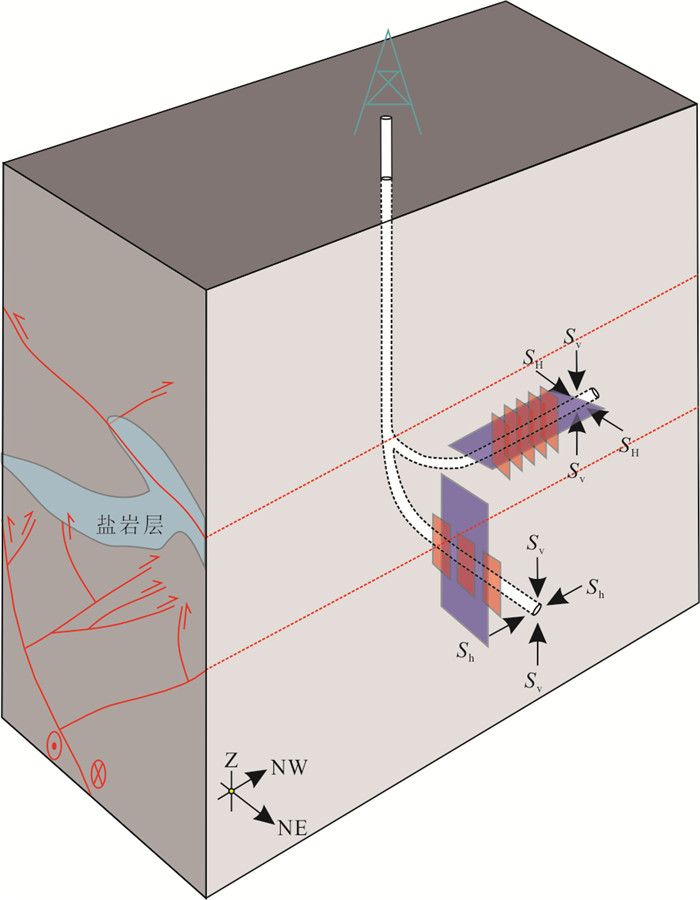
Relation between Effective Fractures and In-Situ Stress as well as Its Significance in Upper Xiaganchaigou Formation in Shizigou Structure, Qaidam Basin
-
摘要: 柴达木盆地西南部狮子沟构造下干柴沟组上段致密湖相碳酸盐岩中普遍发育构造裂缝,是控制油气高产的关键因素.研究旨在建立该段现今地应力状态及裂缝产状分布规律,这对在致密储层中圈定有效裂缝和考虑压裂缝分布的水平井方向设计具有重要意义.本文以岩心、薄片揭示裂缝特征,从三维地震数据体提取断裂与A、B、C井钻井轨迹的空间关系;选取A、B两口井水平段建立地应力剖面;选取A、C两口井成像测井段统计裂缝产状并进一步以极射赤平投影、玫瑰花图和倾角分布图展现产状规律.3口井水平段走向近平行于北西向走滑正花状断裂系.地应力测井显示下干柴沟组上段测量段为走滑断层地应力状态.未充填的高导缝和充填的高阻缝主体走向均为北东,倾角为高角度至近竖直,其形成受控于早中新世以来的最大水平主应力方向为北东向的走滑断层地应力状态.未充填裂缝或发生溶蚀的充填裂缝可作为油气储集空间和运移通道.北东走向未充填的竖直裂缝为最优的有效裂缝.靠近北西向主断裂的北东向水平井将钻遇更多天然裂缝,压裂形成北东向延伸的竖直有效裂缝.在北西向水平井产量不佳情况下,靠近断裂的北东向水平井设计值得考虑.Abstract: In the SW Qaidam Basin, fractures are widely developed in tight lacustrine carbonate rocks of the Upper Xiagnchaigou Formation in the Shizigou structure, which is the key factor controlling the high production of hydrocarbon. The purpose of this study is to establish the present-day in-situ stress state and distribution patterns of fracture attitudes, which is significant to determine effective fractures and to design horizontal well orientations considering hydraulic fracture distribution. In this study, fracture characteristics were revealed in cores and thin sections. The spatial relation between deep faults and trajectories of Well A, Well B and Well C was extracted from 3D seismic data. We selected horizontal intervals of Well A and Well B to construct in-situ stress profiles and image log intervals of Well A and Well C to count fracture attitudes which were further shown by stereonets, rose diagrams and fracture dip histograms. Horizontal intervals of three selected wells are nearly parallel to the NW-trending faults belonging to the strike-slip positive flower structure. Geostress logging shows that the measuring intervals in the Upper Xiaganchaigou Formation are under the strike-slip faulting stress state. Most unfilled conductive fractures and filled resistive fractures have NE strikes and high to near-vertical dips, and they were dominated by the strike-slip faulting stress state whose maximum horizontal principal stress is in the NE direction since the Early Miocene. Unfilled fractures and dissolved fractures which were previously filled can act as hydrocarbon reservoirs and migration pathways. NE-trending unfilled fractures with vertical dips are the most effective fractures. If NE-trending horizontal wells are drilled near NW-trending main faults, more natural fractures will be met, and NE-trending hydraulic fractures with vertical dips are effective. The design of NE-trending horizontal wells is worth considering due to the poor production of NW-trending horizontal wells.
-
Key words:
- fractured reservoir /
- image log /
- in-situ stress state /
- horizontal well /
- Qaidam Basin /
- geomechanics
-
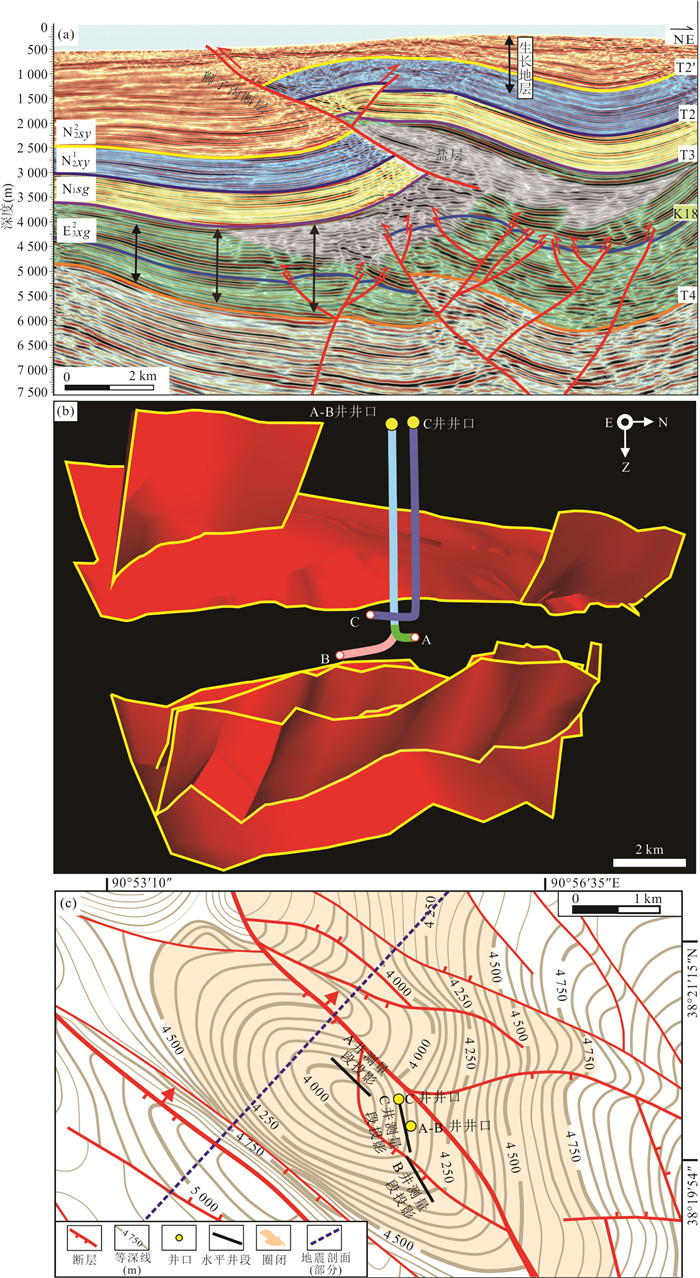
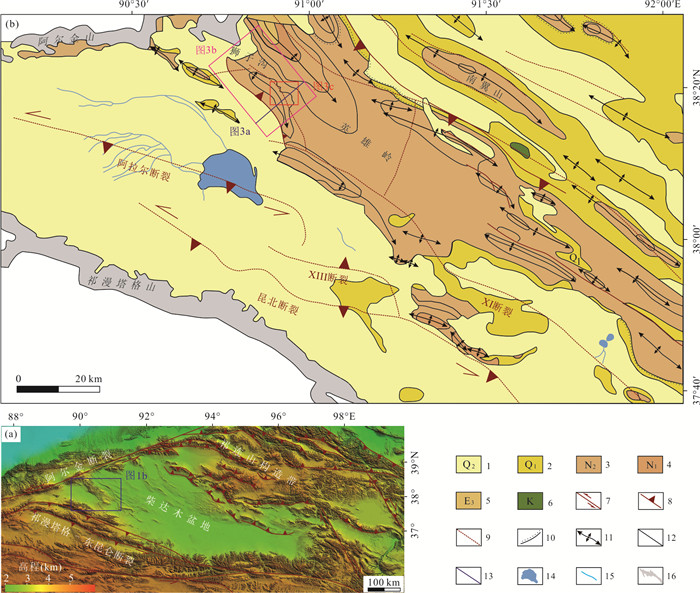
图 4 狮子沟构造主断裂特征及其与选取井段的空间关系
a.狮子沟构造地震剖面图揭示断裂系统分为盐上逆冲断裂和盐下走滑正花状断裂系,剖面具体位置见图 1b;b.三维空间中狮子沟盐上和盐下断裂系统与A、B、C三口井间的关系,三维地震范围见图 1b,深度范围为0~7.5 km;c.下干柴沟组上段中沿K18层显示的构造纲要图,A、B、C三口井测量段投影以及井口坐标标注于图中,具体范围见图 1b
Fig. 4. Characteristics of main faults in the Shizigou structure and faults' relation with selected wells
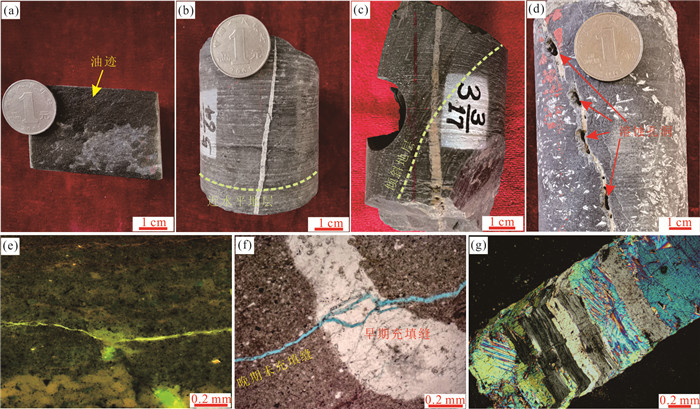
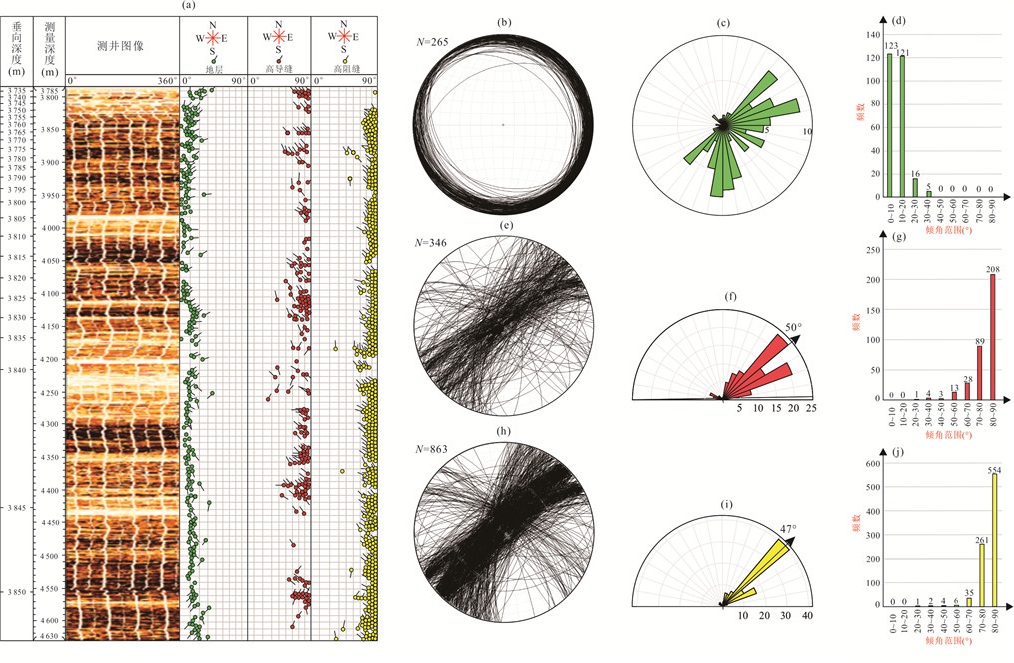
图 5 岩心和薄片中显示的下干柴沟组上段裂缝特征
a.岩心中近竖直未充填缝表面显示油迹;b.岩心中近水平地层发育完全充填的近竖直裂缝;c.岩心中倾斜地层中发育完全充填的近竖直裂缝;d.岩心中,沿高角度充填缝发育溶蚀孔洞;e.荧光薄片中显示裂缝内含油;f.在单偏光镜下,铸体薄片显示裂缝分为两期,第二期未充填裂缝切过第一期完全被硬石膏充填的裂缝;g.在正交偏光镜下,裂缝中充填定向生长的硬石膏
Fig. 5. Characteristics of fractures in the Upper Xiaganchaigou Formation shown in cores and thin sections
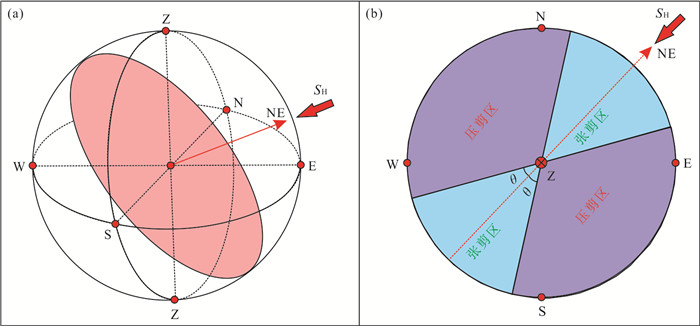
图 10 (a) 北东向水平主应力最大的走滑断层地应力状态下, 任意裂缝面在球状空间中的表达;(b)投影平面中张剪裂缝区与压剪裂缝区的分布(θ为岩石的剪破裂角)
Fig. 10. (a) Under the strike-slip faulting stress state with the NE trending maximum principal stress, any fracture can be expressed in Spherical space; (b) distribution of extension-shear fracture zones and compression-shear fracture zones in a projection plane (θ representing the rupture angle of rocks)
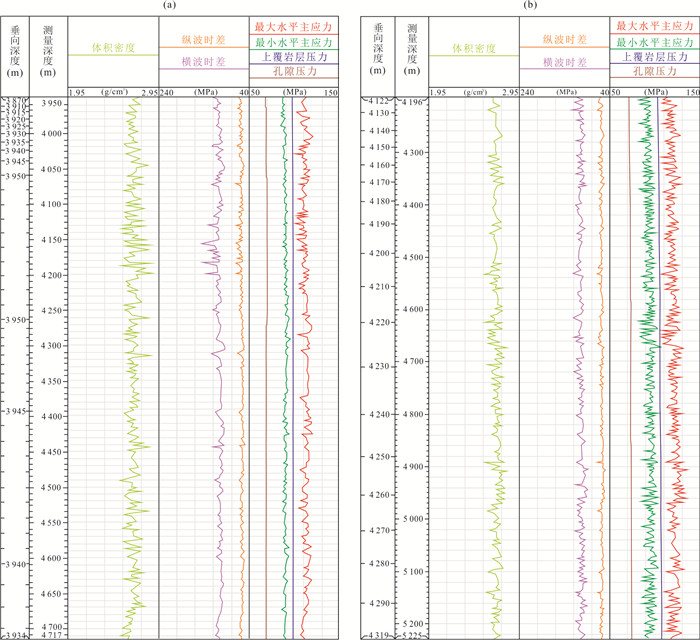
表 1 A、B两口井地应力测量范围及参数
Table 1. Measuring range and parameters of geostress in Well A and Well B
井号 测量深度
(m)垂向深度
(m)最大水平主应力范围
(MPa)最小水平主应力范围
(MPa)垂向主应力范围
(MPa)地应力状态 A 3 900~4 717 3 870~3 934 101~122 84~95 96~99 SF B 4 196~5 225 4 122~4 319 115~125 86~102 104~107 SF -
Ameen, M. S., 2014. Fracture and In-Situ Stress Patterns and Impact on Performance in the Khuff Structural Prospects, Eastern Offshore Saudi Arabia. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 50: 166-184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2013.10.004 Anderson, E. M., 1953. The Dynamics of Faulting: And Dyke Formation with Applications to Britain. Oliver and Boyd, Edinburgh. Bao, Y. S., 2019. Fracture Diversity of Continental Shale under Horizontal Geostress: A Case Study of the Paleogene Shale in Jiyang Depression. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(7): 777-785 (in Chinese with English abstract). Barton, C., Moos, D., Tezuka, K., 2009. Geomechanical Wellbore Imaging: Implications for Reservoir Fracture Permeability. AAPG Bulletin, 93(11): 1551-1569. https://doi.org/10.1306/06180909030 Bian, Q., Zhang, D. W., Yu, X. J., et al., 2019. Transpressional Salt Tectonic System in Western Qaidam Basin, Western China. AAPG Bulletin, 103(3): 547-568. https://doi.org/10.1306/08161817119 Brown, E. T., Hoek, E., 1978. Trends in Relationships between Measured in-Situ Stresses and Depth. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences & Geomechanics Abstracts, 15(4): 211-215. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(78)91227-5 Cheng, F., Jolivet, M., Fu, S. T., et al., 2014. Northward Growth of the Qimen Tagh Range: A New Model Accounting for the Late Neogene Strike-Slip Deformation of the SW Qaidam Basin. Tectonophysics, 632: 32-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2014.05.034 Cheng, X., Zhang, D. W., Jolivet, M., et al., 2018. Cenozoic Structural Inversion from Transtension to Transpression in Yingxiong Range, Western Qaidam Basin: New Insights into Strike-Slip Superimposition Controlled by Altyn Tagh and Eastern Kunlun Faults. Tectonophysics, 723: 229-241. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tecto.2017.12.019 Cheng, X. A., Guo, Z. J., Chen, Y., et al., 2022. Oblique Strike-Slip Superimposed Structure in Yingxiong Range, Western Qaidam Basin and Its Response to Altyn Tagh Fault and Eastern Kunlun Fault. International Geology Review, 64(13): 1912-1932. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2021.1989630 Du, J. M., Zhang, X. L., Wang, Q. C., et al., 2017. Characteristics of the Fractures of E$ {}_{3}^{2} $ Reservoir in Yingxi Area, Qaidam Basin. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences), 53(4): 452-458 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fan, X. Y., Kang, H. T., Gong, M., et al., 2012. Fine Calculation Method Study of Crustal Stress of High-Steep Conformation in Northeast Sichuan. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 34(3): 41-46 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ferrill, D. A., Smart, K. J., Cawood, A. J., et al., 2021. The Fold-Thrust Belt Stress Cycle: Superposition of Normal, Strike-Slip, and Thrust Faulting Deformation Regimes. Journal of Structural Geology, 148: 104362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2021.104362 Fu, S. T., Ma, D. D., Guo, Z. J., et al., 2015. Strike-Slip Superimposed Qaidam Basin and Its Control on Oil and Gas Accumulation, NW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 42(6): 713-722 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gudmundsson, A., Simmenes, T. H., Larsen, B., et al., 2010. Effects of Internal Structure and Local Stresses on Fracture Propagation, Deflection, and Arrest in Fault Zones. Journal of Structural Geology, 32(11): 1643-1655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2009.08.013 Guo, R. T., Ma, D. D., Zhang, Y. S., et al., 2019. Characteristics and Formation Mechanism of Overpressure Pore-Fracture Reservoirs for Upper Member of Xiaganchaigou Formation in the West of Yingxiong Ridge, Qaidam Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(4): 411-422 (in Chinese with English abstract). He, S., Ye, J. R., Xu, S. H., et al., 2010. Petroleum and Natural Gas Geology. China University of Geosciences Press, Wuhan (in Chinese). Ju, W., Jiang, B., Qin, Y., et al., 2019. The Present-Day In-Situ Stress Field within Coalbed Methane Reservoirs, Yuwang Block, Laochang Basin, South China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 102: 61-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.12.030 Li, L., Hou, G. T., Pan, W. Q., et al., 2011. The Constraints of Reverse Fault to the Development of Structural Fractures in Compacted Rocks. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(2): 466-473 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, X., Wang, J. G., Zhang, P., et al., 2018. Fracture Genesis Mechanism and Geological Significance of E$ {}_{3}^{2} $ in Yingxi Area, Qaidam Basin. Lithologic Reservoirs, 30(6): 45-54 (in Chinese with English abstract). Rajabi, M., Tingay, M., Heidbach, O., 2016. The Present-Day State of Tectonic Stress in the Darling Basin, Australia: Implications for Exploration and Production. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 77: 776-790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.07.021 Shi, Y. H., 2019. Establishment and Application of Three-Pressure Profile of Changning Shale Gas Horizontal Well (Dissertation). Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu (in Chinese with English abstract). Snee, J. L., Zoback, M. D., 2022. State of Stress in Areas of Active Unconventional Oil and Gas Development in North America. AAPG Bulletin, 106(2): 355-385. https://doi.org/10.1306/08102120151 Tamagawa, T., Pollard, D. D., 2008. Fracture Permeability Created by Perturbed Stress Fields around Active Faults in a Fractured Basement Reservoir. AAPG Bulletin, 92(6): 743-764. https://doi.org/10.1306/02050807013 Tang, S. H., 2001. Probe into the Influence Factors on Permeability of Coal Reservoirs. Coal Geology of China, 13(1): 28-30, 86 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tingay, M. R. P., Hillis, R. R., Morley, C. K., et al., 2009. Present-Day Stress and Neotectonics of Brunei: Implications for Petroleum Exploration and Production. AAPG Bulletin, 93(1): 75-100. https://doi.org/10.1306/08080808031 Wang, X. F., Wu, H. L., Ma, Y. S., et al., 2006. Controls of the Tectonic Stress Field and Fluid Potential Field on Hydrocarbon Migration and Accumulation in the Western Qaidam Basin, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(S2): 1036-1044 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wen, Z., Kang, Y. S., Deng, Z., et al., 2019. Characteristics and Distribution of Current In-Situ Stress at Shallow-Medium Depth in Coal-Bearing Basins in China. Geological Review, 65(3): 729-742 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, J. W., Wang, Q. Q., Cheng, X., et al., 2023. Formation of Multi-Stage and Clustered Fractures at 3.6-4.9 km in the Shizigou Structure, SW Qaidam Basin. Journal of Structural Geology, 169: 104845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsg.2023.104845 Xiong, T. S., Zhang, C. J., Zhao, E. D., et al., 2019. Feasibility Study of Reservoir Volume Fracturing in Complex Geostress State in Yingxi Area. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 40(5): 579-582 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yan, P., Sun, J. M., Su, Y. D., et al., 2006. The Earth Stress Calculation Using Well Logging Data in Dina Gas Field of Xinjiang. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 27(5): 611-614 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, X. J., Zhang, M., Yan, X, J., 2008. Study on Acoustic Logging-Based Rock Elasticity Parameters. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 22(4): 39-42 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yu, X. J., Guo, Z. J., Zhang, D. W., et al., 2018. Quaternary Shaking: Evidences of Tectonic Intensification from the Qaidam Basin and Its Influence on Multi-Spherical Interaction. Quaternary Sciences, 38(1): 39-53 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yu, X. J., Huang, B. C., Guan, S. W., et al., 2014. Anisotropy of Magnetic Susceptibility of Eocene and Miocene Sediments in the Qaidam Basin, Northwest China: Implication for Cenozoic Tectonic Transition and Depocenter Migration. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 15(6): 2095-2108. https://doi.org/10.1002/2014gc005231 Zeng, L. B., Qi, J. F., 2006. Structural Geology in Stage of Reservoir Development. Geological Science and Technology Information, 25(4): 15-20 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zeng, L. B., Tang, X. M., Qi, J. F., et al., 2012b. Insight into the Cenozoic Tectonic Evolution of the Qaidam Basin, Northwest China from Fracture Information. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 101(8): 2183-2191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-012-0779-y Zeng, L. B., Tang, X. M., Wang, T. C., et al., 2012a. The Influence of Fracture Cements in Tight Paleogene Saline Lacustrine Carbonate Reservoirs, Western Qaidam Basin, Northwest China. AAPG Bulletin, 96(11): 2003-2017. https://doi.org/10.1306/04181211090 Zhang, B., Zhang, F. Q., Zhuo, Q. G., et al., 2022. Distribution Prediction of Tectonic Fractures in the Upper Member of Xiaganchaigou Formation in Yingxi Area, Qaidam Basin. Progress in Geophysics, 37(2): 709-720 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, C. Y., Wu, M. L., Chen, Q. C., et al., 2012. Review of In-Situ Stress Measurement Methods. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University (Natural Science), 31(3): 305-310 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Q. H., Gao, F. R., Zhao, H. Z., et al., 2020. Fine Characterization of Multi-Scale and Multi-Type Natural Fractures for Yingxi E$ {}_{3}^{2} $ Shale Reservoirs. Geological Review, 66(S1): 117-118 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, J. X., Xu, F. Y., Wang, T. C., et al., 2006. Cenozoic Deformation History of the Qaidam Basin, NW China: Results from Cross-Section Restoration and Implications for Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Tectonics. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 243(1-2): 195-210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2005.11.033 包友书, 2019. 陆相泥页岩在水平地应力作用下裂缝的多样性——以济阳坳陷古近系泥页岩为例. 石油学报, 40(7): 777-785. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201907003.htm 杜江民, 张小莉, 王青春, 等, 2017. 柴达木盆地英西地区E$ {}_{3}^{2} $储层裂缝发育特征. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 53(4): 452-458. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LDZK202301008.htm 范翔宇, 康海涛, 龚明, 等, 2012. 川东北山前高陡构造地应力精细计算方法. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 34(3): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNSY201203007.htm 付锁堂, 马达德, 郭召杰, 等, 2015. 柴达木走滑叠合盆地及其控油气作用. 石油勘探与开发, 42(6): 713-722. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201506004.htm 郭荣涛, 马达德, 张永庶, 等, 2019. 柴达木盆地英西地区下干柴沟组上段超压孔缝型储层特征及形成机理. 石油学报, 40(4): 411-422. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201904003.htm 何生, 叶加仁, 徐思煌, 等, 2010. 石油及天然气地质学. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社. 李乐, 侯贵廷, 潘文庆, 等, 2011. 逆断层对致密岩石构造裂缝发育的约束控制. 地球物理学报, 54(2): 466-473. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201102027.htm 李翔, 王建功, 张平, 等, 2018. 柴达木盆地英西地区E$ {}_{3}^{2} $裂缝成因与油气地质意义. 岩性油气藏, 30(6): 45-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YANX202302016.htm 史亚红, 2019. 长宁页岩气水平井三压力剖面的建立及应用(硕士学位论文). 成都: 西南石油大学. 唐书恒, 2001. 煤储层渗透性影响因素探讨. 中国煤田地质, 13(1): 28-30, 86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMT200101009.htm 王小凤, 武红岭, 马寅生, 等, 2006. 构造应力场、流体势场对柴达木盆地西部油气运聚的控制作用. 地质通报, 25(S2): 1036-1044. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD2006Z2007.htm 文卓, 康永尚, 邓泽, 等, 2019. 中国含煤盆地浅‒中深部现今地应力特点和分布规律. 地质论评, 65(3): 729-742. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201903019.htm 熊廷松, 张成娟, 赵恩东, 等, 2019. 英西地区复杂应力条件下油藏体积压裂可行性. 新疆石油地质, 40(5): 579-582. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD201905012.htm 闫萍, 孙建孟, 苏远大, 等, 2006. 利用测井资料计算新疆迪那气田地应力. 新疆石油地质, 27(5): 611-614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSD200605029.htm 杨秀娟, 张敏, 闫相祯, 2008. 基于声波测井信息的岩石弹性力学参数研究. 石油地质与工程, 22(4): 39-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYHN200804015.htm 于祥江, 郭召杰, 张道伟, 等, 2018. 第四纪悸动: 来自柴达木盆地构造增强的证据及其对多圈层的响应. 第四纪研究, 38(1): 39-53. 曾联波, 漆家福, 2006. 油气田开发阶段的构造地质学研究. 地质科技情报, 25(4): 15-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200604003.htm 张博, 张凤奇, 卓勤功, 等, 2022. 柴达木盆地英西地区下干柴沟组上段构造裂缝的分布预测. 地球物理学进展, 37(2): 709-720. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202202023.htm 张重远, 吴满路, 陈群策, 等, 2012. 地应力测量方法综述. 河南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 31(3): 305-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGXB201203010.htm 张庆辉, 高发润, 赵海珠, 等, 2020. 英西E$ {}_{3}^{2} $页岩油藏多尺度多类型天然裂缝精细刻画. 地质论评, 66(增刊1): 117-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP202303025.htm -









 下载:
下载: