An Analysis Method of Thiotungstates in Natural Water
-
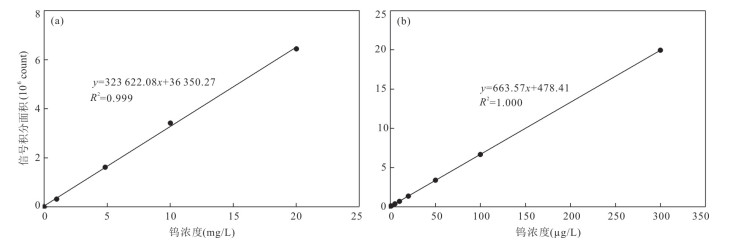
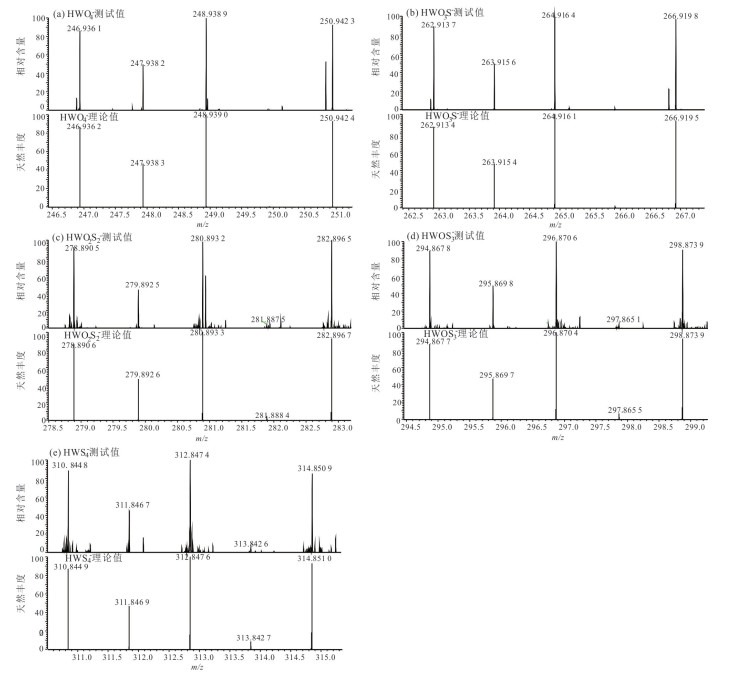
摘要: 天然水中硫代钨酸盐的分析对钨的环境地球化学研究具有重要意义. 建立了利用反相离子对色谱‒电感耦合等离子质谱同时测定天然水中钨酸盐(WO42‒)和4种硫代钨酸盐(WO3S2‒、WO2S22‒、WOS32‒、WS42‒)的方法,并采用电喷雾‒高分辨质谱对这5种钨化合物进行鉴定. 采集富硫化物地热水样品经干冰速冻并在-20 ℃冷冻保存运输至实验室后,在厌氧环境下解冻后,利用优化的色谱及质谱条件在30 min内完成5种钨化合物的分离和测定. 以钨酸盐作为其他钨化合物的标准建立工作曲线,在0.001~20 mg/L浓度范围内具有良好线性关系(相关系数R2 > 0.999),WO42‒、WO3S2‒、WO2S22‒、WOS32‒、WS42‒检出限分别为0.82、0.34、0.22、0.79和0.62 µg/L. 本方法具有灵敏度高、重现性好等优点,为天然水中硫代钨酸盐的检测和研究提供了一种有效途径.
-
关键词:
- 硫代钨酸盐 /
- 天然水 /
- 反相离子对色谱-电感耦合等离子质谱 /
- 同时检测 /
- 分析化学
Abstract: Analysis of thiotungstates in natural water is of great importance for systematically investigating the environmental geochemistry of tungsten. In this paper, a method based on a system combining reversed-phase ion pair chromatography and inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry is proposed to simultaneously determine the concentrations of tungstate (WO42‒) and four thiotungstates (including WO3S2‒, WO2S22‒, WOS32‒ and WS42‒). The speciation analyses of these five tungsten compounds were performed by a high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometer. Sulfide-rich geothermal water samples were snap frozen at -20 ℃ and transported to the laboratory. After thawing under anaerobic conditions, the five tungsten compounds were separated and determined within 30 min using optimized chromatographic and mass spectrometric conditions. The working curves were established using tungstate as the standards for the other tungsten compounds, with good linear relation (correlation coefficient R2 > 0.999) in the concentration range of 0.001-20 mg/L. The limits of detection (LOD) for tungstate, monothiotungstate, dithiotungstate, trithiotungstate and tetrathiotungstate were 0.82 µg/L, 0.34 µg/L, 0.22 µg/L, 0.79 µg/L and 0.62 µg/L, respectively. This method has the advantages of high sensitivity and good reproducibility, and provides an effective way for the detection and research of thiotungstates in natural water. -
表 1 反相色谱法常用溶剂的强度因子
Table 1. Intensity factors of common solvents used in reversed-phase chromatography
试剂 水 甲醇 乙腈 乙醇 异丙醇 溶剂强度因子 0.0 3.0 3.2 3.6 4.2 表 2 RP⁃IPC⁃ICP⁃MS联用法测试实验室配制硫代钨溶液色谱峰结果
Table 2. Analytical RP-IPC-ICP-MS results of the thiotungstates solutions prepared in the laboratory
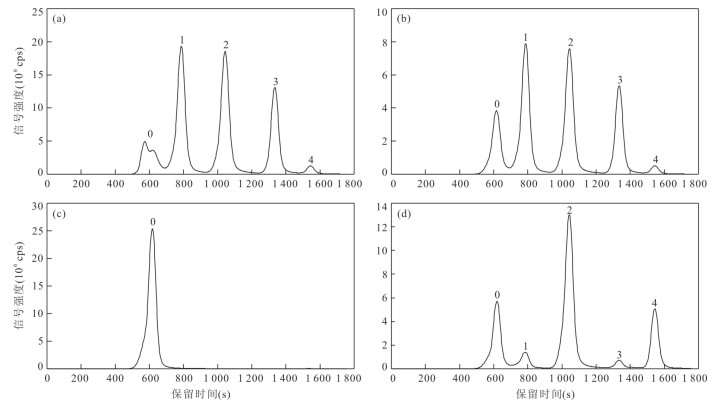
峰 钨形态 化学式a 保留时间(s) 结果 0 钨酸盐 HnWO42‒n 620 单峰(200 µL)/驼峰(500 µL) 1 一硫代钨酸盐 HnWO3S2‒n 790 单峰 2 二硫代钨酸盐 HnWO2S22‒n 1 045 单峰 3 三硫代钨酸盐 HnWOS32‒n 1 335 单峰 4 四硫代钨酸盐 HnWS42‒n 1 545 单峰 注:a.实际水溶液中受pH值的影响存在多种质子化形式(n=0~2), 为方便文中均写为脱质子形式即n=0. 表 3 实验室配制溶液硫代钨测试结果
Table 3. Quantitative analysis of thiotungstates in the solutions prepared in the laboratory

表 4 热泉样品的硫代钨和相关水化学指标分析结果
Table 4. Analysis results of thiotungstates and relevant hydrogeochemical parameters in representative hot spring samples
泉名 地热区 T
(℃)pH Eh
(mV)硫化物
(mg/L)WO42‒
(µg/L)WO3S2‒
(µg/L)WO2S22‒
(µg/L)WOS32‒
(µg/L)WS42‒
(µg/L)钨形态之和
(µg/L)总钨
(µg/L)回收率
(%)WGQ 热海 41 5.52 -41 1.4 2.4
(RSD=
4.46%)0
(RSD=
2.57%)0
(RSD=
0.81%)0
(RSD=
1.22%)0
(RSD=
4.41%)2.4 2.2 109.09 LL10 邦腊掌 91 8.36 -306 8.0 15.0
(RSD=
4.20%)7.7
(RSD=
2.35)13.2
(RSD=
2.13%)175.7
(RSD=
3.54%)62.5
(RSD=
3.79%)274.2 267.8 102.35 表 5 天然水样LL10解冻后置于空气中硫代钨形态相对含量结果
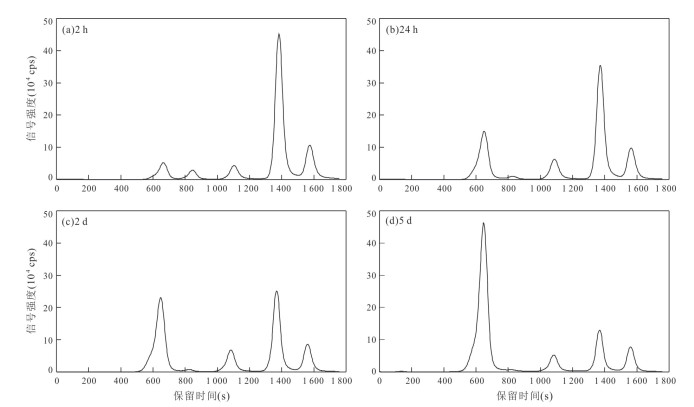
Table 5. Change of relative contents of various thiotungstates in a natural water sample (LL10) which was stored at room temperature and under oxic condition after thawing
接触空气时间 WO42‒
(%)WO3S2‒
(%)WO2S22‒
(%)WOS32‒
(%)WS42‒
(%)< 5 min 5 3 5 64 23 2 h 8 5 6 57 23 24 h 22 2 9 47 20 2 d 36 2 10 34 18 5 d 57 2 8 20 13 -
Bidlingmeyer, B. A., Deming, S. N., Jr Price, W. P., et al., 1979. Retention Mechamism for Reversed⁃Phase Ion⁃Pair Liquid Chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 186: 419-434. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021⁃9673(00)95264⁃6 Couture, R. M., Rose, J., Kumar, N., et al., 2013. Sorption of Arsenite, Arsenate, and Thioarsenates to Iron Oxides and Iron Sulfides: A Kinetic and Spectroscopic Investigation. Environmental Science & Technology, 47(11): 5652-5659. https://doi.org/10.1021/es3049724 Cui, M. M., Johannesson, K. H., 2017. Comparison of Tungstate and Tetrathiotungstate Adsorption onto Pyrite. Chemical Geology, 464: 57-68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.11.034 Dai, M. N., Bao, Z. A., Chen, K. Y., et al., 2017. Simultaneous Measurement of Major, Trace Elements and Pb Isotopes in Silicate Glasses by Laser Ablation Quadrupole and Multi⁃Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Journal of Earth Science, 28(1): 92-102. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583⁃017⁃0742⁃8 Guo, Q. H., Li, Y. M., Luo, L., 2019. Tungsten from Typical Magmatic Hydrothermal Systems in China and Its Environmental Transport. Science of the Total Environment, 657: 1523-1534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.146 Guo, Q. H., Yang, C., 2021. Tungsten Anomaly of the High⁃Temperature Hot Springs in the Daggyai Hydrothermal Area, Tibet, China. Earth Science, 46(7): 2544-2554 (in Chinese with English abstract). Kelly, A. D. R., Lemaire, M., Young, Y. K., et al., 2013. In Vivo Tungsten Exposure Alters B⁃Cell Development and Increases DNA Damage in Murine Bone Marrow. Toxicological Sciences, 131(2): 434-446. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfs324 Lee, M. K., Saunders, J. A., Wilkin, R. T., et al., 2006. Geochemical Modeling of Arsenic Speciation and Mobilization: Implications for Bioremediation. ACS Symposium Series, 915: 398-413. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk⁃2005⁃0915.ch029 Li, H. F., 2010. Comparison of Several Calculation Methods of Detection Limit. Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, 27(6): 2465-2469 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2010.06.082 Mamindy⁃Pajany, Y., Bataillard, P., Séby, F., et al., 2013. Arsenic in Marina Sediments from the Mediterranean Coast: Speciation in the Solid Phase and Occurrence of Thioarsenates. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal, 22(8): 984-1002. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2013.770441 Mohajerin, T. J., Helz, G. R., Johannesson, K. H., 2016. Tungsten⁃Molybdenum Fractionation in Estuarine Environments. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 177: 105-119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2015.12.030 Mohajerin, T. J., Helz, G. R., White, C. D., et al., 2014. Tungsten Speciation in Sulfidic Waters: Determination of Thiotungstate Formation Constants and Modeling Their Distribution in Natural Waters. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 144: 157-172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2014.08.037 Planer⁃Friedrich, B., Forberg, J., Lohmayer, R., et al., 2020. Relative Abundance of Thiolated Species of As, Mo, W, and Sb in Hot Springs of Yellowstone National Park and Iceland. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(7): 4295-4304. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c00668 Planer⁃Friedrich, B., London, J., McCleskey, R. B., et al., 2007. Thioarsenates in Geothermal Waters of Yellowstone National Park: Determination, Preservation, and Geochemical Importance. Environmental Science & Technology, 41(15): 5245-5251. https://doi.org/10.1021/es070273v Planer⁃Friedrich, B., Scheinost, A. C., 2011. Formation and Structural Characterization of Thioantimony Species and Their Natural Occurrence in Geothermal Waters. Environmental Science & Technology, 45(16): 6855-6863. https://doi.org/10.1021/es201003k Roedel, E. Q., Cafasso, D. E., Lee, K. W. M., et al., 2012. Pulmonary Toxicity after Exposure to Military⁃Relevant Heavy Metal Tungsten Alloy Particles. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 259(1): 74-86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2011.12.008 Strigul, N., Galdun, C., Vaccari, L., et al., 2009. Influence of Speciation on Tungsten Toxicity. Desalination, 248(1-3): 869-879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2009.01.016 Weiss, J., Möckel, H. J., Müller, A., et al., 1988. Retention of Thio⁃ and Selenometalates in Mobile⁃Phase Ion Chromatography. Journal of Chromatography A, 439(1): 93-108. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021⁃9673(01)81678⁃2 Yan, K. T., Guo, Q. H., Luo, L., 2022. Methylation and Thiolation of Arsenic in Tengchong Hot Springs. Earth Science, 47(2): 622-632 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, N. F., Welch, K. A., Mohajerin, T. J., et al., 2015. Comparison of Arsenic and Molybdenum Geochemistry in Meromictic Lakes of the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica: Implications for Oxyanion⁃Forming Trace Element Behavior in Permanently Stratified Lakes. Chemical Geology, 404: 110-125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.03.029 Zhuang, Y. Q., Guo, Q. H., Liu, M. L., et al., 2016. Geochemical Simulation of Thioarsenic Speciation in High⁃Temperature, Sulfide⁃Rich Hot Springs: A Case Study in the Rehai Hydrothermal Area, Tengchong, Yunnan. Earth Science, 41(9): 1499-1510 (in Chinese with English abstract). 郭清海, 杨晨, 2021. 西藏搭格架高温热泉中钨的水文地球化学异常. 地球科学, 46(7): 2544-2554. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.287 李海峰, 2010. 检出限几种常见计算方法的分析和比较. 光谱实验室, 27(6): 2465-2469. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8138.2010.06.082 严克涛, 郭清海, 罗黎, 2022. 腾冲热泉中砷的甲基化和巯基化过程. 地球科学, 47(2): 622-632. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.105 庄亚芹, 郭清海, 刘明亮, 等, 2016. 高温富硫化物热泉中硫代砷化物存在形态的地球化学模拟: 以云南腾冲热海水热区为例. 地球科学, 41(9): 1499-1510. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2016.513 -









 下载:
下载: