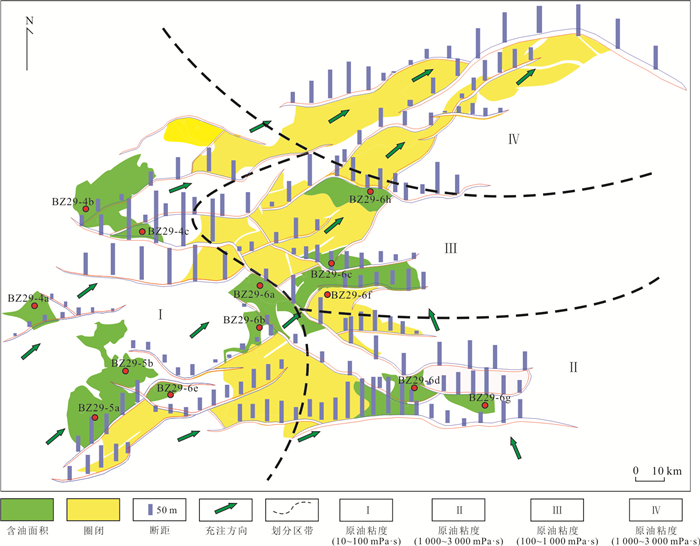
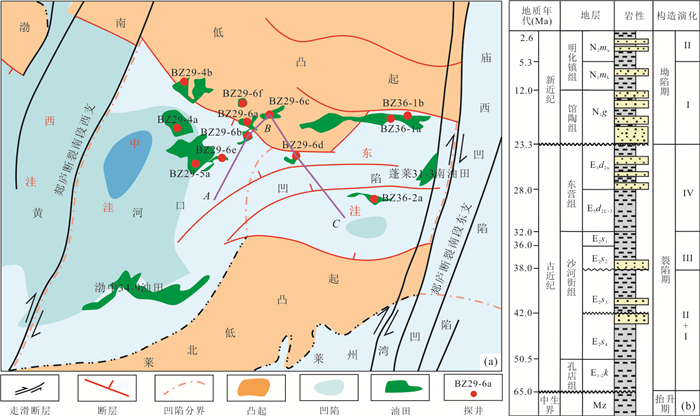
摘要: 渤中29-6油田位于黄河口凹陷北部陡坡带,具有双洼供烃的有利位置,已发现原油整体表现为稠油特征,生标特征复杂多样,其油气来源及稠油成因机理尚不明确.在前人研究基础之上,基于原油分析化验数据,利用地球化学分析方法,系统梳理了渤中29-6油田稠油来源,阐明了该原油稠化机理,并建立了原油的稠化模式及成藏模式,结果表明:(1)渤中29-6油田表现为双洼混合供烃的特征,其中高硫油主要来源于黄河口东洼,而低硫油主要来源于黄河口中洼;(2)渤中29-6油田整体表现为浅层稠油,其原油物性受二次充注作用、断层活动性、母源条件这3个因素的联合控制,其中断层活动性控制整体原油稠化级别,二次充注作用和母源条件分别可以改善和加剧原油稠化作用,并形成了低熟—弱断弱充注、成熟—强断弱充注、成熟—强断强充注、低熟—强断强充注这4种原油稠化模式;(3)渤中29-6油田具有双洼供烃成藏模式,且因距离洼陷远近而不同,近源形成单洼供烃—断裂垂向输导—强/弱充注—强降解—源上稠油成藏模式,远源形成双洼供烃—砂体或不整合侧向输导—弱充注—强/弱降解稠油成藏模式;(4)渤中29-6油田围区可划分为4个区带:I区原油物性最好,II区和IV区稠化最严重,物性最差,III区原油物性居中.由于二次充注作用可以明显改善原油物性,中—轻原油勘探和开发应优选I区和III区.Abstract: Bozhong 29-6 oilfield is located in the northern steep slope zone of Huanghekou sag, which has a favorable position for hydrocarbon supply from double depressions. It has been found that the crude oil is characterized by thickened oil as a whole, and the characteristics of biomarkers are complex and diverse, and the source of oil-gas and the genetic mechanism of thickened oil are not clear. Based on previous studies and crude oil analysis, by using geochemical analysis method, the source and thickening mechanism of heavy oil in Bozhong 29-6 oilfield are clarified, and the thickening model and reservoiring model are established. The results show that (1) Bozhong 29-6 oilfield has the characteristics of double-depression mixed hydrocarbon supply. The high sulfur-oil mainly derives from the eastern depression of the Huanghekou sag, while the low sulfur-oil mainly derives from the middle depression of the Huanghekou sag; (2) Bozhong 29-6 oilfield group is of shallow heavy oil, and its crude oil properties are controlled by the combination of three factors, namely, secondary filling, fault activity and parent source characteristics. The properties of crude oil are controlled by the combination of three factors which are secondary charge, fault activity and maternal characteristics. Based on three factors, four oil thickening modes are identified, including immature-weak faulting-weak secondary charge, mature-strong faulting-weak secondary charge, mature-strong faulting-strong secondary charge, immature-strong faulting-strong secondary charge. (3) Bozhong 29-6 oilfield has double depression hydrocarbon supply and accumulation mode, which varies with the distance to the sag. Single depression hydrocarbon supply vertical transportation fault strong filling strong degradation heavy oil reservoir forming mode is formed near source, and double depression hydrocarbon supply sand body or unconformity lateral transportation weak filling strong/weak degradation heavy oil accumulation mode is formed at far source; the hydrocarbon supply from single depression near the source, vertical transportation of fault, strong/weak filling, strong degradation, and heavy oil accumulation mode above the source are formed, and the hydrocarbon supply sand body in double depression or unconformity lateral transportation weak filling strong/weak degradation heavy oil accumulation mode is formed in the far source. (4) The surrounding areas of Bozhong 29-6 oilfield can be divided into four zones: zone I has the best physical properties of crude oil, zone II and IV have the most severe thickening and the worst physical properties, and the crude oil in zone III is in the middle. Because the secondary filling can obviously improve the physical properties of crude oil, the exploration and development of medium light crude oil should select area I and area III.
-
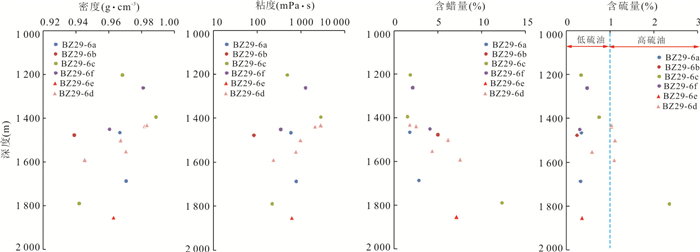
表 1 黄河口中洼和东洼地区油田断层活动性及原油地球化学参数
Table 1. Fault activity and crude oil geochemical parameters in Zhongwa and Dongwa areas of the Yellow River depression
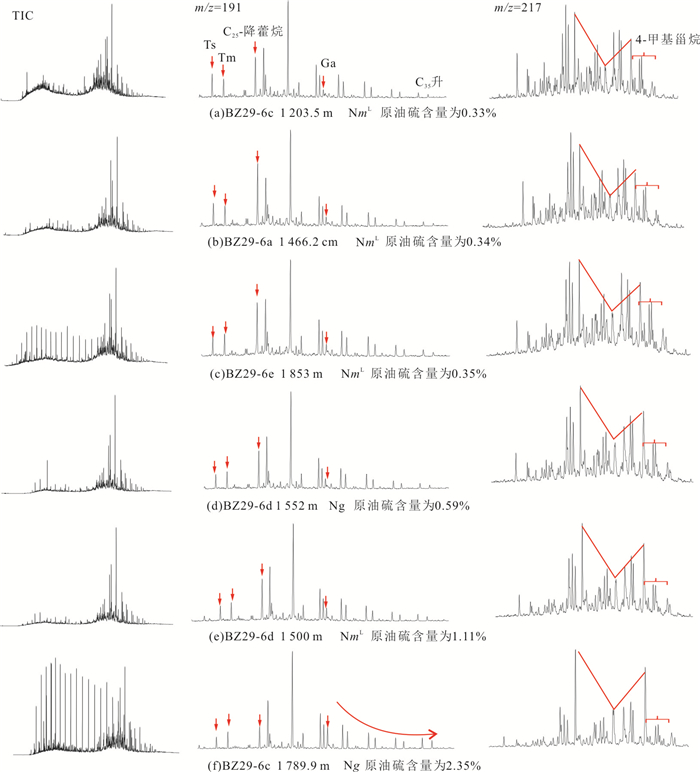
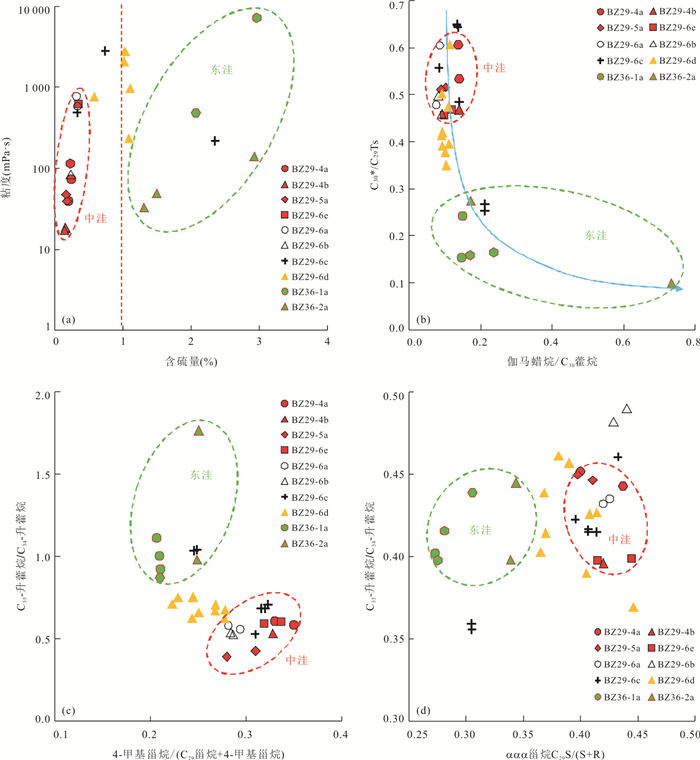
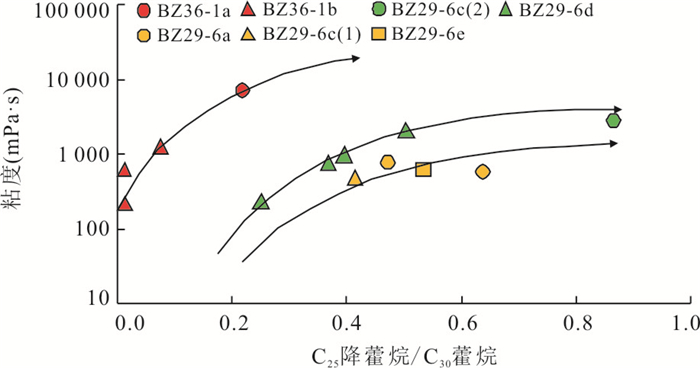
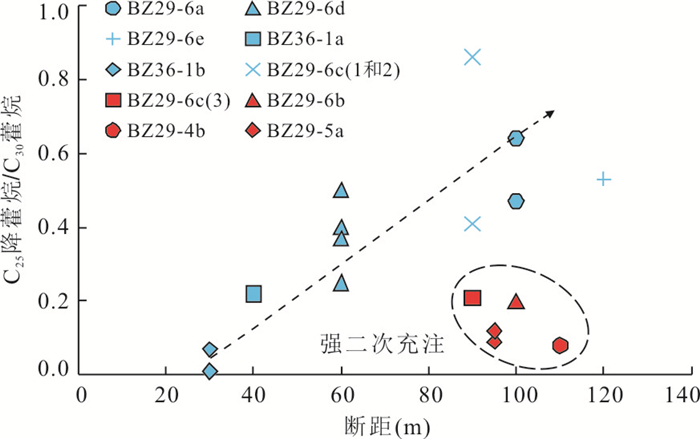
井号 序号 平均深度(m) 层位 断距(m) 粘度(mPa·s) 含硫量(%) C25降藿烷/C30藿烷 (Pr+Ph)/ C30藿烷 BZ29-6a 1 1 466.2 NmL 100 585.2 0.34 064 0.11 2 1 687.4 Ng 100 776.5 0.32 0.47 0.06 BZ29-6b 1 1 477.5 NmL 100 84.0 0.24 0.20 2.36 BZ29-6c 1 1 203.5 NmL 90 486.4 0.33 0.41 0.17 2 1 395.0 NmL 90 2 823.0 0.74 0.86 0.38 3 1 789.9 Ng 90 219.2 2.35 0.21 3.07 BZ29-6d 1 1 436.8 NmL 60 2 088.0 1.02 0.50 0.22 2 1 500.0 NmL 60 969.3 1.11 0.40 0.26 3 1 552.0 Ng 60 763.5 0.59 0.37 0.24 4 1 590.0 Ng 60 234.2 1.09 0.25 0.33 BZ29-6e 1 1 853.0 NmL 120 617.2 0.35 0.53 0.52 BZ29-5a 1 1 413.5 NmL 95 39.4 0.19 0.12 2.88 2 1 391.5 NmL 95 47.8 0.17 0.09 2.88 BZ29-4b 1 1 435.5 NmL 110 18.1 0.16 0.08 7.27 BZ36-1a 1 1 298.4 NmL 40 7 193.0 2.96 0.22 0.06 BZ36-1b 1 1 412.4 NmL 30 1 259.0 3.56 0.07 0.50 2 1 549.3 Ng 30 221.4 2.90 0.01 0.70 3 1 560.7 Ng 30 624.6 3.00 0.01 0.88 -
Aitken, C. M., Jones, D. M., Larter, S. R., 2004. Anaerobic Hydrocarbon Biodegradation in Deep Subsurface Oil Reservoirs. Nature, 431(7006): 291-294. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02922. Connan, J., 1984. Biodegradation of Crude Oils in Reservoirs. In: Brooks, J., Welte, D., Advances in Petroleum Geochemistry. Academic Press, London. Dusseault, M. B., 2001. Comparing Venezuelan and Canadian Heavy Oil and Tar Sands. Canadian International Petroleum Conference, Calgary. Feng, Z. H., Liao, G. Z., Fang, W., et al., 2003. Formation of Heavy Oil and Correlation of Oil-Source in the Western Slope of the Northern Songliao Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 30(4): 25-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/283815064_Formation_of_heavy_oil_and_correlation_of_oil-source_in_the_western_slope_of_the_northern_Songliao_Basin Fu, Q., Liu, B. B., Xia, Q. L., et al., 2013a. Characteristics and Migration-Accumulation Directions of Sulfur-Rich Oils in BZ35/36 Structures in Huanghekou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(1): 37-46 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/286850375_Characteristics_and_migration-accumulation_directions_of_sulfur-rich_oils_in_BZ3536_structures_in_Huanghekou_sag_Bohai_Bay_Basin Fu, Q., Liu, B. B., Xu, C. H., et al., 2013b. The Couple Relationship of Quantitative Analysis of the Structures and Oil & Gas Accumulation in Huanghekou Depression, Bohai Bay Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(S2): 112-119 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2013S2014.htm Guo, Y. H., Zhou, X. H., Li, J. P., et al., 2010. Crude Features and Origins of the Neogene Heavy Oil Reservoirs in the Bohai Bay. Oil & Gas Geology, 31(3): 375-380, 385 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hu, S. Z., Zhang, D. M., Tang, J., et al., 2009. Review of the Genesis of Heavy Oil. Geological Science and Technology Information, 28(2): 94-97 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZKQ200902016.htm Huang, H. P., Larter, S. R., Bowler, B. F. J., et al., 2004. A Dynamic Biodegradation Model Suggested by Petroleum Compositional Gradients within Reservoir Columns from the Liaohe Basin, NE China. Organic Geochemistry, 35(3): 299-316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2003.11.003 Jiang, X., Wu, K. Q., Liu, L. F., et al., 2018. Characteristics of Hydrocarbon Source Rock in Huanghekou Sag and Its Distribution in Sequence Stratigraphic Framework. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 48(5): 709-717 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XBDZ201805013.htm Kong, Q. Y., Zou, H. Y., Hu, Y. F., et al., 2009. Geochemical Characteristics of Paleogene Hydrocarbon Source Rock in Huanghekou Sag. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition), 24(2): 5-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XASY200902003.htm Larter, S., Huang, H. P., Adams, J., et al., 2006. The Controls on the Composition of Biodegraded Oils in the Deep Subsurface: Part II-Geological Controls on Subsurface Biodegradation Fluxes and Constraints on Reservoir-Fluid Property Prediction. AAPG Bulletin, 90(6): 921-938. https://doi.org/10.1306/01270605130 Li, C. M., Li, S. M., Li, X., et al., 2005. Origin of the Heavy Oils from the Bamianhe Oilfield, Dongying Depression. Geoscience, 19(2): 279-286 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ20050200H.htm Li, S. M., Pang, X. Q., Gao, X. Z., et al., 2008. Genetic Mechanism of Heavy Oil in Western Depression of Liaohe River. Science in China (Series D), 38(S1): 138-149 (in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JDXG2008S2018.htm Li, Z. Y., Qiao, M., Ren, W. P., 2012. Current Development of Venezuela Extra Heavy Crude and Canadian Oil Sands Processing. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section), 28(3): 517-524 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/296561912_Current_development_of_Venezuela_extra_heavy_crude_and_Canadian_oil_sands_processing Ni, C. H., Bao, J. P., Wang, P. H., et al., 2005. Novel Progress on Source Correlation of Biodegradation Crude Oil. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 26(6): 711-714 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JHSX2005S5013.htm Niu, J., Huang, H. P., Jiang, W. L., et al., 2016. Factors such as Multi-Stage Charge Mixing and Biodegradation Affecting the Viscosity of Heavy Oil in the Le'an Oilfield. Geochimica, 45(5): 441-450 (in Chinese with English abstract). Peter, K. E., Walters, C. C., Moldowan, J. M., 2005. The Biomarker Guide. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. Qiu, G. Q., Li, S. M., Pang, X. Q., et al., 2004. Characteristics and Genetic Mechanisms of Heavy Oils on the North Steep Slope of the Dongying Depression in the Bohai Bay Basin, East China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 78(6): 854-862 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://epub.cnki.net/grid2008/docdown/docdownload.aspx?filename=DZXE200406017&dbcode=CJFD&year=2004&dflag=pdfdown Rubinstein, I., Stuause, O. P., Spycherelle, C., et al., 1977. The Origin of the Oil Sand Bitumens of Alberta: A Chemical and a Microbiological Simulation Study. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 41(9): 1341-1353. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(77)90077-1 Shang, P., Chen, H. H., Hu, S. Z., et al., 2020. Geochemical Characteristics of Crude Oil and Hydrocarbon Accumulation in the Ordovician of Yuqixi Area, Tarim Basin. Earth Science, 45(3): 1013-1026 (in Chinese with English abstract). Song, C. Y., 2006. Type and Formation Way of Severe Biodegradation Oil in Jiyang Depression. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 13(4): 15-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS200604006.htm Sun, H. F., Zhou, X. H., Peng, W. X., et al., 2011. Late-Stage Hydrocarbon Accumulation and Enrichment in the Huanghekou Sag, Southern Bahai Sea. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 38(3): 307-313 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/279964932_Late-stage_hydrocarbon_accumulation_and_enrichment_in_the_Huanghekou_Sag_southern_Bohai_Sea Tang, G. M., Wang, F. L., Wang, Q. B., et al., 2019. Genesis and Accumulation Models of Sulfur-Rich Heavy Oil in Laizhou Bay Sag, Bohai Sea. Oil & Gas Geology, 40(2): 284-293 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYYT201902008.htm Wang, B. J., Xu, C. G., Wu, K., et al., 2019. The Neogene Extra-Super Heavy Oil Reservoir Characteristics and Formation Mechanism in Liaodong Bay Depression. Earth Science, 44(9): 3088-3100 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201909023.htm Wenger, L. M., Isaksen, G. H., 2002. Control of Hydrocarbon Seepage Intensity on Level of Biodegradation in Sea Bottom Sediments. Organic Geochemistry, 33(12): 1277-1292. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-6380(02)00116-X Wu, K. Q., Jiang, X., Sun, H. F., 2015. Model of Lacustrine Source Rocks in Offshore Oil Kitchen Sags: A Case Study of Paleogene in Huanghekou Sag. Geological Science and Technology Information, 34(2): 63-70 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, K. Q., Wu, J. F., Liu, L. F., et al., 2014. Tectonic Transport and Its Impact on Hydrocarbon Accumulation: Two Cases of Bodong and Miaoxi Sag. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 26(2): 6-11 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZHSD201402002.htm Xu, C. G., Wang, B. J., Wang, F. L., et al., 2016. Neogene Extra Heavy Oil Accumulation Model and Process in Liaodong Bay Depression: A Case Study of Lvda 5-2N Oilfield. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(5): 599-609 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://search.cnki.net/down/default.aspx?filename=SYXB201605004&dbcode=CJFD&year=2016&dflag=pdfdown Xu, T., Hou, D. J., Zhao, Z. B., et al., 2017. Controlling Factors for the Development of High-Quality Source Rocks in Yellow River Mouth East Sag of Bohai Bay Basin. Journal of Northeast Petroleum University, 41(1): 11-20, 32 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQSY201701002.htm Yang, H.F., Wang, D.Y., Gao, Y.F., et al., 2019. Neogene Natural Gas Genesis and Hydrocarbon Differential Enrichment Mechanism in the Basin Marginal Sag of Bohai Bay Basin: A Case Study of the Eastern Subsag of Huanghekou Sag. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(5): 509-518 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-SYXB201905001.htm Zhu, F. B., Xiao, L. L., Tang, X. Y., 2004. Heavy Oil Genetic Types and Oil-Source Correlation in Western Depression, Liaohe Basin. Geological Science and Technology Information, 23(4): 55-58 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200404012.htm 冯子辉, 廖广志, 方伟, 等, 2003. 松辽盆地北部西斜坡区稠油成因与油源关系. 石油勘探与开发, 30(4): 25-28. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2003.04.008 傅强, 刘彬彬, 夏庆龙, 等, 2013a. 黄河口凹陷BZ35/36构造高硫原油特征及运聚方向. 石油学报, 34(1): 37-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201301004.htm 傅强, 刘彬彬, 徐春华, 等, 2013b. 渤海湾盆地黄河口凹陷构造定量分析与油气富集耦合关系. 石油学报, 34(S2): 112-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2013S2014.htm 郭永华, 周心怀, 李建平, 等, 2010. 渤海海域新近系稠油油藏原油特征及形成机制. 石油与天然气地质, 31(3): 375-380, 385. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201003020.htm 胡守志, 张冬梅, 唐静, 等, 2009. 稠油成因研究综述. 地质科技情报, 28(2): 94-97. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.02.017 姜雪, 吴克强, 刘丽芳, 等, 2018. 黄河口凹陷烃源岩特征及其在层序地层格架中的分布. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 48(5): 709-717. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201805013.htm 孔庆莹, 邹华耀, 胡艳飞, 等, 2009. 黄河口凹陷古近系烃源岩的地球化学特征. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 24(2): 5-8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-064X.2009.02.002 李春梅, 李素梅, 李雪, 等, 2005. 山东东营凹陷八面河油田稠油成因分析. 现代地质, 19(2): 279-286. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2005.02.018 李素梅, 庞雄奇, 高先志, 等, 2008. 辽河西部凹陷稠油成因机制. 中国科学(D辑), 38(S1): 138-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK2008S1017.htm 李振宇, 乔明, 任文坡, 2012. 委内瑞拉超重原油和加拿大油砂沥青加工利用现状. 石油学报(石油加工), 28(3): 517-524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8719.2012.03.027 倪春华, 包建平, 王鹏辉, 等, 2005. 生物降解原油的油源对比研究新进展. 新疆石油地质, 26(6): 711-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3873.2005.06.033 牛君, 黄海平, 蒋文龙, 等, 2016. 乐安油田多期充注及生物降解作用对稠油黏度的影响分析. 地球化学, 45(5): 441-450. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2016.05.001 邱桂强, 李素梅, 庞雄奇, 等, 2004. 东营凹陷北部陡坡带稠油地球化学特征与成因. 地质学报, 78(6): 854-862. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2004.06.017 尚培, 陈红汉, 胡守志, 等, 2020. 塔里木盆地于奇西地区奥陶系原油特征及油气充注过程. 地球科学, 45(3): 1013-1026. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.046 宋长玉, 2006. 济阳坳陷严重生物降解油的类型与形成途径. 油气地质与采收率, 13(4): 15-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2006.04.005 孙和风, 周心怀, 彭文绪, 等, 2011. 渤海南部黄河口凹陷晚期成藏特征及富集模式. 石油勘探与开发, 38(3): 307-313. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201103012.htm 汤国民, 王飞龙, 王清斌, 等, 2019. 渤海海域莱州湾凹陷高硫稠油成因及其成藏模式. 石油与天然气地质, 40(2): 284-293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201902008.htm 王冰洁, 徐长贵, 吴奎, 等, 2019. 辽东湾坳陷新近系特-超稠油油藏特征及形成机理. 地球科学, 44(9): 3088-3100. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.186 吴克强, 姜雪, 孙和风, 2015. 近海富生油凹陷湖相烃源岩发育模式: 以黄河口凹陷古近系为例. 地质科技情报, 34(2): 63-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502010.htm 吴克强, 吴景富, 刘丽芳, 等, 2014. 构造迁移及其对油气成藏的影响: 以渤海渤东、庙西凹陷为例. 中国海上油气, 26(2): 6-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201402002.htm 徐长贵, 王冰洁, 王飞龙, 等, 2016. 辽东湾坳陷新近系特稠油成藏模式与成藏过程: 以旅大5-2北油田为例. 石油学报, 37(5): 599-609. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201605004.htm 许婷, 侯读杰, 赵子斌, 等, 2017. 渤海湾盆地黄河口东洼优质烃源岩发育控制因素. 东北石油大学学报, 41(1): 11-20, 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4107.2017.01.002 杨海风, 王德英, 高雁飞, 等, 2019. 渤海湾盆地盆缘洼陷新近系天然气成因与油气差异富集机理: 以黄河口凹陷东洼为例. 石油学报, 40(5): 509-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201905001.htm 朱芳冰, 肖伶俐, 唐小云, 2004. 辽河盆地西部凹陷稠油成因类型及其油源分析. 地质科技情报, 23(4): 55-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2004.04.012 -









 下载:
下载: