Late Pleistocene Paleoseismic Events Recorded by Glacial Erosive Lake in the Litang Plateau, Western Sichuan
-
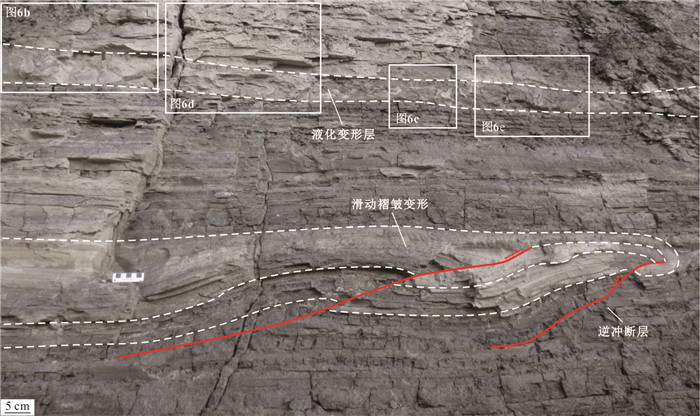
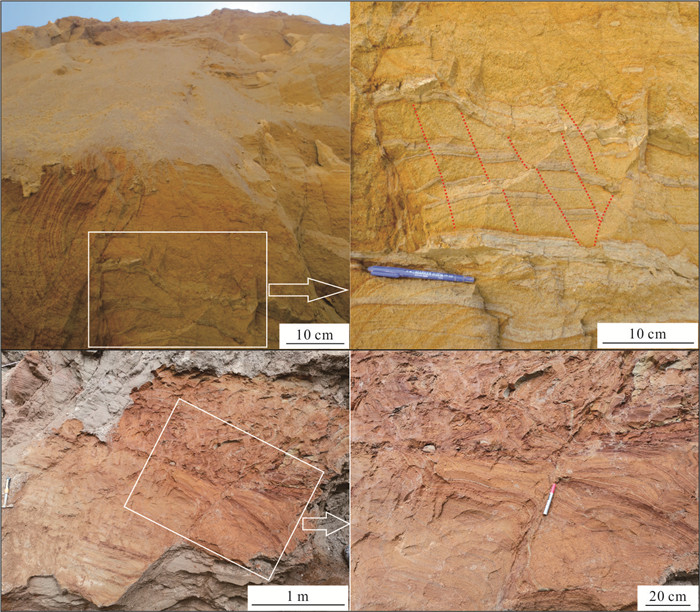
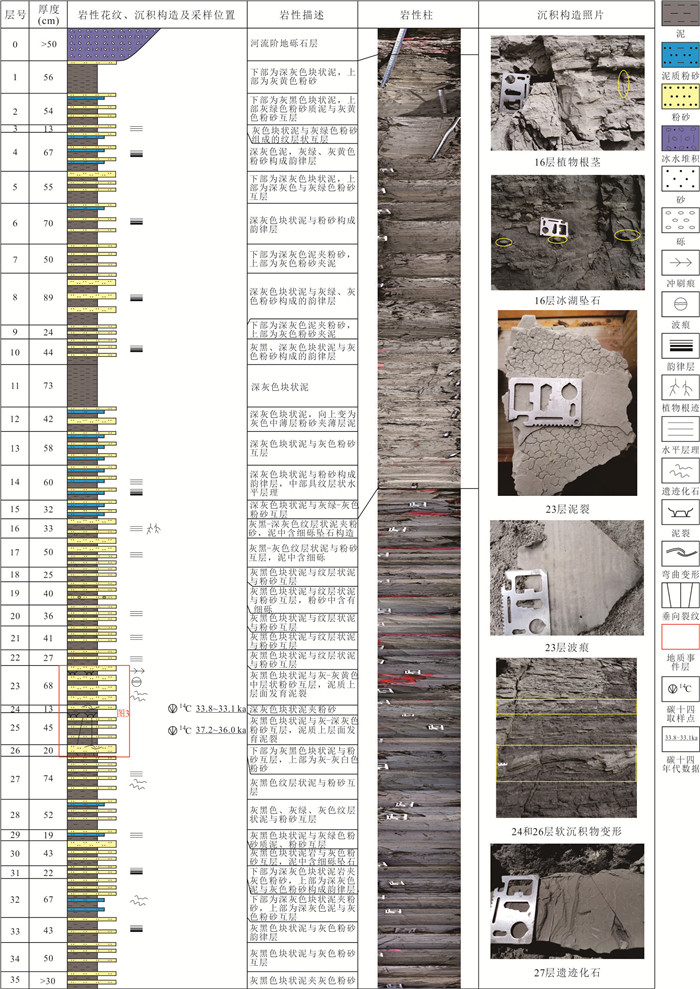
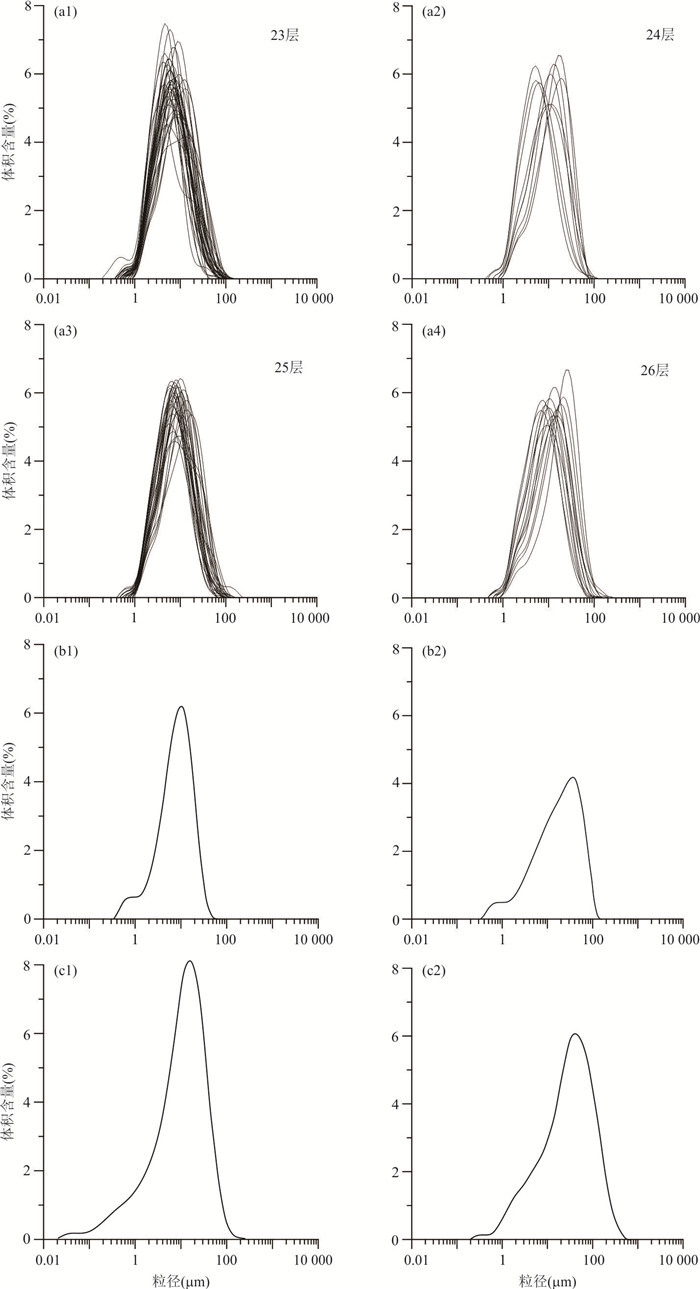
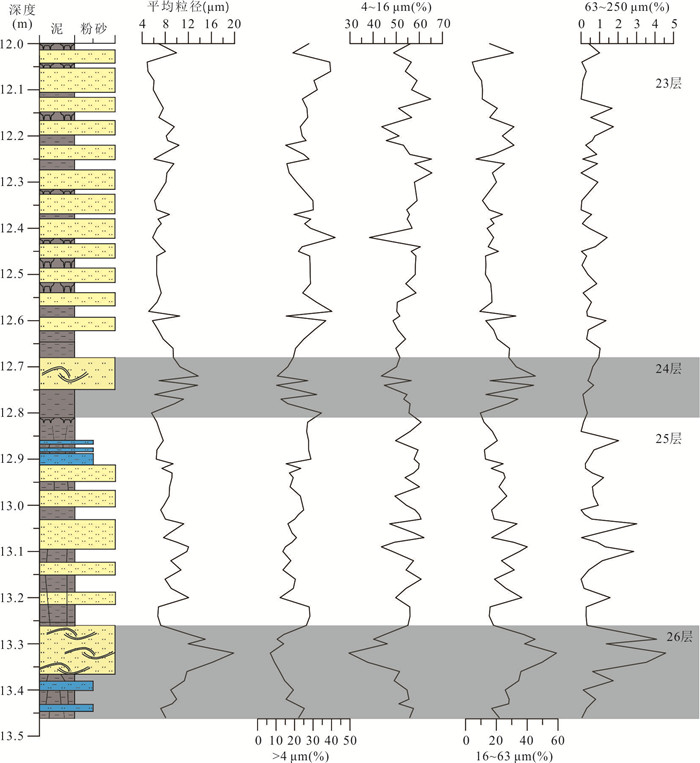
摘要: 湖相沉积具有高分辨率的沉积记录,而更新世以来的冰水湖泊可以记录冰期与间冰期的地质事件,具有重要的地质意义. 川西高原地处青藏高原东南缘,是中国地势变化最为显著的过渡地带,发育较为完整的冰川地貌.川西理塘高原毛垭盆地发育由冰川堰塞湖形成的连续稳定的16 m湖相剖面,为纹层状泥与粉砂互层,在下部层位(深度约12.68 m和13.26 m)发现了由地震触发的软沉积物变形构造,其形态特征主要表现为液化卷曲、球‒枕构造、液化底劈和层间滑动褶皱变形,通过放射性同位素AMS 14C测年得到两期软沉积物变形事件的年龄为33 850~33 110、37 254~36 042 cal. BP. 指示该地区在±37~33 ka期间至少发生过两期古地震事件:早期发生在37~36 ka之前,震级大于7级,晚期则发生于33 ka之后,震级6~7级左右.Abstract: Glacial lacustrine deposit has high-resolution sedimentary records, which has great geological significance. The Quaternary glacial and interglacial events can be recorded by the lacustrine deposit. The Litang Plateau, located in the southeastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, is the transition zone with the most significant terrain changes in China, and it has well developed glacial landform. A continuous 16 m-thick lacustrine section is measured in the Maoya Basin, western side of the Litang Plateau, which is formed in a glacial-dammed lake. It is composed of laminated mud and silty sand layers, and the soft-sediment deformation structures at the depth ranging from 12.68 to13.26 m were triggered by earthquake events. The main structures of the pliable sediment deformation include liquefied curling deformed layer, ball-pillow structure, liquefied diapir and interlayer slipping fold deformation, morphologically. Based on the AMS 14C radionuclide dating, the age interval is obtained at 33 850-33 110 cal. BP and 37 254-36 042 cal. BP. It indicates that at least two paleoseismic events occurred in this area during ± 37-33 ka. The earlier event occurred before 37-36 ka with magnitude above 7, and the later event occurred after 33 ka, with magnitude of around 6-7.
-
表 1 理塘毛垭盆地冰蚀湖含有机碳泥的AMS 14C测年结果
Table 1. Results of AMS 14C dating data of the organic carbon mud from the glacial erosive lake in the Maoya basin, Litang
实验室编号 野外编号 深度(m) 14C年龄(a BP) 校正后的日历年龄(cal. BP)2σ(95.4%) Beta-563214 PM102-3.3 12.95 29 290±150 33 850~33 110 Beta-563215 PM102-3.7 13.35 32 620±200 37 254~36 042 -
Alfaro, P., Delgado, J., Estévez, A., et al., 2002. Liquefaction and Fluidization Structures in Messinian Storm Deposits (Bajo Segura Basin, Betic Cordillera, Southern Spain). International Journal of Earth Sciences, 91(3): 505-513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-001-0241-z Chevalier, M. L., Leloup, P. H., Replumaz, A., et al., 2016. Tectonic-Geomorphology of the Litang Fault System, SE Tibetan Plateau, and Implication for Regional Seismic Hazard. Tectonophysics, 682: 278-292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2016.05.039 Cui, Y., 2019. The 10Be Exposure Dating of the Remote Landslide of Luanshibao High-Speed in Maoyaba Basin, Litang, Westhern Sichuan (Dissertation). Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing (in Chinese with English abstract). Derbyshire, E., Shi, Y. F., Li, J. J., et al., 1991. Quaternary Glaciation of Tibet: The Geological Evidence. Quaternary Science Reviews, 10(6): 485-510. https://doi.org/10.1016/0277-3791(91)90042-S Ding, X. G., Wang, J. S., Zhao, G. M., et al., 2016. Accretion Rate and Controlling Factors of Carbon and Nutrients during Coastal Wetland Evolution in Yellow River Delta. Geology in China, 43(1): 319-328 (in Chinese with English abstract). Du, Y. S., 2011. Discussion about Studies of Earthquake Event Deposit in China. Journal of Palaeogeography, 13(6): 581-586 (in Chinese with English abstract). Du, Y. S., Shi, G., Gong, Y. M., et al., 2007. Permian Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures Related to Earthquake in the Southern Sydney Basin, Eastern Australia. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(4): 511-518 (in Chinese with English abstract). Du, Y. S., Yu, W. C., 2017. Earthquake-Caused and Non-Earthquake-Caused Soft-Sediment Deformations. Journal of Palaeogeography, 19(1): 65-72 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gong, Z., Li, H. B., Sun, Z. M., et al., 2013. Middle Jurassic Strike Slip Movement and Fault Scale of the Altyn Tagh Fault System: Evidence from the Soft Sediment Deformation. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(6): 2233-2250 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo, C. B., Du, Y. B., Tong, Y. Q., et al., 2016. Huge Long-Runout Landslide Characteristics and Formation Mechanism: A Case Study of the Luanshibao Landslide, Litang County, Tibetan Plateau. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(8): 1332-1345 (in Chinese with English abstract). Harris, C., Murton, J., Davies, M. C. R., 2000. Soft-Sediment Deformation during Thawing of Ice-Rich Frozen Soils: Results of Scaled Centrifuge Modelling Experiments. Sedimentology, 47(3): 687-700. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3091.2000.00322.x Jackson, W. T., Robinson, D. M., Weislogel, A. L., et al., 2020. Cenozoic Reactivation along the Late Triassic Ganzi-Litang Suture, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Geoscience Frontiers, 11(3): 1069-1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2019.11.001 Jiang, H. C., Mao, X., Xu, H. Y., et al., 2014. Provenance and Earthquake Signature of the Last Deglacial Xinmocun Lacustrine Sediments at Diexi, East Tibet. Geomorphology, 204: 518-531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2013.08.032 Jiang, H. C., Wang, P., Thompson, J., et al., 2009. Last Glacial Climate Instability Documented by Coarse-Grained Sediments within the Loess Sequence, at Fanjiaping, Lanzhou, China. Quaternary Research, 72(1): 91-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yqres.2009.04.005 Jiang, H. C., Zhong, N., Li, Y. H., et al., 2016. Soft Sediment Deformation Structures in the Lixian Lacustrine Sediments, Eastern Tibetan Plateau and Implications for Postglacial Seismic Activity. Sedimentary Geology, 344: 123-134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.06.011 Ma, D., Wu, Z. H., Li, J. C., et al., 2014. Geometric Distribution and the Quaternary Activity of Litang Active Fault Zone Based on Remote Sensing. Acta Geologica Sinica, 88(8): 1417-1435 (in Chinese with English abstract). Moretti, M., Sabato, L., 2007. Recognition of Trigger Mechanisms for Soft-Sediment Deformation in the Pleistocene Lacustrine Deposits of the SantʻArcangelo Basin (Southern Italy): Seismic Shock Vs. Overloading. Sedimentary Geology, 196(1-4): 31-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2006.05.012 Owen, G., 1996. Experimental Soft-Sediment Deformation: Structures Formed by the Liquefaction of Unconsolidated Sands and Some Ancient Examples. Sedimentology, 43(2): 279-293. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3091.1996.d01-5.x Owen, G., Moretti, M., Alfaro, P., 2011. Recognising Triggers for Soft-Sediment Deformation: Current Understanding and Future Directions. Sedimentary Geology, 235(3-4): 133-140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2010.12.010 Qiao, X. F., Guo, X. P., 2013. Early Jurassic Soft-Sediment Deformation Interpreted as Seismites in the Wuqia Pull-Apart Basin and the Strike-Slip Talas-Ferghana Fault, Xinjiang, China. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 87(3): 730-737. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.12084 Qiao, X. F., Li, H. B., 2009. Effect of Earthquake and Ancient Earthquake on Sediments. Journal of Palaeogeography, 11(6): 593-610 (in Chinese with English abstract). Qiao, X. F., Li, H. B., Su, D. C., et al., 2017. Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures-Earthquakes and Seismic Records. Geological Publishing House, Beijing (in Chinese). Qin, Y. D., Zhang, S. Z., Liu, H., et al., 2020. Earthquake-Induced Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures in Middle Holocene of Xuru Co Area in Tibet and Its Geological Significance. Earth Science, 45(8): 2945-2956 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ramsey, C. B., 2009. Bayesian Analysis of Radiocarbon Dates. Radiocarbon, 51(1): 337-360. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033822200033865 Rana, N., Sati, S. P., Sundriyal, Y., et al., 2016. Genesis and Implication of Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures in High-Energy Fluvial Deposits of the Alaknanda Valley, Garhwal Himalaya, India. Sedimentary Geology, 344: 263-276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2016.06.012 Reimer, P. J., Bard, E., Bayliss, A., et al., 2013. IntCal13 and Marine13 Radiocarbon Age Calibration Curves 0-50 000 Years Cal BP. Radiocarbon, 55(4): 1869-1887. https://doi.org/10.2458/azu_js_rc.55.16947 Rodrı́guez-Pascua, M. A., Calvo, J. P., De Vicente, G., et al., 2000. Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures Interpreted as Seismites in Lacustrine Sediments of the Prebetic Zone, SE Spain, and Their Potential Use as Indicators of Earthquake Magnitudes during the Late Miocene. Sedimentary Geology, 135(1-4): 117-135. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0037-0738(00)00067-1 Shanmugam, G., 2013. New Perspectives on Deep-Water Sandstones: Implications. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(3): 316-324. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1876-3804(13)60038-5 Shi, Y. F., Zheng, B. X., Li, S. J., et al., 1995. Studies on Altitude and Climatic Environment in the Middle and East Parts of Tibetan Plateau during Quaternary Maximum Glaciation. Journal of Glaciolgy and Geocryology, 17(2): 97-112 (in Chinese with English abstract). Sims, J. D., 1975. Determining Earthquake Recurrence Intervals from Deformational Structures in Young Lacustrine Sediments. Tectonophysics, 29(1-4): 141-152. https://doi.org/10.1016/0040-1951(75)90139-0 Su, D. C., van Loon, A. J., Sun, A. P., 2016. How Quiet was the Epeiric Sea when the Middle Cambrian Zhangxia Formation was Deposited in SW Beijing, China? Marine and Petroleum Geology, 72: 209-217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.02.002 Suter, F., Martínez, J. I., Vélez, M. I., 2011. Holocene Soft-Sediment Deformation of the Santa Fe-Sopetrán Basin, Northern Colombian Andes: Evidence for Pre-Hispanic Seismic Activity? Sedimentary Geology, 235(3-4): 188-199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sedgeo.2010.09.018 Wang, P., Zhang, B., Qiu, W. L., et al., 2011. Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures from the Diexi Paleo-Dammed Lakes in the Upper Reaches of the Minjiang River, East Tibet. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(4): 865-872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.04.006 Wei, Y. F., Luo, S. L., Yang, M. W., 2004. An Analysis for Sedimentary System, Evolution, and Paleoclimate in the Litang Basin in West Sichuan in Quaternary. Acta Geologica Sichuan, 24(4): 194-197, 205 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0995.2004.04.002 Xu, X. W., Wen, X. Z., Yu, G. H., et al., 2005. Average Slip Rate, Earthquake Rupturing Segmentation and Recurrence Behavior on the Litang Fault Zone, Western Sichuan Province, China. Science in China (Series D), 35(6): 540-551 (in Chinese). Yuan, J., Chen, X., Tian, H. S., 2006. Formation of Loop Bedding in Jiyang Sub-Basin, Paleogene. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 24(5): 666-671 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zeng, Q. L., Yuan, G. X., Davies, T., et al., 2020. 10Be Dating and Seismic Origin of Luanshibao Rock Avalanche in SE Tibetan Plateau and Implications on Litang Active Fault. Landslides, 17(5): 1091-1104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-019-01319-z Zhang, B., Wang, P., Wang, J. C., 2011. Discussion of the Origin of the Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures in Paleo-Dammed Lake Sediments in the Upper Reaches of the Minjiang River. Journal of Seismological Research, 34(1): 67-74 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, K. Q., Wu, Z. H., Zhou, C. J., et al., 2020. Paleoearthquake Events and Inhomogeneous Activity Characteristics in the Benge-Cunge Section of the Litang Fault Zone in the Western Sichuan Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(4): 1295-1303 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.04.018 Zhang, Y. Z., Replumaz, A., Wang, G. C., et al., 2015. Timing and Rate of Exhumation along the Litang Fault System, Implication for Fault Reorganization in Southeast Tibet. Tectonics, 34(6): 1219-1243. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014tc003671 Zhao, Z. Z., Qiao, Y. S., Joerg, S., et al., 2006. Exposure Ages of Moraines in the Eastern and Central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Their Significance. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(5): 316-320 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zheng, N., Song, T. R., Cheng, M. W., 2020. K1 Xiguayuan Formation Soft-Sediment Deformation Caused by Earthquake in Luanping Basin. Earth Science, 45(11): 4198-4206 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhong, J. H., Li, H., Huang, L. G., et al., 2005. Quaternary Lacustrine Outwash: Significance to the Western Qaidam, China. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 23(2): 284-290 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.02.014 Zhong, J. H., Ni, L. T., Shao, Z. F., et al., 2015. Study on Several Special Sedimentary Structures of Earthquake-Induced Soft Deformations. Chinese Journal of Geology, 50(3): 665-683 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhong, N., Jiang, H. C., Li, H. B., et al., 2019. Last Deglacial Soft-Sediment Deformation at Shawan on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau and Implications for Deformation Processes and Seismic Magnitudes. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 93(2): 430-450. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.13773 Zhong, N., Jiang, H. C., Liang, L. J., et al., 2017. Paleoearthquake Researches via Soft Sediment Deformation of Load, Bal-and-Pillow Structure: A Review. Geological Review, 63(3): 719-738 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhong, N., Jiang, H. C., Li, H. B., et al., 2020. The Genetic Types of Soft Sediment Deformation Structures and Their Characteristics in the Fluvial-Lacustrine Sediments, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 41(1): 23-36 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhong, N., Li, H. B., Jiang, H. C., et al., 2020. Typical Soft-Sediment Deformation Structures Induced by Freeze/Thaw Cycles: A Case Study of Quaternary Alluvial Deposits in the Northern Qiangtang Basin, Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica (English Edition), 94(1): 176-188. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-6724.14345 Zhou, C. J., Wu, Z. H., Zhang, K. Q., et al., 2015. New Chronological Constraint on the Co-Seismic Surface Rupture Segments Associated with the Litang Fault. Seismology and Geology, 37(2): 455-467 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.02.009 Zhou, R. J., Chen, G. X., Li, Y., et al., 2005. Research on Active Faults in Litang-Batang Region, Western Sichuan Province and the Seismogenic Structures of the 1989 Batang M6.7 Earthquake Swarm. Seismology and Geology, 27(1): 31-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, R. J., Ye, Y. Q., Li, Y., et al., 2007. Late-Quaternary Activity of the Shawan Segment of the Litang Faults. Quaternary Sciences, 27(1): 45-53 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2007.01.006 崔豫, 2019. 川西理塘毛垭坝盆地乱石包高速远程滑坡的10Be暴露年代研究(硕士学位论文). 南京: 南京师范大学. 丁喜桂, 王吉松, 赵广明, 等, 2016. 黄河三角洲滨海湿地演化过程中的碳埋藏效率及其控制因素. 中国地质, 43(1): 319-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201601024.htm 杜远生, 2011. 中国地震事件沉积研究的若干问题探讨. 古地理学报, 13(6): 581-586. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201106003.htm 杜远生, Shi, G., 龚一鸣, 等, 2007. 东澳大利亚南悉尼盆地二叠系与地震沉积有关的软沉积变形构造. 地质学报, 81(4): 511-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200704008.htm 杜远生, 余文超, 2017. 地震和非地震引发的软沉积物变形. 古地理学报, 19(1): 65-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201701006.htm 龚正, 李海兵, 孙知明, 等, 2013. 阿尔金断裂带中侏罗世走滑活动及其断裂规模的探讨: 来自软沉积物变形的证据. 岩石学报, 29(6): 2233-2250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201306028.htm 郭长宝, 杜宇本, 佟元清, 等, 2016. 青藏高原东缘理塘乱石包高速远程滑坡发育特征与形成机理. 地质通报, 35(8): 1332-1345. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.08.014 马丹, 吴中海, 李家存, 等, 2014. 川西理塘断裂带的空间展布与第四纪左旋走滑活动的遥感影像标志. 地质学报, 88(8): 1417-1435. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201408005.htm 乔秀夫, 李海兵, 2009. 沉积物的地震及古地震效应. 古地理学报, 11(6): 593-610. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200906004.htm [2] 乔秀夫, 李海兵, 苏德辰, 等, 2017. 软沉积物变形构造: 地震与古地震记录. 北京: 地质出版社. 秦雅东, 张士贞, 刘函, 等, 2020. 西藏许如错地区中全新世地震触发软沉积物变形构造及其地质意义. 地球科学, 45(8): 2945-2956. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.117 施雅风, 郑本兴, 李世杰, 等, 1995. 青藏高原中东部最大冰期时代高度与气候环境探讨. 冰川冻土, 17(2): 97-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT502.000.htm 魏永峰, 罗森林, 杨明文, 2004. 川西理塘第四纪盆地沉积体系、演化及古气候分析. 四川地质学报, 24(4): 194-197, 205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCDB200404000.htm 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 于贵华, 等, 2005. 川西理塘断裂带平均滑动速率、地震破裂分段与复发特征. 中国科学(D辑), 35(6): 540-551. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200506006.htm 袁静, 陈鑫, 田洪水, 2006. 济阳坳陷古近纪软沉积变形层中的环状层理及成因. 沉积学报, 24(5): 666-671. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200605006.htm 张斌, 王萍, 王建存, 2011. 岷江上游堰塞湖沉积中软沉积物变形构造成因讨论. 地震研究, 34(1): 67-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYJ201101012.htm 张克旗, 吴中海, 周春景, 等, 2020. 川西理塘断裂带奔戈‒村戈段古地震事件及其非均匀性活动特征. 地质学报, 94(4): 1295-1303. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE202004018.htm 赵志中, 乔彦松, Joerg, S., 等, 2006. 青藏高原中东部第四纪冰碛物暴露年龄的测定及其意义. 地学前缘, 13(5): 316-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200605004.htm 郑宁, 宋天锐, 程木伟, 2020. 滦平盆地下白垩统西瓜园组震积软沉积变形. 地球科学, 45(11): 4198-4206 doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.021 钟建华, 李浩, 黄立功, 等, 2005. 柴西第四纪湖泊冰水沉积的发现及意义. 沉积学报, 23(2): 284-290. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200502014.htm 钟建华, 倪良田, 邵珠福, 等, 2015. 几种较特殊的地震成因软变形沉积构造. 地质科学, 50(3): 665-683. 钟宁, 蒋汉朝, 梁莲姬, 等, 2017. 软沉积物变形中负载、球‒枕构造的古地震研究综述. 地质论评, 63(3): 719-738. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201703013.htm 钟宁, 蒋汉朝, 李海兵, 等, 2020. 青藏高原东部河湖相沉积中的软沉积物变形的主要成因类型及其特征. 地球学报, 41(1): 23-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202001003.htm 周春景, 吴中海, 张克旗, 等, 2015. 川西理塘活动断裂最新同震地表破裂形成时代与震级的重新厘定. 地震地质, 37(2): 455-467. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ201502009.htm 周荣军, 陈国星, 李勇, 等, 2005. 四川西部理塘‒巴塘地区的活动断裂与1989年巴塘6.7级震群发震构造研究. 地震地质, 27(1): 31-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDZ200501003.htm 周荣军, 叶友清, 李勇, 等, 2007. 理塘断裂带沙湾段的晚第四纪活动性. 第四纪研究, 27(1): 45-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200701005.htm -









 下载:
下载: