Effect of Surface Water-Groundwater Interaction on Arsenic Transport in Shallow Groundwater of Jianghan Plain
-
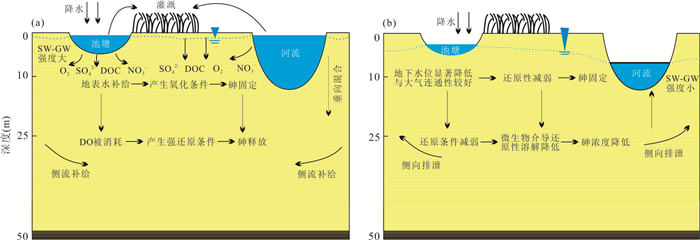
摘要: 地表水‒地下水(SW-GW)相互作用对砷在浅层地下水系统中的运移至关重要,但其模式和强度对地下水中砷运移的影响尚不清楚.本文针对江汉平原仙桃市沙湖原种场野外地下水三维监测试验场,开展野外监测和三维地下水数值模拟.结果发现雨季地表水补给地下水,SW-GW相互作用强度较大,地下水砷浓度升高;旱季地下水补给地表水,SW-GW相互作用强度减弱,地下水砷浓度降低.SW-GW相互作用模式与强度的季节转变导致地下水流速和流向产生季节响应.模型估算出雨季和旱季地面以下10~25 m最大垂向砷交换量分别为457.2 mg/d、191.3 mg/d,地面以下28 m处水平砷交换量分别为4 380.0 mg/d、1 385.6 mg/d.Abstract: Surface water-groundwater (SW-GW) interaction is critical for arsenic transport in shallow groundwater systems, but the role of its pattern and intensity on arsenic transport remains unclear. Field monitoring and numerical simulation were employed to identify the impact of surface water-groundwater interaction mode and intensity on arsenic transport in shallow groundwater of Shahu field site, Jianghan Plain. The results indicate that the surface water recharged into groundwater and had a relatively stronger intensity in the rainy season, which led to the higher arsenic concentration, and vice versa. The seasonal shift of surface water-groundwater interaction mode and intensity could cause the seasonal response of groundwater flow velocity and direction. It is estimated by the numerical simulation that the maximum vertical exchange mass of arsenic is 457.2 mg/d in rainy season and 191.3 mg/d in dry season and the maximum horizontal exchange mass of arsenic is 4 380.0 and 1 385.6 mg/d in rainy and dry season, respectively.
-
Key words:
- surface water /
- groundwater /
- arsenic /
- groundwater flow model /
- Jianghan Plain /
- environmental engineering
-
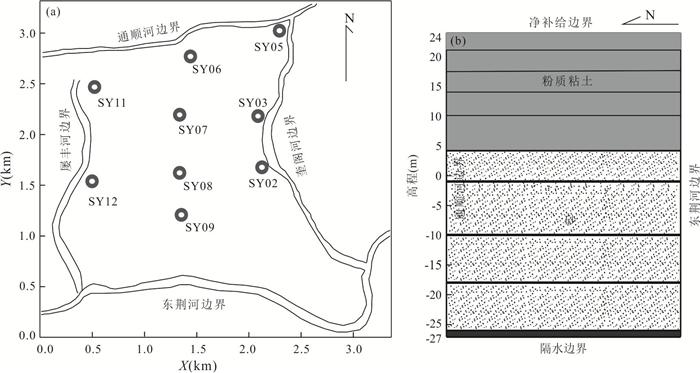
图 1 沙湖试验场监测井示意(据Duan et al.,2015修改)
图b中A表示浅层(即10 m);B表示中层(即25 m)
Fig. 1. Map of monitoring wells of Shahu field site (modified from Duan et al., 2015)
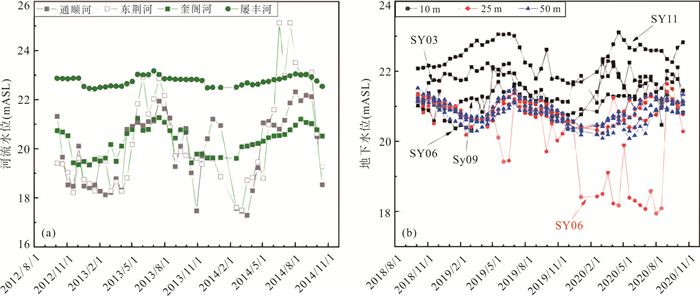
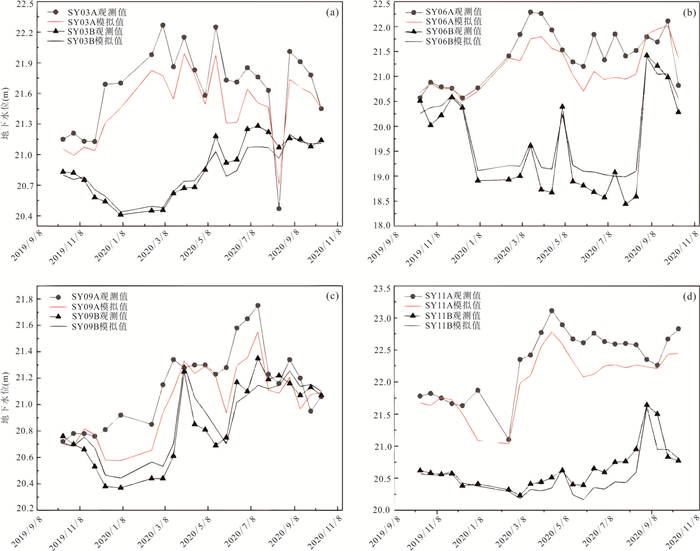
图 3 地表水(a)与地下水(b)水位时间序列
图a为河流水位,参考Schaefer et al.(2016)
Fig. 3. Time series of surface water (a) and groundwater levels (b)
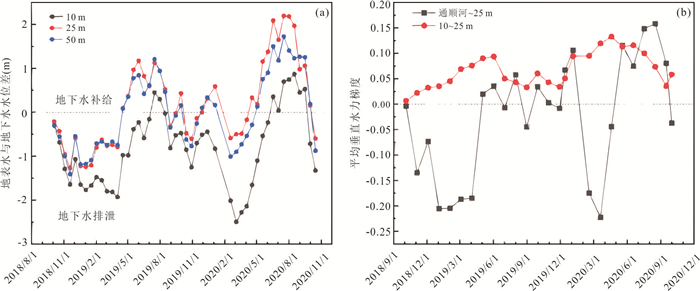
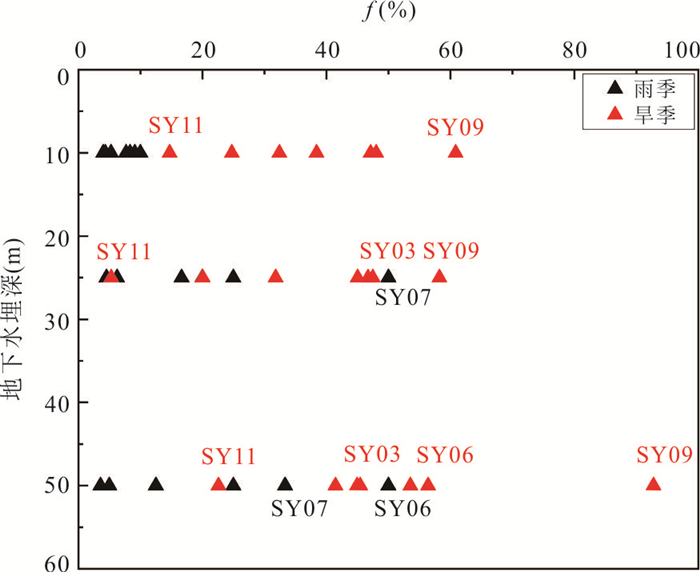
图 4 平均地表水水位与地下水水位之差(a);平均水力梯度(b),黑色为通顺河与监测井SY05、SY06、SY11在25m深度处的垂直水力梯度变化;红色为监测井SY03、SY06、SY09、SY11在10~25 m的垂直水力梯度变化
正值表示地表水补给地下水,负值表示地下水补给地表水
Fig. 4. Difference between surface water and groundwater level (a); the vertical hydraulic gradient between the Tongshun River and three adjacent monitoring wells SY05, SY06, SY11 (red circle) and between 10 m and 25 m of wells SY03, SY06, SY09, SY11(black rectangle) (b)
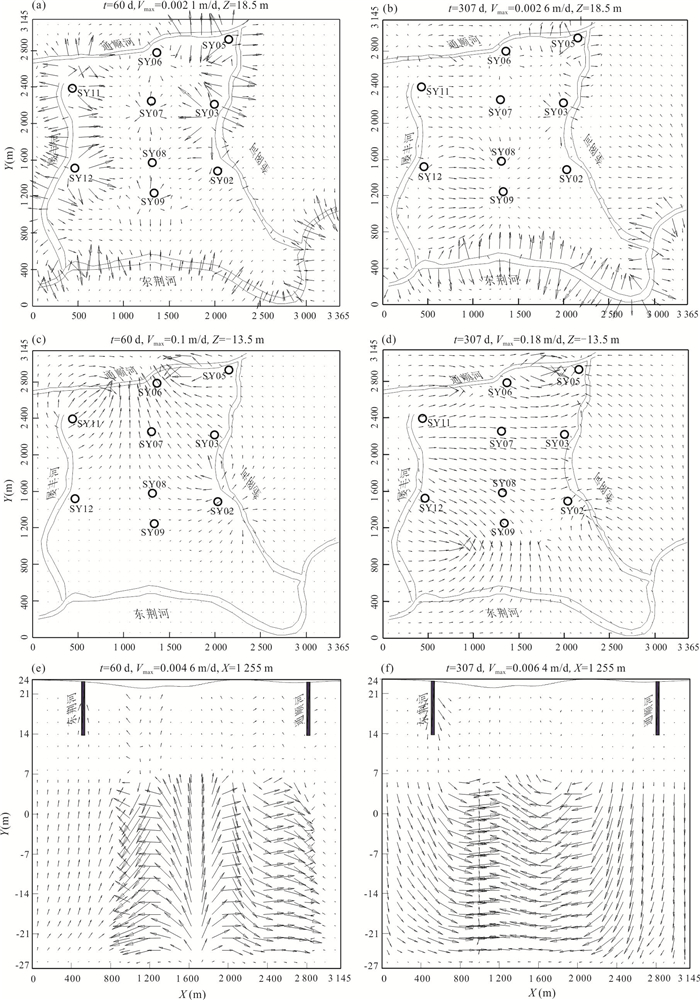
图 8 Z=18.5 m和Z=‒13.5 m深度处水平地下水流速特征((a)(c)为旱季,(b)(d)为雨季)以及X=1 255 m处含水层垂直流速分布特征((e)为旱季,(f)为雨季)
Fig. 8. Distribution of horizontal groundwater velocity at the depth of 18.5 and ‒13.5 m below the ground surface, respectively ((a) (c) and (b) (d) stand for the dry and rainy season, respectively) and vertical groundwater velocity at X=1 255 m ((e) and (f) stand for the dry and rainy season, respectively)
表 1 地下水流模型中的水力学参数表
Table 1. Hydraulic properties of aquifers used in model simulations
-
Chen, X. P., Deng, Y. H., Zhang, Y. Z., et al., 2007. The Epidemiological Survey and Analysis to Arsenism in Nanhong Village of Plain Hubei Province. Chinese Journal of Control of Endemic Diseases, 22(4): 281-282 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1889.2007.04.016 Currell, M., Cartwright, I., Raveggi, M., et al., 2011. Controls on Elevated Fluoride and Arsenic Concentrations in Groundwater from the Yuncheng Basin, China. Applied Geochemistry, 26(4): 540-552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2011.01.012 Deng, Y. M., Wang, Y. X., Li, H. J., et al., 2015. Seasonal Variation of Arsenic Speciation in Shallow Groundwater from Endemic Arsenicosis Area in Jianghan Plain. Earth Science, 40(11): 1876-1886 (in Chinese with English abstract). Du, Y., Ma, T., Deng, Y. M., et al., 2018. Characterizing Groundwater/Surface-Water Interactions in the Interior of Jianghan Plain, Central China. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(4): 1047-1059. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1709-7 Duan, Y. H., Gan, Y. Q., Wang, Y. X., et al., 2015. Temporal Variation of Groundwater Level and Arsenic Concentration at Jianghan Plain, Central China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 149: 106-119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.12.001 Duan, Y. H., Schaefer, M. V., Wang, Y. X., et al., 2019. Experimental Constraints on Redox-Induced Arsenic Release and Retention from Aquifer Sediments in the Central Yangtze River Basin. Science of the Total Environment, 649: 629-639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.08.205 Fendorf, S., Michael, H. A., van Geen, A., 2010. Spatial and Temporal Variations of Groundwater Arsenic in South and Southeast Asia. Science, 328(5982): 1123-1127. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1172974 Gan, Y. Q., Wang, Y. X., Duan, Y. H., et al., 2014. Hydrogeochemistry and Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater in the Jianghan Plain, Central China. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 138: 81-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.12.013 Gan, Y. Q., Zhao, K., Deng, Y. M., 2018. Groundwater Flow and Hydrogeochemical Evolution in the Jianghan Plain, Central China. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(5): 1609-1623. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1778-2 Guo, H. M., Wen, D. G., Liu, Z. Y., et al., 2014. A Review of High Arsenic Groundwater in Mainland and Taiwan, China: Distribution, Characteristics and Geochemical Processes. Applied Geochemistry, 41: 196-217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2013.12.016 Guo, X. X., 2014. Arsenic Mobilization and Transport in Shallow Aquifer Systems of Jianghan Plain, Central China (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Healy, R. W., Cook, P. G., 2002. Using Groundwater Levels to Estimate Recharge. Hydrogeology Journal, 10(1): 91-109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-001-0178-0 Islam, F. S., Boothman, C., Gault, A. G., et al., 2005. Potential Role of the Fe(Ⅲ)-Reducing Bacteria Geobacter and Geothrix in Controlling Arsenic Solubility in Bengal Delta Sediments. Mineralogical Magazine, 69(5): 865-875. https://doi.org/10.1180/0026461056950294 Jha, P. K., Tripathi, P., 2021. Arsenic and Fluoride Contamination in Groundwater: A Review of Global Scenarios with Special Reference to India. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 13: 100576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2021.100576 Khan, M. R., Koneshloo, M., Knappett, P. S. K., et al., 2016. Megacity Pumping and Preferential Flow Threaten Groundwater Quality. Nature Communications, 7: 12833. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12833 Larsen, F., Pham, N. Q., Dang, N. D., et al., 2008. Controlling Geological and Hydrogeological Processes in an Arsenic Contaminated Aquifer on the Red River Flood Plain, Vietnam. Applied Geochemistry, 23(11): 3099-3115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.06.014 McDonald, M. G., Harbaugh, A. W., 1988. A Modular Three-Dimensional Finite-Difference Groundwater Flow Model. U. S. Geological Survey, Reston. Podgorski, J., Berg, M., 2020. Global Threat of Arsenic in Groundwater. Science, 368(6493): 845-850. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba1510 Radloff, K. A., Zheng, Y., Stute, M., et al., 2017. Reversible Adsorption and Flushing of Arsenic in a Shallow, Holocene Aquifer of Bangladesh. Applied Geochemistry, 77: 142-157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2015.11.003 Sathe, S. S., Mahanta, C., 2019. Groundwater Flow and Arsenic Contamination Transport Modeling for a Multi Aquifer Terrain: Assessment and Mitigation Strategies. Journal of Environmental Management, 231: 166-181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.08.057 Schaefer, M. V., Ying, S. C., Benner, S. G., et al., 2016. Aquifer Arsenic Cycling Induced by Seasonal Hydrologic Changes within the Yangtze River Basin. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(7): 3521-3529. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b04986 Simpson, S. C., Meixner, T., 2012. Modeling Effects of Floods on Streambed Hydraulic Conductivity and Groundwater-Surface Water Interactions. Water Resources Research, 48(2): W02515. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011wr011022 Singh, R., Singh, S., Parihar, P., et al., 2015. Arsenic Contamination, Consequences and Remediation Techniques: A Review. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 112: 247-270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.10.009 Song, X. F., Liu, X. C., Xia, J., et al., 2007. Study on the Transformation Relationship between Surface Water and Groundwater in Huaisha River Basin Based on Environmental Isotope Technology. Science in China (Series D), 37(1): 102-110 (in Chinese with English abstract). Swartz, C. H., Blute, N. K., Badruzzman, B., et al., 2004. Mobility of Arsenic in a Bangladesh Aquifer: Inferences from Geochemical Profiles, Leaching Data, and Mineralogical Characterization. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(22): 4539-4557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gca.2004.04.020 van Geen, A., Zheng, Y., Goodbred, S. Jr., et al., 2008. Flushing History as a Hydrogeological Control on the Regional Distribution of Arsenic in Shallow Groundwater of the Bengal Basin. Environmental Science & Technology, 42(7): 2283-2288. https://doi.org/10.1021/es702316k Wang, J., Xie, Z. M., Wang, J., et al., 2021. Influence of Bioreduction of Arsenic-Bearing Goethite by Bacteria under Sulfur Mediation on Migration and Transformation of Arsenic. Earth Science, 46(2): 642-651 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xie, Y. Q., Cook, P. G., Simmons, C. T., 2016. Solute Transport Processes in Flow-Event-Driven Stream-Aquifer Interaction. Journal of Hydrology, 538: 363-373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.04.031 Xu, Y. X., Zheng, T. L., Gao, J., et al., 2021. Effect of Indigenous Sulfate Reducing Bacteria on Arsenic Migration in Shallow Aquifer of Jianghan Plain. Earth Science, 46(2): 652-660 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, S. Z., Guo, H. M., Tang, X. H., et al., 2008. Distribution of Abnormal Groundwater Arsenic in Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(1): 242-249 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.01.030 Yang, Y. J., Yuan, X. F., Deng, Y. M., et al., 2020. Seasonal Dynamics of Dissolved Organic Matter in High Arsenic Shallow Groundwater Systems. Journal of Hydrology, 589: 125120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125120 Ye, R. Y., 2015. Interaction of Surface Water and Groundwater in Yili-Gongnaisi River Valley (Dissertation). Chang'an University, Xi'an (in Chinese with English abstract). Yu, K., Gan, Y. Q., Zhou, A. G., et al., 2018. Organic Carbon Sources and Controlling Processes on Aquifer Arsenic Cycling in the Jianghan Plain, Central China. Chemosphere, 208: 773-781. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.188 Zhao, J. C., Wei, B. H., Xiao, S. B., 2009. Stable Isotopic Characteristics of Atmospheric Precipitation from Yichang, Hubei. Tropical Geography, 29(6): 526-531 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2009.06.004 Zheng, T. L., Deng, Y. M., Wang, Y. X., et al., 2020. Microbial Sulfate Reduction Facilitates Seasonal Variation of Arsenic Concentration in Groundwater of Jianghan Plain, Central China. Science of the Total Environment, 735: 139327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139327 陈兴平, 邓云华, 张裕曾, 等, 2007. 湖北南洪村饮水砷含量及砷中毒调查. 中国地方病防治杂志, 22(4): 281-282. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1889.2007.04.016 邓娅敏, 王焰新, 李慧娟, 等, 2015. 江汉平原砷中毒病区地下水砷形态季节性变化特征. 地球科学, 40(11): 1876-1886. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.168 郭欣欣, 2014. 江汉平原浅层含水层系统中砷释放与迁移过程研究(博士学位论文). 武汉: 中国地质大学. 宋献方, 刘相超, 夏军, 等, 2007. 基于环境同位素技术的怀沙河流域地表水和地下水转化关系研究. 中国科学(D辑), 37(1): 102-110. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200701011.htm 王晶, 谢作明, 王佳, 等, 2021. 硫介导细菌还原载砷铁矿对砷迁移转化的影响. 地球科学, 46(2): 642-651. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.054 徐雨潇, 郑天亮, 高杰, 等, 2021. 江汉平原浅层含水层中土著硫酸盐还原菌对砷迁移释放的影响. 地球科学, 46(2): 652-660. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.063 杨素珍, 郭华明, 唐小惠, 等, 2008. 内蒙古河套平原地下水砷异常分布规律研究. 地学前缘, 15(1): 242-249. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200801032.htm 叶人源, 2015. 新疆伊犁‒巩乃斯河谷地表水与地下水转化关系研究(硕士学位论文). 西安: 长安大学. 赵家成, 魏宝华, 肖尚斌, 2009. 湖北宜昌地区大气降水中的稳定同位素特征. 热带地理, 29(6): 526-531. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RDDD200906006.htm -










 下载:
下载: