Quantitative Susceptibility Assessment of Breach of Moraine-Dammed Lakes
-
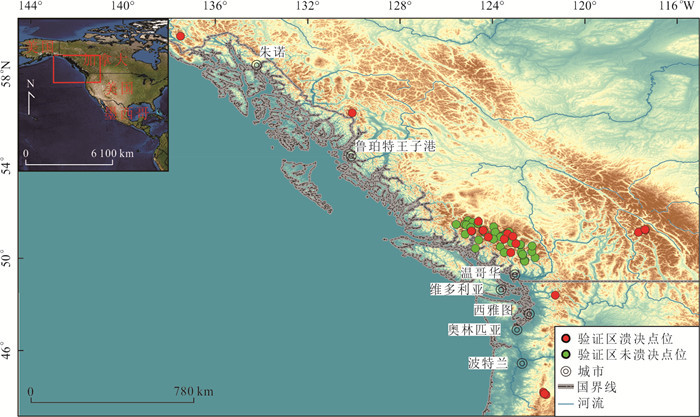
摘要: 世界范围内的冰碛湖溃决往往造成巨大经济损失和人员伤亡.通过分析不含死冰的冰碛坝溃决机理和相关影响因素,采用控制变量法,以喜马拉雅山区21个溃决冰碛湖及其周围未溃决冰碛湖为研究对象,采用6个无量纲影响因子可以合理评估喜马拉雅山区和加拿大哥伦比亚省西南地区以及美国西北部地区的冰湖溃决易发性,但喜马拉雅山区不同级别判别阈值较加拿大哥伦比亚省西南地区偏大.危险冰体坡度因子、危险冰体温度因子、冰川坡向因子、危险冰体与冰碛湖体积因子、危险冰体与冰湖的运动因子、冰碛坝坡度因子是影响不含死冰冰碛湖溃决的主要因子,由这些影响因子构成的冰碛湖溃决易发性定量评价方法,可以用于其他地区的冰碛湖溃决易发性评价.Abstract: Glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs) have caused tens of millions of dollars of damage to infrastructure and have killed thousands of people worldwide. Based on the formation mechanism of GLOF of moraine-dammed lakes without ice core, 21 GLOFs were selected for the analysis of triggering factors in the Himalayan region. A statistical method was used via the Variable-Controlling Approach (VCA). Six dimensionless impact factors can be used to reasonably assess the GLOFs susceptibility in the Himalayan mountains, southwestern part of Canadian Columbia and northwestern part of the United States, but the threshold values in the Himalayan mountains are larger than those in southwestern part of Canadian Columbia. The dangerous glacier slope factor, the dangerous glacier temperature factor, the glacier aspect factor, the dangerous glacier volume and lake volume factor, the dangerous glacier and lake kinetic factor, and the downstream slope of the moraine-dam factor are major factors for the breaching of moraine-dammed lake and GLOF. The assessment model with these factors may thus be used to assess the hazard of GLOFs occurrence in other areas.
-
Key words:
- quantitative study /
- moraine-dammed lake /
- breach /
- hazard assessment /
- geotechnical engineering
-
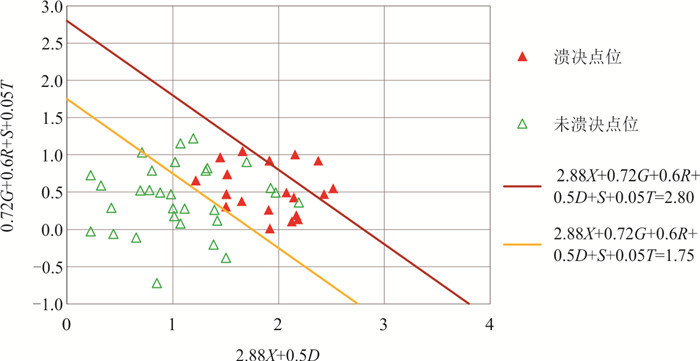
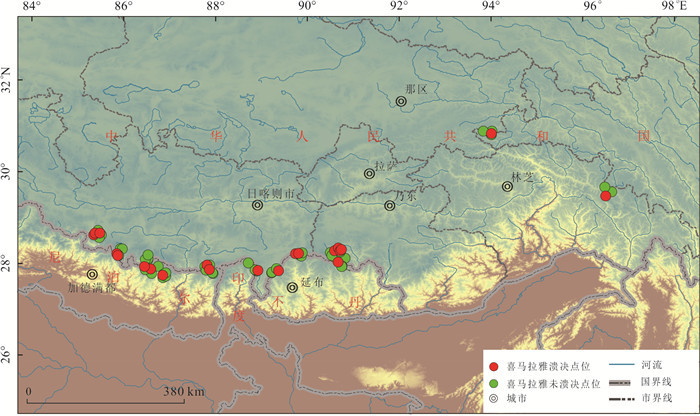
表 1 喜马拉雅山区各子区域溃决与未溃决冰碛湖的评价因子
Table 1. The factors of sub-areas in the Himalayan region with or without GLOFs
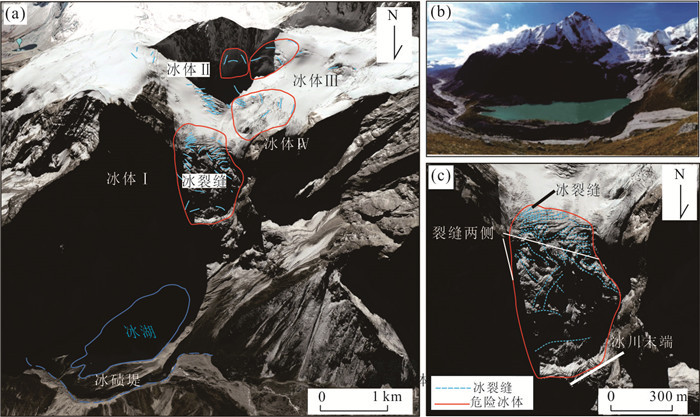
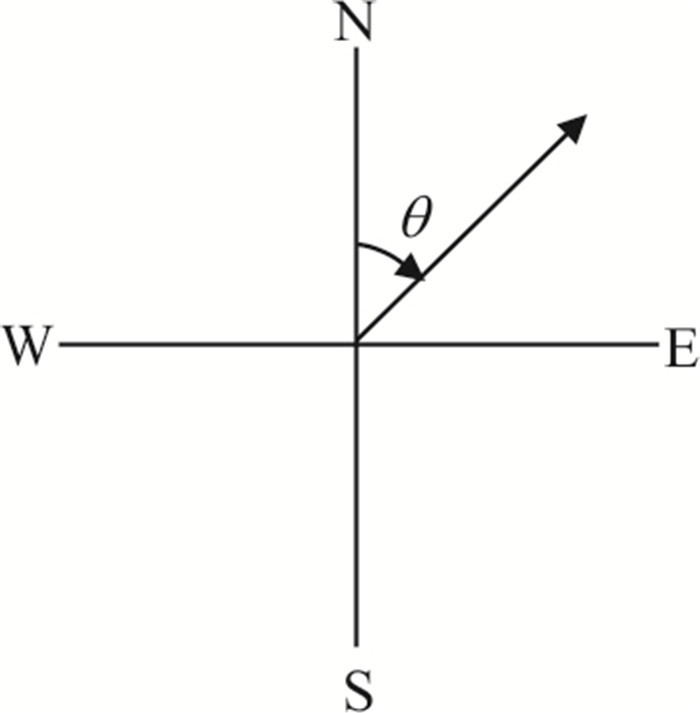
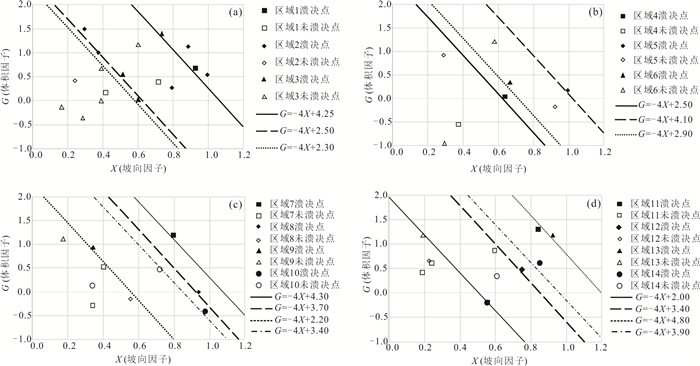
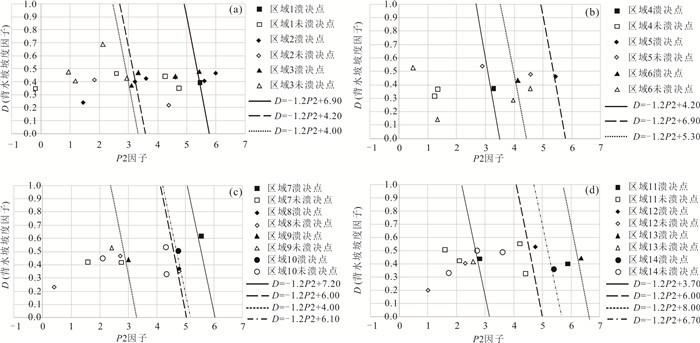
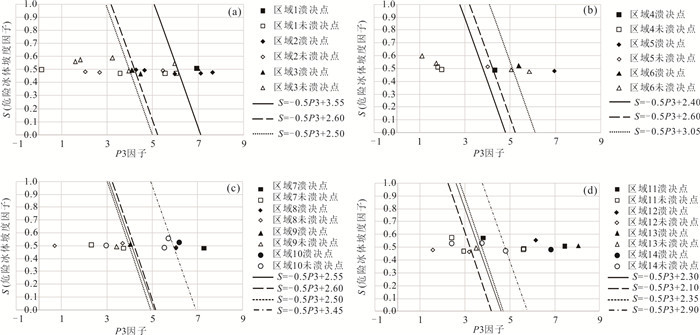
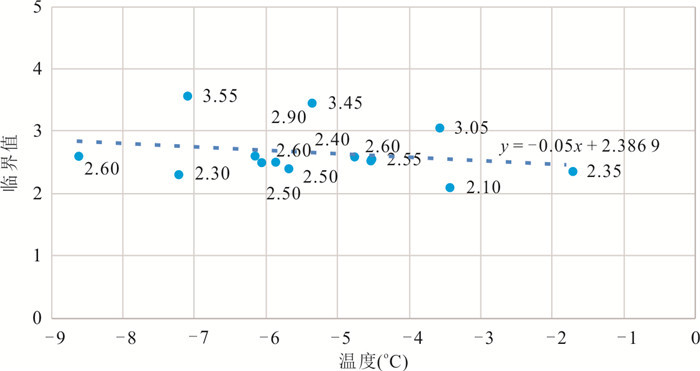
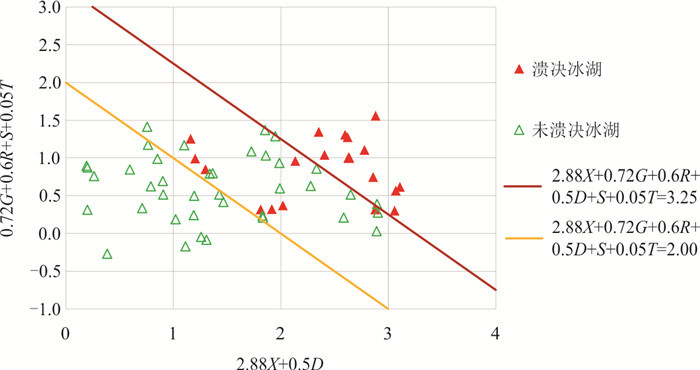
名称 子区域 X S G R D T 溃决 参考文献 穷比吓玛错 1 0.93 0.51 0.68 0.20 0.39 -7.42 是 McKillop and Clague(2007b) 1-1 1 0.42 0.47 0.17 0.39 0.46 -6.19 否 1-2 1 0.86 0.47 0.08 0.51 0.35 -6.34 否 1-3 1 0.71 0.47 0.39 0.36 0.44 -6.73 否 1-4 1 0.07 0.50 -0.67 0.26 0.35 -8.84 否 鲁惹错 2 0.38 0.50 0.99 0.20 0.40 -9.59 是 吕儒仁等(1999) 得嘎错 2 0.33 0.48 1.52 0.20 0.43 -8.78 是 姚晓军等(2014) Upper Jiejiu Tsho 2 0.89 0.48 1.13 0.38 0.45 -8.18 是 刘美(2020) Upper Shegong Tsho 2 0.79 0.47 0.26 0.50 0.44 -8.41 是 刘美(2020) Tarikha Lake 2 0.99 0.47 0.54 0.17 0.41 -7.90 是 Nie et al.(2018) 2-1 2 0.05 0.48 0.81 0.30 0.24 -9.66 否 2-2 2 0.08 0.22 1.57 0.17 0.42 -8.38 否 2-3 2 0.86 0.49 -0.02 0.26 0.21 -8.45 否 2-4 2 0.24 0.48 0.40 0.24 0.41 -7.81 否 2-5 2 0.87 0.46 0.45 0.20 0.22 -7.79 否 2-6 2 0.02 0.47 0.18 0.30 0.33 -9.17 否 2-7 2 0.51 0.25 0.53 0.24 0.39 -8.85 否 2-8 2 0.26 0.37 0.95 0.18 0.35 -9.11 否 隆达错 3 0.51 0.47 0.55 0.22 0.47 -5.31 是 徐道明和冯清华(1989) 扎那泊 3 0.73 0.51 1.40 0.22 0.48 -5.99 是 姚晓军等(2014) 扎隆嘎布 3 0.60 0.50 0.02 0.20 0.37 -6.16 是 刘建康等(2019) 3-1 3 0.39 0.49 0.67 0.27 0.43 -6.83 否 3-2 3 0.39 0.59 0.00 0.26 0.69 -6.49 否 3-3 3 0.28 0.57 -0.36 0.25 0.40 -5.49 否 3-4 3 0.16 0.56 -0.13 0.31 0.48 -6.27 否 3-5 3 0.60 0.55 1.17 0.33 0.44 -5.92 否 吉莱错(吉来普错) 4 0.64 0.49 0.04 0.18 0.37 -5.13 是 刘建康等(2019) 4-1 4 0.37 0.49 -0.55 0.22 0.37 -5.41 否 4-2 4 0.01 0.51 0.77 0.26 0.31 -6.51 否 Nagma Pokhari 5 1.00 0.48 0.18 0.40 0.46 -4.75 是 Nie et al.(2018) 5-1 5 0.29 0.51 0.92 0.40 0.54 -4.99 否 5-2 5 1.00 0.44 0.37 0.36 0.59 -4.61 否 5-3 5 0.97 0.30 1.25 0.31 0.36 -4.27 否 5-4 5 0.92 0.47 -0.18 0.32 0.49 -5.18 否 Dig Tsho 6 0.67 0.52 0.34 0.52 0.43 -2.40 是 Gurung et al.(2017) 6-1 6 0.58 0.48 1.21 0.33 0.37 -3.57 否 6-2 6 0.43 0.54 -0.86 0.30 0.14 -3.66 否 6-3 6 0.29 0.60 -0.95 0.21 0.53 -4.22 否 6-4 6 0.55 0.49 0.78 0.39 0.28 -4.05 否 Upper Langbu Tsho 7 0.79 0.48 1.19 0.31 0.62 -4.31 是 Nie et al.(2018) 7-1 7 0.26 0.36 -0.44 0.22 0.46 -4.96 否 7-2 7 0.72 0.42 1.08 0.27 0.38 -5.17 否 7-3 7 0.40 0.48 0.53 0.19 0.42 -3.55 否 7-4 7 0.34 0.51 -0.28 0.28 0.42 -4.63 否 错嘎 8 0.93 0.48 0.00 0.28 0.37 -6.55 是 姚晓军等(2014) 8-1 8 0.03 0.50 -0.12 0.38 0.23 -6.46 否 8-2 8 0.56 0.52 -0.15 0.20 0.47 -6.45 否 8-3 8 0.94 0.49 -0.11 0.40 0.35 -5.15 否 光谢错 9 0.34 0.51 0.94 0.24 0.44 -6.68 是 刘建康等(2019) 9-1 9 0.17 0.49 1.12 0.24 0.53 -5.39 否 9-2 9 0.99 0.34 0.18 0.47 0.27 -5.52 否 Tam Pokhari 10 0.97 0.52 -0.41 0.56 0.50 -5.35 是 Nie et al.(2018) 10-1 10 0.34 0.28 -0.03 0.31 0.52 -4.33 否 10-2 10 0.72 0.56 0.47 0.31 0.53 -4.43 否 10-3 10 0.34 0.50 0.13 0.33 0.45 -5.91 否 10-4 10 0.95 0.48 -0.34 0.21 0.33 -6.73 否 龙纠错 11 0.55 0.57 -0.19 0.37 0.44 -6.92 是 姚晓军等(2014) Simdong Goi Tsho 11 0.84 0.51 1.30 0.28 0.40 -6.72 是 Nie et al.(2018) 11-1 11 0.24 0.47 0.61 0.22 0.42 -6.88 否 11-2 11 0.59 0.49 1.07 0.30 0.32 -8.16 否 11-3 11 0.59 0.48 0.87 0.32 0.55 -7.28 否 11-4 11 0.19 0.58 0.42 0.19 0.50 -7.35 否 嘉龙错 12 0.74 0.55 0.46 0.54 0.53 -3.34 是 陈晓清等(2006) 12-1 12 0.22 0.47 0.65 0.45 0.42 -4.42 否 12-2 12 0.03 0.48 0.46 0.32 0.21 -2.53 否 Unnamed 6th 13 0.92 0.51 1.18 0.49 0.44 -1.98 是 刘美(2020) 13-1 13 0.19 0.49 1.18 0.24 0.41 -1.49 否 Upper ChokhamTsho 14 0.85 0.48 0.60 0.59 0.36 -5.36 是 Nie et al.(2018) 14-1 14 0.61 0.47 0.34 0.29 0.49 -5.79 否 14-2 14 0.55 0.53 -0.19 0.30 0.50 -6.82 否 14-3 14 0.15 0.53 0.51 0.40 0.33 -5.79 否 注:表中的因子X、S、G、R、D、T等分别表示坡向因子、危险冰体坡度因子、危险冰体与冰湖体积因子、运动因子、背水坡坡度因子、温度因子,详细定义见文章第2部分. 表 2 与冰碛湖溃决的相关参数
Table 2. The factors related to GLOFs
参数 本文采用 参数 本文采用 参数 本文采用 流域集水面积 否 冰湖与危险冰体高差 是 冰碛坝溢流口宽度 否 冰川面积 是 危险冰体与冰湖的运动参数 是 冰碛坝溢流口长度 否 冰川坡向 是 危险冰体体积与冰湖体积比 是 冰碛坝背水坡坡度 是 危险冰体面积 否 冰湖面积 否 冰碛坝岩性 否 危险冰体体积 是 冰湖体积 是 死冰 否 危险冰体坡度 是 冰碛坝高宽比 否 管涌 否 危险冰体裂缝 否 冰碛坝固结程度 否 温度 是 冰川裂缝宽度 否 冰湖湖面与冰碛坝顶距离 否 地震 否 冰湖与危险冰体距离 是 冰湖湖面与冰碛坝顶距离和冰碛坝高之比 否 滑坡 否 -
Allen, S. K., Zhang, G. Q., Wang, W. C., et al., 2019. Potentially Dangerous Glacial Lakes across the Tibetan Plateau Revealed Using a Large-Scale Automated Assessment Approach. Chinese Science Bulletin, 64(7): 435-445. Chai, B., Tao, Y. Y., Du, J., et al., 2020. Hazard Assessment of Debris Flow Triggered by Outburst of Jialong Glacial Lake in Nyalam County, Tibet. Earth Science, 45(12): 4630-4639(in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.3799/dqkx.2020.294 Chen, X. Q., Cui, P., Yang, Z., et al., 2006. Debris Flows of Chongdui Gully in Nyalam County, 2002: Cause and Control. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 28(5): 776-781(in Chinese with English abstract). Cheng, Z. L., Zhu, P. Y., Gong, Y. W., 2003. Typical Debris Flow Triggered by Ice-Lake Break. Journal of Mountain Science, 21(6): 716-720(in Chinese with English abstract). Clague, J. J., Evans, S. G., 1994. Formation and Failure of Natural Dams in the Canadian Cordillera. Bulletin of the Geological Survey of Canada, 464: 35. Ding, Y. J., Liu, J. S., 1992. Glacier Lake Outburst Flood Disasters in China. Annals of Glaciology, 16: 180-184. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0260305500005036 Emmer, A., Vilímek, V., 2013. Review Article: Lake and Breach Hazard Assessment for Moraine-Dammed Lakes: An Example from the Cordillera Blanca (Peru). Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 13(6): 1551-1565. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-13-1551-2013 Gharamti, I. E., Dempsey, J. P., Polojärvi, A., et al., 2021. Fracture of Warm S2 Columnar Freshwater Ice: Size and Rate Effects. Acta Materialia, 202: 22-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.031 Gurung, D. R., Khanal, N. R., Bajracharya, S. R., et al., 2017. Lemthang Tsho Glacial Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) in Bhutan: Cause and Impact. Geoenvironmental Disasters, 4: 17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40677-017-0080-2 Huggel, C., Haeberli, W., Kääb, A., et al., 2004. An Assessment Procedure for Glacial Hazards in the Swiss Alps. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 41(6): 1068-1083. https://doi.org/10.1139/t04-053 Huggel, C., Kääb, A., Haeberli, W., et al., 2002. Remote Sensing Based Assessment of Hazards from Glacier Lake Outbursts: A Case Study in the Swiss Alps. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 39(2): 316-330. https://doi.org/10.1139/t01-099 Lamsal, D., Sawagaki, T., Watanabe, T., et al., 2016. Assessment of Glacial Lake Development and Prospects of Outburst Susceptibility: Chamlang South Glacier, Eastern Nepal Himalaya. Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 7(1): 403-423. https://doi.org/10.1080/19475705.2014.931306 Le, M. H., Tang, C., Zhang, D. D., et al., 2014. Logistic Regression Model- Based Approach for Predicting the Hazard of Glacial Lake Outburst in Tibet. Journal of Natural Disasters, 23(5): 177-184(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, H. K., Zhang, Y. X., 2005. Geological Dictionary (Ⅰ). Geological Publishing House, Beijing(in Chinese). Liu, J. J., Tang, C., Cheng, Z. L., et al., 2011. Impact of Temperature on Glacier-Lake Outbursts in Tibet. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 41(4): 1121-1129(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, J. K., Zhang, J. J., Gao, B., et al., 2019. An Overview of Glacial Lake Outburst Flood in Tibet, China. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 41(6): 1335-1347(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, M., 2020. Glacial Lake Outburst Flood/Debris Flow Disaster Mechanism and Hazards Assessment in Bhote Koshi Basin (Dissertation). Institute of Mountain Hazards and Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Y., 2016. Preliminary Study on the Glacial and Temperature Conditions of Terminal Moraine Dam Glacier Lake Outburst in Tibet (Dissertation). Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu(in Chinese with English abstract). Lliboutry, L., Morales A. B., Pautre, A., et al., 1977. Glaciological Problems Set by the Control of Dangerous Lakes in Cordillera Blanca, Peru. I. Historical Failures of Morainic Dams, Their Causes and Prevention. Journal of Glaciology, 18(79): 239-254. https://doi.org/10.3189/s002214300002133x Lü, R. R., Tang, B. X., Li, D. J., 1999. Debris Flow and the Environment in Tibet. Chengdu University of Science and Technology Press, Chengdu(in Chinese). McKillop, R. J., Clague, J. J., 2007a. Statistical, Remote Sensing-Based Approach for Estimating the Probability of Catastrophic Drainage from Moraine-Dammed Lakes in Southwestern British Columbia. Global and Planetary Change, 56(1/2): 153-171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2006.07.004 McKillop, R. J., Clague, J. J., 2007b. A Procedure for Making Objective Preliminary Assessments of Outburst Flood Hazard from Moraine-Dammed Lakes in Southwestern British Columbia. Natural Hazards, 41(1): 131-157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-006-9028-7 Mergili, M., Schneider, J. F., 2011. Regional-Scale Analysis of Lake Outburst Hazards in the Southwestern Pamir, Tajikistan, Based on Remote Sensing and GIS. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 11(5): 1447-1462. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-11-1447-2011 Nie, Y., Liu, Q., Wang, J. D., et al., 2018. An Inventory of Historical Glacial Lake Outburst Floods in the Himalayas Based on Remote Sensing Observations and Geomorphological Analysis. Geomorphology, 308: 91-106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.02.002 Tang, M. G., Wang, L. N., Liu, X. X., et al., 2022. Distribution and Risk of Ice Avalanche Hazards in Tibetan Plateau. Earth Science, 47(6): 1917-1931(in Chinese with English abstract). https://doi.org/10.1016/10.3799/dqkx.2021.074 Wang, F. W., Sassa, K., Wang, G. H., 2002. Mechanism of a Long-Runout Landslide Triggered by the August 1998 Heavy Rainfall in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan. Engineering Geology, 63(1-2): 169-185. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-7952(01)00080-1 Wang, S. J., Che, Y. J., Ma, X. G., 2020. Integrated Risk Assessment of Glacier Lake Outburst Flood (GLOF) Disaster over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (QTP). Landslides, 17(12): 2849-2863. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10346-020-01443-1 Wang, W. C., Yao, T. D., Gao, Y., et al., 2011. A First-Order Method to Identify Potentially Dangerous Glacial Lakes in a Region of the Southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Mountain Research and Development, 31(2): 122. https://doi.org/10.1659/mrd-journal-d-10-00059.1 Wang, X., Liu, S. Y., Guo, W. Q., et al., 2009. Hazard Assessment of Moraine-Dammed Lake Outburst Floods in the Himalayas, China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 64(7): 782-790(in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, X., Liu, S., Ding, Y., et al., 2012. An Approach for Estimating the Breach Probabilities of Moraine-Dammed Lakes in the Chinese Himalayas Using Remote-Sensing Data. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 12(10): 3109-3122. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-12-3109-2012 Xu, D. M., Feng, Q. H., 1989. Dangerous Glacial Lake and Outburst Features in Xizang Himalayas. Acta Geographica Sinica, 44(3): 343-351, 385(in Chinese with English abstract). Yao, X. J., Liu, S. Y., Sun, M. P., et al., 2014. Study on the Glacial Lake Outburst Flood Events in Tibet since the 20th Century. Journal of Natural Resources, 29(8): 1377-1390(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, S. Z., Zhang, R. Y., Zhang, C., 1997. Meteorology and Climatology. Higher Education Press, Beijing(in Chinese). 柴波, 陶阳阳, 杜娟, 等, 2020. 西藏聂拉木县嘉龙湖冰湖溃决型泥石流危险性评价. 地球科学, 45(12): 4630-4639. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.294 陈晓清, 崔鹏, 杨忠, 等, 2006. 聂拉木县冲堆普2002年泥石流成因分析及防治对策. 冰川冻土, 28(5): 776-781. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.05.023 程尊兰, 朱平一, 宫怡文, 2003. 典型冰湖溃决型泥石流形成机制分析. 山地学报, 21(6): 716-720. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2003.06.013 乐茂华, 唐川, 张丹丹, 等, 2014. 基于逻辑回归法的西藏地区冰湖溃决危险性预测模型. 自然灾害学报, 23(5): 177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201405022.htm 刘海阔, 张义勋, 2005. 地质大辞典(一), 北京: 地质出版社. 刘晶晶, 唐川, 程尊兰, 等, 2011. 气温对西藏冰湖溃决事件的影响. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 41(4): 1121-1129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201104024.htm 刘建康, 张佳佳, 高波, 等, 2019. 我国西藏地区冰湖溃决灾害综述. 冰川冻土, 41(6): 1335-1347. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCDT201906006.htm 刘美, 2020. 流域冰湖溃决成灾机制与危险性评估(博士学位论文). 成都: 中国科学院大学, 中国科学院水利部成都山地灾害与环境研究所. 刘秧, 2016. 西藏终碛堤冰湖溃决冰川、温度条件的初步研究(硕士学位论文). 成都: 成都理工大学 吕儒仁, 唐邦兴, 李德基, 1999. 西藏泥石流与环境. 成都: 成都科技大学出版社. 汤明高, 王李娜, 刘昕昕, 等, 2022. 青藏高原冰崩隐患发育分布规律及危险性. 地球科学, 47(6)1917-1931. 王欣, 刘时银, 郭万钦, 等, 2009. 我国喜马拉雅山区冰碛湖溃决危险性评价. 地理学报, 64(7): 782-790. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.2009.07.002 徐道明, 冯清华, 1989. 西藏喜马拉雅山区危险冰湖及其溃决特征. 地理学报, 44(3): 343-351, 385. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0375-5444.1989.03.011 姚晓军, 刘时银, 孙美平, 等, 2014.20世纪以来西藏冰湖溃决灾害事件梳理. 自然资源学报, 29(8): 1377-1390. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZX201408010.htm 周淑贞, 张如一, 张超, 1997. 气象学与气候学. 北京: 高等教育出版社. -









 下载:
下载: