Sources and Pollution Pathways of Deep Groundwater Sulfate Underneath the Piedmont Plain in the North Henan Province
-
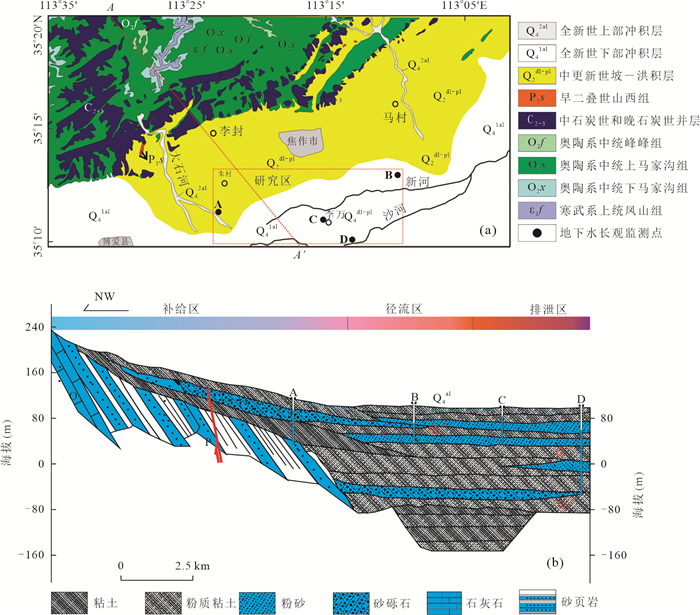
摘要: 豫北山前冲洪积平原深层地下水硫酸盐(SO42-)呈现持续增高趋势,但其机制仍不清楚.为探讨深层地下水SO42-来源与污染机制,选择山前冲洪积平原不同赋存条件深层地下水作对比分析,借助水体水化学、氢氧同位素(δDH2O和δ18OH2O)、硫酸盐硫和氧同位素(δ34SSO4和δ18OSO4),示踪人类活动影响下深层地下水SO42-的来源、污染途径及硫酸盐细菌还原过程.结果表明:深层地下水水化学、δDH2O和δ18OH2O以及δ34SSO4和δ18OSO4组成月际变化相对稳定,但不同地点的地下水组成呈现显著空间差异.研究区未受人为影响的深层地下水SO42-来源包括大气降水、黄铁矿氧化以及石膏溶解,且经历细菌还原作用;人为输入对深层地下水的影响表现为两种不同的途径和过程,一种是在山前补给区,因无显著的隔水层,在降水入渗和河水侧渗作用下,深层地下水显著受到人类活动来源硫酸盐(工业废水)影响.另一种是在排泄区,由于深层地下水过量开采导致地下水水位下降,上伏浅层咸水产生越流补给,造成深层地下水的SO42-浓度显著增加.研究结果很好地揭示了焦作山前冲洪积平原深层地下水受污染的机制,为我们有效管理和保护深层地下水资源提供重要科学依据.
-
关键词:
- 硫酸盐来源 /
- 地下水硫酸盐细菌还原 /
- 硫和氧同位素示踪 /
- 贝叶斯同位素混合模型 /
- 山前冲洪积平原 /
- 水文地质
Abstract: Deep groundwater sulfate in the piedmont alluvial plain in Jiaozuo had been increasing, however, the mechanism is still unclear. To illustrate the pollution mechanism of deep groundwater, deep groundwater in different hosting conditions was sampled to compare, and hydro-chemical compositions, hydrogen and oxygen isotopes (δDH2O and δ18OH2O), sulfate sulfur and oxygen isotopes (δ34SSO4 and δ18OSO4) were determined to constrain the sulfate sources, pollution pathways and sulfate bacterial reduction processes with the presence of anthropogenic activities. The results indicated that there were small variations of monthly hydro-chemical and isotope compositions in respective deep groundwaters, but large spatial differences were found in the hydro-chemical compositions of these deep groundwater. Sulfate in the undisturbed deep groundwater was mainly derived from atmospheric deposition, pyrite oxidation and gypsum dissolution, and the bacterial sulfate reduction obviously occurred; There were two kinds of pollution pathways and processes in the polluted deep groundwater. First was that in the piedmont where deep groundwater was recharged, due to no obvious aquifuge between them, the precipitation and river water containing industrial wastes could easily infiltrate into deep groundwater with the result of increasing sulfate concentrations. Second was that in the discharge zone, increased deep groundwater sulfate was related with leapfrog recharge from the above aquifer where sulfate was rich, and the leapfrog recharge was due to overwhelming deep groundwater pumping. Our results well illustrated the sulfate pollution mechanism in deep groundwater underneath the piedmont alluvial plain in Jiaozuo, and provided vitally scientific evidences on effective management and protection of deep groundwater source. -
表 1 研究区深层地下水水化学以及同位素组成
Table 1. Hydrochemical and isotopic compositions of deep groundwater in studied area
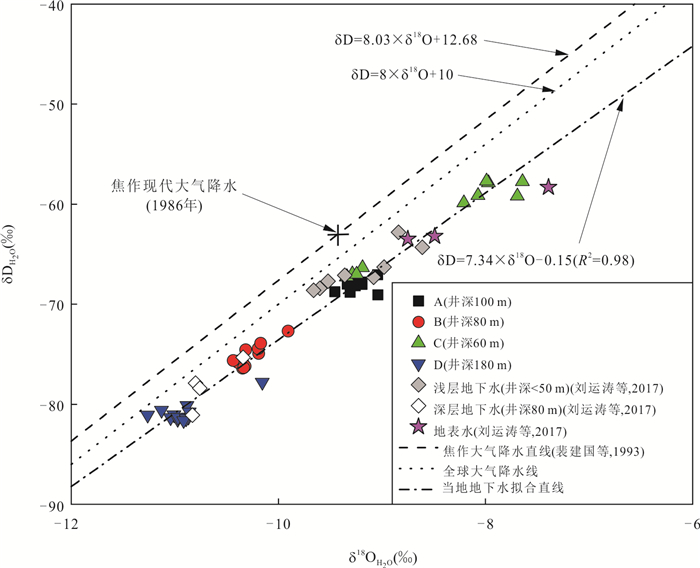
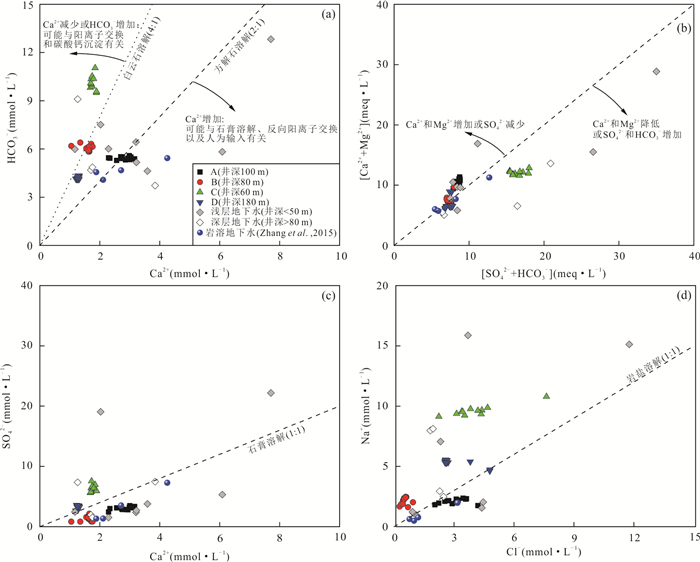
地点 内容 pH值 EC值 DO值 Eh值 K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ HCO3- μS·cm-1 mg·L-1 mv mg·L-1 mg·L-1 mg·L-1 mg·L-1 mg·L-1 A
(100 m)最大值 7.7 1253 8.0 223 1.50 54.54 126.52 66.61 340.87 最小值 7.2 972 4.5 63 0.55 40.23 91.61 52.52 322.56 均值 7.4 1139 5.9 141 0.96 48.36 111.88 58.66 331.57 标准偏差 0.1 85 1.2 48 0.29 4.59 10.81 3.36 5.26 B
(80 m)最大值 7.7 792 8.8 208 0.59 57.06 70.39 76.91 390.35 最小值 7.0 610 2.3 93 0.09 37.10 41.85 47.62 356.29 均值 7.5 728 5.6 139 0.27 48.82 62.83 53.51 369.57 标准偏差 0.2 57 2.3 42 0.23 7.04 7.72 9.67 11.08 C
(60 m)最大值 7.7 2290 8.3 343 4.67 248.10 75.64 110.17 673.94 最小值 7.1 1762 2.9 -49 0.14 210.00 67.39 97.98 579.30 均值 7.5 1910 4.8 82 2.41 221.42 70.72 102.69 618.66 标准偏差 0.1 139 1.6 117 2.00 10.26 2.97 3.58 27.52 D
(180 m)最大值 7.9 1064 6.7 122 0.73 127.66 52.85 77.46 264.53 最小值 7.5 882 3.1 -13 0.08 106.56 48.00 44.00 250.39 均值 7.7 1012 5.2 67 0.32 121.53 50.84 52.22 257.23 标准偏差 0.1 46 1.2 47 0.28 6.80 1.43 11.77 5.57 地点 内容 SO42- Cl- NO3-⁃N NICB* δ18O δD δ34SSO4 δ18OSO4 mg·L-1 mg·L-1 mg·L-1 % ‰ ‰ ‰ ‰ A
(100 m)最大值 166.90 149.07 7.97 13.21 -9.0 -67 14.1 9.4 最小值 117.22 72.64 3.19 -12.17 -9.5 -69 12.4 7.1 均值 146.53 108.86 5.62 4.91 -9.2 -68 13.3 7.9 标准偏差 13.19 20.96 1.44 6.80 0.1 1 0.6 0.8 B
(80 m)最大值 103.00 33.57 4.02 21.66 -9.9 -73 20.2 10.6 最小值 40.16 9.72 0.39 11.61 -10.4 -76 16.8 8.5 均值 64.19 18.94 1.95 16.82 -10.3 -75 19.4 9.4 标准偏差 19.84 6.13 1.19 3.07 0.1 1 0.9 0.6 C
(60 m)最大值 363.00 270.63 8.21 8.29 -7.6 -58 12.4 9.0 最小值 269.94 79.68 3.74 -1.97 -9.3 -67 10.8 6.9 均值 302.65 144.66 5.58 3.79 -8.5 -62 11.6 8.0 标准偏差 28.20 48.44 1.97 3.95 0.7 4 0.5 0.7 D
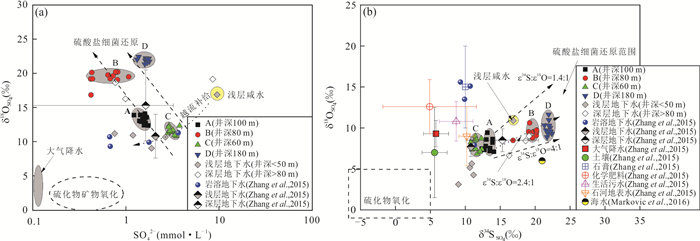
(180 m)最大值 171.64 170.41 2.58 17.76 -10.2 -78 22.4 11.6 最小值 127.00 90.43 0.94 6.80 -11.3 -82 21.3 8.9 均值 156.55 109.09 2.08 12.05 -10.9 -81 21.9 10.0 标准偏差 13.83 31.11 0.64 3.48 0.3 1 0.3 0.8 注:*. NICB=(TZ+-TZ-)/TZ+×100%,TZ+=2Ca2++2Mg2++Na++K+,TZ-=2SO42-+HCO3-+Cl-+NO3-. 表 2 表 2研究区深层地下水潜在硫酸盐来源δ34S和δ18O组成
Table 2. δ34S and δ18O values of potential sources for deep groundwater sulfate in studied area
潜在来源 δ34S(‰) δ18O(‰) 文献 范围 均值 标准偏差 范围 均值 标准偏差 焦作大气降水 3.5~9.2 5.9 1.8 6.2~12.2 9.3 1.6 Zhang et al.(2015) 焦作土壤硫酸盐 3.9~8.5 5.6 1.8 -2.4~12.7 7.0 5.5 Zhang et al.(2015) 岩浆岩黄铁矿 -5~+5 0 5.0 / / / 王艳娟等(2011); 张东等(2019b) 沉积岩黄铁矿 3.4~10.2 6.6 / / / / Xiao and Liu(2011) 石膏 / 10 0 / 15 5 杨郧城等(2008); Turchyn et al.(2013) 邯郸中奥陶石膏 20~24 / / / / / 王艳娟等(2011) 化学肥料 -3.1~+20.7 4.9 6.7 7.5~20.0 12.6 3.3 Zhang et al.(2015) 生活污水 4.2~11.6 8.7 2.4 8.5~17.7 10.8 2.3 Zhang et al.(2015) 浅层咸水体 / 16.8 / / 10.9 / 本研究 石河地表水 9.2~11.4 10.2 1.1 6.6~13.2 9.0 3.6 Zhang et al.(2015) 表 3 研究区浅层地下水和深层地下水硫酸盐含量及δ34S和δ18O组成
Table 3. Concentrations and δ34S coupled with δ18O values of sulfate in shallow and deep groundwater in studied area
ID 类型 Cl-(mmol·L-1)* SO42-(mmol·L-1)* δ34S(‰) δ18O(‰) 1 浅层地下水 1.12 1.89 9.0 3.1 2 浅层地下水 4.39 2.66 10.7 5.2 3 深层地下水 2.28 0.99 16.3 6.6 4 深层地下水 2.47 0.77 18.6 8.4 6 浅层地下水 0.95 0.76 11.2 4.3 7 浅层地下水 0.92 1.19 10.9 5.7 10 深层地下水 1.81 8.58 19.1 9.0 13 浅层地下水 3.70 9.53 16.8 10.9 注:*数据引自文献刘运涛等(2017). 表 4 研究区深层地下水硫酸盐来源混入比例计算结果
Table 4. The mixing ratios of variable sulfate sources in deep groundwater in studied area
来源 深层地下水A 深层地下水Ba 深层地下水C 深层地下水Da 均值±标准偏差(%) 均值±标准偏差(%) 均值±标准偏差(%) 均值±标准偏差(%) 大气降水 19.4±14.2 36.1±15.7 6.4±4.0 32.7±21.6 土壤硫酸盐 9.0±6.2 13.1±9.1 8.3±4.7 9.7±7.9 黄铁矿 13.1±4.3 31.5±5.2 15.0±2.4 21.3±12.1 石膏 9.3±6.4 19.3±11.6 3.8±2.5 36.2±34.8 化学肥料 9.6±6.9 / 3.5±2.0 / 生活污水 20.3±13.2 / 6.0±4.1 / 石河河水 19.2±13.5 / / / 浅层咸水 / 57.1±3.3 / 注:a. 硫和氧同位素分馏系数取值分别为-12‰和-5‰. -
Balci, N., Shanks, Iii., W, C., Mayer, B., et al., 2007. Oxygen and Sulfur Isotope Systematics of Sulfate Produced by Bacterial and Abiotic Oxidation of Pyrite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(15): 3796-3811. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2007.04.017 Egbi, C.D., Anormu, G. K., Ganyaglo, S. Y., et al., 2020. Nitrate Contamination of Groundwater in the Lower Volta River Basin of Ghana: Sources and Related Human Health Risks. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 191: 110227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110227 Fan, B. L., Zhang, D., Tao, Z. H., et al., 2017. Compositions of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Values of Yellow River Water and the Response to Climate Change. China Environmental Science, 37(5): 1906-1914(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGHJ201705038.htm Fan, B.L., Zhao, Z. Q., Tao, F. X., et al., 2014. Characteristics of Carbonate, Evaporite and Silicate Weathering in Huanghe River Basin: A Comparison among the Upstream, Midstream and Downstream. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 96: 17-26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.005 Fouillac, C., Fouillac, A.M., Criaud, A., 1990. Sulphur and Oxygen Isotopes of Dissolved Sulphur Species in Formation Waters from the Dogger Geothermal Aquifer, Paris Basin, France. Applied Geochemistry, 5(4): 415-427. https://doi.org/10.1016/0883-2927(90)90018-Z Gilhooly, III. W.P., Reinhard, C.T., Lyons, T.W., 2016. A Comprehensive Sulfur and Oxygen Isotope Study of Sulfur Cycling in a Shallow, Hyper-Euxinic Meromictic Lake. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 189: 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2016.05.044 Guo, H., Zhou, Y., Jia, Y., et al., 2016. Sulfur Cycling-Related Biogeochemical Processes of Arsenic Mobilization in the Western Hetao Basin, China: Evidence from Multiple Isotope Approaches. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(23): 12650-12659. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b03460 He, J.Y., Zhang, D., Zhao, Z.Q., 2017. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Hydrochemical Composition of River Water in Yellow River Basin, China. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 36(5): 1390-1401(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-STXZ201705028.htm Holser, W.T., Kaplan, I.R., Sakai, H., et al., 1979. Isotope Geochemistry of Oxygen in the Sedimentary Sulfate Cycle. Chemical Geology, 25(1): 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(79)90079-2 Hong, Y.T., Zhang, H.B., Zhu, Y.X., et al., 1994. Sulfur Isotopic Composition of Precipitation in China. Advancesin Natural Sciences-Correspondence of State Key Laboratories, 4(6): 741-745(in Chinese). Huang, Q.B., Qin, X.Q., Liu, P.Y., et al., 2014. The Characteristics and Influencing Factors of SO42- and Sulfate Isotope(δ34S) in Different Types of Groundwater in Fenyang, ShanXi Province. Quaternary Sciences, 34(2): 364-371(in Chinesewith English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ201402010.htm Jia, X. S., Zhang, D., Zhao, Z. Q., 2016. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopic Compositions of Groundwater and Surface Water in South Piedmont Plain of Taihang Mountain and Its Environmental Significance. Earth and Environment, 44(3): 281-289(in Chinesewith English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201603001.htm Jiao, Y. J., Wang, G. C., Cui, L. F., et al., 2014. Characteristics of Hydrochemistry and Stable Hydrogen, Oxygen Isotopes in Surface Water and Groundwater in Jiyuan Basin. Environment Chemistry, 33(6): 962-968(in Chinese with English abstract). http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/hjhx201406015 Lang, Y. C., Liu, C. Q., Satake, H., et al., 2008. δ37Cl and δ34S Variations of Cl- and SO42- in groundwater and Surface Water of Guiyang Area, China. Advances in Earth Science, (2): 151-159(in Chinesewith English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288930235_d37_Cl_and_d34S_Variations_of_Cl-_and_SO42-_in_groundwater_and_surface_water_of_Guiyang_area_China_J Li, W. P., Wang, L. F., Yang, H. F., et al., 2020a. The Groundwater Overexploitation Status and Countermeasure Suggestions of the North China Plain. China Water Resources, (13): 26-30(in Chinese with English abstract). Li, X., Tang, C., Cao, Y., et al., 2020b. A Multiple Isotope (H, O, N, C and S) Approach to Elucidate the Hydrochemical Evolution of Shallow Groundwater in a Rapidly Urbanized Area of the Pearl River Delta, China. Science of The Total Environment, 724: 137930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.137930 Li, X., Zhou, A., Gan, Y., et al., 2011. Controls on the δ34S and δ18O of Dissolved Sulfate in the Quaternary Aquifers of the North China Plain. Journal of Hydrology, 400(3-4): 312-322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.01.034 Li, X.D., Liu, C. Q., Harue, M., et al., 2010. The Use of Environmental Isotopic (C, Sr, S) and Hydrochemical Tracers to Characterize Anthropogenic Effects on Karst Groundwater Quality: A Case Study of the Shuicheng Basin, SW China. Applied Geochemistry, 25(12): 1924-1936. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.10.008 Liu, F., Wang, S., Yeh, T. J., et al., ,2020. Using Multivariate Statistical Techniques and Geochemical Modeling to Identify Factors Controlling the Evolution of Groundwater Chemistry in a Typical Transitional Area between Taihang Mountain and North China Plain. Hydrological Processes, 34(8): 1888-1905. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13701 Liu, Y. T., Zhang, D., Zhao, Z. Q., 2017. Hydro-Chemical and Isotopic Compositions of Groundwater in Piedmont Plain of the South Taihang Mountain. Earth and Environment, 45(2): 203-213(in Chinesewith English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201702012.htm Markovic, S., Paytan, A., Li, H., et al., 2016. A Revised Seawater Sulfate Oxygen Isotope Record for the Last 4 Ma. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 175: 239-251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.12.005 Parnell, A.C., Inger, R., Bearhop, S., et al., 2010. Source Partitioning Using Stable Isotopes: Coping with too Much Variation. PloS one, 5(3): e9672. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0009672 Pei, J. G., Tao, Y.L., Tong, C.S., 1993. Environmental Isotope of Natural Water and Its Application in Karst Hydrogeologyin Jiaozuo Area. Carsologica Sinica, 12(1): 45-53(in Chinesewith English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199301005.htm Qin, Y., Zhang, D., Zhao, Z. Q., 2016. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Hydrochemical Compositions of River Water in Qinhe Basin. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 35(6): 1516-1524(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.cqvip.com/QK/90811X/201606/669054175.html Shi, J.S., Li, G.M., Liang, X., et al., 2014. Evolution Mechanism and Control of Groundwater in the North China Plain. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 35(5): 527-534(in Chinese with English abstract). Song, H. B., Zhang, Z. J., Fei, Y. H., et al., 2007. Down-Movement of the Fresh-Saline Groundwater Interface in the Middle of the Hebei Plain under the Condition of Exploitation. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, (1): 44-46, 52(in Chinesewith English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG200701009.htm Song, X. Q., Peng, Q., Wang, W., et al., 2019. Analysis of Environmental Background Valuesof Chloride and Sulfate in Shallow Groundwater in Karst Area of Guizhou. Earth Science, 44(11): 3926-3938(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DQKX201911027.htm Turchyn, A.V., Tipper, E.T., Galy, A., et al., 2013. Isotope Evidence for Secondary Sulfide Precipitation along the Marsyandi River, Nepal, Himalayas. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 374: 36-46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2013.04.033 Tuttle, M.L.W., Breit, G.N., Cozzarelli, I.M., 2009. Processes Affecting δ34S and δ18O values of Dissolved Sulfate in Alluvium along the Canadian River, Central Oklahoma, USA. Chemical Geology, 265(3-4): 455-467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.05.009 Wang, H. C., 1991. Introduction to Isotopic Hydrogeology. Geology Press, Beijing, 191(in Chinese). Wang, Y. J., Hu, Y. Y., Sheng, J. F., et al., 2011. Sulfur and Lead Isotope Composition and Tracing for Sources of Ore-Forming Materials in Beiming River Iron Deposits, Southern Taihang Mountains. Geoscience, 25(5): 846-852(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201105008.htm Wang, Y. T., Li, J. X., Xue, X. B., et al., 2021. Similarities and Differences of Main Controlling Factors of Natural High Iodine Groundwater between North China Plain and Datong Basin. Earth Science, 46(1): 308-320(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0269749121010642 Xiao, H. Y., Liu, C.Q., 2011. The Elemental and Isotopic Composition of Sulfur and Nitrogen in Chinese coals. Organic Geochemistry, 42(1): 84-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2010.10.011 Xiao, H. Y., Liu, C. Q., Li, S. L., 2003. Geochemical Characteristics of Sulfur and Nitrogen Isotopic Compositions in Rains of Guiyang in Summer. Geochimica, 32(3): 248-254(in Chinesewith English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/288882911_Geochemical_characteristics_of_sulfur_and_nitrogen_isotopic_compositions_in_rains_of_Guiyang_in_summer Xie, X., Ellis, A., Wang, Y., et al., 2009. Geochemistry of Redox-SensitiveElements and Sulfur Isotopes in the High Arsenic Groundwater System of Datong Basin, China. Science of The Total Environment, 407(12): 3823-3835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2009.01.041 Xie, X., Wang, Y., Ellis, A., et al., 2013. Multiple Isotope (O, S and C) Approach Elucidates the Enrichment of Arsenic in the Groundwater from the Datong Basin, Northern China. Journal of Hydrology, 498: 103-112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.06.024 Xue, X. B., Li, J. X., Qian, K., et al., 2018. Spatial Distribution and Mobilization of Iodine in Groundwater System of North China Plain: Taking Hydrogeological Section from Shijiazhuang, Hengshui to Cangzhou as an Example. Earth Science, 43(3): 910-921(in Chinese with English abstract). http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29611121 Xue, D., De, Baets. B., Botte, J., et al., 2012. Use of a Bayesian Isotope Mixing Model to Estimate Proportional Contributions of Multiple Nitrate Sources in Surface Water. Environmental Pollution, 161: 43-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2011.09.033 Yang, X.C., Sheng, Z.L., Wen, D.G., et al., 2008. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Sources of Sulfate in Groundwater of the Ordoscretaceous Goundwater Basin. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, (5): 553-562(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/article_en/cjfdtotal-dqxb200805004.htm Yang, L. Z., Qu, W. L., Zhang, Y., et al., 2013. A Discussion on Deep Groundwater Origin of Dezhou in Shandong Province Based on Water Chemical Composition and Environmental Isotopic Information. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 34(4): 463-469(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201304011.htm Zhang, D., Li, X.D., Zhao, Z.Q., et al., 2015. Using Dual Isotopic Data to Rack the Sources and Behaviors of Dissolved Sulfate in the Western North China Plain. Applied Geochemistry, 52: 43-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.011 Zhang, D., Huang, X. Y., Li, C. J., 2013. Sources of Riverine Sulfate in Yellow River and Its Tributaries Determined by Sulfur and Oxygen Isotopes. Advances in Water Science, 24(3): 418-426(in Chinesewith English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201303017.htm Zhang, D., Li, Y. H., Zhang, H.Y., 2019a. Application of Modified DDARP Method for Purification of Barite in Natural Water Samples. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 38(1): 77-84(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/342782405_Application_of_Modified_DDARP_Method_for_Purification_of_Barite_in_Natural_Water_Samples Zhang, Q., Wang, H., Lu, C., 2020. Tracing Sulfate Origin and Transformation in an Area with Multiple Sources of Pollution in Northern China by Using Environmental Isotopes and Bayesian Isotope Mixing Model. Environmental Pollution, 265: 115105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115105 Zhang, D., Liu, C.Q., Wang, F.S., et al., 2015. Inorganic Carbon Cycling in Subsurface Environment Influenced by Agricultural Activities. China Environmental Science, 35(11): 3359-3370(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Zhi_Qi_Zhao2/publication/288230069_Inorganic_carbon_cycling_in_subsurface_environment_influenced_by_agricultural_activities/links/56e4e74408ae98445c1ef9d1/Inorganic-carbon-cycling-in-subsurface-environment-influenced-by-agricultural-activities.pdf Zhang, D., Yang, J.M., Huang, X.Y., et al., 2019b. Sources of Dissolved Heavy Metals in River Water of the Yiluo River Basin Based on Sulfur Isotope of Sulfate. China Environmental Science, 39(6): 2549-2559(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-ZGHJ201906042.htm Zhang, H.L., Wang, C., Pang, W., et al., 2019. Using Sulfur and Oxygen Isotope to Trace the Source of Sulphate in Baotuquan Spring Area of Jinan. Geological Survey of China, 6(1): 75-80(in Chinese with English abstract). http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-DZDC201901011.htm Zhang, Z.J., Fei, Y.H., Guo, C.Y., et al., 2012. Regional Groundwater Contamination Assessment in the North China Plain. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 42(5): 1456-1461(in Chinese with English abstract). http://www.researchgate.net/publication/281604046_Regional_groundwater_contamination_assessment_in_the_North_China_Plain Zhou, J., Zhang, Y., Zhou, A., et al., 2016. Application of Hydrochemistry and Stable Isotopes (δ34S, δ18O and δ37Cl) to Trace Natural and Anthropogenic Influences on the Quality of Groundwater in the Piedmont Region, Shijiazhuang, China. Applied Geochemistry, 71: 63-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2016.05.018 范百龄, 张东, 陶正华, 等, 2017. 黄河水氢、氧同位素组成特征及其气候变化响应. 中国环境科学, 37(5): 1906-1914. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2017.05.038 何姜毅, 张东, 赵志琦, 2017. 黄河流域河水水化学组成的时间和空间变化特征. 生态学杂志, 36(5): 1390-1401. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201705028.htm 洪业汤, 张鸿斌, 朱詠煊, 等, 1994. 中国大气降水的硫同位素组成特征. 自然科学进展: 国家重点实验室通讯, 4(6): 741-745. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.1994.06.013 黄奇波, 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 等, 2014. 汾阳地区不同类型地下水SO42-、δ34S的特征及影响因素. 第四纪研究, 34(2): 364-371. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7410.2014.02.10 贾新生, 张东, 赵志琦, 2016. 南太行山山前平原地下水和地表水氢氧同位素组成及环境意义. 地球与环境, 44(3): 281-289. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201603001.htm 焦艳军, 王广才, 崔霖峰, 等, 2014. 济源盆地地表水和地下水的水化学及氢、氧同位素特征. 环境化学, 33(6): 962-968. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJHX201406015.htm 郎赟超, 刘丛强, Satake H., 等, 2008. 贵阳地表水-地下水的硫和氯同位素组成特征及其污染物示踪意义. 地球科学进展(2): 151-159. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2008.02.005 李文鹏, 王龙凤, 杨会峰, 等, 2020. 华北平原地下水超采状况与治理对策建议. 中国水利, (13): 26-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1123.2020.13.017 刘运涛, 张东, 赵志琦, 2017. 南太行山山前平原地下水水化学以及同位素组成研究. 地球与环境, 45(2): 203-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201702012.htm 裴建国, 陶友良, 童长水, 1993. 焦作地区天然水环境同位素组成及其在岩溶水文地质中的应用. 中国岩溶, 12(1): 45r53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR199301005.htm 秦勇, 张东, 赵志琦, 2016. 沁河流域水化学组成的空间和时间变化特征. 生态学杂志, 35(6): 1516-1524. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXZ201606017.htm 石建省, 李国敏, 梁杏, 等, 2014. 华北平原地下水演变机制与调控. 地球学报, 35(5): 527-534. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201405001.htm 宋海波, 张兆吉, 费宇红, 等, 2007. 开采条件下河北平原中部咸淡水界面下移. 水文地质工程地质, (1): 44-46, 52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2007.01.009 宋小庆, 彭钦, 王伟, 等, 2019. 贵州岩溶区浅层地下水氯化物及硫酸盐环境背景值. 地球科学, 44(11): 3926-3938. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.166 王恒纯, 1991. 同位素水文地质概论. 北京: 地质出版社, 191. 王艳娟, 胡援越, 申俊峰, 等, 2011. 太行山南段北洺河铁矿S、Pb同位素组成及其对成矿物质来源的示踪. 现代地质, 25(5): 846-852. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2011.05.003 王雨婷, 李俊霞, 薛肖斌, 等, 2021. 华北平原与大同盆地原生高碘地下水赋存主控因素的异同. 地球科学, 46(1): 308-320. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.261 肖化云, 刘丛强, 李思亮, 2003. 贵阳地区夏季雨水硫和氮同位素地球化学特征. 地球化学, 32(3): 248-254. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2003.03.006 薛肖斌, 李俊霞, 钱坤, 等, 2018. 华北平原原生富碘地下水系统中碘的迁移富集规律: 以石家庄-衡水-沧州剖面为例. 地球科学, 43(3): 910-921. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.564 杨丽芝, 曲万龙, 张勇, 等, 2013. 基于水化学组分和环境同位素信息探讨山东德州深层承压地下水起源. 地球学报, 34(4): 463-469. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201304011.htm 杨郧城, 沈照理, 文冬光, 等, 2008. 鄂尔多斯白垩系地下水盆地硫酸盐的水文地球化学特征及来源. 地球学报(5): 553-562. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.05.003 张东, 黄兴宇, 李成杰, 2013. 硫和氧同位素示踪黄河及支流河水硫酸盐来源. 水科学进展, 24(3): 418-426. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKXJ201303017.htm 张东, 李玉红, 张鸿禹, 2019a. 应用改进DDARP方法纯化天然水体样品中硫酸钡固体的效果评价. 岩矿测试, 38(1): 77-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201901011.htm 张东, 杨锦媚, 黄兴宇, 等, 2019b. 基于硫酸盐硫同位素的伊洛河流域河水溶解性重金属来源. 中国环境科学, 39(6): 2549-2559. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHJ201906042.htm 张东, 刘丛强, 汪福顺, 等, 2015. 农业活动干扰下地下水无机碳循环过程研究. 中国环境科学, 35(11): 3359-3370. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2015.11.022 张海林, 王重, 逄伟, 等, 2019. 硫氧同位素示踪污染物来源在济南岩溶水中的应用. 中国地质调查, 6(1): 75-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC201901011.htm 张兆吉, 费宇红, 郭春艳, 等, 2012. 华北平原区域地下水污染评价. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 42(5): 1456-1461. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201205019.htm -









 下载:
下载: