Petrogenesis of Triassic Hongshuihe Granitoids in East Kunlun: Implications for the Paleo-Tethyan Orogeny
-
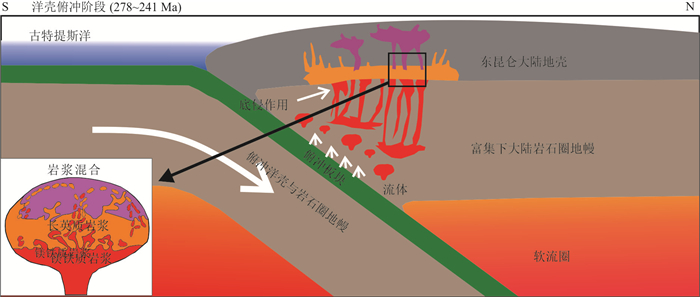
摘要: 东昆仑三叠纪岩浆岩的是研究古特提斯造山作用过程的重要探针. 对东昆仑洪水河地区花岗岩类开展了详细的岩石学、年代学、地球化学和Sr-Nd同位素研究,探讨其成因机制及动力学背景. 锆石U-Pb年代学研究表明,洪水河花岗闪长岩和花岗岩的结晶年龄分别为243.0 Ma±3.3 Ma和244.0 Ma±3.1 Ma. 两类岩石均属于准铝质高钾钙碱性Ⅰ型花岗岩,但花岗闪长岩具有较低的Na2O/K2O比值(0.78~0.96)和较高的Mg#(42~45). 岩石均富集大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素,且具有富集的Sr-Nd同位素组成[εNd(t=243)=-6.53~-4.99,Isr=0.706 871~0.709 126]. 综合分析表明,洪水河地区三叠纪花岗岩类形成于古特提斯洋壳俯冲的陆缘弧环境,岩浆起源于中元代变质杂砂岩的部分熔融,且经历了不同程度的壳幔混合作用和分离结晶作用.研究揭示,古老大陆地壳的重熔与一定量的壳幔混合作用是东昆仑中三叠世大陆地壳的主要演化方式.Abstract: Triassic magmatic rocks in East Kunlun are the key probe to study the Paleo-Tethyan orogeny. This paper presents a detailed petrological, chronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd isotopic study on the Hongshuihe granitoids in the East Kunlun to constrain their petrogenesis and dynamic setting. Zircon U-Pb chronology shows that the crystallization ages of the granodiorite and granites in the Hongshuihe pluton are 243.0 Ma±3.3 Ma and 244.0 Ma±3.1 Ma, respectively. The studied rocks are metaluminous, high-K calc-alkaline Ⅰ-type granitoids, but the granodiorites have lower Na2O/K2O ratios (0.78-0.96) and higher Mg# (42-45) than the granites. All rocks are enriched in large ion lithophile elements but depleted in high field strength elements, and have an enriched Sr-Nd isotopic composition [εNd(t)=-6.53~-4.99, Isr=0.706 871~0.709 126]. Comprehensive studies indicate that the Hongshuihe middle Triassic granitoids were formed in the continental arc environment during the East Kunlun Paleo-Tethyan oceanic crust subduction, and their parental magmas were derived by partial melting of Mesoproterozoic metagreywackes followed by varying degrees of crust-mantle mixing and fractional crystallization. This study also shows that the re-working of ancient continental crust with a certain amount of crust-mantle mixing is the main evolutionary mechanism of Middle Triassic continental crust in the East Kunlun.
-
Key words:
- East Kunlun /
- Middle Triassic /
- Paleo-Tethyan /
- granitoid /
- petrogenesis /
- petrology
-
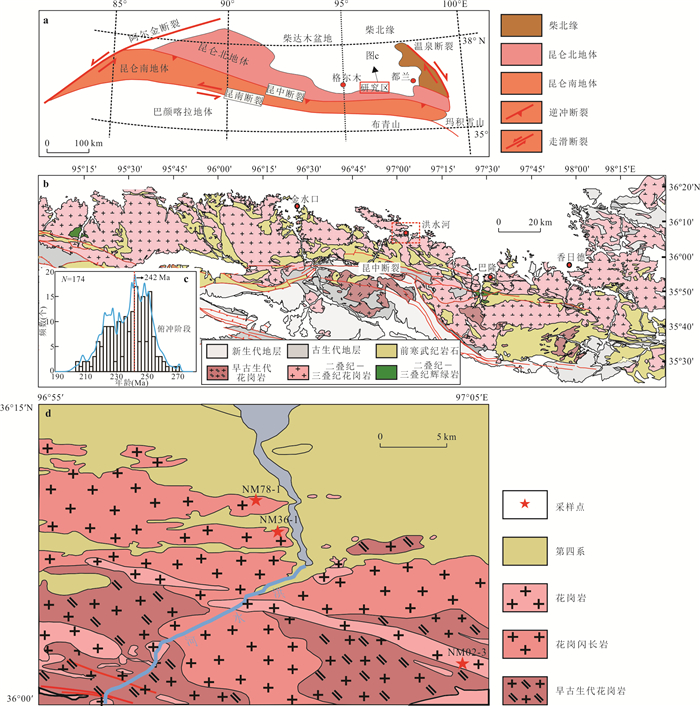
图 1 (a)东昆仑地体及邻区大地构造单元划分简图;(b)东昆仑东段岩浆岩分布简图;(c)东昆仑造山带东段早二叠世-晚三叠世岩浆岩年龄分布直方图;(d)洪水河花岗岩岩体地质简图
a图据 Meng et al.(2013);b图据 Xiong et al.(2019);c图数据引自 Li et al.(2018),Guo et al.(2019),Xiong et al.(2019),Chen et al.(2019);d图据1∶25万香日德农场地质图修改
Fig. 1. (a) Simplifiedtectonic division map of the East Kunlun orogen and its adjacent regions; (b) Sketch map showing the distribution of magmatic rocks in the eastern part of East Kunlun; (c) Age histogram for the early Permian-Late Triassic magmatic rocks in the eastern part of East Kunlun orogen; (d)Simplified geologicalmap of the Hongshuihegranite pluton
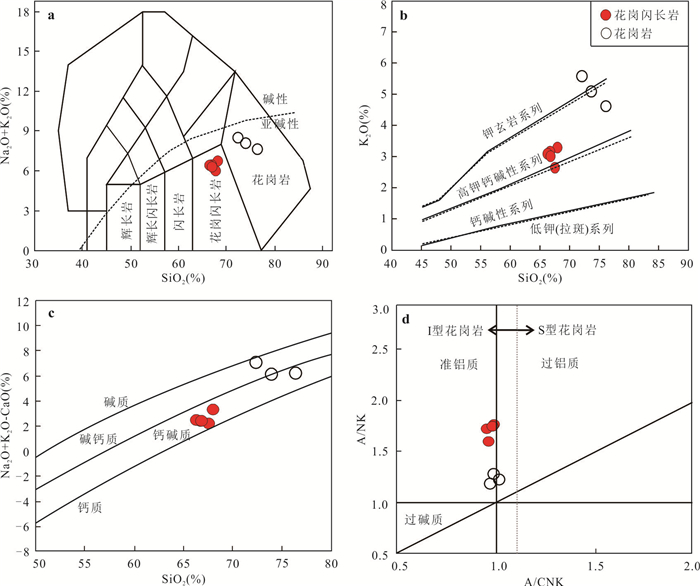
图 4 (a)TAS分类命名图;(b)SiO2 vs. K2O图;(c)SiO2 vs.(Na2O+K2O-CaO)图;(d)A/CNK vs. A/NK图
a图据 Middlemost et al.(1994);b图据 Peccerillo and Taylor(1976);c图据 Frost et al.(2001);d图据 Chappell and White(1974)
Fig. 4. (a) TAS classification and nomenclature diagram; (b) SiO2 vs. K2O diagram; (c) SiO2 vs. (c; Na2O+K2O-CaO) diagram; (d) A/CNK vs. A/NK diagram
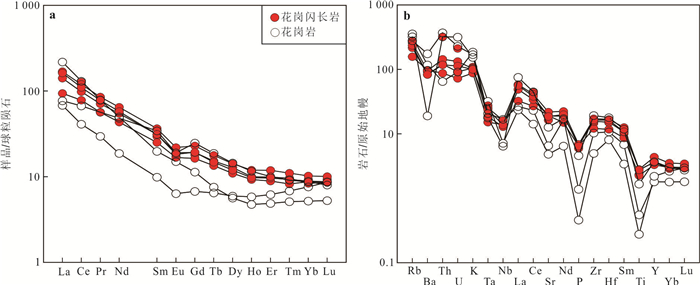
图 6 (a)球粒陨石标准化稀土元素图;(b)原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(据Sun and McDonough, 1989)
Fig. 6. (a) Chondrite-normalized REE patterns; (b) Primitive mantlenormalized trace element spider diagrams(after Sun and McDonough, 1989)
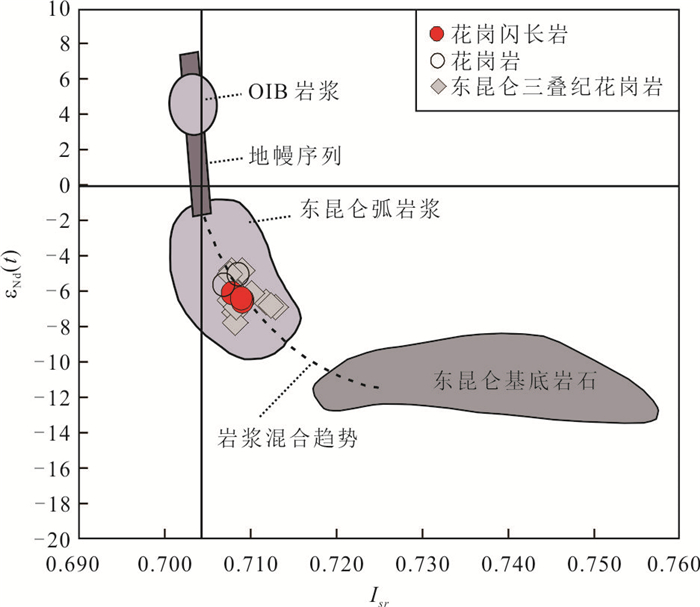
图 7 洪水河花岗岩类的Sr-Nd同位素组成图
洋岛玄武岩和基底资料据郭安林等(2007)和巴金等(2012)
Fig. 7. Whole-rock Sr-Nd isotopic diagram for the Hongshuihe granitic rocks
图 8 花岗闪长岩与花岗岩岩石成因判别图(Whalen et al., 1987)
Fig. 8. Petrogenesis discrimination diagrams of granodiorite and granite(Whalen et al., 1987)
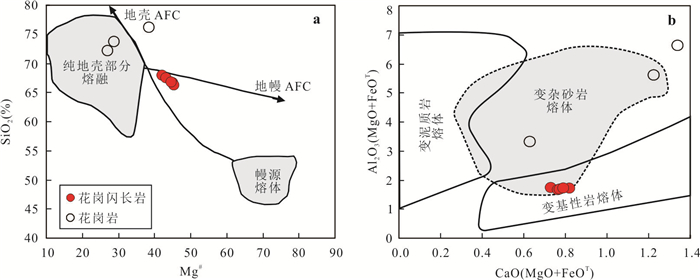
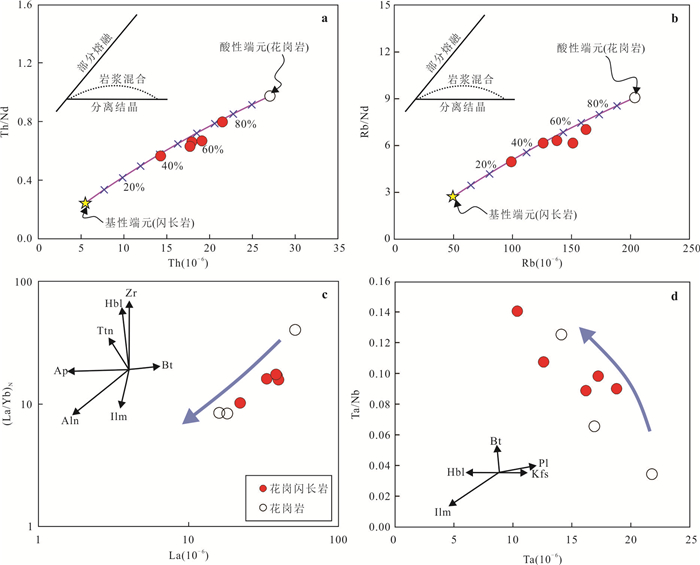
图 9 洪水河地区花岗岩类的源区判别图解
a图据 Vielzeuf et al.(1988);b图据 Kaygusuz et al.(2008)
Fig. 9. Discrimination diagrams for magma sources of the Hongshuihe granitoids
图 11 洪水河地区花岗岩类的构造环境判别图
a. Ta vs.Yb图(Pearce et al.,1984);b. La/Nb vs. Ba/Nb图(Jahn et al.,1999);c. Ta/Ybvs.Th/Yb图(after Pearce et al.,1984);d. Rb/30-Hf-3Ta图(Harris et al.,1986);AV. 弧火山岩,CA. 大陆弧,CCA. 大陆地壳平均值,DOIB. Dupal洋岛玄武岩,OIA. 洋岛弧,MORB. 洋中脊玄武岩,OIB. 洋岛玄武岩,ORG. 洋脊花岗岩,PM. 原始地幔,syn-COLG. 同碰撞花岗岩,VAG. 火山弧花岗岩,WPB. 板内玄武岩,WPG. 板内花岗岩
Fig. 11. Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the Hongshuihe granitoids
表 1 洪水河地区花岗岩类的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年分析结果
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb analysis results of the studied Hongshuihe granitoids
样品编号 元素含量
(×10-6)Th/U 同位素比值 同位素年龄 Th U Ratio 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/235U 207Pb/206Pb 206Pb/238U 1σ 09NM36-1(花岗闪长岩) 1 97 335 0.291 2 0.051 6 0.001 0 0.277 9 0.005 5 0.039 1 0.000 5 249 269 247 3 2 97 246 0.396 1 0.052 5 0.001 0 0.278 6 0.005 7 0.038 5 0.000 5 250 307 243 3 3 57 153 0.370 6 0.053 4 0.001 6 0.274 3 0.007 9 0.037 3 0.000 6 246 344 236 3 4 158 478 0.330 9 0.053 4 0.001 3 0.276 1 0.006 8 0.037 5 0.000 6 248 346 237 4 5 244 511 0.478 4 0.054 2 0.001 4 0.287 0 0.007 0 0.039 1 0.000 6 256 379 247 4 6 206 502 0.410 6 0.053 6 0.001 2 0.283 9 0.006 3 0.038 4 0.000 5 254 355 243 3 7 465 437 1.064 1 0.052 2 0.001 0 0.275 7 0.005 4 0.038 3 0.000 5 247 294 242 3 8 163 509 0.320 2 0.051 9 0.000 8 0.267 0 0.004 6 0.037 3 0.000 5 240 281 236 3 9 176 431 0.408 1 0.058 7 0.001 2 0.306 4 0.006 4 0.037 9 0.000 5 271 556 239 3 10 148 457 0.322 8 0.053 8 0.001 3 0.288 4 0.007 5 0.038 9 0.000 6 257 363 246 4 13NM02-3(花岗岩) 1 212 431 0.493 1 0.050 4 0.002 8 0.271 8 0.014 8 0.038 8 0.000 5 244 213 245 3 2 105 383 0.272 6 0.052 4 0.003 5 0.281 6 0.018 6 0.038 6 0.000 6 252 306 244 4 3 103 371 0.276 6 0.050 9 0.003 4 0.274 6 0.017 2 0.038 6 0.000 6 246 235 244 4 4 105 389 0.269 2 0.052 7 0.003 9 0.285 1 0.020 6 0.038 6 0.000 6 255 322 244 4 5 162 432 0.375 0 0.056 3 0.006 0 0.300 8 0.032 8 0.038 8 0.000 9 267 465 245 5 6 108 365 0.296 8 0.056 7 0.004 9 0.302 6 0.023 2 0.038 7 0.000 7 268 480 245 5 7 51 194 0.263 2 0.056 4 0.004 9 0.306 7 0.024 1 0.039 3 0.000 7 272 465 249 4 8 95 355 0.267 0 0.047 0 0.003 6 0.248 6 0.018 2 0.038 6 0.000 8 225 50 244 5 9 587 861 0.682 0 0.055 2 0.005 1 0.292 6 0.027 1 0.038 3 0.000 7 261 420 242 5 10 93 387 0.240 3 0.056 8 0.004 2 0.296 4 0.021 1 0.038 8 0.000 6 264 483 245 4 11 133 497 0.268 5 0.053 2 0.003 3 0.279 3 0.016 1 0.038 6 0.000 6 250 345 244 4 表 2 洪水河岩体全岩Sr-Nd同位素组成
Table 2. Whole-rock Sr-Nd isotopic compositions for the Hongshui River pluton
岩性 花岗闪长岩 花岗岩 样品号 09NM11-1 09NM78-1 09NM79 09NM80-1 09NM82-2 09NM82-4 87Rb/86Sr 1.462 10 1.000 98 1.027 49 1.102 70 6.421 82 1.915 49 87Sr/86Sr 0.713 287 0.7128 28 0.7128 68 0.713 016 0.730 624 0.715 63 2σ 121.000 02 59.000 02 60.000 02 61.000 02 67.000 02 68.000 02 (87Sr/86Sr)0 0.707 88 0.709 13 0.709 07 0.708 94 0.706 87 0.708 54 147Sm/144Nd 0.098 17 0.112 60 0.111 70 0.107 34 0.104 30 0.078 39 143Nd/144Nd(t) 0.511 99 0.511 97 0.511 97 0.511 98 0.512 02 0.512 05 fSm/Nd -0.500 93 -0.427 55 -0.432 15 -0.454 32 -0.469 75 -0.601 46 εNd(0) -9.32 -9.25 -9.34 -9.32 -8.64 -8.91 εNd(t) -6.06 -6.46 -6.53 -6.36 -5.58 -4.99 TDM2 1 522 1 553 1 559 1 546 1 482 1 436 表 3 花岗岩和花岗闪长岩的常量元素(%)、稀土和微量元素数据(×10-6)
Table 3. Major (%) and trace (×10-6) element compositions of granite and granodiorite
岩性 花岗闪长岩 花岗岩 样品号 09NM11-1 09NM36-1 09NM78-1 09NM79 09NM80-1 09NM42-2 09NM82-2 09NM82-4 SiO2 67.97 67.54 66.72 66.28 66.81 72.19 76.21 73.77 TiO2 0.51 0.49 0.60 0.61 0.60 0.36 0.06 0.12 Al2O3 15.12 15.38 15.69 15.96 15.68 13.79 12.23 13.88 Fe2O3 1.03 1.11 0.75 0.92 0.82 0.52 0.47 0.58 FeO 2.60 2.68 2.85 2.80 2.80 1.67 0.38 0.68 MnO 0.07 0.08 0.06 0.06 0.06 0.03 0.02 0.01 MgO 1.43 1.56 1.61 1.68 1.59 0.44 0.28 0.27 CaO 3.45 3.84 4.08 3.98 3.92 1.43 1.36 1.89 Na2O 3.46 3.38 3.29 3.34 3.30 2.92 3.01 3.00 K2O 3.29 2.64 3.16 3.09 3.01 5.59 4.63 5.10 P2O5 0.13 0.14 0.15 0.15 0.14 0.10 0.01 0.03 H2O+ 0.68 0.83 0.73 0.80 0.84 0.51 0.59 0.30 CO2 0.06 0.10 0.08 0.10 0.21 0.25 0.63 0.13 LOI 0.43 0.58 0.42 0.53 0.63 0.65 1.05 0.29 Total 100.23 100.35 100.19 100.30 100.41 100.45 100.93 100.05 Mg# 41.96 43.05 44.88 45.22 44.48 26.84 38.34 28.60 Fe# 0.58 0.57 0.55 0.55 0.56 0.73 0.62 0.71 ACNK 0.97 1.00 0.97 0.99 0.99 1.02 0.98 1.00 ANK 1.63 1.83 1.78 1.81 1.81 1.27 1.23 1.33 Li 47.15 31.46 47.57 52.83 49.44 16.69 7.77 9.91 Be 2.42 1.85 2.63 3.54 3.39 1.47 2.94 1.96 Sc 8.60 8.08 8.04 9.66 8.08 6.09 2.73 2.38 V 64.96 60.12 57.16 67.38 60.08 10.23 7.03 10.43 Cr 12.06 7.25 13.81 15.05 14.52 5.13 3.58 1.75 Co 8.71 8.06 7.59 8.88 7.99 3.41 1.29 1.51 Ni 6.14 4.50 5.50 5.98 5.39 2.43 1.96 1.68 Cu 3.66 11.46 6.33 4.36 3.93 31.97 5.98 5.16 Zn 57.77 67.97 66.94 70.43 64.84 35.07 11.42 14.21 Ga 19.48 19.17 20.23 23.44 21.48 17.65 14.54 15.53 Rb 174.27 99.92 137.87 163.10 149.55 203.61 226.04 176.81 Sr 345.54 403.05 399.30 460.18 393.17 137.98 102.04 267.60 Y 16.73 15.02 16.45 19.84 16.51 16.96 10.02 8.19 Zr 164.21 135.88 175.00 192.19 184.12 215.30 55.61 115.32 Nb 11.52 9.89 9.21 11.51 9.77 12.01 5.10 4.60 Cs 7.99 1.96 5.52 11.36 8.24 4.22 12.92 5.64 Ba 646.78 682.89 581.88 663.81 580.65 817.82 132.52 1218.32 La 39.19 22.26 33.51 40.06 38.61 18.22 16.14 51.79 Ce 78.02 47.91 60.21 73.26 67.53 40.99 25.14 79.79 Pr 8.00 5.36 6.73 8.12 7.40 5.38 2.81 7.48 Nd 27.79 20.26 25.54 30.21 26.96 22.44 8.74 23.34 Sm 4.51 3.83 4.76 5.58 4.79 5.25 1.51 3.03 Eu 1.00 0.97 1.10 1.27 1.06 1.10 0.37 0.87 Gd 3.70 3.36 3.94 4.70 3.96 5.07 1.38 2.33 Tb 0.53 0.50 0.57 0.66 0.55 0.70 0.24 0.28 Dy 3.00 2.78 3.26 3.61 3.04 3.68 1.51 1.43 Ho 0.55 0.53 0.57 0.68 0.55 0.65 0.33 0.27 Er 1.65 1.48 1.64 1.96 1.60 1.66 1.02 0.81 Tm 0.24 0.21 0.24 0.28 0.24 0.23 0.17 0.13 Yb 1.58 1.48 1.42 1.73 1.51 1.48 1.30 0.88 Lu 0.24 0.22 0.22 0.26 0.22 0.20 0.22 0.13 Hf 4.64 3.63 4.69 5.19 5.04 5.51 2.50 3.32 Ta 1.13 0.62 0.76 1.04 0.97 0.85 1.31 0.73 Pb 25.40 31.25 24.99 23.72 22.25 34.03 50.67 30.26 Th 27.05 7.40 10.26 12.23 10.00 5.52 27.27 31.44 U 4.45 1.52 1.92 2.79 2.37 1.91 6.66 4.79 ∑REE 170.01 111.16 143.72 172.39 158.02 107.07 60.89 172.56 LREE 158.52 100.60 131.86 158.51 146.35 93.39 54.71 166.29 HREE 11.50 10.56 11.86 13.88 11.67 13.68 6.18 6.26 LREE/HREE 13.79 9.53 11.11 11.42 12.54 6.83 8.86 26.54 (La/Yb)N 16.78 10.15 15.91 15.61 17.24 8.33 8.42 39.59 Nb/Ta 10.19 15.90 12.16 11.11 10.05 14.18 3.89 6.33 Zr/Hf 35.41 37.43 37.30 37.07 36.55 39.05 22.25 34.69 Rb/Sr 0.50 0.25 0.35 0.35 0.38 1.48 2.22 0.66 δEu 0.72 0.81 0.76 0.74 0.72 0.64 0.76 0.97 δCe 1.02 1.04 0.93 0.94 0.92 1.00 0.84 0.88 10 000Ga/Al 2.43 2.35 2.44 2.78 2.59 2.42 2.25 2.11 Zr+Nb+Ce+Y 270.48 208.71 260.88 296.81 277.94 285.26 95.87 207.89 -
Ba, J., Chen, N. S., Wang, Q. Y., 2012. Nd-Sr-Pb Isotopic Composition of Cordierite Granites in the Southern Margin of Qaidam Basin and Its Implications for Petrogenesis, Tectonic Attributes and Tectonic Evolution of the Source Area. Earth Science, 37(S1): 80-92(in Chinese with English abstract). Chappell, B. W., White, A. J. R., 1974. Two Contrasting Granite Types. Pacific Geology, 8: 173-174. Chappell, B. W., 1999. Aluminium Saturation in I- And S-Type Granites and the Characterization of Fractionated Haplogranites. Lithos, 46(3): 535-551. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-4937(98)00086-3 Chen, B., Xiong, F. H., Ma, C. Q., et al., 2021. Coupling Relation between Magma Mixing and Igneous Petrological Diversity: an Example of Bairiqili Felsic Pluton in East Kunlun Orogen. Earth Science, 46(6): 2057-2072(in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, G. C., Pei, X. Z., Li, R. B., et al., 2018. Triassic Magmatic Mixing in the Eastern Part of the East Kunlun: an Example from the Granitic Base of XiangJia South Mountain. Acta PetrologicaSinica, 34(08): 2441-80. (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, G. C., Pei, X. Z., Li, X. B., et al., 2019. Lithospheric Extensionof the Post-Collision Stage of the Paleo-Tethys Oceanic System in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt: Insights from Late Triassic Plutons. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(4): 191-208 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, G. C., Pei, X. Z., Li, R. B., et al., 2020. Late Paleozoic-Early Mesozoic Tectonic-Magmatic Evolution and Mineralization in the Eastern Section of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Earth Science Frontiers, 27(4): 33-48(in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, N. S., Sun, M., Wang, Q. Y., et al., 2008. U-Pb Dating of Zircon from the Central Zone of the East Kunlun Orogen and its Implications for Tectonic Evolution. Science in China Series D: Earth Sciences, 51(7): 929-938. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-008-0072-x Chen, S. J., Li, R. S., Ji, W. H., et al., 2010. The Permian Lithofacies Paleogeographic Characteristics and Basin-Mountain Conversion in the Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Geology in China, 37: 374-393 (in Chinese with English abstract). Collins, W. J., Richards, S. W., 2008. Geodynamic Significance of S-Type Granites in Circum-Pacific Orogens. Geology, 36(7): 559. https://doi.org/10.1130/g24658a.1 Ding, S., Huang, H., Niu, Y. L., et al., 2011. Geochemistry, Geochronology and Petrogenesis of East Kunlun High Nb-Ta Rhyolites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(12): 3603-3614 (in Chinese with English abstract). Dostal, J., Chatterjee, A. K., 2000. Contrasting Behaviour of Nb/Ta and Zr/Hf Ratios in a Peraluminous Granitic Pluton (Nova Scotia, Canada). Chemical Geology, 163(1/2/3/4): 207-218. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(99)00113-8 Feng, C. Y., Wang, S., Li, G. C., et al., 2012. Middle to Late Triassic Granitoids in the Qimantage Area, Qinghai Province, China: Chronology, Geochemistry and Metallogenic Significances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(2): 665-678 (in Chinese with English abstract). Frost, B. R., Barnes, C. G., Collins, W. J., et al., 2001. A Geochemical Classification for Granitic Rocks. Journal of Petrology, 42(11): 2033-2048. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/42.11.2033 Gao, S., Rudnick, R. L., Yuan, H. L., et al., 2004. Recycling Lower Continental Crust in the North China Craton. Nature, 432(7019): 892-897. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03162 Gao, P., Garcia-Arias, M., Chen, Y. X., et al., 2020. Origin of Peraluminous A-Type Granites from Appropriate Sources at Moderate to Low Pressures and High Temperatures. Lithos, 352-353: 105287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105287 Green, T. H., 1995. Significance of Nb/Ta as an Indicator of Geochemical Processes in the Crust-Mantle System. Chemical Geology, 120(3/4): 347-359. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-2541(94)00145-x Guo, X. Z., Jia, Q. Z., Li, J. C., et al., 2019. Geochronology and Geochemical Characteristics of Syenogranite from the Zhamaxiuma Area in East Kunlun and Their Tectonic Significance. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(4): 830-842 (in Chinese with English abstract). Harris, N. B. W., Marzouki, F. M. H., Ali, S., 1986. The Jabel Sayid Complex, Arabian Shield: Geochemical Constraints on the Origin of Peralkaline and Related Granites. Journal of the Geological Society, 143(2): 287-295. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsjgs.143.2.0287 Huang, H., Niu, Y. L., Nowell, G., et al., 2014. Geochemical Constraints on the Petrogenesis of Granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau: Implications for Continental Crust Growth through Syn-Collisional Felsic Magmatism. Chemical Geology, 370(1594): 1-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2014.01.010 Huang, X. K., Wei, J. H., Li, H., et al., 2021. Zircon U-Pb Geochronological, Elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf Isotopic Constraints on Petrogenesis of Late Triassic Quartz Diorite in Balong Region, East Kunlun Orogen. Earth Science, 46(6): 2037-2056 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jahn, B. M., Wu, F. Y., Lo, C. H., et al., 1999. Crust-mantle Interaction Induced by Deep Subduction of the Continental Crust: Geochemical and Sr-Nd Isotopic Evidence from Post-Collisional Mafic-Ultramafic Intrusions of the Northern Dabie Complex, Central China. Chemical Geology, 157(1/2): 119-146. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(98)00197-1 Kaygusuz, A., Siebel, W., Şen, C., et al., 2008. Petrochemistry and Petrology of Ⅰ-Type Granitoids in an Arc Setting: The Composite Torul Pluton, Eastern Pontides, NE Turkey. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 97(4): 739-764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-007-0188-9 Kemp, A. I. S., Hawkesworth, C. J., Foster, G. L., et al., 2007. Magmatic and Crustal Differentiation History of Granitic Rocks from Hf-O Isotopes in Zircon. Science, 315(5814): 980-983. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1136154 Li, R. B., Pei, X. Z., Li, Z. C., et al., 2012. Geological Characteristics of Late Palaeozoic-Mesozoic Unconformitiesand their Response to Some Significant Tectonic Events in Eastern Part of Eastern Kunlun. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(5): 244-254(in Chinese with English abstract). Li, R. B., Pei, X. Z., Pei, L., et al., 2018. The Early Triassic Andean-Type Halagatu Granitoids Pluton in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibet Plateau: Response to the Northward Subduction of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Gondwana Research, 62(6): 212-226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2018.03.005 Liu, C. D., Mo, X. X., Luo, Z. H., et al., 2003. Pb-Sr-Nd-O Isotope Characteristics of Granitoids in East Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 24(6): 584-588(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Y. S., Hu, Z. C., Gao, S., et al., 2008. In Situ Analysis of Major and Trace Elements of Anhydrous Minerals by LA-ICP-MS without Applying an Internal Standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1/2): 34-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004 Liu, Y., Gao, S., Hu, Z., et al., 2010. Continental and Oceanic Crust Recycling-Induced Melt-Peridotite Interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb Dating, Hf Isotopes and Trace Elements in Zircons from Mantle Xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1/2): 537-571. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/egp082 Meng, F. C., Zhang, J. X., Cui, M. H., 2013. Discovery of Early Paleozoic Eclogite from the East Kunlun, Western China and its Tectonic Significance. Gondwana Research, 23(2): 825-836. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2012.06.007 Middlemost, E. A. K., 1994. Naming Materials in the Magma/Igneous Rock System. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3/4): 215-224. https://doi.org/10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9 Mo, X. X., Luo, Z. H., Deng, J. F., et al., 2007. Granitoids and Crustal Growth in the East-Kunlun Orogenic Belt. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(3): 403-414 (in Chinese with English abstract). Pan, G. T., Wang, L. Q., Li, R. S., et al., 2012. Tectonic Evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 53: 3-14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.018 Pearce, J. A., Harris, N. B. W., Tindle, A. G., 1984. Trace Element Discrimination Diagrams for the Tectonic Interpretation of Granitic Rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983. https://doi.org/10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 Peccerillo, A., Taylor, S. R., 1976. Geochemistry of Eocene Calc-Alkaline Volcanic Rocks from the Kastamonu Area, Northern Turkey. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 58(1): 63-81. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00384745 Rapp, R. P., Shimizu, N., Norman, M. D., et al., 1999. Reaction between Slab-Derived Melts and Peridotite in the Mantle Wedge: Experimental Constraints at 3.8 GPa. Chemical Geology, 160(4): 335-356. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0009-2541(99)00106-0 Shao, F. L., Niu, Y. L., Kong, J. J., et al., 2021. Petrogenesis and Tectonic Implications of the Triassic Rhyolites in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Geoscience Frontiers, 12(6): 101243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2021.101243 Sun, S. S., McDonough, W. F., 1989. Chemical and Isotopic Systematics of Oceanic Basalts: Implications for Mantle Composition and Processes. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsl.sp.1989.042.01.19 Vielzeuf, D., Holloway, J. R., 1988. Experimental Determination of the Fluid-Absent Melting Relations in the Pelitic System. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 98(3): 257-276. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00375178 Wang, K., Wang, L. X., Ma, C. Q., et al., 2020. Genesis and Geological Significance of Middle Triassic Garnet-Bearing Mica Granites in Jialu River, East Kunlun. Earth Science, 45(2): 400-418(in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, W., Xiong, F. H., Ma, C. Q., et al., 2020. Petrogenesis of the Triassic Suolagousanukitoid-Like Diorite in the East Kunlun Orogen and Its Implications for the Paleo-Tethyan Orogeny. Earth Science, 46(8): 2887-2902 (in Chinese with English abstract). Whalen, J. B., Currie, K. L., Chappell, B. W., 1987. A-Type Granites: Geochemical Characteristics, Discrimination and Petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419. doi: 10.1007/BF00402202 Xia, R., Deng, J., Qing, M., et al., 2017. Petrogenesis of Ca. 240 Ma Intermediate and Felsic Intrusions in the Nan'getan: Implications for Crust-Mantle Interaction and Geodynamic Process of the East Kunlun Orogen. Ore Geology Reviews, 90(Part B): 1099-1117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.04.002 Xiong, F. H., Ma, C. Q., Zhang, J. Y., et al., 2014. Reworking of Old Continental Lithosphere: An Important Crustal Evolution Mechanism in Orogenic Belts, as Evidenced by Triassic Ⅰ-Type Granitoids in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau. Journal of the Geological Society, 171(6): 847-863. https://doi.org/10.1144/jgs2013-038 Xiong, F. H., Ma, C. Q., Chen, B., et al., 2019. Intermediate-Mafic Dikes in the East Kunlun Orogen, Northern Tibetan Plateau: A Window into Paleo-Arc Magma Feeding System. Lithos, 340-341: 152-165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lithos.2019.05.012 Yang, J. S., Wang, X. B., Shi, R. D., et al., 2004. The Dur'ngio Ophiolite in East Kunlun, Northern Qinghai-TibetPlateau: A Fragment of Paleo-Tethyan Oceanic Crust. Geology in China, 31(3): 225-239(in Chinese withEnglish abstract). Yang, J. S., Shi, R. D., Wu, C. L., et al., 2009. Dur'ngoi Ophiolite in East Kunlun, Northeast Tibetan Plateau: Evidence for Paleo-Tethyan Suture in Northwest China. Journal of Earth Science, 20(2): 303-331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-009-0027-y Zhao, X., Fu, L. B., Wei, J. H., et al. 2018. Geochemical Characteristics of An'nage Hornblende Gabbro from East KunlunOrogenic Belt and Its Constraints on Evolution of Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Earth Science, 43(02): 354-370 (in Chinesewith English abstract). 巴金, 陈能松, 王勤燕, 等, 2012. 柴南缘堇青石花岗岩的Nd-Sr-Pb同位素组成及其对岩石成因、源区构造属性和构造演化的启示. 地球科学, 37(S1): 80-92. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2012.S1.008 陈兵, 熊富浩, 马昌前, 等, 2021. 岩浆混合作用与火成岩多样性的耦合关系: 以东昆仑造山带白日其利长英质岩体为例. 地球科学, 46(6): 2057-2072. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.241 陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等, 2018. 东昆仑东段三叠纪岩浆混合作用: 以香加南山花岗岩基为例. 岩石学报, 34(8): 2441-80. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201808016.htm 陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等, 2019. 东昆仑古特提斯后碰撞阶段伸展作用: 来自晚三叠世岩浆岩的证据. 地学前缘, 26(4): 191-208. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201904026.htm 陈国超, 裴先治, 李瑞保, 等, 2020. 东昆仑造山带东段晚古生代-早中生代构造岩浆演化与成矿作用. 地学前缘, 27(4): 33-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY202004004.htm 陈守建, 李荣社, 计文化, 等, 2010. 昆仑造山带二叠纪岩相古地理特征及盆山转换探讨. 中国地质, 37(2) : 374-393. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201002012.htm 丁烁, 黄慧, 牛耀龄, 等, 2011. 东昆仑高Nb-Ta流纹岩的年代学、地球化学及成因. 岩石学报, 27(12): 3603-3614. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201112009.htm 丰成友, 王松, 李国臣, 等, 2012. 青海祁漫塔格中晚三叠世花岗岩: 年代学、地球化学及成矿意义. 岩石学报, 28(2): 311-324. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB202302014.htm 郭安林, 张国伟, 孙延贵, 等, 2007. 青海省共和盆地周缘晚古生代镁铁质火山岩Sr-Nd-Pb同位素地球化学及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 23(4): 747-754. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200704007.htm 黄啸坤, 魏俊浩, 李欢, 等, 2021. 东昆仑巴隆地区晚三叠世石英闪长岩成因: U-Pb年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约. 地球科学, 46(6): 2037-2056. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.286 李瑞保, 裴先治, 李佐臣, 等, 2012. 东昆仑东段晚古生代-中生代若干不整合面特征及其对重大构造事件的响应. 地学前缘, 19(5): 244-254. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201205025.htm 刘成东, 莫宣学, 罗照华, 等, 2003. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩类Pb-Sr-Nd-O同位素特征. 地球学报, 24(6): 584-588. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB200306020.htm 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等, 2007. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长. 高校地质学报, 13(3): 403~414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200703005.htm 王珂, 王连训, 马昌前, 等, 2020. 东昆仑加鲁河中三叠世含石榴石二云母花岗岩的成因及地质意义. 地球科学, 45(2): 400-418. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2018.393 王巍, 熊富浩, 马昌前, 等, 2021. 东昆仑造山带索拉沟地区三叠纪赞岐质闪长岩的成因机制及其对古特提斯造山作用的启示. 地球科学, 46(8): 2887-2902. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.270 杨经绥, 王希斌, 史仁灯, 等. 2004. 青藏高原北部东昆仑南缘德尔尼蛇绿岩: 一个被肢解了的古特提斯洋壳. 中国地质, 31(3): 225-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI200403000.htm -









 下载:
下载: