Rock Exhumation Rates in Motuo Section of Yarlung Tsangpo River: Evidence from Biotite Ar/Ar Chronology
-
摘要: 为揭示东喜马拉雅构造结及其周边区域完整地质演化过程,对采集自雅鲁藏布江墨脱段10块基岩样品进行黑云母40Ar/39Ar测年,并利用“Pecube”软件对年龄代表隆升剥露速率进行定量计算.样品黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄范围为11.25~24.04 Ma,对应隆升剥露速率范围为0.25~0.51 km/Ma.雅鲁藏布江墨脱段地壳隆升剥露速率存在明显南北差异,北段隆升剥露速率高出约0.2 km/Ma.年代学数据及计算结果表明,与东喜马拉雅构造结内部相比,雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段为地壳隆升剥露活动相对较弱区域.与喜马拉雅地体向拉萨地体俯冲过程相关北西、北西西走向逆断层活动,不仅在东喜马拉雅构造结内部区域发育,在其东侧雅鲁藏布江墨脱段也可能发育.Abstract: To reveal the tectonic evolution of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis and its surrounding areas, in this paper it reports 10 40Ar/39Ar ages of biotite from Motuo Section of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. It quantitatively interprets the rock's uplift and exhumation rates represented by these ages, using a modeling code "Pecube". Biotite 40Ar/39Ar ages in this paper are in the range of 11.25-24.04 Ma. Corresponding exhumation rates are in the range of 0.25-0.51 km/Ma. The rock exhumation rates in Motuo Section of the Yarlung Tsangpo River have obvious differences between northern and southern, which is characterized by the northern exhumation rates about 0.2 km/Ma higher than the southern. The ages and simulation results show that relative to the inside of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis, the exhumation rates in Motuo Section of the Yarlung Tsangpo River are lower. And the NW/NWW-trending thrust fault zones which were resulted by the collision between Himalayan terrane and Lhasa terrane, not only located in the inside of the eastern Himalayan syntaxis, but also probably located in Motuo Section of the Yarlung Tsangpo River.
-
Key words:
- eastern Himalayan syntaxis /
- Yarlung Tsangpo River /
- biotite 40Ar/39Ar /
- exhumation /
- thrust fault /
- geochronology
-
0. 引言
近30年来,地球科学逐渐发展演变成为地球系统科学,地球各圈层之间相互作用成为地球科学研究中关键问题.气候、剥蚀等来自地球外部圈层的“外动力因素”,对地壳构造演化过程可能存在的影响受到越来越多关注(Molnar and England, 1990;Raymo and Ruddiman, 1992;Beaumont et al., 2001;Zeitler et al., 2001;Zhang et al., 2001;莫宣学,2019;Govin et al., 2020;Xu et al., 2020).喜马拉雅造山带东部端点东喜马拉雅构造结地区(图 1),因为强烈挤压造山作用、活跃地表作用,成为研究气候、剥蚀与构造相互作用理想野外实验室.部分研究认为东喜马拉雅构造结是河流剥蚀、冰川剥蚀等地表剥蚀作用,诱发快速地壳构造隆升典型区域(Zeitler et al., 2001, 2014;Tu et al., 2015).但也有研究认为构造活动主导东喜马拉雅构造结地质演化,快速地表剥蚀只是对构造隆升的被动响应(Wang et al., 2014;Bracciali et al., 2015;King et al., 2016;Yang et al., 2018).目前,关于地表剥蚀在东喜马拉雅构造结地质演化中所起作用的争论仍然比较激烈.
热年代学年龄反映岩石从地壳某特定温度面运移至地表的时间,是研究地表作用与地壳构造活动相互关系重要依据.东喜马拉雅构造结报道大量年轻热年代学年龄数据,是该区域剥蚀与构造相互关系研究的基础.目前对于东喜马拉雅构造结热年代学研究,大部分集中在其核心南迦巴瓦峰区域及其北侧、西侧318国道经过区域.对于东喜马拉雅构造结东侧雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段区域,由于道路、地形等原因,热年代学研究相对较少(Zeitler et al., 2014).为完善整个东喜马拉雅构造结及其周边区域热年代学研究,本文对采集自雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段10块基岩样品进行黑云母40Ar/39Ar定年,利用“Pecube”软件对年龄结果进行定量模拟计算.基于实测年龄和模拟计算结果,对该区域可能断裂活动特征及整个东喜马拉雅构造结地质演化过程进行讨论.
1. 研究背景
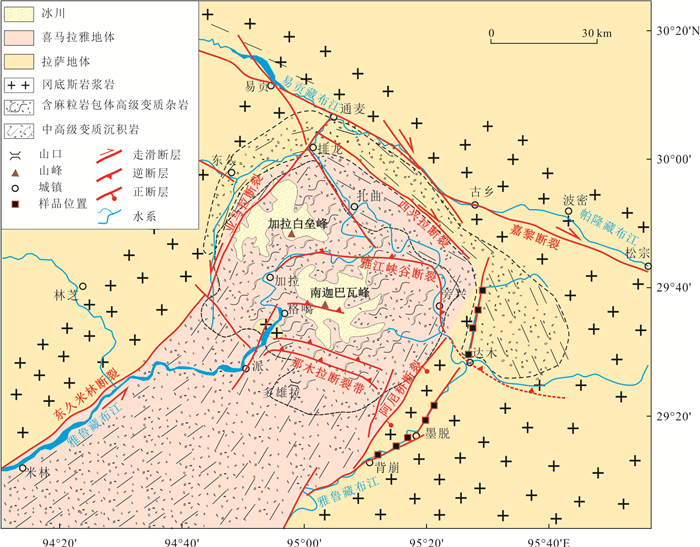
雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段位于东喜马拉雅构造结东部边界(图 1).东喜马拉雅构造结是喜马拉雅造山带挤压造山作用最强的区域之一.又因受到雅鲁藏布江大峡谷水汽通道作用影响,该区域同时具有海拔高、地貌面高差大、地表剥蚀强烈、新构造活动活跃以及地壳隆升快速等多种特征(Zeitler et al., 2001).
1.1 岩石组成
东喜马拉雅构造结及其周边区域主要由两个大地构造单元组成.其周边为拉萨地体,内部为喜马拉雅地体(图 1).拉萨地体主要包括元古代变质基底、古生代到中生代沉积盖层以及中生代到新生代侵位冈底斯岩浆岩带(Yin and Harrison, 2000).在东构造结周边主要出露冈底斯岩浆岩带(图 1).冈底斯岩浆岩带是一条由于新特提斯洋向北俯冲而形成的岛弧岩浆岩带(Yin and Harrison, 2000;Wen et al., 2008).
喜马拉雅地体是印度板块北部边缘.东喜马拉雅构造结内部喜马拉雅地体主要是一套经历绿片岩相到角闪岩相变质的沉积岩地层,其中岩石类型包括石榴黑云片岩、黑云绿帘片岩、矽线石石榴黑云片麻岩、黑云角闪斜长片麻岩以及黑云斜长角闪岩(章振根等,1992;Burg et al., 1998).这一套变质沉积岩中的继承锆石年龄分布在太古代到早古生代的广泛区间内,并且具有2 490 Ma,1 640 Ma,990 Ma和480 Ma四个年龄峰值,代表了印度大陆基底的结晶年龄(Zhang et al., 2012).东喜马拉雅构造结核心南迦巴瓦峰区域变质沉积岩中还出露含基性麻粒岩透镜体的高级变质杂岩体(图 1).该基性麻粒岩记录至少两次800 ℃左右变质作用:第一次变质压力较高为14~15 kbar,第二次压力为8~10 kbar(钟大赉和丁林,1995;丁林和钟大赉,1999).对该麻粒岩年代学研究表明,在40~11 Ma的时间段内,麻粒岩相变质作用在南迦巴瓦峰区域可能持续进行;大约11 Ma以来,该区域地壳经历快速剥露回返,使得麻粒岩相变质岩出露于地表(Burg et al., 1998;Ding et al., 2001;Xu et al., 2012;张泽明等,2019).南迦巴瓦峰区域还出露一套由变质沉积岩原地部分熔融产生的重熔花岗岩.部分熔融发生时间范围为14~3 Ma,其中在8 Ma左右部分熔融规模达到峰值(Burg et al., 1998;Booth et al., 2009;Tu et al., 2016).这一部分熔融事件是该区域快速地壳隆升剥露,而诱发的地壳减压部分熔融事件(Booth et al., 2009;Tu et al., 2016).较年轻的高级变质岩以及年轻重熔花岗岩的出露表明,南迦巴瓦峰区域经历强烈挤压造山作用,并且11~8 Ma以来经历快速地壳隆升剥露过程.
1.2 断裂构造
东喜马拉雅构造结主要以3条断裂为边界(图 1).西部边界是北东走向东久-米林断裂,该断裂近直立略向西倾,为韧性剪切带,剪切带中出露大量糜棱岩,糜棱岩中拖曳构造形迹反映其具有水平方向左旋走滑运动学特征(Burg et al., 1998;Ding et al., 2001;Zhang et al., 2004).东部边界为北东走向阿尼桥断裂,该断裂近直立略向东倾,矿物拉伸线理等证据表明该断裂以垂向运动为主,表现为正断性质,断层东盘相对下降,西盘相对上升(Burg et al., 1998;Ding et al., 2001;Zhang et al., 2004).北部边界为北西西-南东东走向嘉黎断裂,该断裂也是近直立具有水平方向上右旋走滑的运动特征(Burg et al., 1998;Ding et al., 2001;Zhang et al., 2004).阿尼桥断裂带早期走滑活动发生在23 Ma前后,后期正断活动发生在7~6 Ma;东久米林断裂走滑活动主要分为62~59、~23和~13 Ma三个时段(Zhang et al., 2004);嘉黎断裂带走滑活动时限为18~12 Ma(Lee et al., 2003).在东喜马拉雅构造结内部发育一系列北西、北西西走向脆韧性逆冲断裂带,由南至北依次为那木拉断裂带、南迦巴瓦峰断裂带、雅江峡谷断裂带(图 1)(Ding et al., 2001).大量北东和北西走向脆性高角度正断层在南迦巴瓦峰区域广泛发育.这些正断层从8~7 Ma开始活动,靠近南迦巴瓦峰的一盘相对升高.东喜马拉雅构造结地区断裂构造,早期以走滑断层活动为主,晚期(约8 Ma以来)以正断层活动为主,并可能一直持续活动到现在.
1.3 地貌形态与地表作用
东喜马拉雅构造结最显著地貌特征就是雅鲁藏布江的强烈下切以及马蹄型大拐弯.在东喜马拉雅构造结西侧,雅鲁藏布江为正东流向,并且具有宽阔“U”型河谷和低河流梯度的特征;在东侧,雅鲁藏布江开始强烈下切,并且流向急剧向南偏转,河流呈现狭窄“Ⅴ”型河谷形态并具有较大的河流梯度,形成著名的雅鲁藏布江大峡谷.东喜马拉雅构造结还是藏东南地区地貌海拔高差最大的区域,最大海拔高差出现在南迦巴瓦峰区域,约12 km水平距离内地貌海拔高差达到约5 km.由于印度洋季风影响及雅江峡谷“水汽通道”作用,东喜马拉雅构造结是世界上降雨量最大的区域之一,最大年降水量可达4 000 mm以上,降雨季节性强,降雨强度达0.02 mm/hr(Anders et al., 2006).受印度洋季风影响,东喜马拉雅构造结发育独特海洋性冰川.海洋性冰川是海洋性气候条件影响下发育的冰川,由于气候湿润、降雪量大且雪线较低,海洋性冰川的收入多支出也多,活动性强.东喜马拉雅构造结内海洋性冰川主要在南迦巴瓦峰区域发育(施雅风等,2006).
1.4 热年代学研究
东喜马拉雅构造结已报道热年代学研究方法主要包括40Ar/39Ar法、裂变径迹法以及(U⁃Th)/He方法.空间上,东喜马拉雅构造结内部热年代学年龄范围为0.5~8.0 Ma,这一年龄范围明显年轻于其周边地区以及喜马拉雅造山带其他区域.根据这一年轻热年代学年龄范围计算出东喜马拉雅构造结内部,地壳隆升剥露速率为4~5 km/Ma(Burg et al., 1998;Ding et al., 2001;Seward and Burg, 2008;Stewart et al., 2008;Zeitler et al., 2014;Gong et al., 2015;Tu et al., 2015).东喜马拉雅构造结内部热年代学年龄呈现一个越靠近南迦巴瓦峰地区年龄越年轻大致趋势(Gong et al., 2015).这些热年代学年龄表明东构造结的地表剥蚀速率要明显高于其周边区域,并且南迦巴瓦峰区域剥蚀速率最快.时间上,东喜马拉雅构造结内部0.5~8.0 Ma的热年代学年龄范围表明东喜马拉雅构造结内部可能从约8 Ma开始快速冷却.
2. 样品采集
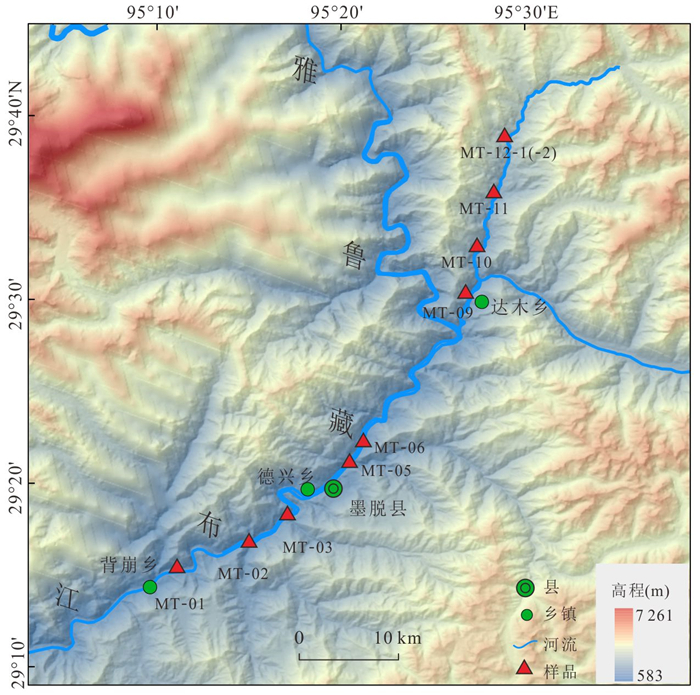
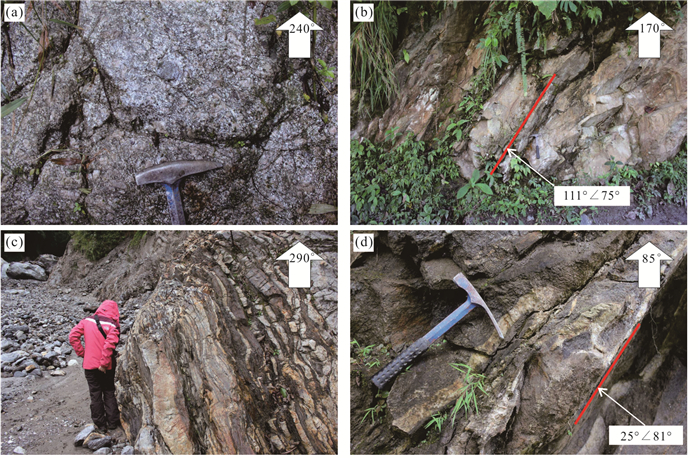
笔者在雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱县背崩乡至达木乡段河谷,以及达木乡以北支流河谷采集10块岩石样品(图 2).采集样品位置垂向海拔高度范围为681~1 859 m,水平距离约为60 km.各样品采样位置、经纬度及岩性见表 1.10块样品中MT 12⁃1和MT⁃12⁃2是重复验证样品,来自同一处岩石露头.采集自南段雅鲁藏布江主河段河谷的5块样品都为花岗岩或花岗闪长岩,属于中生代晚期至新生代早期侵入的冈底斯岩浆岩.岩浆岩变形较弱,部分发育北北东(约20°)走向近直立脆性破裂(图 3a和3b).采集自北段雅鲁藏布江支流河谷的5块样品中1块为闪长岩,4块为片麻岩,属于拉萨地体元古代变质结晶基底.片麻理产状近直立,主要为北西西(约290°)走向(图 3c),部分发育北西西(约295°)走向近直立脆性破裂(图 3d).
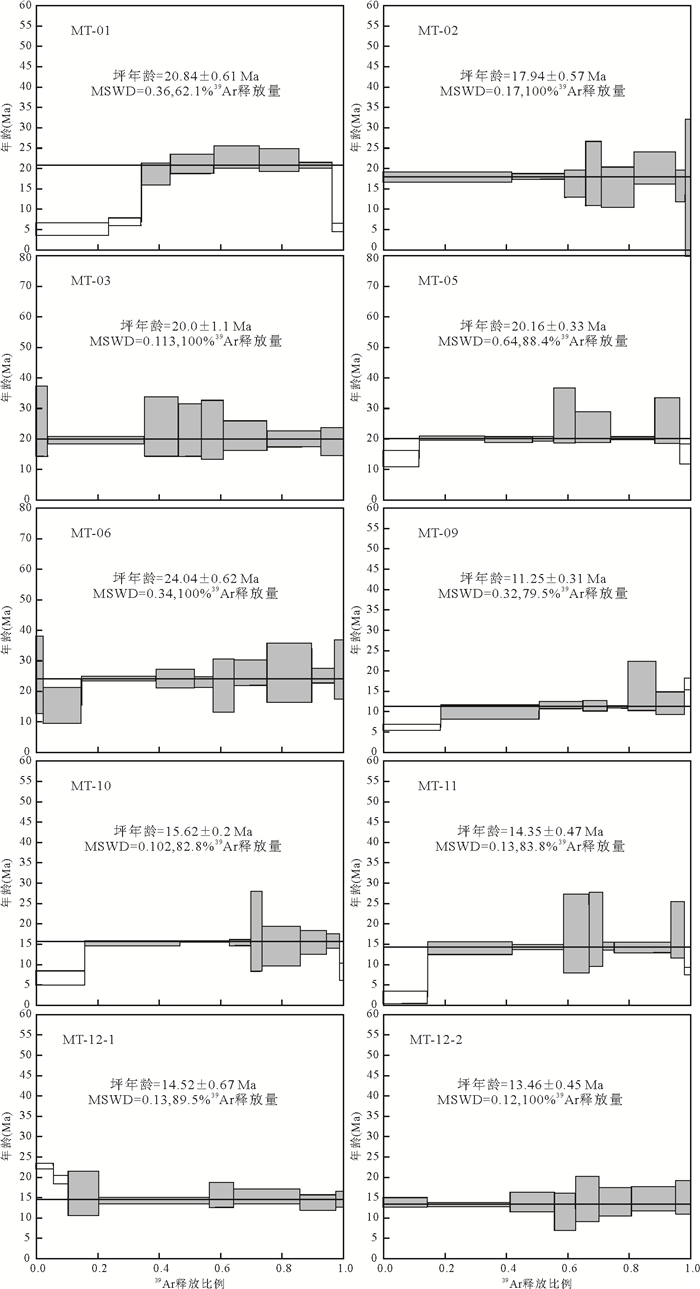
表 1 样品信息及年龄值Table Supplementary Table Sample information and chronology data样品名 经度 纬度 海拔(m) 岩性 黑云母40Ar/39Ar
坪年龄(Ma)2σ误差(Ma) MSWD值 MT-01 E95.186° N29.254° 681 黑云角闪花岗岩 20.84 0.61 0.36 MT-02 E95.251° N29.278° 727 黑云角闪花岗
闪长岩17.94 0.57 0.17 MT-03 E95.286° N29.302° 764 黑云角闪花岗
闪长岩20.00 1.10 0.11 MT-05 E95.343° N29.351° 750 黑云母闪长岩 20.16 0.33 0.64 MT-06 E95.355° N29.369° 790 花岗闪长岩 24.04 0.62 0.34 MT-09 E95.448° N29.502° 957 片麻岩 11.25 0.31 0.32 MT-10 E95.458° N29.545° 1 177 片麻岩 15.62 0.20 0.10 MT-11 E95.473° N29.594° 1 440 闪长岩 14.35 0.47 0.13 MT-12-1 E95.483° N29.645° 1 859 片麻岩 14.52 0.67 0.13 MT-12-2 E95.483° N29.645° 1 859 片麻岩 13.46 0.45 0.12 3. 测试方法
本文对采集的10件岩石样品进行黑云母40Ar/39Ar测年,所有样品年龄测试都是笔者在北京大学造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室K⁃Ar、Ar/Ar年代学实验室进行.样品黑云母矿物颗粒利用磁选法进行挑选.黑云母颗粒在双目显微镜下人工挑纯至纯度99%以上.140~250 μm的矿物颗粒在去离子水中利用超声波进行清洗,并在干燥箱中进行干燥.待测矿物颗粒和标准样品(Bern4⁃Ms)以及纯物质K2SO4、CaF2、KCl(用于K、Ca、Cl同位素监测),被包裹在铝箔中并集中放置在一个密封石英瓶中.包装好的样品在中国原子能研究院(北京)的49⁃2核反应堆H8孔道进行24 h核辐照.核辐照参数(J值)利用辐照国际标准样品Bern4⁃Ms氩同位素含量进行计算,该标准样品40Ar/39Ar年龄为18.62±0.06 Ma(Baksi et al., 1996).
核辐照后样品在一双层坩埚可控温真空加热系统中进行加热.每个样品包装重量大约为70 mg.样品首先在800 ℃加热30 min,以去除矿物表面吸附气体,这一加热步骤释放气体不进行测量.然后,对样品进行温度在900~1 500 ℃范围内由低到高多阶段加热.每一加热阶段对样品加热15 min.加热产生气体利用Zr⁃Al吸气剂进行纯化.纯化后气体利用RGA10质谱仪进行Ar同位素测量.每一步气体进行9个循环测量.每四步加热阶段测量一次系统本底.所有测试工作由电脑自动控制完成.计算中40K衰变常数为5.543×10-10 a-1(Steiger and Jäger,1977).
4. 年龄结果
10件样品测试黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄结果如图 4所示.所有样品都得出形态较好阶步升温年龄坪.绝大多数样品主要释气温阶放射性成因氩比例,达到80%甚至90%以上,阶步升温坪年龄能较准确代表矿物冷却年龄.两个重复验证样品年龄结果在误差范围内相一致,证明年龄测试的可重复性.样品年龄范围为11.25± 0.31~24.04± 0.62 Ma(表 1,图 4).年龄结果呈现南北两段分布特征.南段雅鲁藏布江主河道5块样品年龄相对较老,为17.94~24.04 Ma;北段雅鲁藏布江支流5块样品年龄相对较年轻,为11.25~15.62 Ma.
5. 年龄模拟计算解译
黑云母40Ar/39Ar法是热年代学研究方法的一种,其得出的年龄值,代表样品从黑云母40Ar/39Ar封闭温度(约330 ℃)(Harrison et al., 1985)冷却至地表温度所经历时间.热年代学年龄受到岩石隆升速率、地温梯度、地表面形态等多种因素影响.为准确地解译热年代学年龄蕴含地质信息,笔者利用“Pecube”软件对所获得黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄进行定量解译.“Pecube”是一个对热年代学年龄进行定量解译的热动力学模拟计算软件(Braun et al., 2012).该软件需要用户输入岩石热容值、导热率、运动速率等参数并设定温度场边界值,然后根据三维热传导公式求解出相应地壳空间温度场分布及其随时间变化.该软件求解在一个三维空间有限元网格中进行.计算出地壳温度场后,根据岩石经历温度历史,利用热扩散方程计算出各种热年代学年龄值.用户可以把模拟计算年龄与实测年龄进行对比,然后相应修改模拟参数,直到最终能够获得最佳模拟参数使得模拟年龄与实测年龄匹配度最高.这些最佳模拟参数就是热年代学年龄所代表真实地质信息.“Pecube”软件提出后被广泛用于对热年代学年龄进行定量解译.
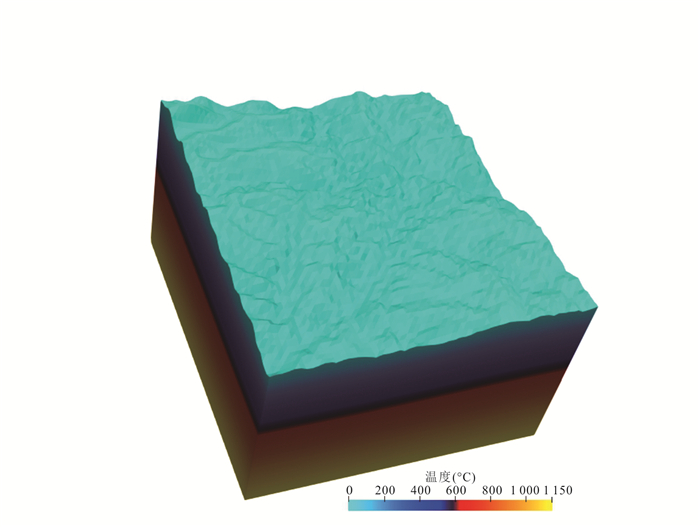
笔者利用“Pecube”软件对热年代学数据进行了8次模拟.8次模拟中大部分模拟参数完全一致.地温场特征方面,Craw et al.(2005)利用流体包裹体中CO2⁃H2O相平衡计算方法计算出,东喜马拉雅构造结及周边区域现今300 ℃地温等温面大致位于海平面附近.根据这一计算结果,模型底部(海平面以下25 km)温度被固定为1 150 ℃,模型顶面温度固定为0 ℃,岩石产热率被固定为6.5 ℃/Ma,岩石热扩散系数被设定为25 km2/Ma.模拟过程模拟40 Ma以前到现在整个过程.模拟过程中使用的地表面形态特征来自90 m精度数字高程数据,地表面范围为东经95.1°~95.6°,北纬29.2°~29.7°.整个模拟过程地表面形态固定不变.模拟过程都在61×61×50三维有限元网格中进行(图 5).水平方向上,有限单元网格分辨率是900 m,即单个有限元单元宽度代表实际水平方向上900 m距离;垂直方向上分辨率为500 m.模拟过程中唯一变化模拟参数是地壳岩石隆升剥露速率(VE),这一参数代表岩石垂向运移速率.模拟过程中VE变化范围为0.2~0.55 km/Ma.
模拟结果见表 2和图 6.根据模拟年龄与实测年龄吻合程度,之后再进行多次模拟计算过程,选取出每个样品所对应最佳隆升剥露速率(表 2),即该隆升剥露速率计算出模拟年龄与样品实测年龄吻合最好.南段雅鲁藏布江主河道5个样品对应最佳隆升剥露速率较低,为0.25~0.33 km/Ma,北段雅鲁藏布江支流5块样品对应最佳隆升剥露速率相对较高,为0.40~0.51 km/Ma(图 6).
表 2 样品实测年龄与模拟计算年龄Table Supplementary Table Samples' observed ages and predicted ages样品名 实测年龄
(Ma)模拟年龄(Ma) 最佳隆升
剥露速率
(km/Ma)VE=0.2
km/MaVE=0.25
km/MaVE=0.3
km/MaVE=0.35
km/MaVE=0.4
km/MaVE=0.45
km/MaVE=0.5
km/MaVE=0.55
km/MaMT-01 20.84 31.57 25.05 20.66 17.51 15.14 13.28 11.80 10.58 0.30 MT-02 17.94 30.29 24.02 19.81 16.78 14.49 12.71 11.28 10.10 0.33 MT-03 20 30.24 23.98 19.77 16.75 14.47 12.69 11.26 10.08 0.30 MT-05 20.16 30.27 24.01 19.79 16.76 14.48 12.70 11.27 10.09 0.30 MT-06 24.04 30.90 24.51 20.21 17.12 14.80 12.98 11.52 10.32 0.25 MT-09 11.25 30.92 24.52 20.22 17.13 14.80 12.98 11.52 10.32 0.51 MT-10 15.62 31.16 24.70 20.37 17.25 14.90 13.06 11.59 10.38 0.40 MT-11 14.35 31.64 25.08 20.67 17.50 15.11 13.24 11.75 10.52 0.42 MT-12-1 14.52 33.61 26.65 21.97 18.60 16.07 14.09 12.50 11.20 0.45 MT-12-2 13.46 33.61 26.65 21.97 18.60 16.07 14.09 12.50 11.20 0.45 6. 讨论
6.1 热年代学年龄代表意义
本文样品采集剖面,南段为花岗岩、花岗闪长岩,属于冈底斯岩浆岩.冈底斯岩浆岩岩浆侵入活动主要发生在中生代晚期至新生代早期(Yin and Harrison, 2000;Wen et al., 2008).北段主要为片麻岩,属于拉萨地体元古代变质结晶基底,其高级变质作用主要发生在元古代(Yin and Harrison, 2000;Zeitler et al., 2014).样品采集剖面南北段晚期构造变形情况基本一致.在花岗岩或片麻岩中主要发育北北东或北西西走向近直立脆性破裂面(图 3b,3d).本文测试获得黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄为新生代晚期,小于岩浆岩侵入年龄以及变质岩变质年龄.这些黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄应该属于拉萨地体隆升剥露年龄.代表被冈底斯岩浆岩侵入后的拉萨地体古老变质基底,新生代晚期持续隆升剥露过程.
6.2 东喜马拉雅构造结内外年代学差异
本文研究区域,雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段,以阿尼桥断裂为界,与西侧的东喜马拉雅构造结核心南迦巴瓦峰区域相分隔.雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段样品黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄范围为11~24 Ma,大于研究背景中介绍东喜马拉雅构造结内部0.5~8.0 Ma年龄范围;雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段平均地壳隆升剥露速率为0.25~0.51 km/Ma,小于东喜马拉雅构造结内部4~5 km/Ma平均隆升剥露速率.这一特征与前人观点基本一致,即快速地壳隆升剥露集中发生在阿尼桥断裂以西东喜马拉雅构造结核心区域;雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段地壳隆升活动相对较弱,相对较稳定.
6.3 逆冲断层活动
雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄及其模拟计算隆升剥露速率存在明显南北分段特征.大致以达木乡为界,南段主河道区域,年龄为18~24 Ma,隆升剥露速率为0.25~0.33 km/Ma;北段支流河道区域,年龄为11~15 Ma,隆升剥露速率为0.40~0.51 km/Ma.北段平均地壳隆升速率比南段高出约0.2 km/Ma(图 6).这一由南向北地壳隆升速率的突变具有什么地质意义?
如上文研究背景所述,东喜马拉雅构造结内部存在一系列北西、北西西走向高角度逆冲断层,包括那木拉逆冲断层、雅江峡谷逆冲断层等(图 1).这一系列逆冲断层运动特征都是断层北盘逆冲到南盘之上(Burg et al., 1998;Ding et al., 2001;Zhang et al., 2004;Zeitler et al., 2014).这些逆冲断层共同组成一个大型逆冲推覆叠瓦构造,实现印度板块喜马拉雅地体对欧亚板块拉萨地体的俯冲(Ding et al., 2001).之前所有研究都认为这些北西、北西西走向逆冲断层只在东喜马拉雅构结内部发育,在东喜马拉雅构结东侧,雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱地区这一系列逆冲断层不发育.而本文揭示的雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段南北地壳隆升速率差异,与该系列逆冲断层运动特征相吻合.断层北盘仰冲到南盘之上,北盘相对向上运移,北盘地壳垂向剥露隆升速率更大.隆升剥露速率突变的边界达木乡,正好位于雅江峡谷逆冲断层向东延长线区域.因此,笔者推测在达木乡区域,可能存在一条北西西走向略向北倾逆冲断层.该断层是雅江峡谷逆冲断层向东延伸(图 1).正因为这一逆冲断层的活动,断层南北两侧地壳隆升剥露速率和热年代学年龄存在差异.
6.4 东喜马拉雅构造结演化
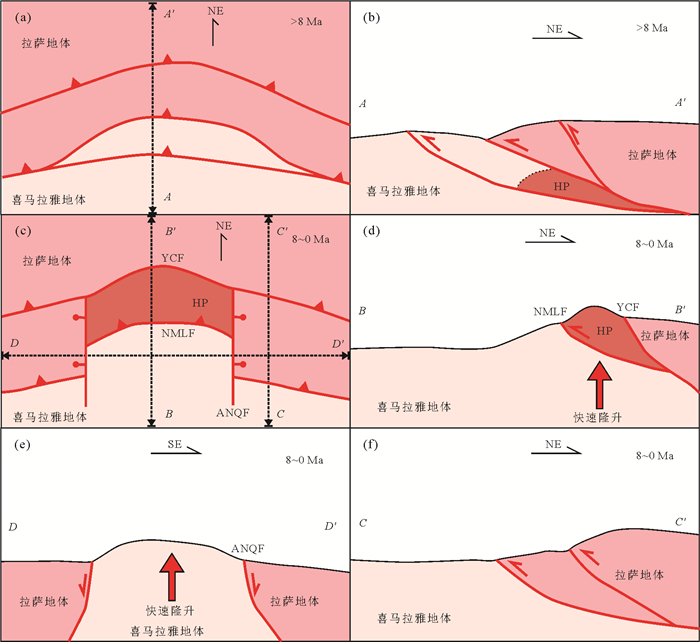
目前,关于东喜马拉雅构结地区构造演化模式,主要有两种观点:第一种是水平挤入模式(Burg et al., 1998;Zhang et al., 2004;Seward and Burg, 2008;King et al., 2016),认为喜马拉雅地体通过阿尼桥断裂和东久米林两条边界断裂水平走滑运动,挤入拉萨地体,在挤压碰撞前缘形成一系列北西、北西西走向逆冲断裂;第二种是俯冲后褶皱(剥露回返)模式(Xu et al., 2012),认为喜马拉雅地体先俯冲到拉萨地体之下,发育一系列北西、北西西走向逆冲断裂.由于压力增加,深部形成高压麻粒岩.后期因为褶皱作用或是地表剥蚀作用影响,东喜马拉雅构结内部地壳快速隆升剥露,深部含高压麻粒岩的喜马拉雅地体出露于地表,并且压力快速降低导致形成年轻重熔花岗岩.Ding et al.(2001)认为上述两种模型是东喜马拉雅构结实际地质演化过程两个端元模型.
本文通过热年代学数据计算地壳隆升速率特征表明,雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段可能也存在与东喜马拉雅构结内部相同的北西、北西西走向逆冲断裂活动.但是雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段平均地壳隆升剥露速率又明显小于东喜马拉雅构结内部.这一特征与上述第二种演化模式更加吻合.早期(约8 Ma以前)喜马拉雅地体持续俯冲到拉萨地体之下,北西、北西西走向逆冲断裂活动在东喜马拉雅构造结内部及其东侧区域都在持续进行(图 7a和7b).晚期(约8 Ma以来)东喜马拉雅构结内部发生地壳快速隆升剥露,隆升剥露速率远大于其东侧雅鲁藏布江下游区域,二者之间通过阿尼桥断裂正断层活动进行调节(图 7c~7f).
关于东喜马拉雅构造结约8 Ma以来快速隆升剥露原因,已有研究大致可以分为两类观点.一类观点认为河流下切侵蚀、冰川剥蚀等地表作用,诱发东喜马拉雅构造结快速隆升剥露.Zeitler et al.(2001)基于对东、西构造结研究提出“构造瘤”模式.该模式认为在东、西喜马拉雅构造结地区,大型河流强烈下切导致快速地表剥蚀作用,使得地壳内应力快速降低,引起地壳深部热的、偏塑性物质向上运移,最终导致高级变质岩、深熔花岗岩的出露及年轻热年代学年龄.Zeitler et al.(2014)根据喜马拉雅构造结热年代学年龄综合研究进一步认为,东喜马拉雅构造结地区雅鲁藏布江10 Ma左右发生的河流袭夺事件是雅鲁藏布江快速下切、地壳快速隆升剥露“构造瘤”模式的触发因素.Tu et al.(2015)根据东喜马拉雅构造结核心南迦巴瓦峰地区剖面热年代学研究结果认为,强烈冰川剥蚀作用可能改变地壳浅部应力状态,最终诱发南迦巴瓦峰地区快速隆升剥露.另一类观点认为喜马拉雅地体挤入,产生一系列逆冲断层等构造活动,使得地壳隆升;即构造活动主导东喜马拉雅构造结演化过程(Burg et al., 1998;Zhang et al., 2004;Wang et al., 2014;King et al., 2016;Yang et al., 2018).
本文研究表明,与喜马拉雅地体向拉萨地体俯冲过程相关的逆冲断层活动,不仅在阿尼桥断层西侧,东喜马拉雅构造结内部区域发育;在阿尼桥断裂东侧雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段也可能发育.而阿尼桥断裂西部地壳隆升剥露速率,要远高于东侧.因此,东喜马拉雅构造结快速地壳隆升剥露过程,应该不是完全由逆冲断层活动所主导.河流袭夺、冰川剥蚀等地表作用应该也是诱发因素之一.在局部区域(如南迦巴瓦峰区域),地表剥蚀作用还可能是诱发快速地壳隆升主要因素.
7. 结论
(1)东喜马拉雅构造结东侧雅鲁藏布江墨脱段,黑云母40Ar/39Ar年龄范围为11.25~24.04 Ma,模拟计算获得该区域地壳隆升剥露速率范围为0.25~0.51 km/Ma.(2)这一隆升剥露速率明显小于东喜马拉雅构造结内部区域.与东喜马拉雅构造结内部相比,雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段为一地壳隆升剥露活动相对较弱区域.(3)雅鲁藏布江墨脱段地壳隆升剥露速率存在明显南北差异,北段隆升剥露速率高出约0.2 km/Ma.可能是一北西走向逆冲断层活动导致上述隆升剥露速率差异.该逆冲断层可能是东喜马拉雅构造结内部,雅江峡谷逆冲断层向东延伸部分.与喜马拉雅地体向拉萨地体俯冲过程相关的逆冲断层活动,不仅在东喜马拉雅构造结内部区域发育;在其东侧雅鲁藏布江下游墨脱段也可能发育.
致谢: 感谢审稿人对本文提出的宝贵意见和建议. -
表 1 样品信息及年龄值
Table 1. Sample information and chronology data
样品名 经度 纬度 海拔(m) 岩性 黑云母40Ar/39Ar
坪年龄(Ma)2σ误差(Ma) MSWD值 MT-01 E95.186° N29.254° 681 黑云角闪花岗岩 20.84 0.61 0.36 MT-02 E95.251° N29.278° 727 黑云角闪花岗
闪长岩17.94 0.57 0.17 MT-03 E95.286° N29.302° 764 黑云角闪花岗
闪长岩20.00 1.10 0.11 MT-05 E95.343° N29.351° 750 黑云母闪长岩 20.16 0.33 0.64 MT-06 E95.355° N29.369° 790 花岗闪长岩 24.04 0.62 0.34 MT-09 E95.448° N29.502° 957 片麻岩 11.25 0.31 0.32 MT-10 E95.458° N29.545° 1 177 片麻岩 15.62 0.20 0.10 MT-11 E95.473° N29.594° 1 440 闪长岩 14.35 0.47 0.13 MT-12-1 E95.483° N29.645° 1 859 片麻岩 14.52 0.67 0.13 MT-12-2 E95.483° N29.645° 1 859 片麻岩 13.46 0.45 0.12 表 2 样品实测年龄与模拟计算年龄
Table 2. Samples' observed ages and predicted ages
样品名 实测年龄
(Ma)模拟年龄(Ma) 最佳隆升
剥露速率
(km/Ma)VE=0.2
km/MaVE=0.25
km/MaVE=0.3
km/MaVE=0.35
km/MaVE=0.4
km/MaVE=0.45
km/MaVE=0.5
km/MaVE=0.55
km/MaMT-01 20.84 31.57 25.05 20.66 17.51 15.14 13.28 11.80 10.58 0.30 MT-02 17.94 30.29 24.02 19.81 16.78 14.49 12.71 11.28 10.10 0.33 MT-03 20 30.24 23.98 19.77 16.75 14.47 12.69 11.26 10.08 0.30 MT-05 20.16 30.27 24.01 19.79 16.76 14.48 12.70 11.27 10.09 0.30 MT-06 24.04 30.90 24.51 20.21 17.12 14.80 12.98 11.52 10.32 0.25 MT-09 11.25 30.92 24.52 20.22 17.13 14.80 12.98 11.52 10.32 0.51 MT-10 15.62 31.16 24.70 20.37 17.25 14.90 13.06 11.59 10.38 0.40 MT-11 14.35 31.64 25.08 20.67 17.50 15.11 13.24 11.75 10.52 0.42 MT-12-1 14.52 33.61 26.65 21.97 18.60 16.07 14.09 12.50 11.20 0.45 MT-12-2 13.46 33.61 26.65 21.97 18.60 16.07 14.09 12.50 11.20 0.45 -
Anders, A.M., Roe, G.H., Hallet, B., et al., 2006. Spatial Patterns of Precipitation and Topography in the Himalaya. Special Papers-Geological Society of America, 398: 39-54. https://doi.org/10.1130/2006.2398(03) Baksi, A.K., Archibald, D.A., Farrar, E., 1996. Intercalibration of 40Ar/39Ar Dating Standards. Chemical Geology, 129(3-4): 307-324. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(95)00154-9 Beaumont, C., Jamieson, R.A., Nguyen, M.H., et al., 2001. Himalayan Tectonics Explained by Extrusion of a Low-Viscosity Crustal Channel Coupled to Focused Surface Denudation. Nature, 414: 738-742. https://doi.org/10.1038/414738a Booth, A.L., Chamberlain, C.P., Kidd, W.S.F., et al., 2009. Constraints on the Metamorphic Evolution of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis from Geochronologic and Petrologic Studies of Namche Barwa. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 121(3-4): 385-407. https://doi.org/10.1130/b26041.1 Bracciali, L., Najman, Y., Parrish, R.R., et al., 2015. The Brahmaputra Tale of Tectonics and Erosion: Early Miocene River Capture in the Eastern Himalaya. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 415: 25-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2015.01.022 Braun, J., van der Beek, P., Valla, P., et al., 2012. Quantifying Rates of Landscape Evolution and Tectonic Processes by Thermochronology and Numerical Modeling of Crustal Heat Transport Using PECUBE. Tectonophysics, 524-525: 1-28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2011.12.035 Burg, J.P., Nievergelt, P., Oberli, F., et al., 1998. The Namche Barwa Syntaxis: Evidence for Exhumation Related to Compressional Crustal Folding. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 16(2-3): 239-252. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0743-9547(98)00002-6 Craw, D., Koons, P.O., Zeitler, P.K., et al., 2005. Fluid Evolution and Thermal Structure in the Rapidly Exhuming Gneiss Complex of Namche Barwa-Gyala Peri, Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 23(9): 829-845. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1314.2005.00612.x Ding, L., Zhong, D.L., 1999. High Pressure Granulite Facies Metamorphism Characteristics and Tectonic Geological Significance in the Namche Barwa Region Tibet. Science in China (Series D), 29(5): 385-397(in Chinese). Ding, L., Zhong, D.L., Yin, A., et al., 2001. Cenozoic Structural and Metamorphic Evolution of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis (Namche Barwa). Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 192(3): 423-438. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(01)00463-0 Gong, J.F., Ji, J.Q., Zhou, J., et al., 2015. Late Miocene Thermal Evolution of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis as Constrained by Biotite 40Ar/39Ar Thermochronology. The Journal of Geology, 123(4): 369-384. https://doi.org/10.1086/682951 Govin, G., van der Beek, P., Najman, Y., et al., 2020. Early Onset and Late Acceleration of Rapid Exhumation in the Namche Barwa Syntaxis, Eastern Himalaya. Geology, 48(12): 1139-1143. https://doi.org/10.1130/g47720.1 Harrison, T.M., Duncan, I., McDougall, I., 1985. Diffusion of 40Ar in Biotite: Temperature, Pressure and Compositional Effects. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 49(11): 2461-2468. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-7037(85)90246-7 King, G.E., Herman, F., Guralnik, B., 2016. Northward Migration of the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis Revealed by OSL Thermochronometry. Science, 353(6301): 800-804. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf2637 Lee, H.Y., Chung, S.L., Wang, J.R., et al., 2003. Miocene Jiali Faulting and Its Implications for Tibetan Tectonic Evolution. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 205(3-4): 185-194. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0012-821x(02)01040-3 Molnar, P., England, P., 1990. Late Cenozoic Uplift of Mountain Ranges and Global Climate Change: Chicken or Egg? Nature, 346: 29-34. https://doi.org/10.1038/346029a0 Mo, X.X., 2019. Magmatism and Deep Geological Process. Earth Science, 44(5): 1487-1493(in Chinese with English abatract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2019.972 Raymo, M.E., Ruddiman, W.F., 1992. Tectonic Forcing of Late Cenozoic Climate. Nature, 359: 117-122. https://doi.org/10.1038/359117a0 Seward, D., Burg, J.P., 2008. Growth of the Namche Barwa Syntaxis and Associated Evolution of the Tsangpo Gorge: Constraints from Structural and Thermochronological Data. Tectonophysics, 451(1-4): 282-289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2007.11.057 Shi, Y.F., Zheng, B.X., Su, Z., 2006. Glaciations, Glacial and Interglacial Cycles and Environment Changes in Quaternary. In: Shi, Y.F., Cui, Z.J., Su, Z., eds., The Quaternary Glaciations and Environmental Variations in China. Hebei Science and Technology Publishing House, Shijiazhuang(in Chinese). Steiger, R.H., Jäger, E., 1977. Subcommission on Geochronology: Convention on the Use of Decay Constants in Geo- and Cosmochronology. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 36(3): 359-362. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821s(77)90060-7 Stewart, R.J., Hallet, B., Zeitler, P.K., et al., 2008. Brahmaputra Sediment Flux Dominated by Highly Localized Rapid Erosion from the Easternmost Himalaya. Geology, 36(9): 711. https://doi.org/10.1130/g24890a.1 Tu, J.Y., Ji, J.Q., Gong, J.F., et al., 2016. Zircon U-Pb Dating Constraints on the Crustal Melting Event around 8 Ma in the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis. International Geology Review, 58(1): 58-70. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2015.1056255 Tu, J.Y., Ji, J.Q., Sun, D.X., et al., 2015. Thermal Structure, Rock Exhumation, and Glacial Erosion of the Namche Barwa Peak, Constraints from Thermochronological Data. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 105: 223-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.03.035 Wang, P., Scherler, D., Liu, Z.J., et al., 2014. Tectonic Control of Yarlung Tsangpo Gorge Revealed by a Buried Canyon in Southern Tibet. Science, 346(6212): 978-981. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1259041 Wen, D.R., Liu, D.Y., Chung, S.L., et al., 2008. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb Ages of the Gangdese Batholith and Implications for Neotethyan Subduction in Southern Tibet. Chemical Geology, 252(3-4): 191-201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.03.003 Xu, Q.Q., Ji, J.Q., Zhong, D.L., et al., 2020. Post-Glacial Entrenchment and Knickpoint Migration of the Yarlung Tsangpo Gorge, Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 195: 104337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104337 Xu, Z.Q., Ji, S.C., Cai, Z.H., et al., 2012. Kinematics and Dynamics of the Namche Barwa Syntaxis, Eastern Himalaya: Constraints from Deformation, Fabrics and Geochronology. Gondwana Research, 21(1): 19-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2011.06.010 Yang, R., Herman, F., Fellin, M.G., et al., 2018. Exhumation and Topographic Evolution of the Namche Barwa Syntaxis, Eastern Himalaya. Tectonophysics, 722: 43-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2017.10.026 Yin, A., Harrison, T.M., 2000. Geologic Evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28(1): 211-280. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211 Zeitler, P.K., Meltzer, A.S., Brown, L., et al., 2014. Tectonics and Topographic Evolution of Namche Barwa and the Easternmost Lhasa Block, Tibet. Geological Society of America Special Papers, 507(23). https://doi.org/10.1130/2014.2507(02) Zeitler, P.K., Meltzer, A.S., Koons, P.O., et al., 2001. Erosion, Himalayan Geodynamics, and the Geomorphology of Metamorphism. GSA Today, 11(1): 4-9. doi: 10.1130/1052-5173(2001)011<0004:EHGATG>2.0.CO;2 Zhang, J.J., Ji, J.Q., Zhong, D.L., et al., 2004. Structural Pattern of Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis in Namjagbarwa and Its Formation Process. Science in China: Earth Sciences, 47(2): 138-150. https://doi.org/10.1360/02yd0042 Zhang, P.Z., Molnar, P., Downs, W.R., 2001. Increased Sedimentation Rates and Grain Sizes 2-4 Myr ago Due to the Influence of Climate Change on Erosion Rates. Nature, 410: 891-897. https://doi.org/10.1038/35073504 Zhang, Z.M., Dong, X., Santosh, M., et al., 2012. Petrology and Geochronology of the Namche Barwa Complex in the Eastern Himalayan Syntaxis, Tibet: Constraints on the Origin and Evolution of the North-Eastern Margin of the Indian Craton. Gondwana Research, 21(1): 123-137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2011.02.002 Zhang, Z.G., Liu, Y.H., Wang, T.W., et al., 1992. Geology of the Namche Barwa Region. Science Press, Beijing(in Chinese). Zhang, Z.M., Ding, H.X., Dong, X., et al., 2019. Two Contrasting Eclogite Types in the Himalayan Orogen and Differential Subduction of Indian Continent. Earth Science, 44(5): 1602-1619(in Chinese with English abatract). Zhong, D.L., Ding, L., 1995. High Pressure Granulite Found in the Namche Barwa Region Tibet. Chinese Science Bulletin, 40(14): 1343(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1995-40-14-1343 丁林, 钟大赉, 1999. 西藏南迦巴瓦峰地区高压麻粒岩相变质作用特征及其构造地质意义. 中国科学(D辑), 29(5): 385-397. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199905000.htm 莫宣学, 2019. 岩浆作用与地球深部过程. 地球科学, 44(5): 1487-1493. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.972 施雅风, 郑本兴, 苏珍, 2006. 第四纪冰川、冰期间冰期旋回与环境变化. 见: 施雅风, 崔之久, 苏珍, 编. 中国第四纪冰川与环境变化. 石家庄: 河北科学技术出版社. 章振根, 刘玉海, 王天武, 等, 1992. 南迦巴瓦峰地区地质. 北京: 科学出版社. 张泽明, 丁慧霞, 董昕, 等, 2019. 喜马拉雅造山带两种不同类型榴辉岩与印度大陆差异性俯冲. 地球科学, 44(5): 1602-1619. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.040 钟大赉, 丁林, 1995. 西藏南迦巴瓦峰地区发现高压麻粒岩. 科学通报, 40(14): 1343. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1995.14.029 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 杜国梁,邹玲,杨志华,孙东彦,谷丽莹. 雅鲁藏布江大拐弯地区滑坡发育分布特征及其对地貌演化的响应. 地质学报. 2024(10): 3062-3076 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-











 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:

 百度学术
百度学术







