Taphonomy of Lycoptera Fossils and Its Paleoclimate and Paleoenvironment Significance from Cretaceous Liwaxia Formation in Liupanshan Area
-
摘要: 为查明六盘山地区白垩纪李洼峡组狼鳍鱼化石的埋藏学特征所表征的古气候和古环境意义,以化石保存层位岩石和其上下层岩石为主要研究对象,对它们进行了全岩X衍射(XRD)、主量元素、微量元素和稀土元素分析.XRD分析显示化石埋藏层位岩石的组成矿物主要以铁白云石(42.70%)和石英(41.50%)为主,其上下层岩石的组成矿物主要以石英(平均含量40.40%)和长石(总平均含量15.98%)为主.主量元素分析显示化石埋藏层位岩石具有较高含量的CaO(平均含量20.61%)和MgO(平均含量10.52%),而其他层岩石具有较高含量的SiO2(平均含量54.58%)和Al2O3(平均含量14.79%).古气候指标MgO/CaO和Sr/Cu指示干热的气候,古盐度指标m值和Sr/Ba指示水体盐度高,古氧化还原环境指标Th/U和V/(V+Ni)指示缺氧和水体分层且底层出现硫化环境.鱼群的大规模死亡是由一次短暂的突发性事件造成,缺氧的水体环境和硫化氢的毒害作用可能是鱼类大规模死亡并得到保存的主要原因.特别需要指出的是,六盘山地区在白垩纪中期出现干热的气候条件以及高盐度、缺氧的水体环境可能是这一时期全球CO2浓度快速升高的结果,也可视为白垩纪Aptian-Albian大洋缺氧事件(OAE1a)在陆相地层的地质响应.Abstract: In order to find out the taphonomy and paleoclimate and paleoenvironment significance of Lycoptera-bearing Liwaxia Formation in the Liupanshan area, multiple methods of analyses are used. XRD analysis shows that the fossil-bearing is mainly composed of ankerite (42.70%) and quartz (41.50%), while its overlying and underlying neighbors are mainly composed of quartz (average 40.40%) and feldspar (total average 15.98%). The major elements of the fossil-bearing unit are CaO (average 20.61%) and MgO (average 10.52%), while its neighboring units are enriched in SiO2 (average 54.58%) and Al2O3 (average 14.79%). The paleoclimate indexes MgO/CaO and Sr/Cu indicate a dry hot climate, the paleo-salinity index m value and Sr/Ba indicate a high salinity environment, and the paleo-redox environment indexes Th/U and V/(V+Ni) indicate a stratified aquatic environment with euxinic bottom water. The mass mortality of fishes was caused by a rapid redox change of the water body and toxicity of H2S. It is likely that the anoxia was a response to OAE1a in the Liupanshan area, and the dry hot climate and high salinity water were caused by the elevated atmospheric CO2 concentration in the Middle Cretaceous. Additionally, the euxinic bottom water provides favorable conditions for the preservation of fish fossils.
-
Key words:
- Liupanshan area /
- Cretaceous /
- taphonomy /
- major and trace element /
- paleoclimate /
- paleoenvironment
-
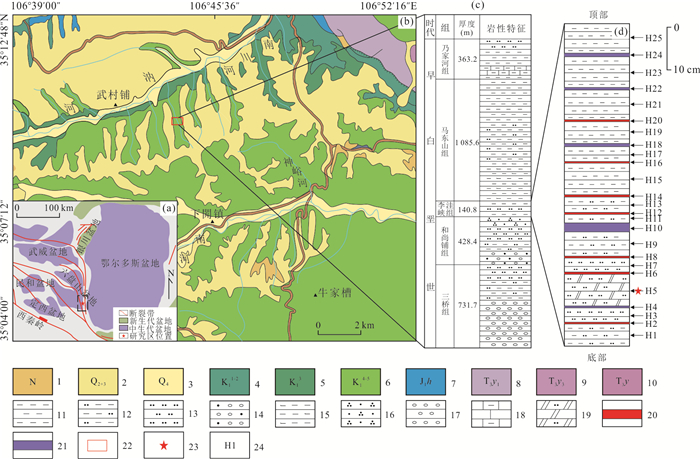
图 1 六盘山盆地构造位置(a);六盘山盆地研究区区域地质简图(b);六盘山盆地早白垩世综合地层柱状图(c);研究区野外剖面分层柱状图(d)
图a、图c据Zhao et al.,2020修改;图b据陇县幅1∶20万地质矿产图, 1966, 陕西省地质局区域地质测量队二十五分队. 1.土黄色、微红色黄土夹古土壤,含钙质结核;2.砾石、砂、漂砾;3. 紫红色砂质泥岩夹砂岩;4.紫红色砾岩夹粗砂岩透镜体;5.杂色泥岩夹砂岩;6.紫红色泥岩夹杂色砂岩,产甘肃狼鳍鱼;7.黄绿色砂岩夹页岩及煤层;8.紫红色砂岩夹砾岩及泥岩;9.灰黄色中粒砂岩夹泥岩、煤线;10.延长群黄绿色中细粒砂岩、长石砂岩与页岩互层;11.泥岩;12.粉砂质泥岩;13.钙质泥岩;14.粉砂岩;15.石英砂岩;16.砂砾岩;17.砾岩;18.泥质灰岩;19.白云质砂岩;20.红褐色黄铁矿层;21.灰色黏土矿物层;22.野外露头位置;23.化石埋藏层位;24.野外露头分层
Fig. 1. Tectonic location map of Liupanshan Basin (a); regional geological sketch of Liupanshan Basin research area (b); column chart of Early Cretaceous comprehensive strata in Liupanshan Basin (c); stratified column chart of the field profile in the study area (d)
图 8 研究区古湖泊环境演变模式(底图据Pan et al., 2015;Fan et al., 2021)
Fig. 8. Evolution model of paleo-lake environment in the study area (after Pan et al., 2015; Fan et al., 2021)
表 1 李洼峡组砂岩样品X射线衍射分析结果(%)
Table 1. X-ray diffraction analysis results (%) of sandstone samples from the Liwaxia Formation
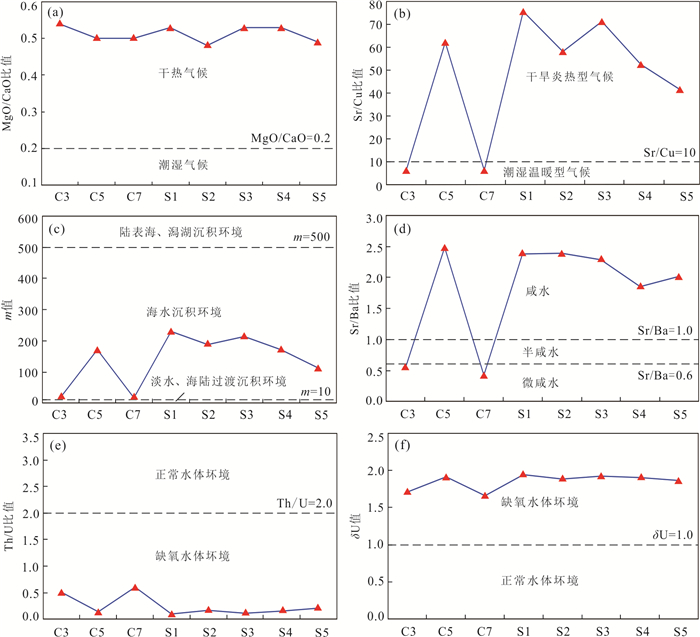
样品编号 石英 斜长石 钾长石 方解石 铁白云石 白云石 伊利石 绿泥石 黄铁矿 方沸石 C2 39.90 9.90 5.30 / / / 5.70 2.90 34.30 2.00 C3 40.60 16.00 5.30 8.60 / / 11.10 11.10 2.00 5.30 C5 41.50 4.00 1.90 1.80 42.70 / 3.40 2.80 / 1.90 C7 39.60 17.70 3.80 7.50 / 4.50 10.40 12.20 / 4.30 平均值 40.40 11.90 4.08 / / / 7.65 7.25 / 3.38 表 2 李洼峡组砂岩样品主量元素含量(%)
Table 2. Major element contents (%) of sandstone samples from the Liwaxia Formation
样号 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO K2O Na2O TiO2 P2O5 MnO 灼失 TFe2O3 C3 53.05 15.16 5.30 2.88 3.41 2.14 0.68 0.15 0.081 13.19 3.82 C5 24.52 5.94 20.46 10.24 1.34 1.12 0.30 0.20 0.50 30.85 4.34 C7 56.12 14.42 5.27 2.61 3.14 2.20 0.70 0.16 0.10 10.94 4.20 S1 21.33 5.03 21.73 11.62 1.12 0.92 0.26 0.34 0.59 32.94 3.92 S2 20.10 5.69 22.44 10.73 1.21 0.90 0.27 0.17 0.56 33.16 4.59 S3 22.34 5.30 21.28 11.28 1.16 0.99 0.28 0.26 0.57 32.31 4.04 S4 23.42 6.18 20.08 10.64 1.33 0.89 0.29 0.24 0.61 31.43 4.66 S5 30.22 7.56 17.64 8.61 1.70 1.34 0.38 0.15 0.43 27.51 4.26 表 3 李洼峡组砂岩样品微量元素含量(10‒6)
Table 3. Trace element contents (10‒6) of sandstone samples from the Liwaxia Formation
样号 Cu Cr Ni Co Sr Ba V U Th C3 39.60 79.50 32.80 15.70 245 455 127 30.40 15.5 C5 16.40 38.90 18.70 8.07 1020 409 112 49.20 7.10 C7 35.30 72.30 37.10 12.20 227 542 111 25.30 15.30 S1 15.10 33.50 15.20 6.05 1140 479 91.1 54.40 5.34 S2 15.30 30.50 18.60 6.92 888 372 109 40.50 6.90 S3 14.60 31.60 15.40 6.26 1040 456 87.6 45.60 5.68 S4 17.30 32.50 18.80 6.58 909 492 94 42.20 6.47 S5 21.30 47.10 21.90 9.38 887 439 125 44.40 9.38 表 4 李洼峡组砂岩样品地球化学参数比值结果
Table 4. Geochemical parameter ratios of sandstone samples from the Liwaxia Formation
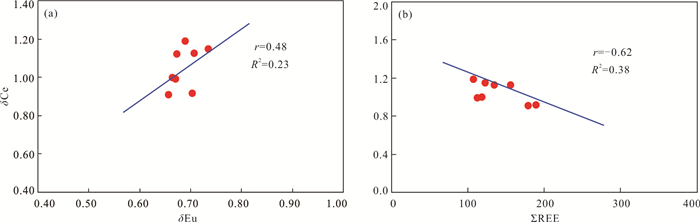
样号 m n Sr/Ba Sr/Cu Ni/Co V/Cr Th/U p δU δCe δEu ΣREE C3 19.00 0.54 0.54 6.19 2.09 1.60 0.51 0.79 1.71 0.91 0.70 189.94 C5 172.39 0.50 2.49 62.20 2.32 2.88 0.14 0.86 1.91 1.12 0.67 134.76 C7 18.10 0.50 0.42 6.43 3.04 1.54 0.60 0.75 1.66 0.91 0.66 179.64 S1 231.01 0.53 2.38 75.50 2.51 2.72 0.10 0.86 1.94 1.15 0.74 122.85 S2 188.58 0.48 2.39 58.04 2.69 3.57 0.17 0.85 1.89 1.00 0.66 119.13 S3 212.83 0.53 2.28 71.23 2.46 2.77 0.12 0.85 1.92 1.19 0.69 107.50 S4 172.17 0.53 1.85 52.54 2.86 2.89 0.15 0.83 1.90 0.99 0.67 112.75 S5 113.89 0.49 2.02 41.64 2.33 2.65 0.21 0.85 1.87 1.13 0.71 156.51 注:m=100×MgO/Al2O3;n=MgO/CaO;p=V/(V+Ni);δU=2U/(U+Th/3);δCe=2(Ce)N/[(La)N+(Pr)N];δEu=2(Eu)N/[(Sm)N+(Gd)N]. 表 5 李洼峡组砂岩样品稀土元素含量(10‒6)
Table 5. Rare earth element contents (10‒6) of sandstone samples from the Liwaxia Formation
样号 La Ce Pr Nd Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu C3 42.90 75.80 8.54 36.20 6.31 1.38 5.41 0.92 4.93 0.99 2.80 0.43 2.89 0.44 C5 25.60 59.00 6.08 23.80 4.40 0.94 3.98 0.68 4.06 0.88 2.32 0.36 2.30 0.36 C7 38.30 71.90 9.19 35.00 6.32 1.24 4.89 0.88 4.70 0.96 2.57 0.46 2.78 0.45 S1 26.10 57.20 5.02 18.60 3.27 0.77 3.03 0.52 3.26 0.68 1.95 0.29 1.87 0.29 S2 24.80 50.70 5.82 20.50 4.29 0.87 3.52 0.58 3.18 0.65 1.87 0.28 1.81 0.26 S3 21.80 51.00 4.60 16.30 3.01 0.66 2.74 0.44 2.55 0.57 1.66 0.25 1.67 0.25 S4 23.80 47.90 5.47 19.60 3.48 0.75 3.24 0.56 3.02 0.62 1.90 0.28 1.87 0.26 S5 30.40 69.50 6.98 26.70 4.86 1.09 4.39 0.79 4.51 0.98 2.81 0.41 2.68 0.41 表 6 鱼化石样品元素半定量结果
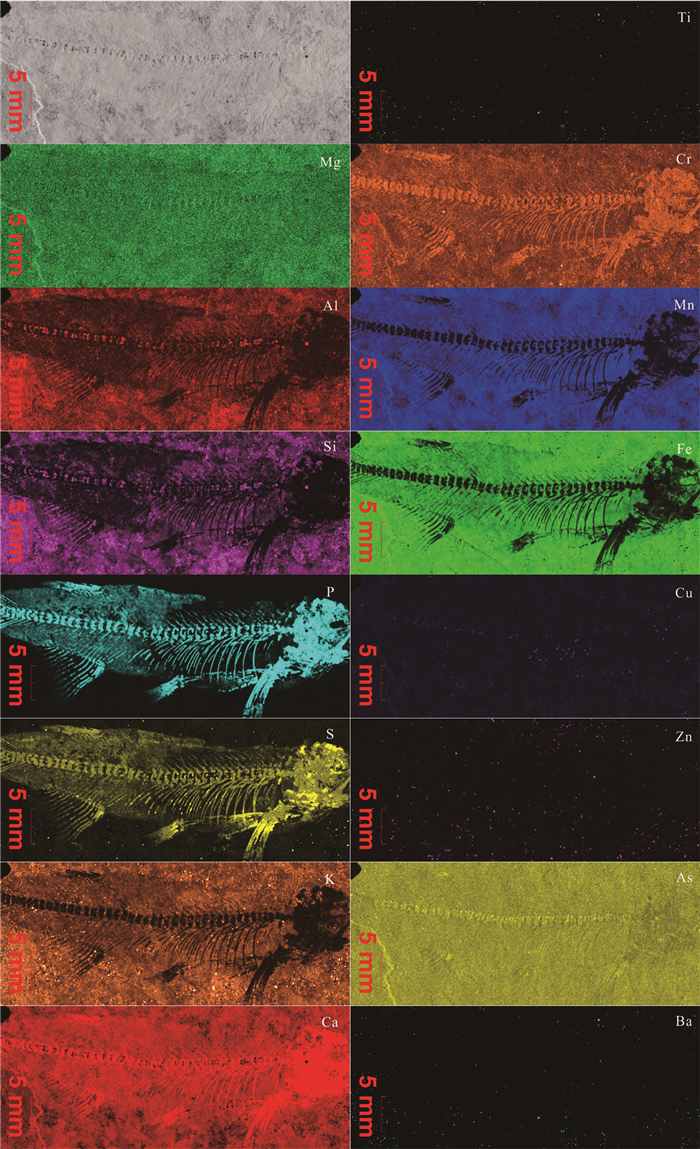
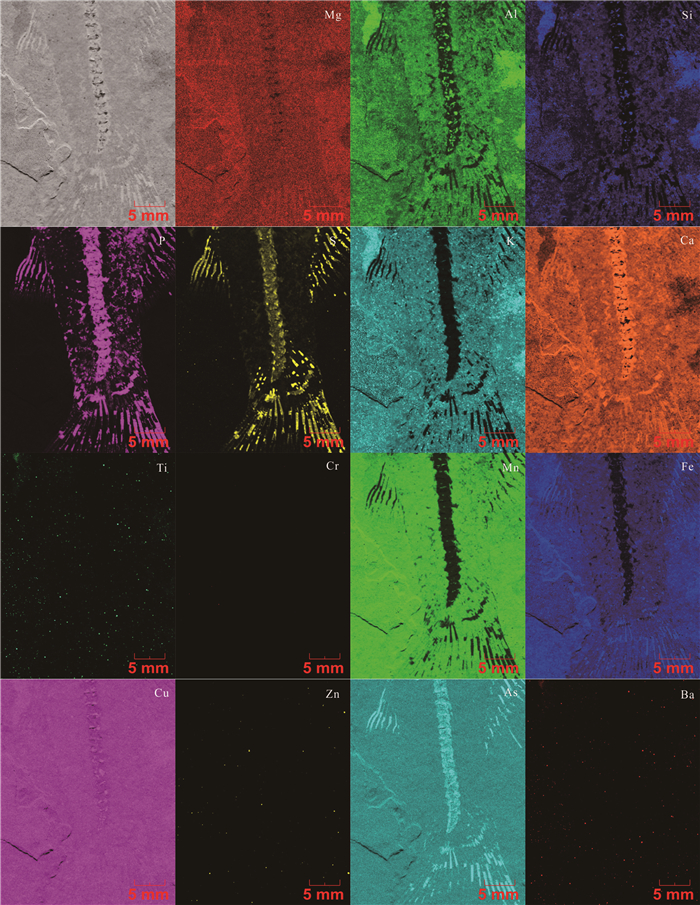
Table 6. Element semi-quantitative results of fish fossil samples
元素 鱼骨化石 鱼尾化石 浓度(%) 浓度(%) Mg 0.489 0.547 Al 1.178 1.660 Si 5.515 7.217 P 3.514 2.538 S 0.347 0.554 K 2.033 1.853 Ca 72.295 69.479 Ti 0.790 0.729 Cr 0.057 0.275 Mn 1.696 1.449 Fe 11.452 12.070 Cu 0.015 0.173 Zn 0.089 0.214 As 0.066 0.077 Ba 0.464 1.164 Total 100 100 -
Arthur, M. A., Sageman, B. B., 1994. Marine Black Shales: Depositional Mechanisms and Environments of Ancient Deposits. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 22: 499-551. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ea.22.050194.002435 Awan, R. S., Liu, C. L., Gong, H. W., et al., 2020. Paleo-Sedimentary Environment in Relation to Enrichment of Organic Matter of Early Cambrian Black Rocks of Niutitang Formation from Xiangxi Area China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 112: 104057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.104057 Chen, P. F., 2000. Fish Taphonomy in the Environmental Inference of Paleolimnology. Geoscience, 14(3): 379-384 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, S. H., Lin, C. L., Xu, W. G., et al., 2020. Age and Tectonic Significance of Volcanic Rocks in Cretaceous Red Beds in Fujian. Earth Science, 45(7): 2508-2523 (in Chinese with English abstract). Chen, W. B., Tan, F. W., Yi, H. S., et al., 2011. REE Characteristics and Its Geological Significance of Buqu Formation Carbonate Source Rocks in Nadigangri Area, Qiangtang Basin of Tibet. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 29(3): 529-536 (in Chinese with English abstract). Coccioni, R., Luciani, V., Marsili, A., 2006. Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Events and Radially Elongated Chambered Planktonic Foraminifera: Paleoecological and Paleoceanographic Implications. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 235(1-3): 66-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2005.09.024 Dai, S., Liu, X., Zhao, J., et al., 2012. The OAEs Record in the Terrestrial Sediments: The Geochemistry of Blackshales in the Liupanshan Group and Its Paleoclimatic Implications. Earth Science Frontiers, 19(4): 255-259 (in Chinese with English abstract). Dai, S., Zhu, Q., Hu, H. F., et al., 2009. Magnetostratigraphy of the Liupanshan Group, Central China. Journal of Stratigraphy, 33(2): 188-192 (in Chinese with English abstract). Donnadieu, Y., Goddéris, Y., Pierrehumbert, R., et al., 2006. A Geoclim Simulation of Climatic and Biogeochemical Consequences of Pangea Breakup. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 7(11): Q11019. https://doi.org/10.1029/2006GC001278 Du, B. X., Lei, X. T., Zhang, M. Z., et al., 2018. Late Early Cretaceous Climate and pCO2 Estimates in the Liupanshan Basin, Northwest China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 503: 26-39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2018.04.023 Du, B. X., Zhang, M. Z., Dai, S., et al., 2014. Discovery of Pseudofrenelopsis from the Lower Cretaceous of Liupanshan Basin and Its Paleoclimatic Significance. Cretaceous Research, 48: 193-204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cretres.2013.12.003 Elder, R. L., Smith, G. R., 1988. Fish Taphonomy and Environmental Inference in Paleolimnology. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 62(1-4): 577-592. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-0182(88)90072-7 Fan, D. J., Shan, X. L., Makeen, Y. M., et al., 2021. Response of a Continental Fault Basin to the Global OAE1a during the Aptian: Hongmiaozi Basin, Northeast China. Scientific Reports, 11: 7229. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-86733-x Fan, Q. C., Xu, Z. K., 2020. A Review of Cretaceous Ocean Anoxia Events. Marine Sciences, 44(2): 138-145 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fan, Y. H., Qu, H. J., Wang, H., et al., 2012. The Application of Trace Elements Analysis to Identifying Sedimentary Media Environment: A Case Study of Late Triassic Strata in the Middle Part of Western Ordos Basin. Geology in China, 39(2): 382-389 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fang, R. S., Liang, Y., Hua, H., et al., 2021. First Report of the Problematic Ediacaran Fossil Shaanxilithes from the Jiucheng Member of Zhujiaqing Section in Huize, Yunnan Province. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 60(1): 25-41 (in Chinese with English abstract). Font, E., Chen, J. B., Regelous, M., et al., 2022. Volcanic Origin of the Mercury Anomalies at the Cretaceous-Paleogene Transition of Bidart, France. Geology, 50(2): 142-146. https://doi.org/10.1130/G49458.1 Fu, G. B., Li, X. L., 2002. The Sedimentary Strata from Mesozoic to the Cenozoic in Liupanshan Basin. Journal of Xinjiang Petroleum Institute, (2): 24-27 (in Chinese with English abstract). Fürsich, F. T., Sha, J. G., Jiang, B. Y., et al., 2007. High Resolution Palaeoecological and Taphonomic Analysis of Early Cretaceous Lake Biota, Western Liaoning (NE-China). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 253(3-4): 434-457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2007.06.012 He, X., Chen, Z. Q., Lu, Z. S., et al., 2015. Exceptionally Preserved Caddisfly Larval Cases (Insecta) from the Lower Cretaceous of the Liupanshan Basin, Western China. Journal of Earth Science, 26(2): 192-202. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-015-0525-z He, X., Lu, Z. S., Weng, P., et al., 2014. Fossil Caddisfly Cases from the Early Cretaceous Aliferous Strata in Liupanshan Basin, China. Earth Science, 39(1): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hecht, F., 1933. Der Verbleib der Organischen Substanz der Tiere bei Meerischer Einbettung. Senckenbergiana, 15(3-4): 165-249. Kimura, H., Watanabe, Y., 2001. Oceanic Anoxia at the Precambrian-Cambrian Boundary. Geology, 29(11): 995-998. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0995:OAATPC>2.0.CO;2 doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0995:OAATPC>2.0.CO;2 Hu, X. M., 2005. Middle Cretaceous Abnormal Geological Events and Global Change. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(2): 222-230 (in Chinese with English abstract). Hu, X. M., Wang, C. S., 2007. Cretaceous Oceanic Red Beds: Characters, Occurrences, and Origin. Geological Journal of China Universities, 13(1): 1-13 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huang, Y. J., Wang, C. S., Gu, J., 2008. Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Events: Research Progress and Forthcoming Prospects. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(1): 21-30 (in Chinese with English abstract). Huber, B. T., Norris, R. D., MacLeod, K. G., 2002. Deep-Sea Paleotemperature Record of Extreme Warmth during the Cretaceous. Geology, 30: 123-126. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0123:DSPROE>2.0.CO;2 doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0123:DSPROE>2.0.CO;2 Jenkyns, H. C., 1980. Cretaceous Anoxic Events: From Continents to Oceans. Journal of the Geological Society, 137(2): 171-188. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsjgs.137.2.0171 Jin, X. Q., Cao, W. H., 2006. Study on Cretaceous Stratum System in Liupanshan Region in Ningxia and Its Environment Changes. Ningxia Engineering Technology, 5(1): 1-3 (in Chinese with English abstract). Jing, Y. L., Zhang, K. X., Lin, Q. X., et al., 2005. Sedimentary Geochemistry Characteristics and Paleoenvironmental Meaning of Helongshan Formation and Nanlinghu Formation in Meishan, Changxing County, Zhejiang Province. Geological Science and Technology Information, 24(1): 35-40 (in Chinese with English abstract). Kelts, K. R., 1988. Environments of Deposition of Lacustrine Petroleum Source Rocks: An Introduction. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 40(1): 3-26. https://doi.org/10.1144/GSL.SP.1988.040.01.02 Kerr, A. C., 1998. Oceanic Plateau Formation: A Cause of Mass Extinction and Black Shale Deposition around the Cenomanian-Turonian Boundary? Journal of the Geological Society, 155(4): 619-626. https://doi.org/10.1144/gsjgs.155.4.0619 Lei, X. T., 2019. Early Cretaceous Cheirolepidiaceae from the Jiuquan and Liupanshan Basins and pCO2 Estimates (Dissertation). Lanzhou University, Lanzhou (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, Q. Q., Lan, B. F., Li, G. Q., et al., 2021. Geochemical Characteristics of Shale Elements of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in the Northern Margin of Central Guizhou Uplift and Its Geological Significance. Earth Science, 46(9): 3172-3188 (in Chinese with English abstract). Li, X. B., Reisz, R., 2020. The Stratigraphy and Paleoenvironment of a 'Lycoptera Bed' Site in Eastern Inner Mongolia, China: Correlation with the Fossiliferous Lower Cretaceous Strata in Western Liaoning. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 559: 109951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2020.109951 Li, X. H., Xu, W. L., Liu, W. H., et al., 2013. Climatic and Environmental Indications of Carbon and Oxygen Isotopes from the Lower Cretaceous Calcrete and Lacustrine Carbonates in Southeast and Northwest China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 385: 171-189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.palaeo.2013.03.011 Liang, J. W., Tao, W. X., Ma, X. J., 2020. Origin and Paleoenvironmental Reconstruction of Phosphorus-Bearing Sandstones of the Cambrian Xinji Formation, Southwestern Margin of the Ordos Basin, China. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 57(8): 903-917. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjes-2019-0087 Liang, Y., Zhang, Z. F., 2018. Exploration of High-Performance Micro-Area X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer in the Study of Cambrian Soft-Bodied Fossils: A Case Study of Brachiopod Fossils. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 57(2): 202-211 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, X. T., Ma, F. Z., Liu, Z. C., 1985. Discovery of Kuntulunia in Shaanxi-Gansu-Ningxia Basin and Its Stratigraphic Significance. Vertebrata Palasiatica, 23(4): 255-263, 319 (in Chinese with English abstract). Liu, Z. S., 1983. Early Cretaceous Sporopollen Assemblage in Liupanshan Area of Ningxia and Its Paleovegetation and Paleoclimate Significance. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 22(5): 517-526, 603 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lu, L. W., 2003. Study on New Materials of Fish Fossils and Biostratigraphy in Jehol Group, Yixian County, Western Liaoning Province (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Lu, Z. J., Na, R., Cui, J. F., et al., 2011. Volcanic Rock Reservoir of the Cretaceous in Honghao'ershute Sag in Erlian Basin, Inner Mongolia. Journal of Palaeogeography, 13(2): 201-208 (in Chinese with English abstract). Ma, W. L., Jiang, X. Q., Li, X., et al., 2021. Geochemical Characteristics and Paleoenvironment Paleoclimate Significance of Mudstone in the Shang-Gan-Chai-Gou Formation at the Northwestern Margin of Qaidam Basin. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 40(5): 1166-1180 (in Chinese with English abstract). Miao, J. Y., Zhou, L. F., Deng, K., et al., 2004. Relationship between the Depositonal Environment and Geochemistry of Permian Hydrocarbon Source Rocks in the Turpan Depression. Geology in China, 31(4): 424-430 (in Chinese with English abstract). O'Brien, C. L., Robinson, S. A., Pancost, R. D., et al., 2017. Cretaceous Sea-Surface Temperature Evolution: Constraints from TEX86 and Planktonic Foraminiferal Oxygen Isotopes. Earth-Science Reviews, 172: 224-247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.07.012 Pan, Y. H., Fürsich, F. T., Zhang, J. Y., et al., 2015. Biostratinomic Analysis of Lycoptera Beds from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation, Western Liaoning, China. Palaeontology, 58(3): 537-561. https://doi.org/10.1111/pala.121602 Pan, Y. H., Sha, J. G., Fürsich, F. T., et al., 2012. Dynamics of the Lacustrine Fauna from the Early Cretaceous Yixian Formation, China: Implications of Volcanic and Climatic Factors. Lethaia, 45: 299-314. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1502-3931.2011.00284.x Qu, H. J., Li, W. H., He, X. P., et al., 2003. Discussion on Sequence Stratigraphy and Petroleum System of the Lower Cretaceous in Liupanshan Basin. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 33(1): 70-74 (in Chinese with English abstract). Rimmer, S. M., 2004. Geochemical Paleoredox Indicators in Devonian-Mississippian Black Shales, Central Appalachian Basin (USA). Chemical Geology, 206(3-4): 373-391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemgeo.2003.12.029 Schäffer, W., 1972. Ecology and Paleoecology of Marine Environments. Oliver & Boyd, Edinburgh, 586. Schlanger, S. O., Jenkyns, H. C., 1976. Cretaceous Oceanic Anoxic Events: Causes and Consequences. Geologie en Mijnbouw, 55(3-4): 179-184. Shi, W., Zhang, Y. Q., Ma, Y. S., et al., 2006. Formation and Modification History of the Liupanshan Basin on the Southwestern Margin of the Ordos Block and Tectonic Stress Field Evolution. Geology in China, 33(5): 1066-1074 (in Chinese with English abstract). Shields, G., Stille, P., 2001. Diagenetic Constraints on the Use of Cerium Anomalies as Palaeoseawater Redox Proxies: An Isotopic and REE Study of Cambrian Phosphorites. Chemical Geology, 175(1-2): 29-48. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0009-2541(00)00362-4 Sinton, C. W., Duncan, R. A., 1997. Potential Links between Ocean Plateau Volcanism and Global Ocean Anoxia at the Cenomanian-Turonian Boundary. Economic Geology, 92(7-8): 836-842. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.92.7-8.836 Tao, W. X., Liang, J. W., Yang, G., et al., 2020. Geochemistry Characteristics of Carbonate and Paleoenvironment Reconstruction of Cambrian Xinji Formation, Southwest Ordos Basin. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 7(3): 8-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). Thomson, J., Jarvis, I., Green, D. R. H., et al., 1998. Mobility and Immobility of Redox-Sensitive Elements in Deep-Sea Turbidites during Shallow Burial. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(4): 643-656. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00378-5 Tonger, Liu, W. H., Xu, Y. C., et al., 2004. The Discussion on Anoxic Environments and Its Geochemical Identifying Indices. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 22(2): 365-372 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2004.02.026 Wallmann, K., 2001. Controls on the Cretaceous and Cenozoic Evolution of Seawater Composition, Atmospheric CO2 and Climate. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 65(18): 3005-3025. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00638-X Wang, D. D., Zhang, W. H., Li, S. Z., et al., 2018. Features and Hydrocarbon Potential of Source Rocks in the Hongdi 1 Well, Hongmiaozi Basin, Liaoning Province. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 40(4): 526-531 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, D. S., Zhang, J. C., Li, Z., et al., 2022. Formation Mechanism of Framboidal Pyrite and Its Theory Inversion of Paleo-Redox Conditions. Geology in China, 49(1): 36-50 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, Y. D., Huang, C. M., Sun, B. N., et al., 2014. Paleo-CO2 Variation Trends and the Cretaceous Greenhouse Climate. Earth-Science Reviews, 129: 136-147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.11.001 Wang, Y. D., Sun, B. N., Huang, C. M., et al., 2015. Variation of Paleo-CO2 and Greenhouse Climate in the Geological History: A Case Study from the Cretaceous of the Mesozoic. Chinese Journal of Nature, 37(2): 108-114 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wu, C. D., Yang, C. Y., Chen, Q. Y., 1999. The Origin and Geochemical Characteristics of Upper Sinian-Lower Cambrian Black Shales in Western Hunan. Acta Petrrologica et Mineralogica, 18(1): 26-39 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xiao, Y., 2020. Analysis of Mesozoic Oil and Gas Exploration Prospect in Hongmiaozi Basin, Liaoning Province (Dissertation). Jilin University, Changchun (in Chinese with English abstract). Xiong, X. H., Xiao, J. F., 2011. Geochemical Indicators of Sedimentary Environments—A Summary. Earth and Environment, 39(3): 405-414 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, F. Z., Hu, S. R., 2001. Tectonic Evolution and Oil-Gas Exploration during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic in Liupanshan Basin. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 22(3): 192-195, 274 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, Q., Lü, J. C., Wang, J. M., et al., 2019. A Study of Early Cretaceous Dinosaur Tracks in Liupanshan Area, Ningxia. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 40(3): 483-491 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, Z. Y., Shen, W. Z., Zheng, L. D., 2009. Elements and Isotopic Geochemistry of Guadalupian-Lopingian Boundary Profile at the Penglaitan Section of Laibin, Guangxi Province, and Its Geological Implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(1): 1-15 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.1111/j.1755-6724.2009.00001.x Zhang, M. Z., Dai, S., Zhang, Y. Q., et al., 2012. Early Cretaceous Palynological Assemblage and Its Environmental Significance in the Sediments of Liupanshan Group (Sikouzi Section), Liupanshan Region, Central China. Arid Land Geography, 35(1): 99-108 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Y. Z., Wang, D. Y., 2012. The Burial Characteristics of Specific Fossils from Yixian Formation in Western Liaoning and Their Indicative Significance. Public Communication of Science & Technology, 4(11): 94-95 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Y. G., Li, K., Cai, K. J., 1998. The Chemical Separation of Mineral Compositions and Trace Element Assemblages from the Dinosaur Skeletal Fossils in Kaijiang, Sichuan. Sedimentary Facies and Palaeogeography, 18(4): 49-56 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhang, Z. L., Hua, H., Zhang, Z. F., 2015. Problematic Ediacaran Fossil Shaanxilithes from the Jiucheng Member of Wangjiawan Section in Jinning, Yunnan Province. Acta Palaeontologica Sinica, 54(1): 12-28 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhao, X. C., Liu, C. Y., Wang, J. Q., et al., 2020. Provenance Analyses of Lower Cretaceous Strata in the Liupanshan Basin: From Paleocurrents Indicators, Conglomerate Clast Compositions, and Zircon U-Pb Geochronology. Journal of Earth Science, 31(4): 757-771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12583-020-1324-8 Zhao, Y. G., Ren, N. Q., Wang, A. J., et al., 2007. The Influence of Fe Elements on Sulfate Reduction Process and the Response of Microbial Community. China Environmental Science, 27(2): 199-203 (in Chinese with English abstract). 陈平富, 2000. 古湖泊学研究中的鱼化石埋藏学方法. 现代地质, 14(3): 379-384. 陈淑华, 林慈銮, 徐维光, 等, 2020. 福建白垩纪红层火山岩夹层时代及构造意义. 地球科学, 45(7): 2508-2523. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.035 陈文彬, 谭富文, 伊海生, 等, 2011. 羌塘盆地那底岗日地区布曲组碳酸盐岩烃源岩稀土元素分布特征及意义. 沉积学报, 29(3): 529-536. 戴霜, 刘学, 赵杰, 等, 2012. 陆地沉积物对大洋缺氧事件的响应——六盘山群黑色页岩地球化学特征及其意义. 地学前缘, 19(4): 255-259. 戴霜, 朱强, 胡鸿飞, 等, 2009. 六盘山群磁性地层年代. 地层学杂志, 33(2): 188-192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4959.2009.02.010 范庆超, 徐兆凯, 2020. 白垩纪大洋缺氧事件研究进展. 海洋科学, 44(2): 138-145. 范玉海, 屈红军, 王辉, 等, 2012. 微量元素分析在判别沉积介质环境中的应用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地西部中区晚三叠世为例. 中国地质, 39(2): 382-389. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.02.010 房瑞森, 梁悦, 华洪, 等, 2021. 埃迪卡拉纪晚期疑难化石Shaanxilithes在云南会泽朱家箐剖面的首现及其意义. 古生物学报, 60(1): 25-41. 付国斌, 李兴亮, 2002. 六盘山盆地中新生代沉积地层. 新疆石油学院学报, (2): 24-27. 何欣, 卢宗盛, 翁平, 等, 2014. 六盘山盆地早白垩世含盐地层中石蚕巢化石. 地球科学, 39(1): 1-9. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2014.001 胡修棉, 2005. 白垩纪中期异常地质事件与全球变化. 地学前缘, 12(2): 222-230. 胡修棉, 王成善, 2007. 白垩纪大洋红层: 特征、分布与成因. 高校地质学报, 13(1): 1-13. 黄永建, 王成善, 顾健, 2008. 白垩纪大洋缺氧事件: 研究进展与未来展望. 地质学报, 82(1): 21-30. 金学强, 曹炜华, 2006. 宁夏六盘山地区白垩纪地层环境演化研究. 宁夏工程技术, 5(1): 1-3. 经雅丽, 张克信, 林启祥, 等, 2005. 浙江长兴煤山下三叠统和龙山组、南陵湖组沉积地球化学特征与古环境意义. 地质科技情报, 24(1): 35-40. 雷向通, 2019. 酒泉及六盘山盆地早白垩世Cheirolepidiaceae及古大气CO2重建(硕士学位论文). 兰州: 兰州大学. 李琪琪, 蓝宝锋, 李刚权, 等, 2021. 黔中隆起北缘五峰‒龙马溪组页岩元素地球化学特征及其地质意义. 地球科学, 46(9): 3172-3188. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.354 梁悦, 张志飞, 2018. 高性能微区X射线荧光光谱仪在寒武纪特异保存软躯体化石研究中的探索: 以腕足动物化石为例. 古生物学报, 57(2): 202-211. 刘宪亭, 马凤珍, 刘智成, 1985. 昆都仑鱼(Kuntulunia)在陕甘宁盆地的发现及其地层意义. 古脊椎动物学报, 23(4): 255-263, 319. 刘兆生, 1983. 宁夏六盘山区早白垩世孢粉组合及其古植被、古气候的意义. 古生物学报, 22(5): 517-526, 603. 卢立伍, 2003. 辽西义县热河群鱼类化石新材料及其生物地层学研究(博士学位论文). 北京: 中国地质大学. 路占军, 娜仁, 崔俊峰, 等, 2011. 内蒙古二连盆地洪浩尔舒特凹陷白垩系火山岩储集层. 古地理学报, 13(2): 201-208. 马万里, 江小青, 李璇, 等, 2021. 柴达木盆地西北缘上干柴沟组泥岩地球化学特征与古环境古气候意义. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 40(5): 1166-1180. 苗建宇, 周立发, 邓昆, 等, 2004. 吐鲁番坳陷二叠系烃源岩地球化学与沉积环境的关系. 中国地质, 31(4): 424-430. 屈红军, 李文厚, 何希鹏, 等, 2003. 六盘山盆地下白垩统沉积层序与含油气系统. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 33(1): 70-74. 施炜, 张岳桥, 马寅生, 等, 2006. 六盘山盆地形成和改造历史及构造应力场演化. 中国地质, 33(5): 1066-1074. 陶文星, 梁积伟, 杨光, 等, 2020. 鄂尔多斯盆地西南缘寒武系辛集组碳酸盐岩地球化学特征及古环境重建. 非常规油气, 7(3): 8-15. 腾格尔, 刘文汇, 徐永昌, 等, 2004. 缺氧环境及地球化学判识标志的探讨——以鄂尔多斯盆地为例. 沉积学报, 22(2): 365-372. 王丹丹, 张文浩, 李世臻, 等, 2018. 辽宁省红庙子盆地烃源岩特征与生烃潜力研究——来自红地1井的证据. 石油实验地质, 40(4): 526-531. 王东升, 张金川, 李振, 等, 2022. 草莓状黄铁矿的形成机制探讨及其对古氧化‒还原环境的反演. 中国地质, 49(1): 36-50. 王永栋, 孙柏年, 黄成敏, 等, 2015. 地史时期古大气二氧化碳变化趋势与温室气候——以中生代白垩纪为例. 自然杂志, 37(2): 108-114. 吴朝东, 杨承运, 陈其英, 1999. 湘西黑色岩系地球化学特征和成因意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 18(1): 26-39. 肖阳, 2020. 辽宁省红庙子盆地中生界油气勘探前景分析(硕士学位论文). 长春: 吉林大学. 熊小辉, 肖加飞, 2011. 沉积环境的地球化学示踪. 地球与环境, 39(3): 405-414. 杨福忠, 胡社荣, 2001. 六盘山盆地中、新生代构造演化和油气勘探. 新疆石油地质, 22(3): 192-195, 274. 杨卿, 吕君昌, 王金敏, 等, 2019. 宁夏六盘山地区早白垩世恐龙足迹研究. 地球学报, 40(3): 483-491. 杨振宇, 沈渭洲, 郑连弟, 2009. 广西来宾蓬莱滩二叠纪瓜德鲁普统‒乐平统界线剖面元素和同位素地球化学研究及地质意义. 地质学报, 83(1): 1-15. 张明震, 戴霜, 张永全, 等, 2012. 六盘山地区寺口子剖面早白垩世晚期的孢粉组合及其环境意义. 干旱区地理, 35(1): 99-108. 张永忠, 王多云, 2012. 辽西义县组特异化石埋藏特征及其指示意义. 科技传播, 4(11): 94-95. 张玉光, 李奎, 蔡开基, 1998. 四川开江恐龙骨骼化石矿物组分分离和微量元素组合的研究. 岩相古地理, 18(4): 49-56. 张志亮, 华洪, 张志飞, 2015. 埃迪卡拉纪疑难化石Shaanxilithes在云南王家湾剖面的发现及地层意义. 古生物学报, 54(1): 12-28. 赵阳国, 任南琪, 王爱杰, 等, 2007. 铁元素对硫酸盐还原过程的影响及微生物群落响应. 中国环境科学, 27(2): 199-203. -









 下载:
下载: