Formation Mechanism and Characterization of Mn(Ⅲ)-Humic Ligands Colloids in Ground Water Environment
-
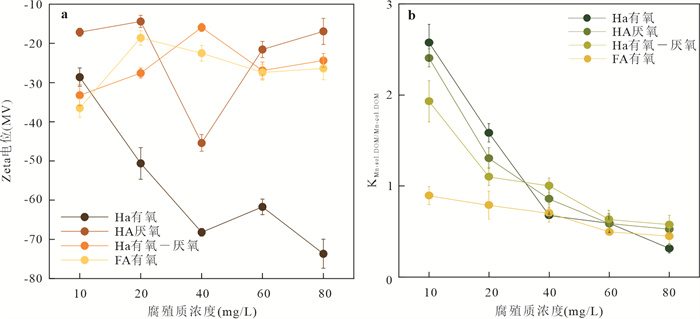
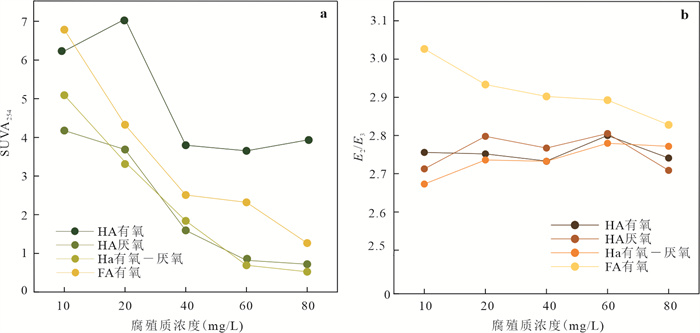
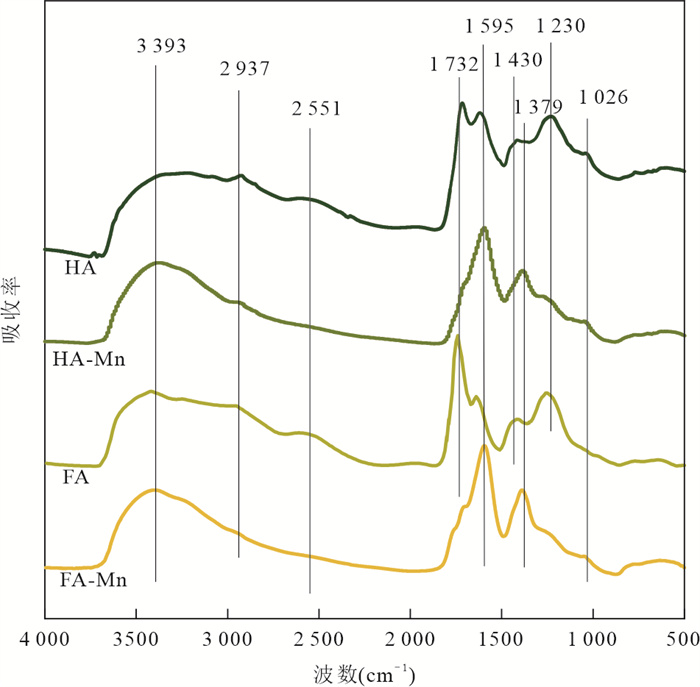
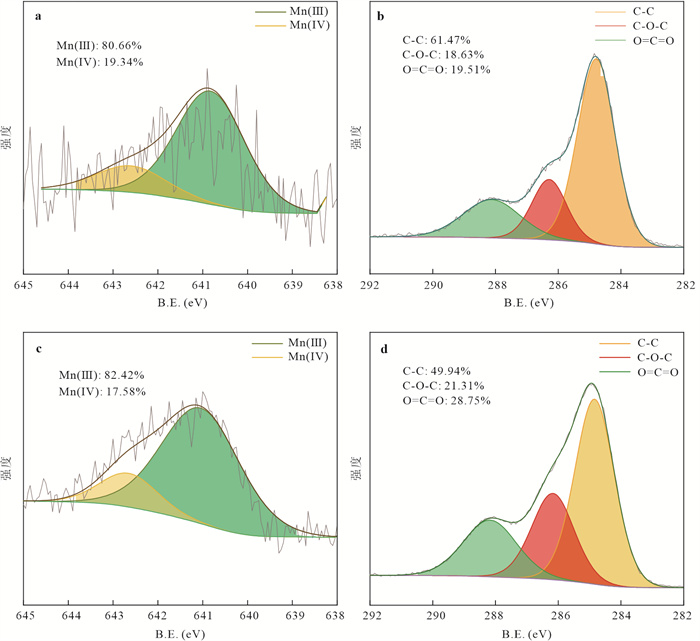
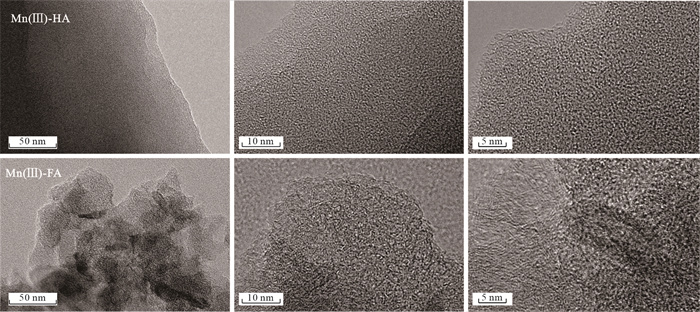
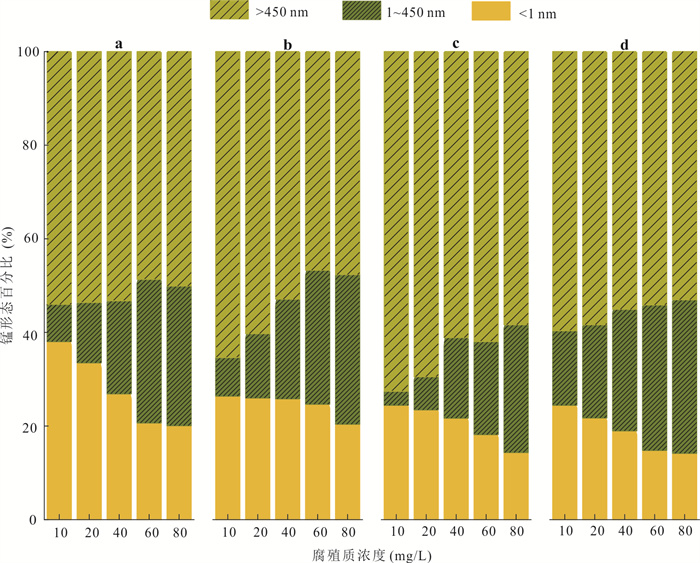
摘要: Mn(Ⅲ)是锰氧化还原循环中电子传递的中间体,广泛参与陆地和海洋生态系统中的碳、铁和硫的地球化学循环. 近年来在厌氧、微氧和有氧水环境中陆续发现了Mn(Ⅲ)有机络合物存在,研究地下水环境中Mn(Ⅲ)-腐殖质胶体的形成机制与行为特征对于认识锰的地球化学循环及其影响的营养物和污染物的迁移转化机制具有重要意义. 通过开展批实验,探讨氧气条件、腐殖质浓度和有机质种类对Mn(Ⅲ)-腐殖质胶体形成的影响,并结合FTIR、XRD、XPS、TEM多种手段表征其理化性质与稳定性.研究发现:厌氧或有氧-厌氧环境有利于Mn(Ⅲ)-腐殖质胶体形成,Mn(Ⅲ)-腐殖质的络合程度随着腐殖质浓度的升高而增强,富里酸更容易与Mn(Ⅲ)络合,但形成的胶体稳定性较Mn(Ⅲ)-胡敏酸胶体差. Mn(Ⅲ)-腐殖质胶体呈无定形形态,腐殖质上的羧基等含氧官能团与Mn(Ⅲ)形成内球络合物,可减缓Mn(Ⅲ)歧化程度. Mn(Ⅲ)-腐殖质胶体具有氧化和吸附能力,对地下水中污染物的迁移转化具有重要的环境意义.Abstract: Mn(Ⅲ) is the intermediate electron transport of manganese cycling, widely involved in the terrestrial and marine ecosystems in the geochemical cycle of carbon, iron and sulfur. Recently, Mn(Ⅲ)-humic ligands colloids are found in oxide, suboxic and anoxic zone.It is of great significance to study the formation mechanism and behavior characteristics of Mn(Ⅲ)-humic colloid in groundwater environment for understanding the geochemical cycle of manganese and the migration and transformation mechanism of nutrients and pollutants affected by it. In this study, batch experiments were conducted to explore the effects of oxygen conditions, humus concentration and organic matter species on the formation of Mn(Ⅲ)-humic ligands colloids andcombined with FTIR, XRD, XPS, TEM and other means to characterize the physicochemical properties and stability. Resultsshow that suboxic and anoxic environments favor Mn(Ⅲ)-humiccolloid formation. The degree of complexation of Mn(Ⅲ)-humic colloid increases with the increase of humic ligands concentration. FA is more easily complexed with Mn(Ⅲ), but the colloidal stability is worse than that of Mn(Ⅲ)-HA colloid.Furthermore, Mn(Ⅲ)-humic colloid is in an amorphous form, and oxygen-containing functional groups such as carboxyl groups on humus form an internal sphere complex with Mn(Ⅲ), which can stabilize Mn(Ⅲ) and slow down the degree of disproportionation.Mn(Ⅲ)-humic colloid has oxidation and adsorption capacity, which has important environmental significance for the migration and transformation of pollutants in groundwater.
-
Key words:
- Mn(Ⅲ) /
- umic ligands /
- olloid stability /
- omplexation mechanism /
- groundwater
-
表 1 标准腐殖质元素组成
Table 1. Elemental composition of standard humicligands
标准腐殖质 C H O N S P TOC (%) (mg/L) PPHA 56.37 3.82 37.34 3.69 0.71 0.03 408.65±3 PPFA 51.31 3.53 43.32 2.34 0.76 < 0.01 371.97±5 -
Alvarez-Puebla, R. A., Garrido, J. J., 2005. Effect of PH on the Aggregation of a Gray Humic Acid in Colloidal and Solid States. Chemosphere, 59(5): 659-667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.10.021 Boyle, E. S., Guerriero, N., Thiallet, A., et al., 2009. Optical Properties of Humic Substances and CDOM: Relation to Structure. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(7): 2262-2268. https://doi.org/10.1021/es803264g Chen, C. M., Dynes, J. J., Wang, J., et al., 2014. Properties of Fe-Organic Matter Associations Via Coprecipitation Versus Adsorption. Environmental Science & Technology, 48(23): 13751-13759. https://doi.org/10.1021/es503669u Chin, Y. P., Aiken, G., O'Loughlin, E., 1994. Molecular Weight, Polydispersity, and Spectroscopic Properties of Aquatic Humic Substances. Environmental Science & Technology, 28(11): 1853-1858. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00060a015 Dalzell, B. J., Minor, E. C., Mopper, K. M., 2009. Photodegradation of Estuarine Dissolved Organic Matter: A Multi-Method Assessment of DOM Transformation. Organic Geochemistry, 40(2): 243-257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orggeochem.2008.10.003 Dellwig, O., Schnetger, B., Brumsack, H. J., et al., 2012. Dissolved Reactive Manganese at Pelagic Redoxclines (part Ⅱ): Hydrodynamic Conditions for Accumulation. Journal of Marine Systems, 90(1): 31-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2011.08.007 Gao, Y., Ming, Y., Gao, L., 2022. Distributions and Seasonal Variations of Dissolved Organic Matter(DOM) in the Changjiang(Yangtze River) Estuary and Its Adjacent Area in 2019. Marine Environmental Science, 41(1): 40-47 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guardado, I., Urrutia, O., Garcia-Mina, J. M., 2008. Some Structural and Electronic Features of the Interaction of Phosphate with Metal-Humic Complexes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56(3): 1035-1042. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf072641k Gui, X. Y., Song, B. Q., Chen, M., et al., 2021. Soil Colloids Affect the Aggregation and Stability of Biochar Colloids. Science of The Total Environment, 771(5): 145414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145414 Hu, E. D., Zhang, Y., Wu, S. Y., et al., 2017. Role of Dissolved Mn(Ⅲ) in Transformation of Organic Contaminants: Non-Oxidative Versus Oxidative Mechanisms. Water Research, 111(5): 234-243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.01.013 Johnson, K. L., McCann, C. M., Wilkinson, J. L., et al., 2018. Dissolved Mn(Ⅲ) in Water Treatment Works: Prevalence and Significance. Water Research, 140(Suppl. C): 181-190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.04.038 Jones, M. E., Nico, P. S., Ying, S., et al., 2018. Manganese-Driven Carbon Oxidation at Oxic-Anoxic Interfaces. Environmental Science & Technology, 52(21): 12349-12357. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b03791 Li, Q. Q., Xie, L., Jiang, Y., et al., 2019. Formation and Stability of NOM-Mn(Ⅲ) Colloids in Aquatic Environments. Water Research, 149(21): 190-201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2018.10.094 Li, S. D., Jiang, Q, L., L, Y., 2017. Spectroscopic Characteristics and Sources of Dissolved Organic Matter from Soils around Dianchi Lake, Kunming. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 37(5): 1448-1454 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Y., 2021. Composition, Spectral Characteristics and Source Analysis of Soils in Different Land Use Types(Dissertation), Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi'an (in Chinese with English abstract). Liang, X. T., 2014. Iron and Manganese Circulation Process and Environmental Effects in Wetland Systems. Journal of Capital Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 35(3): 74-79(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, J. C., Wang, O. M., Li, J. J., et al., 2018. Mechanisms of Extracellular Electron Transfer in the Biogeochemical Manganese Cycle. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 58(4): 546-559 (in Chinese with English abstract). Luo, Y. P., Deng, Y. M., Du, Y., et al., 2022. Occurrence and Formation of High lodine Groundwater Inoxbows of the Middle Reach of the Yangtze River. Earth Science, 47(2): 662-673(in Chinese with English abstract). Ma, A. L., Liu H., Mao S. J., et al., 2022. Distribution Characteristics of Dissolved Manganese in the Lateral Hyporheic Zone between River and Groundwater in the Lower Reaches of the Han River. Earth Science, 47(2): 729-741 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ma, D., Wu, J., Yang, P., et al., 2020. Coupled Manganese Redox Cycling and Organic Carbon Degradation on Mineral Surfaces. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(14): 8801-8810. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c02065 Madison, A. S., Tebo, B. M., Mucci, A., et al., 2013. Abundant Porewater Mn(Ⅲ) is a Major Component of the Sedimentary Redox System. Science, 341(6148): 875-878. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241396 Nowack, B., Stone, A. T., 2003. Manganese-Catalyzed Degradation of Phosphonic Acids. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 1(1): 24-31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-002-0014-3 Oldham, V. E., Mucci, A., Tebo, B. M., et al., 2017. Soluble Mn(Ⅲ)-L Complexes are Abundant in Oxygenated Waters and Stabilized by Humic Ligands. Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta, 199: 238-246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2016.11.043 Oldham, V. E., Owings, S. M., Jones, M. R., et al., 2015. Evidence for the Presence of Strong Mn(Ⅲ)-Binding Ligands in the Water Column of the Chesapeake Bay. Marine Chemistry, 171(3-4): 58-66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2015.02.008 Rathi, B., Jamieson, J., Sun, J., et al., 2020. Process-Based Modeling of Arsenic(Ⅲ) Oxidation by Manganese Oxides under Circumneutral PH Conditions. Water Research, 185(80): 116195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116195 Sharma, P., Ofner, J., Kappler, A., 2010. Formation of Binary and Ternary Colloids and Dissolved Complexes of Organic Matter, Fe and as. Environmental Science & Technology, 44(12): 4479-4485. https://doi.org/10.1021/es100066s Shen, M. H., Hai, X., Shang, Y. X., et al., 2019. Insights into Aggregation and Transport of Graphene Oxide in Aqueous and Saturated Porous Media: Complex Effects of Cations with Different Molecular Weight Fractionated Natural Organic Matter. Science of The Total Environment, 656: 843-851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.11.387 Sun, W. L., Xia, J., Li, S., et al., 2012. Effect of Natural Organic Matter (NOM) on Cu(Ⅱ) Adsorption by Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Relationship with NOM Properties. Chemical Engineering Journal, 200-202: 627-636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.06.118 Wu, J. F., Boyle, E., Sunda, W., et al., 2001. Soluble and Colloidal Iron in the Oligotrophic North Atlantic and North Pacific. Science, 293(5531): 847-849. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1059251 Wu, S. L., Liu, Y. J., Bougoure, J. J., et al., 2019. Organic Matter Amendment and Plant Colonization Drive Mineral Weathering, Organic Carbon Sequestration, and Water-Stable Aggregation in Magnetite Fe Ore Tailings. Environmental Science & Technology, 53(23): 13720-13731. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b04526 Yakushev, E. V., Pollehne, F., Jost, G., et al., 2007. Analysis of the Water Column Oxic/anoxic Interface in the Black and Baltic Seas with a Numerical Model. Marine Chemistry, 107(3): 388-410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2007.06.003 Yang, K., Lin, D. H., Xing, B. S., 2009. Interactions of Humic Acid with Nanosized Inorganic Oxides. Langmuir, 25(6): 3571-3576. https://doi.org/10.1021/la803701b Yang, K., Xing, B. S., 2009. Adsorption of Fulvic Acid by Carbon Nanotubes from Water. Environmental Pollution, 157(4): 1095-1100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.11.007 Ying, C. Y., Lanson, B., Wang, C., et al., 2020. Highly Enhanced Oxidation of Arsenite at the Surface of Birnessite in the Presence of Pyrophosphate and the Underlying Reaction Mechanisms. Water Research, 187(5): 116420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2020.116420 高源, 明玥, 高磊, 2022. 2019年长江口及其邻近海域溶解有机物的分布和季节变化特征海洋环境科学, 41(1): 40-47. 李帅东, 姜泉良, 黎烨, 等, 2017. 环滇池土壤溶解性有机质(DOM)的光谱特征及来源分析. 光谱学与光谱分析, 37: 1448-1454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201705027.htm 李燚, 2021. 不同土地利用类型土壤中DOM组成特征、紫外荧光特性和来源分析(硕士学位论文), 西安: 西安建筑科技大学. 梁夏天, 2014. 湿地系统中铁锰循环过程及环境效应. 首都师范大学学报(自然科学版), 35(3): 74-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDSX201403015.htm 刘进超, 王欧美, 李佳佳, 等, 2018. 生物地球化学锰循环中的微生物胞外电子传递机制. 微生物学报, 58(4): 546-559. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WSXB201804005.htm 罗义鹏, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等, 2022. 长江中游故道区高碘地下水分布与形成机理. 地球科学, 47(2): 662-673. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202202022.htm 马奥兰, 刘慧, 毛胜军, 等, 2022. 汉江下游河水-地下水侧向交互带中溶解态锰的分布特征. 地球科学, 47(2): 729-741. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202202027.htm -









 下载:
下载: