Analysis of Recharge Source of Karst Spring Water Based on Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes
-
摘要: 为了探明喀斯特泉水补给机理. 基于2017年4月~2020年12月监测的黄龙泉域氢氧稳定同位素数据,运用一元线性回归、多元线性回归、三角函数回归等模型,探讨泉域水体氢氧稳定同位素、水文、电导率变化特征及其耦合关系,揭示泉水补给来源过程. 结果表明:(1)泉水、河水的δD、δ18O值在丰水期大于枯水期,洞穴滴水、溪水的δD、δ18O值则与区域大气降水相似,枯水期大于丰水期.(2)泉域的氘过量值(dexcess)在丰水期大于枯水期,泉水水位、δD、δ18O、电导率对降水产生季节性耦合响应,泉水补给过程受喀斯特系统的“活塞效应”及降水的“稀释效应”影响.(3)洞穴滴水的δD、δ18O季节性特征呈现出洞穴内部大于靠近洞口;泉域各水体δD余弦函数拟合出现波谷的时间顺序为:溪水 > 洞穴滴水 > 河水 > 泉水,对大气降水响应的时间依次延迟.(4)泉水受大气降水入渗和流自非喀斯特地区的风化裂隙水的常年混合补给. 剖析喀斯特地区泉域氢氧同位素特征和水文动态、径流过程及补给机理,对喀斯特地区水资源的调控、管理、保护具有重要借鉴意义.Abstract: In order to explore the recharge mechanism of karst spring. Based on the data of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes monitored from April 2017 to December 2020 in Huanglong spring catchment monitored from April 2017 to December 2020, the models of unary linear regression, multiple linear regression, and trigonometric regression were used to explore the characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes, hydrology, and conductivity changes in the spring waters and their coupling relationships to reveal the process of spring recharge sources. The results show that: (1) The δD and δ18O values of spring water and river water were greater in the wet period than in the dry period, and the δD and δ18O values of cave drip water and stream water were similar to the stable isotope value of regional atmospheric precipitation, which were greater in the dry period than in the wet period. (2) The d-excess values of the spring catchment were greater in the wet period than in the dry period, and the water level, δD, δ18O and conductivity of the spring produced a seasonal coupling response to precipitation, and the recharge process of spring was influenced by the "piston effect" of the karst system and the "dilution effect" of the precipitation. (3) The seasonal characteristics of δD and δ18O of cave drips show that the drips inside the cave were larger than those near the cave entrance; the time sequence of troughs in the δD cosine function of the spring domain: stream water > cave drips > river water > spring water, and the response time to atmospheric precipitation was successively delayed. (4) The spring was recharged by the perennial mixture of infiltration of atmospheric precipitation and the weathering fissure water flowing from non-karst areas. The analyses of the characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen isotopes, hydrologic dynamics, runoff process and recharge mechanism in karst region have important reference significance for the control, management and protection of water resources in karst area.
-
Key words:
- karst /
- springs /
- hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes /
- recharge mechanisms /
- Huanglong spring catchment /
- hydrogeology
-
0. 引言
喀斯特水是喀斯特地区重要的淡水资源,全世界有20%~30%的人口将喀斯特地下水作为主要的饮用水源(Ford and Williams, 2007). 中国西南喀斯特地貌分布面积约为5.5×105 km2(李阳兵等,2002),喀斯特水是该地区重要的生活及工农业用水水源. 由于受喀斯特地表地下“二元三维”地质空间结构和复杂季风气候影响,加之人类不合理活动,导致喀斯特地区水资源具有脆弱性(汪莹等,2019),容易发生干旱(贺中华等,2015)、内涝(欧阳资文等,2011)、地下水污染(王波等,2021)等问题. 探明喀斯特地区地下水的赋存特征及其运移规律,可为解决西南喀斯特地区干旱缺水和石漠化治理提供理论依据,对进一步认识和建立喀斯特泉域水循环机制具有重要意义.
利用δD、δ18O可揭示喀斯特地下水的补给来源及过程,国内外学者已取得大量研究成果(王树芳,2014;Lucon et al.,2020). Plummer et al.(1998)通过依据乔治亚州佛罗里达上部含水层的水化学与氢氧同位素等特征,探讨河水与喀斯特水的关系. Aquilina et al.(2005)基于同位素与水化学研究揭示法国南部4个喀斯特泉水对降水的补给响应过程. Al-Charideh(2011)利用δD、δ18O探讨喀斯特泉域地下水的补给来源及运移过程. Murad et al.(2011)综合运用水文地球化学法和同位素法等,揭示阿联酋东北部喀斯特水的区域分布规律. 在中国北方喀斯特地区,赵春红等(2018)通过分析娘子关泉域喀斯特水及地表水δD、δ18O特征,发现泉域内喀斯特水的主要补给来源是大气降水和河流渗漏补给. 林云等(2020)对鹤壁许家沟泉域进行水化学、稳定同位素等分析,查明了喀斯特泉域地下水的补给来源. 在西南喀斯特地区,袁建飞等(2019)通过对西昌市仙人洞喀斯特水系统的水化学组分、氢氧及氚同位素进行分析,探寻该系统中喀斯特水、基岩裂隙水和地表水的形成演化过程. 刘伟江等(2018)对贵阳市喀斯特地下水的水化学及氢氧稳定同位素进行研究,探明该区域地下水的主要补给来源是大气降水. 然而,上述研究在耦合利用稳定同位素、电导率、水文等多种数据揭示喀斯特泉水补给来源、径流过程及动态变化规律等方面仍存在不足.
基于此,本研究以滇中昆明市阿子营黄龙泉域为例,该泉域属典型的喀斯特泉域系统,区域内发育有洞穴滴水、泉水、溪水、河水等多种水体,是研究喀斯特泉的理想场所. 故基于2017‒04~2019‒12月黄龙泉域的δD、δ18O、氘过量值(dexcess)等数据,探讨洞穴滴水‒泉水‒河水和溪水等稳定同位素特征,揭示喀斯特泉水补给来源及水文机理,力求为喀斯特地区水资源的调控、管理、保护等提供科学参考.
1. 研究区域概况
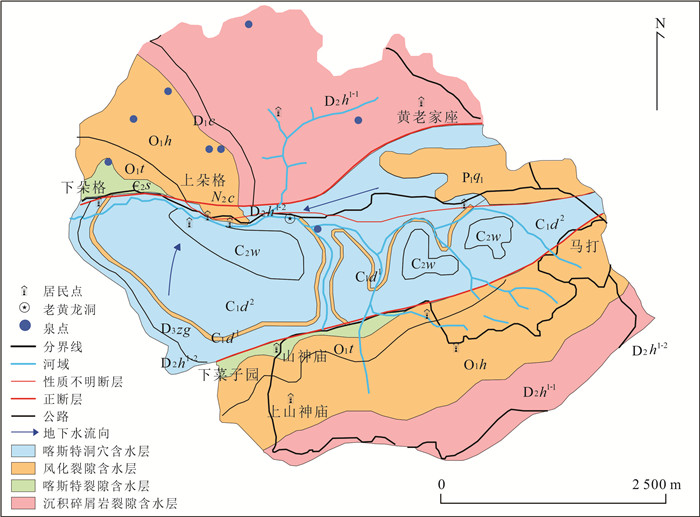
黄龙泉域地处云南省昆明市阿子营乡朵格村,位于昆明市水源保护区范围内. 境内发育牧羊河,其为盘龙江正源,发源于梁王山西麓,汇纳境内溪、潭、泉30余处,其中黄龙泉是其主要补给源头之一(图 1). 该区属北亚热带低纬高原季风气候,气温年际变化小,日温差大,受印度季风、东亚季风的双重影响,干湿季显著分明,雨季为每年的5~10月,旱季则为11月~次年4月. 泉水的丰水期是每年的7~10月,1~4月为枯水期,平水期为5~6月和11~12月. 本区属扬子准地台滇东褶皱带,属于云贵高原组成部分,泉域所在地区为碳酸盐地层,出露有石炭系的中统威宁组(C2w)、下统大塘组上司段(C1d2)、万寿山段(C1d1)和泥盆系中统海口组(D2h1-2)及上统宰格组(D3zg). 区内分布喀斯特洞穴含水层,泉域的南北方向上发育有东西向断层,周边发育有非碳酸盐岩含水层(风化裂隙含水层、沉积碎屑岩裂隙含水层等);有溪流分布,并向中部喀斯特含水层汇集(图 2). 泉域内发育有洞穴滴水、泉水、溪流、河流. 老黄龙洞位于黄龙泉口上方山坡的半山腰处,洞口、泉口间垂直高差约35 m,洞穴滴水最终排泄于黄龙泉口(图 3),黄龙泉具有喀斯特泉水文动态变化特征. 河水发育于黄龙泉所在山区的北侧山谷,且为自东向西流向,溪水位于黄龙泉所在山区的南侧山谷.
2. 样品采集与研究方法
2.1 样品采集
每周一次野外监测采集泉水、河水、溪水、洞穴滴水水样,在装入10 mL棕色玻璃瓶中之前先用纯净水将其润洗2遍,然后将水样装入瓶中,水面呈凸状,防止有气泡,再将盖子合上,统一装入塑料盒中,带回实验室将其放置于冷冻柜中4 ℃恒温保存. 在老黄龙洞内选取具有典型代表性的4个洞穴滴水点,分别为稳定性滴水W1、W2,季节性滴水J1、J2,稳定性滴水分布在洞穴的前部、后部,季节性滴水分布在洞穴的中部,其中J2为间歇性滴水,只有雨季中后期有滴水. 在黄龙泉泉口放置美国Onset公司生产的HOBO U24-001电导率记录仪和HOBO U20L-01水位记录仪,每30 min自动监测并保存泉水电导率(EC)、水温、水位(H)数据(精度分别为1 μS/cm、0.1 ℃、1.0 cm),笔者定期下载并处理这些数据.
2.2 研究方法
水样的δD、δ18O稳定同位素利用美国LGR(Los Gatos Research)公司生产的液态水同位素分析仪进行测量,其中δD的绝对误差小于0.5‰,δ18O的绝对误差小于0.15‰. 采用维也纳标准平均海水(V-SMOW)的同位素数据(梁丽娥等,2017),利用如下方程(1)、(2)计算氢、氧同位素组成(‰)的测量结果:
δD=[(D/H)sample/(D/H)V−SMOW−1]×103, (1) δ18O=[(18O/16O)sample/(18O/16O)V−SMOW−1]×103. (2) 采用回归分析方法探讨各参数间关系,其中一元线性回归模型:
ˆy=ˆa+ˆbx, (3) 式中,ˆa和ˆb分别为参数a与b的拟合值,ˆy是y的估计值,亦称回归值. 多元线性回归模型(Felton and Currens, 1994):
ˆy=b0+b1x1+b2x2+⋯+bkxk, (4) 式中,b0为常数,b1,b2,…,bk为偏回归系数,即当其他自变量都固定时,自变量xi每变化一个单位而使因变量改变的平均数值.
各采样点的氢氧稳定同位素具有季节性变化特征,对其进行余弦函数拟合,公式为:
δ=Acos(wt−φ)+B, (5) 式中,δ指δD拟合同位素的丰度,A为振幅,w(w=2π/T=2π/365)代表角频率,t为时间(d),φ为滞后时间(d),B为拟合年平均同位素值(刘伟等,2011).
利用时间序列自相关对各采样点进行时滞分析,公式为:
r(k)=C(k)C(0), (6) C(k)=1nn−k∑i=1(xt−−x)(xt+k−−x), (7) 式中,C(k)、C(0)分别指δ18O或δD的自协方差、方差,−x、xt分别是δ18O或δD的平均值、单个样本值,t为时间变量,k(0 < k < m < n/3)为滞后时间,n为各采样点δ18O或δD的个数;r(k)为自相关系数,量化时间序列的记忆效应(Larocque et al., 1998;李严等,2021),若r(k) < 0.2,则自相关性弱. r(k)可解译喀斯特含水层结构和岩溶发育程度等.
3. 结果与分析
3.1 氢氧稳定同位素变化特征
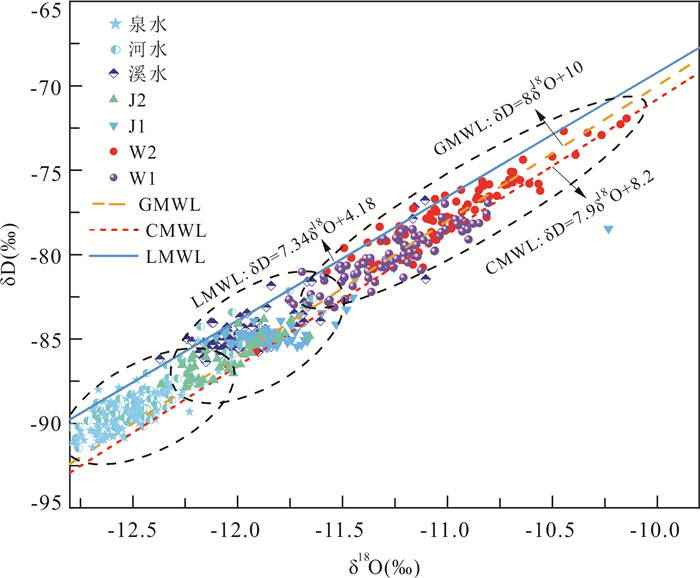
δD、δ18O是研究水循环的天然示踪剂,可揭示喀斯特泉的补给来源及水文过程. Craig et al.(1961)构建了表征降水中δD、δ18O相关关系的全球大气降水线(global meteoric water line,简称GMWL)即δD=8δ18O+10. 郑淑蕙等(1983)研究出中国大气降水线(China meteoric water line,简称CMWL)为:δD=7.9δ18O+8.2. 本研究采用章新平等(2005)根据昆明站月降水中δD和δ18O统计得到的大气降水线:δD=7.34δ18O+4.18,作为当地大气降水线(LMWL)来进行分析. 其斜率和截距小于全球及中国大气降水线,这可能与季风类型、气团来源及其所在地理位置等有关.
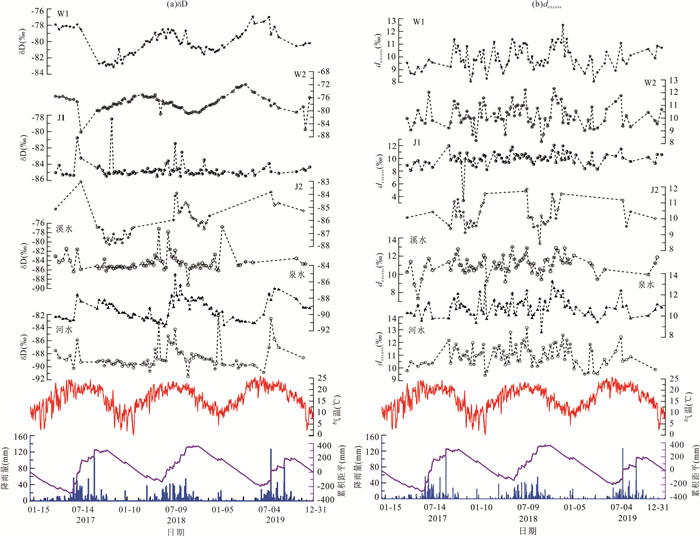
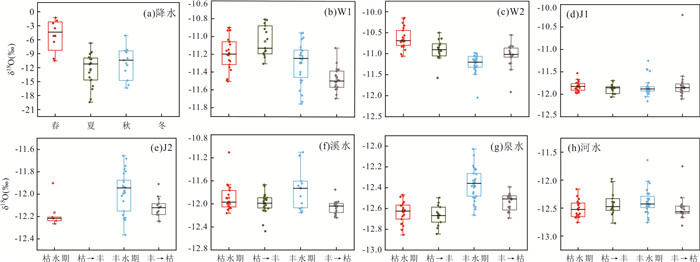
黄龙泉域水体(泉水、河水、溪水及洞内4个滴水)的δD、δ18O、dexcess变化范围如表 1所示,年际变化趋势见图 4(泉水δD、δ18O稳定同位素变化趋势一致,对其进行相关性分析表明两者呈显著正相关(r=0.79,p < 0.01),因此只选取δD为例). 其中泉水的δD、δ18O在研究的整个时间段内变化幅度较小,δD变化范围为-91.42‰~-85.08‰,其平均值为-89.37‰;δ18O变化范围为-12.85‰~-12.03‰,平均值为-12.53‰. 在丰水期泉水δD的变化范围为-89.32‰~-85.61‰,平均值为-87.95‰,枯水期变化范围为-91.25‰~-89.19‰,平均值为-90.39‰;δ18O在丰水期变化范围为-12.66‰~-12.03‰,平均值为-12.37‰,枯水期变化范围为-12.85‰~-12.47‰,平均值为-12.63‰. 泉水在丰水期时δD、δ18O的变化范围及平均值都比枯水期大,与该地区大气降水稳定同位素相反(雨季偏轻、旱季偏重),而稳定性滴水W1、W2继承了降水稳定同位素值旱季偏重、雨季偏轻的特点. 泉水δD、δ18O在研究时间段内与降水量、气温表现为相同的变化趋势. 具体呈现出雨季降水增多,温度升高,此时泉水δD、δ18O偏重,旱季则相反,表明泉水受其他经过蒸发作用后的水体在雨季漫流后经过落水洞、管道、裂隙等喀斯特地貌淋滤补给. 同时,印证了泉水受周边源自非喀斯特区风化裂隙含水层、沉积碎屑岩裂隙含水层等补给,且该类补给水的δD、δ18O明显小于洞穴滴水等喀斯特水.
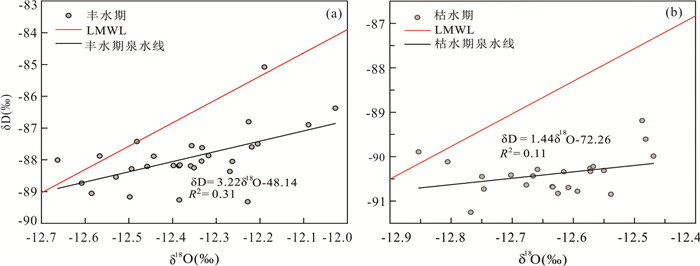
表 1 各采样点δD、δ18O、dexcess变化范围Table Supplementary Table Variation range of δD、δ18O and dexcess at each sampling point采样点 δ18O(‰) δD(‰) dexcess (‰) 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 W1 ‒10.81 ‒11.75 ‒11.26 ‒76.95 ‒83.13 ‒80.16 12.51 8.07 9.95 W2 ‒10.15 ‒12.05 ‒10.97 ‒71.95 ‒86.55 ‒77.59 12.31 8.16 10.21 J1 ‒10.23 ‒12.15 ‒11.83 ‒78.47 ‒85.49 ‒84.71 12.06 3.38 9.90 J2 ‒11.66 ‒12.36 ‒12.04 ‒83.03 ‒87.84 ‒86.11 11.87 8.43 10.25 溪水 ‒11.10 ‒12.48 ‒11.94 ‒76.78 ‒89.23 ‒84.44 13.01 7.37 11.06 泉水 ‒12.03 ‒12.85 ‒12.53 ‒85.08 ‒91.42 ‒89.37 13.30 8.51 10.86 河水 ‒11.64 ‒12.81 ‒12.45 ‒82.16 ‒91.49 ‒88.63 13.15 9.42 10.99 利用泉水、溪水、河水、各滴水的δD、δ18O值绘制δD-δ18O关系(图 5和图 6),发现泉水、河水、溪水、洞穴滴水等水样都落在昆明市大气降水线(LMWL)上或邻近区域,表明大气降水是黄龙泉域的主要补给来源. 丰水期泉水氢氧稳定同位素关系为:δD=3.22δ18O-48.14(R2=0.31);枯水期泉水氢氧稳定同位素关系为:δD=1.44δ18O-72.26(R2=0.11). 截距和斜率均低于昆明市大气降水线,丰水期泉水受到“老水”等活塞补给作用影响,氢氧稳定同位素富集. 丰水期泉水氢氧稳定同位素形成的线性方程斜率相较于枯水期接近LMWL,表明丰水期泉水受大气降水的大量补给. 泉水与河水的δD、δ18O值及分布特征最为相似(图 5),δD平均值分别为-89.37‰、-88.63‰,δ18O平均值分别为-12.53‰、-12.45‰,说明泉水与河水具有相似的补给来源. 季节性滴水J2的δD、δ18O值最接近泉水,因滴水点J2为季节性滴水,且在平水期及枯水期出现较长时间断流,因此推测在雨季时泉水受到喀斯特洞穴水、管道水、裂隙水、孔隙水等补给. 稳定性滴水W1、W2的δD、δ18O值最高,表明其在洞穴顶部滞留时间较长,水岩作用及蒸发效应导致稳定同位素值偏高. 溪水与季节性滴水J1、J2的δD、δ18O值和分布位置相近,说明溪水由多处表层喀斯特带水汇流而成,经实地考察溪水的泉眼点,均位于海拔比黄龙泉高的半山腰上,与分析相符.
总体上,泉水、河水、季节性滴水J2的δD、δ18O平均值在丰水期比枯水期偏重(图 7和图 8),表现出与该地区大气降水相反的现象;溪水、季节性滴水J1的δD、δ18O在丰枯季节变化不明显,在过渡期(枯→丰)最高;稳定性滴水W1、W2的δD、δ18O值表现为丰水期小于枯水期. 洞穴滴水δD、δ18O值在丰水期、枯水期、平水期均表现为:稳定性滴水W2 > 稳定性滴水W1 > 季节性滴水J1,表明稳定性滴水主要受降水入渗补给;与季节性滴水J1、J2补给路径有差异,与上覆洞穴顶板状况及水在顶板滞留时间、补给路径、水岩作用程度有关. 泉水、河水则受两种不同类型的地下水混合补给.
3.2 泉域氘过量分析
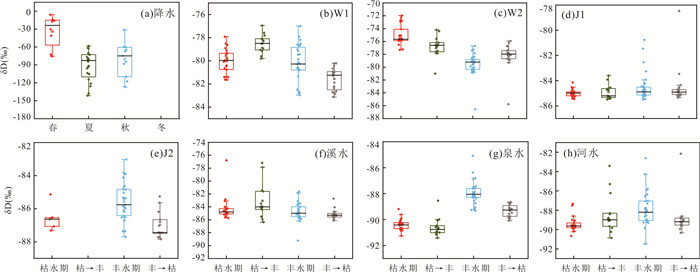
氘过量值(dexcess)反映了地区大气降水与全球大气降水同位素分馏的差异程度(Gat,1981). 也可将其扩展到其他水体研究中,例如其可作为研究地下水动力学的一个十分重要的参数指标(Dansgaard,1964),氘盈余可以指示大气降水补给地下水的滞留时间程度,受水岩作用越强烈,dexcess越小,可探讨地下水径流方向. 泉水、河水、溪水dexcess平均值相近,泉水dexcess变化范围为8.51‰~13.30‰,平均值为10.86‰;河水dexcess变化范围为9.42‰~13.15‰,平均值为10.99‰;溪水dexcess变化范围为7.37‰~13.01‰,平均值为11.06‰;季节性洞穴滴水J1、J2的dexcess变化范围分别为3.38‰~12.06‰、8.43‰~11.87‰,稳定性滴水W1、W2的dexcess变化范围分别为8.07‰~12.51‰、8.16‰~12.31‰(表 1). 总体上,洞穴滴水、泉水、河水的dexcess平均值最为接近,且均接近全球降水dexcess,表明其主要来源是海洋的大气降水且滞留时间相似. 泉水、河水dexcess在丰水期的变化范围分别为8.51‰~13.30‰、10.12‰~13.15‰;平均值分别为10.99‰、11.18‰. 枯水期变化范围分别为9.46‰~12.93‰、9.42‰~11.85‰;平均值分别为10.68‰、10.63‰. 总体上,dexcess在丰水期大于枯水期(图 9),表明丰水期受降水补给量大.
依据公式dexcess=δD-8δ18O(Dansgaard,1964),当δD不变时,δ18O升高,dexcess降低. 通常情况下,因岩石中氢的化学含量低,地下水中的δD基本不受影响;而岩石中含有氧,δ18O丰度会受水岩反应影响产生明显的变化,喀斯特地下水dexcess一般较小(尹观等,2001),黄龙泉域dexcess平均值表现出:J1 < W1 < W2 < J2 < 泉水 < 河水 < 溪水,表明洞穴滴水受喀斯特水补给量远高于其他水体. 在丰水期时泉水、河水δ18O值比枯水期较大,此外dexcess在丰水期大于枯水期,表明丰水期补给来源复杂. 溪水、稳定性滴水W1、W2的δ18O值在丰水期低于枯水期,dexcess则相反. 在所有洞穴滴水中,季节性滴水J1的dexcess最小且变化较小,表明此滴水常年受喀斯特水补给,且水岩作用影响强、蒸发作用影响小等导致其dexcess值相对较小. 另外泉水、溪水、河水的dexcess常年均大于洞穴滴水,表明其还受到周围地区非喀斯特水的常年间接补给.
3.3 泉水补给来源耦合分析
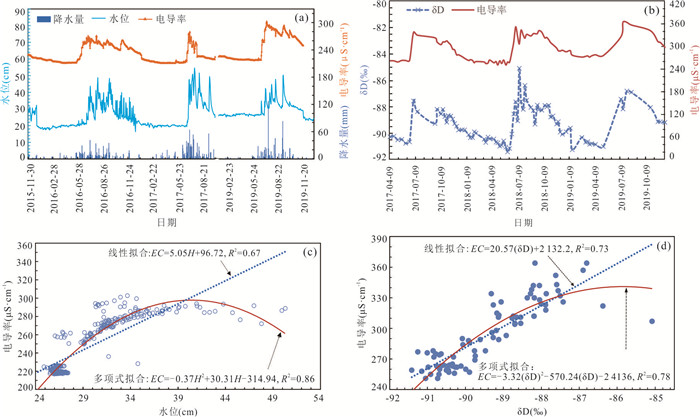
在研究期内泉水水位、电导率变化趋势一致,均对降水产生敏感性响应. 具体表现为雨季降水增多,泉水水位、电导率均增大,旱季则相反,且在不同年份由于降水状况的变化,泉水水位、电导率也随之变化(图 10a). 如2016年雨季降水天数多,使得2016年泉水水位变化频繁;2019年则反之,由于雨季降水天数少,导致泉水变化频次减少. 对泉水水位与电导率进行相关性分析,结果显示两者呈正相关关系,并对二者进行线性与多项式拟合,结果显示多项式拟合(EC=-0.37H2+30.31H-314.94,R2=0.86)优于线性拟合(EC=5.05H+96.72,R2=0.67)(图 10c),且多项式拟合呈现出开口向下的抛物线,在水位40 cm时电导率达到峰值. 表明在雨季初,随着降水量的增加,大气降水“新水”将裂隙、管道、洞穴等喀斯特系统内的“老水”淋滤排出,即“活塞效应”(孙钰霞等,2012). 因此导致电导率增加,雨季后期以“新水”为主,此时电导率降低.
泉水δD与电导率变化趋势一致,且两者呈显著正相关(图 10b). 电导率、δD均对降雨产生显著的季节性响应,响应程度丰水期大于枯水期,枯水期向丰水期的过渡期最小. 对电导率、δD进行线性与多项式拟合,发现多项式(EC=-3.32(δD)2-570.24(δD)-24 136,R2=0.78)拟合优于线性拟合(EC=20.57(δD)+2 132.2,R2=0.73)(图 10d),表明电导率随着泉水δD丰度的增大,先增加后减小. 对比图 10c与图 10d发现泉水水位与电导率的多项式拟合度优于泉水δD与电导率的拟合度,线性拟合度则相反;表明δD受控于喀斯特水文系统“新水”、“老水”的混合作用和活塞效应. 泉水受降雨入渗后的土壤水、表层喀斯特带水、包气带水、落水洞水(王泽君等,2020)等补给,此外还受周边非喀斯特水补给. 另外,验证了喀斯特泉水的水位、电导率、稳定同位素等对降水产生较为显著的耦合响应.
4. 讨论
中国西南地区雨季主要受来自低纬度海洋气团的影响(主要为西南季风、东南季风),降雨量大而蒸发小,δD、δ18O较小;而旱季则受到大陆性气团的影响,水汽主要来源于西风带的输送及内陆再蒸发水汽的补给,降水量小而蒸发旺盛,因此δD、δ18O较大(章新平等,2009). 大气降水雨季偏负,受复杂的区域水文地质环境影响,泉域各采样点稳定同位素值表现出不同特征. 泉水、河水在丰水期时的δD、δ18O表现出与大气降水、稳定性洞穴滴水相反的结果,表明其受喀斯特水、非喀斯特水混合补给,大气降水入渗补给过程产生“活塞效应”,导致δD、δ18O值呈现丰水期大于枯水期.笔者通过对比本研究区与中国贵州省的板寨、陈旗和灯盏河3个喀斯特流域地下水δD、δ18O变化特征,发现黄龙泉水δD、δ18O季节性变化特征与板寨相反,与陈旗和灯盏河则表现出相同的现象,主要受上覆土层厚度、植被覆盖类型等影响(Zhao et al., 2018).
研究区泉水、河水的δD、δ18O、dexcess季节变化规律,与蒲俊兵(2013)所研究的重庆喀斯特地下河水相同,即δ18O、δD、dexcess均在丰水期高于枯水期,主要与喀斯特水在含水层中的滞留时间有关,滞留时间越长,dexcess减小. 朱秀勤等(2013)基于昆明大气降水δD、δ18O,发现大气降水dexcess较高月份出现在7~10月,且呈现出雨季高、旱季低的规律,与其他学者得到的昆明大气降水dexcess特点(夏高冬低)类似(李维杰等,2018),但与云南其他地区的dexcess变化不同(李广等,2013). 结合本研究区所在的地质背景,可以推断泉水、河水的dexcess在丰水期大于枯水期,除受大气降水影响外,还受喀斯特水的滞留时间以及非喀斯特水补给比例影响.
利用大气降水的高度效应,可推测喀斯特水的补给高度及位置(Bhat and Jeelani, 2015),该部分有待以后加以研究. 本文将dexcess拓展应用到洞穴滴水,以此反映大气降水经过洞穴上覆土壤,到达洞穴顶部的滞留时间长短、水岩作用强弱等. 季节性滴水J1、稳定性滴水W1、W2的δ18O、δD表现为在丰水期小于枯水期,且dexcess呈现出丰水期大于枯水期,表明大气降水等在旱季时在洞穴顶部滞留时间较长,水岩相互作用较强,因此导致滴水的dexcess在枯水期降低.
泉域的洞穴滴水、溪水、泉水、河水的稳定同位素值呈现出明显的周期变化,本文以365 d作为周期,对各采样点分别进行时间序列余弦拟合(图 11),拟合度R2呈现出:W1 > J2 > 泉水 > W2 > 河水 > 溪水 > J1,总体上泉水、稳定性滴水、间歇性滴水同位素均具有较强的季节性特征. 振幅A绝对值呈现出:W2 > W1 > 泉水 > J2 > 河水 > 溪水 > J1,表明稳定性滴水、泉水、间歇性滴水等同位素变化大. 其中滴水W1的δD时间序列余弦拟合曲线方程为:δD=1.69cos(2πt/365-2.62)-80.13,R2=0.71;J2拟合曲线方程为:δD=1.52cos(2πt/365-2.83)-85.70,R2=0.66;泉水的拟合曲线方程为:δD=-1.51cos(2πt/365+5.07)-89.41,R2=0.61,笔者发现这3个采样点的稳定同位素值季节性变化显著,表明受降水影响较大.
各采样点δD峰值及波谷出现的时间(表 2),能清楚反映稳定同位素值的极值出现时间及周期变化特征. 其中2017年稳定性滴水W1、W2,季节性滴水J1、J2,溪水,泉水,河水的δD第一个波谷出现时间分别为2017‒12‒01、2017‒09‒18、2018‒02‒13、2017‒12‒13、2017‒10‒27、2018‒03‒12、2018‒01‒20,表明各水体的δD、δ18O对大气降水的显著响应时间不同,稳定性滴水W2及溪水对大气降水的响应较迅速,泉水对大气降水的响应时间最迟缓,其中W1、W2与泉水相比响应时间分别早约101 d、175 d.
表 2 各采样点δD峰值波谷出现时间Table Supplementary Table The time of δD peak trough at each sampling point采样点 日期 波峰 波谷 波峰 波谷 波峰 波谷 W1 2017‒06‒01 2017‒12‒01 2018‒06‒01 2018‒12‒01 2019‒06‒01 2019‒11‒31 W2 / 2017‒09‒18 2018‒03‒19 2018‒09‒18 2019‒03‒19 2019‒08‒18 J1 2017‒08‒04 2018‒02‒13 2018‒08‒14 2019‒02‒13 2019‒08‒14 / J2 2017‒06‒14 2017‒12‒13 2018‒06‒14 2018‒12‒13 2019‒06‒14 2019‒12‒13 溪水 / 2017‒10‒27 2018‒04‒28 2018‒10‒27 2019‒04‒28 2019‒10‒27 泉水 2017‒09‒10 2018‒03‒12 2018‒09‒10 2019‒03‒12 2019‒08‒10 / 河水 2017‒07‒21 2018‒01‒20 2018‒07‒21 2019‒01‒20 2019‒07‒21 / 利用δD进行自相关分析(表 3),时滞时长:W1 > W2 > 泉水 > 河水 > 溪水,与dexcess推算的地下水滞留时间函数相一致.稳定性洞穴滴水W1、W2对降水同位素的时滞较长,分别为50 d、44 d;季节性滴水J1时滞不明显,J2则只有雨季有滴水. 河水、溪水时滞较短,可能受地表降水径流影响. 泉水时滞约41 d,介于溪水与洞穴滴水之间,表明泉水受大气降水入渗后形成的喀斯特水和源自非喀斯特区沉积碎屑岩的风化裂隙水混合补给.
表 3 各采样点的滞留时间Table Supplementary Table Retention time of each sampling pointW1 W2 J1 J2 溪水 泉水 河水 滞留时间(d) 50 44 不明显 / 11 41 16 5. 结论
(1) 泉水的δD、δ18O、dexcess在丰水期大于枯水期,与区域大气降水变化相反,呈现出洞穴滴水 > 溪水 > 河水≥泉水. 泉水受大气降水的入渗补给,此外还受到周围非喀斯特水的间接补给. 在丰水期泉水受到洞穴水、管道水、裂隙水、孔隙水等喀斯特水混合补给.
(2) 泉水的水位、电导率、稳定同位素对降水产生较为显著的耦合响应. 具体表现为泉水的水位、δD与电导率变化趋势一致,笔者发现多项式拟合(EC=-0.37H2+30.31H-314.94,R2=0.86;EC=-3.32(δD)2-570.24(δD)-24 136,R2=0.78)优于线性拟合(EC=5.05H+96.72,R2=0.67;EC=20.57(δD)+2 132.2,R2=0.73),即电导率随泉水水位或δD增大呈先增后减的规律,表明雨季初期存在“活塞效应”,雨季后期则出现“稀释效应”.
(3) 对泉域的δD进行余弦函数拟合,其中泉水、稳定性滴水W1、J2的拟合度较高,拟合曲线方程分别为:δD泉水=-1.51cos(2πt/365+5.07)-89.41,R2=0.61;δDW1=1.69cos(2πt/365-2.62)-80.13,R2=0.71;δDJ2=1.52cos(2πt/365-2.83)-85.70,R2=0.66. 泉域δD拟合峰值出现的时间为:W2 > 溪水 > W1 > J2 > J1 > 河水 > 泉水,发现各水体对降水滞留时间:稳定性滴水 > 泉水 > 河水 > 溪水.表明各水体δD、δ18O对大气降水的响应时间不同,其中W2、溪水对大气降水的响应较为迅速,泉水对大气降水响应比较晚且补给路径复杂,主要由降水→土壤水→表层喀斯特水→包气带水→饱水带水→泉水等和降水→非喀斯特水(裂隙水)→喀斯特水→泉水等两条路径混合补给.
-
表 1 各采样点δD、δ18O、dexcess变化范围
Table 1. Variation range of δD、δ18O and dexcess at each sampling point
采样点 δ18O(‰) δD(‰) dexcess (‰) 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 W1 ‒10.81 ‒11.75 ‒11.26 ‒76.95 ‒83.13 ‒80.16 12.51 8.07 9.95 W2 ‒10.15 ‒12.05 ‒10.97 ‒71.95 ‒86.55 ‒77.59 12.31 8.16 10.21 J1 ‒10.23 ‒12.15 ‒11.83 ‒78.47 ‒85.49 ‒84.71 12.06 3.38 9.90 J2 ‒11.66 ‒12.36 ‒12.04 ‒83.03 ‒87.84 ‒86.11 11.87 8.43 10.25 溪水 ‒11.10 ‒12.48 ‒11.94 ‒76.78 ‒89.23 ‒84.44 13.01 7.37 11.06 泉水 ‒12.03 ‒12.85 ‒12.53 ‒85.08 ‒91.42 ‒89.37 13.30 8.51 10.86 河水 ‒11.64 ‒12.81 ‒12.45 ‒82.16 ‒91.49 ‒88.63 13.15 9.42 10.99 表 2 各采样点δD峰值波谷出现时间
Table 2. The time of δD peak trough at each sampling point
采样点 日期 波峰 波谷 波峰 波谷 波峰 波谷 W1 2017‒06‒01 2017‒12‒01 2018‒06‒01 2018‒12‒01 2019‒06‒01 2019‒11‒31 W2 / 2017‒09‒18 2018‒03‒19 2018‒09‒18 2019‒03‒19 2019‒08‒18 J1 2017‒08‒04 2018‒02‒13 2018‒08‒14 2019‒02‒13 2019‒08‒14 / J2 2017‒06‒14 2017‒12‒13 2018‒06‒14 2018‒12‒13 2019‒06‒14 2019‒12‒13 溪水 / 2017‒10‒27 2018‒04‒28 2018‒10‒27 2019‒04‒28 2019‒10‒27 泉水 2017‒09‒10 2018‒03‒12 2018‒09‒10 2019‒03‒12 2019‒08‒10 / 河水 2017‒07‒21 2018‒01‒20 2018‒07‒21 2019‒01‒20 2019‒07‒21 / 表 3 各采样点的滞留时间
Table 3. Retention time of each sampling point
W1 W2 J1 J2 溪水 泉水 河水 滞留时间(d) 50 44 不明显 / 11 41 16 -
Al-Charideh, A., 2011. Environmental Isotope Study of Groundwater Discharge from the Large Karst Springs in West Syria: A Case Study of Figeh and Al-Sin Springs. Environmental Earth Sciences, 63(1): 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0660-x Aquilina, L., Ladouche, B., Dörfliger, N., 2005. Recharge Processes in Karstic Systems Investigated through the Correlation of Chemical and Isotopic Composition of Rain and Spring-Waters. Applied Geochemistry, 20(12): 2189-2206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2005.07.011 Bhat, N. A., Jeelani, G. H., 2015. Delineation of the Recharge Areas and Distinguishing the Sources of Karst Springs in Bringi Watershed, Kashmir Himalayas Using Hydrochemistry and Environmental Isotopes. Journal of Earth System Science, 124(8): 1667-1676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0629-y Craig, H., 1961. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science, 133(3465): 1702-1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702 Dansgaard, W., 1964. Stable Isotopes in Precipitation. Tellus, 16(4): 436-468. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2153-3490.1964.tb00181.x Felton, G. K., Currens, J. C., 1994. Peak Flow-Rate and Recession-Curve Characteristics of a Karst Spring in the Inner Bluegrass, Central Kentucky. Journal of Hydrology, 162(1-2): 99-118. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1694(94)90006-X Ford, D., Williams, P., 2007. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York. Gat, J. R., 1981. Paleoclimate Conditions in the Levant as Revealed by the Isotopic Composition of Paleowaters. Israel Meteorological Research Papers, 3: 13-28. He, Z. H., Chen, X. X., Liang, H., et al., 2015. Studies on the Mechanism of Watershed Hydrologic Droughts Based on the Combined Structure of Typical Karst Lithologys: Taking Guizhou Province as a Case. Chinese Journal of Geology, 50(1): 340-353 (in Chinese with English abstract). Larocque, M., Mangin, A., Razack, M., et al., 1998. Contribution of Correlation and Spectral Analyses to the Regional Study of a Large Karst Aquifer (Charente, France). Journal of Hydrology, 205(3-4): 217-231. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-1694(97)00155-8 Li, G., Zhang, X. P., Zhang, X. Z., et al., 2013. Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes Characteristics of Atmospheric Precipitation from Tengchong, Yunnan. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 22(11): 1458-1465 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, W. J., Wang, J. L., Wang, J. L., 2018. Characteristics of the Stable Isotopes in Precipitation and the Source of Water Vapor in Different Terrain in the Southwest Region. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 27(5): 1132-1142 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y., Wang, J. L., Jin, M. G., et al., 2021. Hydrodynamic Characteristics of Jinan Karst Spring System Identified by Hydrologic Time-Series Data. Earth Science, 46(7): 2583-2593 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y. B., Hou, J. J., Xie, D. T., 2002. The Recent Development of Research on Karst Ecology in Southwest China. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 22(3): 365-370 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2002.03.019 Liang, L. E., Li, C. Y., Shi, X. H., et al., 2017. Characteristics of Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes of Surface and Ground Water and the Analysis of Source of Lake Water in Hulun Lake Basin, Inner Mongolia. Wetland Science, 15(3): 385-390 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lin, Y., Cao, F. L., Wu, Y. Z., et al., 2020. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of Groundwater in Typical Karst Spring Areas of North China‒A Case Study in the Xujiagou Spring Area, Hebi. Earth and Environment, 48(3): 294-306 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, W., Wang, S. J., Luo, W. J., 2011. The Response of Epikarst Spring to Precipitation and Its Implications in Karst Peak-Cluster Region of Libo County, Guizhou Province, China. Geochimica, 40(5): 487-496 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, W. J., Yuan, X. M., Zhang, Y., et al., 2018. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics and Evolution of Karst Groundwater in Guiyang City. Geological Science and Technology Information, 37(6): 245-251 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lucon, T. N., Costa, A. T., Galvão, P., et al., 2020. Recharge Sources and Hydraulic Communication of Karst Aquifer, São Miguel Watershed, MG, Brazil. Journal of South American Earth Sciences, 100: 102591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsames.2020.102591 Murad, A. A., Garamoon, H., Hussein, S., et al., 2011. Hydrogeochemical Characterization and Isotope Investigations of a Carbonate Aquifer of the Northern Part of the United Arab Emirates. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(1): 213-225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.07.013 Ouyang, Z. W., Song, T. Q., Peng, W. X., et al., 2011. Study on Status of Waterlogging and Comprehensive Countermeasures in Karst Peak-Cluster Depression Region, Guangxi. Research of Agricultural Modernization, 32(1): 107-110 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0275.2011.01.024 Plummer, L. N., Busenberg, E., McConnell, J. B., et al., 1998. Flow of River Water into a Karstic Limestone Aquifer. 1. Tracing the Young Fraction in Groundwater Mixtures in the Upper Floridan Aquifer near Valdosta, Georgia. Applied Geochemistry, 13(8): 995-1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0883-2927(98)00031-6 Pu, J. B., 2013. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotope Geochemistry of Karst Groundwater in Chongqing. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 34(6): 713-722 (in Chinese with English abstract). Sun, Y. X., Li, L. L., Wei, S. Q., 2012. Storm-Scale Hydrochemical Variation in Typical Rock Pendant of Chongqing. Journal of Mountain Science, 30(5): 513-520 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, B., Wang, Y., Zhang, G., et al., 2021. A Study of Quality and Pollution Factors of Karst Groundwater in Lujiang River Basin in Southeast Yunnan. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 42(3): 352-362 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, S. F., 2014. Progress in Study on Precipitation Infiltration Recharge of Karstic Groundwater System. Journal of China Hydrology, 34(6): 1-8 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0852.2014.06.001 Wang, Y., Luo, Z. H., Wu, Y., et al., 2019. Urbanization Factors of Groundwater Vulnerability Assessment in Karst Area: A Case Study of Shuicheng Basin. Earth Science, 44(9): 2909-2919 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Z. J., Zhou, H., Qi, L. X., et al., 2020. Method for Characterizing Structure and Hydrological Response in Karst Water Systems: A Case Study in Y-M System in Three Gorges Area. Earth Science, 45(12): 4512-4523 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yin, G., Ni, S. J., Zhang, Q. C., 2001. Deuterium Excess Parmeter and Geohydrology Significance—Taking the Geohydrology Researches in Jiuzaigou and Yele, Sichuan for Example. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology, 28(3): 251-254 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yuan, J. F., Xu, F., Liu, H. Z., et al., 2019. Application of Hydrochemical and Isotopic Analysis to Research a Typical Karst Groundwater System: A Case Study at Xinrendong, Xichang City. Science Technology and Engineering, 19(17): 76-83 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, X. P., Liu, J. M., Masayoshi, N., et al., 2009. Vapor Origins Revealed by Deuterium Excess in Precipitation in Southwest China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 31(4): 613-619 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, X. P., Sun, W. Z., Liu, J. M., 2005. Stable Isotopes in Precipitation in the Vapor Transport Path in Kunming of Southwest China. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 14(5): 665-669 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, C. H., Liang, Y. P., Lu, H. P., et al., 2018. Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopic Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Karst Water in the Niangziguan Spring Area. Geological Science and Technology Information, 37(5): 200-205 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, M., Hu, Y., Zeng, C., et al., 2018. Effects of land cover on variations in stable hydrogen and oxygen isotopes in karst groundwater: A comparative study of three karst catchments in Guizhou Province, Southwest China. Journal of Hydrology, 565: 374-385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.08.037 Zheng, S. H., Hou, F. G., Ni, B. L., 1983. Study on Stable Isotopes of Hydrogen and Oxygen in Precipitation in China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 28(13): 801-806 (in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/csb1983-28-13-801 Zhu, X. Q., Fan, T., Guan, W., 2013. The Analysis of Stable Isotopes of Precipitation in Kunming. Yunnan Geographic Environment Research, 25(5): 90-95 (in Chinese with English abstract). 贺中华, 陈晓翔, 梁虹, 等, 2015. 典型喀斯特岩性组合结构的流域水文干旱机制研究——以贵州省为例. 地质科学, 50(1): 340-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKX201501023.htm 李广, 章新平, 张新主, 等, 2013. 云南腾冲地区大气降水中氢氧稳定同位素特征. 长江流域资源与环境, 22(11): 1458-1465. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201311012.htm 李维杰, 王建力, 王家录, 2018. 西南地区不同地形降水稳定同位素特征及其水汽来源. 长江流域资源与环境, 27(5): 1132-1142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY201805020.htm 李严, 王家乐, 靳孟贵, 等, 2021. 运用水文时间序列分析识别济南泉域岩溶发育特征. 地球科学, 46(7): 2583-2593. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.236 李阳兵, 侯建筠, 谢德体, 2002. 中国西南岩溶生态研究进展. 地理科学, 22(3): 365-370. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX200203018.htm 梁丽娥, 李畅游, 史小红, 等, 2017. 内蒙古呼伦湖流域地表水与地下水氢氧同位素特征及湖水来源分析. 湿地科学, 15(3): 385-390. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXSD201703010.htm 林云, 曹飞龙, 武亚遵, 等, 2020. 北方典型岩溶泉域地下水水文地球化学特征分析——以鹤壁许家沟泉域为例. 地球与环境, 48(3): 294-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202003002.htm 刘伟, 王世杰, 罗维均, 2011. 贵州荔波岩溶峰丛区表层岩溶泉对大气降雨的响应及其指示意义. 地球化学, 40(5): 487-496. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201105009.htm 刘伟江, 袁祥美, 张雅, 等, 2018. 贵阳市岩溶地下水水化学特征及演化过程分析. 地质科技情报, 37(6): 245-251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806031.htm 欧阳资文, 宋同清, 彭晚霞, 等, 2011. 广西岩溶峰丛洼地内涝现状分析与综合治理对策研究. 农业现代化研究, 32(1): 107-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NXDH201101029.htm 蒲俊兵, 2013. 重庆岩溶地下水氢氧稳定同位素地球化学特征. 地球学报, 34(6): 713-722. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201306009.htm 孙钰霞, 李林立, 魏世强, 2012. 喀斯特槽谷区表层喀斯特水化学的暴雨动态特征. 山地学报, 30(5): 513-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA201205001.htm 王波, 王宇, 张贵, 等, 2021. 滇东南泸江流域岩溶地下水质量及污染影响因素研究. 地球学报, 42(3): 352-362. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202103006.htm 王树芳, 2014. 岩溶含水系统降水入渗补给研究进展. 水文, 34(6): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWZZ201406001.htm 汪莹, 罗朝晖, 吴亚, 等, 2019. 岩溶地下水脆弱性评价的城镇化因子: 以水城盆地为例. 地球科学, 44(9): 2909-2919. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.135 王泽君, 周宏, 齐凌轩, 等, 2020. 岩溶水系统结构和水文响应机制的定量识别方法: 以三峡鱼迷岩溶水系统为例. 地球科学, 45(12): 4512-4523. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.261 尹观, 倪师军, 2001. 氘过量参数及其水文地质学意义: 以四川九寨沟和冶勒水文地质研究为例. 成都理工学院学报, 28(3): 251-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CDLG200103006.htm 袁建飞, 徐芬, 刘慧中, 等, 2019. 基于水化学和同位素的典型岩溶水系统溶质演化过程——以西昌市仙人洞为例. 科学技术与工程, 19(17): 76-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201917010.htm 章新平, 刘晶淼, 中尾正义, 等, 2009. 我国西南地区降水中过量氘指示水汽来源. 冰川冻土, 31(4): 613-619. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT200904003.htm 章新平, 孙维贞, 刘晶淼, 2005. 西南水汽通道上昆明站降水中的稳定同位素. 长江流域资源与环境, 14(5): 665-669. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJLY200505024.htm 赵春红, 梁永平, 卢海平, 等, 2018. 娘子关泉域岩溶水氢氧同位素特征及影响因素浅析. 地质科技情报, 37(5): 200-205. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201805028.htm 郑淑蕙, 侯发高, 倪葆龄, 1983. 我国大气降水的氢氧稳定同位素研究. 科学通报, 28(13): 801-806. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB198313010.htm 朱秀勤, 范弢, 官威, 2013. 昆明大气降水稳定同位素分析. 云南地理环境研究, 25(5): 90-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDL201305015.htm -











 下载:
下载:











 下载:
下载: