Mechanism and Controlling Factors of Sandy Conglomerate Reservoir in Piedmont Thrust Belt: A Case of Kunbei Oilfield, Qaidam Basin, NW China
-
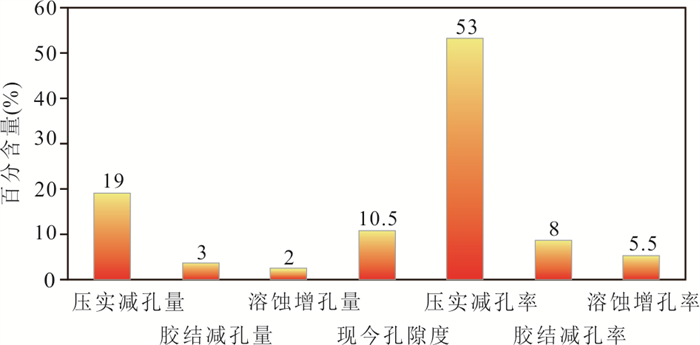
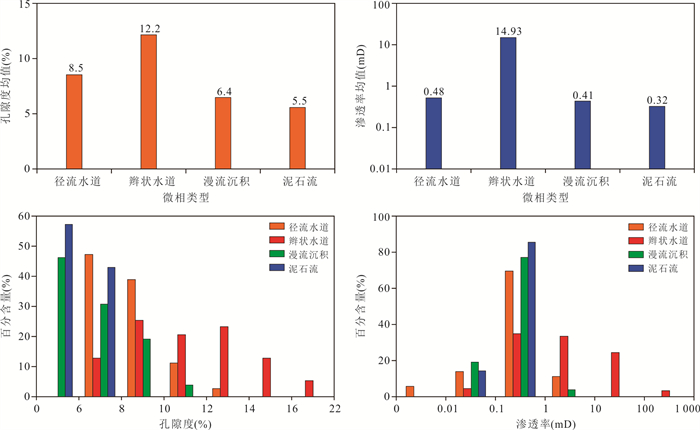
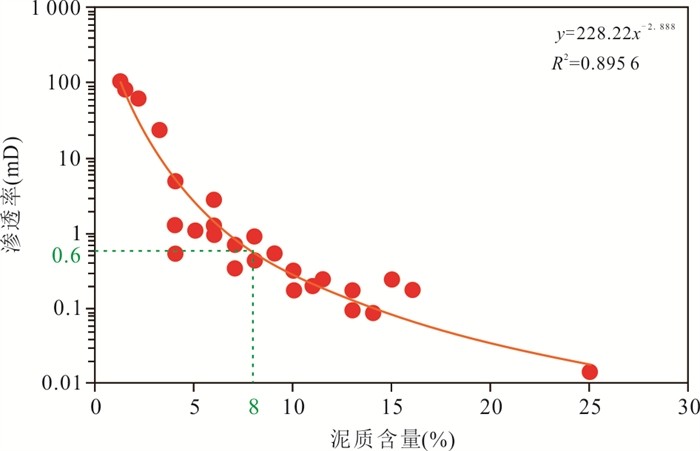
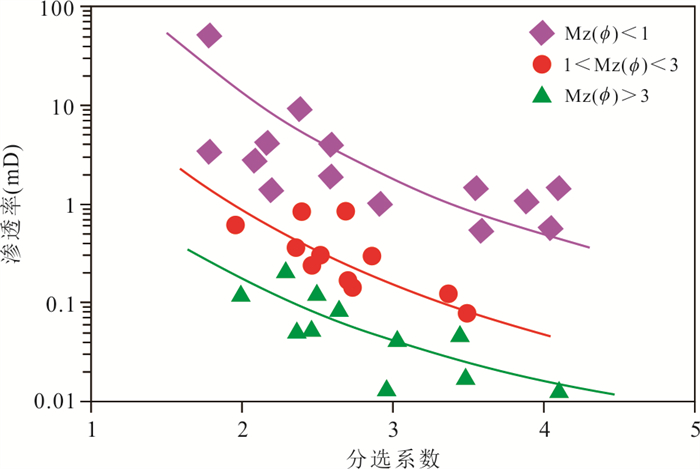
摘要: 柴达木盆地昆北断阶带为大型山前压扭冲断构造带,该构造带上的昆北油田切12区下干柴沟组下段发育厚层冲积扇沉积的砂砾岩储层.明确储层微观特征及发育控制因素,对冲断带砂砾岩储层评价与油藏治理具有重要意义.运用铸体薄片、X-衍射、扫描电镜、常规压汞与恒速压汞等测试分析资料,系统研究冲积扇砂砾岩储层微观特征,明确储层发育的主控因素.结果表明,切12区砂砾岩储层具有成分成熟度低、结构成熟度低的岩石学特征,储集空间类型具双重孔隙介质特征,发育2类储层结构模态、4类储集空间类型、4类储层孔隙结构,储层物性为低孔、特低渗型储层,成岩作用阶段为早成岩阶段B期.在砂岩动力成岩作用相同的地质背景下,成岩作用对储层改造的影响是相对均衡的,储层发育程度的差异主要受控于沉积作用差异而导致的碎屑组成与结构差异,泥质含量是储层发育程度差异的主控因素,明确泥质含量上限为8%,颗粒分选对储层性质起重要控制作用.建立了基于泥质含量、物性、孔隙结构和产能指标的储层评价分类标准,将砂砾岩储层划分为4类;运用该认识指导油藏综合治理,并取得应用实效.Abstract: The Kunbei thrust belt of Qaidam Basin is a large piedmont compression-torsion thrust belt. On the belt, the thick sandy conglomerate reservoir formed in alluvial fan is developed in the lower member of the lower Ganchaigou Formation in Qie12 block of Kunbei Oilfield. Understanding of the microcosmic characteristics and the main development controlling factors of this sandy conglomerate reservoir is significant to reservoir evaluation and the comprehensive reservoir management. In this study, the microcosmic characteristics of alluvial fan sandy conglomerate reservoir were systematically studied by using casting thin sections, XRD, SEM, conventional mercury injection and constant velocity mercury injection, and the main controlling factors of reservoir development were identified. The results show that the sandy conglomerate reservoirs in the area have the petrological characteristics of low compositional maturity and low structural maturity. The reservoir space type is characterized by dual porosity medium. There are 2 types of reservoir structure modes, 4 types of reservoir space types and 4 types of reservoir pore structures. The reservoir is of low porosity, ultra-low permeability and early diagenesis stage B. Under the same geological background of reservoir dynamic diagenesis, the influence of diagenesis on reservoir reconstruction is relatively balanced. The difference of reservoir development degree is mainly controlled by the difference of clastic composition and structure caused by the difference of sedimentation. The shale content is the main controlling factor of the reservoir development degree, and the upper limit of the shale content for reservoir is 8%, while the particle sorting plays an important role in controlling the reservoir properties. The reservoir classification standard based on shale content, physical property, pore structure and productivity index was established, and the sandy conglomerate reservoir was divided into four types. The research findings have guided the comprehensive reservoir management and achieved practical application results.
-
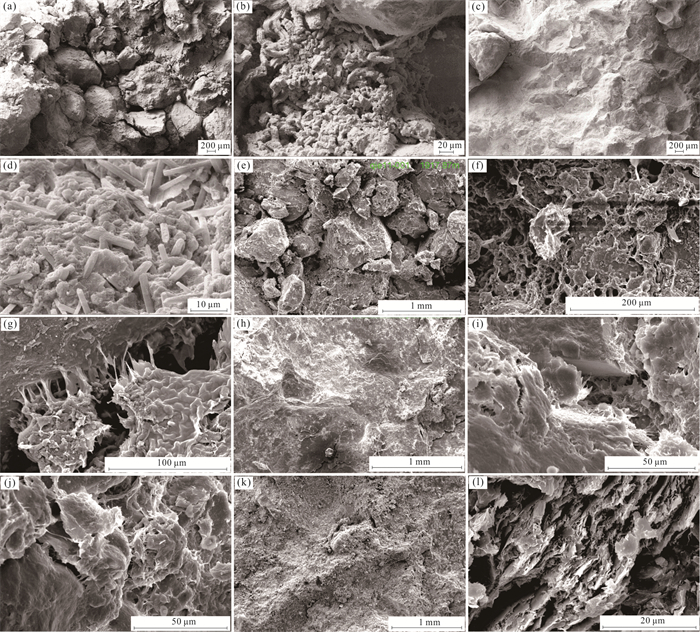
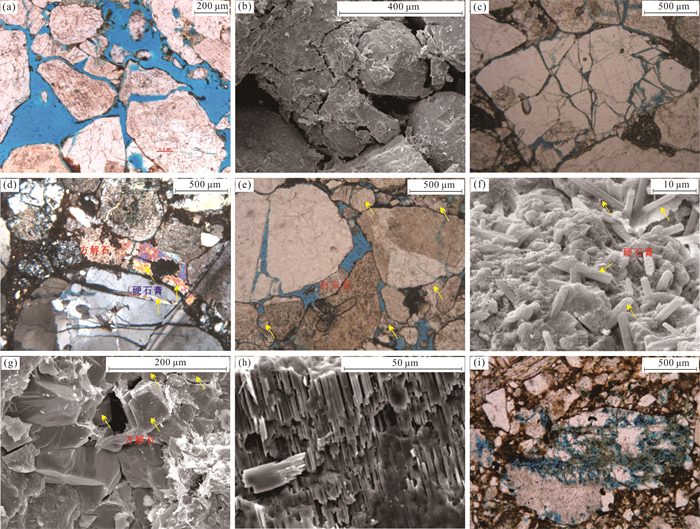
图 4 切12区储层粘土矿物分布特征
a.切12-23-6井,1 911.78 m,砂砾岩,全貌,孔隙发育;b.切12-23-6井,1 911.78 m,砂砾岩,粒间蠕虫状高岭石充填;c.切12-23-6井,1 908.49 m,泥质砂岩,全貌,孔隙不发育;d.切12-23-6井,1 908.49 m,泥质砂岩,粒间蠕虫状高岭石充填,自生硬石膏晶体;e.切11井,1 917.87 m,砂砾岩,全貌,孔隙较发育;f.切11井,1 917.87 m,砂砾岩,粒间蜂窝状伊蒙混层粘土充填,粘土微孔隙;g.切11井,1 917.87 m,砂砾岩,粒间伊利石搭桥状产出;h.切121井,1 936.7 m,砂砾岩,全貌,孔隙不发育;i.切121井,1 936.7 m,砂砾岩,粒间、粒表叶片状伊蒙混层粘土;j.切121井,1 936.7 m,砂砾岩,粒间叶片状、搭桥状的伊蒙混层粘土;k.切12井,1 817.64 m,砂砾岩,全貌,孔隙不发育;l.切12井,1 817.64 m,砂砾岩,粒间叶片状伊利石粘土,微孔隙
Fig. 4. Pattern of clay mineral in Qie12 block
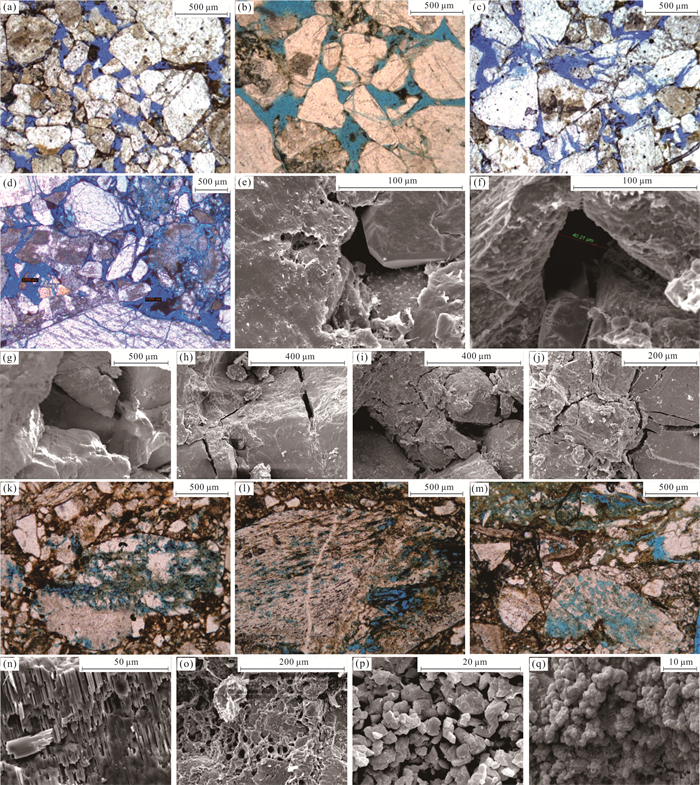
图 5 切12区储层储集空间特征
a.切12-10-8井,1 857.01 m,中‒粗粒长石岩屑砂岩,原生粒间孔;b.切11井,1 920.13 m,含砾粗砂岩,原生粒间孔,(-)×25;c.切12-10-8井,1 858.06 m,含砾中‒粗粒长石砂岩,原生粒间孔、压碎缝;d.切12-10-8井,1 855.06 m,砂砾岩,原生粒间孔、粒内溶蚀孔;e.切11井,1 924.79 m,砂砾岩,原生粒间孔;f.切12-10-8井,1 850.82 m,含砾粗砂岩,原生粒间孔;g.切12-10-8井,1 858.06 m,含砾中‒粗粒长石砂岩,原生粒间孔、压碎缝;h.切11井,1 928.3 m,砂砾岩,压碎缝;i.切121井,1 944.36 m,原生粒间孔、压碎缝;j.切121井,1 946.2 m,压碎缝;k.切12井,1 818.6 m,含砾砂岩,岩屑溶蚀孔,(-)×25;l.切12井,1 820.74 m,砂质砾岩,岩屑溶蚀孔,(-)×25;m.切12井,1 820.5 m,砾状砂岩,长石溶蚀孔,(-)×25;n.切12-7-28井,1 831.72 m,砂砾岩,长石沿解理溶蚀;o.切11井,1 917.87 m,砂砾岩,泥质微孔;p.切12井,1 820.96 m,泥质微孔;q.切12-23-6井,1 913.20 m,泥质微孔
Fig. 5. Characteristics of reservoir storage space in Qie12 block
图 11 切12区储层成岩作用
a.切12-10-8井,1 858.5 m,中‒粗粒长石岩屑砂岩,原生粒间孔,颗粒以线、线‒点接触,(-)×100;b.切121井,1 944.36 m,原生粒间孔、压碎缝;c.切12井,1 830.2 m,细砾岩,石英颗粒压碎缝,(-)×40;d.切11井,1 929.05 m,砂砾岩,方解石、硬石膏斑状胶结,(+)×40;e.切11井,1 924.79 m,砾状砂岩,白云石胶结,(-)×40;f.切12-23-6井,1 908.49 m,泥质砂岩,粒间泥质填隙物中的硬石膏晶体;g.切11井,1 926.05 m,砂砾岩,方解石胶结,残余孔;h.切12-7-28井,1 831.72 m,砂砾岩,长石沿解理溶蚀;i.切12井,1 818.6 m,含砾砂岩,岩屑溶蚀,具风化淋滤特征,(-)×25
Fig. 11. Reservoir diagenesis in Qie12 block
表 1 切12区储层孔隙结构分类参数
Table 1. Sorting parameters of reservoir pore structure in Qie12 block
分类 样品 孔隙度
(%)渗透率
(mD)排驱压力
(MPa)Rd
(μm)SHg-max
(%)P50
(MPa)R50
(μm)We
(%)Ⅰ 最大 11 23.4 31.40 0.317 44.406 91.12 89.66 4.844 61.28 最小 10.1 2.80 0.017 2.317 38.63 0.15 0.008 9.11 平均 13.1 9.94 0.073 17.615 65.08 21.91 0.494 27.27 Ⅱ 最大 14 12.9 3.30 2.083 17.763 81.30 82.76 0.761 40.36 最小 9.3 0.61 0.041 0.353 44.37 0.97 0.009 10.51 平均 10.1 1.88 0.398 6.089 65.13 28.50 0.164 30.47 Ⅲ 最大 12 8.6 1.30 2.069 2.773 81.48 48.97 0.110 35.10 最小 7.2 < 0.05 0.269 0.355 59.31 6.68 0.015 27.39 平均 8.0 0.40 0.877 1.337 70.33 24.26 0.046 30.00 Ⅳ 最大 6 6.8 0.08 32.410 1.332 89.98 106.00 0.097 38.68 最小 5.4 < 0.05 0.552 0.023 39.39 7.59 0.007 29.82 平均 6.2 0.06 10.323 0.318 64.52 55.46 0.022 34.03 合计 43 9.8 9.80 3.100 2.225 11.41 65.34 29.855 0.32 注:Rd为最大连通孔喉半径;SHg-max为最大进汞饱和度;P50为饱和度中值压力;R50为饱和度中值半径;We为退汞效率. 表 2 切12区储层评价分类标准
Table 2. The standard for reservoir classification and evaluation in Qie12 block
储层类型 Ⅰ类 Ⅱ类 Ⅲ类 Ⅳ类 渗透率(mD) > 6.0 2.0~6.0 0.6~2.0 < 0.6 泥质含量(%) < 3.5 3.5~5.0 5.0~8.0 > 8.0 孔隙结构及特征 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ Ⅳ 大孔、中喉型 中孔‒大孔、细喉型 小孔、微孔、微喉型 微孔、微喉型 孔隙度(%) > 10.0 9.0~15.0 8.5~13.0 < 8.5 单层厚度(m) 0.5~1.4 0.3~1.5 0.4~1.4 0.2~0.8 产油强度(m3) > 2.5 1.0~2.5 0.3~1.0 无产能 产能级别(m3) > 12.0 3.0~12.0 1.0~3.0 无产能 -
Bao, Y. C., Liu, Q. H., Du, X. F., et al., 2021. Division of Glutenite Lithofacies Based on the Trielement of Gravel-Matrix-Fracture. Earth Science, 46(6): 2157-2171 (in Chinese with English abstract). Cao, J. J., Luo, J. L., Madina, M., et al., 2021. Influence Mechanism of Micro-Heterogeneity on Densification of Gravel Reservoir: A Case Study of Upper Permian Wutonggou Formation in DN8 Well Area, Dongdaohaizi Depression, Junggar Basin. Earth Science, 46(10): 3435-3452 (in Chinese with English abstract). Cao, Y. C., Yan, M. M., Xi, K. L., et al., 2019. The Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Glutenite Reservoir in the Triassic Baikouquan Formation, Xiazijie Area, Mahu Depression. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 37(5): 945-956 (in Chinese with English abstract). Du, H. Q., Wang, W., Zhou, X., et al., 2016. Characteristics and Controlling Factors of Calcareous Glutenite Reservoir in the Third Member of Xu Formation in Yuanba Area, Northeastern Sichuan. Oil & Gas Geology, 37(4): 565-571 (in Chinese with English abstract). Feng, Z. H., Yin, C. H., Lu, J. M., et al., 2013. Formation and Accumulation of Tight Sandy Conglomerate Gas: A Case from the Lower Cretaceous Yingcheng Formation of Xujiaweizi Fault Depression, Songliao Basin. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(6): 650-656 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fu, S. T., Ma, D. D., Chen, Y., et al., 2016. New Progress in Oil and Gas Exploration in Qaidam Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 37(S1): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fu, S. T., Ma, D. D., Wang, L. Q., et al., 2013. Characteristics and Accumulation Conditions of Paleo-Uplift Reservoirs in Kunbei Thrust Belt, Qaidam Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 34(4): 675-682 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gong, L., Gao, X. Z., Qu, F. T., et al., 2023. Reservoir Quality and Controlling Mechanism of the Upper Paleogene Fine-Grained Sandstones in Lacustrine Basin in the Hinterlands of Northern Qaidam Basin, NW China. Journal of Earth Science, 34(3): 806-823. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-022-1701-6 Gong, Q. S., Liu, Z. G., Pang, X., et al., 2019a. Heterogeneity of Sandy Conglomerate Reservoir and Its Influence on Remaining Oil Distribution: A Case Study of Qie 12 Block of Kunbei Oilfield in Qaidam Basin. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 48(1): 165-174 (in Chinese with English abstract). Gong, Q. S., Liu, Z. G., Song, G. Y., et al., 2019b. Inter-Layers in Alluvial-Fan Thick Sandy Conglomerate Reservoir of Kunbei Oilfield, Qaidam Basin. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 40(2): 152-164 (in Chinese with English abstract). Guo, M. Z., Zhu, G. H., Shou, J. F., et al., 2006. Features, Origin and Petroleum Explorative Significance of Crushed Fracture in Clastic Rock. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 24(4): 483-487 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lei, Z. Y., Lu, B., Wei, Y. J., et al., 2005. Tectonic Evolution and Development and Distribution of Fans on Northwestern Edge of Junggar Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 26(1): 86-91 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, J., Tang, Y., Wu, T., et al., 2020. Overpressure Origin and Its Effects on Petroleum Accumulation in the Conglomerate Oil Province in Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin, NW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 47(4): 679-690 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liao, J. H., Wu, K. Q., Er, C., 2022. Deep Reservoir Characteristics and Effective Reservoir Control Factors in Baiyun Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin. Earth Science, 47(7): 2454-2467 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lin, L., Mu, Z. H., Ma, D. D., et al., 2011. Characteristics and Control Factors of the E31 Clastic Rock Reservoir in the Q12 Block of the Kunbei Oilfield. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 18(4): 26-29, 136 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, J. K., 1983. An Investigation on Structure Model of Conglomeratic Reservoir and Its Evaluation. Petroleum Expoloration and Development, 10(2): 45-56 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Z. G., Gong, Q. S., Zhu, C., et al., 2019. Sedimentary Sequence and Its Controlling Effect on Hydrocarbon Enrichment in Qie12 Block of Qaidam Basin. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(4): 238-249 (in Chinese with English abstract). Luo, M. G., 1991. Quantitative Models for Pore Structures of Clastic Sedimentary Rocks. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 12(4): 27-38, 145 (in Chinese with English abstract). Qu, J. H., Yang, R. R., Tang, Y., 2019. Large-Area Petroleum Accumulation Model of the Triassic Glutenite Reservoirs in the Mahu Sag, Junggar Basin: Triple Controls of Fan, Fault and Overpressure. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(4): 915-927 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tan, X. F., Xia, M. Q., Zhang, Q. X., et al., 2016. Sedimentary Characteristics of Braided River Delta in the Lower Member of Xiaganchaigou Formation in the Southwest Margin of Qaidam Basin. Oil & Gas Geology, 37(3): 332-340 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tang, Y., Guo, W. J., Wang, X. T., et al., 2019. A New Breakthrough in Exploration of Large Conglomerate Oil Province in Mahu Sag and Its Implications. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 40(2): 127-137 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, S. H., Fan, Z., Xu, C. F., et al., 2012. Internal Architecture of Alluvial Fan in the Triassic Lower Karamay Formation in Karamay Oilfield, Xinjiang. Journal of Palaeogeography, 14(3): 331-340 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, S. H., Xiong, Q. H., 1998. Hydrocarbon Reservior Geology. Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing (in Chinese). Wu, S. T., Zhu, R. K., Li, X., et al., 2018. Evaluation and Application of Porous Structure Characterization Technologies in Unconventional Tight Reservoirs. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(2): 191-203 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xiong, S. C., Chu, S. S., Pi, S. H., et al., 2017. Micro-Pore Characteristics and Recoverability of Tight Oil Reservoirs. Earth Science, 42(8): 1379-1385 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, Y. H., Yang, X. H., Mei, L. F., 2020. Reservoir Characteristics and Main Control Factors of Conglomerate Reservoir of El3 in the Northwest Steep Slope Zone of Weixinan Depression. Earth Science, 45(5): 1706-1721 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, T., Cao, Y. C., Wang, Y. Z., et al., 2015. Genesis of High-Quality Reservoirs of Fan Delta Front in Lower Part of the Fourth Member of Shahejie Formation in Bonan Subsag. Earth Science, 40(12): 2067-2080 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yin, S. L., Chen, G. Y., Chen, Y. K., et al., 2019. Mechanism of Complex Modes of the Pore Structure of Sandstone/Conglomerate Reservoirs. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 41(1): 1-17 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yin, S. L., Wu, S. H., Feng, W. J., et al., 2013. Patterns of Inter-Layers in the Alluvial Fan Reservoirs: A Case Study on Triassic Lower Karamay Formation, Yizhong Area, Karamay Oilfield, NW China. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 40(6): 757-763 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yousef, I., Morozov, V., Sudakov, V., et al., 2022. Microfracture Characterization in Sandstone Reservoirs: A Case Study from the Upper Triassic of Syria's Euphrates Graben. Journal of Earth Science, 33(4): 901-915. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-021-1488-x Zhang, Y., Ji, Y. L., Gao, C. L., et al., 2020. Genetic Mechanism, Distribution and Significance for Hydrocarbon Exploration of the Grain-Supported Conglomerate in Alluvial Fans. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 49(2): 352-366 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, H. W., Ning, Z. F., Zhao, T. Y., et al., 2017. Applicability of Rate-Controlled Porosimetry Experiment to Pore Structure Characterization of Tight Oil Reservoirs. Fault-Block Oil and Gas Field, 24(3)413-416 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhong, J., Yang, X. B., Zhu, P. Y., et al., 2019. Porosity Evolution Differences of the Lingshui Formation Reservoir between Baodao and Changchang Sag, Qiongdongnan Basin. Earth Science, 44(8): 2665-2676 (in Chinese with English abstract). 鲍怡晨, 刘强虎, 杜晓峰, 等, 2021. 基于砾石‒基质‒裂缝三元素的砂砾岩岩相划分. 地球科学, 46(6): 2157-2171. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.284 曹江骏, 罗静兰, 马迪娜·马吾提汗, 等, 2021. 微观非均质性对砂砾岩储层致密化的影响机理: 以准噶尔盆地东道海子凹陷DN8井区上二叠统梧桐沟组为例. 地球科学, 46(10): 3435-3452. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.388 操应长, 燕苗苗, 葸克来, 等, 2019. 玛湖凹陷夏子街地区三叠系百口泉组砂砾岩储层特征及控制因素. 沉积学报, 37(5): 945-956. 杜红权, 王威, 周霞, 等, 2016. 川东北元坝地区须三段钙屑砂砾岩储层特征及控制因素. 石油与天然气地质, 37(4): 565-571. 冯子辉, 印长海, 陆加敏, 等, 2013. 致密砂砾岩气形成主控因素与富集规律——以松辽盆地徐家围子断陷下白垩统营城组为例. 石油勘探与开发, 40(6): 650-656. 付锁堂, 马达德, 陈琰, 等, 2016. 柴达木盆地油气勘探新进展. 石油学报, 37(S1): 1-10. 付锁堂, 马达德, 汪立群, 等, 2013. 柴达木盆地昆北冲断带古隆起油藏特征及油气成藏条件. 石油学报, 34(4): 675-682. 宫清顺, 刘占国, 庞旭, 等, 2019a. 砂砾岩油藏储层非均质性及对剩余油分布影响——以柴达木盆地昆北油田切12区为例. 中国矿业大学学报, 48(1): 165-174. 宫清顺, 刘占国, 宋光永, 等, 2019b. 柴达木盆地昆北油田冲积扇厚层砂砾岩储集层内部隔夹层. 石油学报, 40(2): 152-164. 郭沫贞, 朱国华, 寿建峰, 等, 2006. 碎屑岩压裂缝的特征、成因与油气勘探意义. 沉积学报, 24(4): 483-487. 雷振宇, 鲁兵, 蔚远江, 等, 2005. 准噶尔盆地西北缘构造演化与扇体形成和分布. 石油与天然气地质, 26(1): 86-91. 李军, 唐勇, 吴涛, 等, 2020. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷砾岩大油区超压成因及其油气成藏效应. 石油勘探与开发, 47(4): 679-690. 廖计华, 吴克强, 耳闯, 2022. 珠江口盆地白云凹陷深层储层特征与有效储层控制因素. 地球科学, 47(7): 2454-2467. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2022.017 林伶, 牟中海, 马达德, 等, 2011. 昆北油田切12区E31碎屑岩储层特征及控制因素. 特种油气藏, 18(4): 26-29, 136. 刘敬奎, 1983. 砾岩储层结构模态及储层评价探讨. 石油勘探与开发, 10(2): 45-56. 刘占国, 宫清顺, 朱超, 等, 2019. 柴达木盆地切12区沉积层序及对油气富集的控制作用. 地学前缘, 26(4): 238-249. 罗明高, 1991. 碎屑岩储层结构模态的定量模型. 石油学报, 12(4): 27-38, 145. 瞿建华, 杨荣荣, 唐勇, 2019. 准噶尔盆地玛湖凹陷三叠系源上砂砾岩扇‒断‒压三控大面积成藏模式. 地质学报, 93(4): 915-927. 谭先锋, 夏敏全, 张勤学, 等, 2016. 柴达木盆地西南缘下干柴沟组下段辫状河三角洲沉积特征. 石油与天然气地质, 37(3): 332-340. 唐勇, 郭文建, 王霞田, 等, 2019. 玛湖凹陷砾岩大油区勘探新突破及启示. 新疆石油地质, 40(2): 127-137. 吴胜和, 范峥, 许长福, 等, 2012. 新疆克拉玛依油田三叠系克下组冲积扇内部构型. 古地理学报, 14(3): 331-340. 吴胜和, 熊琦华, 1998. 油气储层地质学. 北京: 石油工业出版社. 吴松涛, 朱如凯, 李勋, 等, 2018. 致密储层孔隙结构表征技术有效性评价与应用. 地学前缘, 25(2): 191-203. 熊生春, 储莎莎, 皮淑慧, 等, 2017. 致密油藏储层微观孔隙特征与可动用性评价. 地球科学, 42(8): 1379-1385. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2017.550 徐燕红, 杨香华, 梅廉夫, 2020. 涠西南凹陷西北陡坡带流三段砂砾岩储层特征与主控因素. 地球科学, 45(5): 1706-1721. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.174 杨田, 操应长, 王艳忠, 等, 2015. 渤南洼陷沙四下亚段扇三角洲前缘优质储层成因. 地球科学, 40(12): 2067-2080. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2015.183 印森林, 陈恭洋, 陈玉琨, 等, 2019. 砂砾岩储层孔隙结构复杂模态差异机制. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 41(1): 1-17. 印森林, 吴胜和, 冯文杰, 等, 2013. 冲积扇储集层内部隔夹层样式——以克拉玛依油田一中区克下组为例. 石油勘探与开发, 40(6): 757-763. 张月, 纪友亮, 高崇龙, 等, 2020. 冲积扇"颗粒支撑砾岩"的成因和分布及其油气地质意义. 中国矿业大学学报, 49(2): 352-366. 赵华伟, 宁正福, 赵天逸, 等, 2017. 恒速压汞法在致密储层孔隙结构表征中的适用性. 断块油气田, 24(3)413-416 钟佳, 杨希冰, 朱沛苑, 等, 2019. 琼东南盆地宝岛‒长昌凹陷陵水组储层差异演化特征. 地球科学, 44(8): 2665-2676. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.097 -









 下载:
下载: