Reconstruction of Debris Flow Disasters in Polong Gully Based on Dendrochronology
-
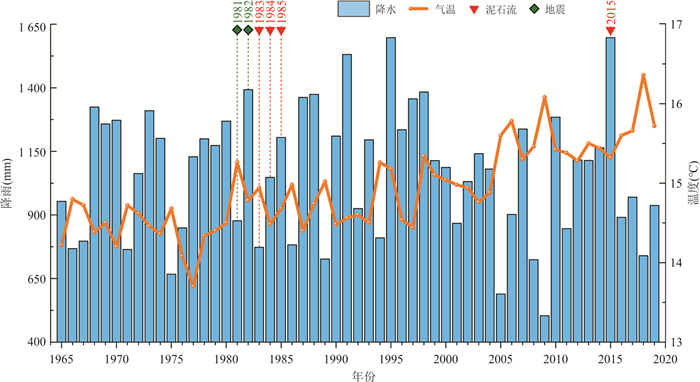
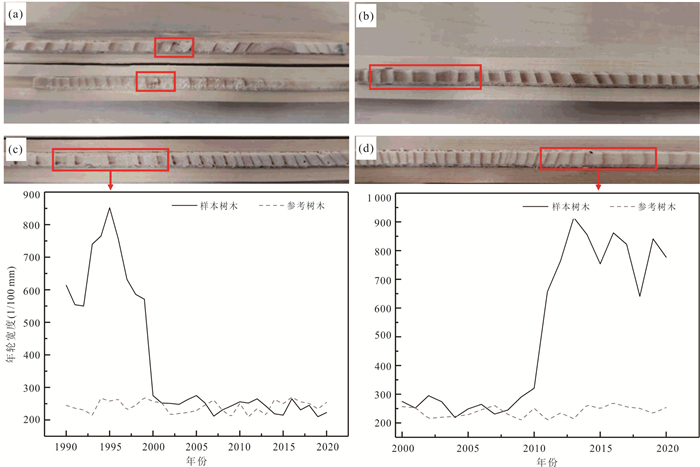
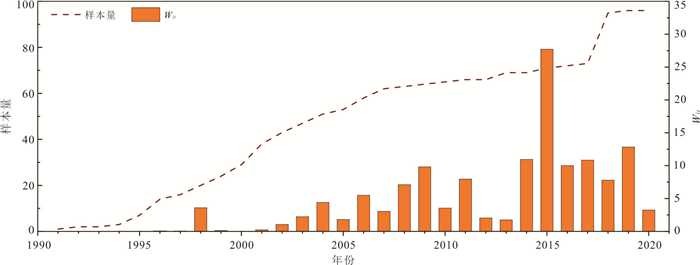
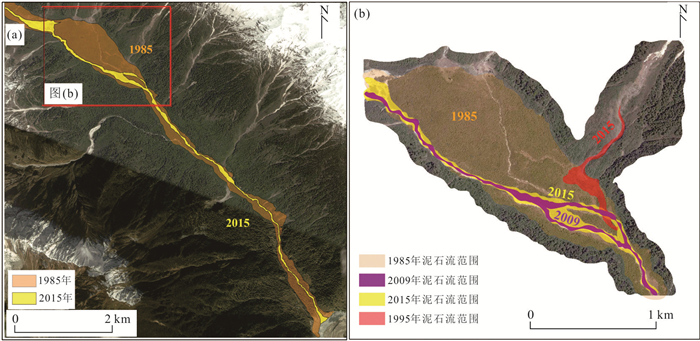
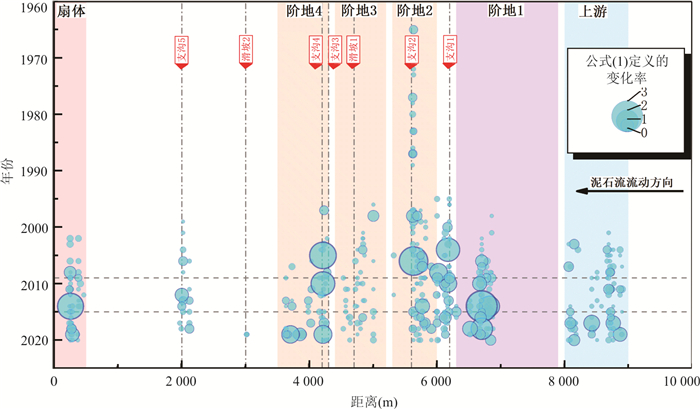
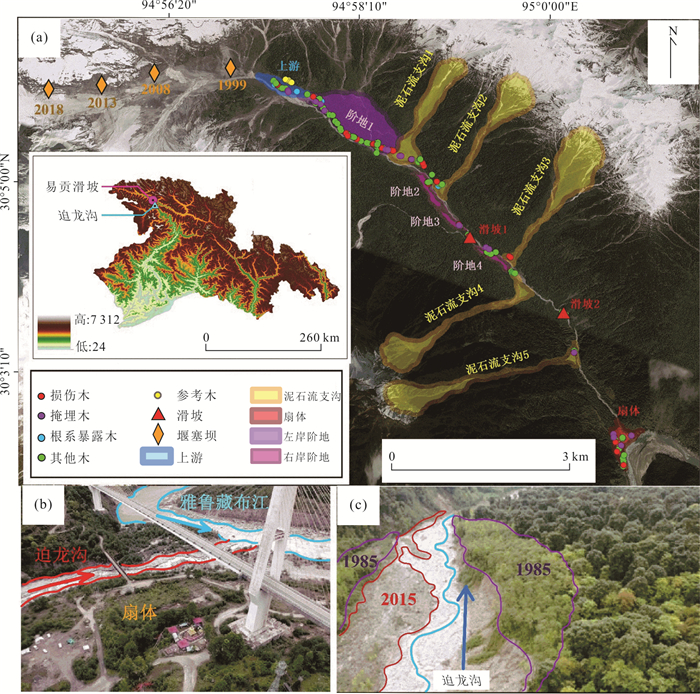
摘要: 迫龙沟是帕隆藏布下游右岸一级支流,1983、1984、1985和2015年爆发过4次泥石流,重复堵江并形成长约1 km的堰塞湖.个别主沟泥石流事件和沟道内部滑坡、支沟泥石流没有冲出沟口,无文献记录,但是造成沟道中上游河床演变和树木扰动.基于树木年代学,通过分析树木年轮损伤组织、生长抑制和释放动态,重建了迫龙沟40年来的主沟泥石流和沟道内部滑坡、支沟泥石流灾害历史;从树木生长扰动强度等方面探讨了泥石流的流动范围;并通过Wit指数进一步分析了没有历史记录的主沟泥石流、沟道内部滑坡、支沟泥石流发生时间和流动范围.树木年代学所反映的泥石流爆发时间的准确性与泥石流规模有关,泥石流规模太大会导致受扰动树木的灾害历史记忆消灭,不利于大规模灾害发生之前的泥石流事件的定年.沟道内的众多支沟泥石流和主沟内的滑坡会对主沟泥石流事件的定年产生干扰,但是与主沟泥石流同一时间发生的支沟泥石流和主沟滑坡事件会增大Wit指数,利于主沟泥石流灾害事件的定年.Abstract: Polong gully is a primary tributary on the right bank of Palong Zangbu River. Four recorded debris flows in 1983, 1984, 1985 and 2015 repeatedly blocked the river and formed a 1 km-long barrier lake. But some individual debris flow was too small to flush out the gully and be recorded. Based on the method of dendrochronology and the analysis of damaged tissue, growth inhibition and release of tree rings, the temporal-spatial distribution of the main debris flow events, debris flows in the tributaries and landslides in the main gully in the past 40 years were reconstructed. From the intensity of tree growth disturbance, the inundate area of debris flow was discussed. The relationship between the occurrence time of debris flow and inundate area was further analyzed by the index of Wit. The results show that the accuracy of debris flow event dating reflected by dendrochronology was related to the debris flow scale. Extra-large-scale of debris flow would lead to the elimination of disaster historical memory of disturbed trees, which was not conducive to the debris flow dating. The debris flows in the tributaries and landslides in the main gully would disturb the debris flow dating in the main gully. Debris flows in the gully tributaries and landslides in the main gully occurring at the same time would increase the value of Wit, which was conducive to debris flows dating in the main gully.
-
Key words:
- debris flow /
- dendrochronology /
- damaged tissue /
- growth inhibition /
- disaster reconstruction /
- engineering geology
-
表 1 各种测年方法优缺点(赖忠平等,2021)
Table 1. Advantages and disadvantages of various dating methods(Lai et al., 2021)
方法 材料 优势 不足 光释光测年法 矿物(石英或长石) 测年范围广、测年物质易于获取、对沉积物进行直接测年 受沉积物的晒退、含水量和周围环境等因素影响,单一样品的不确定性较大,需尽可能密集采样 14C测年法 沉积物中有机质、泥炭、贝壳、骨骼、植物残体等 技术成熟,应用广泛,应用加速器质谱技术后测量精度高、速度快 测定堰塞湖等沉积物时受“碳库效应”会高估年龄;测年物质难寻、测年范围较小 宇宙成因核素暴露年代法 岩石 测年物质分布广泛、测年范围较广、可以直接测定年龄 测试成本高昂、实验条件受限, 难以展开大规模应用 火山灰测年法 火山灰 主要应用于火山地质灾害的测年, 测年精确度较高 测年样本难寻且测年尺度相对较短 树木年代学法 树木年轮 定年准确、分辨率高、连续性强和地域分布广泛 受年轮响应滞后性影响,存在误差;样本采集难度大且测年尺度相对较短 地衣测年法 地衣 测年精确度较高 受环境其他因素影响大,通常用以辅助其他测年法;样本难寻且测年尺度相对较短 表 2 生长扰动强度的分类标准(Kogelnig-Mayer et al., 2011)
Table 2. Classification of growth disturbances (Kogelnig-Mayer et al., 2011)
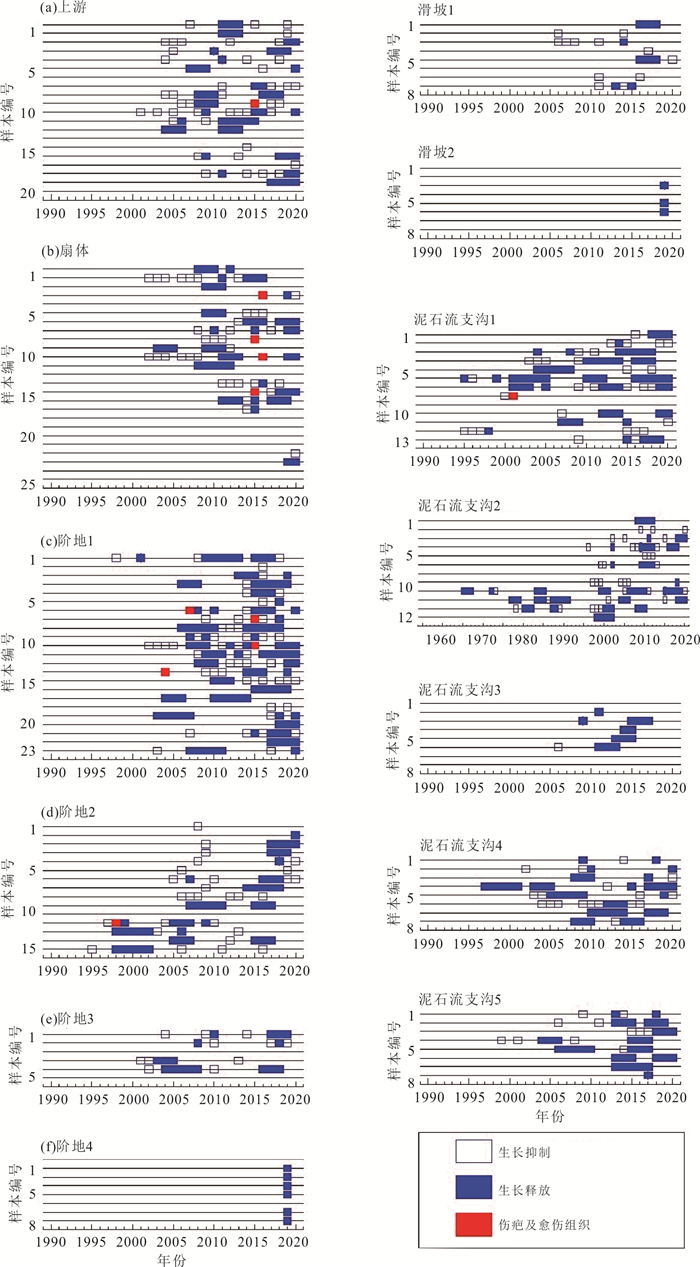
扰动类型 参数 Ti Ts Tm Tw 创伤及愈伤组织 存在创伤及愈伤组织 生长抑制 年轮变化(%) ≥60% ≥60% < 60% 持续时间(a) ≥5 < 5且≥2 ≤2 生长释放 年轮变化(%) ≥60% ≥60% < 60% 持续时间(a) ≥5 < 5且≥2 ≤2 表 3 生长扰动的数量与类型
Table 3. Number and type of growth disturbances
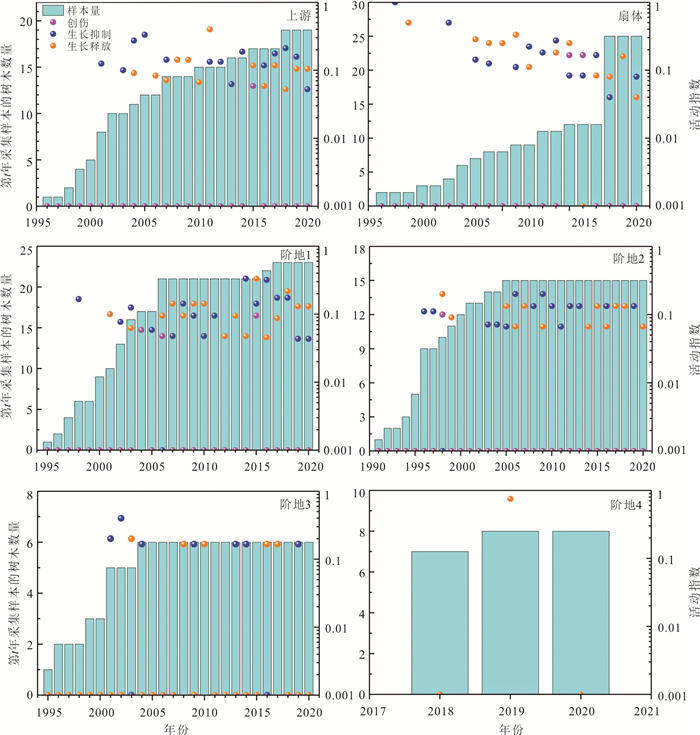
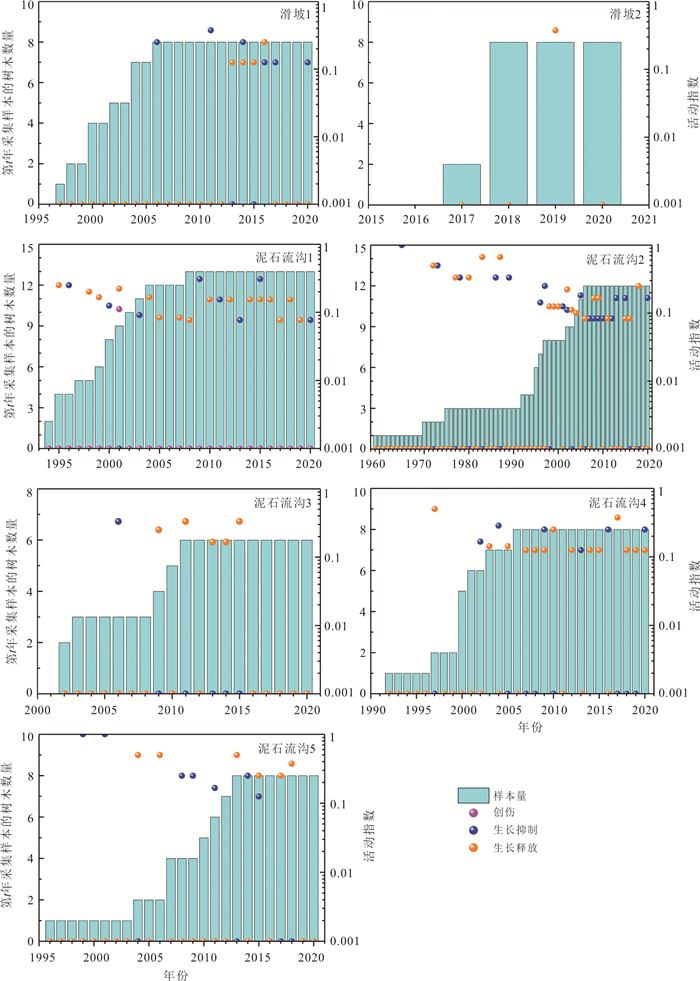
生长扰动区域 生长抑制 生长释放 损伤及愈伤组织 数量 % 数量 % 数量 % 上游 38 60.3 24 38.1 1 1.6 扇体 21 42.9 24 49.0 4 8.1 阶地1 45 50.0 41 45.6 4 4.4 阶地2 25 56.8 18 41.0 1 2.2 阶地3 11 68.8 5 31.3 阶地4 6 100 滑坡1 10 66.7 5 33.3 滑坡2 3 100 泥石流支沟1 23 48.0 24 50.0 1 2.0 泥石流支沟2 27 52.0 25 48.0 泥石流支沟3 1 12.5 7 87.5 泥石流支沟4 14 45.2 17 54.8 泥石流支沟5 9 40.9 13 59.1 -
Alestalo, J., 1971. Dendrochronological Interpretation of Geomorphic Processes. Fennia, 105: 1-139. Ballesteros-Cánovas, J. A., Rodríguez-Morata, C., Garófano-Gómez, V., et al., 2015. Unravelling Past Flash Flood Activity in a Forested Mountain Catchment of the Spanish Central System. Journal of Hydrology, 529: 468-479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.11.027 Bollschweiler, M., Stoffel, M., 2010. Tree Rings and Debris Flows: Recent Developments, Future Directions. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 34(5): 625-645. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133310370283 Bollschweiler, M., Stoffel, M., Schneuwly, D. M., et al., 2008. Traumatic Resin Ducts in Larix Decidua Stems Impacted by Debris Flows. Tree Physiology, 28(2): 255-263. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/28.2.255 Bollschweiler, M., Stoffel, M., Ehmisch, M., et al., 2007. Reconstructing Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Debris-Flow Activity Using Dendrogeomorphological Methods. Geomorphology, 87(4): 337-351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2006.10.002 Hewitt, K., 1998. Catastrophic Landslides and Their Effects on the Upper Indus Streams, Karakoram Himalaya, Northern Pakistan. Geomorphology, 26(1-3): 47-80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-555X(98)00051-8 Hupp, C. R., 1984. Dendrogeomorphic Evidence of Debris Flow Frequency and Magnitude at Mount Shasta, California. Environmental Geology and Water Sciences, 6(2): 121-128. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02509918 Hupp, C. R., Osterkamp, W., Thornton, J. L., 1987. Dendrogeomorphic Evidence and Dating of Recent Debris Flows on Mount Shasta, Northern California. U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper, 1936-B. Kogelnig-Mayer, B., Stoffel, M., Schneuwly-Bollschweiler, M., et al., 2011. Possibilities and Limitations of Dendrogeomorphic Time-Series Reconstructions on Sites Influenced by Debris Flows and Frequent Snow Avalanche Activity. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research, 43(4): 649-658. https://doi.org/10.1657/1938-4246-43.4.649 Korup, O., Montgomery, D. R., 2008. Tibetan Plateau River Incision Inhibited by Glacial Stabilization of the Tsangpo Gorge. Nature, 455(7214): 786-789. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07322 Lai, Z. P., Yang, A. N., Cong, L., et al., 2021. A Review on the Dating Techniques for Mountain Hazards-Induced Sediments. Earth Science Frontiers, 28(2): 1-18 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y., Cui, Y. F., Li, Z. H., et al., 2022. Evolution of Glacier Debris Flow and Its Monitoring System along Sichuan-Tibet Traffic Corridor. Earth Science, 47(6): 1969-1984 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lundström, T., Stoffel, M., Stöckli, V., 2008. Fresh-Stem Bending of Silver Fir and Norway Spruce. Tree Physiology, 28(3): 355-366. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/28.3.355 Lü, L. Q., Zhou, G. Y., Ma, C., et al., 2023. Coupling Process of Debris Flow Erosion and Wavy Flow Caused by Incision on Paleosedimentary Basin. Earth Science, 48(9): 3389-3401 (in Chinese with English abstract). Mayer, B., Stoffel, M., Bollschweiler, M., et al., 2010. Frequency and Spread of Debris Floods on Fans: A Dendrogeomorphic Case Study from a Dolomite Catchment in the Austrian Alps. Geomorphology, 118(1-2): 199-206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2009.12.019 Procter, E., Bollschweiler, M., Stoffel, M., et al., 2011. A Regional Reconstruction of Debris-Flow Activity in the Northern Calcareous Alps, Austria. Geomorphology, 132(1-2): 41-50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2011.04.035 Ruiz-Villanueva, V., Díez-Herrero, A., Stoffel, M., et al., 2010. Dendrogeomorphic Analysis of Flash Floods in a Small Ungauged Mountain Catchment (Central Spain). Geomorphology, 118(3-4): 383-392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geomorph.2010.02.006 Schneuwly, D. M., Stoffel, M., Dorren, L. K. A., et al., 2009. Three-Dimensional Analysis of the Anatomical Growth Response of European Conifers to Mechanical Disturbance. Tree Physiology, 29(10): 1247-1257. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpp056 Schweingruber, F. H., 1997. Tree Rings and Environment Dendroecology. Paul Haupt Publishers, Berne. Šilhán, K., Ružek, I., Frištyk, M., et al., 2021. Growth Responses of Pinus sylvestris (L.) to Burial by Drift Sand and Its Application to the Reconstruction of Aeolian Dune Development. Catena, 196: 104830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104830 Stoffel, M., Beniston, M., 2006. On the Incidence of Debris Flows from the Early Little Ice Age to a Future Greenhouse Climate: A Case Study from the Swiss Alps. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(16): L16404. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006gl026805 Stoffel, M., Bollschweiler, M., Hassler, G. R., 2006. Differentiating Past Events on a Cone Influenced by Debris-Flow and Snow Avalanche Activity-A Dendrogeomorphological Approach. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 31(11): 1424-1437. doi: 10.1002/esp.1363 Stoffel, M., Casteller, A., Luckman, B. H., et al., 2012. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Channel Wall Erosion in Ephemeral Torrents Using Tree Roots-An Example from the Patagonian Andes. Geology, 40(3): 247-250. https://doi.org/10.1130/g32751.1 Stoffel, M., Conus, D., Grichting, M. A., et al., 2008. Unraveling the Patterns of Late Holocene Debris-Flow Activity on a Cone in the Swiss Alps: Chronology, Environment and Implications for the Future. Global and Planetary Change, 60(3-4): 222-234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2007.03.001 Stoffel, M., Bollschweiler, M., 2008. Tree-Ring Analysis in Natural Hazards Research-An Overview. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 8(2): 187-202. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-8-187-2008 Stoffel, M., Lièvre, I., Conus, D., et al., 2005. 400 Years of Debris-Flow Activity and Triggering Weather Conditions: Ritigraben, Valais, Switzerland. Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research, 37(3): 387-395. https://doi.org/10.1657/1523-0430(2005)037[0387:yodaat]2.0.co;2 Strunk, H., 1997. Dating of Geomorphological Processes Using Dendrogeomorphological Methods. Catena, 31(1-2): 137-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0341-8162(97)00031-3 Tie, Y. B., Malik, I., Owczarek, P., 2014. Dendrochronological Dating of Debris Flow Historical Events in High Mountain Area-Take Daozao Debris Flow as an Example. Mountain Research, 32(2): 226-232 (in Chinese with English abstract). Trappmann, D., Corona, C., Stoffel, M., 2013. Rolling Stones and Tree Rings: A State of Research on Dendrogeomorphic Reconstructions of Rockfall. Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment, 37(5): 701-716. https://doi.org/10.1177/0309133313506451 Wang, J., 2019. Influence of Moraine on Debris Flow in Palong Zangbu Basin (Dissertation). University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Z., Hu, K. H., Ma, C., et al., 2021. Landscape Change in Response to Multiperiod Glacial Debris Flows in Peilong Catchment, Southeastern Tibet. Journal of Mountain Science, 18(3): 567-582. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11629-020-6172-6 赖忠平, 杨安娜, 丛禄, 等, 2021. 山地灾害沉积物的测年综述. 地学前缘, 28(2): 1-18. 李尧, 崔一飞, 李振洪, 等, 2022. 川藏交通廊道林波段冰川泥石流发育动态演化分析及监测预警方案. 地球科学, 47(6): 1969-1984. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.194 吕立群, 周冠宇, 马超, 等, 2023. 古沉积盆地下切引发的泥石流侵蚀和波状流动耦合过程. 地球科学, 48(9): 3389-3401. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.329 铁永波, Malik, I., Owczarek, P., 2014. 树木年代学在高寒山区泥石流历史事件重建中的应用——以磨西河流域倒灶沟为例. 山地学报, 32(2): 226-232. 王姣, 2019. 帕隆藏布流域冰碛物对泥石流活动影响(博士学位论文). 北京: 中国科学院大学. -









 下载:
下载: