Indication of Hydrochemistry and δ34S-SO42‒ on Sulfate Pollution of Groundwater in Daye Mining Area
-
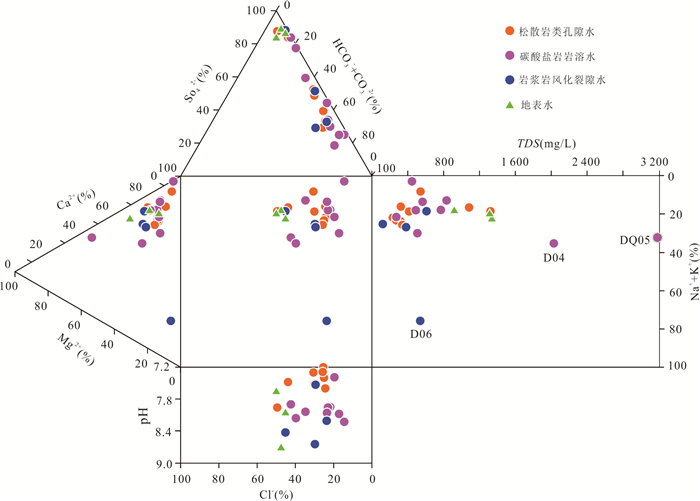
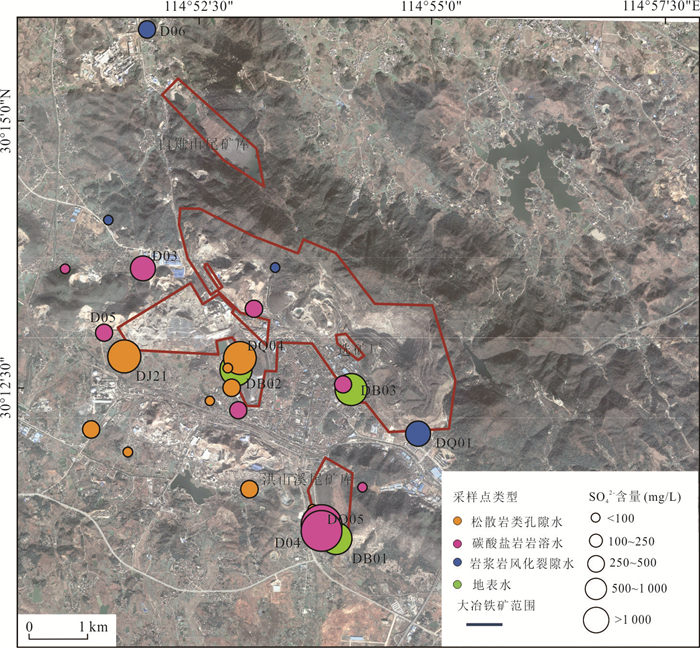
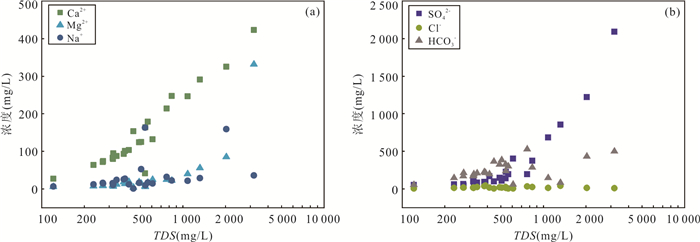
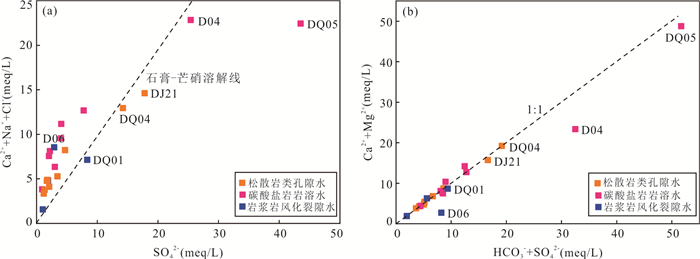
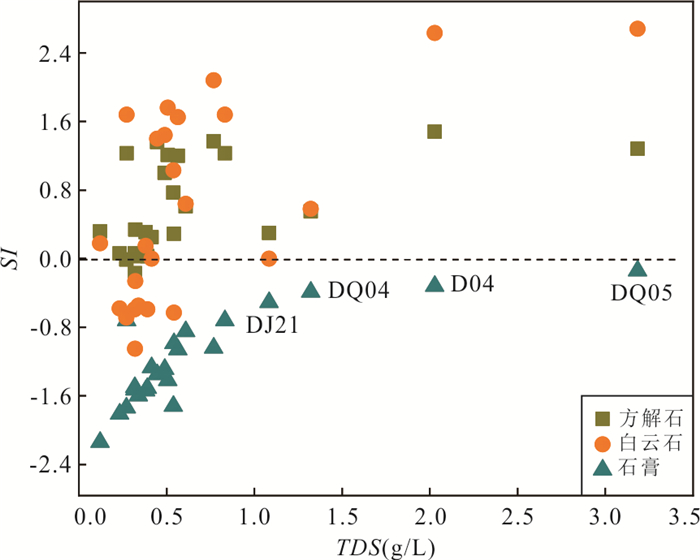
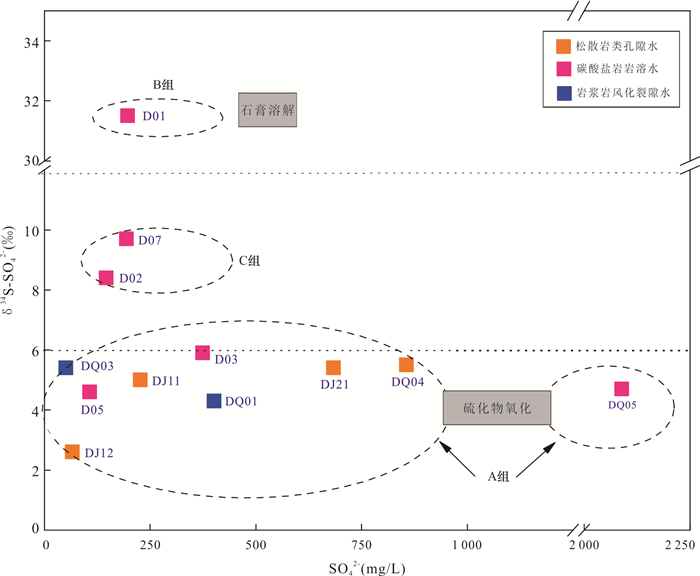
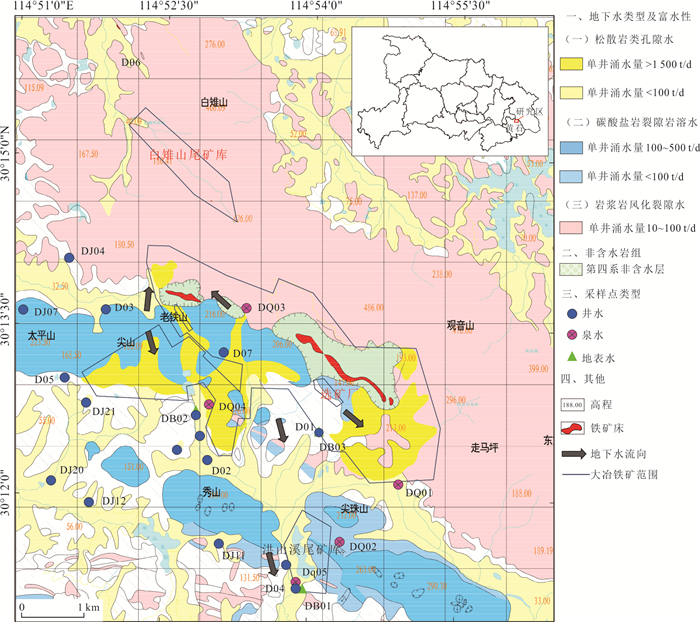
摘要: 铜铁矿区周边地下水硫酸盐污染是生态环境研究关注的热点问题,精确识别硫酸盐来源及迁移途径对于矿区周边地下水污染防控和供水安全至关重要.利用水化学与硫同位素耦合分析,结合矿区水文地质条件和潜在污染源分布,探讨了区内地下水硫酸盐污染特征、来源及迁移途径.区域内地下水包括松散岩类孔隙水、碳酸盐岩裂隙岩溶水及岩浆岩风化裂隙水,水化学类型主要为HCO3∙SO4-Ca型,水化学组分主要来源于硅酸岩、碳酸盐岩和硫酸盐矿物的溶解以及硫化物氧化;地下水中SO42‒含量范围为44.4~2 089.0 mg/L,高值区主要分布在洪山溪尾矿库、矿渣堆存处及矿业生产区附近;地下水中δ34S-SO42‒在2.6‰~31.5‰之间,反映其SO42‒具有多源性.地下水中SO42‒的主要来源包括含水层中石膏矿物的溶解和黄铁矿等含硫矿物氧化输入,高含量的SO42‒主要来源于黄铁矿氧化的贡献;矿坑排水、尾矿渗漏、选矿粉尘沉降淋滤下渗以及废水渗漏是地下水硫酸盐污染的主要途径.Abstract: Sulfate pollution of groundwater around copper and iron mining areas is a hot issue in ecological environment research. It is very important to identify the sources and migration routes of sulfate in the groundwater system for the prevention of groundwater pollution and the safety of water supply in the mining area. Combined with the hydrogeological setting and the distribution of potential pollutant sources in the mining area, the coupled analysis of hydrochemistry and δ34S-SO42‒ was carried to explore the characteristics, sources and migration pathways of groundwater sulfate pollution in the area. The results show that the groundwater in the area included the pore water in the sedimentary aquifers, the karst water of carbonatite and the fissure water of igneous rocks. The main hydrochemical type was HCO3·SO4-Ca. The formation of hydrochemical components mainly included the dissolution of silicate, carbonate and sulfate minerals, as well as the oxidation of sulfide. The content of SO42‒ ranged between 44.4 mg/L and 2 089.0 mg/L. The groundwater with elevated SO42‒ concentration occurred near the Hongshan River tailings reservoir, the slag heap and the industrial areas. The value of δ34S in regional groundwater ranged between 2.6‰ and 31.5‰, indicating that SO42‒ came from multiple sources. The sources of sulfate in groundwater included the dissolution of gypsum, the oxidation of sulfide such as pyrite. The maximum of SO42‒ attributed to the oxidization of pyrite. Mine drainage, tailing leakage, the settling of dust and wastewater infiltration were the main pathways of groundwater pollution.
-
Key words:
- Daye mining area /
- hydrogeochemistry /
- source of sulfate /
- sulfur isotope /
- groundwater /
- environmental engineering
-
表 1 地下水及地表水主要水化学指标统计特征
Table 1. Hydrochemical parameters of groundwater and surface water samples
类型 项目 pH TDS 硬度 Na+ K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl‒ SO42‒ HCO3‒ Fe Mn 地表水
n=3最大值 8.70 1 338.00 951.00 43.72 22.21 290.70 74.78 57.10 884.00 148.00 0.094 0.796 最小值 7.64 918.60 624.80 21.85 6.31 199.10 30.50 13.50 613.00 67.83 0.005 0.003 平均值 8.12 1 190.00 810.40 29.68 13.64 248.60 45.33 28.20 772.30 104.80 0.037 0.268 CV 0.05 0.16 0.17 0.34 0.48 0.15 0.46 0.72 0.15 0.31 1.078 1.394 地下水
n=22最大值 8.65 3 184.00 2 437.00 163.00 46.98 422.80 331.20 41.30 2 089.00 528.00 6.820 2.970 最小值 7.20 121.20 92.75 0.89 0.14 27.31 4.27 2.96 44.40 55.50 < 0.050 < 0.050 平均值 7.82 708.80 523.00 32.16 7.57 140.19 37.18 16.64 340.20 254.00 0.770 0.220 CV 0.05 0.96 0.95 1.31 1.51 0.72 2.14 0.59 1.41 0.50 2.020 2.900 注:CV为变异系数;除pH外,其他指标单位均为mg/L. 表 2 研究区地下水中δ34S-SO42-分析结果
Table 2. Analytical results of δ34S-SO42- of groundwater in the study area
样品编号 调查点类型 水位埋深
(m)地下水类型 δ34S-SO42‒
(‰)DJ11 井水 0.70 松散岩类孔隙水 5.0 DJ12 井水 1.10 松散岩类孔隙水 2.6 DJ21 井水 1.80 松散岩类孔隙水 5.4 DQ01 泉水 / 岩浆岩风化裂隙水 4.3 DQ05 泉水 / 碳酸盐岩岩溶水 4.7 DQ04 泉水 / 碳酸盐岩岩溶水 5.5 DQ03 泉水 / 岩浆岩风化裂隙水 5.4 D01 井水 4.36 碳酸盐岩岩溶水 31.5 D02 井水 2.26 碳酸盐岩岩溶水 8.4 D03 井水 7.83 碳酸盐岩岩溶水 5.9 D05 井水 15.57 碳酸盐岩岩溶水 4.6 D07 井水 18.65 碳酸盐岩岩溶水 9.7 -
Cai, B. J., 1981. The Conditions for the Formation of Iron Ore Deposits of Daye Type Significance of Evaporite Beds for the Formation of Iron Ore Deposits. Bulletin of Institute of Geomechanics of the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, (1): 110-118 (in Chinese with English abstract). Cao, Z. H., 2012. The Geological Feature and Metallogenic Model Study of Daye Iron Deposit. China Mine Engineering, 41(6): 32-35 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-609X.2012.06.010 Fan, H. Y., Li, W. D., Wang, W. B., 1995. On the Relationship between the Marine Triassic Evaporite Horizons and Cu(Au), Fe Deposits in the middle-Lower Yangtze Area. Volcanology & Mineral Resources, 16(2): 32-41 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gammons, C. H., Brown, A., Poulson, S. R., et al., 2013. Using Stable Isotopes (S, O) of Sulfate to Track Local Contamination of the Madison Karst Aquifer, Montana, from Abandoned Coal Mine Drainage. Applied Geochemistry, 31: 228-238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.01.008 Hong, Y. T., Zhang, H. B., Zhu, Y. X., et al., 1994. Sulfur Isotopic Composition Characteristics of Precipitation in China. Progress in Natural Science, 4(6): 741-745 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.1994.06.013 Jia, X. C., Zhou, J. W., Zhu, H. H., et al., 2020. Characteristics of Sulfur Isotope in Water Bodies near the Zhaoyuan Gold Mine Area and Its Indicative Function of Pollution Sources. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 47(5): 179-188 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jiang, W. R., Tu, Z. H., Zhou, S., et al., 2021. A Brief Overview on the Mechanism and Kinetic Influencing Factors of the Pyrite Surface Oxidation. Metal Mine, (3): 88-102 (in Chinese with English abstract). Kim, D. M., Yun, S. T., Cho, Y., et al., 2017. Hydrochemical Assessment of Environmental Status of Surface and Ground Water in Mine Areas in South Korea: Emphasis on Geochemical Behaviors of Metals and Sulfate in Ground Water. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 183: 33-45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.09.014 Li, Y., Jiang, Y. H., Zhou, X., et al., 2010. Characteristics of Sulfur Isotope in Groundwater of the Yangzhou–Taizhou–Jingjiang Area. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 37(4): 12-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2010.04.003 Liu, C. Q., Lang, Y. C., Satake, H., et al., 2008. Identification of Anthropogenic and Natural Inputs of Sulfate and Chloride into the Karstic Ground Water of Guiyang, SW China: Combined δ37Cl and δ34S Approach. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(15): 5421-5427. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800380w Ma, Y. H., Su, C. L., Liu, W. J., et al., 2016. Identification of Sulfate Sources in the Groundwater System of Zaozhuang: Evidences from Isotopic and Hydrochemical Characteristics. Environmental Science, 37(12): 4690-4699 (in Chinese with English abstract). Maurya, P., Kumari, R., Mukherjee, S., 2019. Hydrochemistry in Integration with Stable Isotopes (δ18O and δD) to Assess Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifers of Kachchh District, Gujarat, India. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 196: 42-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2018.09.013 Miao, Z. H., Carreón–Diazconti, C., Carroll, K. C., et al., 2014. The Impact of Biostimulation on the Fate of Sulfate and Associated Sulfur Dynamics in Groundwater. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 164: 240-250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2014.06.010 Park, I., Tabelin, C. B., Jeon, S., et al., 2019. A Review of Recent Strategies for Acid Mine Drainage Prevention and Mine Tailings Recycling. Chemosphere, 219: 588-606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.11.053 Shi, Z. L., Xiong, P. F., Wang, D. Y., et al., 1983. Some Genetic Problems of Daye-Type Iron Deposit in Tieshan, Hubei Province. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2(S1): 10-29 (in Chinese with English abstract). Su, C. L., Zhang, Y., Ma, Y. H., et al., 2019. Hydrochemical Evolution Processes of Karst Groundwater in Guiyang City: Evidences from Hydrochemistry and 87Sr/86Sr Ratios. Earth Science, 44(9): 2829-2838 (in Chinese with English abstract). Sun, J., Kobayashi, T., Strosnider, W. H. J., et al., 2017. Stable Sulfur and Oxygen Isotopes as Geochemical Tracers of Sulfate in Karst Waters. Journal of Hydrology, 551: 245-252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2017.06.006 Sun, Y., Zhou, J. L., Liang, X., et al., 2021. Distribution and Genesis of Shallow High–Iodine Groundwater in Southern Margin of Tarim Basin: A Case Study of Plain Area in Minfeng County, Xinjiang. Earth Science, 46(8): 2999-3011 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tang, C. L., Zheng, X. Q., Liang, Y. P., 2020. Hydrochemical Characteristics and Formation Causes of Ground Karst Water Systems in the Longzici Spring Catchment. Environmental Science, 41(5): 2087-2095 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2020.05.027 Wang, K. X., Dong, Z., 2013. Study on Geology and Mineralization Characteristics of Daye Iron Mine. Science & Technology Association Forum, (4): 139-140 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wei, X., Zhou, J. L., Nai, W. H., et al., 2019. Chemical Characteristics and Sources of Groundwater Sulfate in the Kashgar Delta, Xinjiang. Environmental Science, 40(8): 3550-3558 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, S. B., Jeschke, C., Dong, R. J., et al., 2011. Sulfur Transformations in Pilot–Scale Constructed Wetland Treating High Sulfate-Containing Contaminated Groundwater: A Stable Isotope Assessment. Water Research, 45(20): 6688-6698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.10.008 Yang, W. C., Qi, S. H., Xing, X. L., et al., 2020. Study on the Contribution Mechanism of Daye Smelter to the Heavy Metals in the Surrounding Soil. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(S1): 110-115 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zeng, H. B., Su, C. L., Xie, X. J., et al., 2021. Mechanism of Salinization of Shallow Groundwater in Western Hetao Irrigation Area. Earth Science, 46(6): 2267-2277 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, D., Li, X. D., Zhao, Z. Q., et al., 2015. Using Dual Isotopic Data to Track the Sources and Behaviors of Dissolved Sulfate in the Western North China Plain. Applied Geochemistry, 52: 43-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.11.011 蔡本俊, 1981. 鄂东大冶式铁矿床形成条件: 蒸发岩对铁矿床形成的意义. 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所所刊, (1): 110-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLX198101007.htm 曹中煌, 2012. 大冶铁矿地质特征及成矿模式研究. 中国矿山工程, 41(6): 32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKS201206012.htm 范洪源, 李文达, 王文斌, 1995. 长江中下游海相三叠系膏盐层与铜(金)、铁矿床. 火山地质与矿产, 16(2): 32-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HSDZ199502002.htm 洪业汤, 张鸿斌, 朱詠煊, 等, 1994. 中国大气降水的硫同位素组成特征. 自然科学进展, 4(6): 741-745. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJZ199406012.htm 贾晓岑, 周建伟, 朱恒华, 等, 2020. 招远金矿区水体中硫同位素特征及其对污染来源的指示. 水文地质工程地质, 47(5): 179-188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG202005021.htm 蒋文瑞, 涂志红, 周姝, 等, 2021. 黄铁矿表面氧化机理及动力学影响因素研究进展. 金属矿山, (3): 88-102. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSKS202103014.htm 李云, 姜月华, 周迅, 等, 2010. 扬泰靖地区地下水硫同位素组成特征及其意义. 水文地质工程地质, 37(4): 12-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201004005.htm 马燕华, 苏春利, 刘伟江, 等, 2016. 水化学和环境同位素在示踪枣庄市南部地下水硫酸盐污染源中的应用. 环境科学, 37(12): 4690-4699. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201612029.htm 石准立, 熊鹏飞, 王定域, 等, 1983. 湖北铁山"大冶式"铁矿床的某些成因问题. 地质科技情报, 2(S1): 10-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ1983S1001.htm 苏春利, 张雅, 马燕华, 等, 2019. 贵阳市岩溶地下水水化学演化机制: 水化学和锶同位素证据. 地球科学, 44(9): 2829-2838. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.214 孙英, 周金龙, 梁杏, 等, 2021. 塔里木盆地南缘浅层高碘地下水的分布及成因: 以新疆民丰县平原区为例. 地球科学, 46(8): 2999-3011. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.260 唐春雷, 郑秀清, 梁永平, 2020. 龙子祠泉域岩溶地下水水化学特征及成因. 环境科学, 41(5): 2087-2095 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202005012.htm 王可祥, 董珍, 2013. 大冶铁矿地质及矿化特征研究. 科协论坛, (4): 139-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXLT201304082.htm 魏兴, 周金龙, 乃尉华, 等, 2019. 新疆喀什三角洲地下水SO42-化学特征及来源. 环境科学, 40(8): 3550-3558. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ201908018.htm 杨文聪, 祁士华, 邢新丽, 等, 2020. 大冶冶炼厂对周边土壤重金属贡献机制研究. 环境科学与技术, 43(S1): 110-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJKS2020S1019.htm 曾邯斌, 苏春利, 谢先军, 等, 2021. 河套灌区西部浅层地下水咸化机制. 地球科学, 46(6): 2267-2277. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.259 -









 下载:
下载: