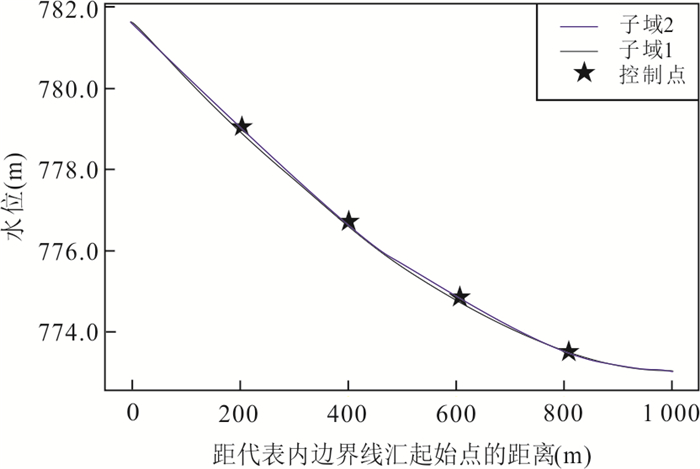
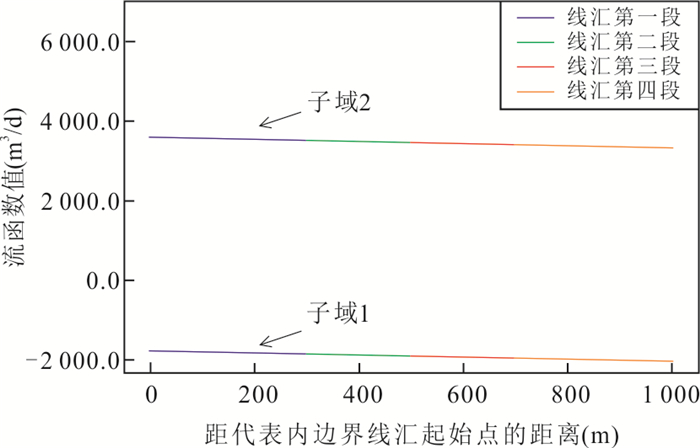
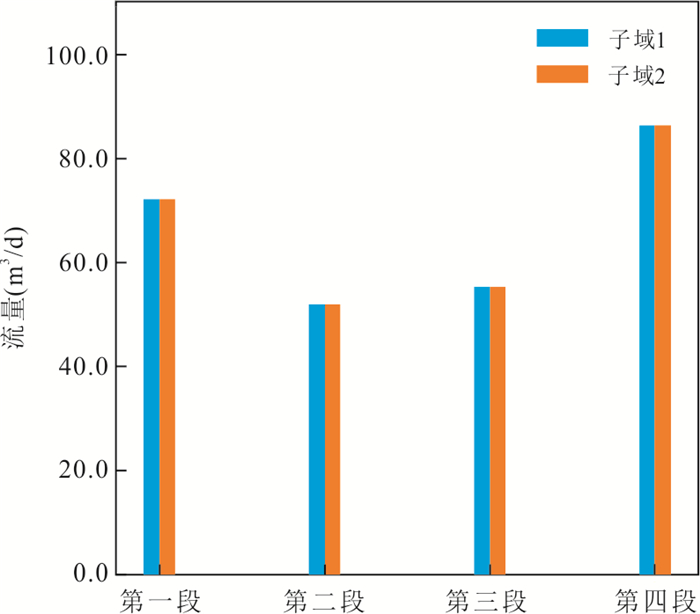
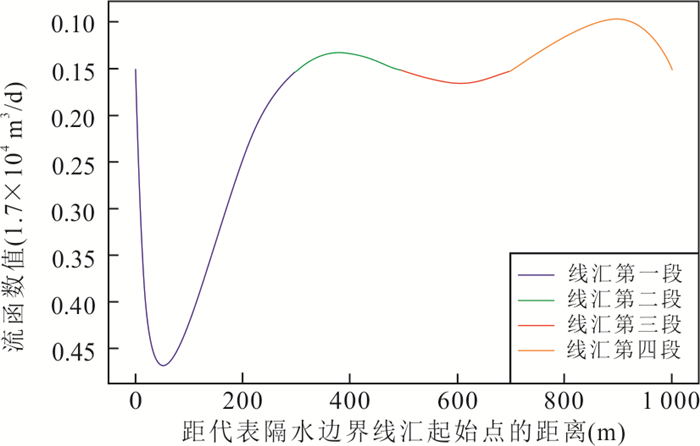
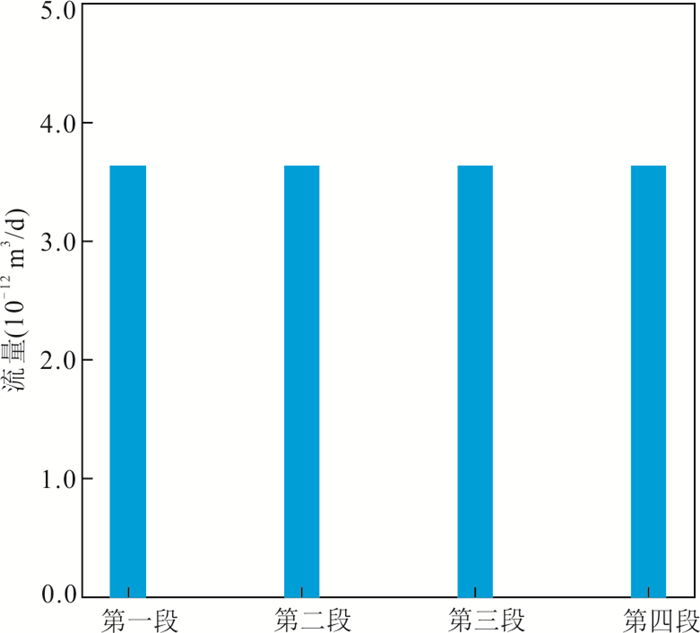
|
Bakker, M., 2014. Python Scripting: The Return to Programming. Groundwater, 52(6): 821-822. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12269 |
|
Bakker, M., 2019. Data-Sharing Requires Script-Sharing. Groundwater, 57(2): 187. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12852 |
|
Bakker, M., Kelson, V. A., 2009. Writing Analytic Element Programs in Python. Groundwater, 47(6): 828-834. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2009.00583.x |
|
Chen, C.X., Tang, Z.H., Hu, L.T., 2014. Theoretical Method and Model Design of Groundwater Flow Numerical Simulation. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). |
|
Fienen, M. N., Bakker, M., 2016. HESS Opinions: Repeatable Research: What Hydrologists can Learn from the Duke Cancer Research Scandal. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 20(9): 3739-3743. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-3739-2016 |
|
Fitts, C. R., 1997. Analytic Modeling of Impermeable and Resistant Barriers. Groundwater, 35(2): 312-317. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1997.tb00088.x |
|
Fitts, C. R., 2010. Modeling Aquifer Systems with Analytic Elements and Subdomains. Water Resources Research, 46(7): W07521. https://doi.org/10.1029/2009wr008331 |
|
Fitts, C. R., 2012. Groundwater Science (2nd Edition). Elsevier/Academic Press, San Diego. |
|
Fitts, C. R., 2018. Modeling Dewatered Domains in Multilayer Analytic Element Models. Groundwater, 56(4): 557-561. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12645 |
|
Fitts, C. R., Godwin, J., Feiner, K., et al., 2015. Analytic Element Modeling of Steady Interface Flow in Multilayer Aquifers Using AnAqSim. Groundwater, 53(3): 432-439. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12225 |
|
Haitjema, H.M., 1995. Analytic Element Modeling of Groundwater Flow. Academic Press, San Diego. |
|
Haitjema, H. M., 2015. The Cost of Modeling. Groundwater, 53(2): 179. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12321 |
|
Haitjema, H. M., Hunt, R. J., Jankovic, I., et al., 2006. Foreword: Ground Water Flow Modeling with the Analytic Element Method. Groundwater, 44(1): 1-2. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.2005.00144.x |
|
Jiang, L.Q., Sun, R.L., Liang, X., 2020. Predicting Groundwater Flow and Transport in the Heterogeneous Aquifer Sandbox Using Different Parameter Estimation Methods. Earth Science (in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2020.268 |
|
Li, J.Z., Zhou, A.G., Zhou, J.W., et al., 2020. Risk Assessment of Aquifer Destruction in Underground Mining Coal of North China: A Case Study of Hongshan Mine in Zibo City. Earth Science, 45(3): 1027-1040 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10056-z |
|
Liu, S.Q., 2012. Research on the Evaluation Method of Coal Seam Floor Water Bursting and Its Application (Dissertation). China University of Mining & Technology, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
National Coal Mine Safety Supervision Bureau, 2018. Coal Mine Water Prevention and Control Regulations. Coal Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese). |
|
Ranjram, M., Craig, J. R., 2018. Closed Analytic Elements with Flexible Geometry. Groundwater, 56(5): 816-822. https://doi.org/10.1111/gwat.12649 |
|
Steward, D. R., 2015. Analysis of Discontinuities across Thin Inhomogeneities, Groundwater/Surface Water Interactions in River Networks, and Circulation about Slender Bodies Using Slit Elements in the Analytic Element Method. Water Resources Research, 51(11): 8684-8703. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015wr017526. |
|
Strack, O.D.L., 1989. Groundwater Mechanics. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs. |
|
Strack, O. D. L., 2003. Theory and Applications of the Analytic Element Method. Reviews of Geophysics, 41(2): 1005. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002rg000111 |
|
Strack, O. D. L., 2017a. Vertically Integrated Flow in Stratified Aquifers. Journal of Hydrology, 548: 794-800. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.01.039 |
|
Strack, O.D.L., 2017b. Analytical Groundwater Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. |
|
Strack, O. D. L., 2018. Limitless Analytic Elements. Water Resources Research, 54(2): 1174-1190. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017wr022117 |
|
Toller, E. A. L., Strack, O. D. L., 2019. Interface Flow with Vertically Varying Hydraulic Conductivity. Water Resources Research, 55(11): 8514-8525. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019wr024927 |
|
Wang, X.S., Wan, L., 2011. Groundwater Movement Equations. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). |
|
Wu, Q., 2014. Progress, Problems and Prospects of Prevention and Control Technology of Mine Water and Reutilization in China. Journal of China Coal Society, 39(5): 795-805 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/96550X/201405/49847171.html |
|
Wu, Q., Cui, F.P., Zhao, S.Q., et al., 2013a. Type Classification and Main Characteristics of Mine Water Disasters. Journal of China Coal Society, 38(4): 561-565 (in Chinese with English abstract). |
|
Wu, Q., Zhao, S.Q., Sun, W.J., et al., 2013b. Classification of the Hydrogeological Type of Coal Mine and Analysis of Its Characteristics in China. Journal of China Coal Society, 38(6): 901-905 (in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/jccs/jccs/2013/00000038/00000006/art00001 |
|
Zhang, Z. Y., Wang, W. K., Yeh, T. C. J., et al., 2016. Finite Analytic Method Based on Mixed-Form Richards' Equation for Simulating Water Flow in Vadose Zone. Journal of Hydrology, 537: 146-156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.03.035 |
|
陈崇希, 唐仲华, 胡立堂, 2014. 地下水流数值模拟理论方法及模型设计. 北京: 地质出版社. |
|
国家煤矿安全监察局, 2018. 煤矿防治水细则. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社. |
|
蒋立群, 孙蓉琳, 梁杏, 2020. 含水层非均质性不同刻画方法对地下水流和溶质运移预测的影响. 地球科学. https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2020.268 |
|
李建中, 周爱国, 周建伟, 等, 2020. 华北煤田矿山开采导致含水层破坏风险评估: 以淄博洪山煤矿为例. 地球科学, 45(3): 1027-1040. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.088 |
|
刘守强, 2012. 煤层底板突水评价方法与应用研究(博士学位论文). 北京: 中国矿业大学. |
|
王旭升, 万力, 2011. 地下水运动方程. 北京: 地质出版社. |
|
武强, 2014. 我国矿井水防控与资源化利用的研究进展、问题和展望. 煤炭学报, 39(5): 795-805. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201405001.htm |
|
武强, 崔芳鹏, 赵苏启, 等, 2013a. 矿井水害类型划分及主要特征分析. 煤炭学报, 38(4): 561-565. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201304006.htm |
|
武强, 赵苏启, 孙文洁, 等, 2013b. 中国煤矿水文地质类型划分与特征分析. 煤炭学报, 38(6): 901-905. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201306003.htm |









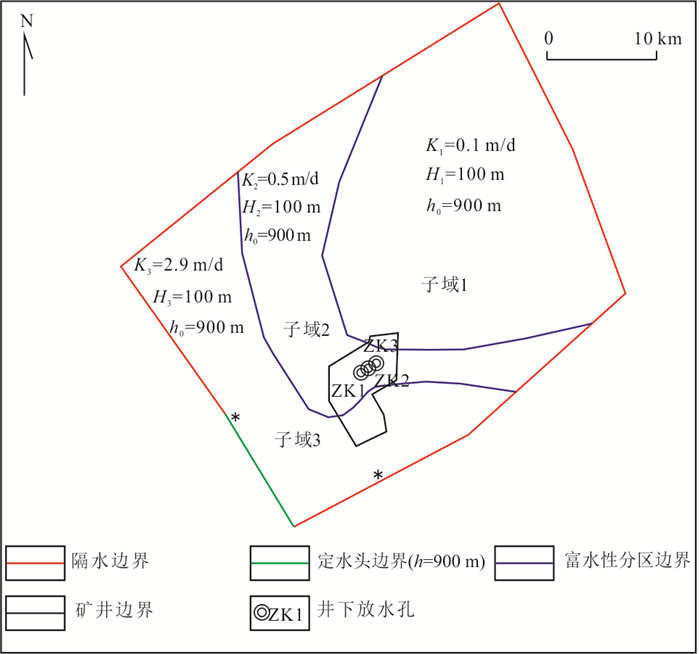
 下载:
下载: