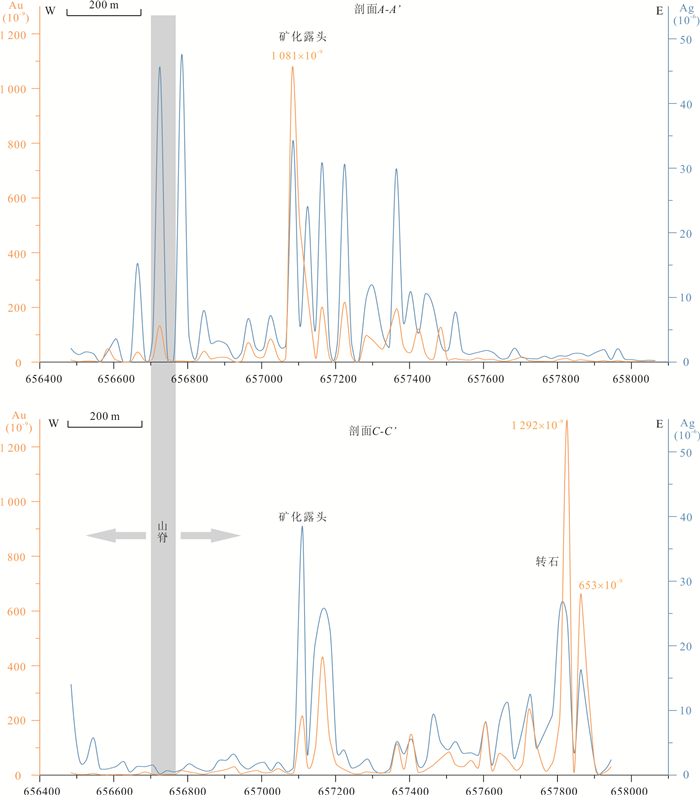
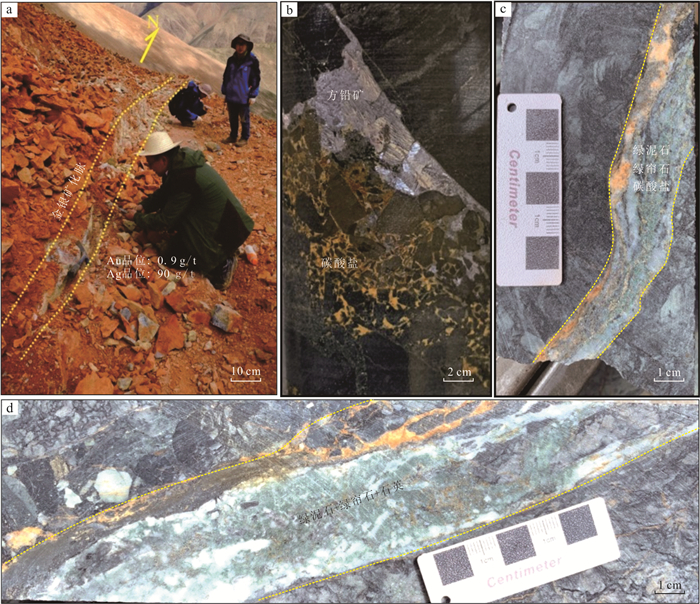
Geochemical and Geophysical Exploration in Sinongduo Ag Polymetallic Deposit, Xizang
-
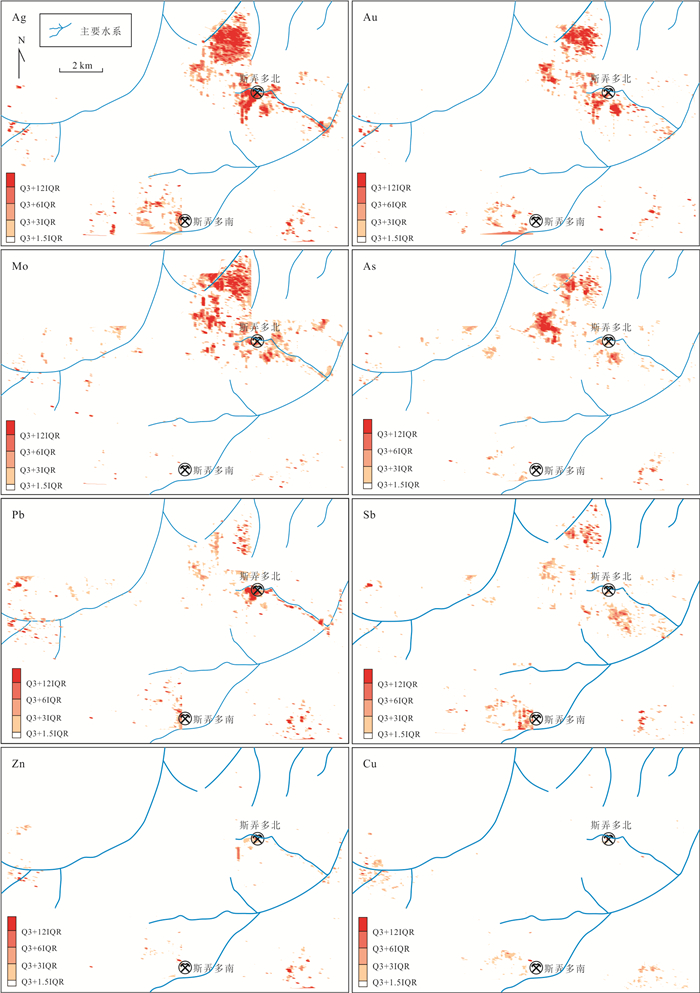
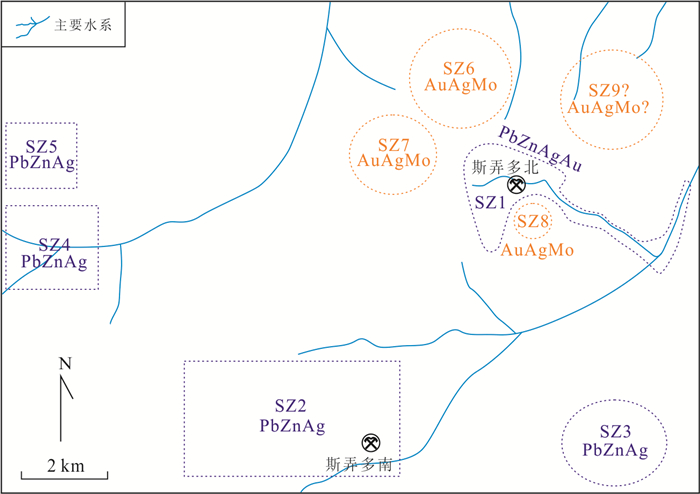
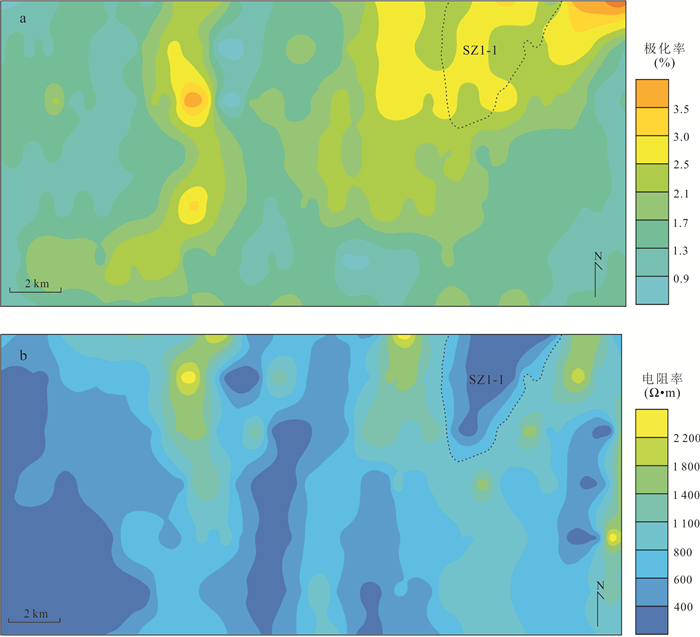
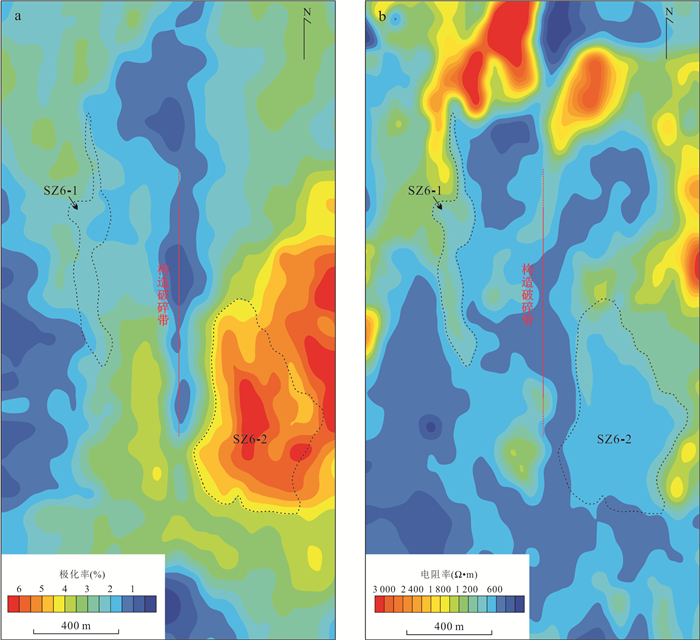
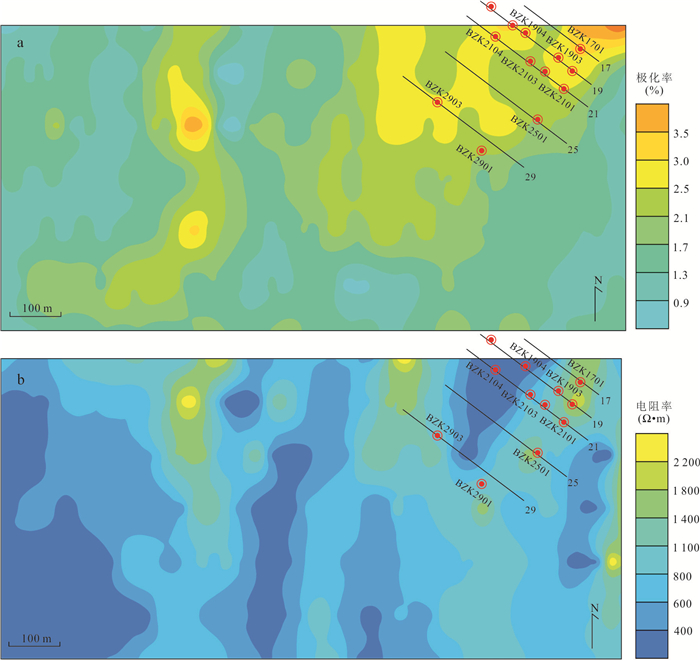
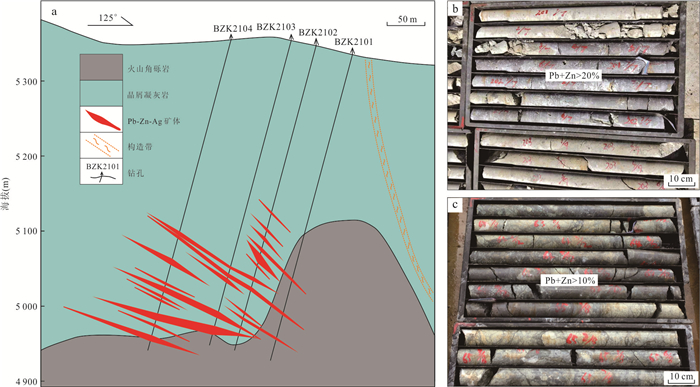
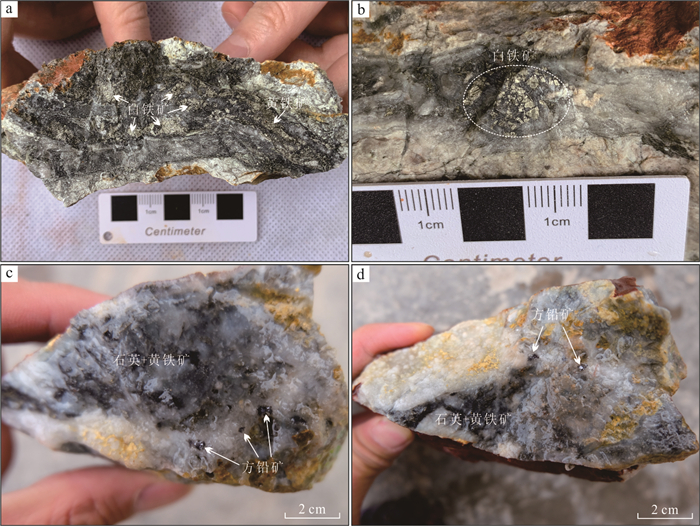
摘要: 近年来在西藏冈底斯‒念青唐古拉成矿带林子宗群火山岩分布区发现一系列中‒大型铅锌银矿床,该区显示出巨大的找矿潜力.由于林子宗群火山岩分布范围广,如何有效地圈定成矿远景区,缩小找矿靶区是取得找矿突破的关键.选取产于谢通门县娘热地区典中组火山岩中的斯弄多银多金属矿床为研究对象,开展了大量勘查地球化学测量和激电中梯测量.结果显示典中组火山岩中铅锌银成矿作用具有Au、Mo、Pb、Zn、Ag异常,金银成矿作用具有强Au、Ag、Mo、As、Sb异常,主成矿元素变异系数大于3.以极化率大于2.5%和电阻率小于800 Ω·m圈定隐伏铅锌银矿体的找矿靶区,取得了很好的找矿效果.上述结果表明激电中梯方法在林子宗群火山岩中寻找浅成低温热液型铅锌银矿体效果良好,能够为西藏冈底斯‒念青唐古拉成矿带林子宗群火山岩中的找矿工作提供十分重要的指导.Abstract: In recent years, many medium-large Pb-Zn-Ag deposits have been found in the Linzizong volcanic rocks in the Gangdese Nyainqêntanglha metallogenic belt, showing great potential for exploration. However, the key to exploration is how to conduct exploration targeting in the widespread Linzizong volcanic rocks. In this contribution, we conduct work of geochemical survey and induced polarization intermediate gradient in the Sinongduo Ag polymetallic deposit in the Dianzhong volcanic rocks. The results show that the Pb-Zn-Ag mineralization in the Linzizong volcanic rocks has Au, Mo, Pb, Zn and Ag anomalies, and the Au-Ag mineralization has strong Au, Ag, Mo, As and Sb anomalies, and the variation coefficient of the main mineralizing elements is more than 3. The target of the potential epithermal Pb-Zn-Ag mineralization is given based on the > 2.5% polarizability and the < 800 Ω·m resistivity, which has achieved good exploration results. Our findings demonstrate that the induced polarization (IP) intermediate gradient is effective in exploration for epithermal Pb-Zn-Ag deposits in the Linzizong volcanic rocks, and thus can provide an important guide for the exploration in the Linzizong volcanic rocks in the Gangdese Nyainqêntanglha metallogenic belt.
-
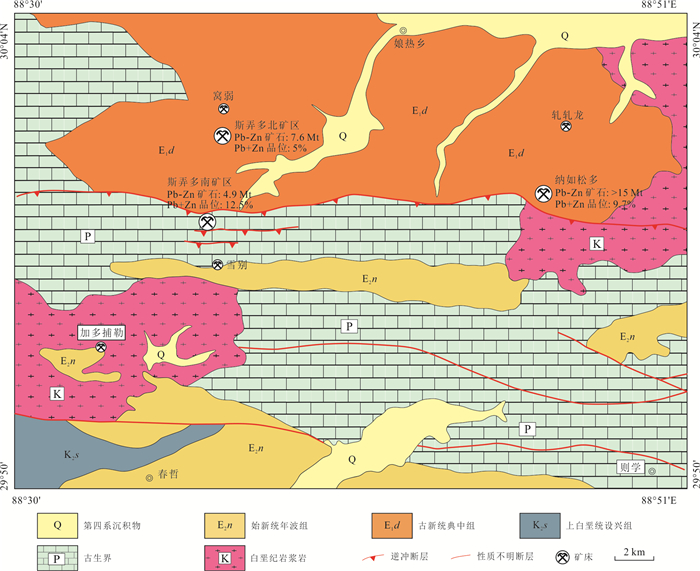
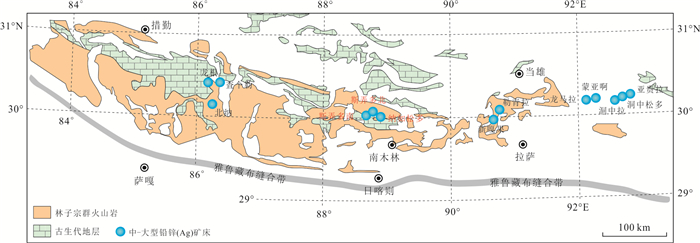
图 1 冈底斯‒念青唐古拉成矿带北亚带主要矿床分布(据杨宗耀等,2020a)
Fig. 1. Geological map of the northern Gangdese-Nyainqêntanglha metallogenic sub-belt showing the location of main deposits (Yang et al., 2020a)
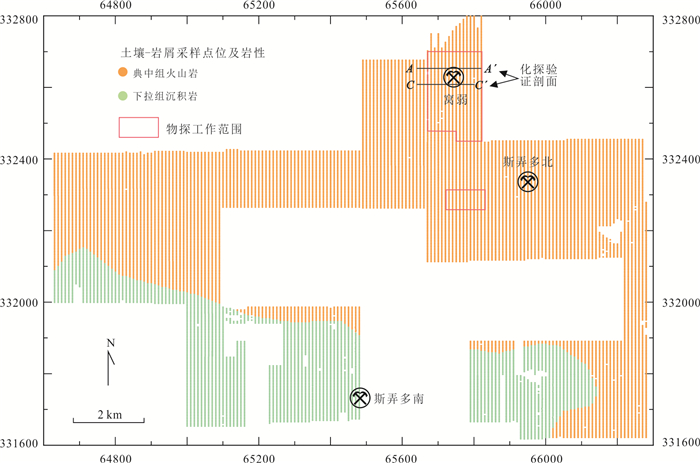
图 2 斯弄多矿集区地质概况(Yang et al., 2022)
Fig. 2. Geological map of the Sinongduo ore district (Yang et al., 2022)
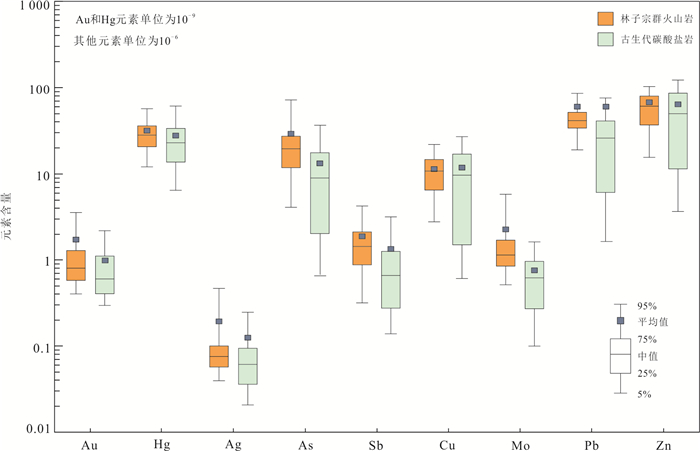
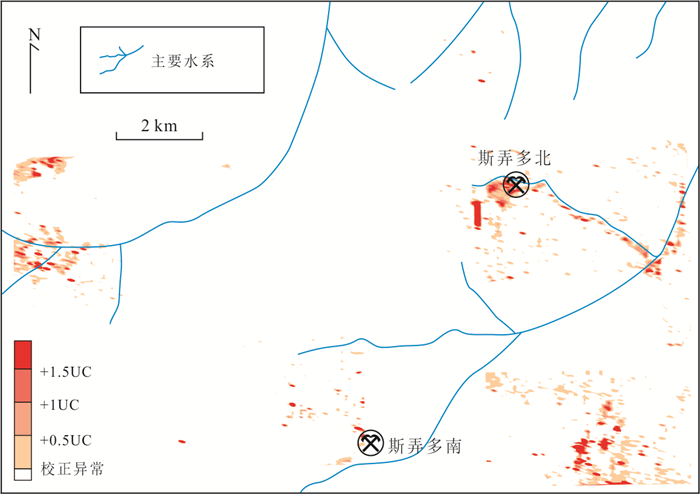
表 1 斯弄多矿区岩石地球化学测量结果
Table 1. Statistical results of trace elements in rock samples from the Sinongduo area
元素 Au Hg Ag As Sb Cu Mo Pb Zn 上地壳丰度(UC) 1.8 / 0.05 1.5 0.2 25 1.5 20 71 测试检出限 0.2 0.000 4 0.02 0.11 0.01 0.2 0.05 0.9 0.4 典中组火山岩(n=16 208) 均值 1.7 31.4 0.19 29.4 1.89 11.3 2.26 59.8 67.3 标准差 8.3 30.1 1.56 70.1 5.12 8.3 8.55 508.2 462.1 变异系数 4.8 1 8.02 2.4 2.72 0.7 3.79 8.5 6.9 下四分位数(Q1) 0.6 20.8 0.06 11.6 0.88 6.6 0.85 34.4 37.2 中位数 0.8 28.0 0.08 19.5 1.43 10.8 1.14 41.5 61.2 上四分位数(Q3) 1.3 36.0 0.10 27.5 2.08 14.7 1.69 51 79.5 四分位距(IQR) 0.7 15.3 0.04 15.9 1.21 8.14 0.84 16.6 42.3 下拉组碳酸盐岩(n=5 589) 均值 1 27.6 0.13 13.3 1.32 11.8 0.75 59.8 63.7 标准差 2.2 33.5 2.01 23 7.65 64.7 1.36 2 009.8 315 变异系数 2.3 1.2 15.92 1.7 5.78 5.5 1.81 33.6 4.9 上四分位数(Q1) 0.4 13.9 0.04 2.0 0.28 1.5 0.27 6.0 11.5 中位数 0.6 23.0 0.06 8.9 0.66 9.6 0.62 26.1 49.9 下四分位数(Q3) 1.1 33.7 0.10 17.5 1.22 16.9 0.94 40.7 86.1 四分位距(IQR) 0.7 19.8 0.06 15.5 0.94 15.5 0.67 34.7 74.6 注:Au和Hg单位为10‒9,其余元素单位为10‒6.上地壳元素含量据Taylor and McLennan (1995). 表 2 基于箱型图的斯弄多矿区岩石地球化学测量异常分带
Table 2. Trace element anomaly levels of rock samples from the Sinongduo area based on box-plots
元素 Au Hg Ag As Sb Cu Mo Pb Zn 典中组火山岩(n=16 208) Q3+1.5IQR 2.4 58.89 0.16 51.4 3.90 26.91 2.95 75.9 143.0 Q3+3IQR 3.4 81.78 0.22 75.2 5.71 39.12 4.21 100.8 206.4 Q3+6IQR 5.5 127.56 0.34 122.9 9.34 63.54 6.73 150.6 333.3 Q3+12IQR 9.7 219.12 0.58 218.3 16.60 112.38 11.77 250.2 587.1 异常值个数 1 226 741 2 252 1 319 991 327 1 884 1 184 283 下拉组碳酸盐岩(n=5 589) Q3+1.5IQR 2.2 63.4 0.19 40.8 2.63 40.1 1.95 92.8 198.0 Q3+3IQR 3.2 93.1 0.28 64.0 4.04 63.3 2.95 144.8 309.9 Q3+6IQR 5.3 152.5 0.46 110.5 6.86 109.6 4.96 248.9 533.7 Q3+12IQR 9.5 271.3 0.82 203.5 12.50 202.3 8.98 457.1 981.3 异常值个数 297 258 448 229 370 63 169 198 89 注:Au和Hg含量单位为10‒9,其余元素含量单位为10‒6. 表 3 斯弄多矿区典中组火山岩样品各元素相关性矩阵
Table 3. Correlation matrix of elements in Dianzhong Formation volcanic rocks from the Sinongduo area
元素 Au Hg Ag As Sb Cu Mo Pb Zn Au 1 Hg 0.15 1 Ag 0.35 0.18 1 As 0.45 0.15 0.27 1 Sb 0.29 0.27 0.34 0.48 1 Cu 0.00 0.13 0.31 0.02 0.05 1 Mo 0.39 0.12 0.36 0.32 0.30 ‒0.03 1 Pb 0.06 0.09 0.83 0.06 0.08 0.42 0.06 1 Zn 0.01 0.03 0.23 0.01 0.01 0.34 0.00 0.30 1 表 4 斯弄多矿区下拉组碳酸盐岩样品各元素相关性矩阵
Table 4. Correlation matrix of elements in Xiala Formation carbonate rocks from the Sinongduo area
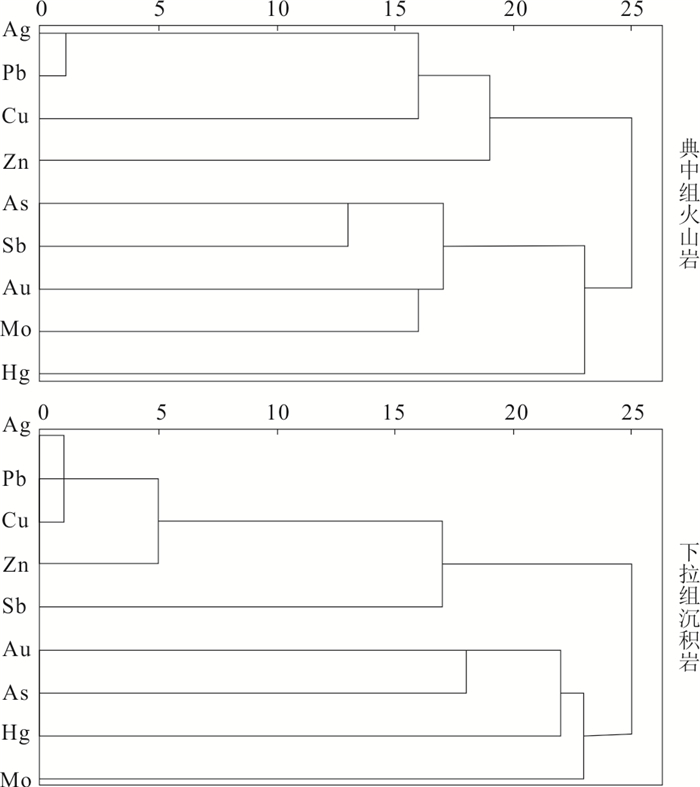
元素 Au Hg Ag As Sb Cu Mo Pb Zn Au 1 Hg 0.30 1 Ag 0.20 0.10 1 As 0.43 0.26 0.25 1 Sb 0.17 0.13 0.48 0.28 1 Cu 0.20 0.11 0.99 0.28 0.48 1 Mo 0.25 0.26 0.12 0.26 0.10 0.13 1 Pb 0.18 0.08 0.99 0.22 0.47 0.99 0.11 1 Zn 0.20 0.13 0.84 0.36 0.43 0.83 0.13 0.82 1 表 5 斯弄多矿区岩石地球化学测量因子分析结果
Table 5. Factor analysis of elements of rock samples from the Sinongduo area
典中组火山岩 下拉组碳酸盐岩 因子 FL1 FL2 因子 FP1 F P2 As 0.753 ‒0.037 Ag 0.981 0.076 Au 0.718 ‒0.003 Pb 0.979 0.05 Sb 0.707 0.046 Cu 0.973 0.102 Mo 0.67 ‒0.003 Zn 0.88 0.162 Hg 0.367 0.129 Sb 0.564 0.214 Pb 0.132 0.877 Au 0.126 0.725 Ag 0.51 0.735 As 0.244 0.684 Cu ‒0.042 0.709 Hg 0.019 0.667 Zn ‒0.075 0.596 Mo 0.045 0.62 特征值 2.803 1.836 特征值 4.296 1.655 方差贡献 31.144 20.403 方差贡献 47.732 18.393 累计方差 31.144 51.547 累计方差 47.732 66.125 旋转法:具有Kaiser标准化的正交旋转法,旋转在3次迭代后收敛. -
Carlson, C. A., 1991. Spatial Distribution of Ore Deposits. Geology, 19(2): 111-114. https://doi.org/10.1130/0091-7613(1991)0190111:sdood>2.3.co;2 doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1991)0190111:sdood>2.3.co;2 Cooke, D. R., Wilkinson, J. J., Baker, M., et al., 2020. Using Mineral Chemistry to Aid Exploration: A Case Study from the Resolution Porphyry CuMo Deposit, Arizona. Economic Geology, 115(4): 813-840. https://doi.org/10.5382/econgeo.4735 Han, M. H., Shin, S. W., Park, S., et al., 2016. Induced Polarization Imaging Applied to Exploration for LowSulfidation Epithermal AuAg Deposits, Seongsan Mineralized District, South Korea. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 13(5): 817-823. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-2132/13/5/817 Han, Z. X., Liao, J. G., Zhang, Y. L., et al., 2017. Review of DeepPenetrating Geochemical Exploration Methods. Advances in Earth Science, 32(8): 828-838 (in Chinese with English abstract). Holley, E. A., Bissig, T., Monecke, T., 2016. The Veladero HighSulfidation Epithermal Gold Deposit, El IndioPascua Belt, Argentina: Geochronology of Alunite and Jarosite. Economic Geology, 111(2): 311-330. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.111.2.311 Hosseini, S. T., Asghari, O., Haroni, H. A., 2020. Multivariate Anomaly Modeling of Primary Geochemical Halos by USpatial Statistic Algorithm Development: A Case Study from the Sari Gunay Epithermal Gold Deposit, Iran. Ore Geology Reviews, 127: 103845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103845 Huang, H. X., Liu, H., Li, G. M., et al., 2019. Zircon UPb, Molybdenite ReOs and Quartz Vein RbSr Geochronology of the Luobuzhen AuAg and Hongshan Cu Deposits, Tibet, China: Implications for the OligoceneMiocene PorphyryEpithermal Metallogenic System. Minerals, 9(8): 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/min9080476 Ishida, M., Romero, R., Leisen, M., et al., 2022. Auriferous Pyrite Formed by Episodic Fluid Inputs in the Akeshi and Kasuga HighSulfidation Deposits, Southern Kyushu, Japan. Mineralium Deposita, 57(1): 129-145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00126-021-01053-4 Kapp, P., DeCelles, P. G., Leier, A. L., et al., 2007. The Gangdese Retroarc Thrust Belt Revealed. GSA Today, 17(7): 4-9. https://doi.org/10.1130/GSAT01707A.1 Krzywinski, M., Altman, N., 2014. Visualizing Samples with Box Plots. Nature Methods, 11(2): 119-120. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2813 Lang, X. H., Tang, J. X., Li, Z. J., et al., 2014. The Role of Geochemical Exploration in the Discovery of No. Ⅱ and No. Ⅲ Orebodies in the Xiongcun Ore District, Tibet. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 38(4): 667-672 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lang, X. H., Tang, J. X., Yang, Z. Y., et al., 2017. Geophysical Characteristics and Prospecting Direction of the Sinongduo PbZn Deposit in Xietongmen County, Tibet. Geology and Exploration, 53(3): 508-518 (in Chinese with English abstract). Lu, M. X., 2015. Evaluation to the Effectiveness of IP Intermediate Gradient in Duolong Ore District, Tibet (Dissertation). Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu (in Chinese with English abstract). Ning, M. H., Wen, C. Q., 2010. Geological and Geophysical Characteristics and Analysis on Enlarging the Prospect for Prospecting Work of Tibetan Bangpu PorphyryType MolybdenumCopper Mine Area. Mineral Resources and Geology, 24(6): 542-546 (in Chinese with English abstract). Oldenburg, D. W., Li, Y. G., Ellis, R. G., 1997. Inversion of Geophysical Data over a Copper Gold Porphyry Deposit: A Case History for Mt. Milligan. Geophysics, 62(5): 1419-1431. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.1444246 Sanderson, D. J., Roberts, S., Gumiel, P., 1994. A Fractal Relationship between Vein Thickness and Gold Grade in Drill Core from La Codosera, Spain. Economic Geology, 89(1): 168-173. https://doi.org/10.2113/gsecongeo.89.1.168 Sillitoe, R. H., Tolman, J., Van Kerkvoort, G., 2013. Geology of the Caspiche Porphyry GoldCopper Deposit, Maricunga Belt, Northern Chile. Economic Geology, 108(4): 585-604. https://doi.org/10.2113/econgeo.108.4.585 Tang, J. X., Deng, S. L., Zheng, W. B., et al., 2011. An Exploration Model for Jiama Copper Polymetallic Deposit in Maizhokunggar County, Tibet. Mineral Deposits, 30(2): 179-196 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tang, J. X., Ding, S., Meng, Z., et al., 2016. The First Discovery of the Low Sulfidation Epithermal Deposit in Linzizong Volcanics, Tibet: A Case Study of the Sinongduo Ag Polymetallic Deposit. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 37(4): 461-470 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tang, J. X., Dorji, Liu, H. F., et al., 2012. Minerogenetic Series of Ore Deposits in the East Part of the Gangdise Metallogenic Belt. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 33(4): 393-410 (in Chinese with English abstract). Tang, J. X., Wang, Q., Yang, H. H., et al., 2017. Mineralization, Exploration and Resource Potential of PorphyrySkarnEpithermal Copper Polymetallic Deposits in Tibet. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 38(5): 571-613 (in Chinese with English abstract). Taylor, S. R., McLennan, S. M., 1995. The Geochemical Evolution of the Continental Crust. Reviews of Geophysics, 33(2): 241-265. https://doi.org/10.1029/95rg00262 Tian, W. F., Hao, J. J., Yan, J. Y., et al., 2010. Application of Synthetic Geophysical Methods to Deep Exploration of HanxingType Iron Deposit. Progress in Geophysiscs, 25(4): 1442-1452 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, F. C., Li, Y. L., Lu, H. F., et al., 2016. GeophysicalGeochemical Anomaly Characteristics and Prospecting Model of the Narigongma Porphyry CuMo Deposit in Southern Qinghai Province. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 40(6): 1055-1062 (in Chinese with English abstract). Wang, J., Zuo, R. G., Caers, J., 2017. Discovering Geochemical Patterns by FactorBased Cluster Analysis. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 181: 106-115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2017.07.006 Wang, Q. F., Deng, J., Zhao, J. C., et al., 2012. The Fractal Relationship between Orebody Tonnage and Thickness. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 122: 4-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2012.06.018 Wang, X. Q., Xie, X. J., Cheng, Z. Z., et al., 1999. Delineation of Regional Geochemical Anomalies Penetrating through Thick Cover in Concealed Terrains: A Case History from the Olympic Dam Deposit, Australia. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 66(1): 85-97. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0375-6742(99)00036-9 Wang, X. Q., 2013. A Decade of Exploration Geochemistry. Bulletin of Mineralogy Petrology and Geochemistry, 32(2): 190-197 (in Chinese with English abstract). Xie, X. J., Wang, X. Q., 2003. Recent Developments on Deep Penetrating Geochemistry. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(1): 225-238 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, J., Liu, Z. P., Wang, L., 2008. Effectiveness of Natural Field Induced Polarization for Detecting Polymetallic Deposits. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(4): 217-221. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-5791(08)60056-1 Yang, S. P., Zhang, H., Kong, M., et al., 2014. Study on Surficial Soil Geochemistry in the HighElevation and Frigid Mountainous Region: A Case of Qulong Porphyry Copper Deposit in Tibet. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 139: 144-151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.06.001 Yang, X., Tang, J. X., Yang, Z. Y., et al., 2021. Late Cretaceous Adakite in Sinongduo Area, Tibet: Implications for Petrogenesis and Mineralization. Earth Science, 46(5): 1597-1612 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, Z. Y., Tang, J. X., Santosh, M., et al., 2021. Microcontinent Subduction and SType Volcanism Prior to IndiaAsia Collision. Scientific Reports, 11: 14882. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-94492-y Yang, Z. Y., Tang, J. X., Zhao, X. Y., et al., 2022. Direct Dating of the Sinongduo Thrust System in Southern Tibet: Immediate Response to IndiaAsia Collision. International Geology Review, 64(14): 2074-2084. https://doi.org/10.1080/00206814.2021.1978110 Yang, Z., 2017. Geological Characteristics and Prospecting Prediction of Gangjiang Porphyry CuMo Deposit in Nimu, Tibet (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, Z. Y., Tang, J. X., Zhang, L. J., et al., 2020a. Geological and Geochemical Characteristics of Lithocaps in Sinongduo Area, Tibet: Implications for the Mineralization in Linzizong Group Volcanic Rocks. Earth Science, 45(3): 789-803 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, Z. Y., Zhang, C. H., Zhang, L. J., et al., 2020b. The Application of Induced Polarization Method and Audio Magnetotelluric Sounding to the Exploration of the Sinongduo Deposit, Tibet. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 41(1): 107-116 (in Chinese with English abstract). Yang, Z. Y., Zhang, C. H., Zhao, X. Y., et al., 2019. Characteristics of Rock Geochemical Anomalies and Prospecting Potential of the Sinongduo Silver Polymetallic Deposit, Tibet. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 43(4): 702-708 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zheng, S. L., 2020. Construction and Application of Exploration Indicator of Zhunuo Porphyry Copper Deposit (Dissertation). China University of Geosciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhou, W. Y., Yan, J. Y., Chen, C. X., 2021. Multiscale Geophysics and Mineral System Detection: Status and Progress. Progress in Geophysics, 36(3): 1208-1225 (in Chinese with English abstract). Zhu, W. P., Liu, S. H., Zhu, H. W., et al., 2017. Study on the Exploration Depth of Geophysical Methods Commonly Used. Progress in Geophysiscs, 32(6): 2608-2618 (in Chinese with English abstract). 韩志轩, 廖建国, 张聿隆, 等, 2017. 穿透性地球化学勘查技术综述与展望. 地球科学进展, 32(8): 828-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXJZ201708006.htm 郎兴海, 唐菊兴, 李志军, 等, 2014. 化探在西藏雄村矿区Ⅱ、Ⅲ号矿体发现中的作用. 物探与化探, 38(4): 667-672. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201404007.htm 郎兴海, 唐菊兴, 杨宗耀, 等, 2017. 西藏自治区谢通门县斯弄多铅锌矿区地球物理特征及找矿方向. 地质与勘探, 53(3): 508-518. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201703010.htm 陆茂欣, 2015. 西藏多龙矿集区激电中梯方法有效性评价(硕士学位论文). 成都: 成都理工大学. 宁墨奂, 温春齐, 2010. 西藏邦铺斑岩型钼铜矿区地质及地球物理特征与扩大找矿前景分析. 矿产与地质, 24(6): 542-546. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCYD201006012.htm 唐菊兴, 邓世林, 郑文宝, 等, 2011. 西藏墨竹工卡县甲玛铜多金属矿床勘查模型. 矿床地质, 30(2): 179-196. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201102003.htm 唐菊兴, 丁帅, 孟展, 等, 2016. 西藏林子宗群火山岩中首次发现低硫化型浅成低温热液型矿床——以斯弄多银多金属矿为例. 地球学报, 37(4): 461-470. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201604010.htm 唐菊兴, 多吉, 刘鸿飞, 等, 2012. 冈底斯成矿带东段矿床成矿系列及找矿突破的关键问题研究. 地球学报, 33(4): 393-410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201204003.htm 唐菊兴, 王勤, 杨欢欢, 等, 2017. 西藏斑岩‒矽卡岩‒浅成低温热液铜多金属矿成矿作用、勘查方向与资源潜力. 地球学报, 38(5): 571-613. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201705002.htm 田文法, 郝俊杰, 严加永, 等, 2010. 综合地球物理方法在邯邢式铁矿深部找矿中的应用. 地球物理学进展, 25(4): 1442-1452. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201004037.htm 王富春, 李玉龙, 鲁海峰, 等, 2016. 青南纳日贡玛斑岩型铜钼矿床物化探异常特征及找矿模型. 物探与化探, 40(6): 1055-1062. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201606001.htm 王学求, 2013. 勘查地球化学近十年进展. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 32(2): 190-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201302004.htm 谢学锦, 王学求, 2003. 深穿透地球化学新进展. 地学前缘, 10(1): 225-238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200301041.htm 杨昕, 唐菊兴, 杨宗耀, 等, 2021. 西藏斯弄多地区晚白垩世埃达克岩: 岩石成因及成矿潜力指示. 地球科学, 46(5): 1597-1612. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2020.157 杨震, 2017. 西藏尼木岗讲斑岩铜钼矿床地质特征及成矿预测(博士学位论文). 北京: 中国地质大学. 杨宗耀, 唐菊兴, 张乐骏, 等, 2020a. 西藏斯弄多地区岩帽地质地球化学特征: 林子宗群火山岩中成矿的指示. 地球科学, 45(3): 789-803. doi: 10.3799/dqkx.2019.044 杨宗耀, 张崇海, 张乐骏, 等, 2020b. 激发极化法和音频大地电磁测深在西藏斯弄多矿区找矿中的应用. 地球学报, 41(1): 107-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202001011.htm 杨宗耀, 张崇海, 赵晓彦, 等, 2019. 西藏斯弄多银多金属矿床岩石地球化学特征及找矿前景. 物探与化探, 43(4): 702-708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH201904003.htm 郑顺利, 2020. 朱诺斑岩铜矿勘查标识的构建及其应用(硕士学位论文). 北京: 中国地质大学. 周文月, 严加永, 陈昌昕, 2021. 多尺度地球物理与成矿系统探测: 现状与进展. 地球物理学进展, 36(3): 1208-1225. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ202103037.htm 朱卫平, 刘诗华, 朱宏伟, 等, 2017. 常用地球物理方法勘探深度研究. 地球物理学进展, 32(6): 2608-2618. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201706043.htm -









 下载:
下载: