Effect Mechanistic of Partially Penetrating Well on Single-Well Push-Pull Tests for Groundwater Velocity Estimation
-
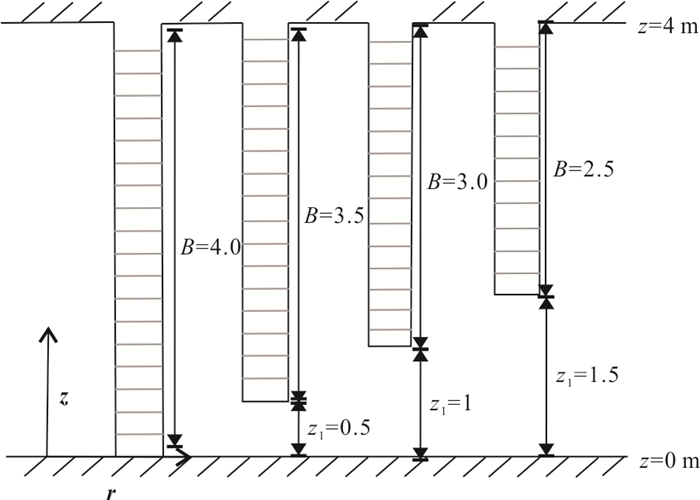
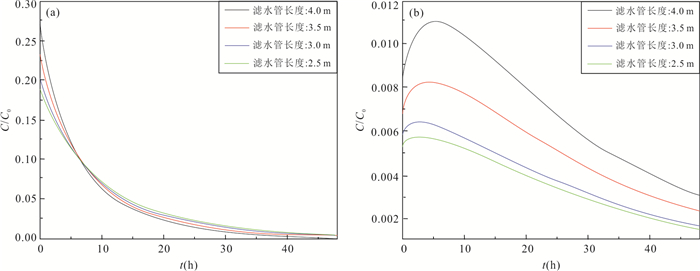
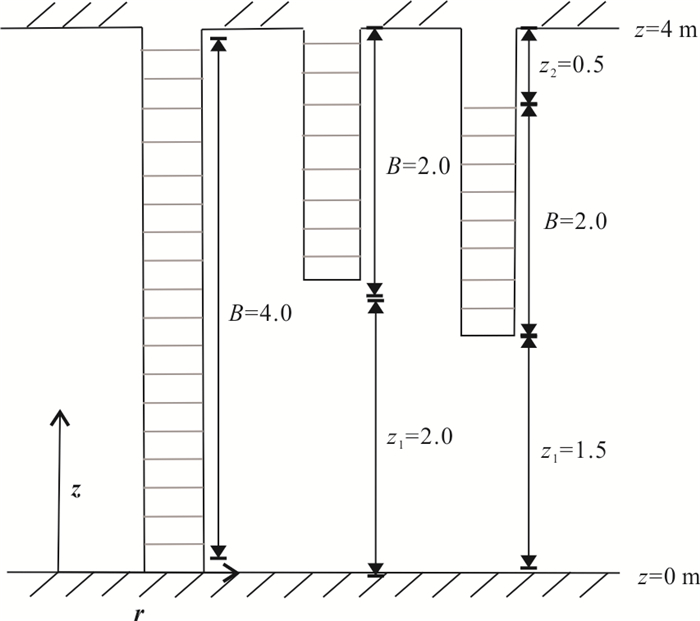
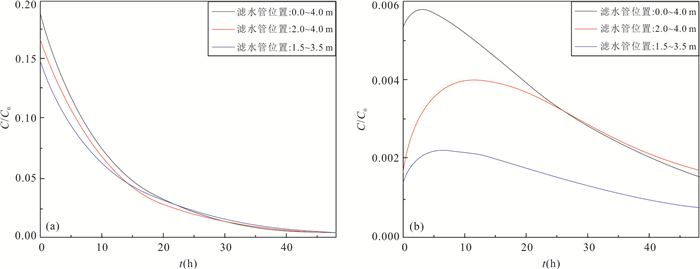
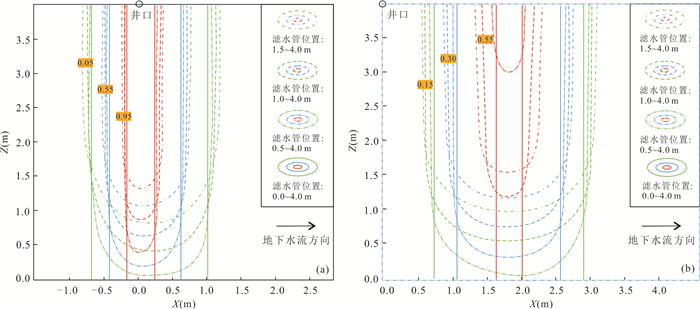
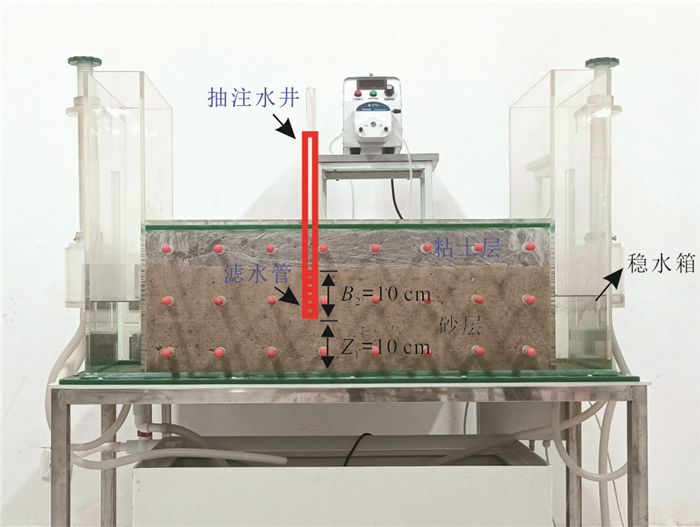
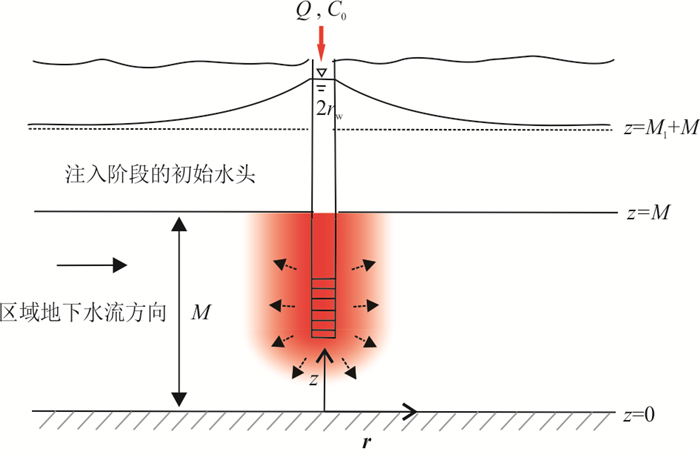
摘要: 为了探究非完整井结构对单井注抽试验测算地下水流速的影响机理,采用COMSOL Multiphysics软件建立非完整井条件下的单井注抽试验数值模型,分析了非完整井滤管长度与位置对穿透曲线的影响.同时开展了非完整井单井注抽试验室内试验研究,并利用数值模型拟合示踪剂穿透曲线来进一步验证模型的可靠性.结果表明:滤水管长度越短,示踪剂穿透曲线早期浓度越低;滤水管位置越靠近含水层上部,穿透曲线早期的浓度越高;参数反演误差分析表明数值模型能较好地反演地下水流速、孔隙度以及弥散度.总体而言,非完整井附近复杂流场导致溶质空间的不均匀分布,进而对穿透曲线有显著影响,增大传统完整井模型的参数反演误差;而本文建立的非完整井单井注抽试验模型拟合精度高,能够适用于非完整井条件下的单井注抽试验.Abstract: For the purpose of analyzing the influencing mechanism of partially penetrating well on single-well push-pull (SWPP) tests, this study employed COMSOL Multiphysics to develop a numerical model of SWPP test, in which the impacts of the length and location of screen on breakthrough curves (BTCs) were investigated. Meanwhile, a laboratory experiment of SWPP test with partially penetrating well was conducted, verifying the reliability of the proposed model by fitting the observed and simulated BTCs. The results show that a shorter screen length leads to a lower concentration of BTC in the early stage; meanwhile a shorter unscreened segment near the top of aquifer results in a lower concentration in the early stage. Additionally, the error analysis of parameter inversion indicates that the numerical model is quantified for the estimations of groundwater flow velocity, porosity and dispersion by fitting BTCs. Overall, the complicated flow field in the vicinity of partially penetrating wells leads to a non-uniform spatial distribution of solute, which has a significant effect on the BTCs and increases the parameter inversion error if using the traditional fully penetrating well model. Nevertheless, the SWPP test model developed in this paper has high fitting accuracy and can be applied to SWPP test under partially penetrating conditions.
-
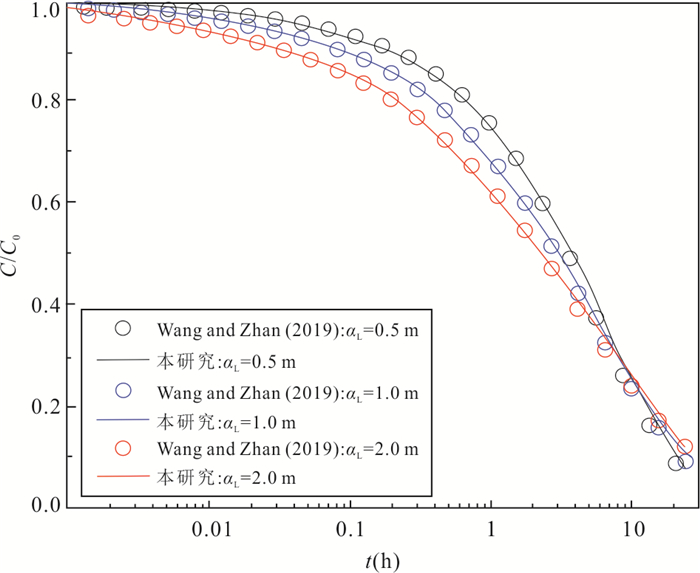
图 4 数值解与Wang and Zhan(2019)解析解的穿透曲线对比
Fig. 4. Comparison of breakthrough curves between the numerical and analytical solutions Wang and Zhan (2019)
表 1 模型中默认参数取值
Table 1. Default parameter values used in the model
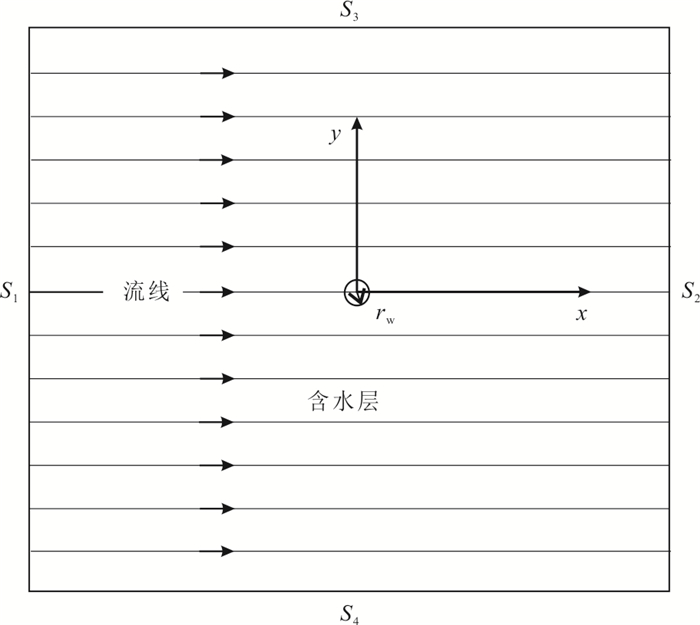
参数 符号 值 含水层宽度(m) W 50 含水层长度(m) L 50 含水层厚度(m) M 4 滤管长度(m) B 2 含水层有效孔隙度 θ 0.3 含水层的渗透系数(m/d) K 8 边界S1的水头(m) H1 21.08 边界S2的水头(m) H2 20 纵向弥散度(m) αL 0.1 注入与抽取的流量(m3/d) Q 15,15 注入阶段时间(h) tinj 2 自由迁移时间(h) tdrift 48 抽水阶段时间(h) tpump 48 表 2 不同地下水流速数值模拟结果
Table 2. Numerical simulation results with different groundwater velocities
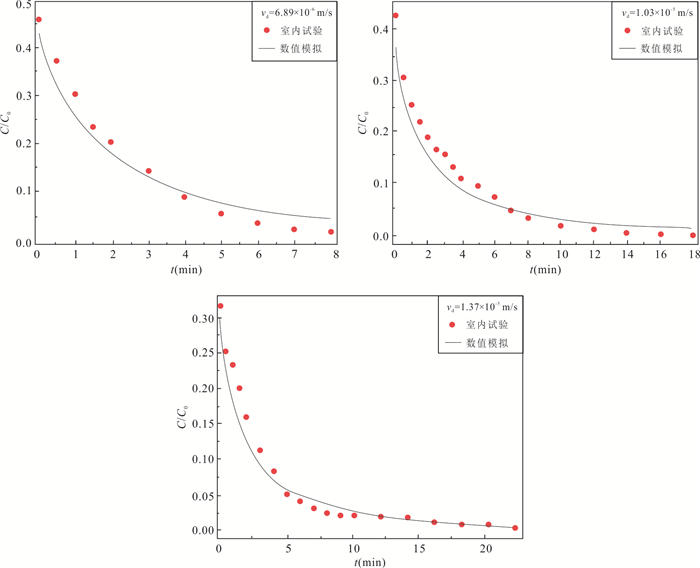
室内实测值 数值模拟值 r2 Ev(%) Eθ(%) trest(min) vobs (m/s) θobs vs(m/s) θ αL(m) 25 6.89×10‒6 0.443 7.576×10‒6 0.435 0.017 0.953 9.96 1.81 25 1.03×10‒5 0.443 9.643×10‒6 0.430 0.018 0.933 6.38 2.93 25 1.37×10‒5 0.443 1.309×10‒5 0.425 0.018 0.949 4.48 4.06 表 3 不同自由迁移时间数值模拟结果
Table 3. Numerical simulation results with different rest times
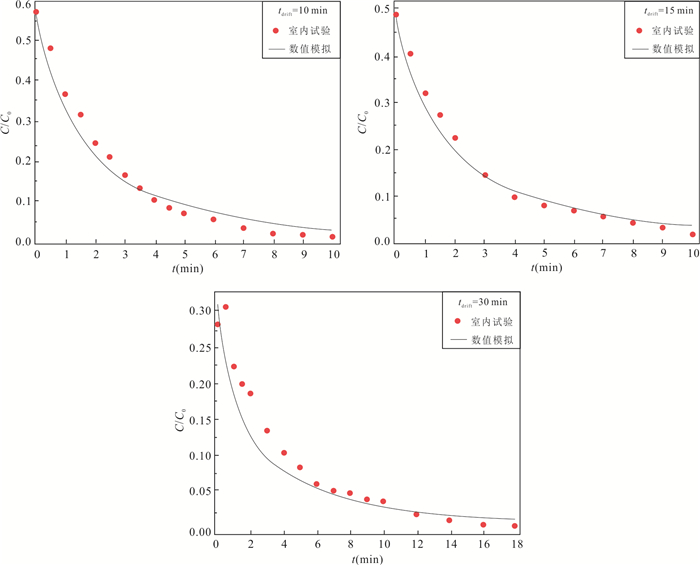
室内实测值 数值模拟值 r2 Ev(%) Eθ(%) trest(min) vobs (m/s) θobs vs(m/s) θ αL(m) 10 1.03×10‒5 0.443 9.298×10‒6 0.437 0.014 0.978 9.73 1.35 15 1.03×10‒5 0.443 8.954×10‒6 0.440 0.020 0.975 13.07 0.68 30 1.03×10‒5 0.443 9.643×10‒6 0.428 0.018 0.900 6.38 3.39 -
Chen, K. W., Zhan, H. B., Yang, Q. A., 2017. Fractional Models Simulating Non-Fickian Behavior in Four-Stage Single-Well Push-Pull Tests. Water Resources Research, 53(11): 9528-9545. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017wr021411 Fan, C. H., Gao, Y. L., Fan, Q., 2017. Regression Analysis of Flow Velocity and Initial Concentration about Repair Lead Contaminated Groundwater with Permeable Reactive Barrier. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 35(2): 23-27, 55 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gelhar, L. W., Collins, M. A., 1971. General Analysis of Longitudinal Dispersion in Nonuniform Flow. Water Resources Research, 7(6): 1511-1521. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr007i006p01511 Gu, H. C., Wang, Q. R., Zhan, H. B., 2020. An Improved Approach in Modeling Injection-Withdraw Test of the Partially Penetrating Well. Earth Science, 45(2): 685-692 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hall, S. H., Luttrell, S. P., Cronin, W. E., 1991. A Method for Estimating Effective Porosity and Ground-Water Velocity. Groundwater, 29(2): 171-174. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6584.1991.tb00506.x Huang, J. Q., Christ, J. A., Goltz, M. N., 2010. Analytical Solutions for Efficient Interpretation of Single-Well Push-Pull Tracer Tests. Water Resources Research, 46(8): W08538. https://doi.org/10.1029/2008wr007647 Leap, D. I., Kaplan, P. G., 1988. A Single-Well Tracing Method for Estimating Regional Advective Velocity in a Confined Aquifer: Theory and Preliminary Laboratory Verification. Water Resources Research, 24(7): 993-998. https://doi.org/10.1029/wr024i007p00993 Li, X., Su, S. L., Wen, Z., et al., 2022. Numerical Analysis of Estimating Groundwater Velocity through Single-Well Push-Pull Test. Earth Science, 47(2): 633-641 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, X., Wen, Z., Zhan, H. B., et al., 2019. Skin Effect on Single-Well Push-Pull Tests with the Presence of Regional Groundwater Flow. Journal of Hydrology, 577: 123931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123931 Matsumoto, S., Machida, I., Hebig, K. H., et al., 2020. Estimation of Very Slow Groundwater Movement Using a Single-Well Push-Pull Test. Journal of Hydrology, 591: 125676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125676 Pang, Z. H., Kong, Y. L., Pang, J. M., et al., 2017. Geothermal Resources and Development in Xiongan New Area. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 32(11): 1224-1230 (in Chinese with English abstract). Paradis, C. J., McKay, L. D., Perfect, E., et al., 2018. Push-Pull Tests for Estimating Effective Porosity: Expanded Analytical Solution and In Situ Application. Hydrogeology Journal, 26(2): 381-393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1672-3 Paradis, C. J., McKay, L. D., Perfect, E., et al., 2019. Correction: Push-Pull Tests for Estimating Effective Porosity: Expanded Analytical Solution and In Situ Application. Hydrogeology Journal, 27(1): 437-439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1879-y Shi, X. Q., Jiang, B. L., Wu, J. C., et al., 2012. Numerical Analysis of the Effect of Leakage Rate on Dense Non-Aqueous Phase Liquid Transport in Heterogonous Porous Media. Advances in Water Science, 23(3): 376-382 (in Chinese with English abstract). Shu, L. C., Zhang, Y. J., Xu, Y., et al., 2017. Experimental Studies on Gas-Clogging Characteristics during Groundwater Artificial Recharge. Advances in Water Science, 28(5): 756-762 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Q. R., Zhan, H. B., 2019. Reactive Transport with Wellbore Storages in a Single-Well Push-Pull Test. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 23(4): 2207-2223. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-23-2207-2019 Zhang, W., Shi, X. Q., Wu, J. F., et al., 2013. Impacts of the Spatial Variation of Permeability on the Transport of Dense Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids in Porous Media. Geological Journal of China Universities, 19(4): 677-682 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Y., Xu, B., Liu, X. H., 2018. Groundwater Contamination and Human Health Risk Assessment in Jinghui Irrigation District, Shaanxi Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 48(5): 1451-1464 (in Chinese with English abstract). 范春辉, 高雅琳, 樊琼, 2017. 流速和初始浓度对可渗透反应墙修复模拟铅污染地下水的回归分析研究. 陕西科技大学学报(自然科学版), 35(2): 23-27, 55. 顾昊琛, 王全荣, 詹红兵, 2020. 非完整井下单井注抽试验数值模拟方法改进. 地球科学, 45(2): 685-692. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.366 李旭, 苏世林, 文章, 等, 2022. 单井注抽试验测算地下水流速的数值分析. 地球科学, 47(2): 633-641. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2021.102 庞忠和, 孔彦龙, 庞菊梅, 等, 2017. 雄安新区地热资源与开发利用研究. 中国科学院院刊, 32(11): 1224-1230. 施小清, 姜蓓蕾, 吴吉春, 等, 2012. 非均质介质中重非水相污染物运移受泄漏速率影响数值分析. 水科学进展, 23(3): 376-382. 束龙仓, 张永杰, 许杨, 等, 2017. 地下水人工回灌气相堵塞特征的试验研究. 水科学进展, 28(5): 756-762. 张蔚, 施小清, 吴剑锋, 等, 2013. 渗透率空间变异性对重非水相流体运移的影响. 高校地质学报, 19(4): 677-682. 张艳, 徐斌, 刘秀花, 2018. 陕西省泾惠渠灌区地下水污染与人体健康风险评价. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 48(5): 1451-1464. -









 下载:
下载: