Distribution and Environmental Implication of GDGTs in Lake Surface Sediments from Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River
-
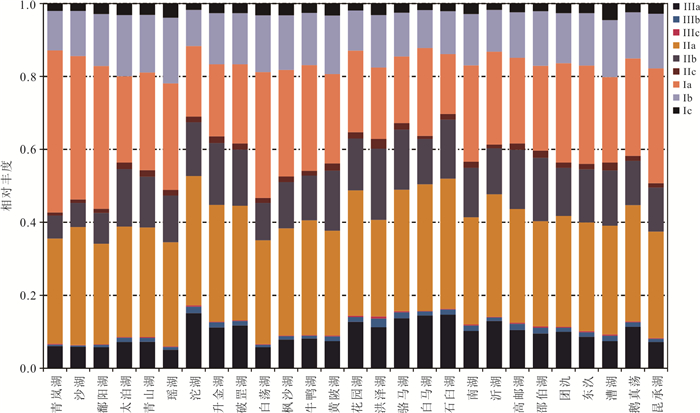
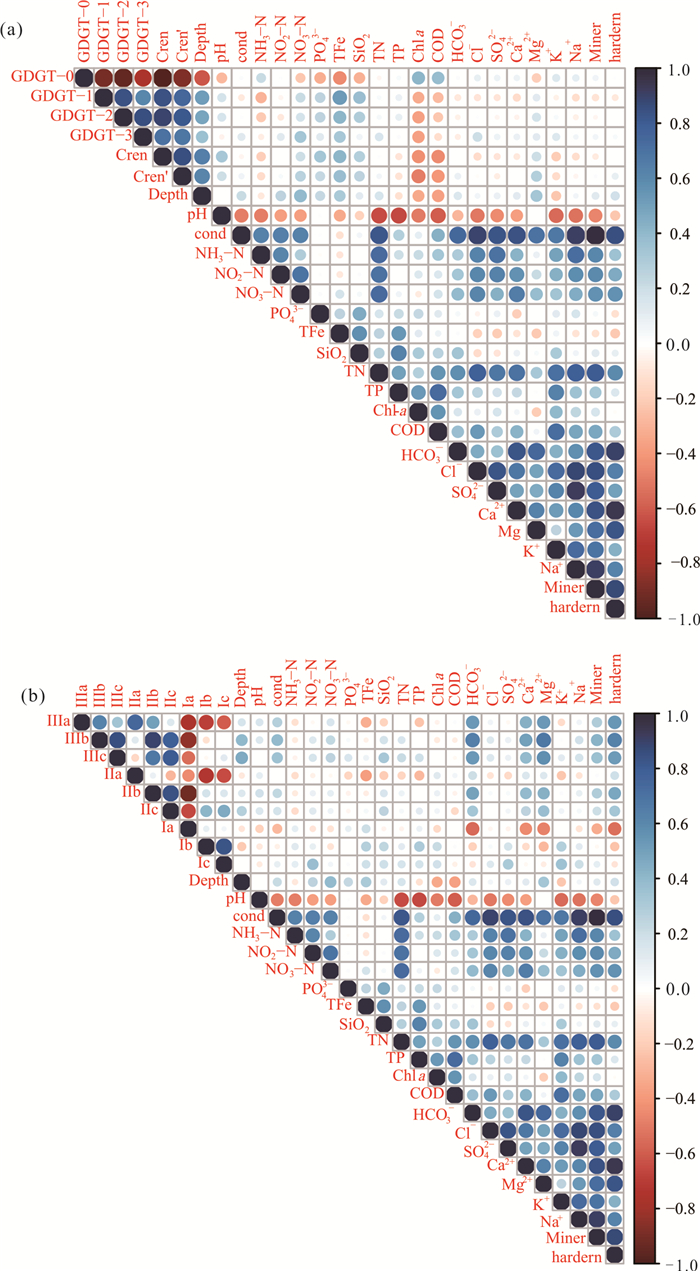
摘要: 本研究以长江中下游28个湖泊为研究对象,分析不同类型GDGTs化合物的分布特征,包括相对含量以及GDGTs各相关指标.并通过对比中国境内土壤GDGTs的分布情况,以探讨湖泊GDGTs的来源问题,研究结果表明:可能受产甲烷古菌的影响,这些浅水湖泊中古菌来源isoGDGTs与土壤存在较大差异,然而细菌来源的brGDGTs与土壤差异并不显著,据此推测很有可能来源于湖泊周边土壤的贡献.此外,这些受不同程度富营养化影响的湖泊表层沉积物GDGTs与水体化学参数的相关性分析结果显示,环境参数似乎并不能影响GDGTs的分布,然而水深与crenarchaeol之间存在显著正相关,表明在这些湖泊中,水深会影响古菌特别是奇古菌的分布.Abstract: In this study, it aims to examine the fractional abundance of GDGTs and GDGT-based proxies in 28 lakes in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River. It compares the GDGT distributions of these lakes with the published Chinese soil data to determine the lacustrine GDGT sources. The results indicate that there are different distributions of isoGDGTs between lake sediments and soils, however, the brGDGT distributions show no significant difference between lake sediments and soils, indicating that brGDGTs from lacustrine sediments may come from soils surrounding the lakes. It further measured the relationship between chemical parameters and GDGT distributions of these lakes affected by varying degrees of eutrophication. Our results show that only the water depth displays significant correlation with crenarchaeol, which implies that water depth may influence the production of Thaumarchaeota in these lake environments.
-
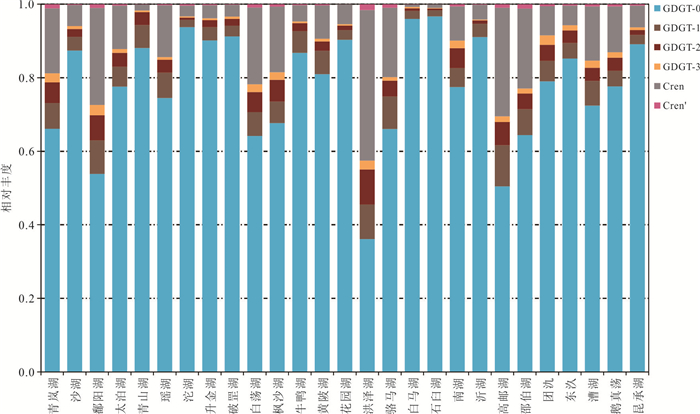
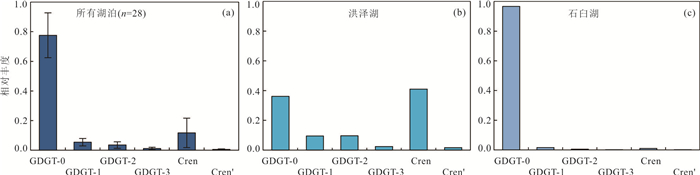
图 3 28个长江中下游湖泊表层沉积物isoGDGTs平均相对丰度(a);洪泽湖表层沉积中isoGDGTs的相对丰度(b);石臼湖表层沉积物isoGDGTs的相对丰度(c)
Fig. 3. The average fractional abundance of isoGDGTs from 28 lake surface sediments in the middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River (a); fractional abundances of isoGDGTs in surface sediments from Hongze Lake (b) and Shijiu Lake (c)
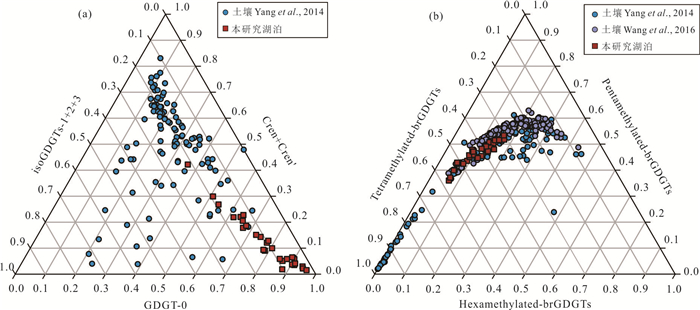
图 5 本研究中湖泊表层沉积物与中国土壤isoGDGTs和brGDGTs分布的三角示意图
a.基于isoGDGTs的GDGT-0,crenarchaeol和crenarchaeol’以及GDGT-1,-2,-3之和的三角图,中国土壤数据来源于Yang et al. (2014);b.基于brGDGTs三种不同类型化合物,即Ⅲ,Ⅱ以及Ⅰ的三角图,中国土壤数据来源于Yang et al. (2014)以及Wang et al. (2016)
Fig. 5. Ternary diagrams revealing distribution of isoGDGTs and brGDGTs in this study and Chinese soils
表 1 本研究中28个湖泊主要环境参数变化范围
Table 1. The main environmental parameters of 28 lakes in this study
环境指标名称 取值范围 水深(m) 1.2~3.9 pH 7.6~8.3 总磷(mg/L) 0.01~0.39 总氮(mg/L) 0.32~3.32 电导率(μs/cm) 83.0~700.5 化学需氧量(mg/L) 3.8~7.9 叶绿素(mg/m3) 1.2~38.5 表 2 28个湖泊的GDGTs相关指标
Table 2. The GDGT-based proxies of 28 lake surface sediments
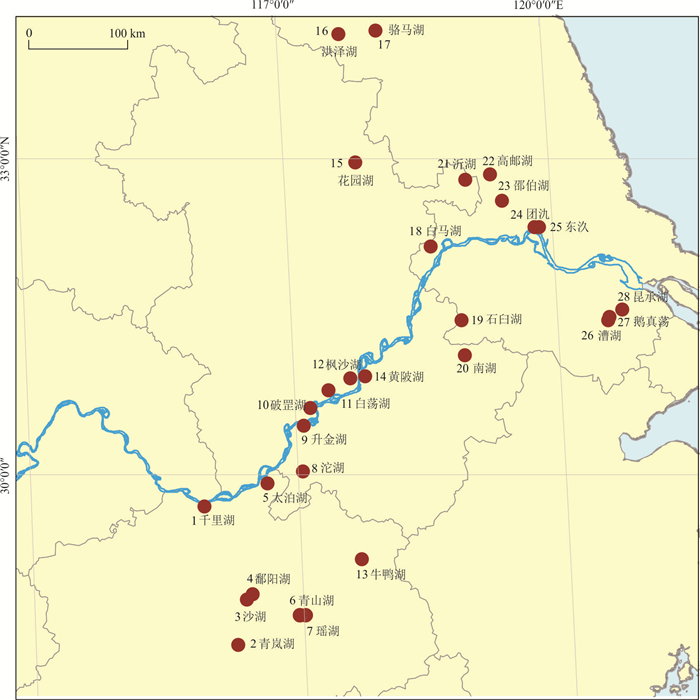
编号 名称 经纬度 水深(m) pH TEX86 MBT CBT BIT Ri/b MI RI %GDGT-0(%) Cren/Cren' 1 七里湖 29°42′N, 115°56′E 3.2 7.90 0.51 0.34 0.20 0.75 0.30 0.41 1.17 74 12 2 青岚湖 28°23′N, 116°15′E 2.6 7.83 0.57 0.57 0.63 0.82 0.31 0.45 1.01 79 15 3 沙湖 28°49′N, 116°22′E 2.3 8.01 0.46 0.54 0.58 0.93 0.13 0.53 0.34 94 27 4 鄱阳湖 28°52′N, 116°26′E 3.8 7.59 0.54 0.56 0.47 0.73 0.38 0.41 1.41 67 27 5 太泊湖 29°55′N, 116°39′E 2.4 7.96 0.49 0.44 0.22 0.84 0.15 0.45 0.65 87 30 6 青山湖 28°40′N, 116°57′E 1.3 7.63 0.40 0.46 0.28 0.98 0.58 0.86 0.21 98 16 7 瑶湖 28°40′N, 116°01′E 1.5 7.77 0.40 0.51 0.27 0.82 0.12 0.44 0.74 84 48 8 沱湖 30°02′N, 117°03′E 2.4 7.72 0.39 0.31 0.35 0.96 0.24 0.46 0.17 97 7 9 升金湖 30°28′N, 117°05′E 1.8 7.84 0.42 0.36 0.22 0.95 0.34 0.61 0.24 96 12 10 破罡湖 30°38′N, 117°10′E 1.5 7.89 0.48 0.38 0.25 0.95 0.35 0.62 0.22 97 20 11 白荡湖 30°48′N, 117°23′E 1.7 8.28 0.57 0.53 0.39 0.77 0.15 0.39 1.11 75 24 12 枫沙湖 30°55′N, 117°38′E 1.3 8.13 0.60 0.47 0.33 0.79 0.26 0.43 0.98 79 26 13 牛鸭湖 29°12′N, 117°40′E 1.9 7.92 0.33 0.46 0.36 0.94 0.27 0.64 0.30 95 17 14 黄陂湖 30°56′N, 117°48′E 1.2 7.93 0.36 0.44 0.21 0.87 0.10 0.50 0.51 90 26 15 花园湖 32°58′N, 117°49′E 2.3 7.80 0.39 0.35 0.35 0.93 0.30 0.44 0.28 94 193 16 洪泽湖 34°11′N, 117°51′E 3.9 8.17 0.59 0.37 0.13 0.58 0.33 0.33 2.06 47 26 17 骆马湖 34°13′N, 118°08′E 3.8 8.00 0.41 0.33 0.26 0.78 0.21 0.42 1.00 78 20 18 白马湖 32°10′N, 118°37′E 1.3 8.10 0.35 0.36 0.41 0.99 0.38 0.81 0.08 99 9 19 石臼湖 31°28′N, 118°55′E 2.1 8.12 0.29 0.30 0.27 0.99 0.27 0.69 0.07 99 21 20 南湖 31°08′N, 118°56′E 2.9 7.59 0.61 0.43 0.30 0.88 0.18 0.56 0.62 89 15 21 沂湖 32°48′N, 119°03′E 2.6 7.87 0.26 0.39 0.39 0.95 0.57 0.54 0.23 96 32 22 高邮湖 32°51′N, 119°20′E 3.2 8.08 0.44 0.38 0.28 0.69 0.21 0.39 1.50 63 32 23 邵伯湖 32°36′N, 119°27′E 2.6 7.94 0.49 0.40 0.21 0.74 0.17 0.36 1.11 75 19 24 团氿 32°21′N, 119°48′E 1.2 7.67 0.58 0.44 0.33 0.90 0.21 0.60 0.56 91 15 25 东汣 32°21′N, 119°51′E 1.4 7.68 0.55 0.44 0.29 0.92 0.22 0.61 0.38 94 15 26 漕湖 31°28′N, 120°34′E 3.4 7.76 0.48 0.44 0.24 0.80 0.19 0.44 0.81 83 25 27 鹅真荡 31°30′N, 120°35′E 3.0 7.67 0.57 0.42 0.37 0.85 0.35 0.42 0.68 86 21 28 昆承湖 31°34′N, 120°44′E 2.2 7.55 0.50 0.49 0.35 0.92 0.32 0.42 0.33 94 16 -
Auguet, J. C., Barberan, A., Casamayor, E. O., 2010. Global Ecological Patterns in Uncultured Archaea. The ISME Journal, 4(2): 182-190. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2009.109 Bechtel, A., Smittenberg, R. H., Bernasconi, S. M., et al., 2010. Distribution of Branched and Isoprenoid Tetraether Lipids in an Oligotrophic and a Eutrophic Swiss Lake: Insights into Sources and GDGT-Based Proxies. Organic Geochemistry, 41(8): 822-832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2010.04.022 Blaga, C. I., Reichart, G. J., Heiri, O., et al., 2009. Tetraether Membrane Lipid Distributions in Water-Column Particulate Matter and Sediments: A Study of 47 European Lakes along a North-South Transect. Journal of Paleolimnology, 41(3): 523-540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-008-9242-2 Castañeda, I. S., Schouten, S., 2011. A Review of Molecular Organic Proxies for Examining Modern and Ancient Lacustrine Environments. Quaternary Science Reviews, 30(21/22): 2851-2891. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2011.07.009 Chen, L., Huang, Z. D., Niu, L. L., et al., 2021. GDGTS-Based Quantitative Reconstruction of Water Level Changes and Precipitation at Daye Lake, Qinling Mountains (Central-East China), over the Past 2 000 Years. Quaternary Science Reviews, 267: 107099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.quascirev.2021.107099 Damsté, J. S., Schouten, S., Hopmans, E. C., et al., 2002. Crenarchaeol: The Characteristic Core Glycerol Dibiphytanyl Glycerol Tetraether Membrane Lipid of Cosmopolitan Pelagic Crenarchaeota. Journal of Lipid Research, 43(10): 1641-1651. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.m200148-jlr200 Fietz, S., Huguet, C., Bendle, J., et al., 2012. Co-Variation of Crenarchaeol and Branched GDGTS in Globally-Distributed Marine and Freshwater Sedimentary Archives. Global and Planetary Change, 92/93: 275-285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2012.05.020 Hopmans, E. C., Weijers, J. W. H., Schefuß, E., et al., 2004. A Novel Proxy for Terrestrial Organic Matter in Sediments Based on Branched and Isoprenoid Tetraether Lipids. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 224(1/2): 107-116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2004.05.012 Huguet, C., Hopmans, E. C., Febo-Ayala, W., et al., 2006. An Improved Method to Determine the Absolute Abundance of Glycerol Dibiphytanyl Glycerol Tetraether Lipids. Organic Geochemistry, 37(9): 1036-1041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2006.05.008 Inglis, G. N., Farnsworth, A., Lunt, D., et al., 2015. Descent toward the Icehouse: Eocene Sea Surface Cooling Inferred from GDGT Distributions. Paleoceanography, 30(7): 1000-1020. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014pa002723 Li, J. J., Naafs, B. D. A., Pancost, R. D., et al., 2017. Distribution of Branched Tetraether Lipids in Ponds from Inner Mongolia, NE China: Insight into the Source of BRGDGTS. Organic Geochemistry, 112: 127-136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2017.07.005 Li, J. J., Pancost, R. D., Naafs, B. D. A., et al., 2016. Distribution of Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraether (GDGT) Lipids in a Hypersaline Lake System. Organic Geochemistry, 99: 113-124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.06.007 Li, J. J., Pancost, R. D., Naafs, B. D. A., et al., 2019. Multiple Environmental and Ecological Controls on Archaeal Ether Lipid Distributions in Saline Ponds. Chemical Geology, 529: 119293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2019.119293 Li, J. J., Yang, H., Zheng, F. F., et al., 2021. Occurrence and Distribution of Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers in Lake Water Column: A Review. Journal of Lake Sciences, 33(5): 1334-1349 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18307/2021.0504 Ma, R. H., Yang, G. S., Duan, H. T., et al., 2011. China's Lakes at Present: Number, Area and Spatial Distribution. Science China Earth Sciences, 54(2): 283-289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-010-4052-6 Naeher, S., Peterse, F., Smittenberg, R. H., et al., 2014. Sources of Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers (GDGTS) in Catchment Soils, Water Column and Sediments of Lake Rotsee (Switzerland)-Implications for the Application of GDGT-Based Proxies for Lakes. Organic Geochemistry, 66: 164-173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2013.10.017 Pearson, E. J., Juggins, S., Talbot, H. M., et al., 2011. A Lacustrine GDGT-Temperature Calibration from the Scandinavian Arctic to Antarctic: Renewed Potential for the Application of GDGT-Paleothermometry in Lakes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(20): 6225-6238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2011.07.042 Powers, L., Werne, J. P., Vanderwoude, A. J., et al., 2010. Applicability and Calibration of the TEX86 Paleothermometer in Lakes. Organic Geochemistry, 41(4): 404-413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.11.009 Powers, L. A., Werne, J. P., Johnson, T. C., et al., 2004. Crenarchaeotal Membrane Lipids in Lake Sediments: A New Paleotemperature Proxy for Continental Paleoclimate Reconstruction?. Geology, 32(7): 613-616. https://doi.org/10.1130/g20434.1 Schouten, S., Hopmans, E. C., Schefuß, E., et al., 2002. Distributional Variations in Marine Crenarchaeotal Membrane Lipids: A New Tool for Reconstructing Ancient Sea Water Temperatures?. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 204(1-2): 265-274. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00979-2 Schouten, S., Hopmans, E. C., Sinninghe Damsté, J. S., 2013. The Organic Geochemistry of Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraether Lipids: A Review. Organic Geochemistry, 54: 19-61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2012.09.006 Schouten, S., van der Meer, M. T. J., Hopmans, E. C., et al., 2007. Archaeal and Bacterial Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraether Lipids in Hot Springs of Yellowstone National Park. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 73(19): 6181-6191. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00630-07 Sinninghe Damsté, J. S., Rijpstra, W. I., Hopmans, E. C., et al., 2014. Ether- and Ester-Bound Iso-Diabolic Acid and other Lipids in Members of Acidobacteria Subdivision 4. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 80(17): 5207-5218. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01066-14 Sun, Q., Chu, G. Q., Liu, M. M., et al., 2011. Distributions and Temperature Dependence of Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraethers in Recent Lacustrine Sediments from China and Nepal. Journal of Geophysical Research, 116(G1): G01008. https://doi.org/10.1029/2010jg001365 Tierney, J. E., Russell, J. M., 2009. Distributions of Branched GDGTS in a Tropical Lake System: Implications for Lacustrine Application of the MBT/CBT Paleoproxy. Organic Geochemistry, 40(9): 1032-1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2009.04.014 van Bree, L. G. J., Peterse, F., Baxter, A. J., et al., 2020. Seasonal Variability and Sources of In Situ BRGDGT Production in a Permanently Stratified African Crater Lake. Biogeosciences, 17(21): 5443-5463. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-17-5443-2020 Wang, H. Y., Dong, H. L., Zhang, C. L., et al., 2014. Water Depth Affecting Thaumarchaeol Production in Lake Qinghai, Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Implications for Paleo Lake Levels and Paleoclimate. Chemical Geology, 368: 76-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.01.009 Wang, H. Y., Liu, W. G., Lu, H. X., 2016. Appraisal of Branched Glycerol Dialkyl Glycerol Tetraether-Based Indices for North China. Organic Geochemistry, 98: 118-130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2016.05.013 Wang, M. D., Tian, Q., Li, X. M., et al., 2020. TEX86 as a Potential Proxy of Lake Water pH in the Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 538: 109381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2019.109381 Weijers, J. W. H., Schouten, S., Hopmans, E. C., et al., 2006. Membrane Lipids of Mesophilic Anaerobic Bacteria Thriving in Peats have Typical Archaeal Traits. Environmental Microbiology, 8(4): 648-657. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2005.00941.x Weijers, J. W. H., Schouten, S., van den Donker, J. C., et al., 2007. Environmental Controls on Bacterial Tetraether Membrane Lipid Distribution in Soils. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(3): 703-713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2006.10.003 Xie, S., Pancost, R. D., Chen, L., et al., 2012. Microbial Lipid Records of Highly Alkaline Deposits and Enhanced Aridity Associated with Significant Uplift of the Tibetan Plateau in the Late Miocene. Geology, 40(4): 291-294. https://doi.org/10.1130/g32570.1 Xie, S. C., Hu, C. Y., Gu, Y. S., et al., 2015. Paleohydrological Variation since 13 ka BP in Middle Yangtze Region. Earth Science, 40(2): 198-205 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, H., Pancost, R. D., Dang, X. Y., et al., 2014. Correlations between Microbial Tetraether Lipids and Environmental Variables in Chinese Soils: Optimizing the Paleo-Reconstructions in Semi-Arid and Arid Regions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 126: 49-69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2013.10.041 Yao, Y., Zhao, J. J., Bauersachs, T., et al., 2019. Effect of Water Depth on the TEX86 Proxy in Volcanic Lakes of Northeastern China. Organic Geochemistry, 129: 88-98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2019.01.014 Zhang, Y. G., Pagani, M., Wang, Z. R., 2016. Ring Index: A New Strategy to Evaluate the Integrity of TEX86 Paleothermometry. Paleoceanography, 31(2): 220-232. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015pa002848 Zhang, Y. G., Zhang, C. L., Liu, X. L., et al., 2011. Methane Index: A Tetraether Archaeal Lipid Biomarker Indicator for Detecting the Instability of Marine Gas Hydrates. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 307(3/4): 525-534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2011.05.031 Zheng, F. F., Chen, Y. F., Wang, Y. L., et al., 2018. Influence of Seasonal Temperature Variation and pH Disparity on BGDGTS Thermometers in Soils. Earth Science, 43(S1): 71-83 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, G. W., Xu, H., Zhu, M. Y., et al., 2019. Changing Characteristics and Driving Factors of Trophic State of Lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River in the Past 30 Years. Journal of Lake Sciences, 31(6): 1510-1524 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18307/2019.0622 Zhu, X. C., Wang, Y. B., Dang, X. Y., et al., 2022. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Microbial Tetraether Lipids in a Lake and Its Inflowing River: Implications for the Identification of Flooding Events. Journal of Earth Science, 33(6): 1601-1613. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1552-6 李婧婧, 杨欢, 郑峰峰, 等, 2021. 湖泊水体微生物四醚膜脂化合物研究进展. 湖泊科学, 33(5): 1334-1349. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX202105004.htm 谢树成, 胡超涌, 顾延生, 等, 2015. 最近13 ka以来长江中游古水文变化. 地球科学, 40(2): 198-205. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.015 郑峰峰, 陈雨霏, 王永莉, 等, 2018. 季节温度变化及土壤pH差异对土壤bGDGTs温度指标的影响. 地球科学, 43(S1): 71-83. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.950 朱广伟, 许海, 朱梦圆, 等, 2019. 三十年来长江中下游湖泊富营养化状况变迁及其影响因素. 湖泊科学, 31(6): 1510-1524. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201906003.htm -









 下载:
下载: