Iodine Species and Causes of Iodine Enrichment in Saline Groundwater in Plain Area of Lower Reaches of Kashigar River
-
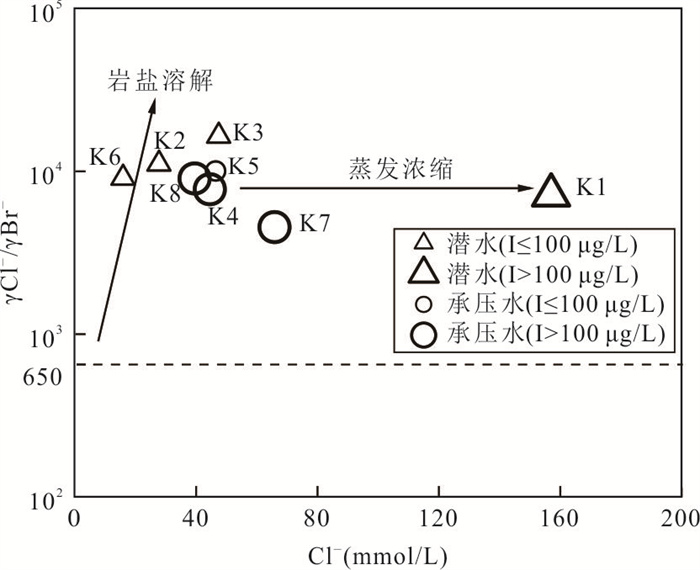
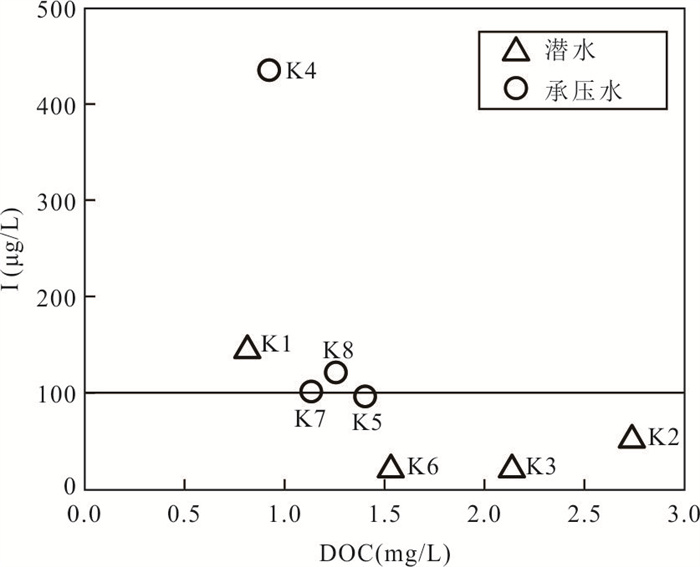
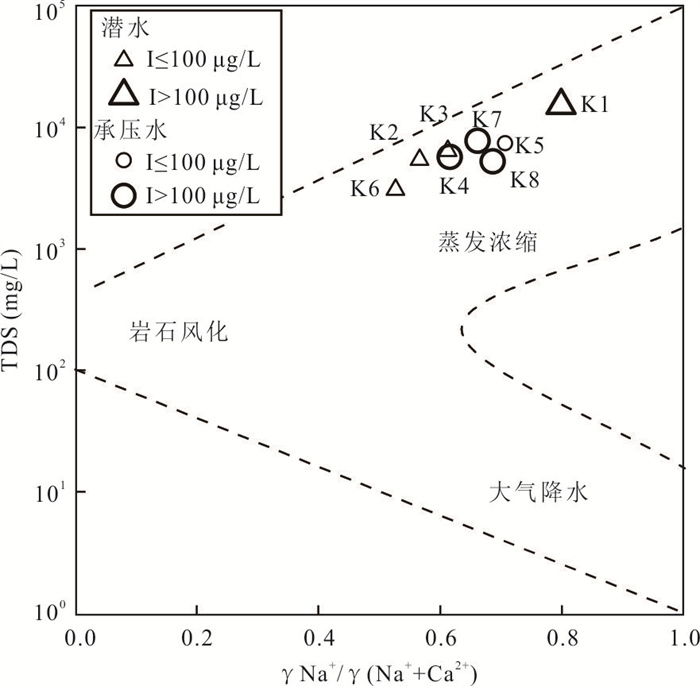
摘要: 新疆喀什噶尔河位于典型的干旱-半干旱区,河流下游平原区地下水溶解性总固体(TDS)和碘含量异常,严重威胁当地用水安全. 以喀什噶尔河下游平原区为研究区,通过对地下水水化学特征、Cl/Br摩尔比、氢氧稳定同位素、赋存环境与水文地球化学作用的分析确定该区地下咸水中碘的分布与碘富集的影响因素. 结果表明,研究区地下水碘含量变化范围为 < 0.40~435.00 μg/L(均值为123.50 μg/L),其中潜水和承压水碘含量均值分别为58.75 μg/L和188.25 μg/L,高碘水占比分别为25.0%和75.0%,水化学类型主要为Cl·SO4型和SO4·Cl型. 地下水TDS变化范围为3 079.13~15 249.50 mg/L,主要为中性至弱碱性咸水(87.5%),其次为盐水(12.5%). 碘元素的存在形态主要为I-(87.5%),其次为IO3-(12.5%),且无共存形态,亚氧化环境和亚还原环境分别利于碘元素以IO3-和I-形态存在. 高TDS、细粒岩性、平缓的地势、地下水浅埋条件及碱性环境均有利于地下水碘的富集. 潜水碘富集主要受蒸发浓缩作用和蒸发岩溶解作用的影响,承压水碘富集主要受还原条件下含铁矿物的溶解和冲积-湖积物的影响. Cl-与Cl/Br摩尔比值表明高碘潜水受到一定程度蒸发浓缩作用的影响.Abstract: Kashgar River in Xinjiang is located in a typical arid and semi-arid area. The abnormal contents of total dissolved solids (TDS) and iodine in groundwater in the lower reaches of the river seriously threaten the local water security. Taking the plain area in the lower reaches of Kashigar River as the study area, the distribution of iodine in saline groundwater and its influence on iodine enrichment were determined through analysis of the hydrochemical characteristics, Cl/Br mole ratio, stable isotopes of hydrogen and oxygen, occurrence environment of groundwater and hydrogeochemical process. The results showed that the iodine content of groundwater in the study area varies from < 0.40 μg/L to 435.00 μg/L (mean 123.50 μg/L). The mean iodine content of unconfined groundwater and confined groundwater is 58.75 μg/L and 188.25 μg/L, respectively, and the proportion of high iodine groundwater is 25.0% and 75.0%, respectively. The main hydrochemical types are Cl·SO4 and SO4·Cl. TDS of groundwater ranged from 3 079.13 mg/L to 15 249.50 mg/L, mainly in neutral to slightly alkaline saline groundwater (87.5%), followed by saline groundwater (12.5%). The main form of iodine is I- (87.5%), followed by IO3-(12.5%), and there is no coexistence form. The existence of iodine in IO3- and I- forms in the suboxidizing environment and the subreducing environment is favorable, respectively. High TDS, fine lithology, gentle topography, shallow burial conditions of groundwater and alkaline environment are all conducive to the accumulation of iodine in groundwater. The iodine enrichment in unconfined groundwater is mainly affected by evaporation concentration and the dissolution of evaporite, while the iodine enrichment in confined groundwater is mainly affected by the dissolution of iron-bearing minerals under reduction conditions and alluvial-lacustrine sediments. The Cl- to Cl/Br mole ratio indicates that the high iodine water in unconfined groundwater is obviously affected by evaporation.
-
Key words:
- high iodine /
- Kashgar River /
- groundwater /
- saline groundwater /
- iodine species /
- hydrogeochemical process
-
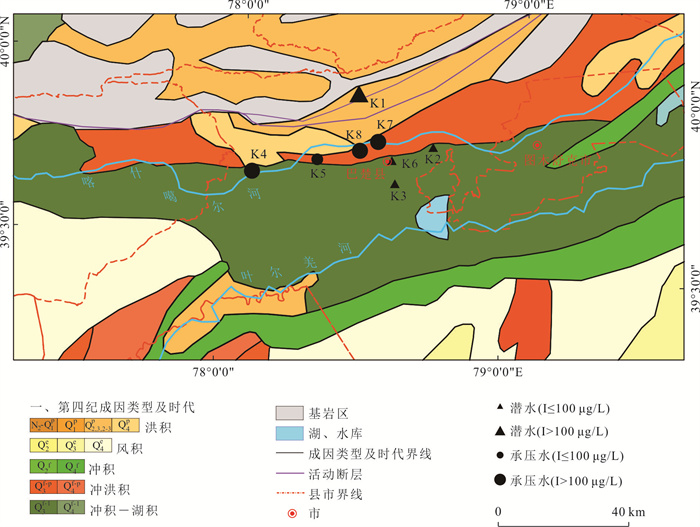
表 1 研究区地下水化学组分含量统计表
Table 1. Statistics of hydrogeochemical composition content in groundwater
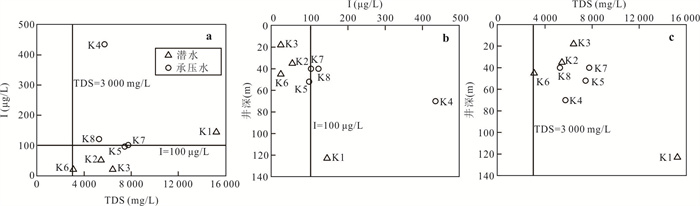
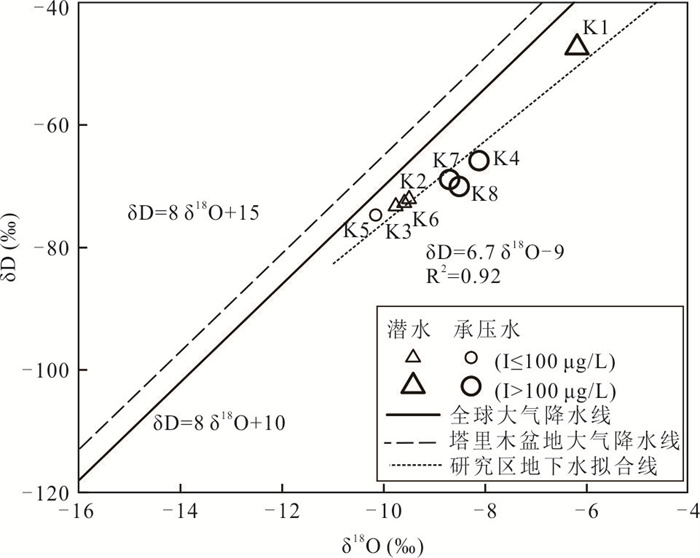
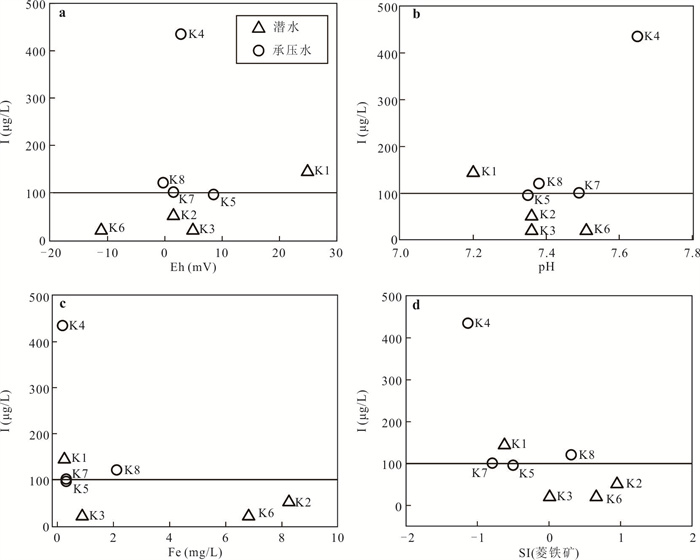
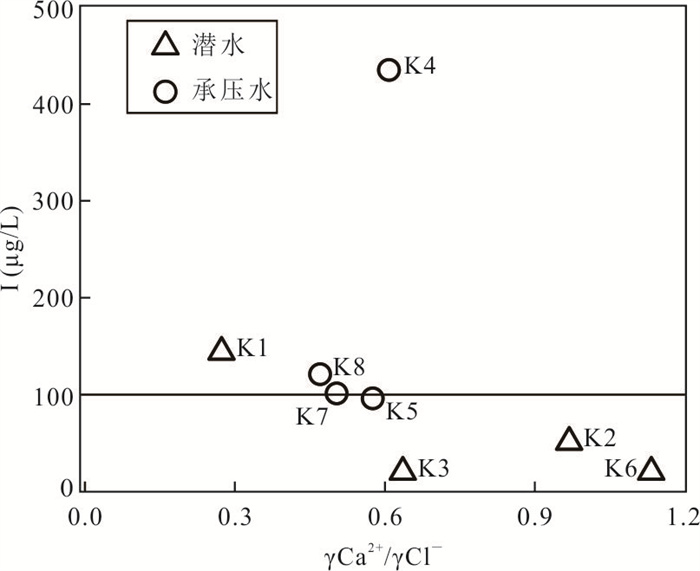
样品编号 K1 K2 K3 K4 K5 K6 K7 K8 地下水类型 潜水 潜水 潜水 承压水 承压水 潜水 承压水 承压水 井深(m) 123 35 18 70 52 45 40 40 Eh(mV) 24.90 1.50 4.90 2.80 8.50 -11.10 1.50 -0.30 pH值 7.20 7.36 7.36 7.65 7.35 7.51 7.49 7.38 K++Na+(mg/L) 4 254.02 877.27 1 191.38 1 087.74 1 609.80 502.79 1 624.04 1 017.36 Ca2+(mg/L) 858.96 538.11 603.48 542.13 535.09 361.69 663.83 372.15 Mg2+(mg/L) 411.18 308.08 331.87 277.58 333.09 135.68 336.75 333.09 Cl-(mg/L) 5 574.51 985.51 1 683.88 1 581.07 1 648.43 566.49 2 339.70 1 403.82 SO42-(mg/L) 3 887.76 2 489.01 2 359.42 2 084.10 3 098.04 1 340.00 2 651.30 1 934.57 HCO3-(mg/L) 521.32 463.94 512.77 324.76 452.95 329.64 277.14 411.44 I(μg/L) 144.0 51.0 < 40.0 435.0 96.0 < 40.0 101.0 121.0 总Fe(mg/L) 0.25 8.25 0.89 0.19 0.32 6.82 0.32 2.11 TH(mg/L) 3 837.58 2 611.97 2 873.16 2 496.44 2 707.41 1 461.70 3 043.95 2 300.54 TDS(mg/L) 15 249.50 5 439.40 6 428.22 5 736.79 7 452.60 3 079.13 7 755.45 5 269.71 Br-(mg/L) 1.76 0.20 0.23 0.46 0.37 0.14 1.16 0.35 DOC(mg/L) 0.81 2.74 2.14 0.92 1.40 1.53 1.14 1.26 δD (‰) -47.40 -72.08 -73.30 -65.86 -74.71 -72.73 -68.94 -70.07 δ18O(‰) -6.19 -9.50 -9.76 -8.12 -10.16 -9.59 -8.70 -8.51 -
Amiri, V., Sohrabi, N., Dadgar, M. A., 2015. Evaluation of Groundwater Chemistry and Its Suitability for Drinking and Agricultural Uses in the Lenjanat Plain, Central Iran. Environmental Earth Sciences, 74(7): 6163-6176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4638-6 Andersson, M., Karumbunathan, V., Zimmermann, M. B., 2012. Global Iodine Status in 2011 and Trends Over the Past Decade. The Journal of Nutrition, 142(4): 744-750. https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.112.161729 Cartwright, I., Weaver, T. R., Fulton, S., et al., 2004. Hydrogeochemical and Isotopic Constraints on the Origins of Dryland Salinity, Murray Basin, Victoria, Australia. Applied Geochemistry, 19(8): 1233-1254. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.apgeochem.2003.12.006 doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.12.006 Chen, J. L., Yang, H. X., Liu, W., et al., 2017. Study on the Total Iodine and Iodine Speciation Characteristics in Xilingol League, Inner Mongolia and Tacheng, Xinjiang High Iodine Area by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 36(6): 614-623(in Chinese with English abstract). Craig, H., 1961. Isotopic Variations in Meteoric Waters. Science, 133: 1702-1703. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.133.3465.1702 Gaillardet, J., Dupré, B., Louvat, P., et al., 1999. Global Silicate Weathering and CO2 Consumption Rates Deduced from the Chemistry of Large Rivers. Chemical geology, 159(1-4): 3-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00031-5 Gibbs, R. J., 1970. Mechanisms Controlling World Water Chemistry. Science, 170(3962): 1088-1090. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.170.3962.1088 Hao, S., Li, F. D., Li, Y. H., et al., 2019. Stable Isotope Evidence for Identifying the Recharge Mechanisms of Precipitation, Surface Water, and Groundwater in the Ebinur Lake Basin. Science of the Total Environment, 657: 1041-1050. https://doi.org/10. 1016/j.scitotenv. 2018. 12.102 doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.12.102 Hou, X. L., Hansen, V., Aldahan, A., et al., 2009. A Review on Speciation of Iodine-129 in the Environmental and Biological Samples. Analytica Chimica Acta, 632(2): 181-196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2008.11.013 Hu, Q. H., Zhao, P. H., Moran, J. E., et al., 2005. Sorption and Transport of Iodine Species in Sediments from the Savannah River and Hanford Sites. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 78(3): 185-205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconhyd.2005.05.007 Jia, Y. F., 2021. Geogenic-Contaminated Groundwater in China. Global Groundwater, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 229-242. Li, L., Qiu, S. J., Tan, F. F., et al., 2013. Effects of Salinity and Exogenous Substrates on the Decomposition and Transformation of Soil Organic carbon in the Yellow River Delta. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 33(21): 6844-6852 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.5846/stxb201206290914 Li, J. X., Wang, Y. X., Guo, W., et al. 2014. Iodine Mobilization in Groundwater System at Datong Basin, China: Evidence from Hydrochemistry and Fluorescence Characteristics. Science of the Total Environment, 468: 738-745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.08.092 Li, J. X., Wang, Y. X., Xie, X. J., 2016. Cl/Br Ratios and Chlorine Isotope Evidences for Groundwater Salinization and Its Impact on Groundwater Arsenic, Fluoride and Iodine Enrichment in the Datong Basin, China. Science of the Total Environment, 544: 158-167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.08.144 Li, J. X., Wang, Y. X., Xue, X. B., et al., 2020. Mechanistic Insights into Iodine Enrichment in Groundwater During the Transformation of Iron Minerals in Aquifer Sediments. Science of the Total Environment, 745: 140922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140922 Li, W. P., Hao, A. B., Zheng, Y. J., et al., 2006. Regional Environmental Isotopic Features of Groundwater and Their Hydrogeological Explanation in the Tarim Basin. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(1): 191-198(in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Y. L., 2019. Groundwater Salinization Mechanism and Interaction Processes of the Evaporation and Salt Accumulation in an Arid Inland Basin (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Wuhan (in Chinese with English abstract). Okin, G. S., Gillette, D. A., Herrick, J. E., 2006. Multi-Scale Controls on and Consequences of Aeolian Processes in Landscape Change in Arid and Semi-Arid Environments. Journal of Arid Environments, 65(2): 253-275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2005.06.029 Orr, C. A., 2017. Warren JK: Evaporites: A Geological Compendium, 2nd Ed. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76: 687. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6965-2 Pang, Z. H., Kong, Y. L., Li, J., et al., 2017. An Isotopic Geoindicator in the Hydrological Cycle. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 17: 534-537. https://doi.org/ 10.1016/j.proeps.2016. 12.135 doi: 10.1016/j.proeps.2016.12.135 Qian, C., Wu, X., Mu, W. P., et al., 2016. Hydrogeochemical Characterization and Suitability Assessment of Groundwater in an Agro-Pastoral Area, Ordos Basin, NW China. Environmental Earth Sciences, 75(20): 1356-1371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-016-6123-2 Qian, K., Li, J. X., Chi, Z. Y., et al., 2020. Natural Organic Matter-Enhanced Transportation of Iodine in Groundwater in the Datong Basin: Impact of Irrigation Activities. Science of the Total Environment, 730: 138460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.138460 Schwehr, K. A., Santschi, P. H., Kaplan, D. I., et al., 2009. Organo-Iodine Formation in Soils and Aquifer Sediments at Ambient Concentrations. Environmental Science & Technology, 43(19): 7258-7264. https://doi.org/10.1021/es900795k Schofield, R., Thomas, D. S. G., Kirkby, M. J., 2001. Causal Processes of Soil Salinization in Tunisia, Spain and Hungary. Land Degradation & Development, 12(2): 163-181. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.446 Shen, H. M., Zhang, S. B., Liu, S. J., et al., 2007. Study on the Geographic Distribution of National High Water Iodine Areas and the Contours of Water Iodine in High Iodine Areas. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 26(6): 658-661(in Chinese with English abstract). Sun, Y., Zhou, J. L., Liang, X., et al., 2021. Distribution and Genesis of Shallow High-Iodine Groundwater in Southern Margin of Tarim Basin: A Case Study of Plain Area in Minfeng County, Xinjiang. Earth Science, 46(8): 2999-3011(in Chinese with English abstract). Voutchkova, D. D., Ernstsen, V., Kristiansen, S. M., et al., 2017. Iodine in Major Danish Aquifers. Environmental Earth Sciences, 76(13): 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6775-6 Wang, H. T., Zhou, J. L., Zeng, Y. Y., et al., 2019. Spatial Distribution and Enrichment Factors of Iodine in Drinking Groundwater in Kashgar Prefecture of Xinjiang. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 42(2): 145-150(in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Y. X., Li, J. X., Ma, T., et al., 2021. Genesis of Geogenic Contaminated Groundwater: As, F and I. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 51(24): 2895-2933. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389. 2020.1807452 doi: 10.1080/10643389.2020.1807452 Wang, Y. T., Li, J. X., Xue, X. B., et al., 2021. Similarities and Differences of Main Controlling Factors of Natural HighIodine Groundwater between North China Plain and Datong Basin. Earth Science, 46(1): 308-320. (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Z., Du, H. B., 2003. Discussion on Groundwater Resources and Development and Utilization Mode in Bachu County. Xinjiang Water Resources, (2): 16-19(in Chinese). Wei, X., Zhou, J. L., Jia, R. L., et al., 2017. Distribution and Resource Estimation of Shallow Groundwater with Different TDS in Kashgar Region of Xinjiang. Water Saving Irrigation, (9): 51-54(in Chinese with English abstract). Xu, F., Ma, T., Shi, L., et al., 2012. Hydrogeochemical Characteristics of High Iodine Groundwater in the Hetao Plain, Inner Mongolia. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 39(5): 8-15(in Chinese with English abstract). Xue, J. K., Deng, Y. M., Du, Y., et al., 2021. Molecular Characterization of Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) in Shallow Aquifer along the Middle Reaches of Yangtze River and Its Implications for Iodine Enrichment. Earth Science, 46(11): 4140-4149 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zeng, H. B., Su, C. L., Xie, X. J., et al., 2021. Mechanism of Salinization of Shallow Groundwater in Western Hetao Irrigation Area. Earth Science, 46(6): 2267-2277(in Chinese with English abstract). Zeng, Y. Y., 2018. Study on Formation Mechanism of Poor Quality Groundwater in Western Kashgar Prefecture of Xinjiang (Dissertation). Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, E. Y., Zhang, F. C., Qian, Y., et al., 2010. The Distribution of High Iodine Groundwater in Typical Areas of China and Its Inspiration. Geology in China, 37(3): 797-802(in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, L. Y., 2012. Using Hydrochemistry and Strontium Isotopes to Identify the Sources of Salt in Groundwater Waters of the Tianjin Coastal Area(Dissertation). Tianjin Normal University, Tianjin (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, R. Q., Liang, X., Jin M. G., et al., 2018. Fundamentals of Hydrogeology. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, 90-95(in Chinese). Zhou, Y. Z., Sun, Y., Zhou, J. L., et al., 2021. Distribution and Co-Enrichment Factors of Arsenic and Iodine in Groundwater in the Shihezi Area, Xinjiang. Environmental Chemistry, 40(11): 3464-3473 (in Chinese with English abstract). 陈俊良, 杨红霞, 刘崴, 等, 2017. HPLC-ICP-MS法研究内蒙古锡盟和新疆塔城高碘地区地下水的总碘及碘形态特征. 岩矿测试, 36(6): 614-623. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YKCS201706009.htm 李玲, 仇少君, 檀菲菲, 等, 2013. 盐分和底物对黄河三角洲区土壤有机碳分解与转化的影响. 生态学报, 33(21): 6844-6852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201321010.htm 李文鹏, 郝爱兵, 郑跃军, 等, 2006. 塔里木盆地区域地下水环境同位素特征及其意义. 地学前缘, 13(1): 191-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200601026.htm 刘亚磊, 2019. 干旱内陆盆地地下水咸化与蒸发-累盐相互作用机理研究(博士学位论文). 武汉: 中国地质大学. 申红梅, 张树彬, 刘守军, 等, 2007. 全国高水碘地区地理分布及高碘地区水碘等值线研究. 中国地方病学杂志, 26(6): 658-661. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDFB200706027.htm 孙英, 周金龙, 梁杏, 等, 2021. 塔里木盆地南缘浅层高碘地下水的分布及成因: 以新疆民丰县平原区为例. 地球科学, 46(8): 2999-3011. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202108024.htm 王红太, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等, 2019. 新疆喀什地区饮用地下水碘分布及其富集因素分析. 新疆农业大学学报, 42(2): 145-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJNY201902011.htm 王雨婷, 李俊霞, 薛肖斌, 等, 2021. 华北平原与大同盆地原生高碘地下水赋存主控因素的异同. 地球科学, 46(1): 308-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202101024.htm 王智, 杜海波, 2003. 巴楚县地下水资源及开发利用模式的探讨. 新疆水利, (2): 16-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXSN200805049.htm 魏兴, 周金龙, 贾瑞亮, 等, 2017. 喀什地区不同TDS浅层地下水分布及资源量估算. 节水灌溉, (9): 51-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGU201709014.htm 徐芬, 马腾, 石柳, 等, 2012. 内蒙古河套平原高碘地下水的水文地球化学特征. 水文地质工程地质, 39(5): 8-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201205001.htm 薛江凯, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等, 2021. 长江中游沿岸地下水中有机质分子组成特征及其对碘富集的指示. 地球科学, 46(11): 4140-4149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202111026.htm 曾邯斌, 苏春利, 谢先军, 等, 2021. 河套灌区西部浅层地下水咸化机制. 地球科学, 46(6): 2267-2277. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202106023.htm 曾妍妍, 2018. 新疆喀什地区西部劣质地下水形成机理研究(博士学位论文). 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学. 张二勇, 张福存, 钱永, 等, 2010. 中国典型地区高碘地下水分布特征及启示. 中国地质, 37(3): 797-802. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201003037.htm 张琳怡, 2012. 天津滨海地区地下水咸化的水化学及锶同位素示踪研究(博士学位论文). 天津: 天津师范大学. 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵, 等, 2018. 水文地质学基础. 北京: 地质出版社, 57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JYDZ202301013.htm 周殷竹, 孙英, 周金龙, 等,2021. 新疆石河子地区地下水砷、碘分布规律及共富集因素分析. 环境化学,40(11):3464-3473. -










 下载:
下载: