Failure Mechanism of Thick Colluvium Landslide Triggered by Heavy Rainfall Based on Model Test
-
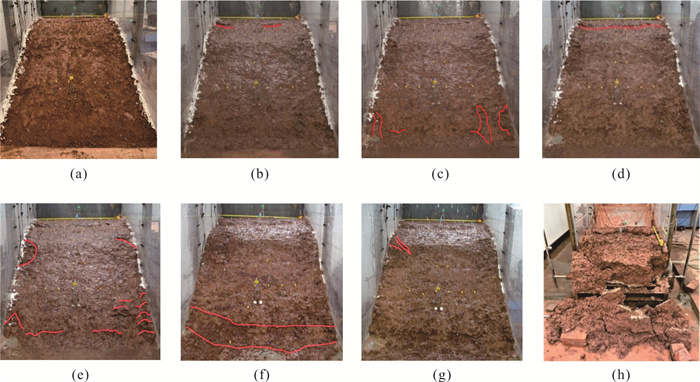
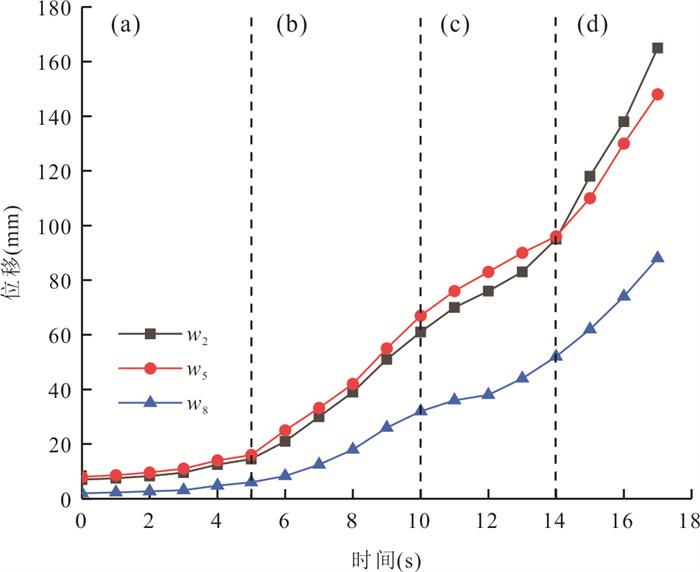
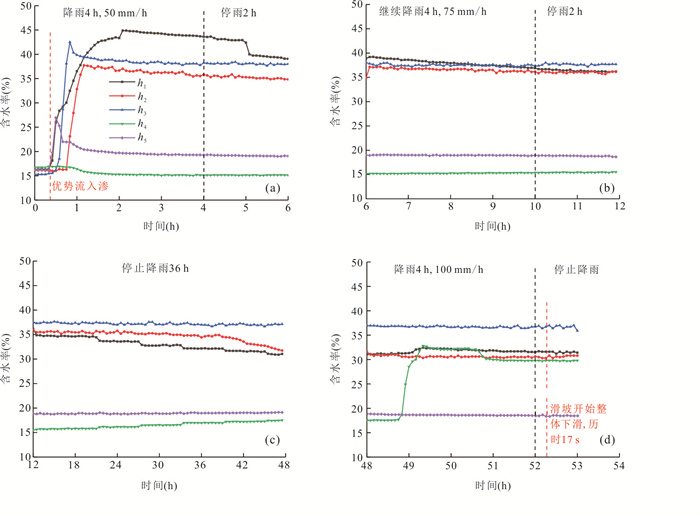
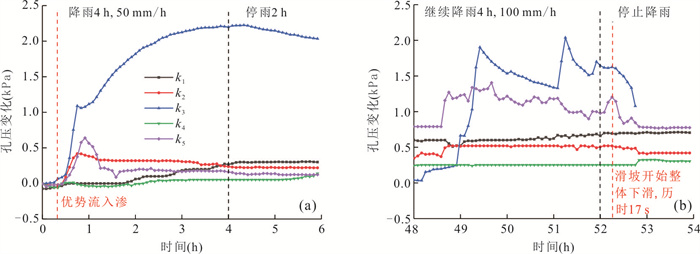
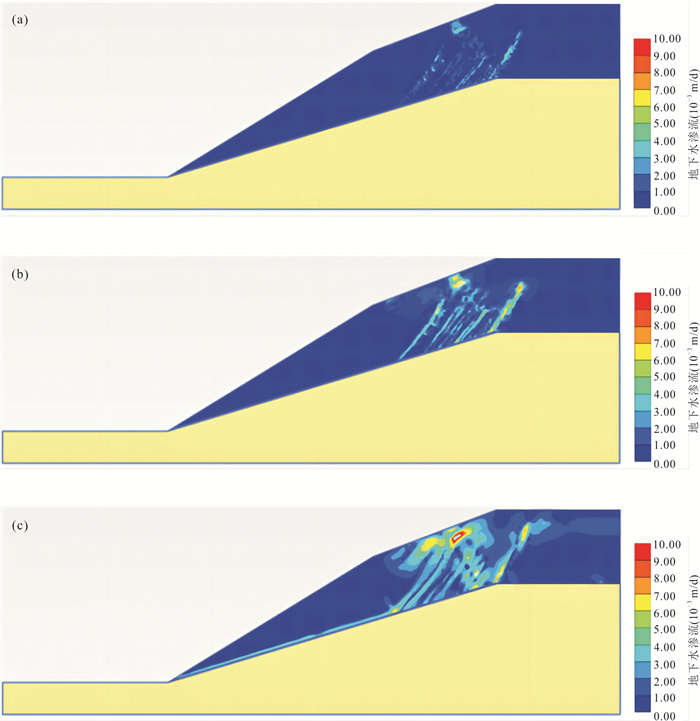
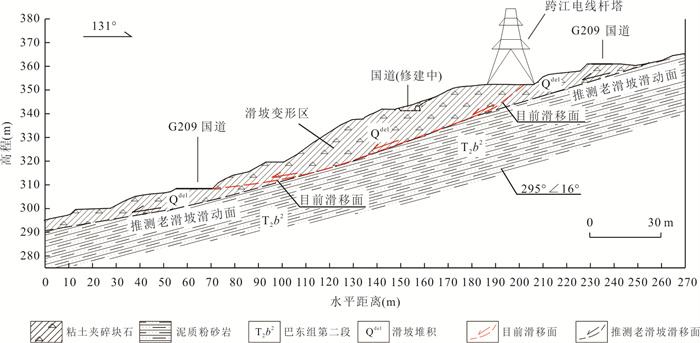
摘要: 降雨触发滑坡机制是开展滑坡灾害气象预警、风险评价和工程治理的关键科学问题.选择三峡库区巴东燕子滑坡作为典型实例,设计制作滑坡物理模型,通过设置3种强降雨工况,实时监测滑坡不同位置土压力、孔隙水压力和含水率数据,结合数值模拟与堆积层滑坡动力学理论分析,探讨了厚层堆积层滑坡在强降雨条件下的变形特征与破坏机制.试验表明:强降雨条件下滑坡变形始发于坡体上部地形转折处的后缘裂隙;强降雨导致滑坡内部土压力、孔隙水压力和含水率不同程度上升,且滑带处的上升幅度明显大于滑坡浅表处;100 mm/h极端降雨结束后,滑坡开始缓慢蠕滑,随后经历加速、短暂减速、再次加速下滑直至滑移停止的破坏演化过程.滑坡触发机制为:降雨初期,坡表以孔隙流入渗为主,后缘裂隙的形成构成了雨水入渗的优势渗流通道,雨水入渗造成滑坡地下水位上升,坡脚冲刷垮塌导致滑坡前缘出现渗流排泄点,产生动水压力,同时滑带在长时间浸泡软化作用下强度持续降低.滑坡最终在滑带剪切破坏下发生了整体推移式滑动.Abstract: The mechanism of rainfall-triggered landslides is a key issue for the development of meteorological warning, risk assessment and engineering treatment of landslide disasters. In this paper, the Badong Yanzi landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area was selected as a typical example, and the physical model of the landslide was designed and produced. By setting three heavy rainfall conditions, the soil pressure, pore water pressure and moisture content data at different positions of the landslide can be monitored at all times. According to the test results, combined with the dynamic theory of colluvium landslide and numerical simulation analysis, the deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of thick colluvium landslide under heavy rainfall conditions were discussed. Test results show that under the condition of heavy rainfall, the deformation of the landslide started from the topographic turning point at the trailing edge of the slope. Heavy rainfall caused the soil pressure, pore pressure and moisture content data inside the landslide to rise to varying degrees, and the rise in the slip zone was significantly greater than the shallow surface of the landslide; after the extreme rainfall of 100 mm/h, the landslide began to creep slowly and then underwent a failure evolution process of acceleration, short deceleration, and acceleration again until the destruction process stopped. The trigger mechanism of the landslide is analyzed as follows. In the early stage of rainfall, the slope surface is dominated by pore infiltration, and the formation of rear edge fissures has become the dominant seepage channel for rainwater infiltration. The infiltration of rainwater causes the groundwater level of the slope to rise, the hydrostatic pressure of the fissure at the trailing edge of the landslide increases, and the erosion and collapse of the slope toe leads to seepage drainage points on the front edge of the landslide, resulting in hydrodynamic pressure. And the strength of the sliding belt continues to decrease under the effect of long-term soaking and softening. The landslide eventually undergoes overall slippage caused by shifting under the shear failure of the sliding zone.
-
Key words:
- colluvium landslide /
- heavy rainfall /
- model test /
- numerical simulation /
- failure mechanism /
- engineering geology
-
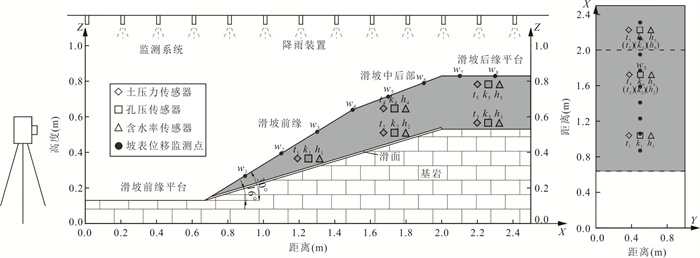
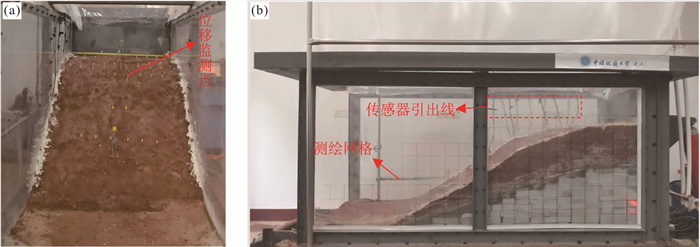
表 1 原型滑坡及相似材料部分参数对照
Table 1. Comparison of some parameters of Yanzi landslide and model landslide
滑坡结构设计 密度ρ
(g·cm-3)粘聚力c
(kPa)内摩擦角φ
(°)渗透系数k
(cm·s-1)坡体 原型坡体 1.76 25.8 23.8 3.66×10-4 配制坡体 1.80 5.6 23.0 1.15×10-5 配制方案 原状土∶河砂∶碎石∶膨润土∶水=10∶8∶2∶3∶4 滑带 原型滑带 1.95 4.67 21.3 \\ 配制滑带 1.89 0.50 22.0 \\ 配制方案 膨润土∶玻璃珠∶水=3∶3∶1 滑床 制作方案 砖砌基岩 表 2 降雨工况设置
Table 2. Setting of rainfall conditions
降雨工况 模拟实际雨强(mm/h) 观测时长(h) 工况一 50 降雨4 h,停2 h 工况二 75 降雨4 h,停2 h 工况三 100 降雨4 h,停2 h 注:工况二观测结束后静置36 h开始工况三. -
Chen, S. X., Xu, X. C., Xu, H. B., 2005. Features and Stability Analysis of Rainfall-Induced Colluvial Landslides. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 26(S2): 6-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, X. W., 2014. The Model Test Study on Rainfall-Induced Eluvial Gravel Soil Landslide (Dissertation). Xiangtan University, Xiangtan (in Chinese with English abstract). Du, F., Xu, M., Xiao, X. X., et al., 2018. Physical Simulation Modeling for Stability Analysis of Reservoir Landslide in Gently Underdip Slopes: A Case Study of Xiangjiaping Landslide. Journal of Engineering Geology, 26(3): 694-702 (in Chinese with English abstract). He, C. C., Hu, X. L., Tannant, D. D., et al., 2018. Response of a Landslide to Reservoir Impoundment in Model Tests. Engineering Geology, 247: 84-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.10.021 He, K. Q., Yang, J. B., Wang, S. J., 2007. Displacement Dynamics Theory on Debris Landslides & Its Application. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese). He, K. Q., Zhou, D. Y., Wang, S. J., 2004. Features of Load-Unload Response Ratio and Its Significance in Predication of Colluvial Landslide Induced by Rainfall. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 23(16): 2665-2670 (in Chinese with English abstract). Iverson, R. M., 2000. Landslide Triggering by Rain Infiltration. Water Resources Research, 36(7): 1897-1910. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000wr900090 Iverson, R. M., Reid, M. E., Iverson, N. R., et al., 2000. Acute Sensitivity of Landslide Rates to Initial Soil Porosity. Science, 290(5491): 513-516. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5491.513 Kong, Y. F., Zhou, M. J., Song, E. X., et al., 2014. Slope Stability Analysis in Consideration of Rainfall Influence Based on PLAXIS Software. Hydro-Science and Engineering, (3): 70-76 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2014.03.011 Li, B., Feng, Z., Zhao, R. X., et al., 2016. Mechanism of "14·9"Rainstorm Triggered Landslides and Debris-Flows in the Three Gorges Area. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 43(4): 118-127(in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y., Meng, H., Dong, Y., et al., 2004. Main Types and Characterisitics of Geo-Hazard in China—Based on the Results of Geo-Hazard Survey in 290 Counties. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 15(2): 29-34 (in Chinese with English abstract). Luo, X. Q., Liu, D. F., Wu, J., et al., 2005. Model Test Study on Landslide under Rainfall and Reservoir Water Fluctuation. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 24(14): 2476-2483(in Chinese with English abstract). Shao, W., Bogaard, T. A., Bakker, M., et al., 2015. Quantification of the Influence of Preferential Flow on Slope Stability Using a Numerical Modelling Approach. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 19(5): 2197-2212. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-19-2197-2015 Shi, Z. M., Zhao, S. Y., Su, Y., 2016. An Experimental Study of the Deposit Slope Failure Caused by Rainfall. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 43(4): 135-140(in Chinese with English abstract). Tang, X. S., Zheng, Y. R., Wu, A. Q., et al., 2006. Stability Analysis of Soil Slope under Seepage by PLAXIS Finite Element Program. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 23(4): 13-16(in Chinese with English abstract). Van Asch, T. W. J., Buma, J., van Beek, L. P. H., 1999. A View on Some Hydrological Triggering Systems in Landslides. Geomorphology, 30(1-2): 25-32. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(99)00042-2 Wang, S. T., 2018. Study on Weakening Effect and Stability Evolution Regularity of Rainfall Seepage in the Debris Landslide (Dissertation). Qingdao Tehcnology University, Qingdao(in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, W. Z., 2017. Study on Formation Mechanism of Gentle Inclined and Shallow Accumulative Landslide Induced by Heavy Rainfall (Dissertation). Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu(in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, H. Z., Feng, M. G., Jiao, Y. Y., et al., 2010. Analysis of Sliding Mechanism of Accumulation Horizon Landslide under Rainfall Condition. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 31(S1): 324-329(in Chinese with English abstract). Xiao, J. F., Li, Y. A., Cai, J. M., 2020. Model Test Research on Response Characteristics of Outang Landslide under Water Level Fluctuation. Journal of Engineering Geology, 28(5): 1049-1056(in Chinese with English abstract). Xiao, X. X., Xu, M., 2014. Deformation Behavior of Landslide in Reservoir by Model Tests. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 41(5): 107-112(in Chinese with English abstract). Xie, S. Y., Xu, W. Y., 1999. Mechanism of Landslides Induced by Precipitation. Journal of Wuhan University of Hydraulic and Electric Engineering, 32(1): 21-23(in Chinese with English abstract). Yan, E. C., Zhu, D. P., Song, K., et al., 2012. Deformation Prediction Method of Typical Accumulative Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Based on Numerical Modeling. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 42(2): 422-429(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, C. B., Li, D. Q., 2009. Advances in Rainfall-Induced Landslides Mechanism and Risk Mitigation. Advances in Earth Science, 24(5): 477-487(in Chinese with English abstract). Zuo, S. Y., Pu, Q., Shi, W. B., et al., 2021. Back Analysis of Critical Rainfall Threshold for Landslide in Low Permeable Stacking Based on Displacement Criteria on PFC3D. Journal of Natural Disasters, 30(3): 160-170(in Chinese with English abstract). Zuo, Z. B., 2013. Investigation on Rainfall-Induced Colluvium Landslides Using Laboratory Model Tests (Dissertation). Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai(in Chinese with English abstract). 陈善雄, 许锡昌, 徐海滨, 2005. 降雨型堆积层滑坡特征及稳定性分析. 岩土力学, 26(增刊2): 6-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2005S2003.htm 陈玺文, 2014. 堆积碎石土滑坡降雨致滑模型试验研究(硕士学位论文). 湘潭: 湘潭大学. 杜锋, 许模, 肖先煊, 等, 2018. 顺层缓倾型水库滑坡稳定性物理模拟试验研究: 以向家坪滑坡为例. 工程地质学报, 26(3): 694-702. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201803016.htm 贺可强, 阳吉宝, 王思敬, 2007. 堆积层滑坡位移动力学理论及其应用: 三峡库区典型堆积层滑坡例析. 北京: 科学出版社. 贺可强, 周敦云, 王思敬, 2004. 降雨型堆积层滑坡的加卸载响应比特征及其预测作用与意义. 岩石力学与工程学报, 23(16): 2665-2670. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200416000.htm 孔郁斐, 周梦佳, 宋二祥, 等, 2014. 利用PLAXIS软件计算考虑降雨的边坡稳定性. 水利水运工程学报, (3): 70-76. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLSY201403011.htm 李滨, 冯振, 赵瑞欣, 等, 2016. 三峡地区"14·9"极端暴雨型滑坡泥石流成灾机理分析. 水文地质工程地质, 43(4): 118-127. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201604022.htm 李媛, 孟晖, 董颖, 等, 2004. 中国地质灾害类型及其特征: 基于全国县市地质灾害调查成果分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 15(2): 29-34. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200402005.htm 罗先启, 刘德富, 吴剑, 等, 2005. 雨水及库水作用下滑坡模型试验研究. 岩石力学与工程学报, 24(14): 2476-2483. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200514013.htm 石振明, 赵思奕, 苏越, 2016. 降雨作用下堆积层滑坡的模型试验研究. 水文地质工程地质, 43(4): 135-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201604024.htm 唐晓松, 郑颖人, 邬爱清, 等, 2006. 应用PLAXIS有限元程序进行渗流作用下的边坡稳定性分析. 长江科学院院报, 23(4): 13-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB200604005.htm 王世通, 2018. 堆积层滑坡降雨渗流弱化效应与稳定性演化规律研究: 以三峡库区典型堆积层滑坡分析为例(硕士学位论文). 青岛: 青岛理工大学. 王维早, 2017. 强降雨诱发平缓浅层堆积层滑坡成因机理研究: 以南江县红层滑坡为例(博士学位论文). 成都: 成都理工大学. 吴火珍, 冯美果, 焦玉勇, 等, 2010. 降雨条件下堆积层滑坡体滑动机制分析. 岩土力学, 31(增刊1): 324-329. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX2010S1053.htm 肖捷夫, 李云安, 蔡浚明, 2020. 水位涨落作用下藕塘滑坡响应特征模型试验研究. 工程地质学报, 28(5): 1049-1056. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202005014.htm 肖先煊, 许模, 2014. 水库滑坡变形特征的模型试验研究. 水文地质工程地质, 41(5): 107-112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201405020.htm 谢守益, 徐卫亚, 1999. 降雨诱发滑坡机制研究. 武汉水利电力大学学报, 32(1): 21-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSDD901.005.htm 晏鄂川, 朱大鹏, 宋琨, 等, 2012. 基于数值模拟的三峡库区典型堆积层滑坡变形预测方法. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 42(2): 422-429. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ201202018.htm 周创兵, 李典庆, 2009. 暴雨诱发滑坡致灾机理与减灾方法研究进展. 地球科学进展, 24(5): 477-487. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ200905004.htm 左双英, 蒲泉, 史文兵, 等, 2021. 基于PFC3D位移判据的低渗堆积层滑坡临界降雨阈值反演. 自然灾害学报, 30(3): 160-170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH202103018.htm 左自波, 2013. 降雨诱发堆积体滑坡室内模型试验研究(硕士学位论文). 上海: 上海交通大学. -









 下载:
下载: