Methylation and Thiolation of Arsenic in Tengchong Hot Springs
-
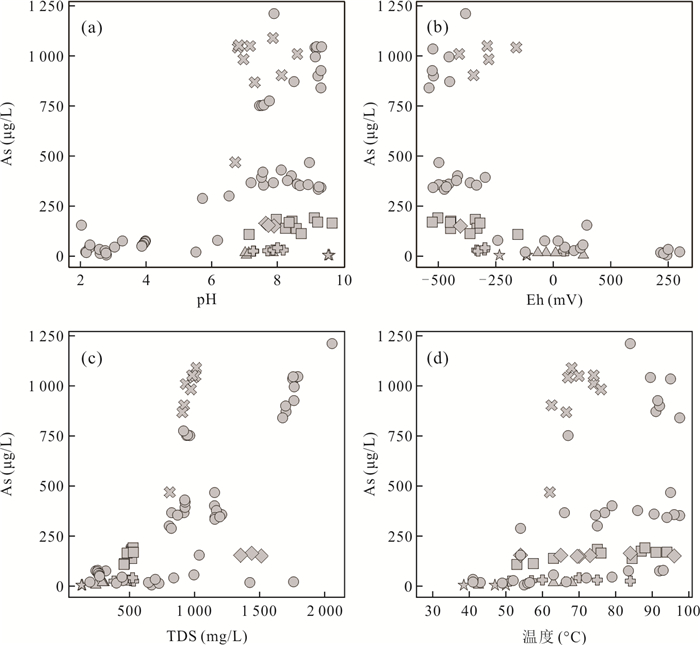
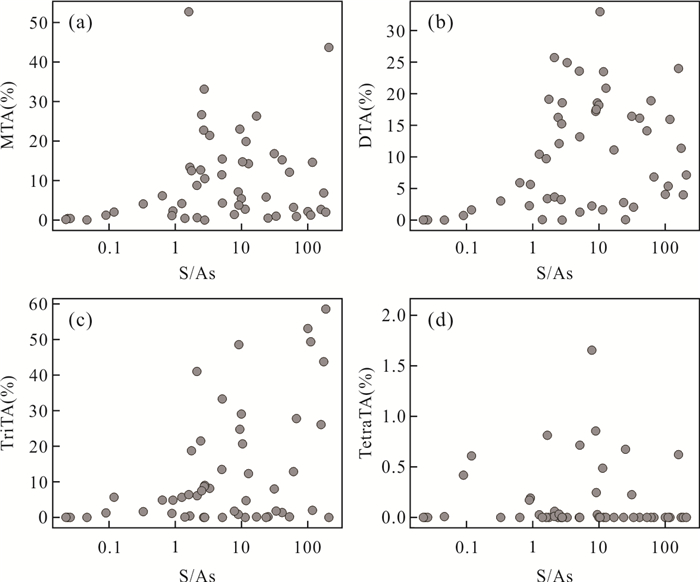
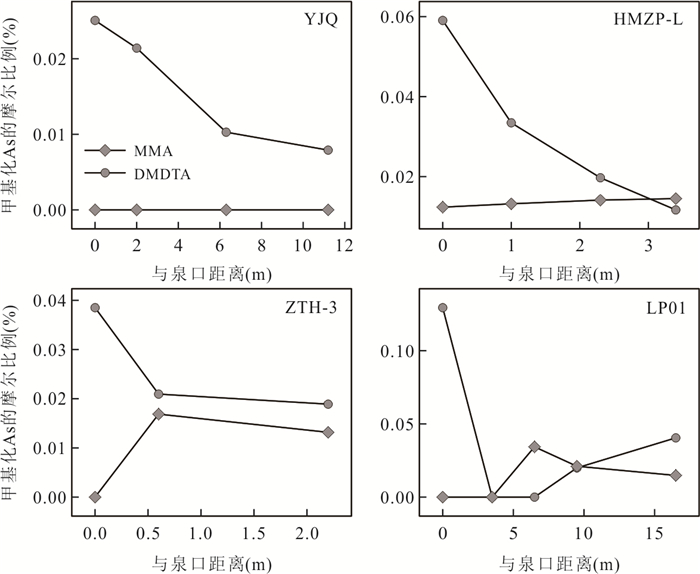
摘要: 为了研究热泉中砷的形态及其分布、转化规律,针对云南腾冲热泉各种砷形态进行了IC-ICP-MS测试和水文地球化学分析.在91处热泉中检出了11种砷形态,包括(亚)砷酸盐、无机硫代砷和甲基(硫代)砷.其中(亚)砷酸盐含量>无机硫代砷含量>甲基砷含量.热泉中无机硫代砷含量及其巯基化程度与硫/砷比正相关.甲基砷含量低是富硫化物热泉中甲基硫代砷形成的主要限制因素,硫/砷摩尔比、总砷、温度、pH、Eh和TDS可影响甲基硫代砷的形成和转化.甲基硫代砷在热泉地表流径上可经历脱巯基、脱甲基然后被沉积物吸附,也可在流径下游重新形成.砷的巯基化和甲基化形态在热泉中广泛分布,甲基硫代砷在热泉环境中具有高迁移性和重现性,应引起相关研究重视.Abstract: In order to study the speciation of arsenic (As) in hot springs and their distribution and transformation patterns, IC-ICP-MS quantification and hydrogeochemical analyses were conducted for various arsenic species in Tengchong hot springs in Yunnan Province. In 91 hot spring samples, 11 As species were detected, which include arsenate, arsenite, inorganic thioarsenates, methylated oxyarsenates and methylated thioarsenates. Arsenate and arsenite were predominate species followed by inorganic thioarsenates, unlike inorganic species, methylated As occurred as minor species in Tengchong hot springs. The content of thioarsenates and their degree of thiolation are positively correlated with S/As molar ratios. The lack of methylated oxyarsenates was probably the reason for low methylated thioarsenate levels, besides, the S/As molar ratio, total As, temperature, pH, Eh and TDS can also affect the formation and transformation of methylated thioarsenates. Methylated thioarsenates may undergo a series of transformations and interfacial reactions on the surface drainage of hot springs such as de-thiolation, de-methylation and then adsorption by sediments. Other As species can be converted to methylated thioarsenate in downstream areas with relatively low temperatures, low flow rates and significant microbial activity. The thiolated and methylated species of As are widely distributed in hot springs, and the highly toxic methylated thioarsenates have high mobility and are likely to reappear in hot spring drainage environment, which should attract the attention of relevant studies.
-
Key words:
- Arsenic species /
- methylated thioarsenates /
- hot spring /
- Tengchong /
- hydrogeology
-
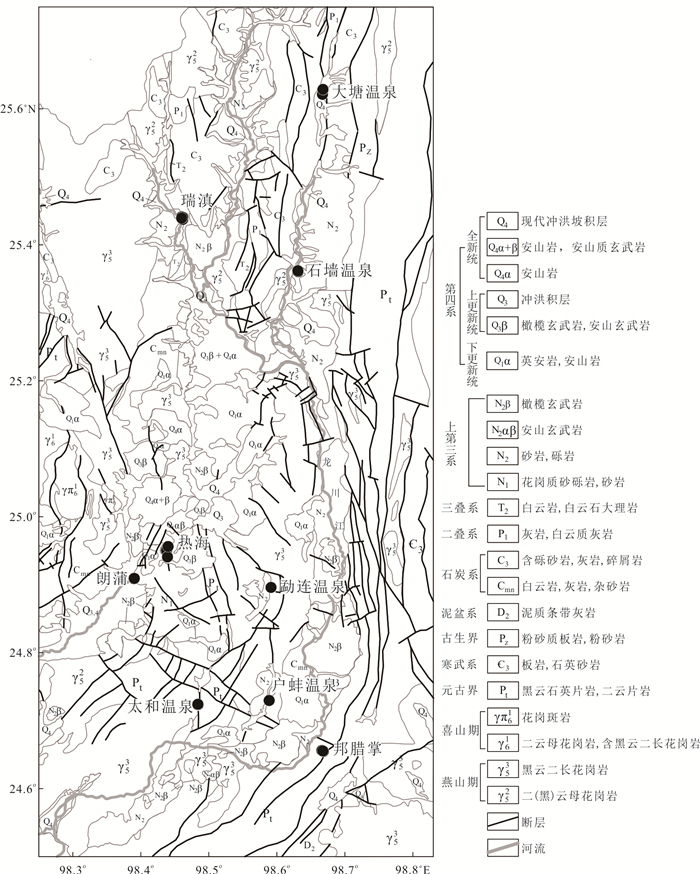
图 1 腾冲地热区地质图和采样点分布(参考自Guo et al., 2012)
Fig. 1. Sampling location and geological map of Tengchong geothermal area (modified from Guo et al., 2012)
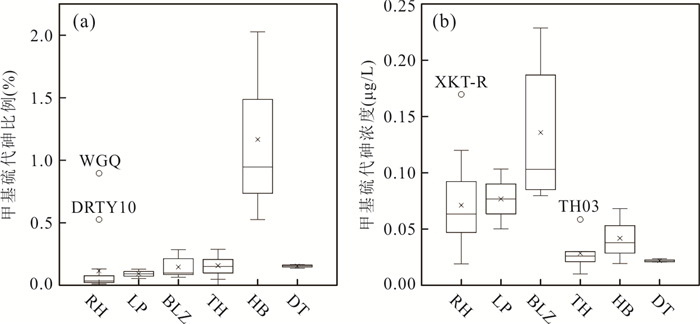
表 1 水化学变量与甲基硫代砷摩尔比例之间的斯皮尔曼相关性分析
Table 1. Spearman's correlation analysis for methylated thioarsenate proportions (%) and hydrochemical parameters
变量 rs 变量 rs 甲基砷(%) 0.47 F-(mg/L) -0.24 无机硫代砷(%) -0.05 Cl-(mg/L) -0.74 硫化物(mg/L) -0.13 SO42-(mg/L) 0.05 S/As摩尔比 0.39 Na+(mg/L) -0.66 总As(μg/L) -0.77 K+(mg/L) -0.76 pH -0.09 Ca2+(mg/L) 0.38 Eh(mV) 0.45 Mg2+(mg/L) 0.19 温度(℃) -0.57 SiO2(mg/L) -0.10 TDS(mg/L) -0.74 三价铁(μg/L) -0.37 DOC(mg/L) -0.41 Li+(μg/L) -0.75 成熟度(MI) -0.49 Rb+(μg/L) -0.81 HCO3-(mg/L) -0.23 Cs+(μg/L) -0.60 注:n=43,加粗表示P值< 0.05. -
Bai, D. H., Liao, Z. J., Zhao, G. Z., et al., 1994. The Inference of Magmatic Heat Source Beneath the Rehai (Hot Sea) Field of Tengchong From the Result of Magnetotelluric Sounding. Chinese Science Bulletin, 39(4): 344-347 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1994-39-4-344 Ballantyne, J. M., Moore, J. N., 1988. Arsenic Geochemistry in Geothermal Systems. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 52(2): 475-483. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(88)90102-0 Conklin, S. D., Fricke, M. W., Creed, P. A., et al., 2008. Investigation of the PH Effects on the Formation of Methylated Thio: Arsenicals, and the Effects of PH and Temperature on Their Stability. Journal of Analytical Atomic Spectrometry, 23(5): 711. https://doi.org/10.1039/b713145c Couture, R. M., Rose, J., Kumar, N., et al., 2013. Sorption of Arsenite, Arsenate, and Thioarsenates to Iron Oxides and Iron Sulfides: A Kinetic and Spectroscopic Investigation. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(11): 5652-5659. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3049724 Ellis, A. J., Mahon, W. A. J., 1964. Natural Hydrothermal Systems and Experimental Hot Water/rock Interactions (Part Ⅱ). Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 31(4): 519-538. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(67)90032-4 Guo, Q. H., Wang, Y. X., 2012. Geochemistry of Hot Springs in the Tengchong Hydrothermal Areas, Southwestern China. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 215-216: 61-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2011.12.003 Guo, Q. H., Liu, M. L., Li, J. X., 2017. Thioarsenic Species in the High-Temperature Hot Springs from the Rehai Geothermal Field (Tengchong) and Their Geochemical Geneses. Earth Science, 42 (2): 286-297 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo, Q. H., Planer-Friedrich, B., Liu, M. L., et al., 2017. Arsenic and Thioarsenic Species in the Hot Springs of the Rehai Magmatic Geothermal System, Tengchong Volcanic Region, China. Chemical Geology, 453(1): 12-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2017.02.010 Guo, Q. H., Planer-Friedrich, B., Liu, M. L., et al., 2019. Magmatic Fluid Input Explaining the Geochemical Anomaly of Very High Arsenic in Some Southern Tibetan Geothermal Waters. Chemical Geology, 513: 32-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.03.008. Hinrichsen, S., Geist, F., Planer-Friedrich, B., 2015. Inorganic and Methylated Thioarsenates Pass the Gastrointestinal Barrier. Chem Res Toxicol, 28: 1678-1680. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrestox.5b00268. Hirano, S., Kobayashi, Y., Cui, X., et al., 2004. The Accumulation and Toxicity of Methylated Arsenicals in Endothelial Cells: Important Roles of Thiol Compounds. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol, 198: 458-67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2003.10.023. Hug, K., Maher, W. A., Stott, M. B., et al., 2014. Microbial Contributions to Coupled Arsenic and Sulfur Cycling in the Acid-Sulfide Hot Spring Champagne Pool, New Zealand. Front Microbiol, 5: 569. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00569 Kerl, C. F., Ballaran, T. B., Planer-Friedrich, B., 2019a. Iron Plaque at Rice Roots: No Barrier for Methylated Thioarsenates. Environmental Science & Technology, 53: 13666-13674. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b04158 Kerl, C. F., Schindele, R. A., Bruggenwirth, L., et al., 2019b. Methylated Thioarsenates and Monothioarsenate Differ in Uptake, Transformation, and Contribution to Total Arsenic Translocation in Rice Plants. Environmental Science & Technology, 53: 5787-5796. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b00592 Kim, Y. T., Lee, H., Yoon, H. O., et al., 2016. Kinetics of Dimethylated Thioarsenicals and the Formation of Highly Toxic Dimethylmonothioarsinic Acid in Environment. Environmental Science & Technology, 50: 11637-11645. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.6b02656 Lang, S. Q., Butterfield, D. A., Schulte, M., et al., 2010. Elevated Concentrations of Formate, Acetate and Dissolved Organic Carbon Found at The Lost City Hydrothermal Field. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74: 941-952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2009.10.045 Langner, H. W., Jackson, C. R., Mcdermott, T. R., et al., 2001. Rapid Oxidation of Arsenite in a Hot Spring Ecosystem, Yellowstone National Park. Environmental Science & Technology, 35: 3302-3309. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0105562. Li, Y. R., Low, G. K., Scott J. A., et al., 2011. Microbial Transformation of Arsenic Species in Municipal Landfill Leachate. Journal of hazardous materials, 188: 140-147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.01.093 Liu, M. L., He, T., Wu, Q. F., et al., 2019. Hydrogeochemistry of Geothermal Waters from Xiongan New Area and Its Indicating Significance. Earth Science, 45: 2221-2231 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liao, Z., Zhao, P., 1999. Yunnan-Tibet Geothermal Belt-Geothermal Resources and Case Histories. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Naranmandura, H., Carew, M. W., Xu, S., et al., 2011. Comparative Toxicity of Arsenic Metabolites in Human Bladder Cancer EJ-1 Cells. Chem Res Toxicol, 24: 1586-96. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx200291p Naranmandura, H., Ibata, K., Suzuki, K. T., 2007. Toxicity of Dimethylmonothioarsinic Acid Toward Human Epidermoid Carcinoma A431 Cells. Chemical Research in Toxicology, 20: 1120-1125. https://doi.org/10.1021/tx700103y Planer-Friedrich, B., Forberg, J., Lohmayer, R., et al., 2020. Relative Abundance of Thiolated Species of As, Mo, W, and Sb in Hot Springs of Yellowstone National Park and Iceland. Environmental Science & Technology, 54: 4295-4304. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00668 Planer-Friedrich, B., Hartig, C., Lohmayer, R., et al., 2015. Anaerobic Chemolithotrophic Growth of the Haloalkaliphilic Bacterium Strain MLMS-1 by Disproportionation of Monothioarsenate. Environmental Science & Technology, 49: 6554-63. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b01165 Planer-Friedrich, B., Lehr, C., Matschullat, J., et al., 2006. Speciation of Volatile Arsenic at Geothermal Features in Yellowstone National Park. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70: 2480-2491. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2006.02.019 Planer-Friedrich, B., London, J., McCleskey, R. B., et al., 2007. Thioarsenates in Geothermal Waters of Yellowstone National Park: Determination, Preservation, and Geochemical Importance. Environmental Science & Technology, 41: 5245-5251. https://doi.org/10.1021/es070273v Qin, J., Lehr, C. R., Yuan, C., et al., 2009. Biotransformation of Arsenic by A Yellowstone Thermoacidophilic Eukaryotic Alga. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106: 5213-5217. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0900238106 Rodríguez-Lado, L., Sun, G., Berg, M., et al., 2013. Groundwater Arsenic Contamination Throughout China. Science, 341: 866-868. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1237484 Sharma, A. K., Tjell, J. C., Sloth, J. J., et al., 2014. Review of Arsenic Contamination, Exposure Through Water and Food and Low Cost Mitigation Options for Rural Areas. Applied Geochemistry, 41: 11-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.11.012. Song, X. Q., Peng, Q. Duan, Q. S., et al., 2019. Hydrochemistry Characteristics and Origin of Geothermal Water in Northeastern Guizhou. Earth Science, 44: 2874-2886 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tong, W., Zhang, M. T., 1989. Geothermics in Tengchong. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Wallschläger, D., London, J., 2008. Determination of Methylated Arsenic-Sulfur Compounds in Groundwater. Environmental Science & Technology, 42: 228-234. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0707815 Wang, J., Halder, D., Wegner, L., et al., 2020a. Redox Dependence of Thioarsenate Occurrence in Paddy Soils and the Rice Rhizosphere. Environmental Science & Technology, 54: 3940-3950. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05639 Wang, J., Kerl, C. F., Hu, P., et al., 2020b. Thiolated Arsenic Species Observed in Rice Paddy Pore Waters. Nature Geoscience, 13: 282-287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-020-0533-1 Webster, J.G., Nordstrom, D.K., 2003. Geothermal Arsenic. In: Welch, A.H., Stollenwerk, K.G. (eds) Arsenic in Ground Water. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-47956-7_4 Wu, G., Huang, L., Jiang, H., et al., 2017. Thioarsenate Formation Coupled with Anaerobic Arsenite Oxidation by A Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated From A Hot Spring. Frontiers in microbiology, 8: 1336. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01336 Zhu, Y. G., Xue, X. M., Kappler, A., et al., 2017. Linking Genes to Microbial Biogeochemical Cycling: Lessons from Arsenic. Environmental Science & Technology, 51: 7326-7339. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.7b00689 Zhuang, Y. Q., Guo Q. H., Liu M. L., et al., 2016. Geochemical Simulation of Thioarsenic Speciation in High-Temperature, Sulfide-Rich Hot Springs: A Case Study in the Rehai Hydrothermal Area, Tengchong, Yunnan. Earth Science, 41(9): 1499-1510 (in Chinese with English abstract). 白登海, 廖志杰, 赵国泽, 等, 1994. 从MT探测结果推论腾冲热海热田的岩浆热源. 科学通报, 39(4): 344-347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB199404017.htm 郭清海, 刘明亮, 李洁祥, 2017. 腾冲热海地热田高温热泉中的硫代砷化物及其地球化学成因. 地球科学. 42(2): 286-297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201702010.htm 廖志杰, 赵平, 1999. 滇藏地热带: 地热资源和典型地热系统. 北京: 科学出版社. 刘明亮, 何曈, 吴启帆, 等, 2019. 雄安新区地热水化学特征及其指示意义. 地球科学, 45(6): 2221-2231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202006032.htm 宋小庆, 彭钦, 段启杉, 等, 2019. 黔东北地区地热水化学特征及起源. 地球科学, 44(9): 2874-2886. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201909006.htm 佟伟, 章铭陶, 1989. 腾冲地热. 北京: 科学出版社. 庄亚芹, 郭清海, 刘明亮, 等, 2016. 高温富硫化物热泉中硫代砷化物存在形态的地球化学模拟: 以云南腾冲热海水热区为例. 地球科学. 41(9): 1499-1510. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201609006.htm -









 下载:
下载: